Abstract
With increased awareness and liberal screening of trauma patients with identified risk factors, recent case series demonstrate improved early diagnosis of carotid artery trauma before they become problematio. There remains a need for unified screening criteria for both intracranial and extracranial carotid trauma. In the absence of contraindications, antithrombotic agents should be considered in blunt carotid artery injuries, as there is a significant risk of progression of vessel injury with observation alone. Despite CTA being used as a common screening modality, it appears to lack sufficient sensitivity. DSA remains to be the gold standard in screening. Endovascular techniques are becomingmore widely accepted as the primary surgicalmodality in the treatment of blunt extracranial carotid injuries and penetrating/blunt intracranial carotid lessions. Nonetheless, open surgical approaches are still needed for the treatment of penetrating extracranial carotid injuries and in patients with unfavorable lesions for endovascular intervention.
Overview
Head and neck trauma is commonly encountered and man-aged by general plastic surgeons, oral maxillofacial surgeons, and otolaryngologists. It is important to be aware of the relative prevalence of carotid artery injury found in asymptomatic blunt facial trauma patients, as they can develop devastating ischemic stroke or even death. With improved screening criteria, studies have demonstrated increased detection of blunt carotid injury (BCI) occurring in of 1–2.6% of blunt trauma cases. Skull base fractures, facial fractures, cervical spine fractures, and thoracic injuries, along with a host of other risk factors, have been identified as risk factors for BCI. The importance of early diagnosis and initiation of immediate treatment of BCI is highlighted by high rates of ischemic stroke (60%) and mortality (19–43%) associated with untreated extracranial carotid artery injuries (ECAI) that could be reduced significantly with timely treatment [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Similarly, intracranial carotid artery injuries (ICAIs) carry poor prognosis and require prompt management. With increased awareness of screening criteria and improved detection, there is a growing consensus for aggressive, early antithrombotic therapy. The majority of surgical interventions consist predominantly of endovascular techniques. Although long-term data are lacking, endovascular techniques have shown efficacy in reducing neurologic complications and demonstrated safety measures in both select extracranial and ICAIs.
Anatomy
The carotid artery is located adjacent to vital neurovascular structures and is responsible for supplying adequate blood flow to the brain. It is divided by a segmental classification popularized by Bouthillier et al. (Figure 1) [7]. The cervical segment (C1) of the ICA begins at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. The cervical carotid is located adjacent to cranial nerves IX, X, XI, and XII and the sympathetic chain. After the bifurcation of the common carotid artery at the level of hyoid, the C1 ICA travels deep to the mandible to enter the skull base medial to the styloid process through the carotid canal. As opposed to the external carotid artery (ECA) with its multiple branches, the ICA is devoid of arteries, which can be a useful feature during an open approach for identification with confidence. Unlike the ICA, surgical ligation of ECA can be performed safely without any consequence to cerebral perfusion. In the vast majority of patients, ligation or acute occlusion of the ICA is poorly tolerated with poor collateral flow. The petrous segment of the ICA (C2) travels within the petrous portion of the temporal bone until the foramen lacerum is encountered. The lacerum segment of carotid (C3) begins superior to the foramen lacerum and extends to the petrolingual ligament, which consists of a reflection of the periosteum between the lingula and petrous apex of sphenoid bone. The cavernous portion of ICA (C4) travels within the cavernous sinus where cranial nerves III, IV, V1, V2, and VI are located in close approximation to the ICA. This portion of the ICA travels along the lateral and superior side walls of sphenoid sinus in a posterior-to-anterosuperior direction and exits medial to the anterior clinoid process to become intradural segment. The clinoid segment of the ICA (C5) originates as the artery exits the cavernous sinus at the proximal dural ring. The optic nerve travels superomedial to the ophthalmic segment of the ICA (C6), as the ophthalmic artery and superior hypophyseal artery branch from the C6 segment. The communicating segment of the ICA (C7) includes the origin of the posterior communicating artery to the bifurcation of the ICA into the anterior cerebral artery and the middle cerebral artery. The anterior choroidal artery and the posterior communicating artery both arise from the C7 portion of the ICA.7 Adequate patency and flow through the ICA is vital for brain function and survival in trauma patients.
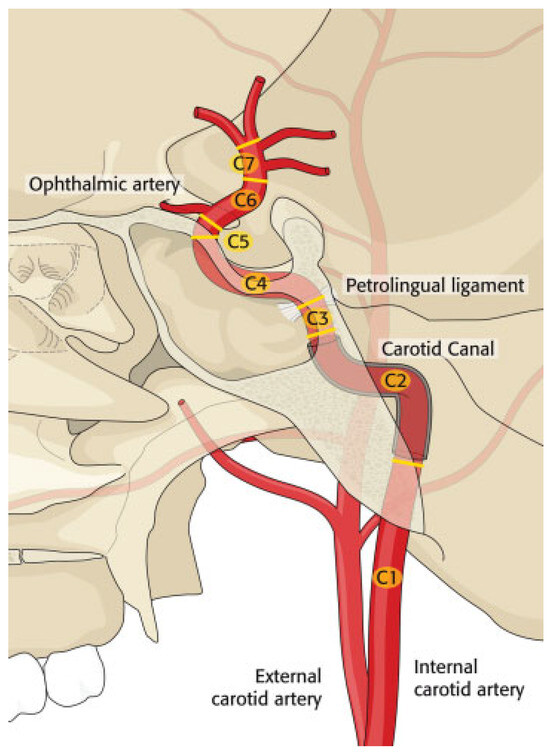
Figure 1.
Segmental classification of internal carotid artery.
Although intracranial and extracranial blunt carotid artery injuries commonly occur from similar traumatic mechanisms, clinical characteristics appear different. As such, medical and surgical treatments of ECAI and ICAI differ. For the purpose of discussion, the management of extracranial and intracranial carotid injuries will be discussed in two distinct sections.
Blunt Extracranial Carotid Artery Trauma
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology
Historically, BCI was initially considered to be a rare clinical condition, thought to occur in 0.1% of blunt trauma patients [8]. However, landmark studies published in the late 1990s by groups in Memphis and Denver demonstrated the presence of blunt ECAI in approximately 1% of all blunt trauma cases [4,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. This finding led to the widespread adoption of routine screening for ECAI by nationwide trauma centers in select cases of blunt trauma.
The proposed mechanisms of ECAI include (1) hyperextension, rotation, or flexion of neck leading to vessel stretch injury; (2) vessel laceration from bony fracture; and (3) direct vessel impact [16]. Extreme neck movement can lead to ECAI in various ways. Hyperextension, rotation, or lateral flexion places the contralateral carotid at risk, as it can be stretched against the second and third cervical vertebral bodies [17]. The ICA may also be injured by the styloid process during sudden rotation or compressed by the angle of mandible during hyperflexion [1,17,18]. These findings are reflected in the presence of BCI in the setting of motor vehicle accidents, cervical spine fractures, mandible fractures, LeFort II and III fractures, and chiropractic manipulation. The presence of an elongated styloid process can contribute to ECAI. One study demonstrated a significantly longer styloid process in ECAI patients compared with case-matched controls (30.3 vs. 26.6 mm) [19].
Vessel stretch may result in intimal injury, creating the potential for vessel dissection (separation of vessel wall tissue layers) or intramural thrombus formation, leading to vessel stenosis or complete occlusion. Further vessel degeneration may lead to a pseudoaneurysm, which is a hematoma in communication with the true vessel lumen through a vessel wall defect that transverses all three tissue layers. BCI may also lead to failure of brain perfusion due to thromboembolic events leading to devastating ischemic stroke. In addition, bony fractures along the carotid canal or skull base that occur along the course of ICA can impinge upon the vessel or lead to gross vessel wall laceration. BCI from a direct vessel insult can occur following assault, seat belt injury, or hanging. Consistently, the most common reported etiology of BCI is motor vehicle accidents (41–89%), followed by assault (6–20%), fall (5–15%), and hanging [9,10,20,21,22]. Bilateral carotid injuries may be present in up to 30% of cases [9].
Presentation and Natural Progression of Blunt ECAI
Blunt ECAI is known to carry a high rate of devastating neurologic morbidity (60%) and mortality (19–43%) [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Interestingly, a significant number of (66–73%) BCI patients may be asymptomatic upon initial presentation, developing delayed neurologic symptoms anywhere from 1 hour to 7 days after injury [2,23]. The onset of ischemic events can range from a few minutes to 31 days after injury, with the majority (82%) occurring within the first 7 days [2,23]. ECAI patients (33.7%) may present with an ischemic event (transient ischemic attack [TIA], stroke) at the time of presentation [2]. Other associated presenting signs and symptoms of ECAI include TIA (11%), ipsilateral headache (58–92%), Horner syndrome (9–75%), neck pain (18–46%), bruit (12–39%), and tinnitus (13%) [2,24]. Patients (73%) who presented with only localized symptoms (neck pain, Horner syndrome, tinnitus) develop TIA (30%) and stroke (43%). Patients (55%) who presented with TIA develop stroke 6 hours to 31 days after injury. The total stroke rate was 52% despite antithrombotic treatment in the series by Biousse et al [2]. The majority of ischemic strokes appear to be embolic in nature [25,26,27].
