SEPT9 Upregulation in Satellite Glial Cells Associated with Diabetic Polyneuropathy in a Type 2 Diabetes-like Rat Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
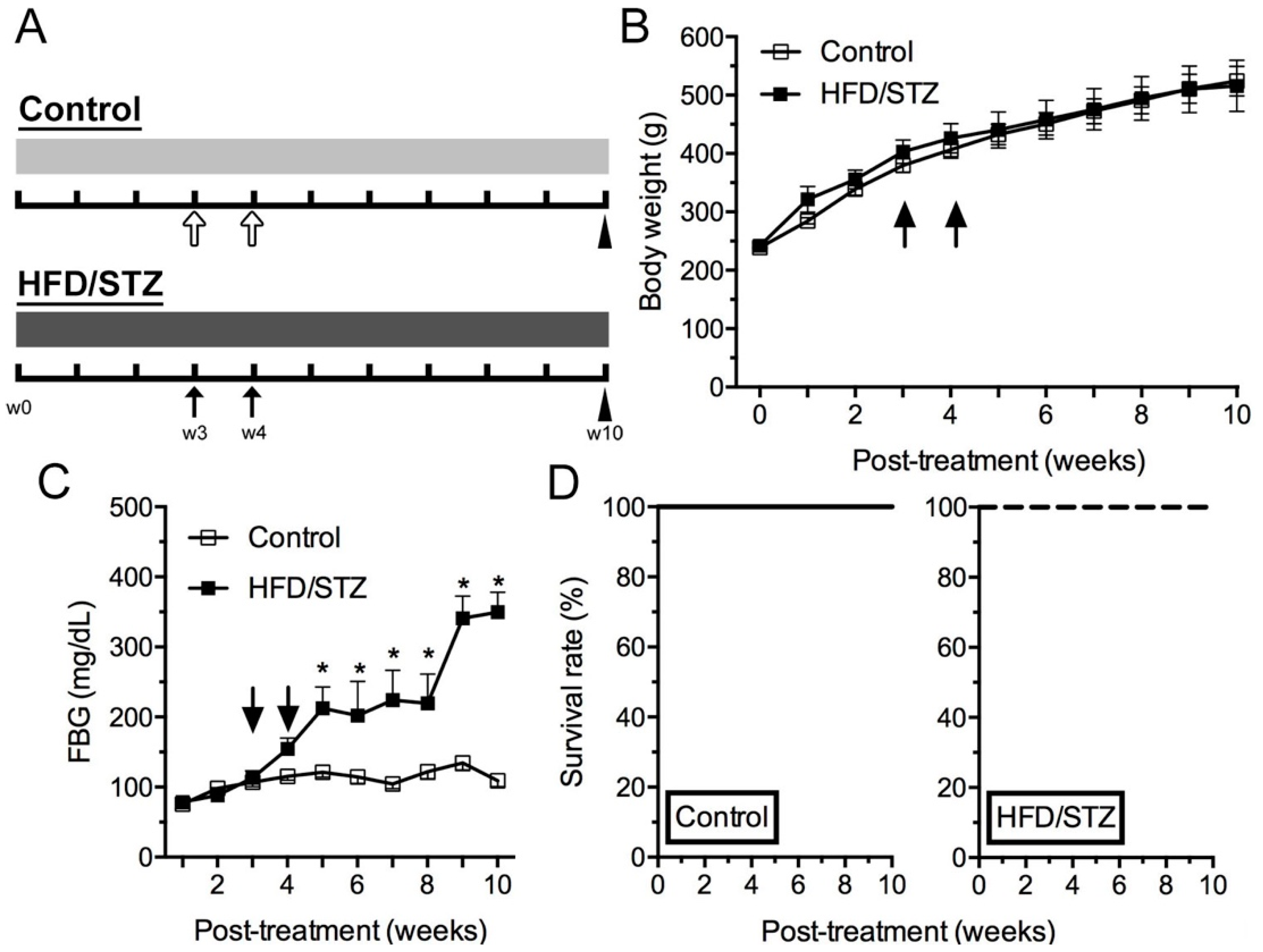
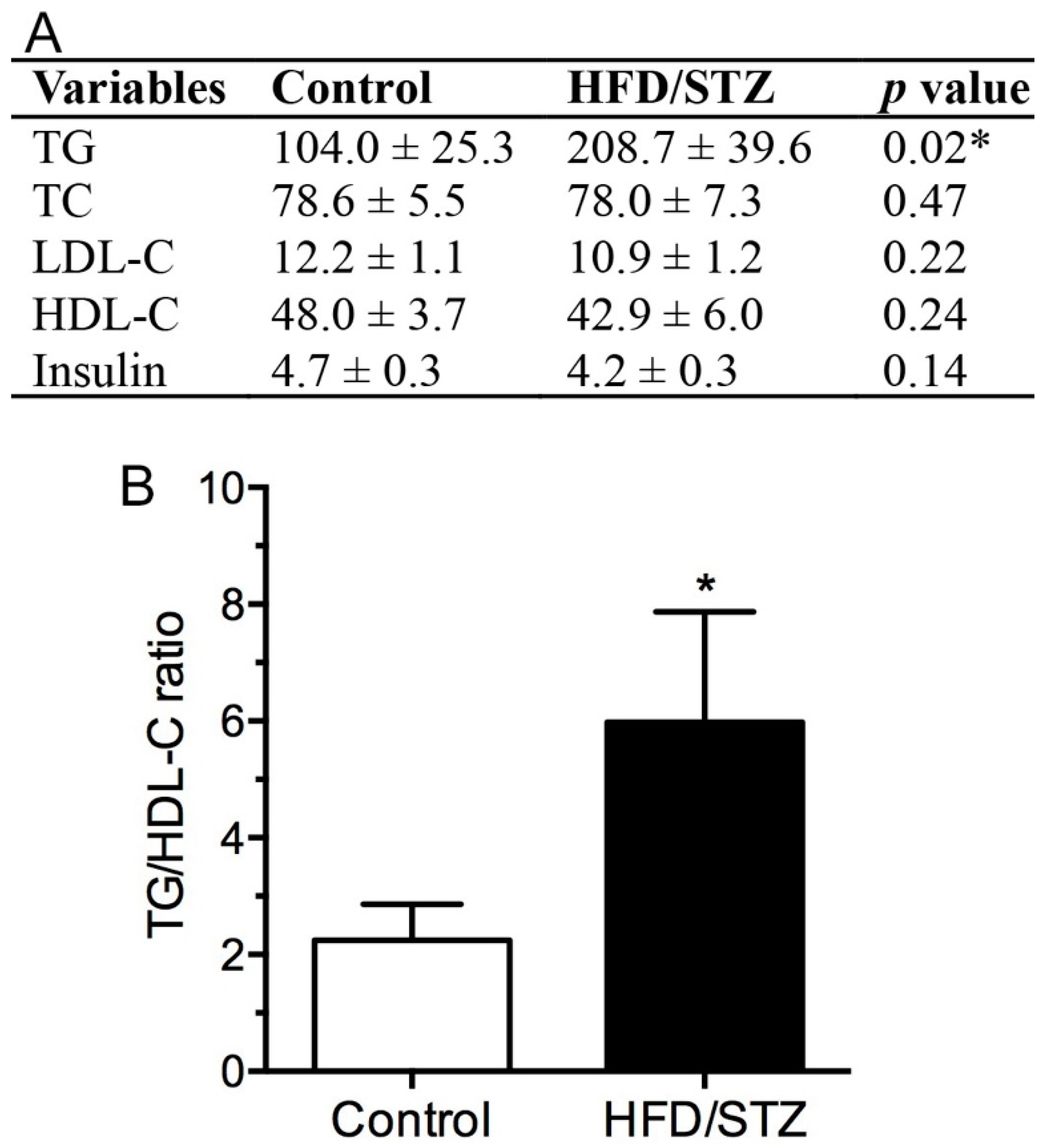
2.1. Physical and Biochemical Assessment in HFD/STZ and Control Group
2.2. Development of Mechanical Hyperalgesia and Reduced Free Navigation Activity in the HFD/STZ Group
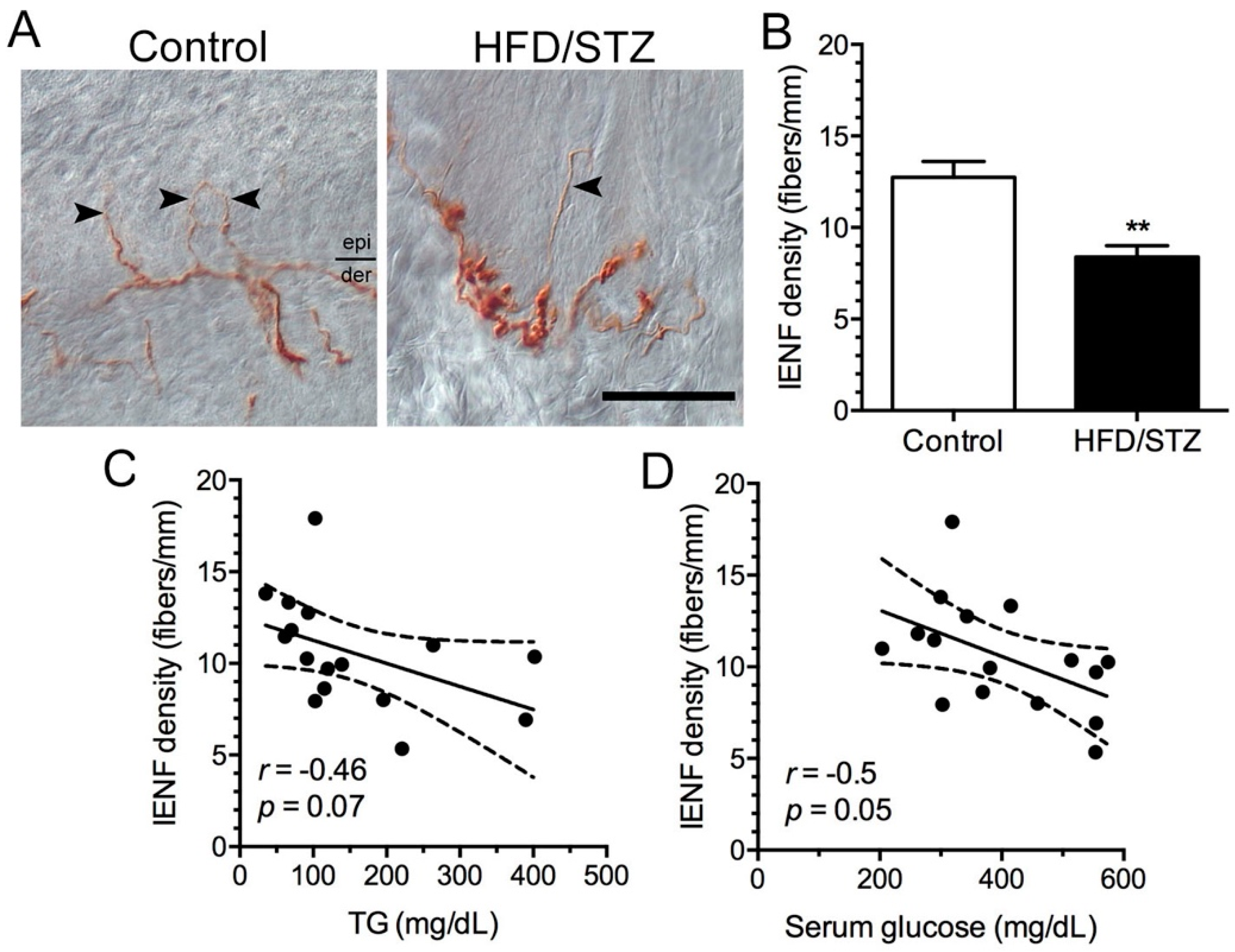
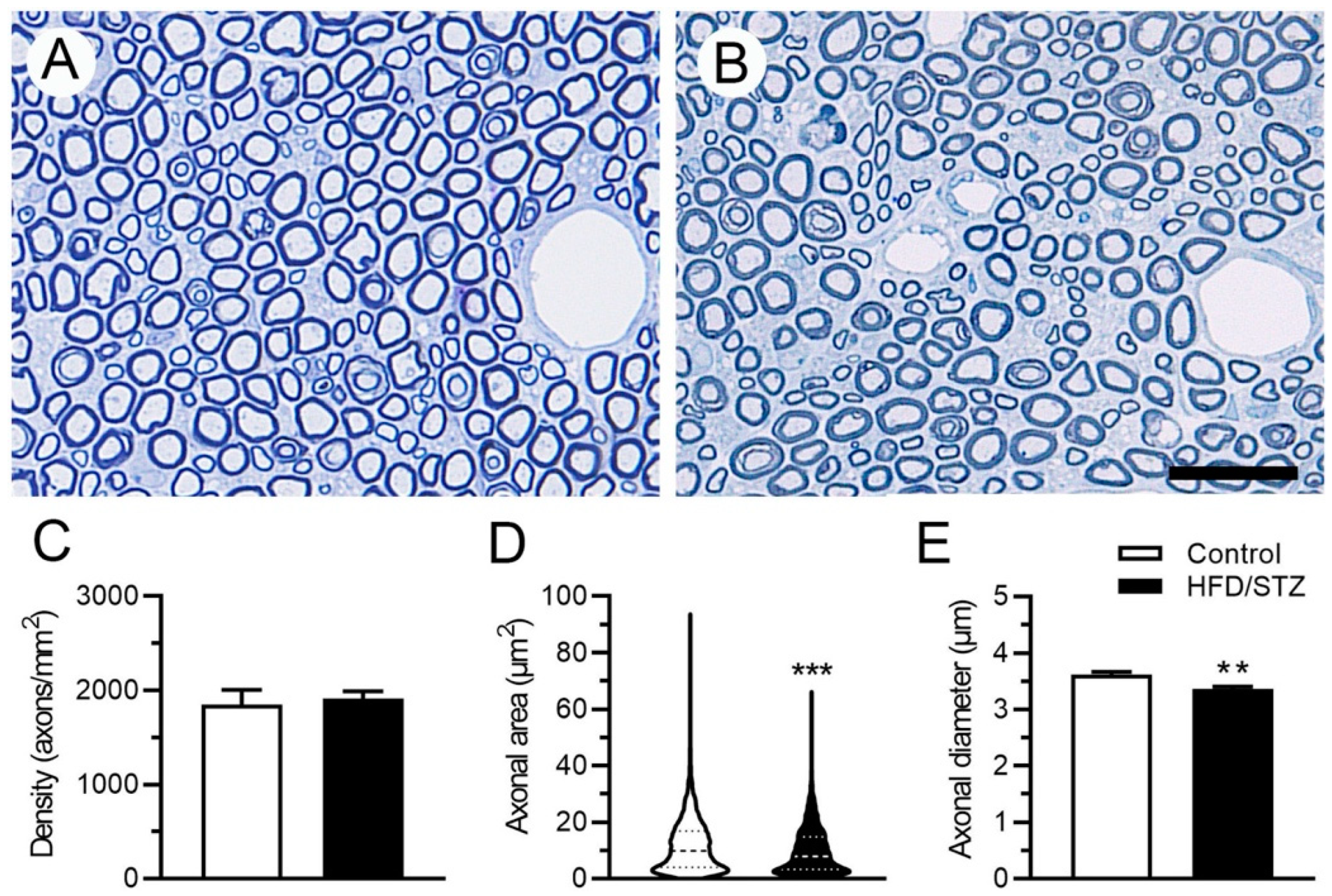
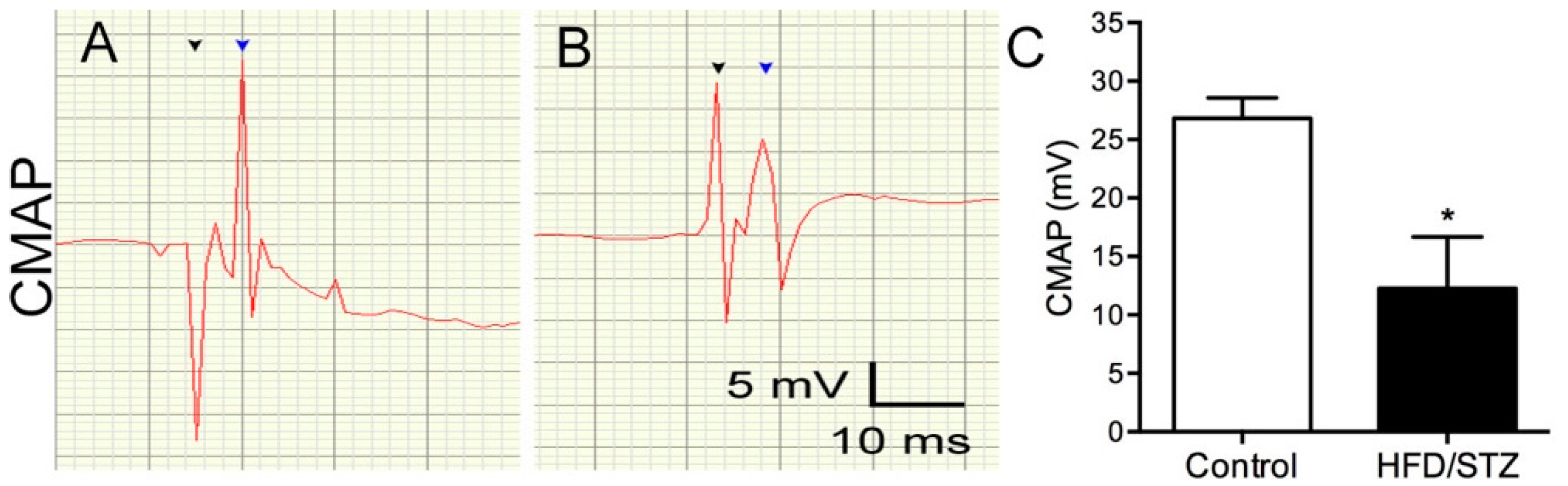
2.3. Neuropathological and Neuroelectrophysiological Characteristics in the HFD/STZ Group
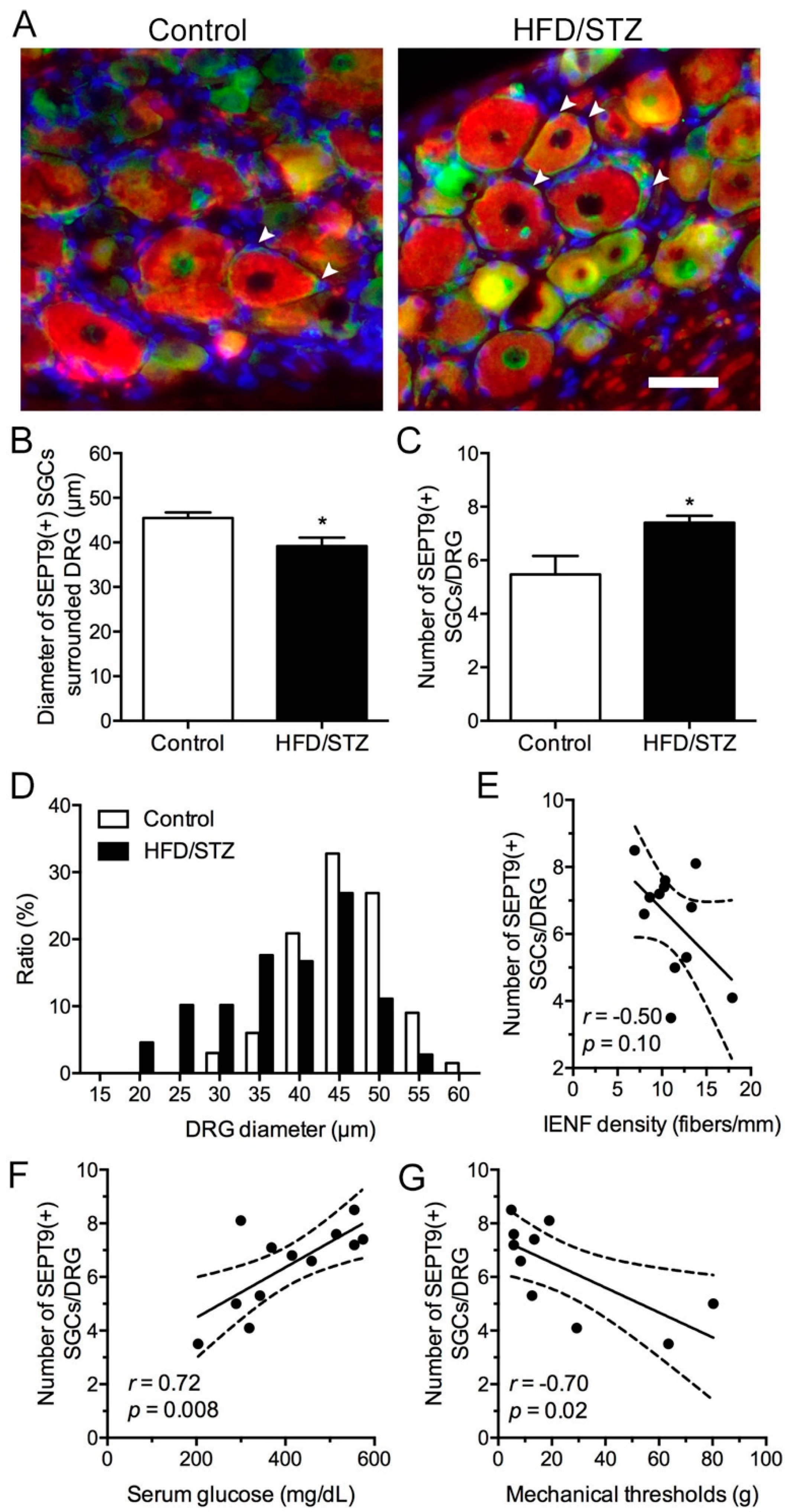
2.4. Increased SEPT9 in SGCs in the HFD/STZ Group
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of T2DM-like Diabetic Rodent Model through HFD and STZ Induction
4.2. Neurobehavioral Assessment
4.3. Serum Analysis
4.4. Nerve Conduction Study
4.5. Immunohistochemical Analysis and IENF Innervation Quantification
4.6. DRG Immunofluorescence Staining
4.7. Sural Nerve Morphometry Quantification
4.8. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hicks, C.W.; Selvin, E. Epidemiology of Peripheral Neuropathy and Lower Extremity Disease in Diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2019, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bril, V. Status of current clinical trials in diabetic polyneuropathy. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 28, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, P.J.; Kratz, K.M.; Karnes, J.L.; Litchy, W.J.; Klein, R.; Pach, J.M.; Wilson, D.M.; O’Brien, P.C.