Resorbable Versus Titanium Rigid Fixation for Pediatric Mandibular Fractures: A Systematic Review, Institutional Experience and Comparative Analysis
Abstract
:Introduction
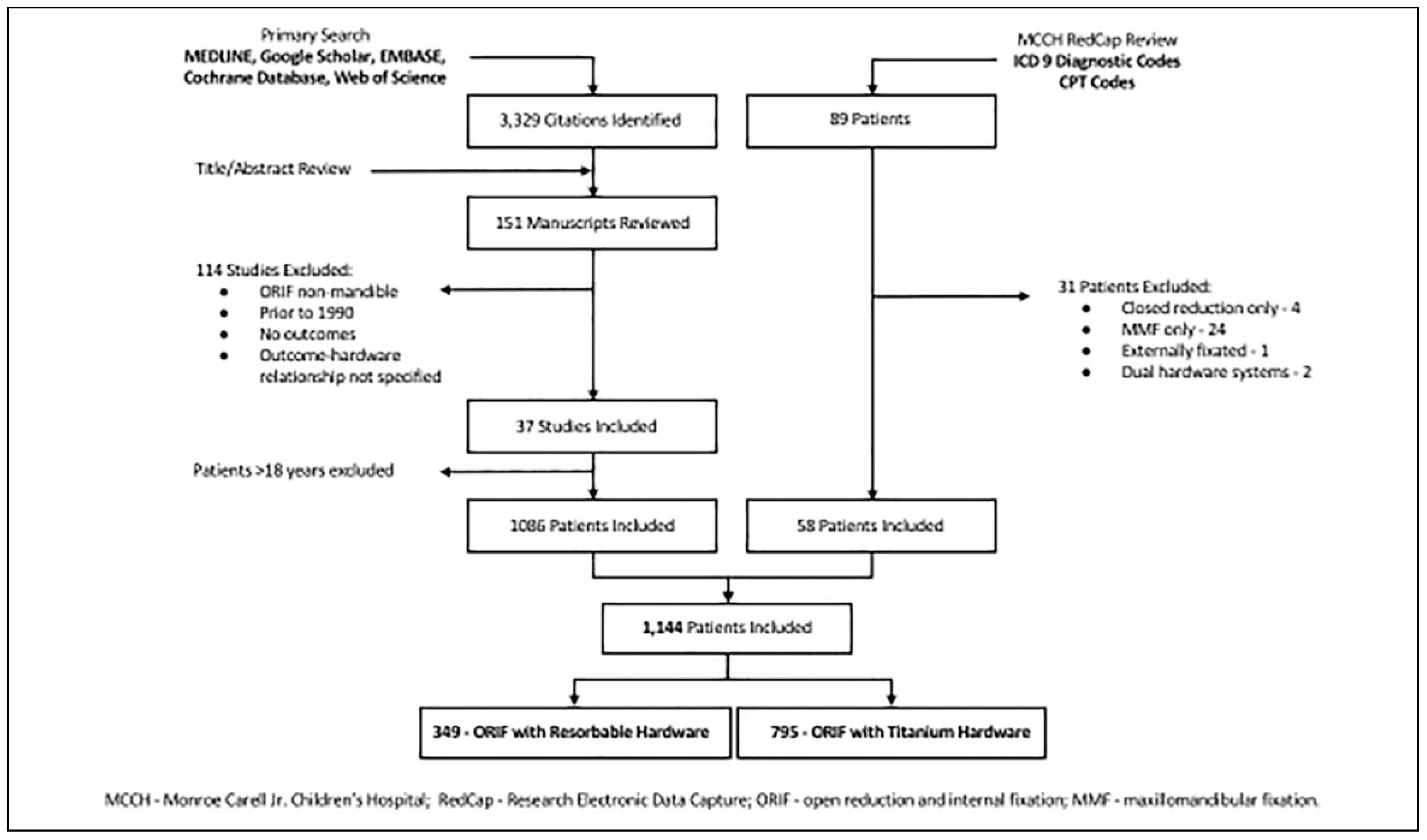
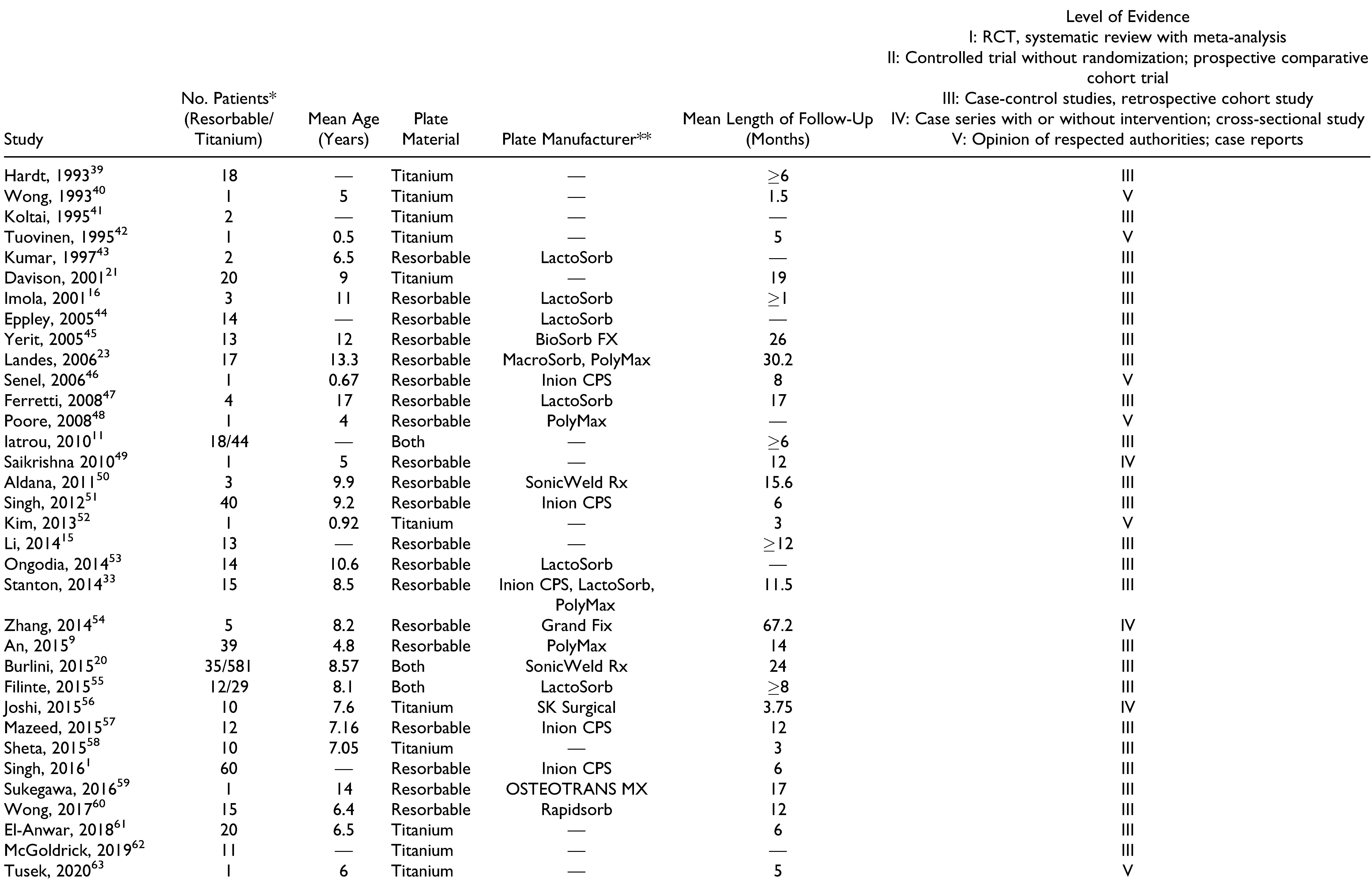
Materials and Methods
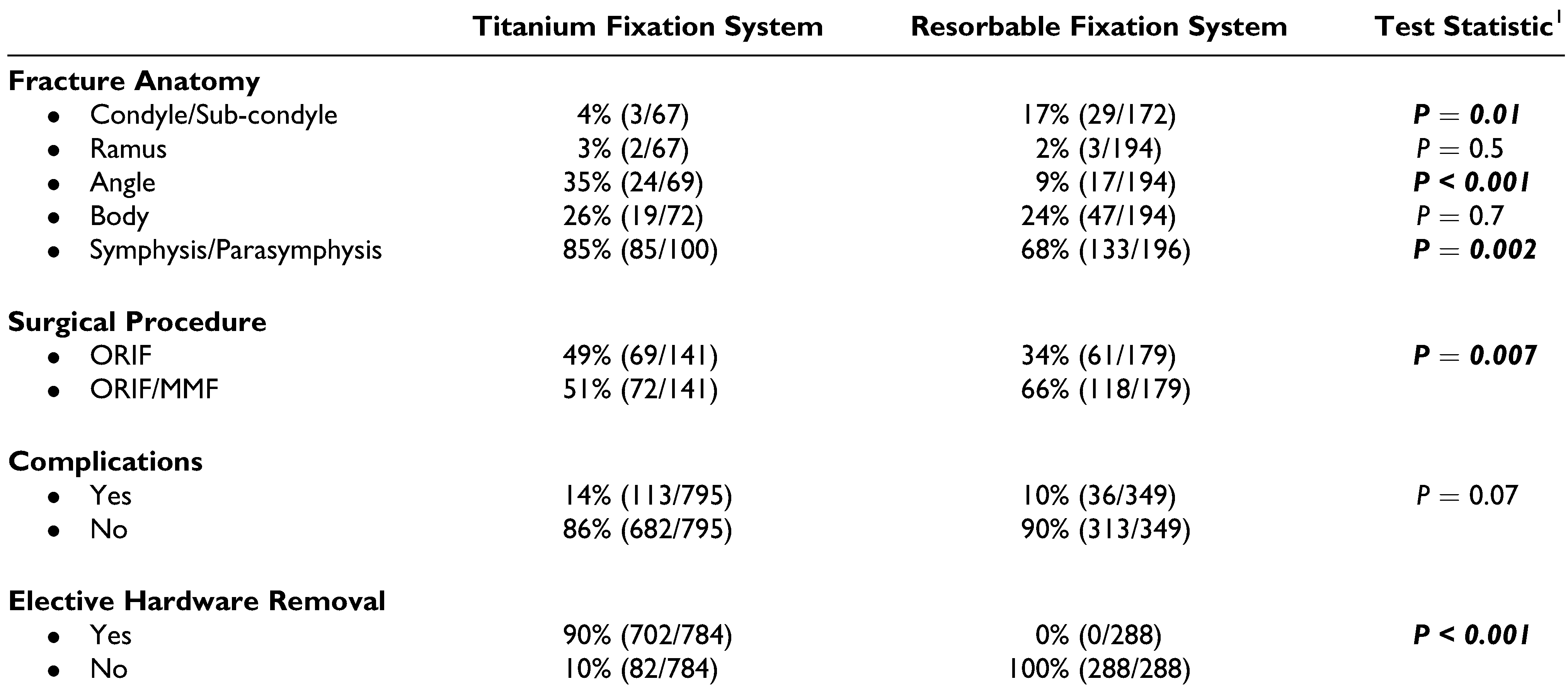
Results
Discussion
Titanium Hardware
Resorbable Hardware
Maxillomandibular Fixation
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, M.; Singh, R.K.; Passi, D.; Aggarwal, M.; Kaur, G. Management of pediatric mandibular fractures using bioresorbable plating system—efficacy, stability, and clinical outcomes: our experiences and literature review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2016, 6, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, F.J.; Chandler, R.A.; Crow, M.L. Facial fractures in children. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966, 37, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, P.C.; Barbosa, J.; Braga, J.M.; Rodrigues, A.; Silva, A.C.; Amarante, J.M. Pediatric facial fractures: a review of 2071 Fractures. Ann Plast Surg. 2016, 77, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Haug, R.H.; Foss, J. Maxillofacial injuries in the pediatric patient. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000, 90, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassner, R.; Tuli, T.; Hachl, O.; Moreira, R.; Ulmer, H. Craniomaxillofacial trauma in children: a review of 3,385 cases with 6,060 injuries in 10 years. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004, 62, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassner, R.; Tuli, T.; Hachl, O.; Rudisch, A.; Ulmer, H. Craniomaxillofacial trauma: a 10 year review of 9,543 cases with 21,067 injuries. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2003, 31, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, N.J.; Stewart, T.C.; Armstrong, J.E.; Girotti, M.J. Epidemiology of maxillofacial injuries at trauma hospitals in Ontario, Canada, between 1992 and 1997. J Trauma. 2000, 49, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hatef, D.A.; Cole, P.D.; Hollier, L.H., Jr. Contemporary management of pediatric facial trauma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009, 17, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Jia, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, X.; Han, X.; He, Y. Application of biodegradable plates for treating pediatric mandibular fractures. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015, 43, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Grunwaldt, L.; Smith, D.M.; Zuckerbraun, N.S.; et al. Pediatric facial fractures: demographics, injury patterns, and associated injuries in 772 consecutive patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011, 128, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou, I.; Theologie-Lygidakis, N.; Tzerbos, F. Surgical protocols and outcome for the treatment of maxillofacial fractures in children: 9 years’ experience. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2010, 38, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottgers, S.A.; Decesare, G.; Chao, M.; et al. Outcomes in pediatric facial fractures: early follow-up in 177 children and classification scheme. J Craniofac Surg. 2011, 22, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, C.E.; Troulis, M.J.; Kaban, L.B. Pediatric facial fractures: recent advances in prevention, diagnosis and management. