The Moderating Role of Auditor Experience on Determinants of Computer-Assisted Auditing Tools and Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of the Literature and Development of Hypotheses
2.1. Performance Expectancy (PE) and Adoption of CAATs
2.2. Effort Expectancy and Adoption of CAATs
2.3. Social Influence and Adoption of CAATs
2.4. Facilitating Conditions and Adoption of CAATs
2.5. Moderating Effect of Auditor Experience
3. Methods
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Framework of This Study
3.3. Study Instrument Variables
3.4. Pilot Study
4. Results and Empirical Analysis
4.1. The Outer Model for Measuring
4.2. Analysis of Structural Models
5. Conclusions
5.1. Concluding Remarks
5.2. This Study’s Theoretical and Practical Implications
5.3. Limitations and Further Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Hiyari, A., Al Said, N., & Hattab, E. (2019). Factors that influence the use of computer assisted audit techniques (CAATs) by internal auditors in Jordan. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 23(3), 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Almagrashi, A., Mujalli, A., Khan, T., & Attia, O. (2023). Factors determining internal auditors’ behavioral intention to use computer-assisted auditing techniques: An extension of the UTAUT model and an empirical study. Future Business Journal, 9(1), 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X., Chai, C. S., Li, Y., Zhou, Y., & Yang, B. (2023). Modeling students’ perceptions of artificial intelligence assisted language learning. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A., Baniata, H., Othman, O., Ali, B., Abughaush, S., Aljundi, N., & Ahmad, A. (2024). The impact of computer assisted auditing techniques in the audit process: An assessment of performance and effort expectancy. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 8(2), 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouziane, A. (2025). Assessing the influence of technological tools on the quality of computer-assisted audits: The case of Moroccan audit firms. EDPACS, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, L. (2023). Predictors of auditors’ usage of CAATS: The role of top management support and trust. Information Sciences Letters, 12(5), 1841–1850. [Google Scholar]