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Service, F.J. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology 1993, 43, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Kan, H.W.; Hsieh, Y.L. Activating transcription factor 3 modulates protein kinase C epsilon activation in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, H.W.; Chang, C.H.; Chang, Y.S.; Ko, Y.T.; Hsieh, Y.L. Genetic loss-of-function of activating transcription factor 3 but not C-type lectin member 5A prevents diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.T.; Medress, Z.A.; Barres, B.A. Axon degeneration: Molecular mechanisms of a self-destruction pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwell, L.H. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. IV. Genes controlling bud emergence and cytokinesis. Exp. Cell Res. 1971, 69, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadares, N.F.; Ulian Araujo, A.P.; Garratt, R.C. Septin structure and filament assembly. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 481–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, I.R.; Wittinghofer, A. The guanine nucleotide-binding switch in three dimensions. Science 2001, 294, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostowy, S.; Cossart, P. Septins: The fourth component of the cytoskeleton. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 13, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuvanov, L.; Mota, D.M.D.; Araujo, A.P.U.; DeMarco, R. A blueprint of septin expression in human tissues. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2019, 19, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, G.M.; Bauer, C.; Kopp, B.; Schrader, C.; Osmanovic, A. Identification of a rare SEPT9 variant in a family with autosomal dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collie, A.M.; Landsverk, M.L.; Ruzzo, E.; Mefford, H.C.; Buysse, K.; Adkins, J.R.; Knutzen, D.M.; Barnett, K.; Brown, R.H., Jr.; Parry, G.J.; et al. Non-recurrent SEPT9 duplications cause hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannibal, M.C.; Ruzzo, E.K.; Miller, L.R.; Betz, B.; Buchan, J.G.; Knutzen, D.M.; Barnett, K.; Landsverk, M.L.; Brice, A.; LeGuern, E.; et al. SEPT9 gene sequencing analysis reveals recurrent mutations in hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy. Neurology 2009, 72, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlenbaumer, G.; Hannibal, M.C.; Nelis, E.; Schirmacher, A.; Verpoorten, N.; Meuleman, J.; Watts, G.D.; De Vriendt, E.; Young, P.; Stogbauer, F.; et al. Mutations in SEPT9 cause hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhusal, A.; Rahman, M.H.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, I.K.; Suk, K. Satellite glia as a critical component of diabetic neuropathy: Role of lipocalin-2 and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-2 axis in the dorsal root ganglion. Glia 2021, 69, 971–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, M.; Blum, E.; Liu, S.; Peng, L.; Liang, S. Satellite glial cells in dorsal root ganglia are activated in streptozotocin-treated rodents. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 2367–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, M. Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: From form to function. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2005, 48, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Dvorakova, M.C. Future Perspective of Diabetic Animal Models. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, K.; Bouhassira, D.; De Bacquer, D.; Weiss, S.; Matthys, K.; Raemen, H.; Mathieu, C.; Colin, I.M. Prevalence and impact on quality of life of peripheral neuropathy with or without neuropathic pain in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients attending hospital outpatients clinics. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.J.; Meszaros, K.; Entes, L.J.; Claypool, M.D.; Pinkett, J.G.; Gadbois, T.M.; Reaven, G.M. A new rat model of type 2 diabetes: The fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rat. Metabolism 2000, 49, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Ashhar, M.U.; Aeri, V.; Katare, D.P. Development and characterization of late-stage diabetes mellitus and -associated vascular complications. Life Sci. 2019, 216, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skovso, S. Modeling type 2 diabetes in rats using high fat diet and streptozotocin. J. Diabetes Investig. 2014, 5, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Lv, X.Y.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.G.; Chen, L. The characterization of high-fat diet and multiple low-dose streptozotocin induced type 2 diabetes rat model. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2008, 2008, 704045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaye, S.; Chaturvedi, N.; Eaton, S.E.; Ward, J.D.; Manes, C.; Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Witte, D.R.; Fuller, J.H.; Group, E.P.C.S. Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensink, R.P.; Zock, P.L.; Kester, A.D.; Katan, M.B. Effects of dietary fatty acids and carbohydrates on the ratio of serum total to HDL cholesterol and on serum lipids and apolipoproteins: A meta-analysis of 60 controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessels, G.J.; Bril, V.; Calcutt, N.A.; Cameron, N.E.; Cotter, M.A.; Dobrowsky, R.; Feldman, E.L.; Fernyhough, P.; Jakobsen, J.; Malik, R.A.; et al. Phenotyping animal models of diabetic neuropathy: A consensus statement of the diabetic neuropathy study group of the EASD (Neurodiab). J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2014, 19, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, M.; Brandenburg, N.A.; Dukes, E.; Hoffman, D.L.; Tai, K.S.; Stacey, B. Pain severity in diabetic peripheral neuropathy is associated with patient functioning, symptom levels of anxiety and depression, and sleep. J. Pain Symptom. Manag. 2005, 30, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zheng, Z.M. Animal models of diabetic neuropathic pain. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2014, 122, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Jin, Y.X.; Shen, W.; Neng, J.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.J.; Fu, Z.W. Low dose streptozotocin (STZ) combined with high energy intake can effectively induce type 2 diabetes through altering the related gene expression. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16 (Suppl. 1), 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, R.A.; Fall, T.; Pasko, D.; Barker, A.; Sharp, S.J.; Arriola, L.; Balkau, B.; Barricarte, A.; Barroso, I.; Boeing, H.; et al. Common genetic variants highlight the role of insulin resistance and body fat distribution in type 2 diabetes, independent of obesity. Diabetes 2014, 63, 4378–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Ye, C.; Li, G.; Ding, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, H.; Chen, G.; Luo, T.; Guang, M.; Liu, Y.; et al. The rat model of type 2 diabetic mellitus and its glycometabolism characters. Exp. Anim. 2003, 52, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Feldman, E.; Liu, J.; Kerber, K.; Pop-Busui, R.; Moffet, H.; Karter, A.J. Triglycerides and amputation risk in patients with diabetes: Ten-year follow-up in the DISTANCE study. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggin, T.D.; Sullivan, K.A.; Pop-Busui, R.; Amato, A.; Sima, A.A.; Feldman, E.L. Elevated triglycerides correlate with progression of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1634–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.G.; Singleton, J.R. Obesity