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006, 35, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Goth, S.; Sawatari, Y.; Peleg, M. Management of pediatric mandible fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2012, 23, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; David, O.; Li, Z.B. The use of resorbable plates in association with dental arch stabilization in the treatment of mandibular fractures in children. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014, 42, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imola, M.J.; Hamlar, D.D.; Shao, W.; Chowdhury, K.; Tatum, S. Resorbable plate fixation in pediatric craniofacial surgery: long-term outcome. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2001, 3, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- McNichols, C.H.; Hatef, D.A.; Cole, P.D.; Hollier, L.H., Jr. Optimizing pediatric interdental fixation by use of a paramedian palatal fixation site. J Craniofac Surg. 2012, 23, 605–607. [Google Scholar]
- Aizenbud, D.; Emodi, O.; Rachmiel, A. Nonsurgical orthodontic splinting of mandibular fracture in a young child: 10-year follow-up. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008, 66, 575–577. [Google Scholar]
- Posnick, J.C.; Wells, M.; Pron, G.E. Pediatric facial fractures: evolving patterns of treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993, 51, 836–844; discussion 844–835. [Google Scholar]
- Burlini, D.; Conti, G.; Amadori, F.; Bardellini, E.; De Giuli, C. Management of paediatric maxillofacial fractures: conventional methods and resorbable materials. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2015, 16, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, S.P.; Clifton, M.S.; Davison, M.N.; Hedrick, M.; Sotereanos, G. Pediatric mandibular fractures: a free hand technique. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2001, 3, 185–189; discussion 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demianczuk, A.N.; Verchere, C.; Phillips, J.H. The effect on facial growth of pediatric mandibular fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 1999, 10, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landes, C.A.; Ballon, A. Indications and limitations in resorbable P(L70/30DL)LA osteosyntheses of displaced mandibular fractures in 4.5-year follow-up. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006, 117, 577–587; discussion 588–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, T.G.; Paige, K.T.; Davis, T.L.; Campbell, T.A.; Rosen, B.R.; Yaremchuk, M.J. Comparison of artifact from craniomaxillofacial internal fixation devices: magnetic resonance imaging. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994, 93, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiala, T.G.; Novelline, R.A.; Yaremchuk, M.J. Comparison of CT imaging artifacts from craniomaxillofacial internal fixation devices. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993, 92, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Katou, F.; Andoh, N.; Motegi, K.; Nagura, H. Immunoinflammatory responses in the tissue adjacent to titanium miniplates used in the treatment of mandibular fractures. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1996, 24, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, D.S.; Mayer, M.H.