Global Feedback Control for Coordinated Linear Switched Reluctance Machines Network with Full-State Observation and Internal Model Compensation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Notations and Theoretical Background
2.1. Concept of Graph Theory
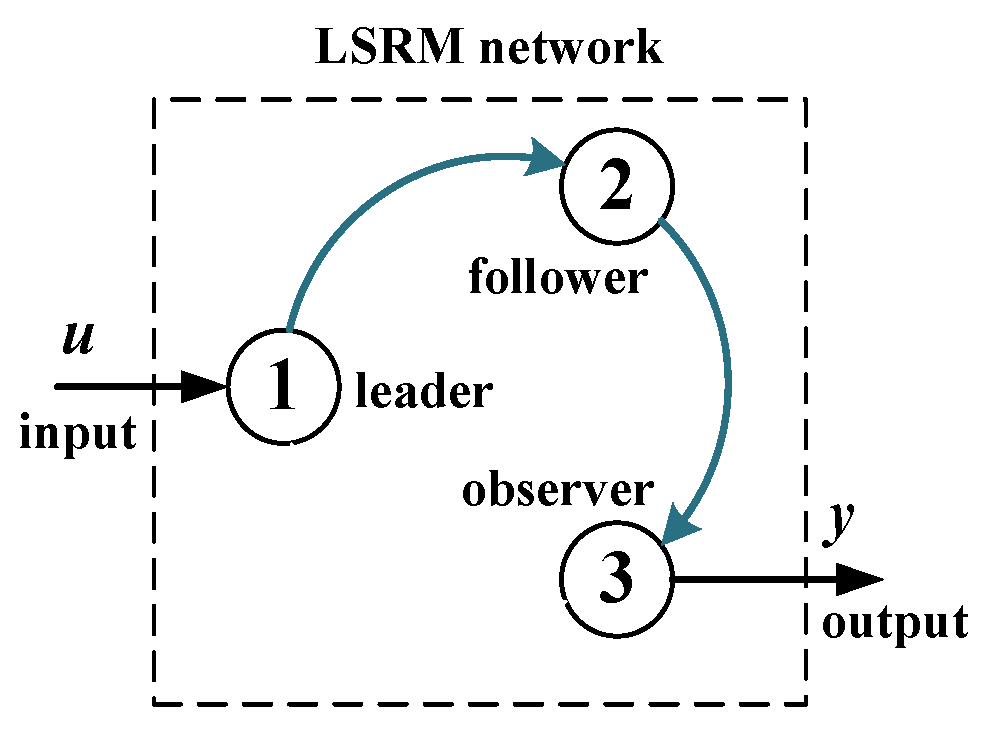
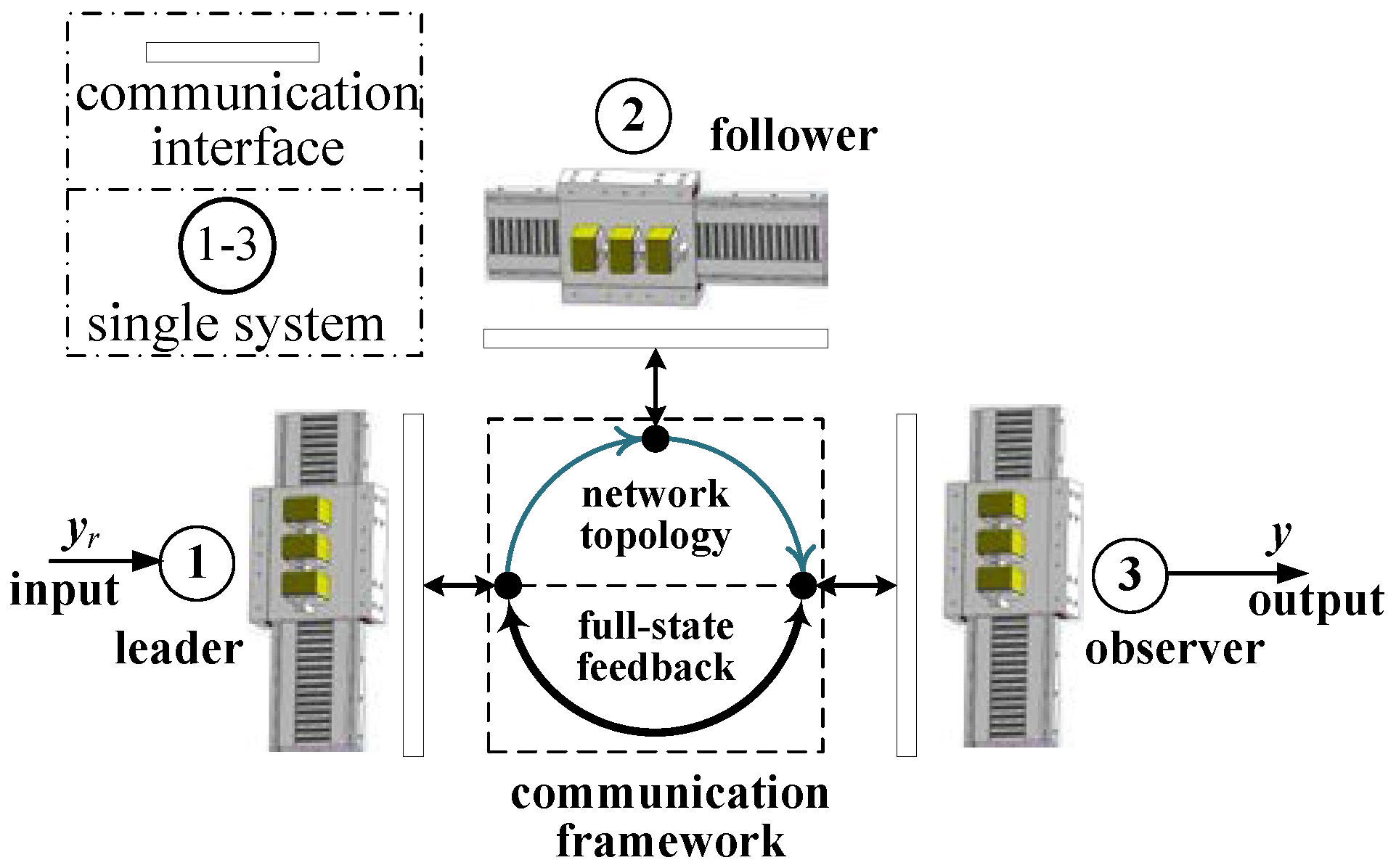
2.2. Leader–Follower–Observer Network
2.3. Notation Preliminaries and Problem Statements
3. Modeling of the LSRMs Network
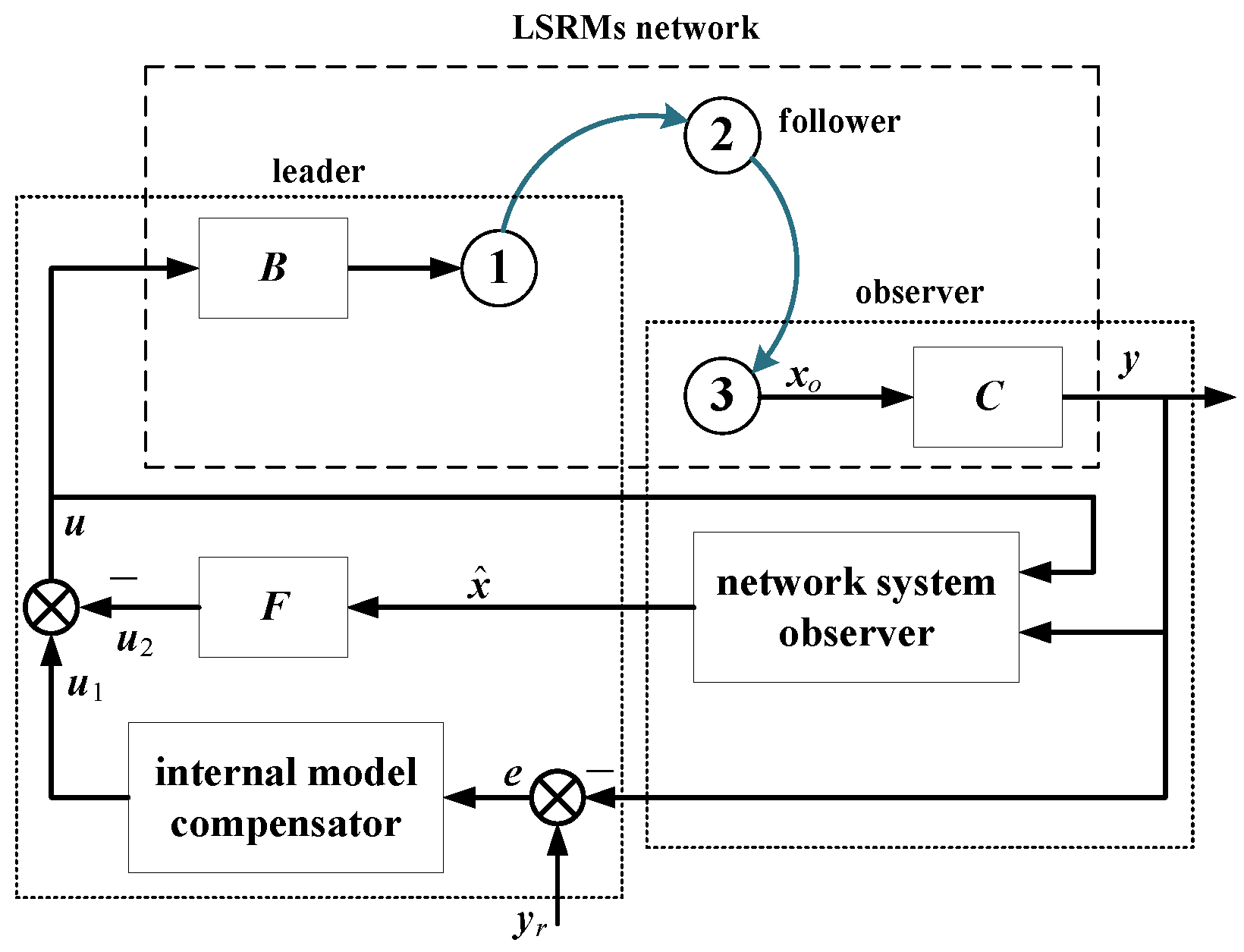
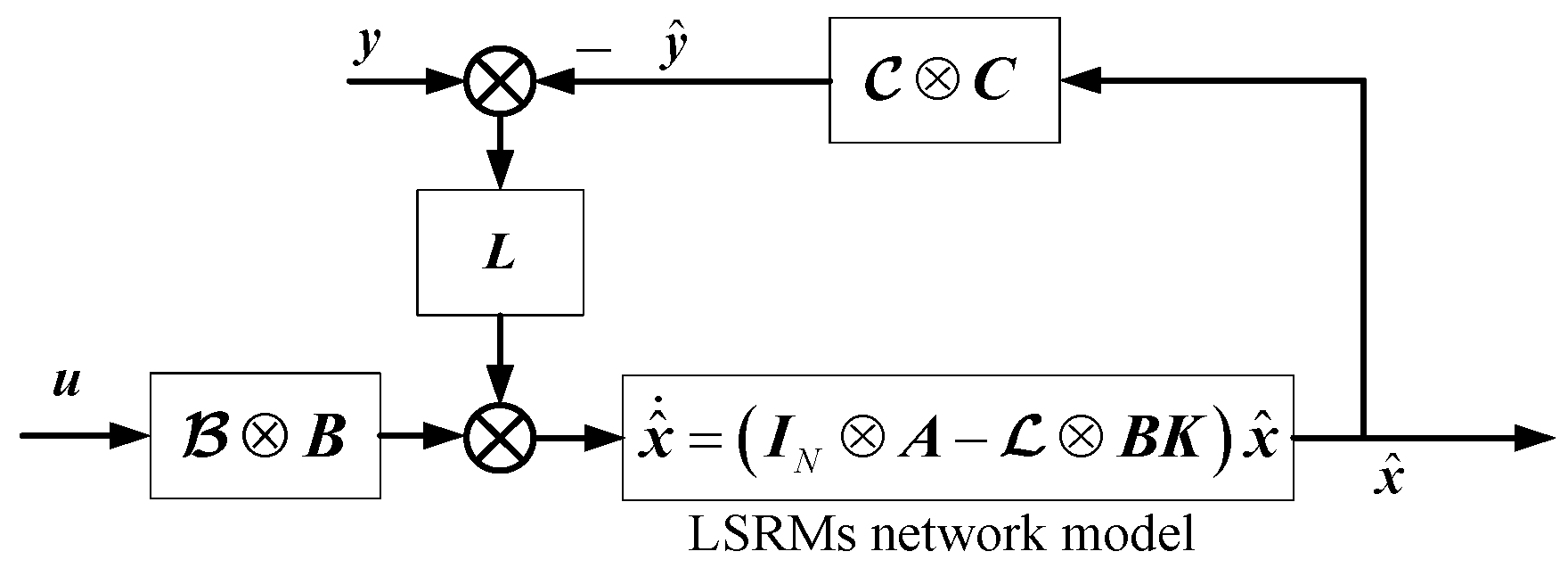
4. LSRMs Network with IMC
4.1. Internal Model Compensator Design
4.2. Controllability of LSRMs Network with IMC
- 1.
- The LSRM network is fully controllable.
- 2.
- of the IMC is a controllable matrix pair.
- 3.
- The LSRM network with the IMC should be satisfied by that.
- 4.
- All roots of the unstable equation of should satisfy.
5. Global Controller and Observer Design
5.1. Controller Design
5.2. Observer Design
5.3. Control Algorithms of Leader, Follower, and Observer
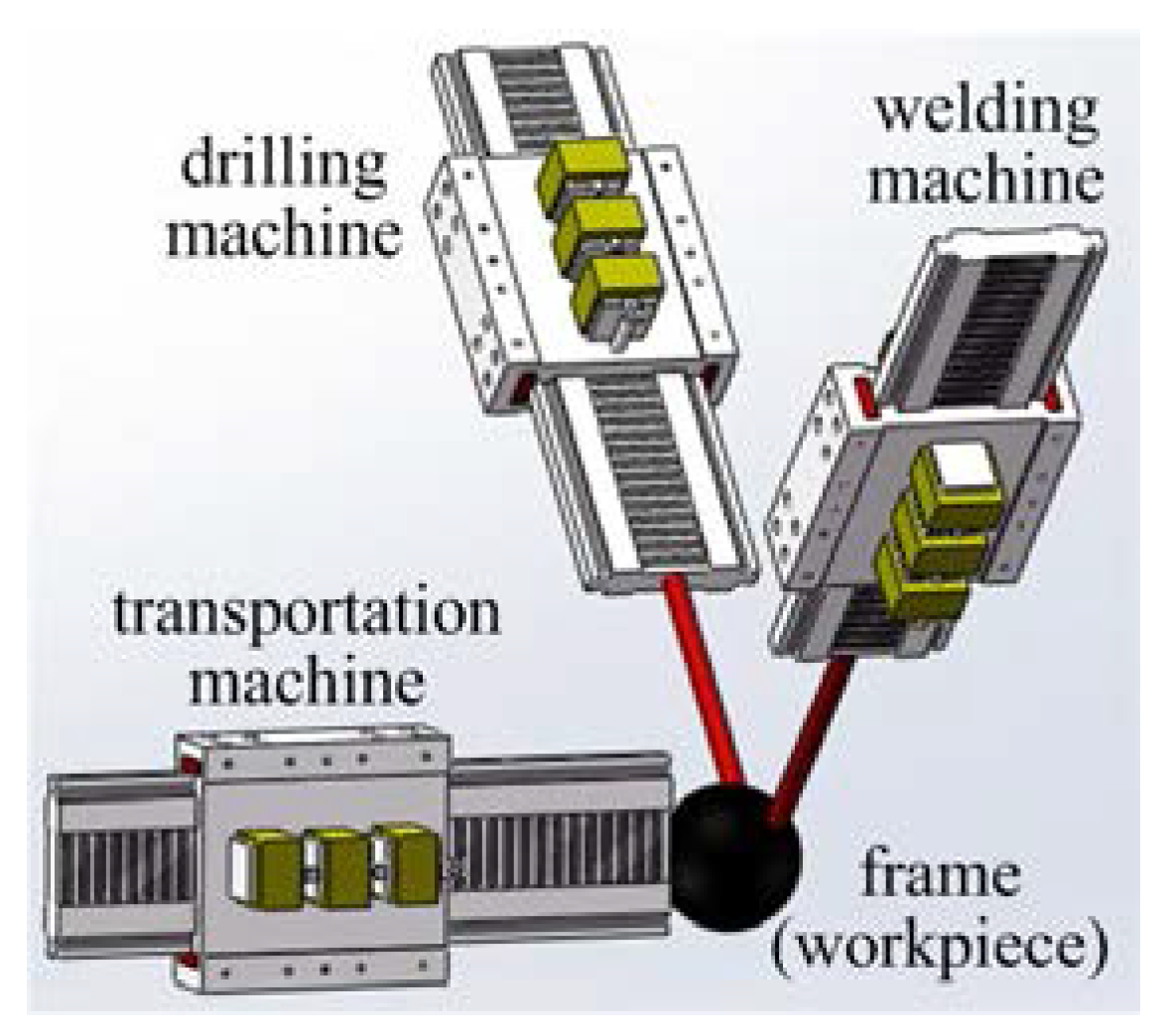
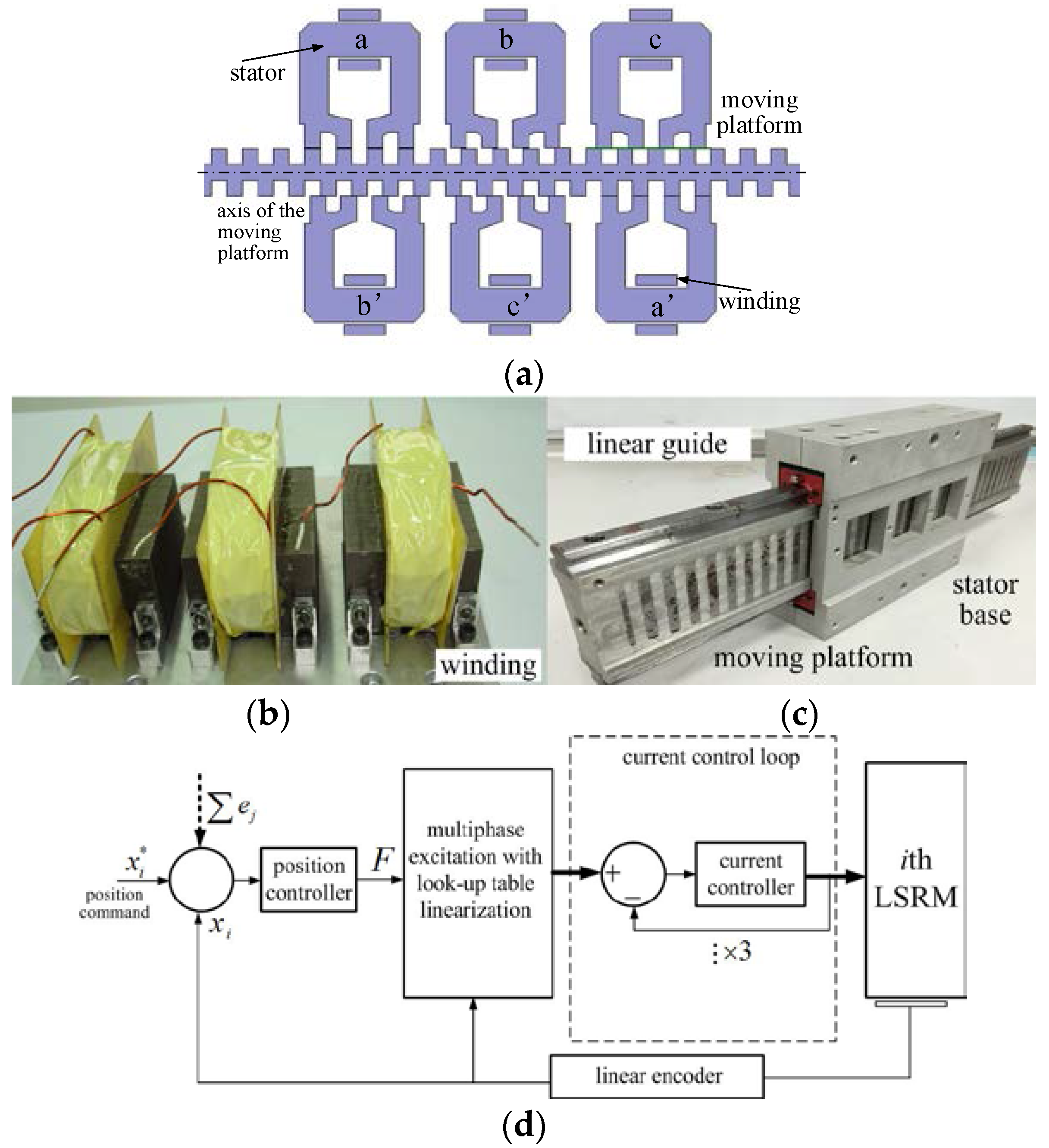
6. LSRMs Network Construction
6.1. LSRM Node
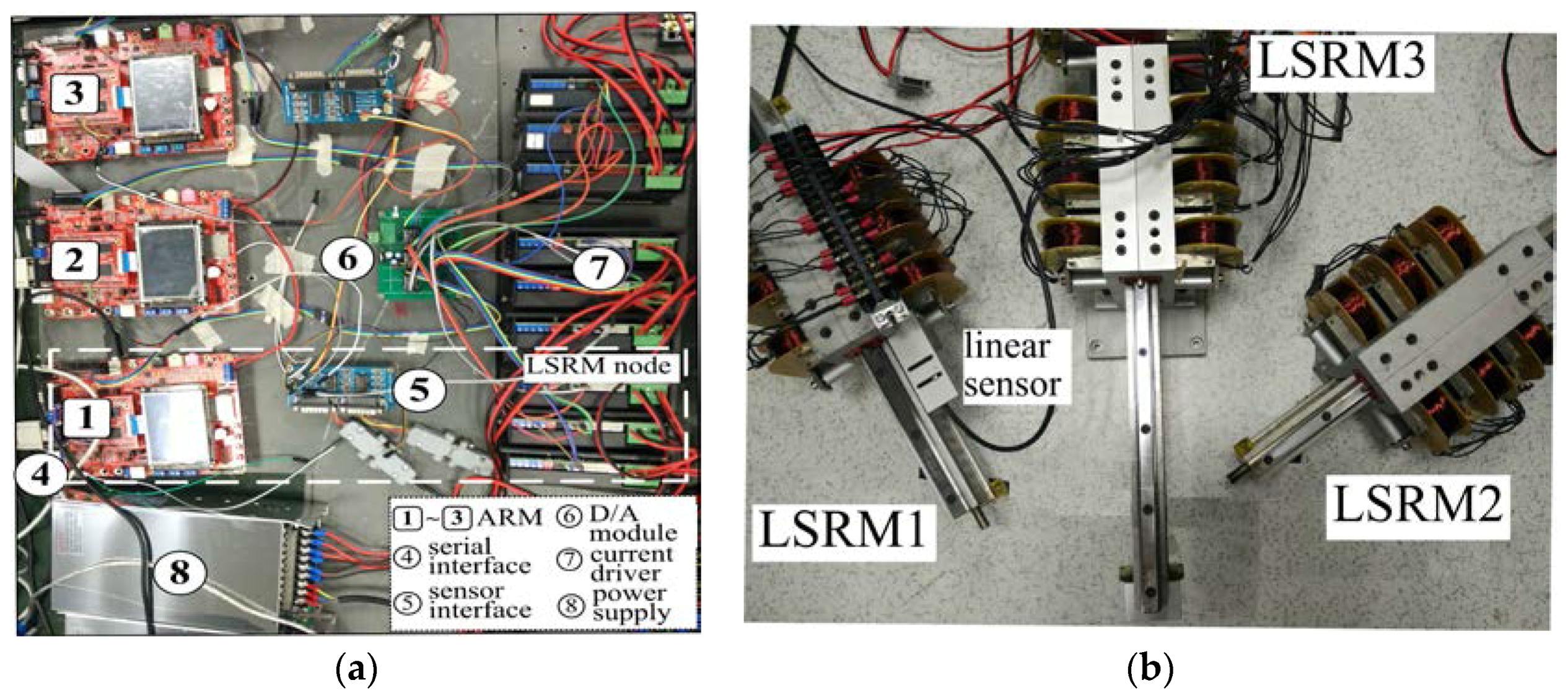
6.2. Construction of LSRMs Network
