Minimization of the Electromagnetic Torque Ripple Caused by the Coils Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault in Dual-Redundancy Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Structure of the Novel DRPMSM
3. The Mathematical Model of the DRPMSM
- The influence of the saturation of the magnetic circuit is ignored;
- The stator magnetic field is sinusoidal ignoring the saturation of the magnetic circuit and the higher harmonics;
- The sine wave electromotive force is induced in the phase windings;
- The eddy current and hysteresis loss are ignored.
4. Analysis of Short Circuit Fault of DRPMSM
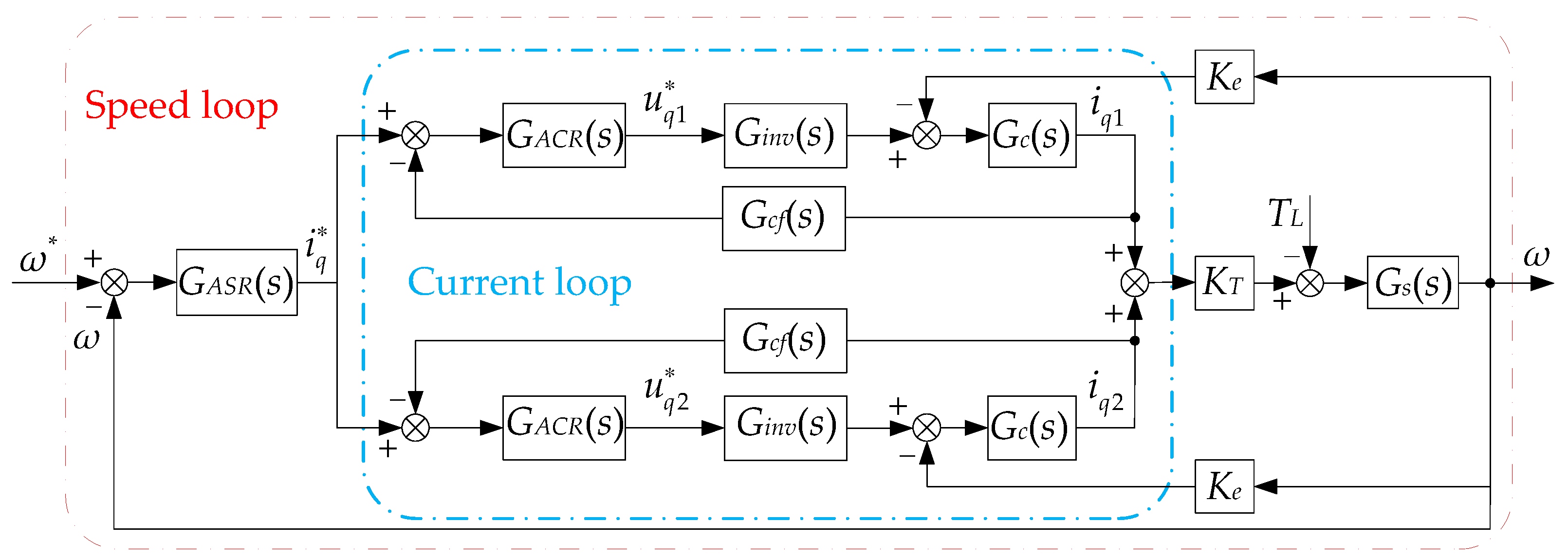
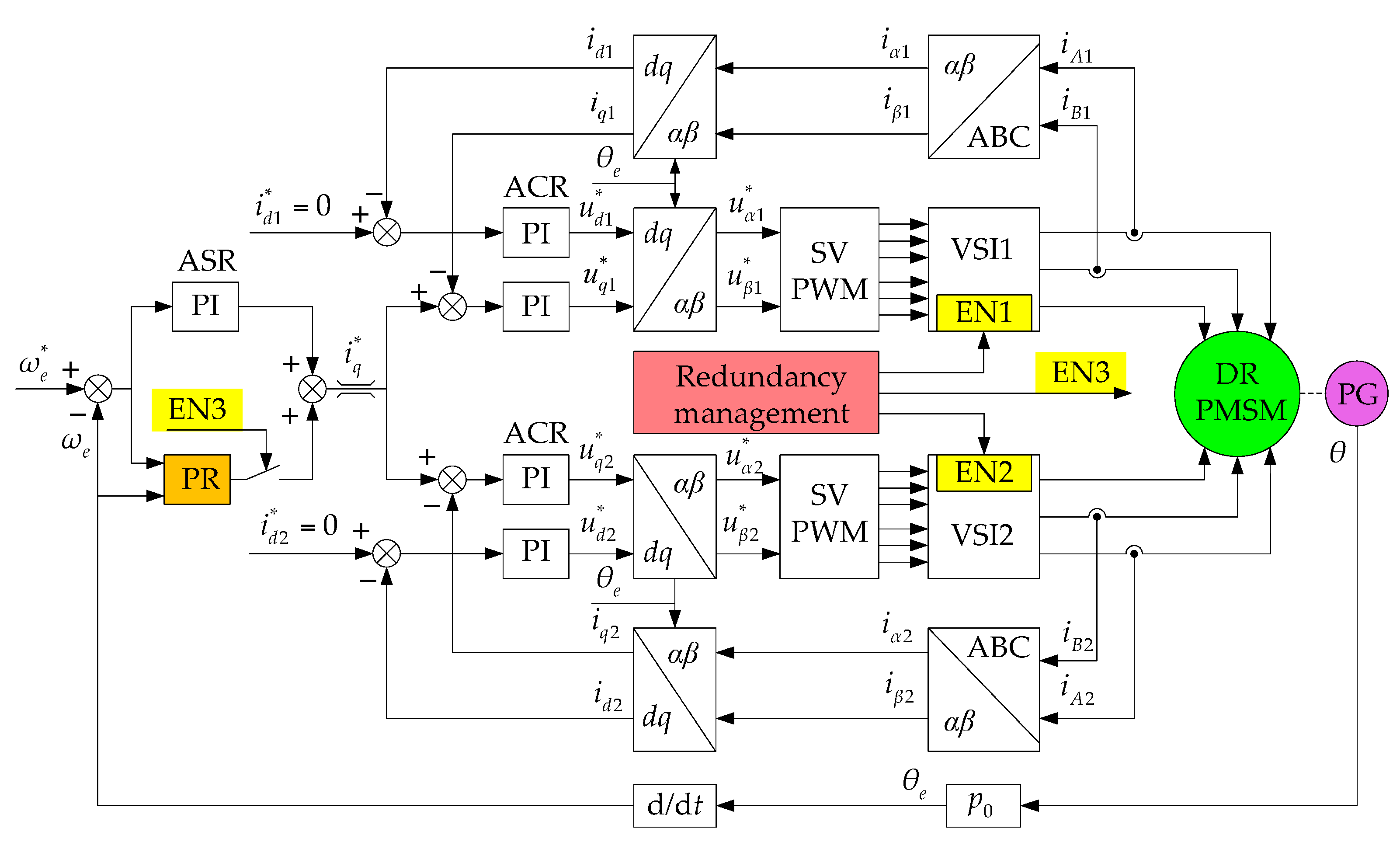
5. Suppression Strategy of Torque Ripple Caused by Short-Circuited Coils
5.1. The Principle of Suppression of Short Torque Ripple Caused by Short-Circuited Coils
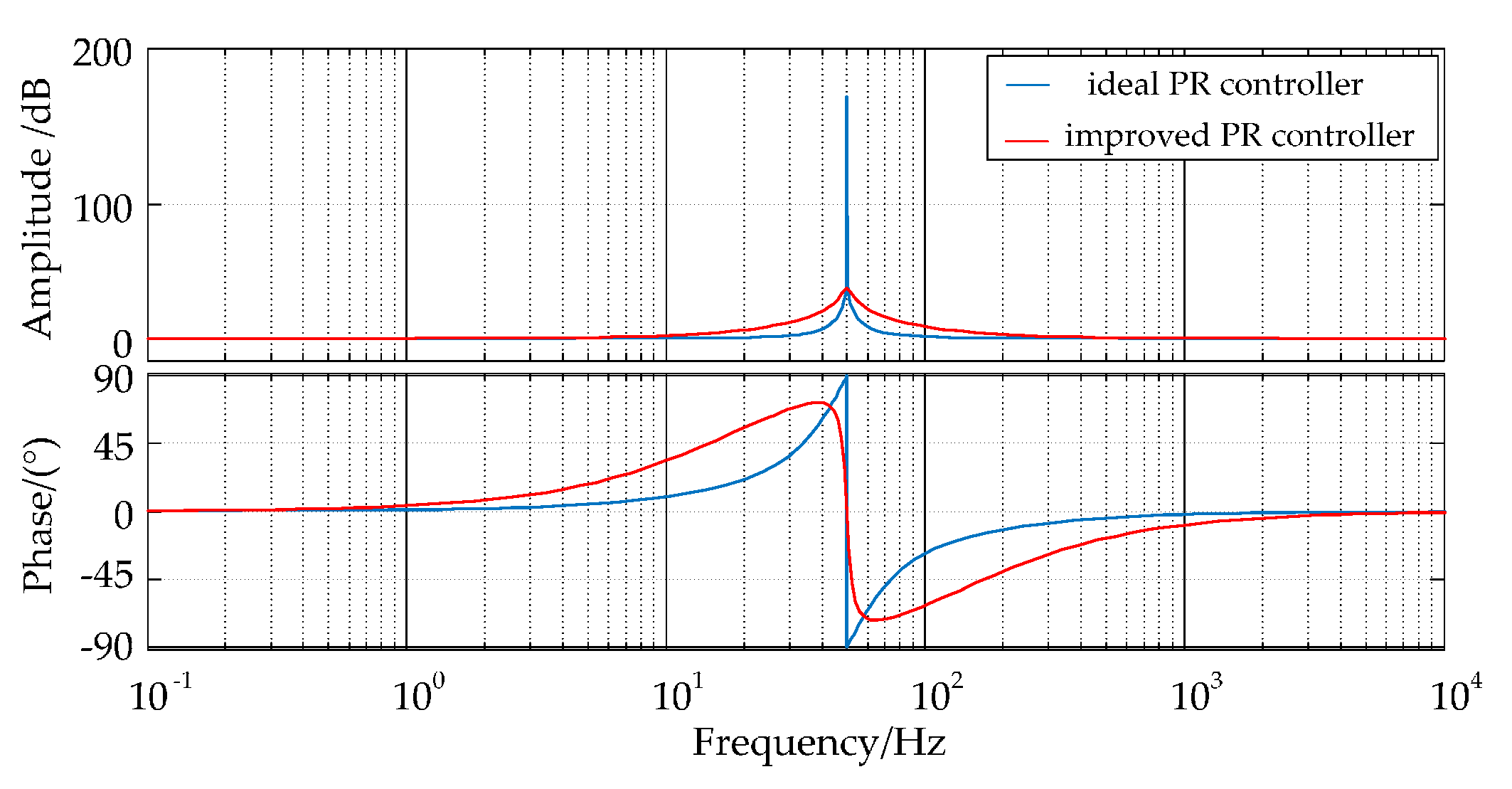
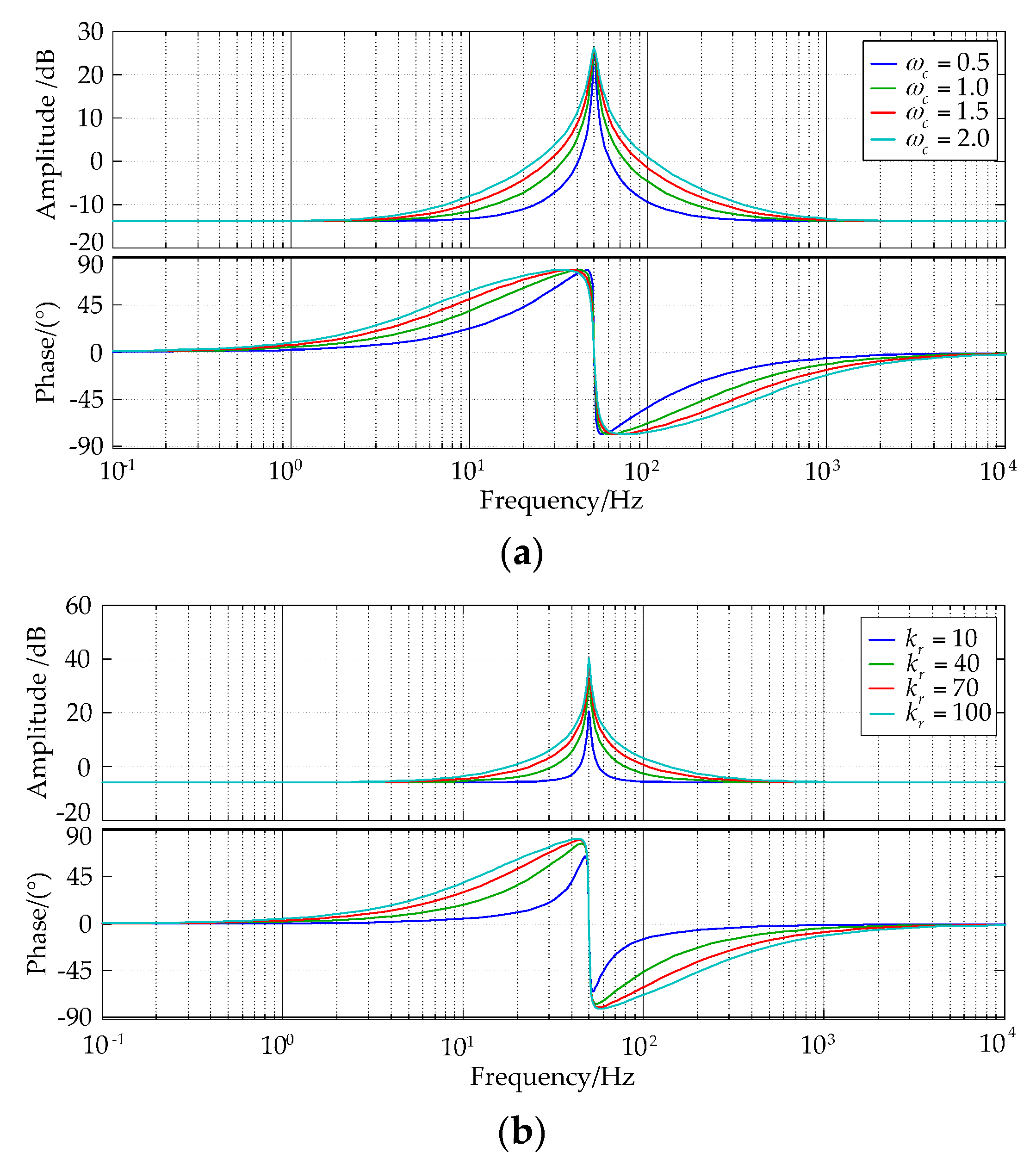
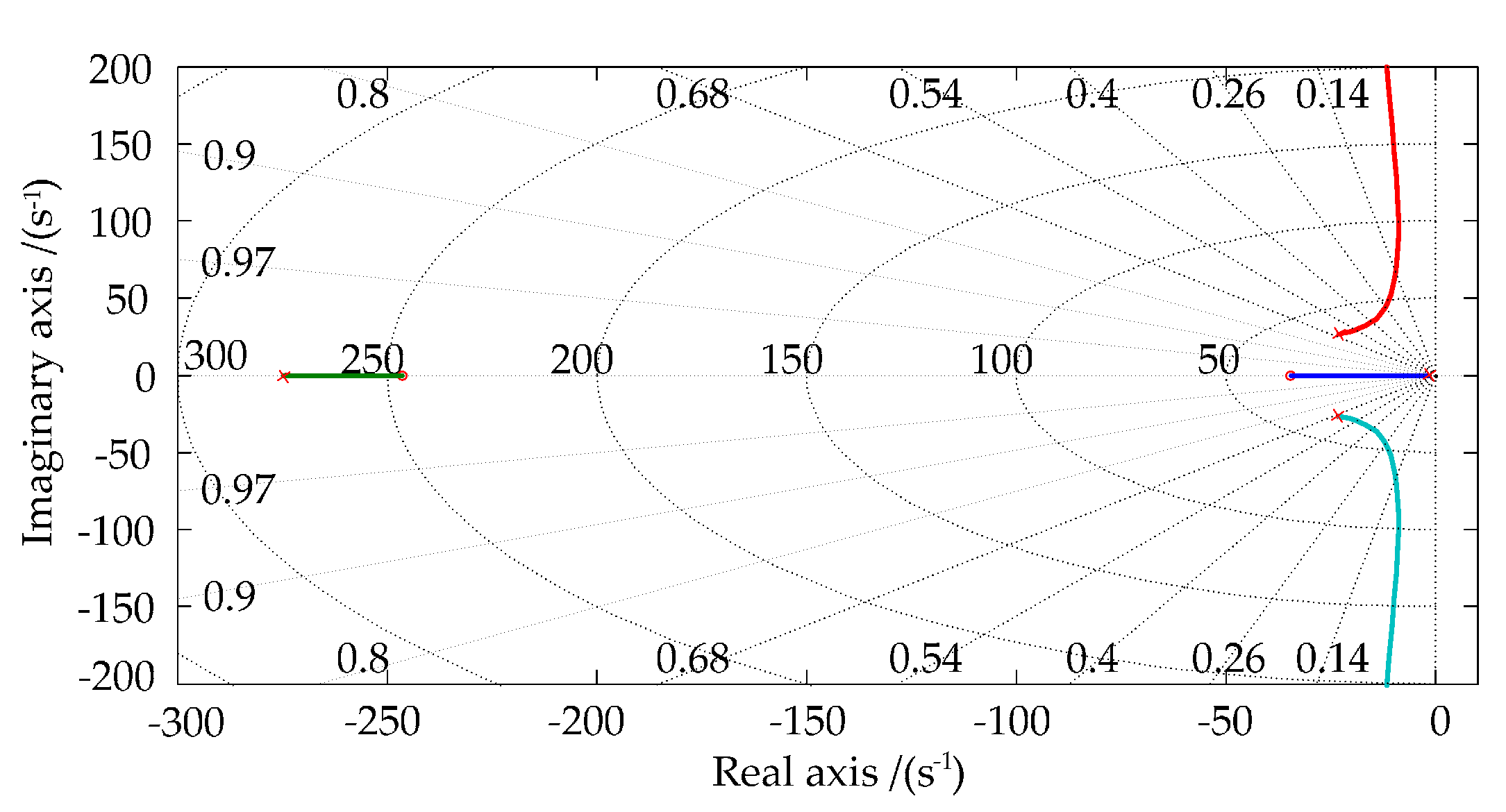
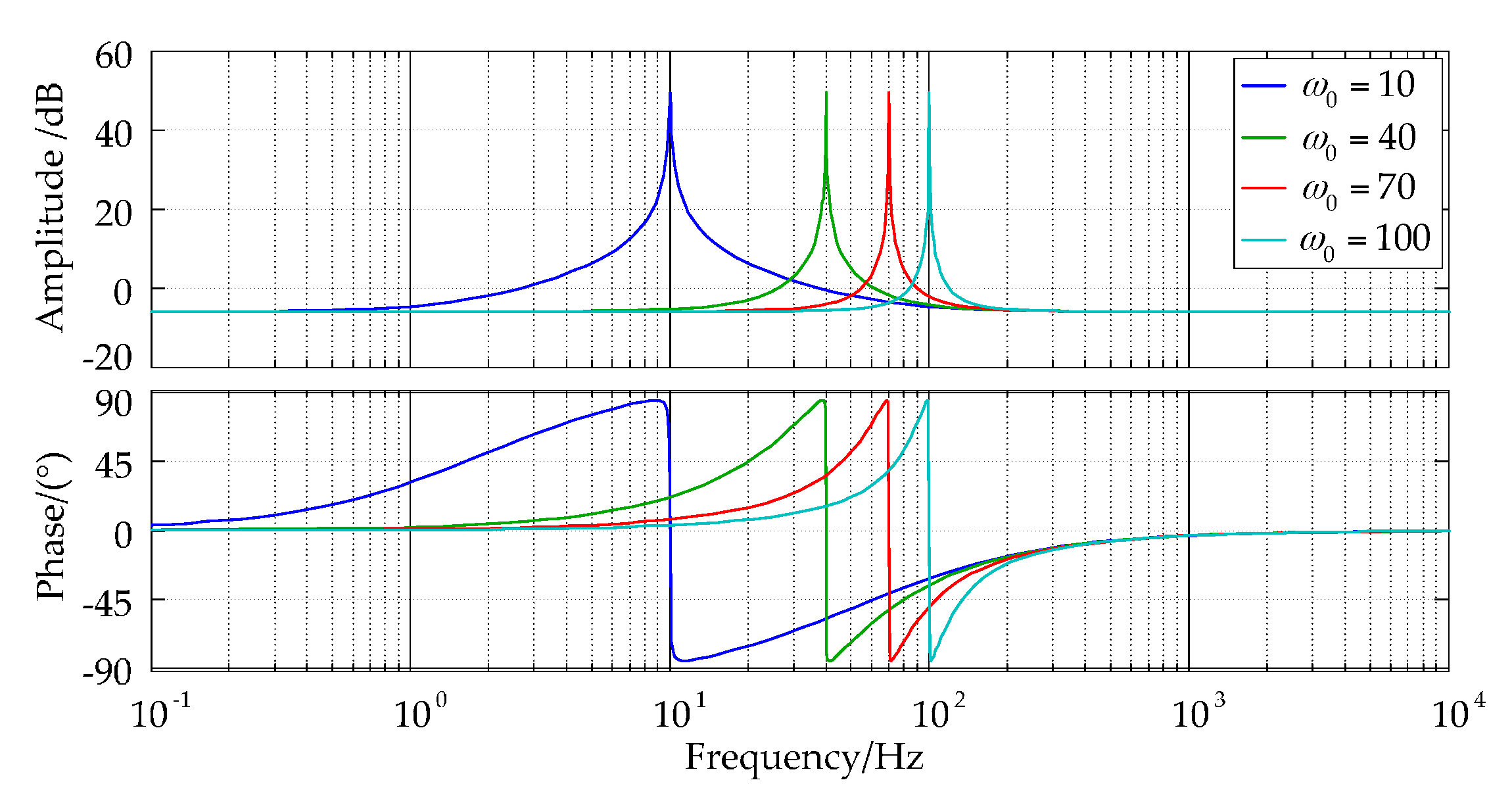
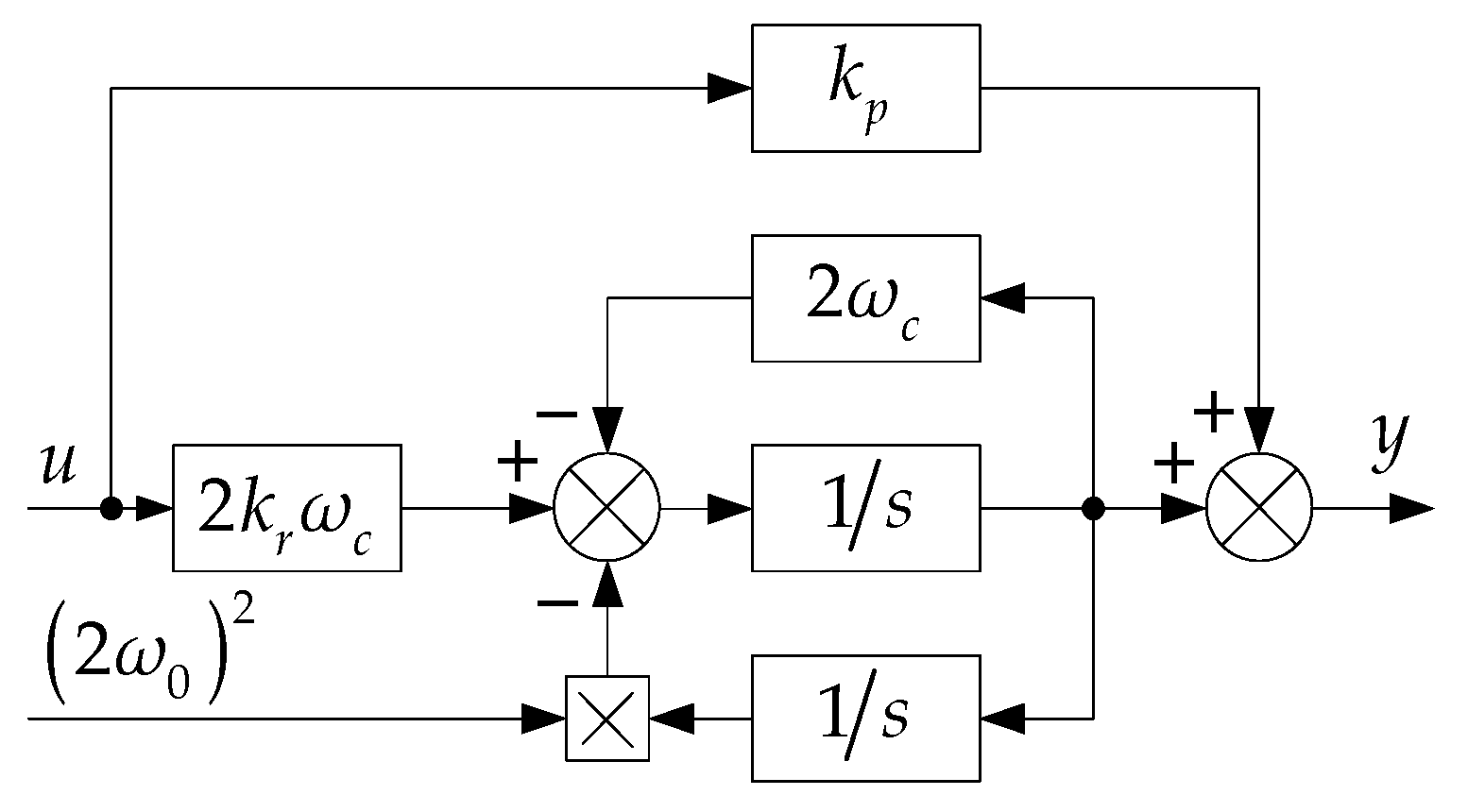
5.2. Principle of Frequency Adaptive PR Controller
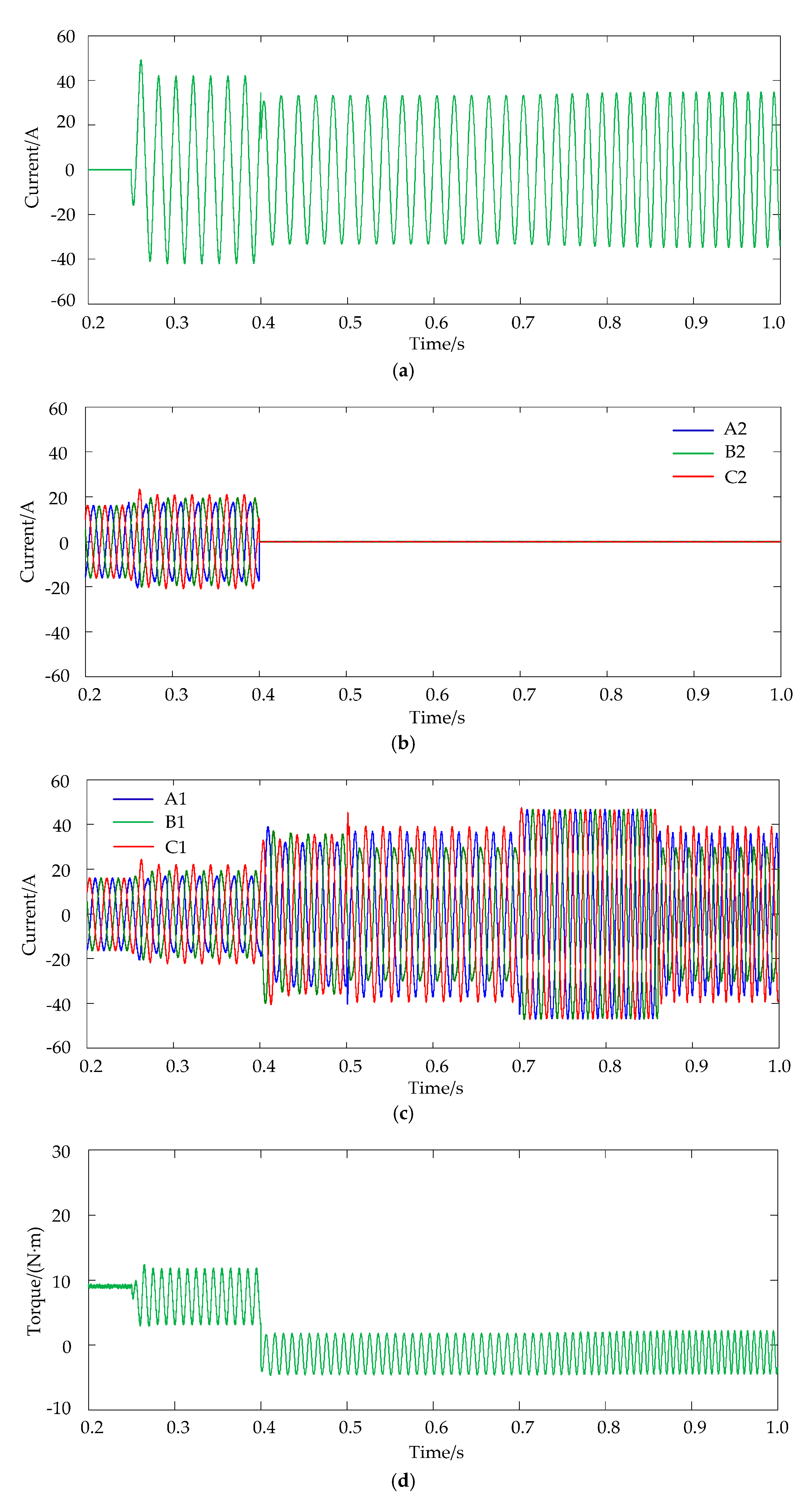
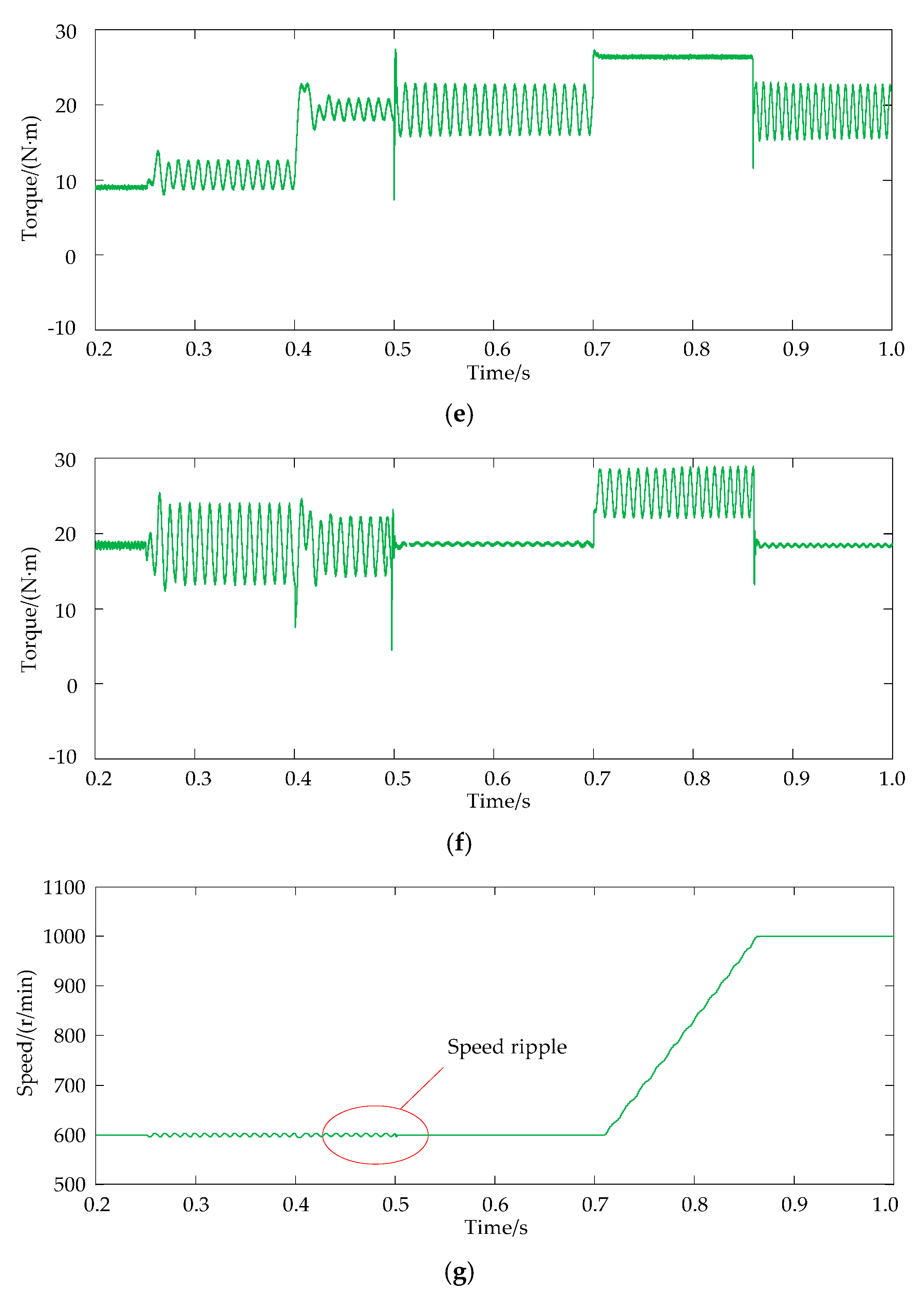
6. Simulation Results Analysis
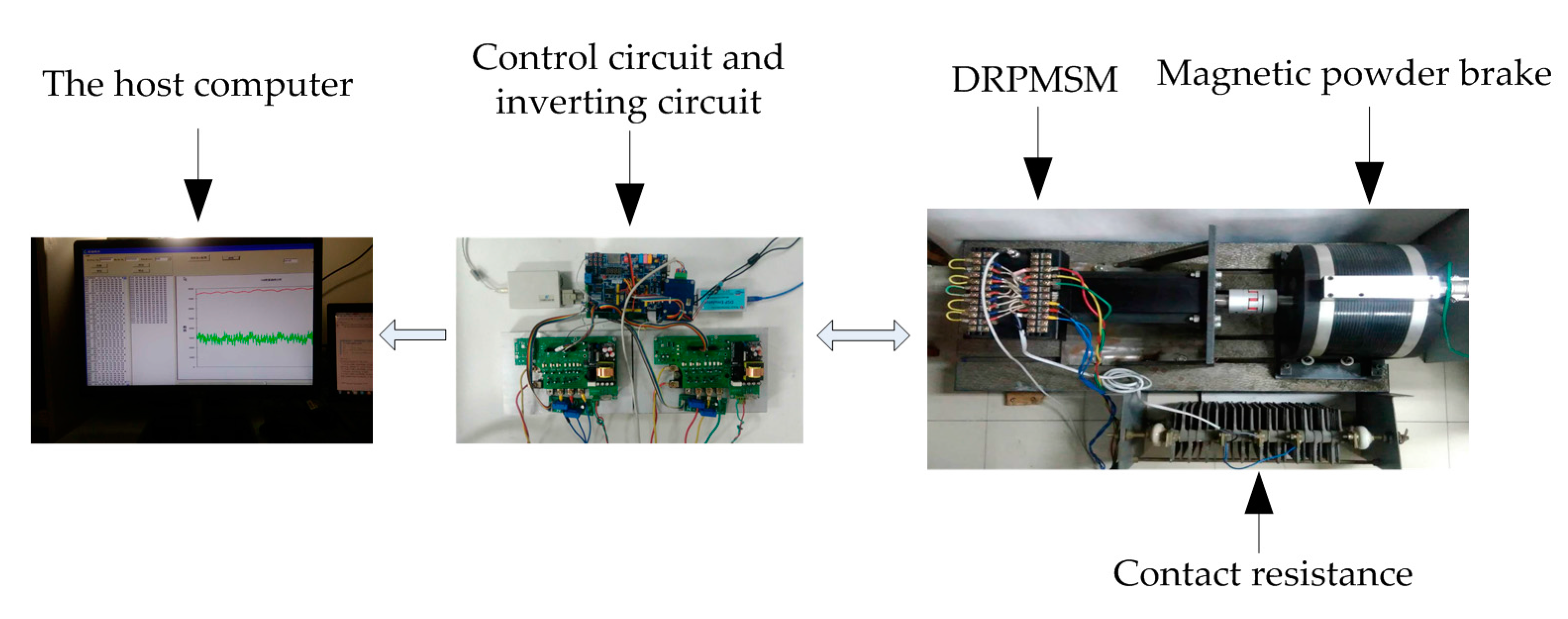
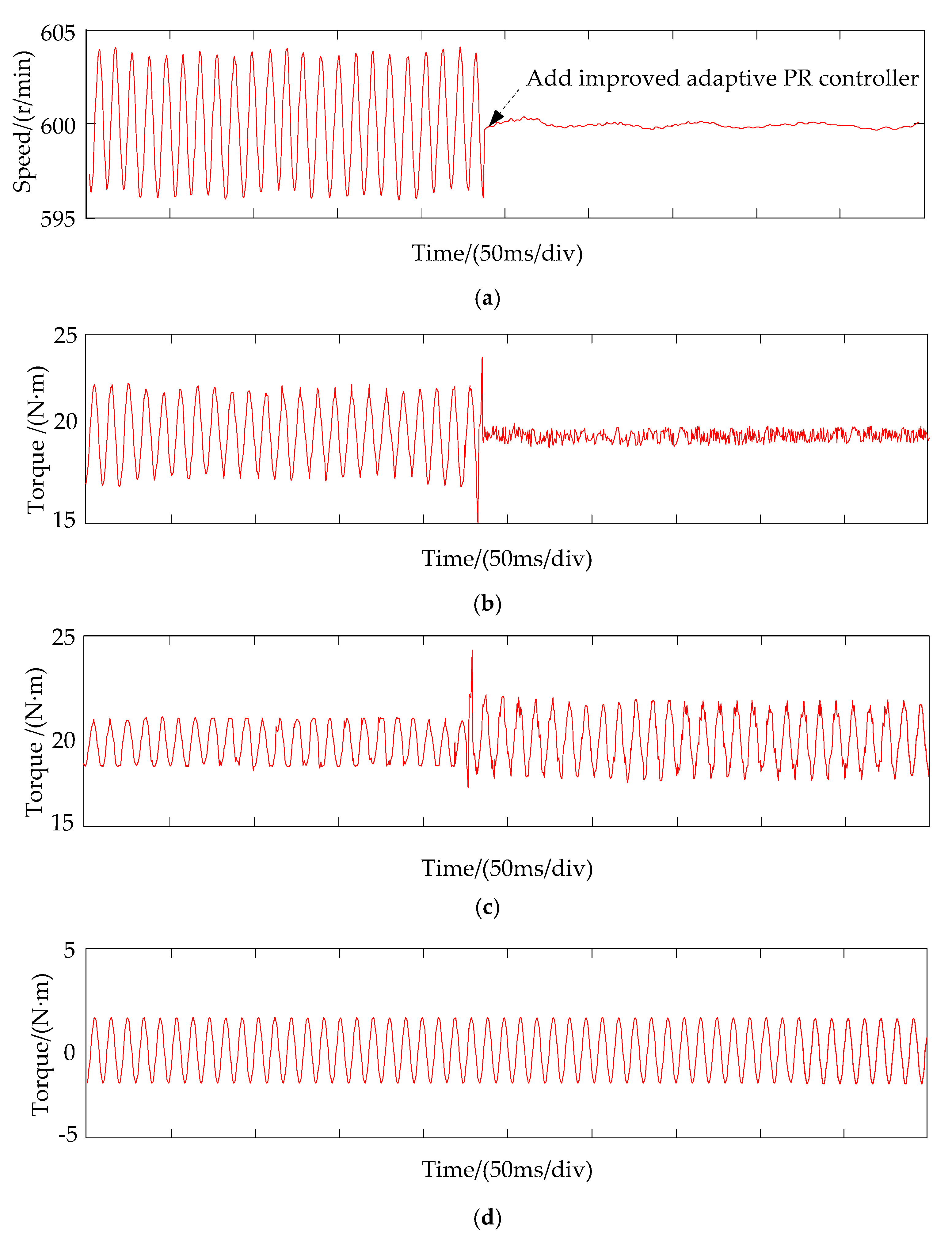
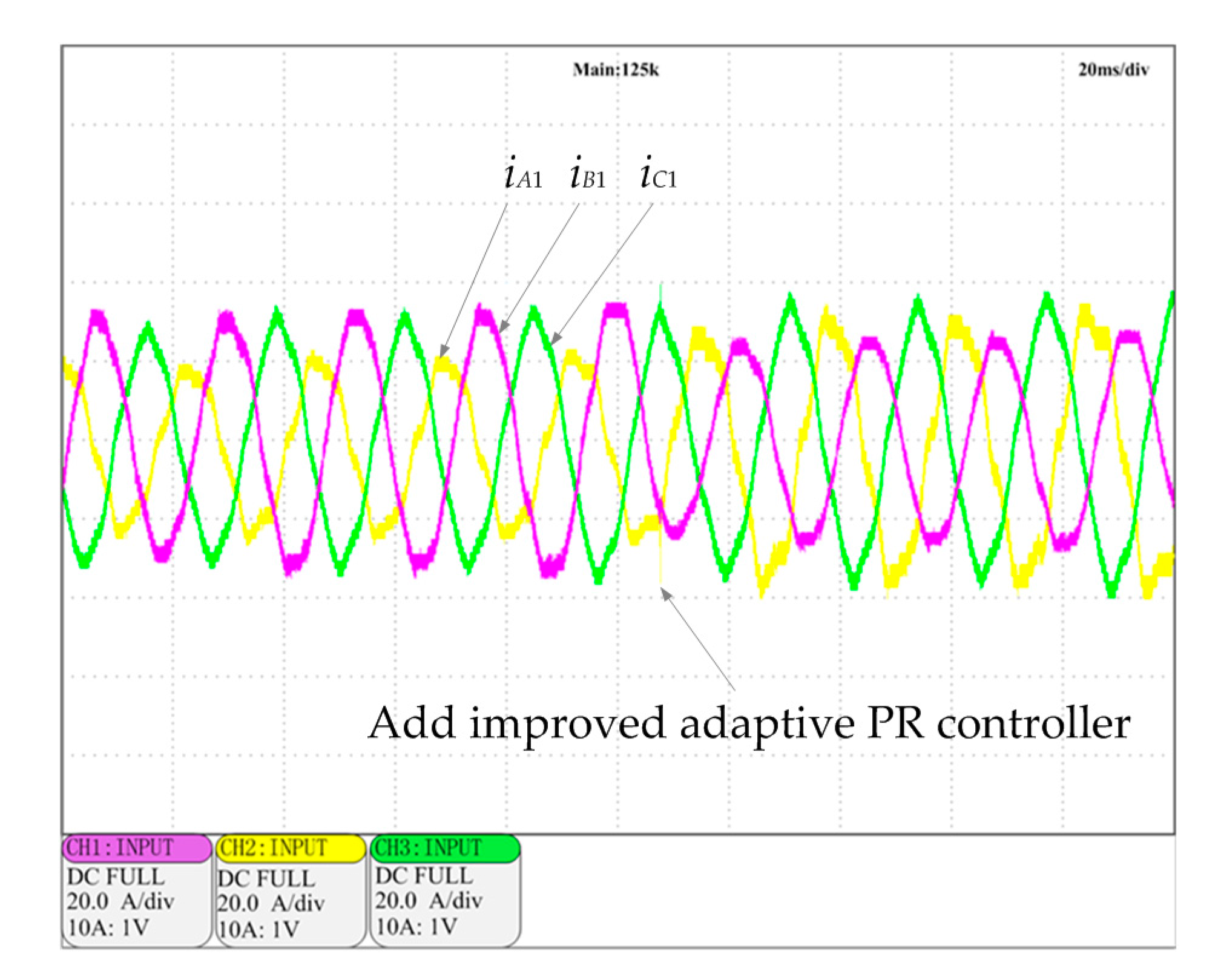
7. Experimental Results Analysis
8. Conclusions
- (1)
- The mutual inductance between any two phases of the DRPMSM is proved to be zero by using the finite element method. The mutual inductance between phases is smaller than the phase winding inductance by at least two orders of magnitude. The faulty windings will have no electromagnetic effects on the normal windings. This will improve the reliability of the DRPMSM.