- Flathmann, C., Duan, W., Mcneese, N. J., Hauptman, A., & Zhang, R. (2024). Empirically understanding the potential impacts and process of social influence in human-AI teams. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, 8(CSCW1), 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornel, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fülöp, M. T., Ionescu, C. A., Măgdaș, N., & Topor, D. I. (2024). Factors influencing the use of computer-assisted audit techniques in the digital era. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 25(6), 1140–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GC, S. B., Bhandari, P., Gurung, S. K., Srivastava, E., Ojha, D., & Dhungana, B. R. (2024). Examining the role of social influence, learning value and habit on students’ intention to use ChatGPT: The moderating effect of information accuracy in the UTAUT2 model. Cogent Education, 11(1), 2403287. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J. F., Jr., & Alamer, A. (2022). Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) in second language and education research: Guidelines using an applied example. Research Methods in Applied Linguistics, 1(3), 100027. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J. F., Jr., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., Danks, N. P., & Ray, S. (2021a). Evaluation of formative measurement models. In Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using R: A workbook (pp. 91–113). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J. F., Jr., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., Danks, N. P., & Ray, S. (2021b). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using R: A workbook. Springer Nature. [Google Scholar]
- Handoko, B. L., & Chu, N. C. (2021, July 17–19). UTAUT model in predicting auditor intention in adopting CAATs. Proceedings of the 2021 12th International Conference on E-business, Management and Economics, Beijing, China. [Google Scholar]
- Hendi, H. E., & Kuntadi, C. (2024). Faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi implementasi computer assisted audit techniques: Per-formance Expectations, Effort Expectations dan Social Influence. Jurnal Manajemen, Akuntansi dan Logistik (JUMATI), 2(4), 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hezabr, A. A., Qeshta, M. H., Al-Msni, F. M., Jawabreh, O., & Ali, B. J. (2023). Audit committee characteristics and firm performance: Evidence from the insurance sector in Oman. International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences, 10(5), 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- JS, K., Senani, K., & Ajward, R. (2024). Examining determinants of auditors’ intention to use CAATs in external auditing using an extended UTAUT model; evidence from Sri Lanka. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. A. (2025). Contextual considerations of audit technology acceptance, accounting regulations, administrative influ-ences, and organizational efficiency: A Novel I-TOE adoption formulation. Pakistan Journal of Life and Social Sciences, 23(1), 4563–4582. [Google Scholar]
- Lutfi, A., & Alqudah, H. (2023). The influence of technological factors on the computer-assisted audit tools and techniques usage during COVID-19. Sustainability, 15(9), 7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahzan, N., & Lymer, A. (2008). Adoption of computer assisted audit tools and techniques (CAATTs) by internal auditors: Current issues in the UK. BAA Annual Conference. [Google Scholar]
- Mahzan, N., & Lymer, A. (2014). Examining the adoption of computer-assisted audit tools and techniques: Cases of generalized audit software use by internal auditors. Managerial Auditing Journal, 29(4), 327–349. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H., Lu, X., & Xu, J. (2025). The impact of chatbot response strategies and emojis usage on customers’ purchase intention: The mediating roles of psychological distance and performance expectancy. Behavioral Sciences, 15(2), 117. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, H. A., Rabiu, N. B., & Barde, I. M. (2023). Determinants of adoption of computer assisted auditing techniques: A survey of auditors in Kano State, Nigeria. FUDMA Journal of Accounting and Finance Research [FUJAFR], 1(3), 146–161. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrah, H., Muda, I., & Kesuma, S. A. (2023). Computer assisted audit tools and techniques adoption: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Social Service and Research, 3(3), 630–638. [Google Scholar]
- Nurlaela, N., Irfan, A. M., Rahman, M. H., Putra, K. P., Mahmud, A., & Setialaksana, W. (2025). Understanding AR/VR Adoption through heutagogy and cybergogy: Insights from the UTAUT2 model in vocational education. Education and Information Technologies, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktavianie, H., & Teresa, V. (2023, June 15–17). Understanding determinants of computer assisted audit techniques (CAATs) adoption intention among auditors in Indonesia. 2022 3rd International Conference on Internet and E-Business (pp. 117–124), Madrid, Spain. [Google Scholar]