The Denver group has created the most widely used classification for BCI in the literature (Table 1). This scheme also provides useful prognostic information in assessing the risks of stroke and mortality [28]. As the severity of vessel injury worsens, stroke and mortality rates consequently increase. It is widely accepted that early, aggressive medical therapy can reduce the incidence of ischemic events [9,29,30]. Nonetheless, despite medical intervention, Biffl et al. demonstrated that ECAI can progress in severity. Despite heparinization, 5% of grade I injury progressed to grade III; 66% of grade II injury progressed to grade III or IV. Only 4% of grade III injury resolved with heparinization and 81% of grade III lesions required surgical intervention. No grade IV injury resolved with heparinization, and 63% of grade V injury patients died. Class III–V patients generally require careful angiographic monitoring and surgical treatment when indicated [31]. In light of rapid progression of BCI, there are a large number of clinicians who advocate for early screening in select trauma patients [9,10,32,33].

Table 1.
Blunt extracranial carotid artery classification and associated rates of stroke and mortality.
Screening Criteria
The relative rarity of BCI, paired with the need for prompt diagnosis, poses a clinical challenge when attempting to identify those patients with carotid injury. Berne et al [34] identified a median time to diagnosis of carotid injury of 12.5 hours in survivors and 19.5 hours for nonsurvivors. In their case series, patients whose diagnosis was delayed by greater than 48 hours suffered a mortality rate of 80% [34]. There is an increasing body of literature identifying various clinical signs as potential risk factors for the presence of BCI.
The Denver and Memphis groups were among the first to establish screening criteria that have gained wide acceptance (Table 2) [9,35]. Biffl et al [34] identified Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) < 6, petrous bone fracture, diffuse axonal injury, and LeFort II or III fractures as significant risk factors for BCI. Patients with one of these injuries had a 41% risk of blunt carotid artery injury, which increased to 93% in the presence of all four signs [35]. Using the National Trauma Data Bank, involving 2.6 million reported traumas between 2002 and 2006, Mulligan et al. identified a relatively common incidence of concurrent facial fractures found in 13.5% of cervical spine injury patients, 21.7% of head injury patients, and 24% of combined cervical spine and head injured trauma patients [36].

Table 2.
Suggested screening criteria for blunt carotid injury by different institutions.
In addition, patients who present with signs and symptoms highly suspicious for BCI should undergo immediate screening to definitively rule out vascular injury. The indicators of potential BCI include arterial bleeding from the neck, nose or mouth, cervical bruit, expanding cervical hematoma, focal neurologic deficits (TIA, hemiparesis, vertebrobasilar symptoms, Horner syndrome), stroke identified on computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and neurologic findings inconsistent with head CT. Furthermore, patients presenting with risk factors associated with blunt cerebrovascular injuries (BCVIs) should also be considered for screening. These risk factors include LeFort II/III fractures, skull base fractures, occipital condyle fractures, carotid canal fractures, cervical spine injuries, anoxic brain injuries from hanging, a clothesline type injury, or a seat belt sign [23].
A recently updated study from the Denver group reviewed a 14-year study period including 158 patients with carotid injuries and 62 patients with combined carotid and vertebral artery injuries (Figure 2) [23]. Additional predictive risk factors for BCVI were identified: mandible fractures, frontal skull fractures with orbital involvement, diffuse axonal injury with GCS < 6 and thoracic injuries, scalp degloving injuries, and cardiac or great vessel injuries (Table 2) [11,12,23]. Other authors have identified additional risk factors [37,38]. Using a polytrauma triage scale known as the Injury Severity Score (ISS), 2.7% of patients with ISS ≥ 16 were identified to have BCVI [37]. This mirrors significantly higher mean ISS scores noted in BCI patients with either ECAI (35.1 vs. 14.1) or ICAI (38.5 vs. 16) when compared with blunt trauma control without respective BCI (p < 0.05) [38]. Multivariate analysis revealed that the ECAI group had increased associations with thoracic injury (abbreviated injury score (AIS) ≥ 3) and GCS ≤ 8 (p < 0.05). Contrastingly, intracranial CAI demonstrated an association with GCS ≤ 8 and facial fractures (p < 0.05) [38].
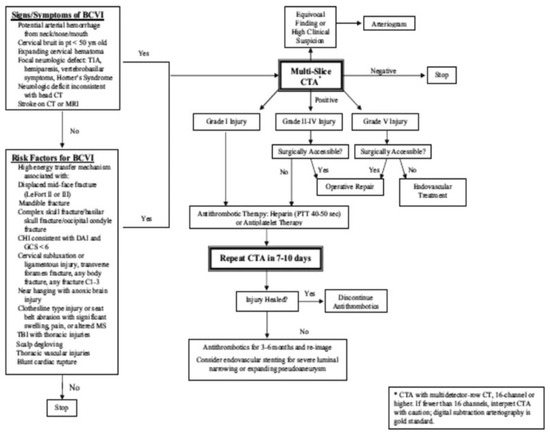
Figure 2.
An updated screening criteria from the Denver group and their management algorithm [23]. Although CTA is recommended as the initial screening modality of choice in this algorithm, there is controversy regarding CTA’s insufficient sensitivity. Some authors recommend DSA as the initial screening modality of choice instead. Most authors strongly recommend antithrombotic therapy if there is no contraindication. Surgical decision making is individualized for each patient and is not strictly dependent on the injury grading system. CTA, computed tomography angiography; DSA, digital subtraction angiography.
With wider acceptance of the above-mentioned screening criteria and risk factors, there appears to be significant improvements in detecting carotid artery injury. Miller et al. screened 3.5% of all blunt trauma patients (216 patients) in a 2-year period and had a 29% diagnostic yield of blunt carotid and vertebral artery injuries [11]. Another study by Kerwin et al. using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) as a screening modality as well as additional screening criteria (anisocoria, unexplained mono-/hemiparesis, unexplained neurologic exam, basilar skull fracture through or near carotid canal, foramen transversarum fracture, cerebrovascular attack or TIA, massive epistaxis, severe flexion or extension cervical fractures, facial fractures, and neck hematoma) screened 48 patients and had 44% diagnostic yield in identifying BCI/blunt vertebral artery injury (BVI) (Table 2) [12]. There is a trend in the literature that advocates more liberal screening of high-risk blunt trauma patients. The cost analysis of screening for carotid injury in blunt trauma victims has revealed that screening at risk patients is both cost-effective and associated with improved neurologic outcome and survival [39,40].
Screening Modality
Four imaging modalities have been used to investigate BCI in the literature: computed tomography angiography (CTA), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), conventional angiography, and Doppler ultrasonography. Clinicians should recognize the strengths and weaknesses of each imaging technique, as the cost of missing a BCI can lead to devastating consequences. There is little consensus as to which imaging modality is best suited for routine screening of BCI. In a recent survey of 785 clinicians with different specialty backgrounds (trauma surgeon, general surgeon, neurosurgeon, vascular surgeon, neurologist, interventional radiologist) who manage blunt carotid and vertebral artery injuries, wide variation existed in these physicians’ preferred screening imaging modality. By far the most commonly preferred imaging was CTA (60.5%), followed by MRI/MRA (22.8%), angiogram (15%), and Doppler (1.7%) [41].
Although most authors advocate the use of CTA as an initial screening method, four-vessel DSA is the gold standard against which all other modalities are compared [32,33]. DSA offers the clinician the ability to definitively rule out the presence of BCI and can also permit intervention via endovascular techniques when indicated. However, DSA is invasive with a complication rate of approximately 1%, resource intensive, and is not readily available at many hospitals. DiCocco et al. performed 764 DSA procedures screening for BCI and noted puncture site hematomas in 0.5% of cases and femoral vessel occlusion requiring surgical repair in 0.5% [42]. In addition, there was one occurrence of iatrogenic dissection of the vertebral artery. Renal insufficiency occurred in 3.5% of DSA patients but did not require hemodialysis and resolved by the time of discharge. Although there are obvious advantages of using DSA as an initial screening tool, it may not be practical to perform DSA in an expedient fashion. Contrastingly, CTA is more readily available and can be obtained in matter of minutes. Several authors recommend the use of CTA followed by DSA [32,33].
Although both the Eastern Trauma Association and the Western Trauma Association have recommended CTA as the initial screening modality of choice, there is a growing body of recent studies that suggest CTA lacks sufficient sensitivity and may not be appropriate as a lone screening tool [32,33]. CTA has the advantages of being readily available, noninvasive, and requires only minutes to obtain. As such, it is by far the most preferred screening modality [41]. However, older studies examining the diagnostic efficacy of CTA generally performed DSA only after abnormal CTA [14,43,44]. As such, true sensitivity and specificity of CTA as a screening tool cannot be determined because a normal CTA (false negative) in the presence of BCI would not be followed up with DSA. To circumvent this issue, recent studies have performed CTA and DSA in all patients being screened.
An ideal screening tool has high sensitivity, high negative predictive value, and low false-negative rate. Malhotra et al. compared CTA and DSA in 92 patients undergoing screening for BCVI [45]. There were four cases in which BCI was identified on DSA but read as normal on CTA. The authors determined that CTA possesses a 67% sensitivity rate, 96% specificity rate, a 73% positive predictive value, and a 95% negative predictive value. Similarly, DiCocco et al [42] from the Memphis group reviewed 684 patients who underwent both CTA and DSA for screening purposes and discovered 128 occurrences of misdiagnosed CTA with 47 (6%) missed BCI/BVI. Notably, 79% of missed injuries were grade II or higher. The authors concluded that CTA has an unsatisfactory sensitivity of 51% (97% specificity, 43% positive predictive value, 98% negative predictive value) in detecting BCI and is inappropriate as a reliable screening tool [42].
