LMP1-EBV Gene Deletion Mutations and HLA Genotypes of Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients in Vietnam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Selection Criteria
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
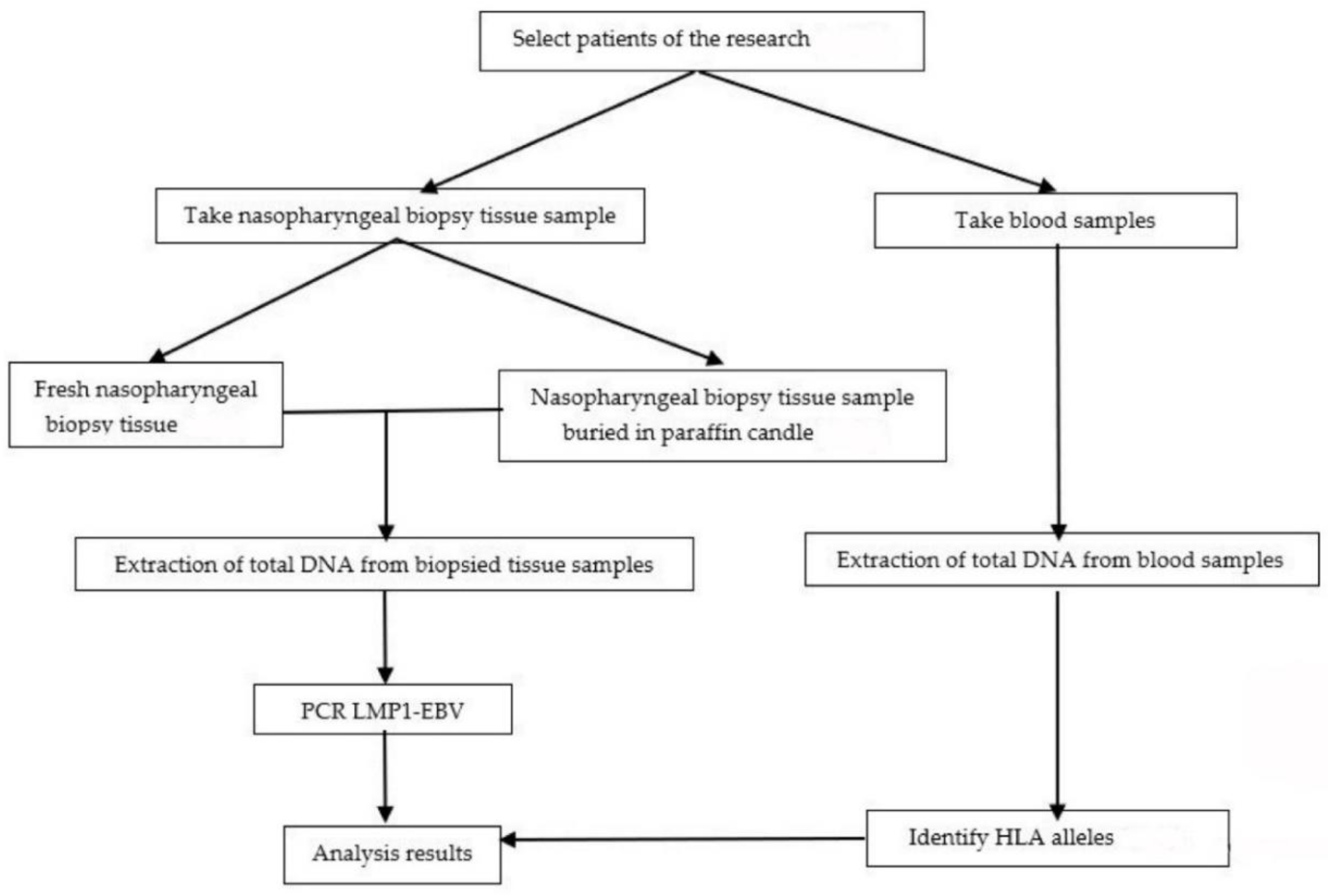
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Study Design
2.2.2. Sample Selection
2.3. Study Equipment
2.3.1. DNA extraction chemicals
2.3.2. PCR Reaction Chemicals
2.3.3. Chemicals Required for Automated Gene Sequencing
2.3.4. Chemicals Needed for PCR-SSO Technique to Determine HLA Gene Type Using One Lambda
2.4. Study Content and Techniques
2.4.1. Techniques
- (1)
- Extracting the total DNA from biopsy tissue samples (including viral genomes) using an Invisorb® Spin Tissue Mini Kit, measuring DNA concentration (OD260), and evaluating the purity of the DNA by calculating OD260/OD280 (1.6–2.1) with a BioDrop system.