- Oudat, M. S., Ali, B., Hazaimeh, H., & El-Bannany, M. (2024). The effect of financial risks on the performance of Islamic and com-mercial banks in UAE. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 9, 1250227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudat, M. S., Ali, B., & Qeshta, M. H. (2021). Financial performance and audit committee characteristics: An empirical study on bahrain services sector. Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business and Government, 27(2), 4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qeshtaa, M., & Ali, B. (2020). The moderating effect of the effectiveness of the audit committee between ownership concentration and intellectual capital disclosures among companies in gulf cooperation council. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, 24(1), 5979–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachael, E., & Wijaya, S. V. (2025). The influence of social media marketing activity, performance expectancy, and effort expectancy on repurchase intention through the mediator of behavioral intention for cotton mom products on Shopee. Majalah Ilmiah Bijak, 22(1), 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, M. H., Jawabreh, O., & Ali, B. J. (2023). The role of performance Jordanian insurance companies in economic growth: Evidence from the PMG Panel-ARDL Approach. Cuadernos de Economía, 46(131), 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, N. P. W. P., Duong, M.-P. T., Li, D., Nguyen, M.-H., & Vuong, Q.-H. (2024). Rethinking the effects of performance expectancy and effort expectancy on new technology adoption: Evidence from Moroccan nursing students. Teaching and Learning in Nursing, 19(3), e557–e565. [Google Scholar]
- Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2016). Research methods for business: A skill building approach (7th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Sengkalit, D., & Abdullah, T. M. K. (2025). Factors influencing technology adoption among SMES: A case study of Youtap and the role of performance expectancy and effort expectancy. Syntax Literate; Jurnal Ilmiah Indonesia, 10(1), 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, R., Xiao, X., Dong, G., Zhang, Z., & Wen, Q. (2022). The influence of accounting computer information processing technology on enterprise internal control under panel data simultaneous equation. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences, 8(1), 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Management Science, 46(2), 186–204. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, Y. H., Johari, A. S., & Mohd Rahmatullah, D. (2023). Industry revolution 4.0: Rapid growth of technology may affect job security in auditing profession: A concept paper. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 13(3), 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
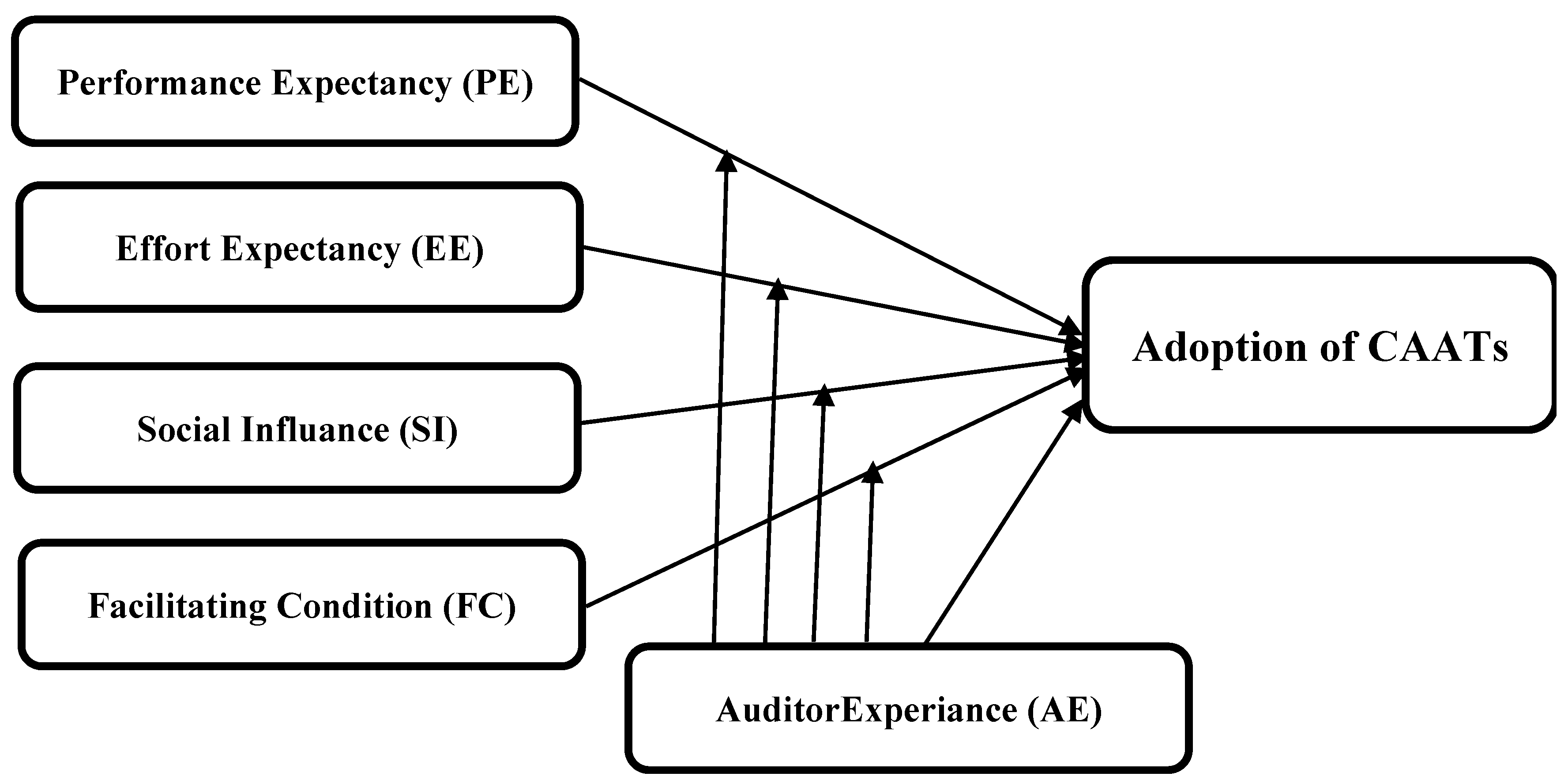
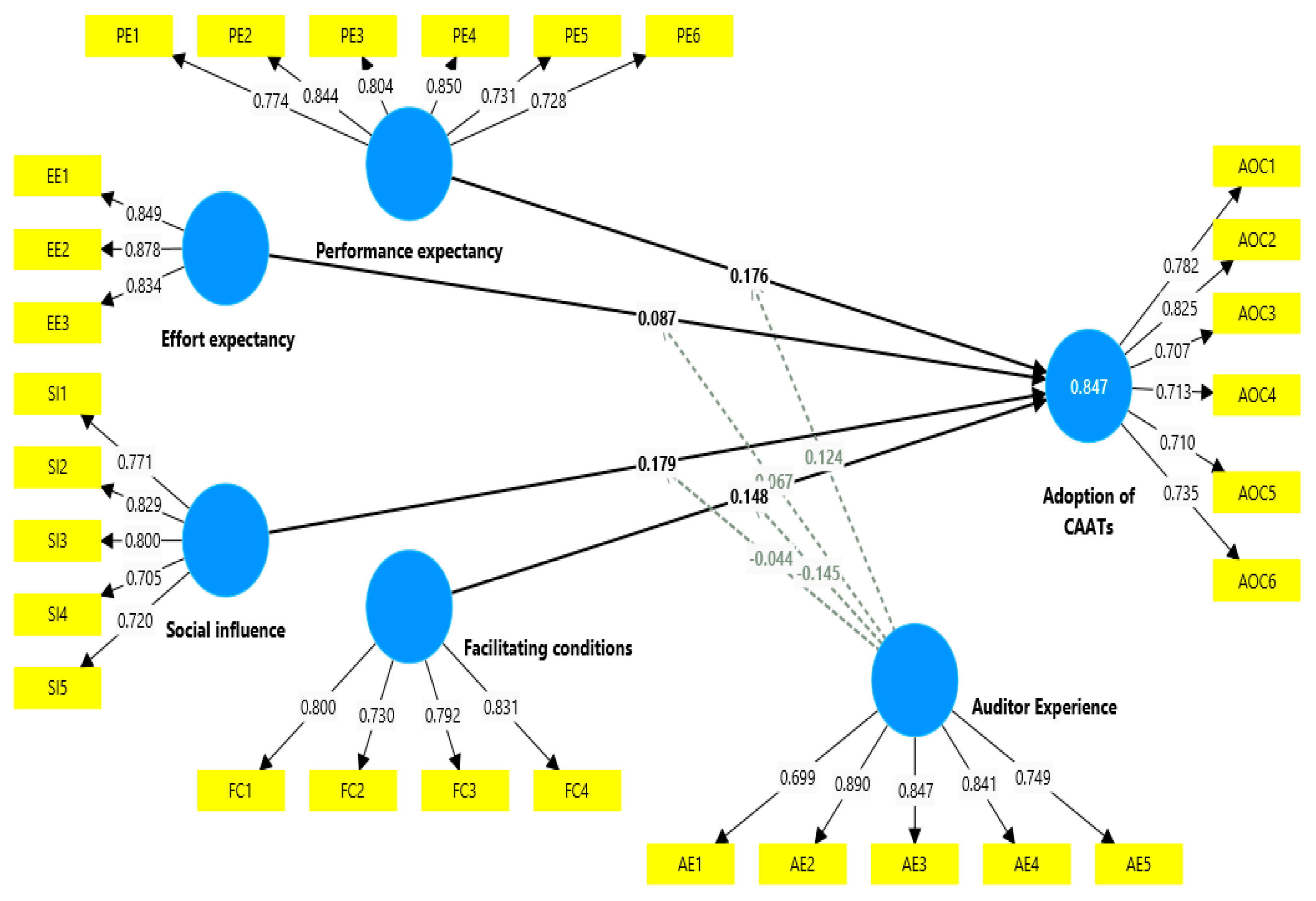
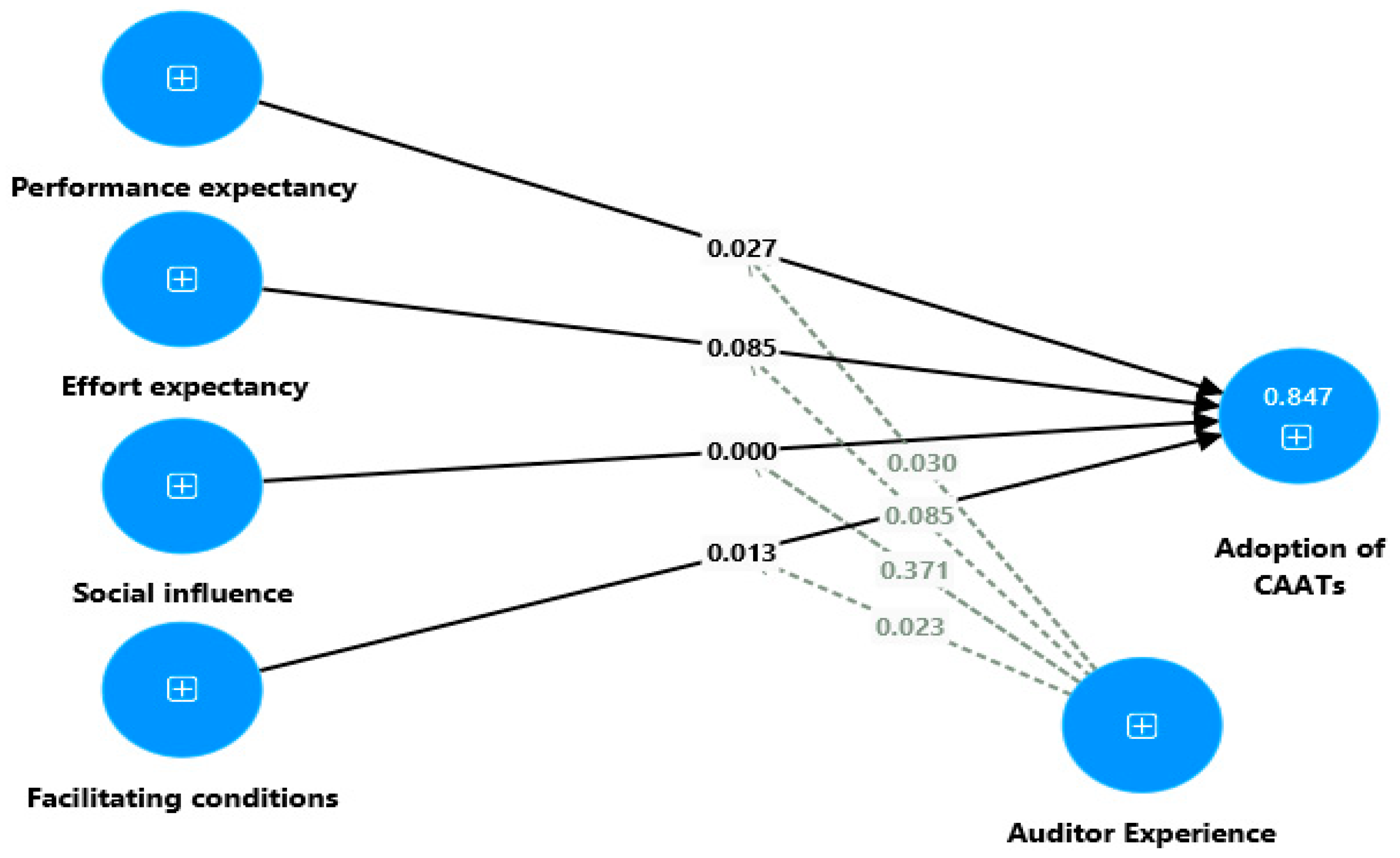
| Variables of the Study | Items |
|---|---|
| PE |
|
| EE |
|
| SI |
|
| FC |
|
| Adoption of CAATs |
|
| AE |
|
| Cronbach’s Alpha | Composite Reliability (rho_a) | Composite Reliability (rho_c) | Average Variance Extracted (AVE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adoption of CAATs | 0.840 | 0.844 | 0.883 | 0.558 |
| AE | 0.865 | 0.873 | 0.903 | 0.654 |
| EE | 0.815 | 0.821 | 0.890 | 0.729 |
| FC | 0.797 | 0.802 | 0.868 | 0.622 |
| PE | 0.878 | 0.881 | 0.909 | 0.624 |
| SI | 0.823 | 0.825 | 0.876 | 0.587 |
| Adoption of CAATs | IE | EE | FC | PE | SI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE1 | 0.699 | |||||
| AE2 | 0.890 | |||||
| AE3 | 0.847 | |||||
| AE4 | 0.841 | |||||
| AE5 | 0.749 | |||||
| AOC1 | 0.782 | |||||
| AOC2 | 0.825 | |||||
| AOC3 | 0.707 | |||||
| AOC4 | 0.713 | |||||
| AOC5 | 0.710 | |||||
| AOC6 | 0.735 | |||||
| EE1 | 0.849 | |||||
| EE2 | 0.878 | |||||
| EE3 | 0.834 | |||||
| FC1 | 0.800 | |||||
| FC2 | 0.730 | |||||
| FC3 | 0.792 | |||||
| FC4 | 0.831 | |||||
| PE1 | 0.774 | |||||
| PE2 | 0.844 | |||||
| PE3 | 0.804 | |||||
| PE4 | 0.850 | |||||
| PE5 | 0.731 | |||||
| PE6 | 0.728 | |||||
| SI1 | 0.771 | |||||
| SI2 | 0.829 | |||||
| SI3 | 0.800 | |||||
| SI4 | 0.705 | |||||
| SI5 | 0.720 |
| Adoption of CAATs | IE | EE | FC | PE | SI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adoption of CAATs | ||||||
| AE | 1.016 | |||||
| EE | 0.855 | 0.758 | ||||
| FC | 0.953 | 0.868 | 0.934 | |||
| PE | 0.997 | 0.983 | 0.858 | 0.949 | ||
| SI | 0.888 | 0.799 | 0.743 | 0.769 | 0.861 |
| Adoption of CAATs | IE | EE | FC | PE | SI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adoption of CAATs | 0.747 | |||||
| AE | 0.869 | 0.808 | ||||
| EE | 0.71 | 0.642 | 0.854 | |||
| FC | 0.785 | 0.727 | 0.747 | 0.789 | ||
| PE | 0.858 | 0.858 | 0.725 | 0.794 | 0.79 | |
| SI | 0.743 | 0.68 | 0.609 | 0.628 | 0.737 | 0.766 |