Instead, the Memphis group recommends performing DSA as a screen for BCI. Both DiCocco et al [42]. and Malhotra et al [45] use either a 16- or 32-channel CTA detector. Goodwin et al. found that using a higher resolution, 64-channel CTA failed to improve sensitivity [46]. A meta-analysis by Roberts et al. involving 5,704 carotid CTAs had a pooled sensitivity and specificity of 66 and 97%, respectively. Even with CTAs performed on machines with 16 or greater channels, sensitivity remained around 80% [47].
An additional weakness of CTA includes inherent radiation exposure, which may pose a problem especially in pediatric population. In addition, radiologic interpretation of CTA is affected by the experience of the radiologist reading it [45]. Finally, there are variables such as inadequate timing of contrast injection and the presence of metal or dental artifact that may result in insufficient image quality. Suboptimal or inadequate CTAs have a reported frequency of 7–17% [42,45]. Despite the advantages of CTA, it remains to be seen how trauma centers will tailor screening protocols in light of the growing body of evidence that CTA lacks sufficient sensitivity.
MRA has also been used as a screening tool. MRA has the advantage of avoiding radiation exposure and has been recommended in evaluation of pediatric patients [48]. However, MRA is not readily available at most hospitals and also requires a significant amount of time to obtain the study. In pediatric patients, anesthesia may be required to minimize motion artifact. Most authors agree that MRA lacks sufficient sensitivity to be used as a reliable screening tool. MRA has sensitivity ranging from 50 to 75% [11,49]. Similarly, Doppler ultrasonography is not adequate as an initial screening tool, as it has poor sensitivity (38.5%) [37]. Nonetheless, it may be useful as a follow-up imaging modality.
Treatment
Goals of BCI treatment include minimizing the progression of vessel injury, decreasing the incidence of ischemic events in asymptomatic patients, and improving overall neurologic and survival outcomes. In the literature, there appears to be a growing consensus for using antiplatelet or anticoagulant agents for class I and II lesions with greater agreement on the use of concurrent antithrombotic therapy and endovascular intervention for injuries of class III and higher. Both the Western Trauma Association and the Eastern Association of Surgery of Trauma recommend antithrombotic therapy for grade I and II injuries in the absence of contraindications to anticoagulation. Simple observation is no longer recommended [32,33].
In grade I and II injuries, there is a potential for stroke and development of more severe vessel injuries. Seven percent of grade I injuries may progress to grade II or higher. Resolution of injury occurred in 63% of patients with grade I or II injuries who underwent observation alone compared with 70% of patients who received heparin. There was no significant difference in outcomes with the use heparin versus antiplatelet medication, while a 3% stroke rate was noted in the grade I observation group (Figure 3 and Figure 4).
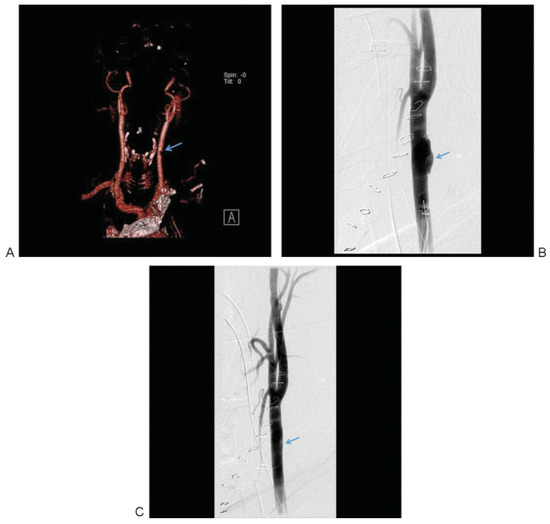
Figure 3.
(A) A grade I lesion identified as a luminal narrowing of the left common carotid is seen on the reconstructed CTA. (B) DSA demonstrates progressive worsening of the common carotid injury. (C) Endovascular intervention with a stent was placed successfully. The arrows indicate the site of grade I carotid injury before and after endovascular stenting. CTA, computed tomography angiography; DSA, digital subtraction angiography.
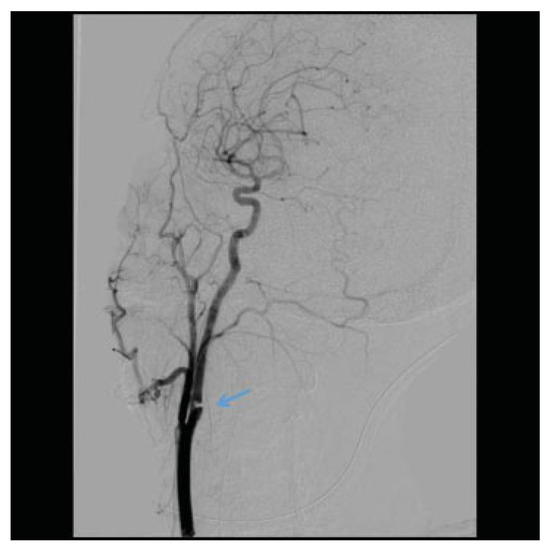
Figure 4.
A grade II lesion with a significant luminal irregularity (≥ 25%) of the internal carotid artery can be seen as marked by the arrow.
Seventy percent of grade II injuries progressed to a higher grade, while 11% of observation-alone patients suffered a stroke. Resolution was noted in 10% of grade II patients treated with heparin [28]. On follow-up angiography, 57% of grade I and 8% of grade II patients healed with anticoagulation, while 8% of grade I and 43% of grade II lesions progressed to pseudoaneurysm [13]. Due to the significant concern for progression of vessel injury despite antithrombotic therapy, most authors recommend that follow-up angiography be performed in 7 to 10 days in the case of new clinical neurologic findings [32]. On follow-up angiography performed 7 to 10 days following injury, the majority of grade III (93%) and grade IV (82%) lesions remained unchanged. However, a significant number of grade I and II lesions were found to have progressed, with these patients’ treatment plans being altered accordingly in 65 and 51% of these grade I and II patients, respectively [13].
Both heparin and antiplatelet therapies appear equally effective in minimizing the risk of stroke in asymptomatic patients and improving neurologic outcomes in symptomatic patients [30,50,51,52,53]. In a prospective, observational study by Cothren et al., 19% of asymptomatic BCVI patients who were observed developed ischemic neurologic events, while no patients in the anticoagulation group developed an ischemic event [30]. Several retrospective, case series reported a similar efficacy and safety profiles with heparin or antiplatelet drugs (325 mg aspirin daily or 75 mg clopidogrel daily) [30,50,51,52,53]. Advocates for antiplatelet therapy state the relative ease administration and monitoring as a major advantage for these compounds over heparin.
Advantages of heparin over antiplatelet agents include the ability to reverse anticoagulation in the case of a planned procedure or resultant hemorrhagic complications. Although there is a reported trend for improved stroke prevention and survival with heparin over antiplatelet therapy, studies have generally failed to detect true statistical significance [13,53]. Currently, there is no prospective, randomized, controlled study to definitively determine which of the two therapies is superior.
In a prospective, observational study, the Canadian Stroke Consortium examined 116 patients with 67 vertebral artery and 49 carotid artery dissections, 59% of which occurred after trauma [54]. The authors found no significant difference in the rate of recurrent neurologic events when patients were treated with either anticoagulants or aspirin. A relatively high annual neurologic adverse event rate of 10.4% was noted, despite antithrombotic therapy. These authors estimated that a two-arm clinical trial comparing anticoagulant with antiplatelet therapy would require a large number of patients (2,000 patients) to reliably detect a statistically significant difference [54]. In light of the ongoing debate, a large, prospective, randomized clinical trial appears warranted.
Bleeding complications from antithrombotic agents are relatively rare and the potential benefit appears to outweigh the risks. When using heparin, aggressive anticoagulation is not recommended. A partial thromboplastin time (PTT) of 40 to 50 is recommended and should be achieved without using an initial bolus [13,33]. This protocol was found to be well tolerated with a low rate (4%) of bleeding complications [13]. In contrast, more aggressive anticoagulation with higher PTT of 60 to 80, in conjunction with a 70 unit/kg heparin bolus demonstrated a significantly higher rate of bleeding complications (43%) [13]. Similarly, case series by Fabian et al. and Cothren et al. both reported relatively low bleeding complications: a 2.7% rate of visceral bleeding and a 4.2% rate of subdural hematoma [9,30]. Furthermore, Hinson et al. reported that traumatic cervical artery dissection patients (including 22 vertebral artery, 44 ICA, and 2 common carotid artery injuries) who were noted to have posttrauma intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) did not experience progression of their ICH and no bleeding complications were seen in seven patients who were treated with antithrombotic therapy [55]. However, 3.5% of cervical artery dissection patients without preexisting ICH developed interval hematomas; 10% of untreated patients developed ischemic stroke, while none of the treated patients suffered stroke in this case series. Hinson et al. reported relative safety of antithrombotic therapy even in the presence of ICH [55].
Endovascular therapy is gaining wider acceptance in treating grade III and higher injuries that are often unresponsive to medical therapy. Grade III and IV lesions demonstrate a low rate of resolution with antithrombotic therapy alone. Only 5% of grade III lesions and no grade IV lesion healed with heparin [13]. Reported indications for endovascular stent placement include (1) failed medical management as defined as a new ischemic event, progression of initial symptoms, or enlarging pseudoaneurysm; (2) stroke; and (3) contraindications to anticoagulation [56]. Biffl et al. recommend stenting for grade II or III lesions that display progressive vessel stenosis with risk for vessel occlusion. Embolization or balloon occlusion techniques are reserved for transected vessels (grade V), pseudoaneurysms not amenable to stenting and arteriovenous fistulae [13]. A prospective study by Cothren et al. demonstrated a high rate of stent occlusion when antithrombotic therapy was not used [57]. As such, the use of antithrombotic therapy is encouraged after stenting, but the treatment duration is unknown (Figure 5 and Figure 6) [32,33].