- (2)
- An adaptive improved PR controller parallel with the PI controller in the speed loop is proposed to suppress the torque ripple generated by the short-circuited coils. It can be seen from the simulation and experimental results that the peak-to-peak value of torque ripple decreased from 7 N·m to 1 N·m when the speed of the DRPMSM is 600 r/min. The torque ripple is 1 N·m which is significant as it is 5.6% of rated torque.
- (3)
- In the operation of DRPMSMs, short-circuit faults may occur at various speeds, and a frequency adaptive improved PR controller is adopted to suppress the short-circuited torque ripple at various speeds. The simulation results show that the proposed torque ripple suppression strategy can suppress torque ripple at various speeds of the DRPMSM.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, P.; Wu, F.; Lei, Y.; Sui, Y.; Yu, B. Investigation of a novel 24-slot/14-pole six-phase fault-tolerant modular permanent-magnet in-wheel motor for electric vehicles. Energies 2013, 6, 4980–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Mecrow, B.C.; Atkinson, G.J.; Bennett, J.W.; Atkinson, D.J. Overview of electric motor technologies used for more electric aircraft (MEA). IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar]
- An, Q.T.; Liu, J.; Peng, Z.; Li, S.; Sun, L.Z. Dual-space vector control of open-end windings permanent magnet synchronous motor drive fed by dual inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 8329–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Xu, Y.X.; Zou, J.B. A phase current reconstruction approach for three-phase