and hyperlipidemia are risk factors for early diabetic neuropathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2013, 27, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraham, O.; Deng, P.Y.; Jones, S.; Kuruvilla, R.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Klyachko, V.A.; Cavalli, V. Satellite glial cells promote regenerative growth in sensory neurons. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, L.H.; Gong, K.; Adedoyin, M.; Ng, J.; Bhargava, A.; Ohara, P.T.; Jasmin, L. Evidence for glutamate as a neuroglial transmitter within sensory ganglia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Karasmanis, E.P.; Spiliotis, E.T. Septin 9 interacts with kinesin KIF17 and interferes with the mechanism of NMDA receptor cargo binding and transport. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.F.; Lotufo, C.M.; Araldi, D.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Macedo, L.P.; Ferreira, S.H.; Parada, C.A. Inflammatory sensitization of nociceptors depends on activation of NMDA receptors in DRG satellite cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18363–18368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.T.; Hur, S.S.; Chang, J.; Wang, K.C.; Chiu, J.J.; Li, Y.S.; Chien, S. Matrix stiffness regulates endothelial cell proliferation through septin 9. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, C.R.; Twigg, S.M. Fibrosis in diabetes complications: Pathogenic mechanisms and circulating and urinary markers. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 575–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.W.; Chiang, H.; Lin, W.M.; Yu, I.S.; Lin, S.W.; Hsieh, S.T. Sensory nerve degeneration in a mouse model mimicking early manifestations of familial amyloid polyneuropathy due to transthyretin Ala97Ser. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 44, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kan, H.-W.; Ho, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-S.; Hsieh, Y.-L. SEPT9 Upregulation in Satellite Glial Cells Associated with Diabetic Polyneuropathy in a Type 2 Diabetes-like Rat Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169372
Kan H-W, Ho Y-C, Chang Y-S, Hsieh Y-L. SEPT9 Upregulation in Satellite Glial Cells Associated with Diabetic Polyneuropathy in a Type 2 Diabetes-like Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):9372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169372
Chicago/Turabian StyleKan, Hung-Wei, Yu-Cheng Ho, Ying-Shuang Chang, and Yu-Lin Hsieh. 2022. "SEPT9 Upregulation in Satellite Glial Cells Associated with Diabetic Polyneuropathy in a Type 2 Diabetes-like Rat Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 9372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169372
APA StyleKan, H.-W., Ho, Y.-C., Chang, Y.-S., & Hsieh, Y.-L. (2022). SEPT9 Upregulation in Satellite Glial Cells Associated with Diabetic Polyneuropathy in a Type 2 Diabetes-like Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 9372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169372