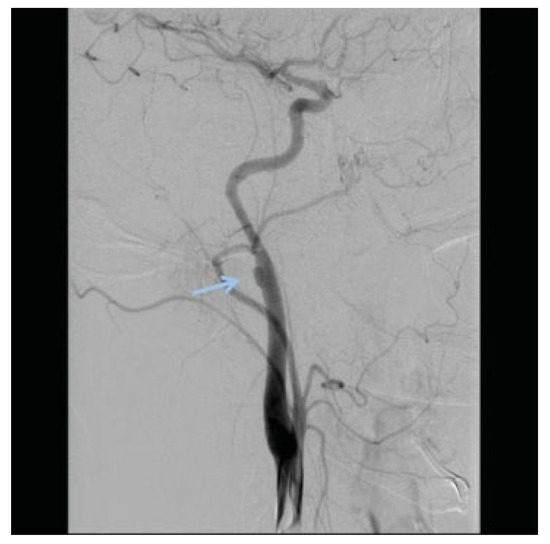
Figure 5.
A grade III lesion with a pseudoaneurysm of the ICA is demonstrated in the DSA. The arrow points to the psuedoaneurysm. DSA, digital subtraction angiography; ICA, intracranial carotid artery.
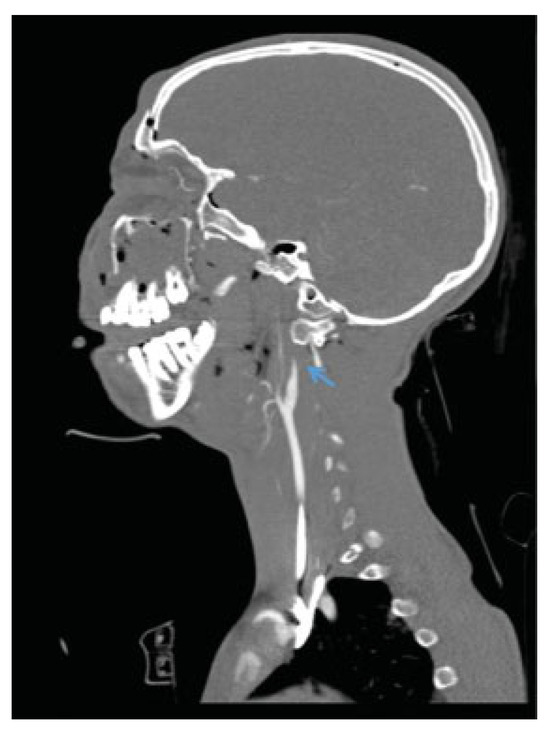
Figure 6.
A grade IV lesion with occlusion of the ICA is seen in the CTA as marked by the arrow. CTA, computed tomography angiography; ICA, internal carotid artery.
Several retrospective case series on endovascular intervention report success with treating traumatic carotid injuries with relatively low complications [58,59,60,61,62]. Seth et al.63 retrospectively reviewed 47 blunt/penetrating traumatic carotid injury patients who underwent endovascular intervention. Twenty-one patients were initially treated with medical therapy followed by endovascular repair [63]. Of these patients, 87.5% presented with no-flow limiting grade 3 lesions and 14.3% with no-flow limiting grade 2 lesions. Vessel lumen restoration was completed in 50% and acceptable to good in the other 50%. No mortality or morbidity was attributed to endovascular repair. Of these patients, 6.4% had transient complications, consisting of temporary weakness and transient vision loss, all of which resolved without further surgery. In addition, there was one incidence of complete stent occlusion (2%), although the patient remained asymptomatic.
The meta-analysis by Pham et al. analyzed the safety and efficacy of endovascular intervention for BCI [56]. These authors identified 153 ECAIs in 140 patients who were treated with endovascular techniques. Of the 153 carotid injuries, 48% were traumatic in origin. The technical success rate was 99% (152/153 vessels) in this series. Wallstents (Boston Scientific, Natick, MA; Schneider, Minneapolis, MN) were the most commonly used stents (54%), followed by SMART stents (Cordis, Bridgewater, NJ) in 18%. Out of 61, 60 vessels (98.4%) of pseudoaneurysm cases were either successfully stented or occluded when appropriate. Only 2 of the 138 patients with a mean follow-up of 17.7 months (1–72 months) developed neurologic sequelae, consisting of TIAs, one at 2.7 months and the other at 12 months following procedure. All other patients demonstrated either unchanged or improved neurologic status. Procedural complications were seen in 2 of the 153 vessels (1.3%).
Kadkhodayan et al. reported a new intimal flap creation that occurred before stent deployment [64]. Lavallée et al. reported embolic infarcts that occurred along the anterior cerebral artery during the procedure, although the patient returned to baseline neurologic status [65]. There were three stents with in-stent stenosis or occlusion that occurred 22 days to 23 months after initial stenting with all patients remaining asymptomatic. For postdeployment antithrombotic therapy, 57% of authors use a combination of clopidogrel and aspirin, while 26% use a combination of ticlopidine and aspirin [56]. No uses of distal protection filters were reported. It is claimed that the endovascular technique is effective and relatively safe [56]. Early vessel reconstruction is recommended, due to a higher incidence of stroke in the first 30 days after vessel dissection and increased thromboembolic complications associated with persistently stenotic or nonhealing dissections [56]. Another meta-analysis of endovascular management of a combination of blunt (77%) and penetrating (23%) ICA injuries involving 113 patients identified successful stent placement in 76.1% of cases, with stent patency achieved in 79.6%. New postprocedure neurologic deficits occurred in 3.5%, with one observed mortality (99.1% survival) [66]. Despite the early promising results, long-term follow-up studies are needed.
Grade IV and grade V lesions pose a challenge for the endovascular technique and may be complemented by open surgical intervention. Grade IV lesions by definition involve total vessel occlusion. As such, passing an endovascular catheter may be technically impossible. Cohen et al. reported successful endovascular reconstruction of critically stenotic (> 90%) or occluded (grade IV) traumatic internal carotid lesions in 16 patients with the use of coaxial microcatheters and soft-tip micro-guide wires to navigate across dissected segments, identifying the true vessel lumen. In the occluded traumatized ICA, these authors used a delayed double-contrast road map and flap fenestration to achieve recanalization [67].
BCI grade V lesions with vessel transection and frank extravasation are highly lethal, with a mortality rate approaching 100%, and require immediate surgical intervention whenever possible. Due to rare survival associated with grade V injury, there is limited clinical data and no prospective, randomized study comparing endovascular with open surgical approaches. The urgency of adequate surgical management of grade V BCI mirrors that of penetrating carotid injuries (Figure 7).
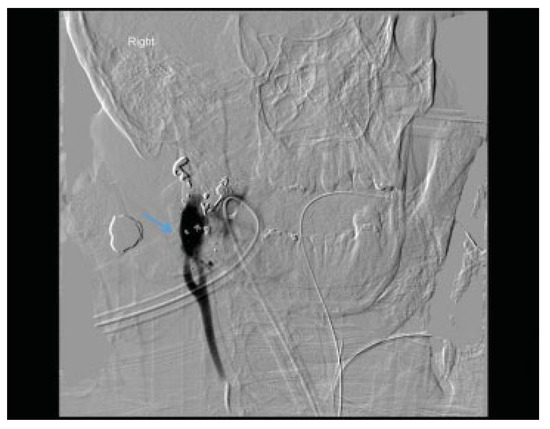

Figure 7.
A grade V lesion with frank extravasation of contrast from the transected internal carotid artery. The arrow marks the contrast extravasation.
Penetrating Extracranial Carotid Artery Trauma
Penetrating carotid artery injury occurs in 4.9 to 6% of penetrating neck trauma [68,69]. Penetrating carotid can be highly lethal if left untreated, approaching a mortality rate of 100%. In patients who survive surgery, there is a significant improvement in mortality, with a rate of 6 to 33% [66,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80]. Penetrating carotid injuries require immediate surgical treatment. Angiography should generally be reserved for stable patients, but if it can be performed in conjunction with an open approach, in an angiography suite with full operative capability, it may facilitate in obtaining proximal vessel control as well as in the identification of vessel injury during emergent surgical intervention. Although open surgical technique remains to be the gold standard for all zones of penetrating carotid injuries, there is an increasing trend to use a combined endovascular approach [81].
Conventional open-surgical approaches involve surgical repair or surgical ligation. Whenever possible, all attempts should be made at surgical repair, as it offers the best chance of survival with decreased risks of permanent neurologic deficits. Surgical repair can consist of primary arteriorrhaphy, end-to-end anastomosis, vein grafting, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) patching, and transposition of external carotid to injured ICA [69,71]. Surgical ligation is associated with notably higher rates of mortality and stroke and should only be reserved for situations where surgical repair is not feasible. The reported indications for surgical ligation vary and remain controversial among different studies. The indications put forth by Reva et al. for surgical ligation include refractory “systolic blood pressure less than 70 mm Hg; unconsciousness or bilateral mydriasis; an associated gunshot wound of the brain; a very severe neck injury (AIS ¼ 5); presence of injuries of several anatomic areas requiring immediate treatment when simultaneous operations are not possible; zone III ICA injury in the skull base, and extensive distal-ICA thrombosis.” [82]. These authors cautioned against surgical repair of the distal ICA near the skull base due to technical difficulty and discouraged thrombectomy from the distal portion of ICA due to the risks of thrombus migration. Instead, an endovascular approach for select zone III and zone I injuries is advised. The indications for ligation put forth by Navsaria et al [69]. are similar. They include established ischemic infarct or severe cerebral edema seen on CT; technically difficult high ICA injuries, coma of more than 4 to 6 hours duration, absent backflow at surgery, and neurologically intact patients with occlusion seen on angiography [69]. When surgical ligation is performed, adequate surgical debridement of the injured area and the ligation of the injured carotid should be performed outside the zone of injury to allow for adequate vessel stump coverage with healthy tissue and to avoid delayed rupture of the vessel stump from infection [83].
