Energy Performance and Radial Force of a Mixed-Flow Pump with Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Tip Clearances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physical Model and Computational Domain
2.1. Parameters of the Mixed-Flow Pump
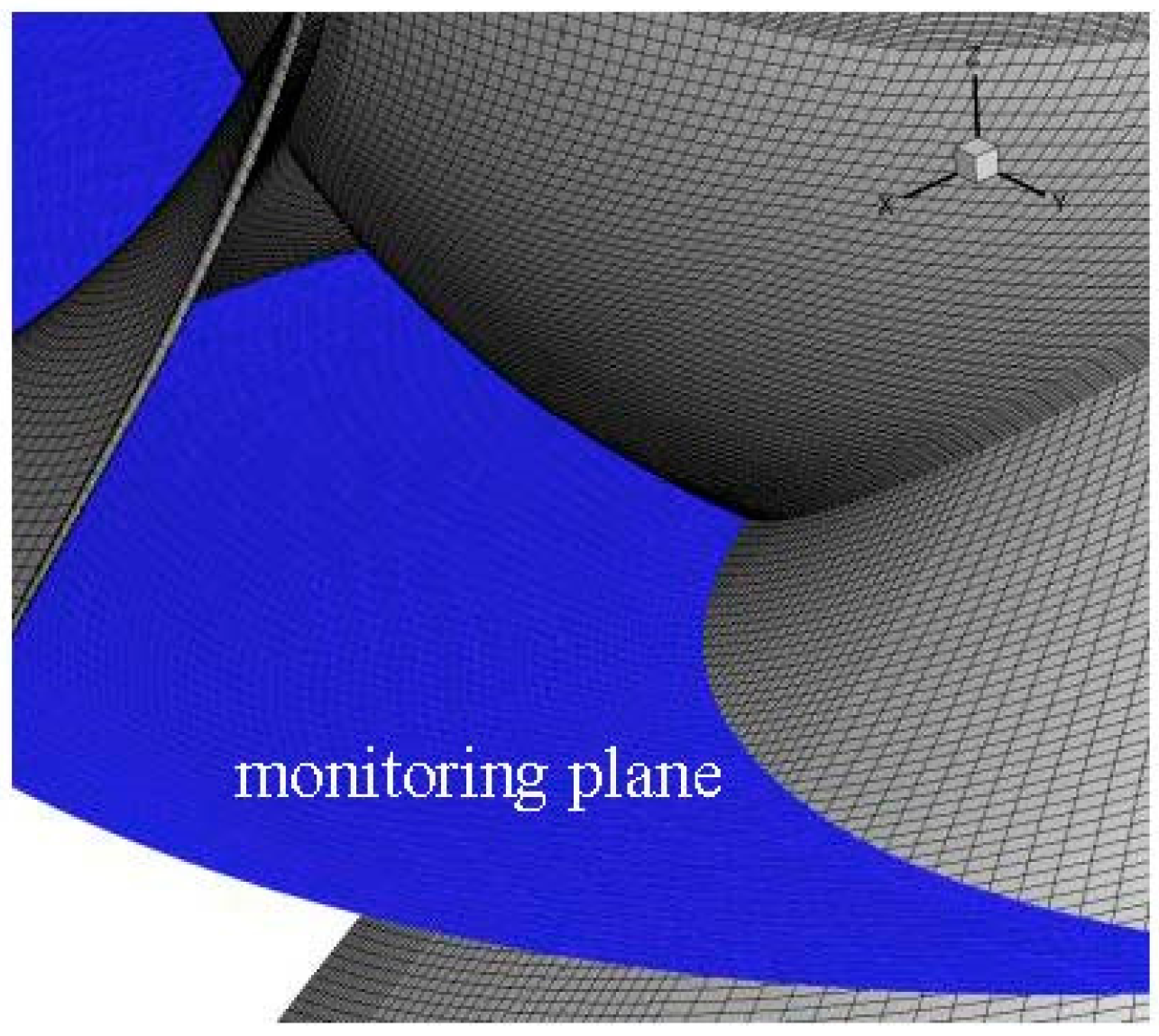
2.2. Computational Domain of the Mixed-Flow Pump
3. Numerical Method and Settings
3.1. Mathematical Model and Method
3.2. Mesh Independence Test
3.3. Time Step Independence Test
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Energy Performance
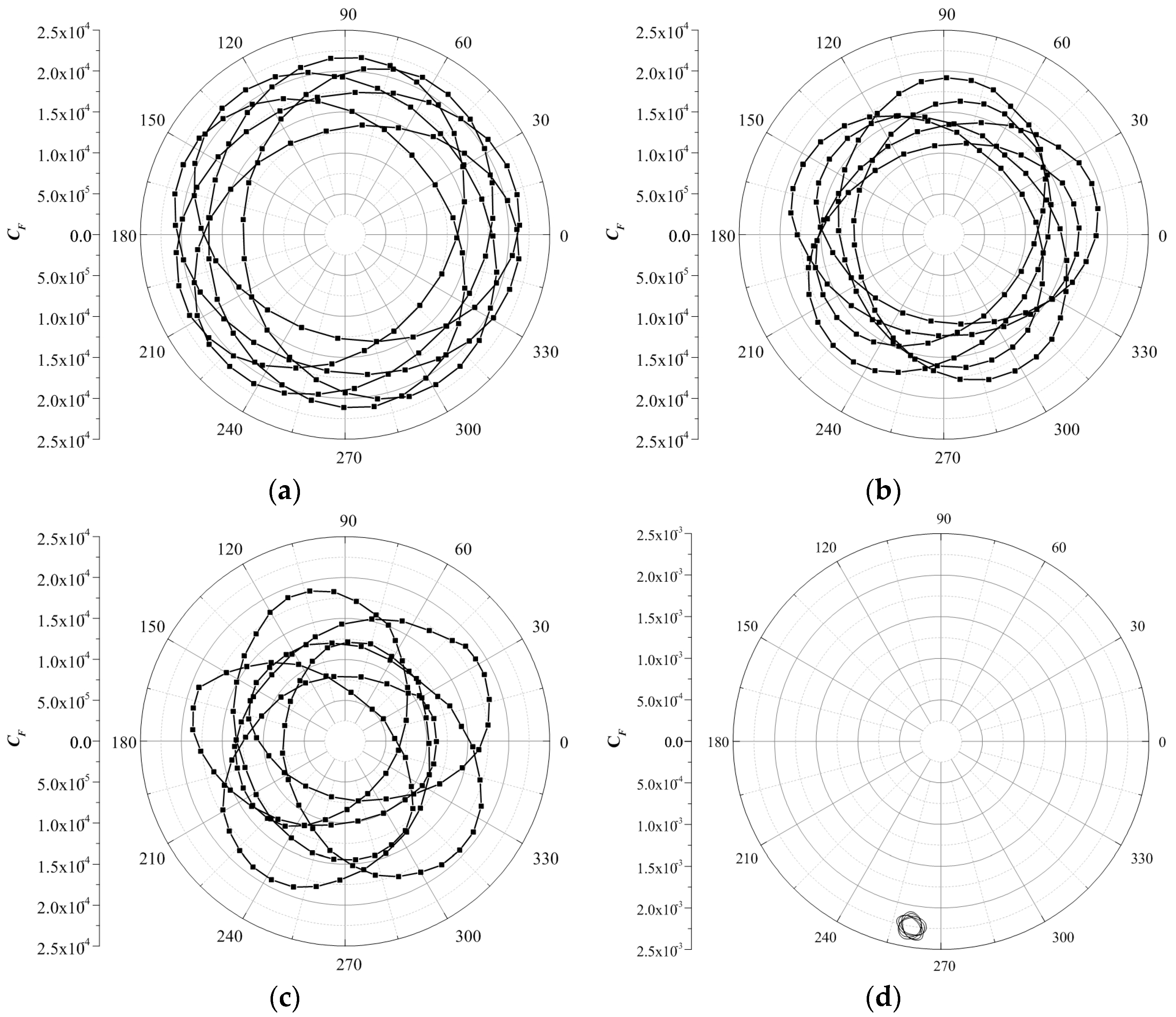
4.2. Radial Force on Principal Axis for Different Tip Clearances
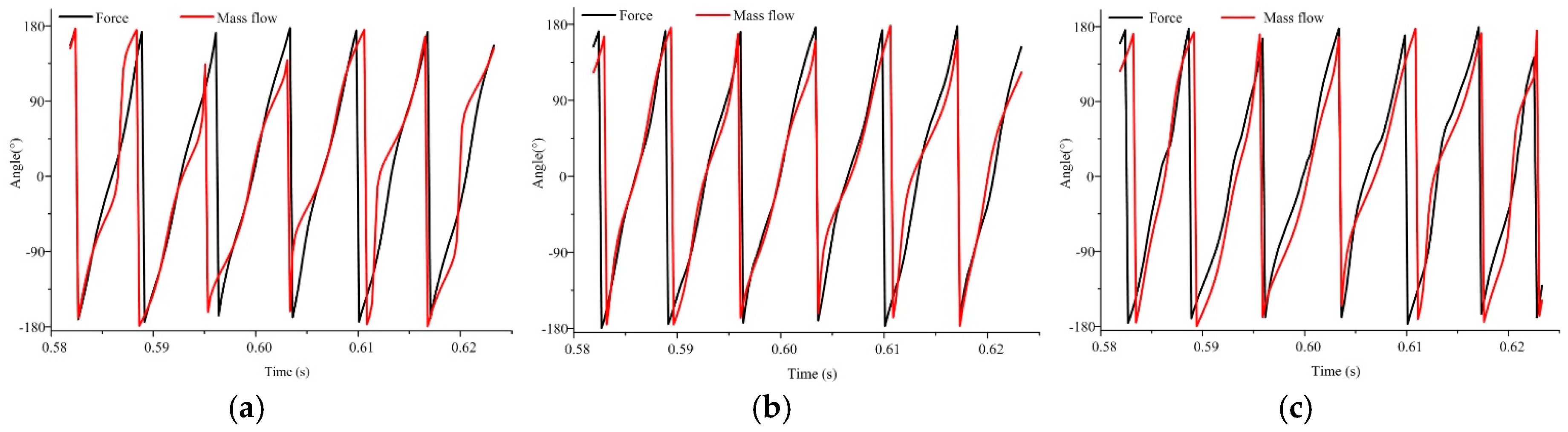
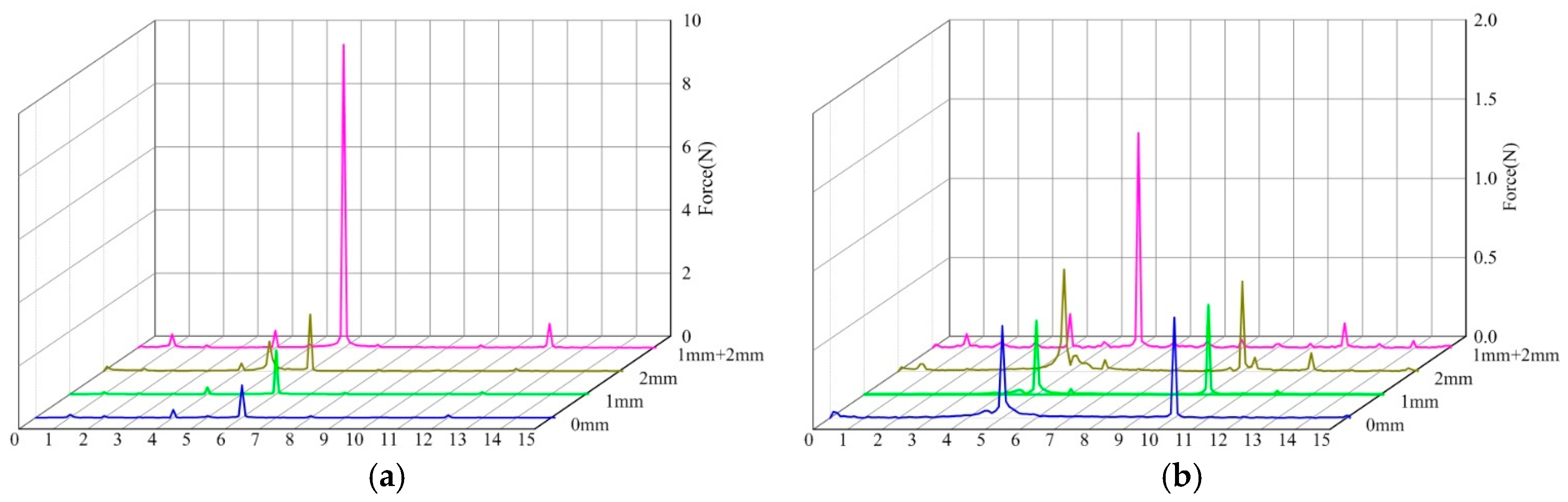
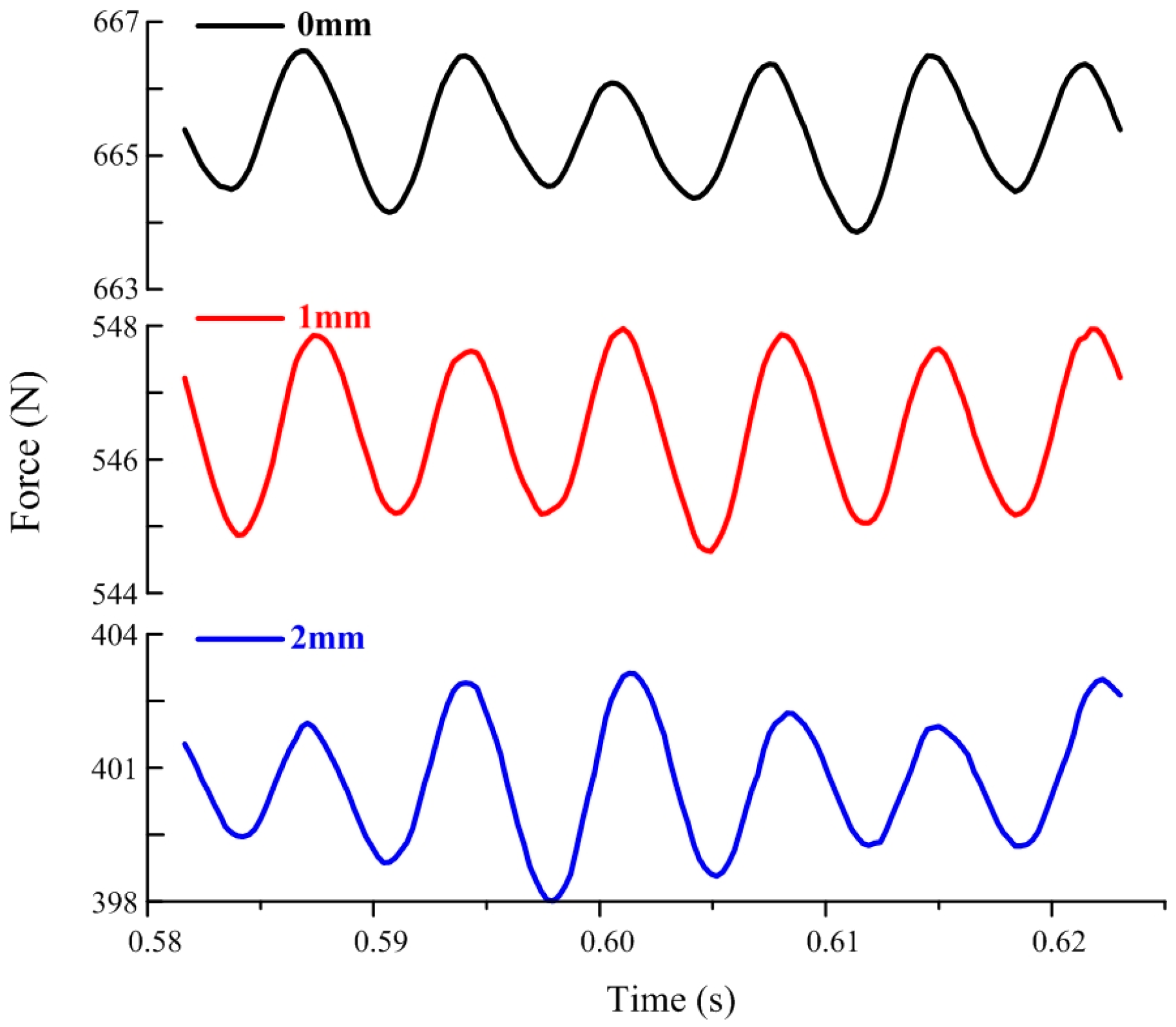
4.3. Spectral Analysis of Radial Force for Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Tip Clearances
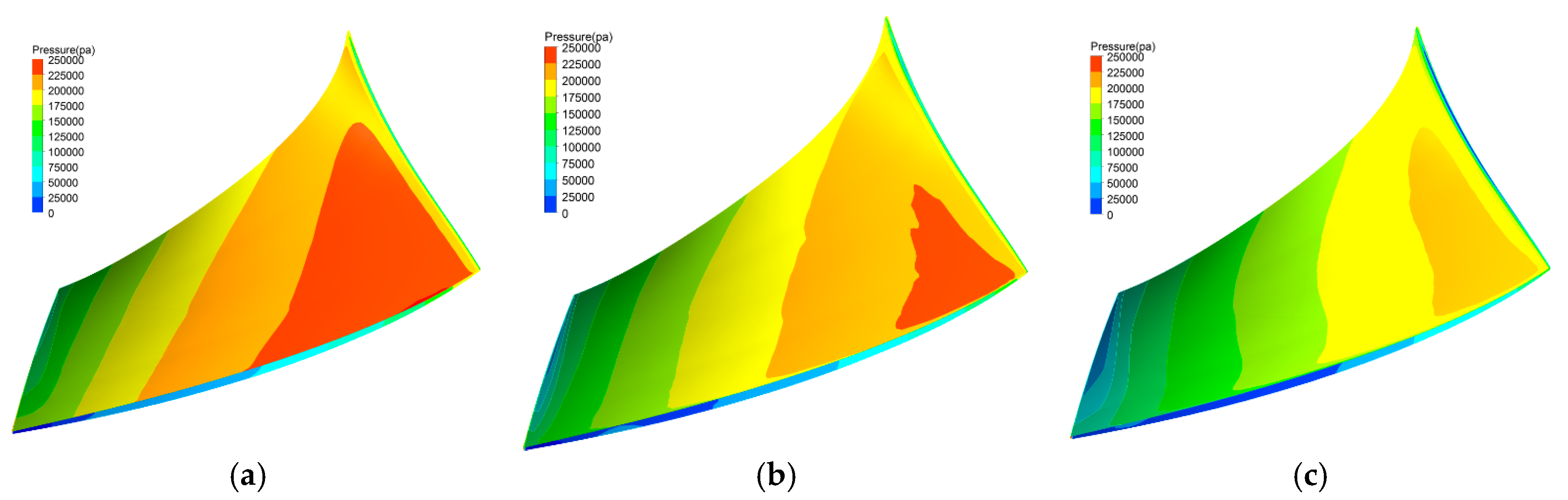
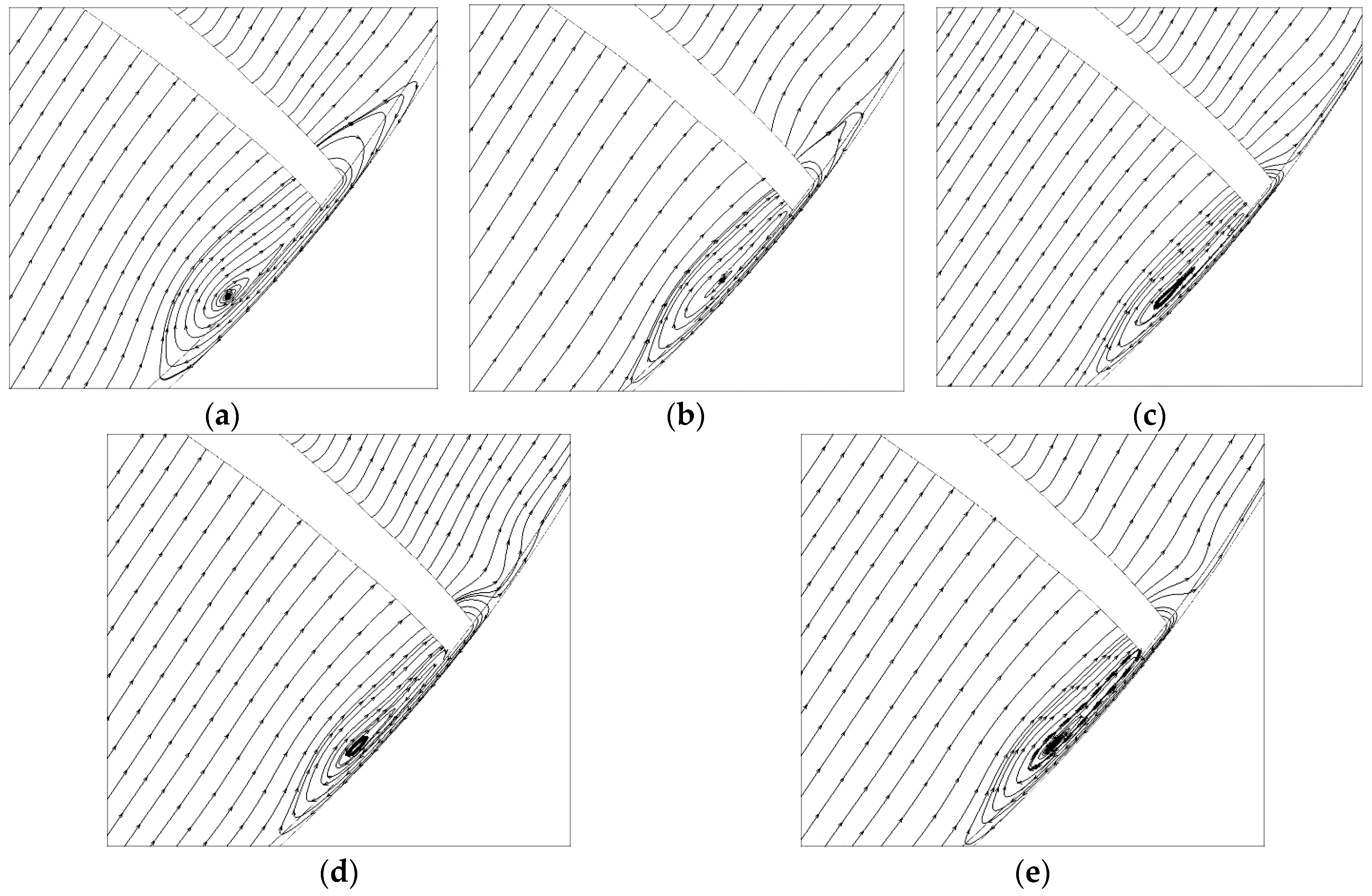
4.4. Analysis of Symmetrical Tip Clearance
4.5. Analysis of Unsymmetrical Tip Clearance
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Tip clearance markedly influences pump head and efficiency. The energy performance of the pump decreases as the tip clearance increases. In the comparison of symmetrical tip clearance, the pump head and efficiency of the unsymmetrical tip clearance 1 mm × 4 + 2 mm × 1 is between that of the symmetrical tip clearance 1 mm × 5 and tip clearance 2 mm × 5.