- (2)
- Performing a PCR reaction with an LMP1-EBV primer pair with sequences at the following position: 168,373 (5′-CTA GCG ACT CTG CTG GAA AT-3′) and 168,174 (5′-CGC GGA TCC TTA GTC ATA GTA GCT TAG-3′). The composition used for the PCR reaction was 2.5 µL DNA, 3 µL dNTPs, 1 µL each primer, 3 µL MgCl2, 0.5 µL Taq DNA polymerase, 5 µL buffer, and 34 µL distilled water. The total volume was 50 µL. The heat cycle was as follows: 95 °C for 7 min, 35 cycles of 94 °C for 1 min and 30 s, 55 °C for 1 min, 72 °C for 1 min and 30 s, and 72 °C for 7 min.
- (3)
- Reading the results after 1 h: electrophoresis was performed with 9 µL PCR product on 2% agarose gel in 1 × TBE buffer at a voltage of 50 V.
2.4.2. Study Content
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Research Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of LMP1-EBV Gene Mutations in Nasopharyngeal Biopsy Tissue Samples of Patients with NPC
3.2. Prevalence of HLA Gene in Blood Samples of Patients with NPC
3.3. Association between 30 bp Deletion Mutation Rate of LMP1-EBV Gene and Frequency of HLA Alleles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hang, N.T.; Pham Phi, P.T.; Phan, H.; Bach, K.; Chinh, T.T. Frequency and mutation of latent membrance protein 1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharynx biopsy specimens of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patient. J. Med. Resenasopharyngeal—Ha Noi Med. Univ. 2003, 23, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, V.N.; Enrberg, I.; Phi, T.P.P. Epstein Barr virus genetic variation in Vietnamese patients with Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Full-length analysis of LMP 1. Virus Genes 2008, 37, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, Q.; Merhi, M.; Raza, A.; Inchakalody, V.P.; Abdelouahab, N.; Gul, A.R.Z.; Uddin, S.; Dermime, S. Role of Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of head and neck cancers and its potential as an immunotherapeutic target. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Yajima, M.; Ikuta, K. Epstein-Barr Virus strain variation and cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.M.; Tsao, S.W. The role of Epstein-Barr virus infection in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Virol. Sin. 2015, 30, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzellos, S.; Paul, J.F. Epstein-Barr virus sequence variation-biology and disease. Pathogens 2010, 1, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, S.W.; Tsang, C.M.; To, K.F.; Lo, K.W. The role of Epstein-Barr virus in epithelial malignancies. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, S.W.; Tsang, C.M.; Lo, K.W. Epstein-Barr virus infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. (R. Soc.) 2017, 372, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, P.; Hu, L.F.; Chen, F.; Christensson, B.; Masucci, M.G.; Klein, G.; Winberg, G. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded membrane protein LMP1 from a nasopharyngeal carcinoma is non-immunogenic in a murine model system, in contrast to a B cell-derived homologue. Eur. J. Cancer. 1994, 30A, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.F.; Chen, F.; Zheng, X.; Ernberg, I.; Cao, S.L.; Christensson, B.; Klein, G.; Winberg, G. Clonability and tumorigenicity of human epithelial cells expressing the EBV encoded membrane protein LMP1. Oncogene 1993, 8, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierre, B. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Keys for Translational Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X. Association analysis between HLA-A, -B, -C-DRB1, and DQB1 with nasopharyngeal carcinoma among a Han population in Northwestern China. Hum. Immunol. 