Most authors agree to recommend surgical repair in patients who present without neurologic deficits [69,72,82,83]. Zone II injuries are generally amenable to open surgical repair due to the relative ease of access offered through a vertical, anterior neck incision. Contrastingly, zone III injuries may sometimes require mandibulotomy, while zone I injuries may require sternotomy for adequate exposure. Ramadan et al. performed a retrospective examination of penetrating and BCIs from civilian patients with unspecified, varying injury severity before the popularization of endovascular techniques [72]. For patients who presented initially without neurologic deficits, the stroke rate in the surgical repair group was 8%, 50% in the surgical ligation group, and 41% in the nonoperative group. The mortality rates in neurologically intact patients were 18% in the nonoperative group and 0% in both the surgical repair and the surgical ligation groups. Penetrating carotid injuries were significantly more lethal with a 22% mortality rate, compared with a 7% mortality rate in the BCI group. The presence of shock was associated with a higher mortality rate of 41%, compared with 8% in the no-shock group.
Similarly, war-time penetrating carotid injuries also have similarly high mortality and morbidity. Reva et al. reported combat-related penetrating CCA and ICA injuries occurring in 29 wounded soldiers during the Second Chechen War from 1999 to 2002 and 17 civilians between 2003 and 2009 [82]. Of these patients, 19% were treated with surgical ligation and the rest were treated with surgical repair, consisting of end-to-end anastomosis (37%), lateral sutures (22%), and vein grafting (22%). The surgical repair technique was individualized based on the length of vessel injury and the mechanism of injury. Patients (78%) with high-velocity missile-induced injuries underwent resection of the injured segment followed by surgical repair using a reversed long saphenous vein when there was marked carotid artery segment defect (exceeding 2.5–3 cm in length). The total mortality rate for the study of Reva et al. was 28% with a higher trend for mortality seen in the ICA injury group (42%) than in the common carotid injury group (24%).
Similar to other reports by Rich et al. from the Vietnam War and Fox et al. from the Afghanistan and Iraq Wars, Reva et al. identified improved survival and neurologic outcomes associated with surgical repair than with surgical ligation [84,85,86]. The carotid ligation group had a higher, but statistically insignificant, mortality rate of 44%, compared with 24% mortality in the surgical repair group. The carotid ligation group demonstrated statistically worse postoperative neurologic deficits seen in 56% of the ligation patients, compared with 10% in the surgical repair group. The authors concluded that there was a statistically higher rate of poor outcomes (defined as death or permanent neurologic deficits) in the carotid ligation patients (100%) compared with the patients undergoing surgical repair (30%) [82].
The optimal surgical management of penetrating carotid injury patients presenting with neurologic deficits remain controversial. Due to the concern of converting an ischemic stroke into a hemorrhagic stroke that can occur after reestablishment of cerebral flow, several authors advise against surgical repair [69,87,88,89,90]. Recently, several studies have dismissed such concern, arguing that the majority of autopsy findings demonstrate cerebral edema as the most common cause of death with hemorrhagic strokes contributing to relative minority of cases [68]. As such, Navsaria et al. and Demetriades et al. discourage surgical repair in patients with established ischemic infarct or cerebral edema seen on CT imaging [68,69].
Contrastingly, Reva et al. recommended surgical repair even in the presence of prolonged neurologic damage and irrespective of preoperative neurologic deficits, as improvement or resolution of initial neurologic impairment has been reported after a surgical repair [82]. Another point of controversy surrounds the use of temporary shunting during surgical repair without clear consensus and conflicting data [68,69,73,82,91]. Similar to BCI where antithrombotic therapy is widely accepted to prevent further progression of vessel injury, several authors recommend the use of anticoagulation in the setting of penetrating carotid injury, though an insufficient number of studies are available [81]. Future studies with a larger patient population appear warranted to address these controversies.
Recently, endovascular techniques have also been applied to penetrating carotid injuries, either alone or in conjunction with an open approach, with promising results. Starnes and Arthurs suggest the use of endovascular balloon occlusion to help identify the site of transection and to temporarily occlude the proximal, injured segment for a more controlled open exploration [81]. As mentioned previously, the endovascular technique can be useful in level III neck injuries near skull base where surgical exposure and repair of the distal ICA can be challenging. In addition, an endovascular approach can be performed without general anesthesia, allowing for the monitoring of the patient’s neurologic status during surgical intervention in select cases.
Du Toit et al. reported their experience in treating 19 out of 128 penetrating carotid injury patients using endovascular technique alone [92]. A majority of their patients were treated with an open approach (109 patients), primarily involving zone II injuries. All procedures were performed in an angiography suite with full operative capability. An initial fourvessel arteriogram was performed to identify the site of injury. A conventional open approach was performed for easily accessible zone II insults with relatively easy proximal and distal control. The reported contraindications to arteriography include the presence of a significant discrepancy between the proximal and distal lumen of the involved artery and the inability to safely traverse a guide wire past the site of injury. The reported contraindications to stent-grafting include uncontrolled hemorrhage, airway compromise, concomitant aerodigestive injuries, and infected wounds. Excluding these contraindications, endovascular stenting was performed whenever possible with a goal of oversizing the proximal and distal diameter by 1 mm and overlapping the injury by at least 1 cm proximally and distally. Embolic protection devices were not used.
Their technical success rate was observed in 100%. One patient died within the first week of procedure, while another patient had an early stroke. Fourteen patients were followed up for a mean duration of 4 years and showed no late, graft-related complications except in one patient, who had asymptomatic stent occlusion. Unfortunately, due to the relative rarity of patients, most studies fail to distinguish penetrating injuries from blunt injuries in their analyses. Despite early reports of high success rates ranging from 78 to 100% of successful stent placement and a favorable stent patency rate (> 90%), future prospective studies with a larger cohorts appear warranted [66,92].
Using the National Trauma Data Bank (NTDB), there are ongoing efforts aimed at trying to identify factors in surgical management and surgical technique that may potentially minimize morbidity and optimize survival. It appears that a certain subset of patients may benefit from early endovascular intervention, while others may benefit from open surgery. Avery et al. examined the NTDB from 2002 to 2006 and 2008, involving 45,220 surgical patients. Of these cases, 2,236 involved carotid artery injury, of which 57% were blunt and 43% were penetrating in nature [93]. There was a notable increase in endovascular treatment being performed early (less than 24 hours from admission).
Patients treated with endovascular techniques tended to be older, more severely injured with lower GCS scores, more likely to involve a blunt mechanism, and had longer ICU and in-hospital days. Despite the severity of injuries in the endovascular group, when compared with the open-approach patients, there were similar in-hospital mortality and hypotension rates. Notably, in the early endovascular intervention group, there was a significantly lower risk of in-hospital mortality when compared with the patients who were treated with a conventional open approach. The authors stressed the potential benefit of early endovascular intervention [93].
Dua et al. examined 313 BCIs reported from the 2008 NTDB and found improved survival with an open approach in a subset of patients with high ISS [3]. ISS is a scoring system designed to assess multisystem trauma patients and the score ranges from 0 to 75. The patients with ISS between 0 and 30 showed no statistically significant difference between nonoperative management (0.6% mortality rate), endovascular treatment (2% mortality), or open surgery (4% mortality). However, for patients with ISS between 61 and 75, there was a statistically higher survival in the open surgery group (88%) than in the observation group (63%). There was no significant survival difference between the open (88%) and the endovascular approach groups (74% survival) [3].
Intracranial Carotid Artery Trauma
Traumatic ICAIs are rarer than extracranial carotid injuries. The types of ICAIs that can be seen include vessel occlusion, traumatic aneurysm, and arteriovenous fistula. With the popularization of the endovascular technique, its application is becoming widely accepted for intracranial carotid injuries as the primary surgical therapy, while open surgical approach is often reserved for select cases.
Traumatic carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF) is a type of arteriovenous fistula that can occur as a complication of intracranial carotid artery trauma. It occurs at a rarer frequency than traumatic aneurysm and is more commonly found after blunt head trauma [94]. There is a significant association with sphenoid sinus and carotid canal fractures. The reported incidence of CCF is 4% of all BCVI patients [29]. The Barrow classification is commonly cited in the literature [95]. Type A is the most common type of CCF and consists of a direct communication between the internal carotid artery and cavernous sinus. This is a high-flow AV fistula. Types B, C, and D are indirect types of CCF and they are dural arteriovenous fistulae with low flow.
Clinical presentations differ between the direct and indirect CCFs. Direct CCFs have a more acute and sudden onset with the classic triad of pulsatile exophthalmos, episcleral venous congestion, and cranial bruit. Indirect CCFs generally have a more gradual onset with less prominent findings. Ipsilateral ophthalmoplegia can occur with the abducens nerve being affected in 85% of direct CCFs [96]. Anterior or posterior visual loss can also occur but may be reversible if treated promptly. Angiography is the preferred imaging modality of choice, as other imaging techniques may fail to demonstrate CCF, particularly in low-flow lesions [96].