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; et al. Detection of titanium in human tissues after craniofacial surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997, 99, 976–979; discussion 980–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaushu, G.; Manor, Y.; Shoshani, Y.; Taicher, S. Risk factors contributing to symptomatic plate removal in maxillofacial trauma patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000, 105, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, W.S.; Eppley, B.L. Resorbable polymer fixation for craniomaxillofacial surgery: development and engineering paradigms. J Craniofac Surg. 2000, 11, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, D.Y.; Courtemanche, D.J.; Peters, D.A. Plate removal in traumatic facial fractures: 13-year practice review. Ann Plast Surg. 2005, 55, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francel, T.J.; Birely, B.C.; Ringelman, P.R.; Manson, P.N. The fate of plates and screws after facial fracture reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992, 90, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bayram, B.; Araz, K.; Uckan, S.; Balcik, C. Comparison of fixation stability of resorbable versus titanium plate and screws in mandibular angle fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009, 67, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stanton, D.C.; Liu, F.; Yu, J.W.; Mistretta, M.C. Use of bioresorbable plating systems in paediatric mandible fractures. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014, 42, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Morales, D.E.; Dyalram-Silverberg, D.; Lazow, S.K.; Berger, J.R. Treatment of mandible fractures using resorbable plates with a mean of 3 weeks maxillomandibular fixation: a prospective study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013, 115, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chocron, Y.; Azzi, A.J.; Cugno, S. Resorbable implants for mandibular fracture fixation: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019, 7, e2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorri, M.; Nasser, M.; Oliver, R. Resorbable versus titanium plates for facial fractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009, CD007158. [Google Scholar]
- Dorri, M.; Oliver, R. Withdrawn: Resorbable versus titanium plates for facial fractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018, 5, CD007158. [Google Scholar]
- Chocron, Y.; Azzi, A.J.; Davison, P. Management of pediatric mandibular fractures using resorbable plates. J Craniofac Surg. 2019, 30, 2111–2114. [Google Scholar]
- Hardt, N.; Gottsauner, A. The treatment of mandibular fractures in children. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1993, 21, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, G.B. Pediatric mandibular fractures treated by rigid internal fixation. J Can Dent Assoc. 1993, 59, 759–760. [Google Scholar]
- Koltai, P.J.; Amjad, I.; Meyer, D.; Feustel, P.J. Orbital fractures in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995, 121, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tuovinen, V.; van Steenis, K.; Sindet-Pedersen, S. Internal fixation of a mandibular fracture in a 6-month-old girl—a case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995, 24, 210–211. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.V.; Staffenberg, D.A.; Petronio, J.A.; Wood, R.J. Bioabsorbable plates and screws in pediatric craniofacial surgery: a review of 22 cases. J Craniofac Surg. 1997, 8, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Eppley, B.L. Use of resorbable plates and screws in pediatric facial fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005, 63, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yerit, K.C.; Hainich, S.; Enislidis, G.; et al. Biodegradable fixation of mandibular fractures in children: stability and early results. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005, 100, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, F.C.; Tekin, U.S.; Imamoglu, M. Treatment of a mandibular fracture with biodegradable plate in an infant: report of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006, 101, 448–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, C. A prospective trial of poly-L-lactic/polyglycolic acid co-polymer plates and screws for internal fixation of mandibular fractures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008, 37, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poore, M.C.; Penna, K.J. The use of resorbable hardware for fixation of pediatric mandible fracture. Case report. N Y State Dent J. 2008, 74, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Saikrishna, D.; Gupta, N. Comparison of circummandibular wiring with resorbable bone plates in pediatric mandibular fractures. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2010, 9, 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Aldana, P.R.; Wieder, K.; Postlethwait, R.A.; James, H.E.; Steinberg, B. Ultrasound-aided fixation of biodegradable implants in pediatric craniofacial surgery. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2011, 47, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Mohammad, S.; Chak, R.K.; Lepcha, N.; Singh, N.; Malkunje, L.R. Bio-resorbable plates as effective implant in paediatric mandibular fracture. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012, 11, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W.; Seo, E.W.; Song, S.I. Open reduction and internal fixation of mandibular fracture in an 11-month-old infant: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013, 39, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongodia, D.; Li, Z.; Xing, W.Z.; Li, Z.B. Resorbable plates for fixation of complicated mandibular fractures in children. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2014, 13, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, R.M. Open reduction and internal fixation of severely dislocated fractures of condylar neck and base using bioabsorbable miniplate in children: a 3-10 years follow-up study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylan Filinte, G.; Akan, I.M.; Aycicek Cardak, G.N.; Ozkaya Mutlu, O.; Akoz, T. Dilemma in pediatric mandible fractures: Resorbable or metallic plates? Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2015, 21, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Kshirsagar, R.; Mishra, A.; Shah, R. Clinical efficacy of open reduction and semirigid internal fixation in management of displaced pediatric mandibular fractures: a series of 10 cases and surgical guidelines. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2015, 33, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeed, A.S.; Shoeib, M.A.; Saied, S.M.; Elsherbiny, A. Early experience with biodegradable fixation of pediatric mandibular fractures. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2015, 8, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheta, M.S.; Shoushan, M.M.; Hussein, M.M.; Abd Elaal, S.E. Evaluation of using microplates osteosynthesis for pediatric mandibular fractures. Tanta Dental Journal. 2015, 12, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukegawa, S.; Kanno, T.; Katase, N.; Shibata, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Furuki, Y. Clinical evaluation of an unsintered hydroxyapatite/poly-L-lactide osteoconductive composite device for the internal fixation of maxillofacial fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2016, 27, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.K.; Adams, S.; Hudson, D.A.; Ozaki, W. Use of resorbable fixation system in pediatric facial fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2017, 28, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Anwar, M.W.; Salah, M.; Abdulmonaem, G. C-arm-assisted internal fixation of pediatric mandibular fracture. Egypt J Otolaryngol. 2018, 34, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGoldrick, D.M.; Parmar, P.; Williams, R.; Monaghan, A.; McMillan, K. Management of pediatric condyle fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2019, 30, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusek, I.; Ilic, M.P.; Tusek, J.; Ivic, S.; Tusek, B. Pediatric mandibular fracture therapy—a case report. Vojnosanitetski Pregled. 2020, 77, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.C.; Moreira, E.M.; Martínez, A.P. Mandible fracture in children: a case report. South Sudan Medical Journal. 2020, 13, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Yesantharao, P.S.; Lopez, J.; Reategui, A.; et al. Managing isolated symphyseal and parasymphyseal fractures in pediatric patients. J Craniofac Surg. 2020, 31, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siy, R.W.; Brown, R.H.; Koshy, J.C.; Stal, S.; Hollier, L.H., Jr. General management considerations in pediatric facial fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2011, 22, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.B.; Kindsfater, C.S. The use of biodegradable plates and screws to stabilize facial fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006, 64, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, R.R. Treatment of pediatric facial fractures: the case for metallic fixation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005, 63, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, P.N. Commentary on the long-term effects of rigid fixation on the growing craniomaxillofacial skeleton. J Craniofac Surg. 1991, 2, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, A.S.; Lehman, J.A., Jr. Symptomatic plate removal in maxillofacial trauma: a review of 76 cases. Ann Plast Surg. 2005, 55, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatum, S.A., 3rd. Retrospective review of resorbable plate fixation in pediatric craniofacial surgery: long-term outcome. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2012, 14, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryhill, W.E.; Rimell, F.L.; Ness, J.; Marentette, L.; Haines, S.J. Fate of rigid fixation in pediatric craniofacial surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999, 121, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degala, S.; Shetty, S.; Ramya, S. Fixation of zygomatic and mandibular fractures with biodegradable plates. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2013, 3, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenslag, J.W.; Pennings, A.J.; Bos, R.R.; Rozema, F.R.; Boering, G. Resorbable materials of poly(L-lactide). VII. In vivo and in vitro degradation. Biomaterials 1987, 8, 311–314. [Google Scholar]