permanent-magnet synchronous motor drive. Energies 2016, 9, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H. Detuning minimization of induction motor drive system for alternative energy vehicles. Energies 2015, 8, 9117–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lipo, T.A. Space vector PWM control of dual three-phase induction machine using vector space decomposition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecrow, B.C.; Jack, A.G.; Atkinson, D.J.; Green, S.R.; Atkinson, G.J.; King, A.; Green, B. Design and testing of a four-phase fault-tolerant permanent-magnet machine for an engine fuel pump. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2004, 19, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Goodman, A.; Gerada, C.; Fang, Y.; Lu, Q. Design of a five-phase brushless dc motor for a safety critical aerospace application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 3532–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Bolognani, S.; Pré, M.D. Design of a Fault-tolerant IPM Motor for Electric Power Steering. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2005, 55, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Y. Design and realization of dual redundancy PMSM electrical drive systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Xi’an, China, 25–27 May 2009; pp. 1985–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, K.D.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Foster, M. Modified switching-table strategy for reduction of current harmonics in direct torque controlled dual-three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machine drives. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, A.V.; Khadkikar, V.; Xiao, W.; Zeineldin, H.H. Four-axis vector-controlled dual-rotor PMSM for plug-in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3202–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.S.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liu, K. Current control for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motors accounting for current unbalance and harmonics. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 272–284. [Google Scholar]
- Karttunen, J.; Kallio, S.; Peltoniemi, P.; Silventoinen, P.; Pyrhönen, O. Decoupled vector control scheme for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, X. Research on the integration of hybrid energy storage system and dual three-phase PMSM drive in EV. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, Y.; Aydin, M. A novel dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor with asymmetric stator winding. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, M.; Li, S. Fault-tolerant control of dual three-phase permanent-magnet synchronous machine drives under open-phase faults. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.F.; Huang, W.X.; Cao, R.G.; Hao, Z.Y.; Jiang, W. Electric drive system of dual-windings fault-tolerant permanent-magnet motor for aerospace applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7322–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseghi, B.; Takorabet, N.; Caron, J.P.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Meibody-Tabar, F.; Humbert, G. Study of different architectures of fault-tolerant actuator using a two-channel PM motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Kou, P.; Liang, D. A fault tolerant control strategy for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor servo system based on frequency domain analysis. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER), Monte Carlo, Monaco, 6–8 April 2016; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Velly, N.; Takorabet, N.; Meibody-Tabar, F.; Liegeois, P.Y.; Nierlich, F.; Leynaert, F.N.; Humbertet, G. Double channel PM motor for avionic applications: Impact of winding topologies. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2009; pp. 2387–2394. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.G.; Zhai, W.C.; Shen, Y.H. Analysis on temperature field distribution of dual-redundancy PMSM. J. Tianjin Univ. 2015, 488–493. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Cheng, M.; Chau, K.T.; Hua, W.; Jia, H.Y.; Ji, J.H.; Li, W.L. Stator-flux-oriented fault-tolerant control of flux-switching permanent-magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 4191–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Tong, C.; Sui, Y.; Cheng, L.M.; Zheng, P. Influence of third harmonic back EMF on modeling and remediation of windings short circuit in a multiphase PM machine with FSCWs. IEEE Ind. Electron. Soc. 2016, 63, 6031–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.S.; Ge, B.J.; Tao, D.J.; Wen, R.X.; Xing, G. Influence of stator windings inter-turn short-circuit fault on generator electromagnetic torque characteristics. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2016, 31, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Xu, H.P.; Xue, S.S.; Huang, Q.P.; Xue, S. Torque ripple and losses of direct-drive multi-phase permanent magnet synchronous machines. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2014, 29, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, V.; Jeevananthan, S. Commutation torque ripple reduction in BLDC motor using modified SEPIC converter and three-level NPC inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischer, C.B.; Tibola, J.R.; Scherer, L.G.; de Camargo, R.F. Proportional-resonant control applied on voltage regulation of standalone SEIG for micro-hydro power generation. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2017, 11, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcugil, H.; Altin, N.; Ozdemir, S.; Sefa, I. Lyapunov-function and proportional-resonant-based control strategy for single-phase grid-connected VSI with LCL filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2838–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Pan, Y.L.; He, X. Magnetomotive force in permanent magnet synchronous machine with concentrated fractional-slot windings. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2010, 25, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, G.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D. A new feedback method for PR current control of LCL-filter-based grid-connected inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devassy, S.; Singh, B. Performance analysis of proportional resonant and ADALINE-based solar photovoltaic-integrated unified active power filter. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2017, 11, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Q.; Hao, W.Y.; Zhao, Q.L. Comparative analysis and digital implementation of novel control strategies for grid-connected inverters. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2007, 22, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.L.; Ji, B.; Yan, Y. Smooth Speed Control for Low-Speed High-Torque Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Using Proportional-Integral-Resonant Controller. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, A.G.; Freujedo, F.D.; Lopez, O.; Doval-Gandoy, J. High-performance digital resonant controllers implemented with two integrators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, A.G.; Freijedo, F.D.; Lopez, O.; Doval-Gandoy, J. Correction to high performance digital resonant controllers implemented with two integrators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
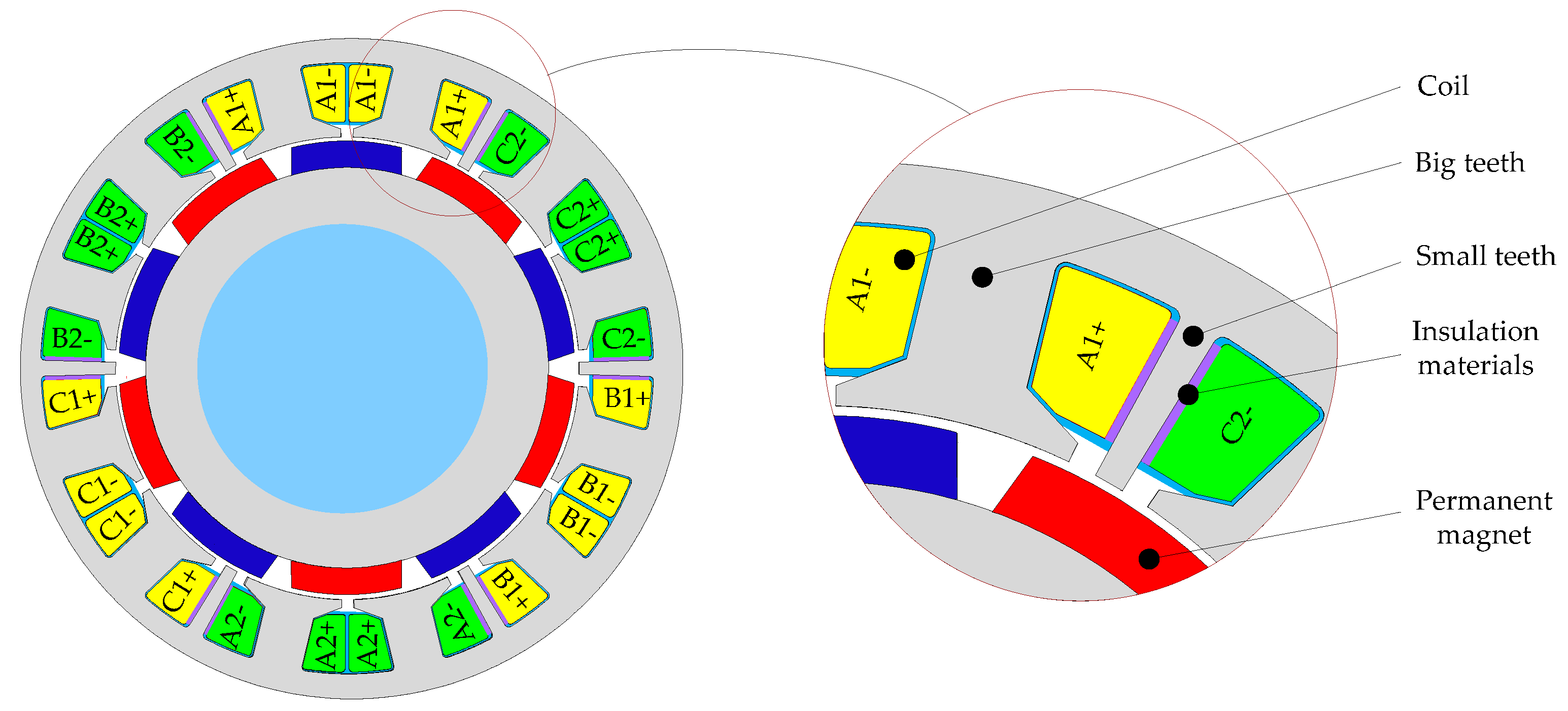
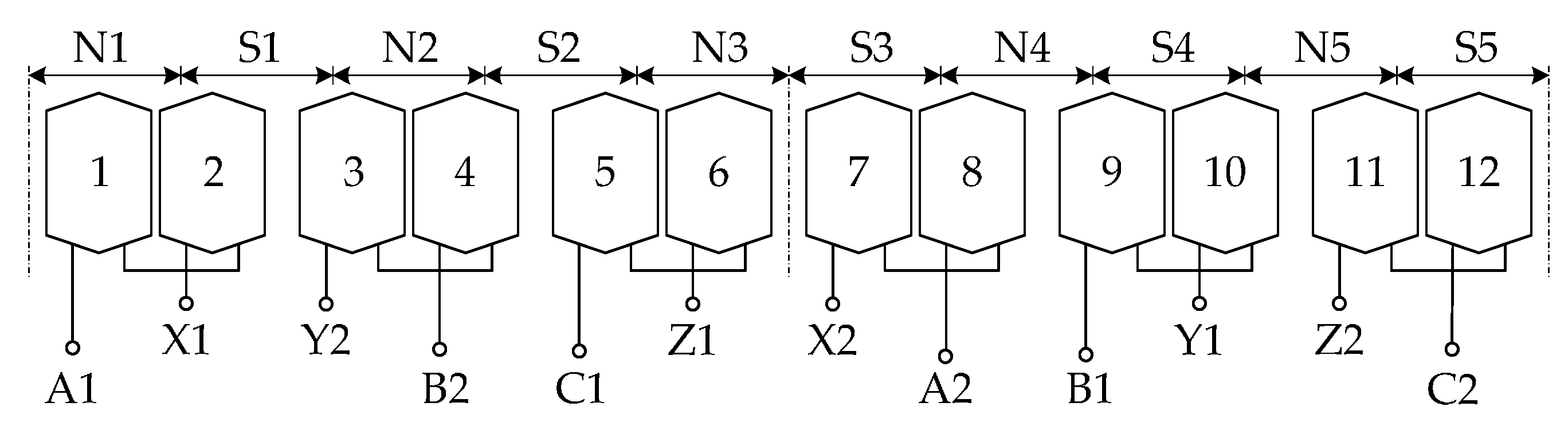
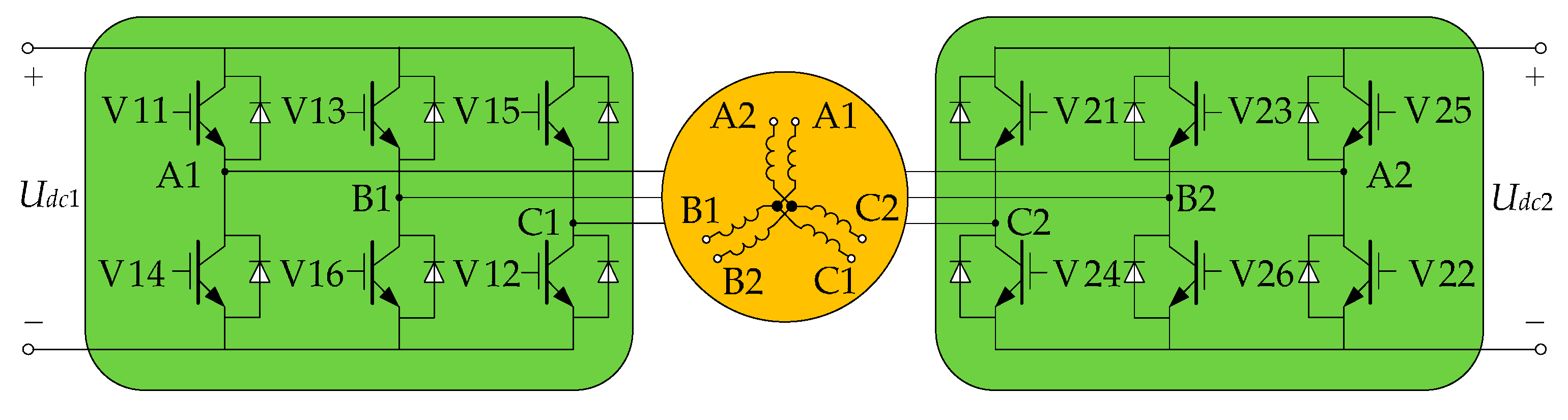
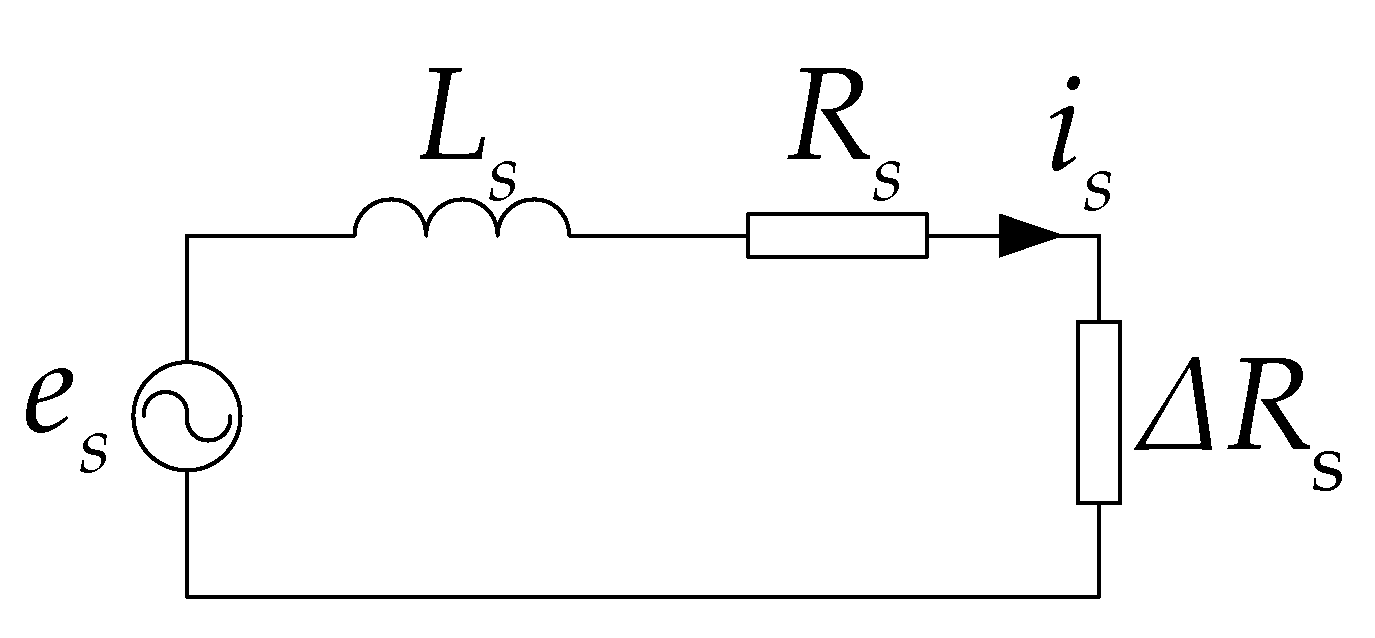


| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Core length/mm | 150 |
| Outer diameter of stator/mm | 120 |
| Inner diameter of stator/mm | 61 |
| Outer diameter of rotor/mm | 58 |
| Permanent magnet thickness L | 4.46 |
| Air gap length/mm | 1.5 |
| Slot width/mm | 2.5 |
| Lamination factor of stator/mm | 0.95 |
| Tooth depth/mm | 22.5 |
| L/mH | A1 | B1 | C1 | A2 | B2 | C2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 2.19 | 1.31 × 10−2 | 5.47 × 10−5 | 5.09 × 10−5 | 6.38 × 10−5 | 1.42 × 10−2 |
| B1 | 1.31 × 10−2 | 2.19 | 1.44 × 10−2 | 6.42 × 10−5 | 4.85 × 10−5 | 5.68 × 10−5 |
| C1 | 5.47 × 10−5 | 1.44 × 10−2 | 2.19 | 1.40 × 10−2 | 5.69 × 10−5 | 5.65 × 10−5 |
| A2 | 5.09 × 10−5 | 6.42 × 10−5 | 1.40 × 10−2 | 2.19 | 1.32 × 10−2 | 5.45 × 10−5 |
| B2 | 6.38 × 10−5 | 4.85 × 10−5 | 5.69 × 10−5 | 1.32 × 10−2 | 2.19 | 1.44 × 10−2 |