- (2)
- In the comparison of the symmetrical tip clearance, the magnitude of the radial force on the principal axis of the unsymmetrical tip clearance considerably increases, to approximately 15 times that of the symmetrical tip clearance, and the center of it moves from the coordinate origin to the third quadrant.
- (3)
- Spectrum analysis shows that the dominant frequencies of the radial force on the hub and the blade are 5fi, 6fi, or 10fi. In the comparison of the symmetrical tip clearance, the maximum amplitudes on the dominant frequency of the unsymmetrical tip clearance substantially increase to approximately 7 times that of the symmetrical tip clearance.
- (4)
- The leakage flow rates through blade tips vary in an impeller with unsymmetrical tip clearance, thereby making the flow pattern in each single channel uneven, generating a strong radial force on the principal axis, and thus affecting the operation stability of a mixed flow pump.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bing, H.; Tan, L.; Cao, S.L.; Lu, L. Prediction method of impeller performance and analysis of loss mechanism for mixed-flow pump. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2012, 55, 1988–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Cao, S.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhu, B.S. Direct and inverse iterative design method for centrifugal pump impellers. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2012, 226, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhu, B.S.; Cao, S.L.; Wang, Y.M. Influence of blade wrap angle on centrifugal pump performance by numerical and experimental study. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 27, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearhart, W.S. Tip clearance cavitation in shrouded underwater propulsors. J. Aircr. 1966, 3, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Laborde, R.; Chantrel, P.; Mory, M. Tip clearance and tip vortex cavitation in an axial flow pump. J. Fluids Eng. 1997, 119, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Wang, M.; Moin, P.; Mittal, R. Study of tip-clearance flow in turbomachines using large-eddy simulation. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2004, 6, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.X.; Miorini, R.L.; Katz, J. Measurements of the tip leakage vortex structures and turbulence in the meridional plane of an axial water-jet pump. Exp. Fluids 2011, 50, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.X.; Tan, D.; Miorini, R.L.; Katz, J. Three-dimensional