For treatment, endovascular embolization is preferred, which can be performed transarterially, transvenously, or using a combination of both. After treatment, vision loss generally improves but varying degrees of ophthalmoplegia persist [97]. Currently, open surgery is reserved only for patients who are poor endovascular candidates, such as patients with a narrow access artery, no direct venous access to the CCF, or a wide-necked cavernous carotid aneurysm. Open surgical techniques involve trapping of the cavernous ICA or packing the cavernous sinus [98,99,100]. A balloon occlusion test must first be performed to see if a patient is intolerant of ICA sacrifice and needs a bypass procedure. Due to the presence of multiple cranial nerves in the cavernous sinus, permanent cranial nerve palsies occur in a significant number of patients who undergo open surgical approaches [96]. As such, the endovascular technique is currently the preferred, primary surgical modality.
Traumatic intracranial carotid aneurysms (TICAs) occur more commonly than traumatic arteriovenous fistulas. TICA represents 0.15 to 0.4% of all intracranial aneurysms [101]. TICA is estimated to be present in 1.495% of all facial trauma [102]. TICA can occur from both blunt and penetrating mechanisms, although penetrating mechanisms are much more commonly associated with TICA formation [103]. Early detection before a TICA becomes symptomatic or rupture remains a major challenge. Once the TICA ruptures, the mortality rate approaches 50% and is associated with catastrophic neurologic consequence [104,105,106,107,108,109]. TICA can present as blindness, massive epistaxis, delayed neurologic deterioration due to unexplained intracranial bleed, cranial nerve palsy, and profound neurologic deficits [104,105,106,107,108,109].
There are several identified risk factors for TICA, such as penetrating trauma involving frontal, basal, or pterional windows, and the presence of sphenoid sinus or carotid canal fractures [94,101]. However, there is no widely accepted screening criteria and the exact timing of screening angiogram remains controversial. As CTA can miss aneurysms less than or equal to 3 mm in size, most authors agree that CT brain or CTA is not adequate for TICA detection and recommend DSA as a preferred screening modality [94,103].
Bell et al. established the following screening criteria after treating U.S. soldiers in the Operation Iraqi Freedom: “penetrating head injury of any kind; a known surgically treated TICA; non-penetrating head injury associated with blast and presenting GCS ≤ 8; transcranial Doppler evidence of vasospasm; spontaneous decrease in partial pressure of brain-tissue oxygen or cerebral blood flow in an otherwise stable patient.”94 The soldiers meeting these screening criteria underwent arteriogram generally within 10 days of injury and they successfully identified intracranial carotid injuries in 26.2% of patients studied.
Cohen et al. established screening criteria after treating a civilian population in Jerusalem [103]. These authors performed an arteriogram within 1 to 3 days following injury in patients with the following indications: penetrating brain injury with a tract entering the pterional area, passing through middle cerebral artery candelabra, and crossing midline; cranial base fracture (sphenoid sinus fractures, carotid canal fractures). They successfully identified and treated 61.5% of lesions before they became symptomatic and 84.6% of aneurysms before bleeding. The timing of these screening criteria remains controversial. Because some aneurysms take time to develop, an initial screening angiogram may be normal and TICA may not be detected until a follow-up angiogram is performed. The recommended timing of screening varies widely, from immediately after injury to 2 to 3 weeks after injury [94,101].
Goal of TICA surgical management is complete aneurysm occlusion with parent artery preservation. TICA can present significant challenges, such as a poorly defined neck of the aneurysm, greater fragility than congenital aneurysms, and common occurrences in patients with multiorgan trauma. Although there are rare incidences of spontaneous resolution of small TICA, Bell et al. strongly recommend obliteration of larger TICA due to the high risks of rupture and a 50% mortality rate associated with ruptured aneurysms. In the case series of Bell et al., ruptured aneurysms were 8.275 mm in size (2.5–15 mm range) and increased in size on subsequent angiograms. An average time to rupture of 15 days (4–32 days) [94].
Before the introduction of endovascular approaches, open surgery was used but was associated with significant surgical morbidity and mortality (18–29%) [103]. Most authors currently recommend endovascular surgical management as the primary surgical modality, with open surgical approach being reserved for select cases [94,101,110]. Endovascular management offers unique advantages over open surgery, allowing minimally invasive approach to the site of injury, and avoiding craniotomy, brain retraction, and cerebral dissection. The endovascular management of TICA includes coils, stent-assisted coiling, and liquid embolic agents [94,101,110].
Ideally, the parent vessel is left intact with the obliteration of aneurysm. However, there are situations in which intracranial internal carotid must be sacrificed. In such situations, a balloon occlusion study can be performed while the patient is awake to assess for neurologic changes. If the patient can tolerate it, internal carotid artery occlusion can be performed. If patient is intolerant of the balloon occlusion or there is bilateral carotid injury, open microvascular extracranial–intracranial bypass must be performed. In select patients, endovascular treatment may fail or need to be performed in conjunction with an open approach.
Open surgical techniques include clipping and vessel ligation with microvascular extracranial–intracranial by-pass [111,112,113,114]. Early results from several case series using predominantly endovascular surgical management show promising results. Endovascular treatment in the study by Cohen et al. in 13 TICAs demonstrated no incidence of delayed bleeding and no procedure-related complications or mortality [103]. Similarly, Uzan et al. treated nine TICAs with endovascular intervention, and experienced no additional neurologic morbidity and no mortality [101]. Bells et al. treated 24 TICAs in 23 soldiers using endovascular techniques [94]. These investigators achieved a 50% rate of parent artery preservation in the endovascular group compared with 30.8% in the open surgery group. Three of the endovascular patients went on to require open surgery for definitive treatment. There was no occurrence of vessel rupture or mortality reported in the endovascular treatment group.
Conclusion
With increased awareness and liberal screening of trauma patients with identified risk factors, recent case series demonstrate improved early diagnosis of carotid artery trauma before they become problematic. There remains a need for unified screening criteria for both intracranial and extracranial carotid trauma. In the absence of contraindications, antithrombotic agents should be considered in blunt carotid artery injuries, as there is a significant risk for progression of vessel injury with observation alone.
Despite CTA being used as a common screening modality, it appears to lack sufficient sensitivity. DSA remains to be the gold standard in screening. Endovascular techniques are becoming more widely accepted as the primary surgical modality in the treatment of blunt extracranial carotid injuries and penetrating/blunt intracranial carotid lesions. Nonetheless, open surgical approaches are still needed for the treatment of penetrating extracranial carotid injuries and in patients with unfavorable lesions for endovascular intervention. Despite significant advancements in understanding carotid trauma, there is a clear need for prospective, randomized clinical studies, with large sample sizes, to address several controversies that exist in the treatment of carotid injuries.