7. Experimental Results
7.1. Experimental Setup
7.2. Control Parameter Derivations
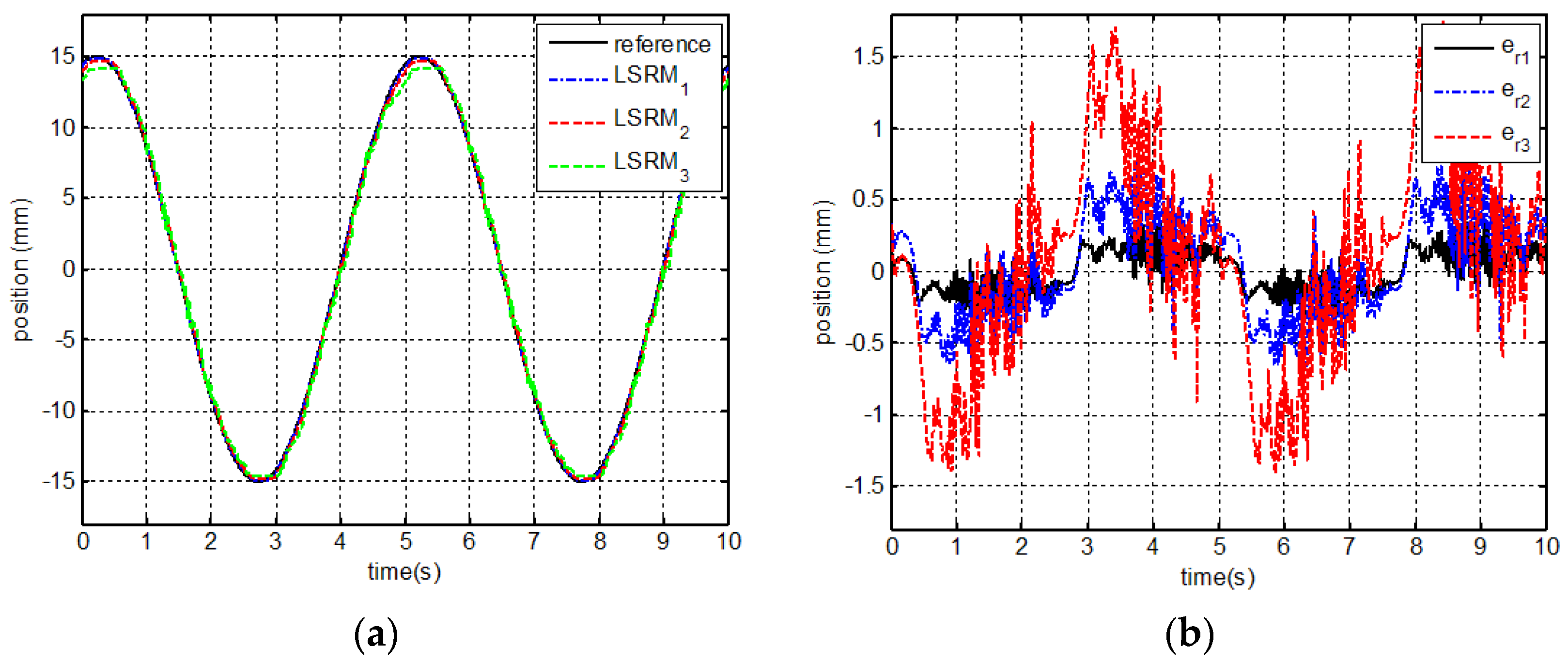
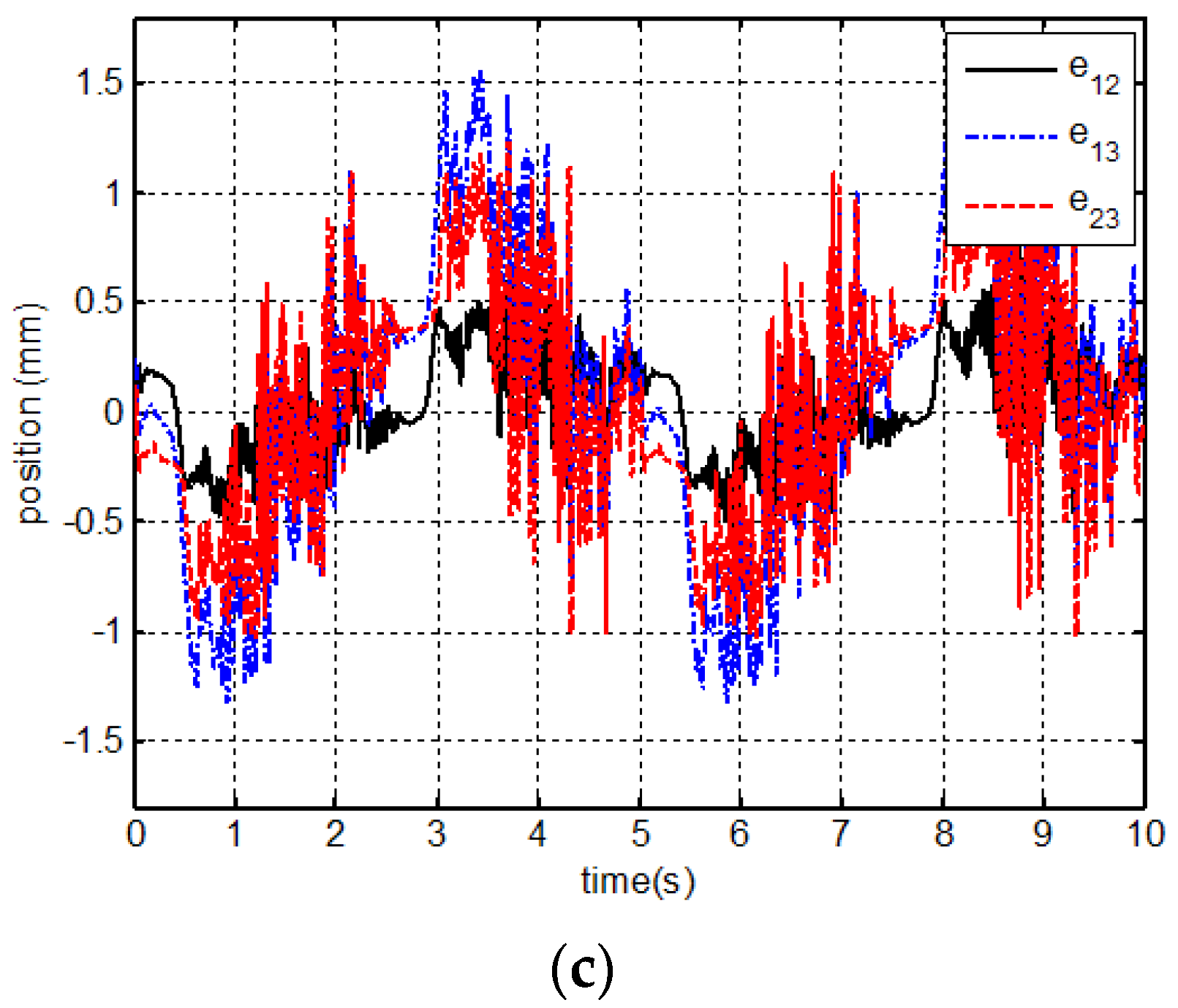
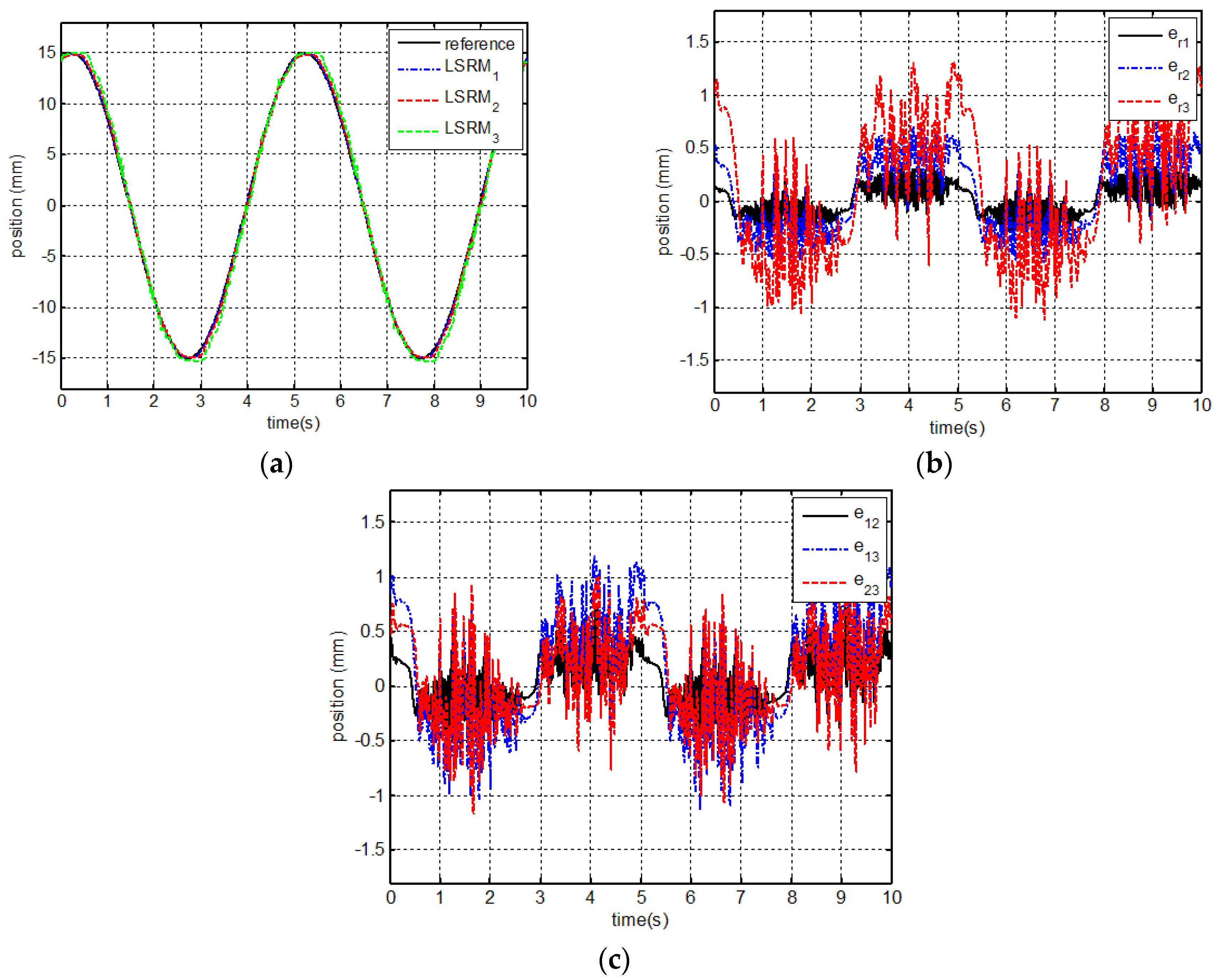
7.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
8. Conclusions and Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, B.; Pan, J.F.; Yuan, J.; Rao, W.; Qiu, L.; Luo, J.; Dai, H. Tracking control with zero phase-difference for linear switched reluctance machines network. Energies 2017, 10, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, J.F.; Luo, J.; Wu, X.; Qiu, L.; Pan, J.F. Hierarchical distributed motion control for multiple linear switched reluctance machines. Energies 2017, 10, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Karray, F.; Basir, O.; Insop, S. A framework for coordinated control of multiagent systems and its applications. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2008, 38, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yuan, J.; Qiu, L.; Cheung, N.; Pan, J.F. Distributed coordinated motion tracking of the linear switched reluctance machine-based group control system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabattini, L.; Secchi, C.; Cocetti, M.; Levratti, A.; Fantuzzi, C. Implementation