- Leenslag, J.W.; Pennings, A.J.; Bos, R.R.; Rozema, F.R.; Boering, G. Resorbable materials of poly(L-lactide). VI. Plates and screws for internal fracture fixation. Biomaterials 1987, 8, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashammakhi, N.; Peltoniemi, H.; Waris, E.; et al. Developments in craniomaxillofacial surgery: use of self-reinforced bioabsorbable osteofixation devices. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001, 108, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tormala, P. Biodegradable self-reinforced composite materials; manufacturing structure and mechanical properties. Clin Mater. 1992, 10, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheung, L.K.; Chow, L.K.; Chiu, W.K. A randomized controlled trial of resorbable versus titanium fixation for orthognathic surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004, 98, 386–397. [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin, R.M.; Block, M.S.; Wilk, R.; Malloy, R.B.; Kent, J.N. Resorbable plates for the fixation of mandibular fractures: a prospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007, 65, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg, J.M.; Wittenberg, R.H.; Hipp, J.A. Biomechanical properties of resorbable poly-L-lactide plates and screws: a comparison with traditional systems. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991, 49, 512–516; discussion 517–518. [Google Scholar]
- Esen, A.; Ataoglu, H.; Gemi, L. Comparison of stability of titanium and absorbable plate and screw fixation for mandibular angle fractures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008, 106, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kallela, I.; Iizuka, T.; Salo, A.; Lindqvist, C. Lag-screw fixation of anterior mandibular fractures using biodegradable polylactide screws: a preliminary report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999, 57, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.B.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, S.G.; et al. Comparison of titanium and biodegradable miniplates for fixation of mandibular fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010, 68, 2065–2069. [Google Scholar]
- Yerit, K.C.; Enislidis, G.; Schopper, C.; et al. Fixation of mandibular fractures with biodegradable plates and screws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002, 94, 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Gupta, A.; Grevious, M.; Reid, R.R. Use of resorbable implants for mandibular fixation: a systematic review. J Craniofac Surg. 2009, 20, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turvey, T.A.; Bell, R.B.; Phillips, C.; Proffit, W.R. Self-reinforced biodegradable screw fixation compared with titanium screw fixation in mandibular advancement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006, 64, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackool, R.; Yim, J.; McCarthy, J.G. Delayed degradation in a resorbable plating system. J Craniofac Surg. 2006, 17, 194–197; discussion 197–198. [Google Scholar]