2014, 75, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.Z.; Zhang, D.G.; Wu, R.; Hu, Y.H.; Peng, Y.C.; Chang, C.; Dong, T.; Wang, X.Y. HLA-A*02-B*46 haplotype: An adverse prognostic factor in Han patient nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cua, T.T.H.; Dung, T.N.; Nam, T.V.B.; Phi, P.T.P. The ratio of EBV LMP1 gene in fresh samples of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients at Can Tho oncology hospital. Vietnam. Med. J. 2018, 469, 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Cua, T.T.H.; Dung, T.N.; To, T.V.; Phi, P.T.P. Frequency and mutation of latent membrane protein 1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharynx biopsy specimens of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients at the Cantho Oncology Hospital. CTU J. Sci. 2019, 55, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.S.; Song, K.H.; Mai, H.Q.; Jia, W.H.; Feng, B.J.; Xia, J.C.; Zhang, R.H.; Huang, L.X.; Yu, X.J.; Feng, Q.S.; et al. The 30-deletion variant: A polymorphism of latent membrane protein 1 prevalent in endemic and non-endemic areas of nasopharyngeal carcinomas in China. Cancer Lett. 2002, 176, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.L.; Peh, S.C.; Sam, C.K. Analyses of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 in Malaysian from nasopharyngeal carcinoma: High prevalence of 30-bp deletion, Xho1 polymorphism and evidence of dual infections. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 69, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardari, R.; Meriem, K.; Paulo, C.; Mohieddine, O.; Brahim, E.; Mohammad, H.; Menezes, J. High frequency of latent membrane protein-1 30-bp deletion variant with specific single mutations in Epstein-Barr-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Moroccan patients. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutheina, H.G.; Khabir, A.M.; Raja, M.G.; Ghorbel, A.M.; Drira, M.; Daoud, J.; Frikha, M.; Jlidi, R.; Gargouri, A. Various 30 and 69 bp deletion variants of the Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 may arise by homologous recombination in nasopharyngeal carcinoma of Tunisian patients. Virus Resenasopharyngeal 2006, 11, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dung, T.N. Kinetic Study of Some Immuno-Biological Indicators to Help Prognosis and Predict the Recurrence of Nasopharyngeal Cancer, Try the Treatment of M after Radiation Therapy. Doctor of Medicine Thesis, Ha Noi Medical University, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hildesheim, A.; Apple, R.J.; Chen, C.J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Y.J.; Klitz, W.; Mack, S.J.; Chen, I.H.; Hsu, M.M.; Yang, C.S.; et al. Associated of HLA class I and II alleles and extended haplotypes with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwan. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Zeng, Y.; Poisson, A.; Marti, D.; Guan, L.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, H.; Liao, J.; Guo, X.; Sun, S.; et al. Haplotype-dependent HLA susceptibility to nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a Southern Chinese population. Genes Immun. 2010, 11, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehla, M.B.; Gorgi, Y.; Elghourabi, M.; Makhlouf, M.; Boussen, H.; Gritli, S.; Elmay, M.; Gamoudi, A.; Elmay, A. HLA-A*26-A*30 and HLA-DRB1*10 could be predictors of nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk in high-risk Tunisia families. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 59, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Binh, N.D. Human Leucocyte Antigen (HLA) and Essential Hypertension. Vietnam. Natl. Heart Assoc. 2014, 66, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, X.T.; Hu, Y.H.; Dong, T.; Wang, R.Z. Associations of human leukocyte antigen-DRB1 alleles with nasopharyngeal carcinoma and Its clinical significance in Xinjiang Uyghur autonomous region of China. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 119, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfitri, M. No association between HLA-DQB1 genotypes with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Batak ethnic groups in Indonesia. Biomed. Resenasopharyngeal 2011, 22, 235–240. [Google Scholar]


| LMP1-EBV Gene Amplification Products | Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Amplification product of 200 bp (30 bp deletion mutation) | 51 | 72.9 |
| Amplification product of 230 bp | 19 | 27.1 |
| Total | 70 | 100 |
| LMP1-EBV Gene Mutation Type | Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 30 bp deletion mutation (168,266–168,295) | 25 | 75.8 |