of coordinated complex dynamic behaviors in multirobot systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1018–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, L. Leader–follower flocking of multiple robotic fish. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 1372–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Alomair, B.; Bushnell, L.; Poovendran, R. Minimizing convergence error in multi-agent systems via leader selection: A supermodular optimization Approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2014, 59, 1480–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Rong, Z.; Chen, M.Z.Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, H. Decentralized adaptive pinning control for cluster synchronization of complex dynamical networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, S.; Twomey, C.; Hartnett, A. Revealing the hidden networks of interaction in mobile animal groups allows prediction of complex behavioral contagion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4690–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Liu, F.; Cao, J.; Yu, W. M-matrix strategies for pinning-controlled leader-following consensus in multiagent systems with nonlinear dynamics. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, J.; Ren, W. Leader–follower consensus of linear multi-agent systems with unknown external disturbances. Syst. Control Lett. 2015, 82, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, Y. Consensus for linear multi-agent systems with time-varying delays: A frequency domain perspective. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 8, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, B.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Chang, Y. Design and implementation of non-uniform sampling cooperative control on a group of two-wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 6, 5035–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Y. Integral sliding mode flight controller design for a quadrotor and the application in a heterogeneous multi-agent system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 12, 9389–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Chow, M. Resilient distributed control in the presence of misbehaving agents in networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 