flow structures and associated turbulence in the tip region of a waterjet pump rotor blade. Exp. Fluids 2011, 51, 1721–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miorini, R.L.; Wu, H.X.; Katz, J. The internal structure of the tip leakage vortex within the rotor of an axial waterjet pump. J. Turbomach. 2012, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.X.; Miorini, R.L.; Tan, D.; Katz, J. Turbulence within the tip-leakage vortex of an axial waterjet pump. AIAA J. 2012, 50, 2574–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.S.; Shi, W.D.; van Esch, B.P.M.; Shi, L.; Dubussion, M. Numerical and experimental investigation of tip leakage vortex trajectory and dynamics in an axial flow pump. Comput. Fluids 2015, 112, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.S.; Shi, L.; Shi, W.D.; Zhao, R.J.; Wang, H.Y.; van Esch, B.P.M. Numerical analysis of unsteady tip leakage vortex cavitation cloud and unstable suction-side-perpendicular cavitating vortices in an axial flow pump. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2015, 77, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.S.; Shi, W.D.; Pan, D.Z.; Dubussion, M. Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Tip Leakage Vortex Cavitation Patterns and Mechanisms in an Axial Flow Pump. J. Fluids Eng. 2015, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhu, B.S.; Cao, S.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, B.B. Numerical simulation of unsteady cavitation flow in a centrifugal pump at off-design conditions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2014, 228, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Zhu, B.S.; Wang, Y.C.; Cao, S.L.; Gui, S.B. Numerical study on characteristics of unsteady flow in a centrifugal pump volute at partial load condition. Eng. Comput. 2015, 32, 1549–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Tan, L.; Zhu, B.S.; Cao, S.L.; Wang, B.B. Numerical investigation of influence of inlet guide vanes on unsteady flow in a centrifugal pump. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2015, 18, 3405–3416. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.S.; Tan, L.; Cao, S.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Xu, Y. Numerical investigation of clocking effect on a centrifugal pump with inlet guide vanes. Eng. Comput. 2016, 33, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.J.; Okamoto, H. An experimental study on the fluid forces induced by rotor-stator interaction in a centrifugal pump. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2003, 9, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.G.; Egusquiza, E.; Santos, I.F. Frequencies in the vibration induced by the rotor stator interaction in a centrifugal pump turbine. J. Fluids Eng. 2007, 129, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Prunieres, R.; Horiguchi, H.; Tsukiya, T.; Taenaka, Y.; Tsujimoto, Y. Measurements of rotordynamic forces on an artificial heart pump impeller. J. Fluids Eng. 2007, 129, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, R.; Blanco, E.; Parrondo, J.; González, J.; Fernández, J. The effect of impeller cutback on the fluid-dynamic pulsations and load at the blade-passing frequency in a centrifugal pump. J. Fluids Eng. 2008, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, R.; Fernándezb, J.; Blancoa, E.; Parrondoa, J. Estimation of radial load in centrifugal pumps using computational fluid dynamics. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2011, 30, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Cao, S.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhu, B.S. Numerical simulation of cavitation in a centrifugal pump at low flow rate. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2012, 29, 147021–147024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhu, B.S.; Cao, S.L.; Wang, Y.M. Cavitation flow simulation for a centrifugal pump at a low flow rate. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 949–952. [Google Scholar]
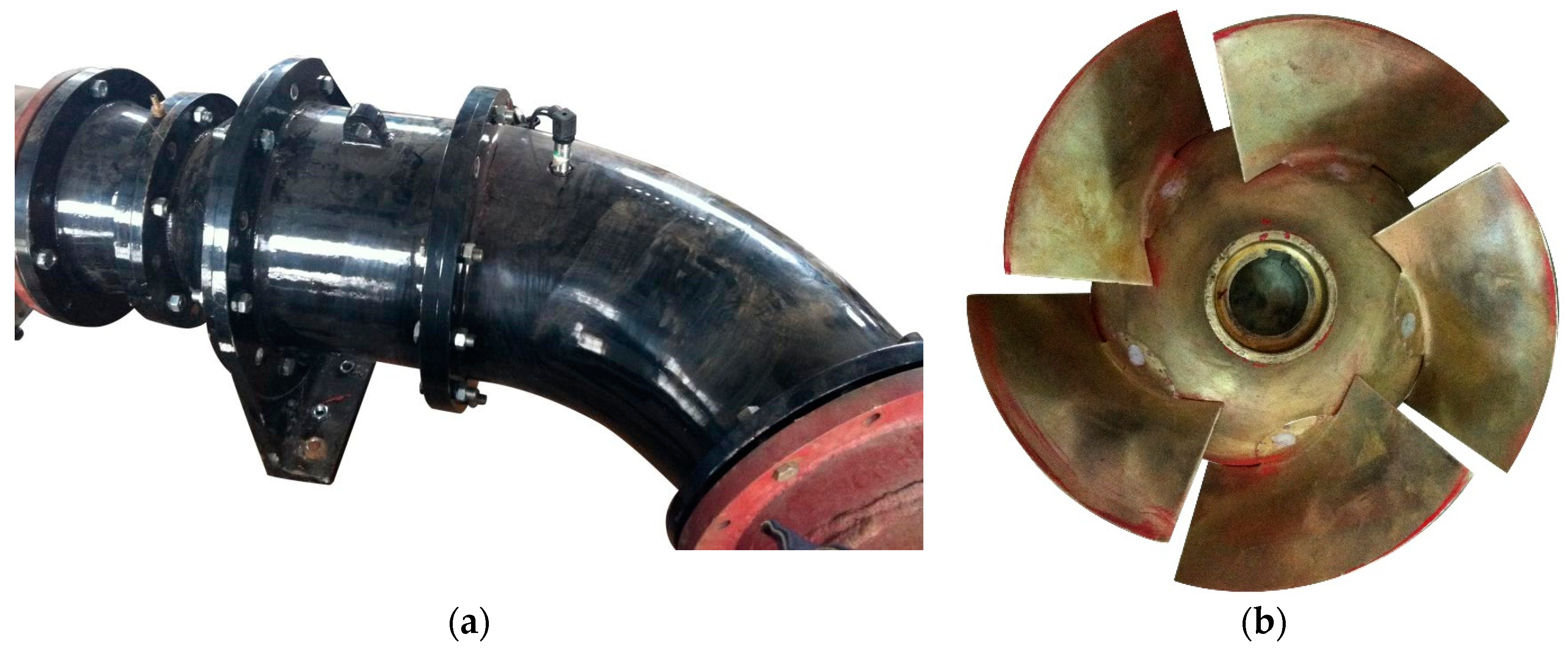
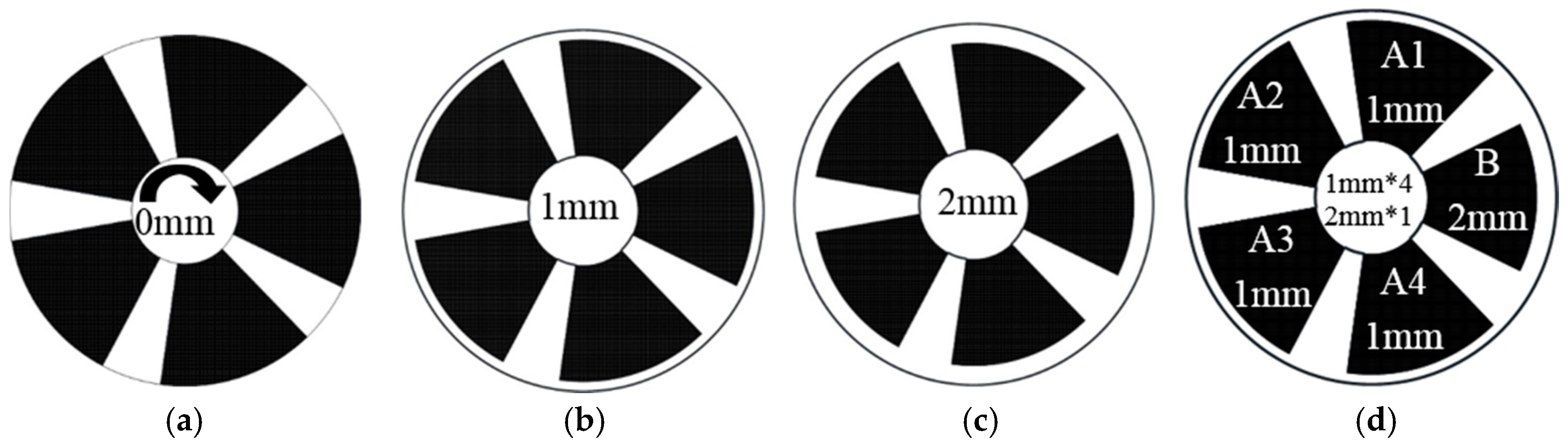

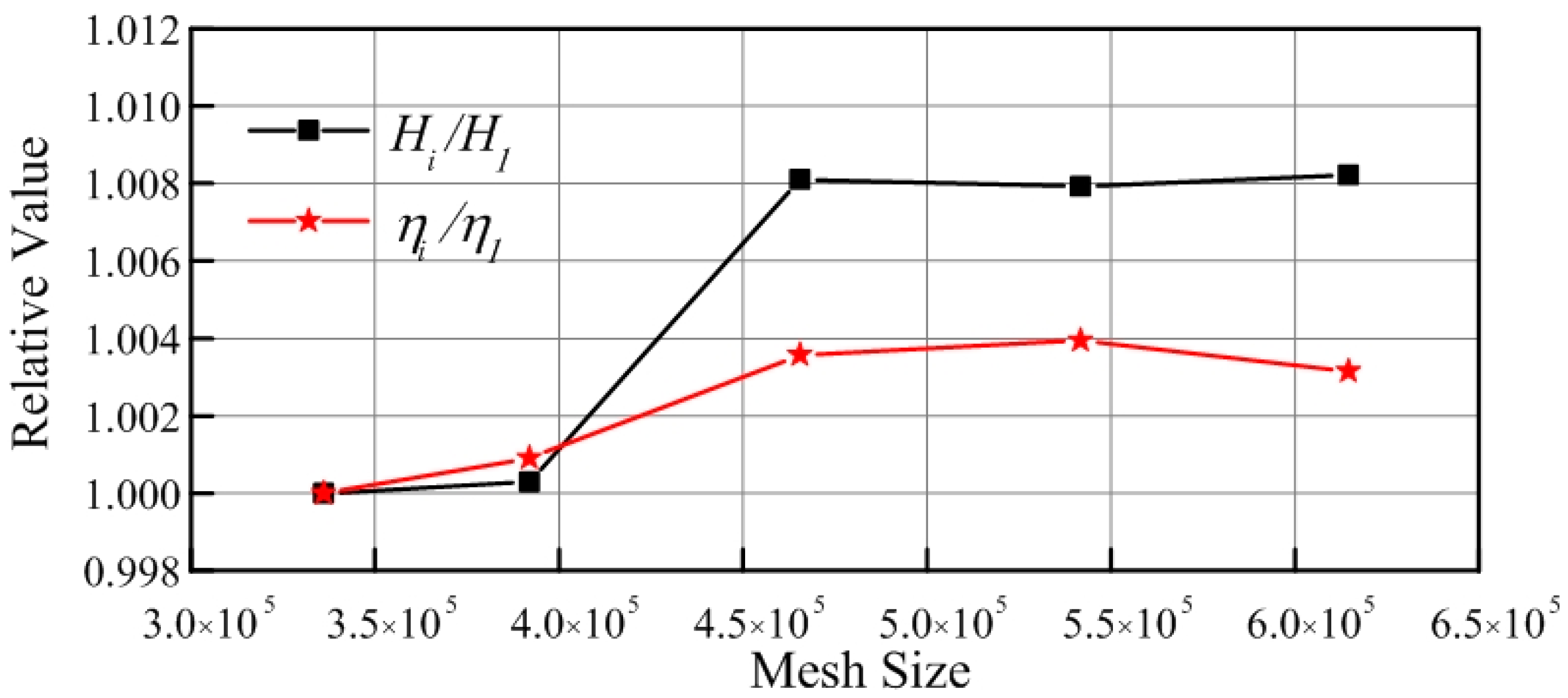
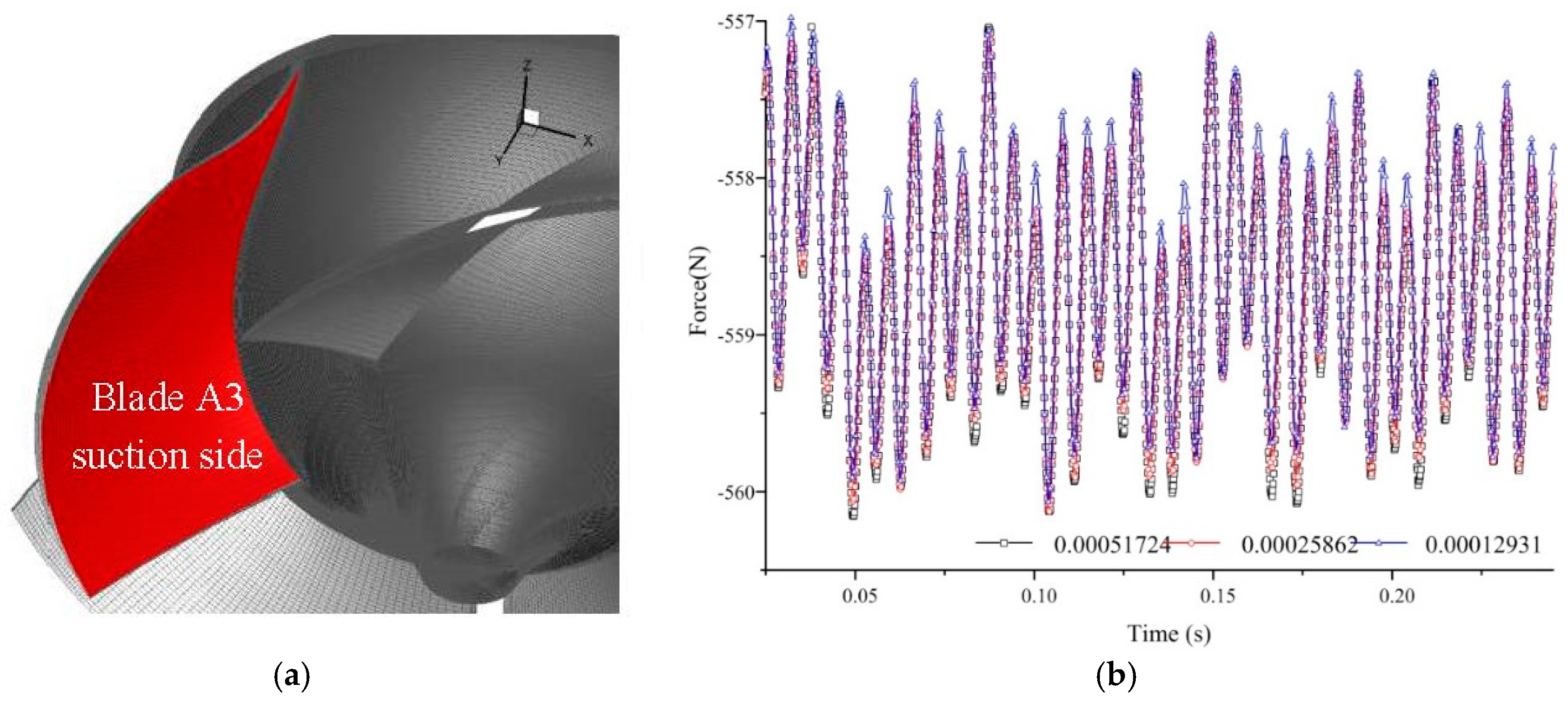


| Parameter | Symbol | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated Flow Rate | Qd | m3/s | 0.54 |
| Rated Head | H | m | 17 |
| Rotational Speed | n | rpm | 1450 |
| Number of Guide Vane | Zg | 6 | |
| Number of Impeller Blade | Zi | 5 | |
| Diameter of Impeller Inlet | D1 | mm | 278 |
| Diameter of Impeller Outlet | D2 | mm | 420 |
| Tip Clearance (mm) | Average Leakage Flow Rate (kg/s) | Average Pressure Side Radial Force (N) | Average Suction Side Radial Force (N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 2174.96 | 665.34 |
| 1 | 2.04 | 1972.96 | 546.41 |
| 2 | 4.42 | 1687.52 | 400.31 |
| Tip Clearance Type | Head (m) | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| 0 mm × 5 | 16.92 | 0.8552 |
| 1 mm × 5 | 15.26 | 0.8148 |
| 2 mm × 5 | 12.82 | 0.7536 |
| 1 mm × 4 + 2 mm × 1 | 14.79 | 0.8027 |
| Tip Name | Tip Clearance (mm) | Time Average Leakage Flow Rate (kg/s) | Time Average Radial Force on Pressure Side (N) | Time Average Radial Force on Suction Side (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blade-B | 2 | 4.59 | 1873 | 560 |
| Blade-A1 | 1 | 2.11 | 1926 | 518 |
| Blade-A2 | 1 | 2.03 | 1948 | 511 |
| Blade-A3 | 1 | 2.05 | 1942 | 518 |
| Blade-A4 | 1 | 2.05 | 1932 | 500 |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, Y.; Tan, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, B. Energy Performance and Radial Force of a Mixed-Flow Pump with Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Tip Clearances. Energies 2017, 10, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010057
Hao Y, Tan L, Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhang J, Zhu B. Energy Performance and Radial Force of a Mixed-Flow Pump with Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Tip Clearances. Energies. 2017; 10(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Yue, Lei Tan, Yabin Liu, Yun Xu, Jinsong Zhang, and Baoshan Zhu. 2017. "Energy Performance and Radial Force of a Mixed-Flow Pump with Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Tip Clearances" Energies 10, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010057
APA StyleHao, Y., Tan, L., Liu, Y., Xu, Y., Zhang, J., & Zhu, B. (2017). Energy Performance and Radial Force of a Mixed-Flow Pump with Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Tip Clearances. Energies, 10(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010057