| Hypothesis Results | Original Sample (O) | Standard Deviation (STDEV) | T Value | p Value | Supported or Rejected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1: PE positively influences the adoption of CAATs. | 0.176 | 0.079 | 2.213 | 0.027 | Supported |
| H2: EE positively influences the adoption of CAATs. | 0.087 | 0.050 | 1.725 | 0.085 | Rejected |
| H3: SI positively influences the adoption of CAATs. | 0.179 | 0.046 | 3.858 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H4: FCs positively influence the adoption of CAATs. | 0.148 | 0.059 | 2.485 | 0.013 | Supported |
| H5: AE positively influences the adoption of CAATs. | 0.466 | 0.079 | 5.898 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H6: AE moderates the relationship between PE and the adoption of CAATs. | 0.124 | 0.057 | 2.170 | 0.030 | Supported |
| H7: AE moderates the relationship between EE and the adoption of CAATs. | 0.067 | 0.039 | 1.725 | 0.085 | Rejected |
| H8: AE moderates the relationship between SI and the adoption of CAATs. | −0.044 | 0.050 | 0.894 | 0.371 | Rejected |
| H9: AE moderates the relationship between FCs and the adoption of CAATs. | −0.145 | 0.064 | 2.270 | 0.023 | Supported |
| R Square | Adjusted R Square | |
|---|---|---|
| Adoption of CAATs | 0.847 | 0.839 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsarayrah, T.; Ali, B.J.A. The Moderating Role of Auditor Experience on Determinants of Computer-Assisted Auditing Tools and Techniques. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2025, 18, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18040206
Alsarayrah T, Ali BJA. The Moderating Role of Auditor Experience on Determinants of Computer-Assisted Auditing Tools and Techniques. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2025; 18(4):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18040206
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsarayrah, Tasneem, and Basel J. A. Ali. 2025. "The Moderating Role of Auditor Experience on Determinants of Computer-Assisted Auditing Tools and Techniques" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 18, no. 4: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18040206
APA StyleAlsarayrah, T., & Ali, B. J. A. (2025). The Moderating Role of Auditor Experience on Determinants of Computer-Assisted Auditing Tools and Techniques. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 18(4), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm18040206