- Yerit, K.C.; Hainich, S.; Turhani, D.; et al. Stability of biodegradable implants in treatment of mandibular fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005, 115, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Kocabay, C.; Atac, M.S.; Oner, B.; Gungor, N. The conservative treatment of pediatric mandibular fracture with prefabricated surgical splint: a case report. Dent Traumatol. 2007, 23, 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- Glazer, M.; Joshua, B.Z.; Woldenberg, Y.; Bodner, L. Mandibular fractures in children: analysis of 61 cases and review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 75, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, P.C.; Barbosa, J.; Amarante, J.M.; Carvalho, J.; Rodrigues, A.G.; Silva, A.C. Associated injuries in pediatric patients with facial fractures in Portugal: analysis of 1416 patients. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015, 43, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Erasmus, F.; Gerlach, K.L.; et al. Open reduction and internal fixation versus closed treatment and mandibulomaxillary fixation of fractures of the mandibular condylar process: a randomized, prospective, multicenter study with special evaluation of fracture level. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008, 66, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, P.; Silva, N.; Silva, A.; et al. Pediatric facial fractures. Characteristics of Portuguese population. Acta Med Port. 2004, 17, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

 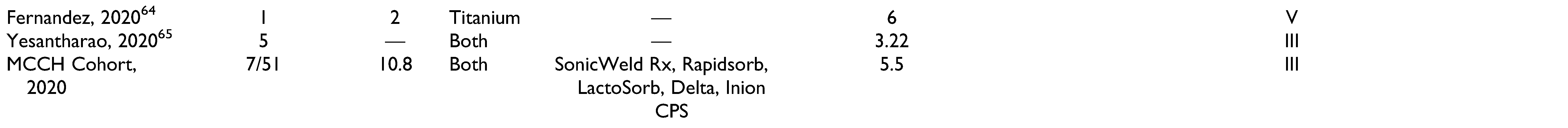 |
 |
 |
| Titanium System Complications | Resorbable System Complications | Test Statistic1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dentition Stage | |||
| • Primary | 12.5% (3/24) | 13.3% (4/30) | P = 1.00 |
| • Mixed | 12% (3/25) | 6.7% (3/45) | P = 0.66 |
| • Adult | 11.1% (3/27) | 6.1% (2/33) | P = 0.65 |
© 2021 by the author. The Author(s) 2021.
Share and Cite
Pontell, M.E.; Niklinska, E.B.; Braun, S.A.; Jaeger, N.; Kelly, K.J.; Golinko, M.S. Resorbable Versus Titanium Rigid Fixation for Pediatric Mandibular Fractures: A Systematic Review, Institutional Experience and Comparative Analysis. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2022, 15, 189-200. https://doi.org/10.1177/19433875211022573
Pontell ME, Niklinska EB, Braun SA, Jaeger N, Kelly KJ, Golinko MS. Resorbable Versus Titanium Rigid Fixation for Pediatric Mandibular Fractures: A Systematic Review, Institutional Experience and Comparative Analysis. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction. 2022; 15(3):189-200. https://doi.org/10.1177/19433875211022573
Chicago/Turabian StylePontell, Matthew E., Eva B. Niklinska, Stephane A. Braun, Nolan Jaeger, Kevin J. Kelly, and Michael S. Golinko. 2022. "Resorbable Versus Titanium Rigid Fixation for Pediatric Mandibular Fractures: A Systematic Review, Institutional Experience and Comparative Analysis" Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction 15, no. 3: 189-200. https://doi.org/10.1177/19433875211022573
APA StylePontell, M. E., Niklinska, E. B., Braun, S. A., Jaeger, N., Kelly, K. J., & Golinko, M. S. (2022). Resorbable Versus Titanium Rigid Fixation for Pediatric Mandibular Fractures: A Systematic Review, Institutional Experience and Comparative Analysis. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction, 15(3), 189-200. https://doi.org/10.1177/19433875211022573