References
- Kraus, R.R.; Bergstein, J.M.; DeBord, J.R. Diagnosis, treatment, and outcome of blunt carotid arterial injuries. Am J Surg 1999, 178, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biousse, V.; D’Anglejan-Chatillon, J.; Touboul, P.J.; Amarenco, P.; Bousser, M.G. Time course of symptoms in extracranial carotid artery dissections. A series of 80 patients. Stroke 1995, 26, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, A.; Desai, S.S.; Kuy, S.; et al. Predicting outcomes using the National Trauma Data Bank: optimum management of traumatic blunt carotid and blunt thoracic injury. Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther 2012, 24, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidereit, N.P.; Simons, R.; Nicolaou, S.; et al. Utility of screening for blunt vascular neck injuries with computed tomographic angiography. J Trauma 2006, 60, 209–215, discussion 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogbill, T.H.; Moore, E.E.; Meissner, M.; et al. The spectrum of blunt injury to the carotid artery: a multicenter perspective. J Trauma 1994, 37, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; D’Ayala, M.; Hirshberg, A.; Briggs, W.; Wise, L.; Tortolani, A. Comparison of conservative and operative treatment for blunt carotid injuries: analysis of the National Trauma Data Bank. J Vasc Surg 2010, 51, 593–599, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouthillier, A.; van Loveren, H.R.; Keller, J.T. Segments of the internal carotid artery: a new classification. Neurosurgery 1996, 38, 425–432, discussion 432–433. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.W.; Holbrook, T.L.; Hoyt, D.B.; Mackersie, R.C.; Field, T.O., Jr.; Shackford, S.R. Blunt carotid artery dissection: incidence, associated injuries, screening, and treatment. J Trauma 1990, 30, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, T.C.; Patton JHJr Croce, M.A.; Minard, G.; Kudsk, K.A.; Pritchard, F.E. Blunt carotid injury. Importance of early diagnosis and anticoagulant therapy. Ann Surg 1996, 223, 513–522, discussion 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Ryu, R.K.; et al. The unrecognized epidemic of blunt carotid arterial injuries: early diagnosis improves neurologic outcome. Ann Surg 1998, 228, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.R.; Fabian, T.C.; Croce, M.A.; et al. Prospective screening for blunt cerebrovascular injuries: analysis of diagnostic modalities and outcomes. Ann Surg 2002, 236, 386–393, discussion 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerwin, A.J.; Bynoe, R.P.; Murray, J.; et al. Liberalized screening for blunt carotid and vertebral artery injuries is justified. J Trauma 2001, 51, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Ray CEJr Moore, E.E.; et al. Treatment-related outcomes from blunt cerebrovascular injuries: importance of routine follow-up arteriography. Ann Surg 2002, 235, 699–706, discussion 706–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, J.D.; Reuland, K.S.; Villarreal, D.H.; McGovern, T.M.; Rowe, S.A.; Norwood, S.H. Sixteen-slice multi-detector computed tomographic angiography improves the accuracy of screening for blunt cerebrovascular injury. J Trauma 2006, 60, 1204–1209, discussion 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastman, A.L.; Chason, D.P.; Perez, C.L.; McAnulty, A.L.; Minei, J.P. Computed tomographic angiography for the diagnosis of blunt cervical vascular injury: is it ready for primetime? J Trauma 2006, 60, 925–929, discussion 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crissey, M.M.; Bernstein, E.F. Delayed presentation of carotid intimal tear following blunt craniocervical trauma. Surgery 1974, 75, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Zelenock, G.B.; Kazmers, A.; Whitehouse, W.M., Jr.; et al. Extracranial internal carotid artery dissections: noniatrogenic traumatic lesions. Arch Surg 1982, 117, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anson, J.; Crowell, R.M. Cervicocranial arterial dissection. Neurosurgery 1991, 29, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raser, J.M.; Mullen, M.T.; Kasner, S.E.; Cucchiara, B.L.; Messé, S.R. Cervical carotid artery dissection is associated with styloid process length. Neurology 2011, 77, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Offner, P.J.; Burch, J.M. Blunt carotid and vertebral arterial injuries. World J Surg 2001, 25, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, D.M.; Boswell, S.; Sliker, C.W.; Lui, F.Y.; Scalea, T.M. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: does treatment always matter? J Trauma 2009, 66, 132–143, discussion 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKevitt, E.C.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Vertesi, L.; Granger, R.; Simons, R.K. Blunt vascular neck injuries: diagnosis and outcomes of extracranial vessel injury. J Trauma 2002, 53, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlew, C.C.; Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Barnett, C.C.; Johnson, J.L.; Bensard, D.D. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: redefining screening criteria in the era of noninvasive diagnosis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2012, 72, 330–335, discussion 336–337, quiz 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterling, M.; Carlström, C.; Konrad, P. Internal carotid artery dissection. Acta Neurol Scand 2000, 101, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, J.; Newell, D.W.; Sturzenegger, M.; Mayberg, M.R.; Winn, H.R. Transcranial Doppler in the evaluation of internal carotid artery dissection. Stroke 1996, 27, 1226–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheid, R.; Zimmer, C.; Schroeter, M.L.; Ballaschke, O.; von Cramon, D.Y. The clinical spectrum of blunt cerebrovascular injury. Neurologist 2006, 12, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Shima, T.; Nishida, M.; Yamane, K.; Kagawa, R. Traumatic dissection of the common carotid artery after blunt injury to the neck. Surg Neurol 1999, 51, 513–519, discussion 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Offner, P.J.; Brega, K.E.; Franciose, R.J.; Burch, J.M. Blunt carotid arterial injuries: implications of a new grading scale. J Trauma 1999, 47, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.R.; Fabian, T.C.; Bee, T.K.; et al. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: diagnosis and treatment. J Trauma 2001, 51, 279–285, discussion 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cothren, C.C.; Moore, E.E.; Biffl, W.L.; et al. Anticoagulation is the gold standard therapy for blunt carotid injuries to reduce stroke rate. Arch Surg 2004, 139, 540–545, discussion 545–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Offner, P.J.; Brega, K.E.; Franciose, R.J.; Burch, J.M. Therapeutic implications of a new grading scale in 100 blunt carotid arterial injuries. J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care 1999, 46, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Cothren, C.C.; Moore, E.E.; et al. Western Trauma Association critical decisions in trauma: screening for and treatment of blunt cerebrovascular injuries. J Trauma 2009, 67, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, W.J.; Collier, B.C.; Diebel, L.N.; et al. Blunt cerebrovascular injury practice management guidelines: the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J Trauma 2010, 68, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berne, J.D.; Norwood, S.H.; McAuley, C.E.; Vallina, V.L.; Creath, R.G.; McLarty, J. The high morbidity of blunt cerebrovascular injury in an unscreened population: more evidence of the need for mandatory screening protocols. J Am Coll Surg 2001, 192, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Offner, P.J.; et al. Optimizing screening for blunt cerebrovascular injuries. Am J Surg 1999, 178, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, R.P.; Friedman, J.A.; Mahabir, R.C. A nationwide review of the associations among cervical spine injuries, head injuries, and facial fractures. J Trauma 2010, 68, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutze, S.; Rademacher, G.; Matthes, G.; Hosten, N.; Stengel, D. Blunt cerebrovascular injury in patients with blunt multiple trauma: diagnostic accuracy of duplex Doppler US and early CT angiography. Radiology 2005, 237, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKevitt, E.C.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Vertesi, L.; Granger, R.; Simons, R.K. Identifying patients at risk for intracranial and extracranial blunt carotid injuries. Am J Surg 2002, 183, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cothren, C.C.; Moore, E.E.; Ray, C.E., Jr.; et al. Screening for blunt cerebrovascular injuries is cost-effective. Am J Surg 2005, 190, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, D.; Brasel, K.J.; Neideen, T.; Weigelt, J.A. Screening for blunt cerebrovascular injuries is cost-effective. J Trauma 2011, 70, 1051–1056, discussion 1056–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan, M.R.; Weinberg, J.A.; Peaks, Y.S.; et al. Management of blunt extracranial traumatic cerebrovascular injury: a multidisciplinary survey of current practice. World J Emerg Surg 2011, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiCocco, J.M.; Emmett, K.P.; Fabian, T.C.; Zarzaur, B.L.; Williams, J.S.; Croce, M.A. Blunt cerebrovascular injury screening with 32-channel multidetector computed tomography: more slices still don’t cut it. Ann Surg 2011, 253, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffl, W.L.; Egglin, T.; Benedetto, B.; Gibbs, F.; Cioffi, W.G. Sixteen-slice computed tomographic angiography is a reliable noninvasive screening test for clinically significant blunt cerebrovascular injuries. J Trauma 2006, 60, 745–751, discussion 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utter, G.H.; Hollingworth, W.; Hallam, D.K.; Jarvik, J.G.; Jurkovich, G.J. Sixteen-slice CT angiography in patients with suspected blunt carotid and vertebral artery injuries. J Am Coll Surg 2006, 203, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.K.; Camacho, M.; Ivatury, R.R.; et al. Computed tomographic angiography for the diagnosis of blunt carotid/vertebral artery injury: a note of caution. Ann Surg 2007, 246, 632–642, discussion 642–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, R.B.; Beery, P.R.I.I.; Dorbish, R.J.; et al. Computed tomographic angiography versus conventional angiography for the diagnosis of blunt cerebrovascular injury in trauma patients. J Trauma 2009, 67, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.J.; Chaubey, V.P.; Zygun, D.A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomographic angiography for blunt cerebrovascular injury detection in trauma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 2013, 257, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, R.B.; Mawad, M.E.; Whitehead, W.E.; Luerssen, T.G.; Jea, A. Extracranial traumatic carotid artery dissections in children: a review of current diagnosis and treatment options. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2008, 2, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Ray CEJr Moore, E.E.; Mestek, M.; Johnson, J.L.; Burch, J.M. Noninvasive diagnosis of blunt cerebrovascular injuries: a preliminary report. J Trauma 2002, 53, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, J.J.; Diamond, D.L. Blunt carotid injury: reassessing the role of anticoagulation. Am Surg 1996, 62, 212–217. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, N.M.; Fabian, T.C.; Claridge, J.A.; Timmons, S.D.; Fischer, P.E.; Croce, M.A. Antithrombotic therapy and endovascular stents are effective treatment for blunt carotid injuries: results from long term followup. J Am Coll Surg 2007, 204, 1007–1013, discussion 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eachempati, S.R.; Vaslef, S.N.; Sebastian, M.W.; Reed, R.L. II. Blunt vascular injuries of the head and neck: is heparinization necessary? J Trauma 1998, 45, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, W.L.; Brandt, M.M.; Thompson, B.G.; Taheri, P.A.; Greenfield, L.J. Antiplatelet therapy: an alternative to heparin for blunt carotid injury. J Trauma 2002, 52, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beletsky, V.; Nadareishvili, Z.; Lynch, J.; Shuaib, A.; Woolfenden, A.; Norris, J.W.; Canadian Stroke Consortium. Cervical arterial dissection: time for a therapeutic trial? Stroke 2003, 34, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinson, H.E.; Stallmeyer, M.J.; Furuno, J.P.; Yarbrough, K.L.; Cole, J.W. Antithrombotic therapy and outcomes of cervical arterial dissection in the trauma patient: a case series. J Trauma Manag Outcomes 2010;4, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, M.H.; Rahme, R.J.; Arnaout, O.; et al. Endovascular stenting of extracranial carotid and vertebral artery dissections: a systematic review of the literature. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 856–866, discussion 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cothren, C.C.; Moore, E.E.; Ray, C.E., Jr.; et al. Carotid artery stents for blunt cerebrovascular injury: risks exceed benefits. Arch Surg 2005, 140, 480–485, discussion 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhodayan, Y.; Moran, C.J.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Cross, D.T., III. Outcomes of angioplasty and stenting at the common carotid origin. Surg Neurol 2009, 72, 451–455, discussion 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.Y.; Paulsen, R.D.; Marcellus, M.L.; Steinberg, G.K.; Marks, M.P. Longterm outcomes after carotid stent placement treatment of carotid artery dissection. Neurosurgery 1999, 45, 1368–1373, discussion 1373–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coldwell, D.M.; Novak, Z.; Ryu, R.K.; et al. Treatment of posttraumatic internal carotid arterial pseudoaneurysms with endovascular stents. J Trauma 2000, 48, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, A.C.; Palmer, E.; Luh, G.Y.; Jacobson, J.P.; Smith, D.C. Endovascular treatment of carotid and vertebral pseudoaneurysms with covered stents. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008, 29, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, B.J.; Ryu, R.K.; Coldwell, D.M.; Brega, K.E. Treatment of blunt injury to the carotid artery by using endovascular stents: an early experience. J Neurosurg 1997, 87, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, R.; Obuchowski, A.M.; Zoarski, G.H. Endovascular repair of traumatic cervical internal carotid artery injuries: a safe and effective treatment option. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2013, 34, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhodayan, Y.; Jeck, D.T.; Moran, C.J.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Cross, D.T., III. Angioplasty and stenting in carotid dissection with or without associated pseudoaneurysm. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005, 26, 2328–2335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavallée, P.C.; Mazighi, M.; Saint-Maurice, J.P.; et al. Stent-assisted endovascular thrombolysis versus intravenous thrombolysis in internal carotid artery dissection with tandem internal carotid and middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 2007, 38, 2270–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuBose, J.; Recinos, G.; Teixeira, P.G.; Inaba, K.; Demetriades, D. Endovascular stenting for the treatment of traumatic internal carotid injuries: expanding experience. J Trauma 2008, 65, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.E.; Gomori, J.M.; Itshayek, E.; et al. Single-center experience on endovascular reconstruction of traumatic internal carotid artery dissections. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2012, 72, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriades, D.; Asensio, J.A.; Velmahos, G.; Thal, E. Complex problems in penetrating neck trauma. Surg Clin North Am 1996, 76, 661–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navsaria, P.; Omoshoro-Jones, J.; Nicol, A. An analysis of 32 surgically managed penetrating carotid artery injuries. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2002, 24, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stannard, A.; Brown, K.; Benson, C.; Clasper, J.; Midwinter, M.; Tai, N.R. Outcome after vascular trauma in a deployed military trauma system. Br J Surg 2011, 98, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, R.E.; Fry, W.J. Extracranial carotid artery injuries. Surgery 1980, 88, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, F.; Rutledge, R.; Oller, D.; Howell, P.; Baker, C.; Keagy, B. Carotid artery trauma: a review of contemporary trauma center experiences. J Vasc Surg 1995, 21, 46–55, discussion 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetriades, D.; Skalkides, J.; Sofianos, C.; Melissas, J.; Franklin, J. Carotid artery injuries: experience with 124 cases. J Trauma 1989, 29, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlin, R.M.; Marks, C. Extracranial carotid artery injury. Current surgical management. Am J Surg 1983, 146, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.P.; Walsh, J.; Barrett, J.; et al. Analysis of 18 recent cases of penetrating injuries to the common and internal carotid arteries. Am J Surg 1988, 156, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.D.; Simpson, C.; Miller, F.B. Management of carotid artery trauma. Surgery 1988, 104, 673–680. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.F.; Graham, J.M.; Feliciano, D.V.; Mattox, K.L.; Beall, A.C., Jr.; DeBakey, M.E. Carotid artery injuries. Am J Surg 1982, 144, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbs, J.V.; Human, R.R.; Rajaruthnam, P. Extracranial arterial reconstruction for chronic cerebral ischaemia. An audit of experience in the Durban Teaching Hospitals. S Afr Med J 1986, 70, 653–657. [Google Scholar]
- Ledgerwood, A.M.; Mullins, R.J.; Lucas, C.E. Primary repair vs ligation for carotid artery injuries. Arch Surg 1980, 115, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, S.W.; Tucker WSJr Mrdeza, M.A.; Wellons, H.A., Jr.; Chandler, J.G. Carotid arterial trauma. Surgery 1980, 87, 477–487. [Google Scholar]
- Starnes, B.W.; Arthurs, Z.M. Endovascular management of vascular trauma. Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther 2006, 18, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reva, V.A.; Pronchenko, A.A.; Samokhvalov, I.M. Operative management of penetrating carotid artery injuries. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2011, 42, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, D.L. Comments regarding ’operative management of penetrating carotid artery injuries’. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2011, 42, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rich, N.M.; Baugh, J.H.; Hughes, C.W. Acute arterial injuries in Vietnam: 1,000 cases. J Trauma 1970, 10, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.J.; Gillespie, D.L.; O’Donnell, S.D.; et al. Contemporary management of wartime vascular trauma. J Vasc Surg 2005, 41, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.J.; Gillespie, D.L.; Weber, M.A.; et al. Delayed evaluation of combat-related penetrating neck trauma. J Vasc Surg 2006, 44, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, E.L., III. Management of penetrating carotid injuries: an alternative approach. J Trauma 1973, 13, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, E.J.; Hein, M.F.; Adams, J.E. Intracranial hemorrhage following surgical revascularization for treatment of acute strokes. J Neurosurg 1964, 21, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.A.; Brief, D.; Mathewson, C., Jr. Carotid artery injuries. An analysis of eighty-five cases. Am J Surg 1970, 120, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, E.R.; Snyder, W.H.I.I.I.; Hays, R.J.; Perry, M.O. Management of carotid artery injuries. Surgery 1974, 76, 955–962. [Google Scholar]
- Robbs, J.V.; Human, R.R.; Rajaruthnam, P.; Duncan, H.; Vawda, I.; Baker, L.W. Neurological deficit and injuries involving the neck arteries. Br J Surg 1983, 70, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Toit, D.F.; Coolen, D.; Lambrechts, A.; de VOdendaal, J.; Warren, B.L. The endovascular management of penetrating carotid artery injuries: long-term follow-up. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2009, 38, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, L.E.; Stahlfeld, K.R.; Corcos, A.C.; et al. Evolving role of endovascular techniques for traumatic vascular injury: a changing landscape? J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2012, 72, 41–46, discussion 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.S.; Vo, A.H.; Roberts, R.; Wanebo, J.; Armonda, R.A. Wartime traumatic aneurysms: acute presentation, diagnosis, and multimodal treatment of 64 craniocervical arterial injuries. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 66–79, discussion 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, D.L.; Spector, R.H.; Braun, I.F.; Landman, J.A.; Tindall, S.C.; Tindall, G.T. Classification and treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas. J Neurosurg 1985, 62, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytle, T.L.; Punukollu, P.K. Carotid cavernous fistula. Semin Cerebrovasc Dis Stroke 2001, 1, 83–111. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, R.C.; Wilkinson, M.; Ahmed, R.M.; et al. Interventional treatment of carotid cavernous fistula. J Clin Neurosci 2011, 18, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamby, W.B. Carotid-cavernous fistula. Report of 32 surgically treated cases and suggestions for definitive operation. J Neurosurg 1964, 21, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, D. Carotid cavernous fistula: direct repair with preservation of the carotid artery. Technical note. J Neurosurg 1973, 38, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullan, S. Treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas by cavernous sinus occlusion. J Neurosurg 1979, 50, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzan, M.; Cantasdemir, M.; Seckin, M.S.; et al. Traumatic intracranial carotid tree aneurysms. Neurosurgery 1998, 43, 1314–1320, discussion 1320–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Maillard, A.A.; Urso, R.G.; Jarolimek, A.M. Trauma to the intracranial internal carotid artery. J Trauma 2010, 68, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.E.; Gomori, J.M.; Segal, R.; et al. Results of endovascular treatment of traumatic intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 476–485, discussion 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, M.B.; Kopitnik, T.A.; Landreneau, F.; et al. Multidisciplinary approach to traumatic intracranial aneurysms secondary to shotgun and handgun wounds. Surg Neurol 1999, 51, 31–41, discussion 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, B.; Harbaugh, R.E. Traumatic intracranial aneurysms: a contemporary review. J Trauma 1993, 35, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, A.S.; Patton, J.M.; Tindall, G.T. Cerebral aneurysms of traumatic origin. Surg Neurol 1975, 4, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Amirjamshidi, A.; Rahmat, H.; Abbassioun, K. Traumatic aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas of intracranial vessels associated with penetrating head injuries occurring during war: principles and pitfalls in diagnosis and management. A survey of 31 cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 1996, 84, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M.J.; Crone, K.R.; Ball, W.S.; Tomsick, T.A.; Berger, T.S.; Tew, J.M., Jr. Traumatic intracranial aneurysms in childhood: two cases and a review of the literature. Neurosurgery 1988, 22, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, P.S.; Reisner, A.; Morassutti, D.J.; Abdulhadi, B.; Harpring, J.E. Traumatic intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurg Focus 2000, 8, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansagra, A.P.; Cooke, D.L.; English, J.D.; et al. Current trends in endovascular management of traumatic cerebrovascular injury. J Neurointerv Surg 2014, 6, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelber, B.R.; Sundt, T.M., Jr. Treatment of intracavernous and giant carotid aneurysms by combined internal carotid ligation and extrato intracranial bypass. J Neurosurg 1980, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, C.G.; Peerless, S.J.; Ferguson, G.G. Hunterian proximal arterial occlusion for giant aneurysms of the carotid circulation. J Neurosurg 1994, 81, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavinzski, G.; Killer, M.; Knosp, E.; Ferraz-Leite, H.; Gruber, A.; Richling, B. False aneurysms of the intracavernous carotid artery—report of 7 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1997, 139, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Trevou, M.; Bullock, R.; Teasdale, E.; Quin, R.O. False aneurysms of the carotid tree due to unsuspected penetrating injury of the head and neck. Injury 1991, 22, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the author. The Author(s) 2014.