| No 30 bp deletion mutation (168,266–168,295) | 8 | 24.2 |
| Total | 33 | 100 |
| No. | HLA-A Allele | Frequency (n = 52) | Percentage (%) | HLA-B Allele | Frequency (n = 52) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A*02 | 21 | 40.4 | B*15 | 13 | 25.0 |
| 2 | A*11 | 11 | 21.2 | B*46 | 12 | 23.1 |
| 3 | A*24 | 11 | 21.2 | B*38 | 5 | 9.6 |
| 4 | A*33 | 5 | 9.6 | B*07 | 4 | 7.7 |
| 5 | A*01 | 2 | 3.8 | B*18 | 2 | 3.8 |
| 6 | A*14 | 1 | 1.9 | B*35 | 2 | 3.8 |
| 7 | A*30 | 1 | 1.9 | B*44 | 2 | 3.8 |
| 8 | B*56 | 2 | 3.8 | |||
| 9 | B*57 | 2 | 3.8 | |||
| 10 | B*58 | 2 | 3.8 | |||
| 11 | B*13 | 1 | 1.9 | |||
| 12 | B*27 | 1 | 1.9 | |||
| 13 | B*39 | 1 | 1.9 | |||
| 14 | B*40 | 1 | 1.9 | |||
| 15 | B*51 | 1 | 1.9 | |||
| 16 | B*54 | 1 | 1.9 |
| No. | HLA-DRB1 Allele | Fre. (n = 58) | Per. (%) | HLA-DQB1 Allele | Fre. (n = 56) | Per. (%) | HLA-DQA1 Allele | Fre. (n = 56) | Per. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DRB1*12 | 10 | 17.3 | DQB1*03 | 25 | 44.7 | DQA1*01 | 20 | 35.7 |
| 2 | DRB1*09 | 8 | 13.8 | DQB1*05 | 12 | 21.4 | DQA1*03 | 16 | 28.6 |
| 3 | DRB1*04 | 7 | 12.1 | DQB1*06 | 10 | 17.9 | DQA1*06 | 12 | 21.4 |
| 4 | DRB1*08 | 7 | 12.1 | DQB1*02 | 5 | 8.9 | DQA1*02 | 6 | 10.7 |
| 5 | DRB1*15 | 7 | 12.1 | DQB1*04 | 4 | 7.1 | DQA1*04 | 2 | 3.6 |
| 6 | DRB1*14 | 6 | 10.3 | ||||||
| 7 | DRB1*07 | 6 | 10.3 | ||||||
| 8 | DRB1*10 | 3 | 5.2 | ||||||
| 9 | DRB1*03 | 1 | 1.7 | ||||||
| 10 | DRB1*06 | 1 | 1.7 | ||||||
| 11 | DRB1*13 | 1 | 1.7 | ||||||
| 12 | DRB1*16 | 1 | 1.7 |
| HLA | Mutation of 30 bp Deletion of LMP1-EBV Gene | OR | 95% CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutation | Non-Mutation | ||||
| A*02 Non-A*02 | 16 (47.1) 18 (52.9) | 5 (27.8) 13 (72.2) | 0.43 | 0.13–1.48 | 0.178 |
| A*11 Non-A*11 | 5 (14,7) 29 (85,3) | 6 (33,3) 12 (66,7) | 2,90 | 0.74–11.35 | 0.118 |
| A*24 Non-A*24 | 7 (20.6) 27 (79.4) | 4 (22.2) 14 (77.8) | 1.10 | 0.28–4.42 | 0.891 |
| B*15 Non-B*15 | 5 (14.7) 29 (85.3) | 8 (44.4) 10 (55.6) | 4.64 | 1.23–17.52 | 0.018 |
| B*38 Non-B*38 | 4 (11.8) 30 (882) | 1 (5.6) 17 (94.4) | 0.44 | 0.05–4.27 | 0.729 |
| B*46 Non-B*46 | 8 (23.5) 26 (76.5) | 4 (22.2) 14 (77.8) | 0.93 | 0.24–3.64 | 0.915 |
| DRB1*12 Non-DRB1*12 | 7 (17.5) 33 (82.5) | 3 (16.7) 15 (83.3) | 0.94 | 0.21–4.16 | 0.938 |
| DRB1*09 Non-DRB1*09 | 5 (12.5) 35 (87.5) | 3 (16.7) 15 (83.3) | 1.40 | 0.30–6.62 | 0.670 |
| DQB1*03 Non-DQB1*03 | 11 (30.6) 25 (69.4) | 5 (25.0) 15 (75.0) | 0.76 | 0.22–2.61 | 0.659 |
| DQA1*01 Non-DQA1*01 | 13 (36.1) 23 (63.9) | 7 (35.0) 13 (650) | 0.95 | 0.30–2.99 | 0.934 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trinh, C.T.H.; Tran, D.N.; Nguyen, L.T.T.; Tran, N.T.; Nguyen, M.T.G.; Nguyen, V.T.P.; Vu, N.T.H.; Dang, K.D.; Van Vo, K.; Chau, H.C.; et al. LMP1-EBV Gene Deletion Mutations and HLA Genotypes of Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients in Vietnam. Pathophysiology 2023, 30, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology30010001
Trinh CTH, Tran DN, Nguyen LTT, Tran NT, Nguyen MTG, Nguyen VTP, Vu NTH, Dang KD, Van Vo K, Chau HC, et al. LMP1-EBV Gene Deletion Mutations and HLA Genotypes of Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients in Vietnam. Pathophysiology. 2023; 30(1):1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology30010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrinh, Cua Thi Hong, Dung Ngoc Tran, Linh Thi Thao Nguyen, Nghia Tin Tran, Minh Trinh Gia Nguyen, Vy Tran Phuong Nguyen, Nhung Thi Hong Vu, Khanh Duy Dang, Kha Van Vo, Hoa Chieu Chau, and et al. 2023. "LMP1-EBV Gene Deletion Mutations and HLA Genotypes of Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients in Vietnam" Pathophysiology 30, no. 1: 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology30010001
APA StyleTrinh, C. T. H., Tran, D. N., Nguyen, L. T. T., Tran, N. T., Nguyen, M. T. G., Nguyen, V. T. P., Vu, N. T. H., Dang, K. D., Van Vo, K., Chau, H. C., Phan, P. T. P., & Truc Phuong, M. H. (2023). LMP1-EBV Gene Deletion Mutations and HLA Genotypes of Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients in Vietnam. Pathophysiology, 30(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology30010001