2038–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Slotine, J.; Barabási, A. Controllability of complex networks. Nature 2011, 473, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruths, J.; Ruths, D. Control profiles of complex networks. Science 2014, 343, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Slotine, J.J.; Barabási, A. Observability of complex systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2460–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Kachroo, P.; Contreras, S. A Dynamic Network Modeling-Based Approach for Traffic Observability Problem. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, S.; Kachroo, P.; Agarwal, S. Observability and Sensor Placement Problem on Highway Segments: A Traffic Dynamics-Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, S.; Agarwal, S.; Kachroo, P. Quality of Traffic Observability on Highways with Lagrangian Sensors. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2017, PP, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.O.; Gharesifard, B. Graph controllability classes for the Laplacian leader-follower Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.; Hadjicostis, C.N. Structural controllability and observability of linear systems over finite fields with applications to multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerstedt, M.; Martini, S.; Cao, M.; Camlibel, K.; Bicchi, A. Interacting with networks: How does structure relate to controllability in single-leader consensus networks? IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2012, 32, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T. On the controllability and observability of networked dynamic systems. Automatica 2015, 52, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commault, C.; Dion, J. Input addition and leader selection for the controllability of graph-based systems. Automatica 2013, 49, 3322–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrom, K.J.; Murray, R.M. Feedback Systems: An Introduction for Scientists and Engineers; Princeton University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 201–220. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Li, Z.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Chen, S. Delay-induced synchronization of identical linear multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, A.; Nabi-Abdolyousefi, M.; Mesbahi, M. Controllability and observability of network-of-networks via Cartesian products. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2014, 59, 2668–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.F.; Zou, Y.; Cao, G. An asymmetric linear switched reluctance motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.Z. Linear System Theory; Tsinghua University Publishing House: Beijing, China; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Yuan, J.; Pan, J.; Wu, X.; Luo, J.; Qiu, L. Controllability and Leader-Based Feedback for Tracking the Synchronization of a Linear-Switched Reluctance Machine Network. Energies 2017, 10, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.F.; Zou, Y.; Cao, G. Adaptive controller for the double-sided linear switched reluctance motor based on the nonlinear inductance modeling. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2013, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
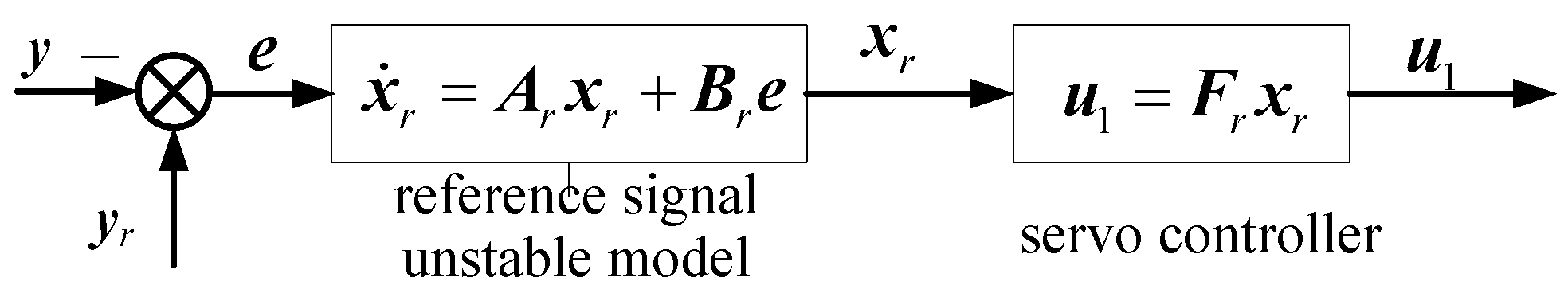
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| mass of moving platform | 3.8 kg |
| pole width | 6 mm |
| pole pitch | 12 mm |
| phase resistance | 2 ohm |
| air gap length | 0.3 |
| number of turns | 160 |
| stack length | 50 mm |
| Parameter | Controller | Observer |
|---|---|---|
| Gain |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Yuan, J.; Pan, J.F.; Wu, X.; Luo, J.; Qiu, L. Global Feedback Control for Coordinated Linear Switched Reluctance Machines Network with Full-State Observation and Internal Model Compensation. Energies 2017, 10, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122019
Zhang B, Yuan J, Pan JF, Wu X, Luo J, Qiu L. Global Feedback Control for Coordinated Linear Switched Reluctance Machines Network with Full-State Observation and Internal Model Compensation. Energies. 2017; 10(12):2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122019
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bo, Jianping Yuan, J. F. Pan, Xiaoyu Wu, Jianjun Luo, and Li Qiu. 2017. "Global Feedback Control for Coordinated Linear Switched Reluctance Machines Network with Full-State Observation and Internal Model Compensation" Energies 10, no. 12: 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122019
APA StyleZhang, B., Yuan, J., Pan, J. F., Wu, X., Luo, J., & Qiu, L. (2017). Global Feedback Control for Coordinated Linear Switched Reluctance Machines Network with Full-State Observation and Internal Model Compensation. Energies, 10(12), 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122019