| C2 | 1.42 × 10−2 | 5.68 × 10−5 | 5.65 × 10−5 | 5.45 × 10−5 | 1.44 × 10−2 | 2.19 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated power PN | 3.5 kW |
| Rated speed n | 1200 r/min |
| Rated current IN | 17.7 A |
| Pole pairs p0 | 5 |
| Phase inductance L | 2.19 mH |
| Phase resistance R | 0.157 Ω |
| Permanent magnetic flux ψM | 0.094 Wb |
| System inertia J | 0.055 kg·m2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Zhang, B. Minimization of the Electromagnetic Torque Ripple Caused by the Coils Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault in Dual-Redundancy Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. Energies 2017, 10, 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111798
Chen Y, Zhang B. Minimization of the Electromagnetic Torque Ripple Caused by the Coils Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault in Dual-Redundancy Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. Energies. 2017; 10(11):1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111798
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yiguang, and Bo Zhang. 2017. "Minimization of the Electromagnetic Torque Ripple Caused by the Coils Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault in Dual-Redundancy Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors" Energies 10, no. 11: 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111798
APA StyleChen, Y., & Zhang, B. (2017). Minimization of the Electromagnetic Torque Ripple Caused by the Coils Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault in Dual-Redundancy Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. Energies, 10(11), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111798




