Axillary Management in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Upfront Surgery: Results from a Nationwide Survey on Behalf of the Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Group (COBCG) and the Breast Cancer Study Group of the Italian Association of Radiotherapy and Clinical Oncology (AIRO)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. General Items: Demographics and Expertise in BC Treatment
3.2. Surgical Management in Patients with Early Breast Cancer and 1–2 Macrometastases after BLS
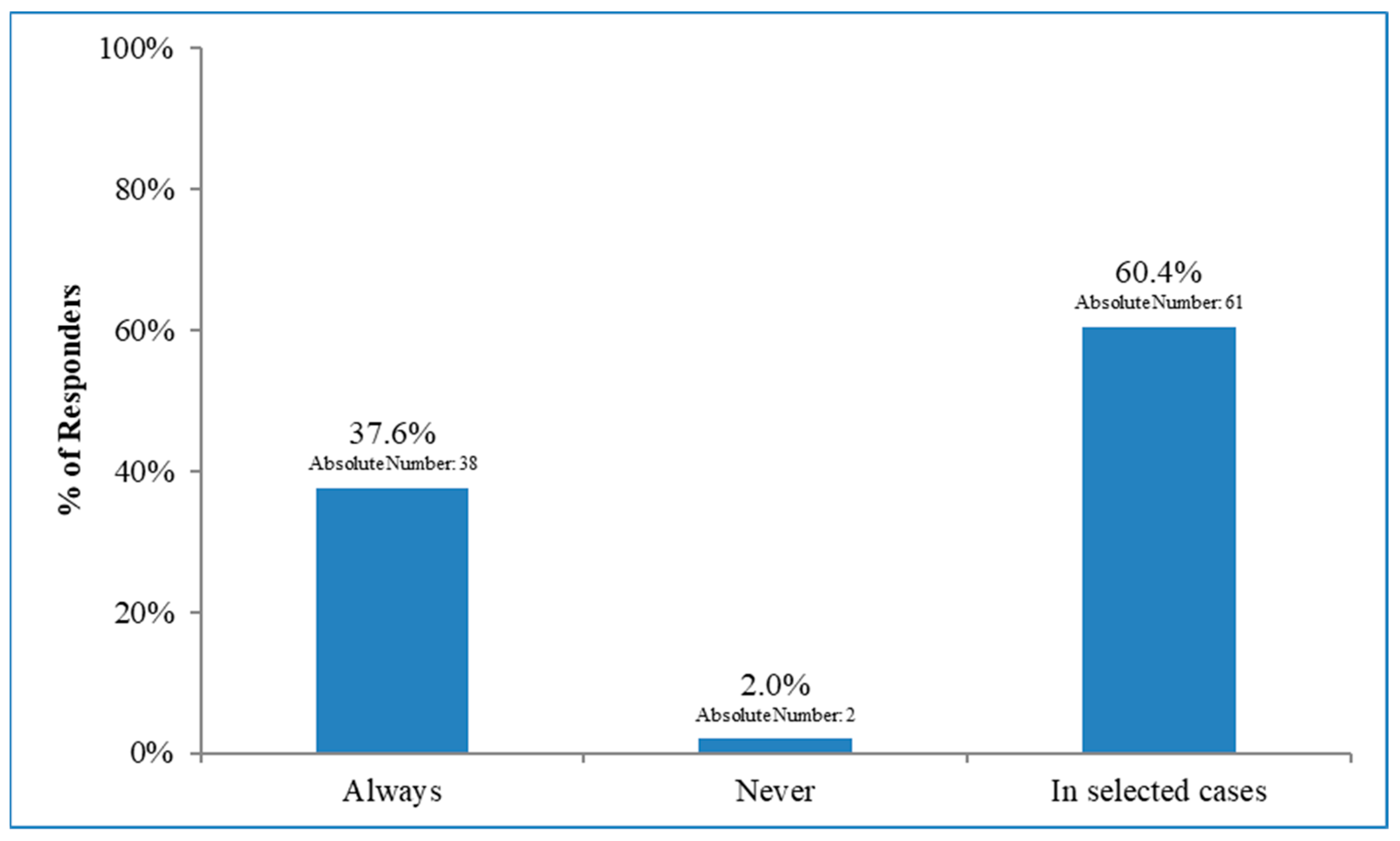
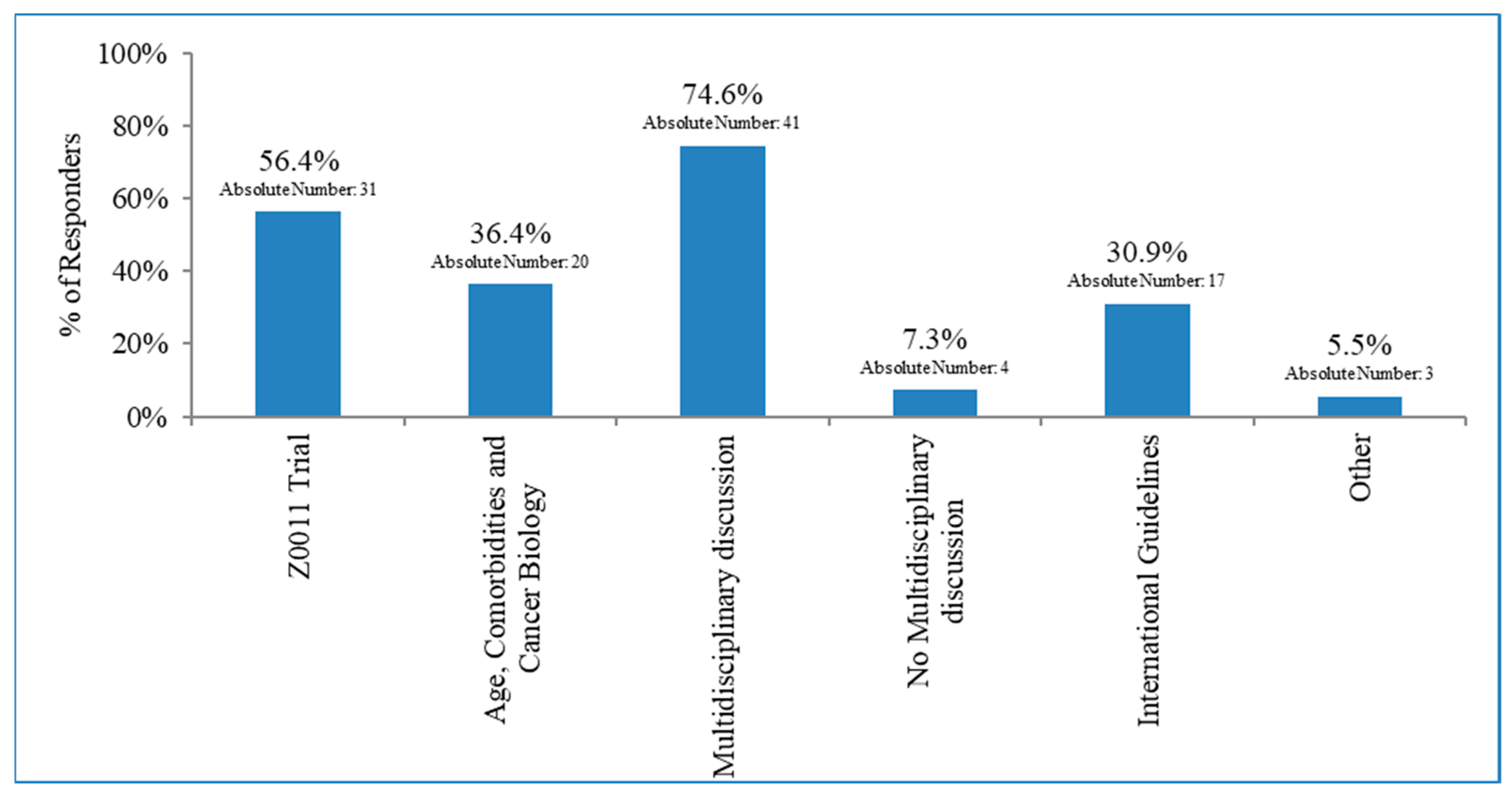
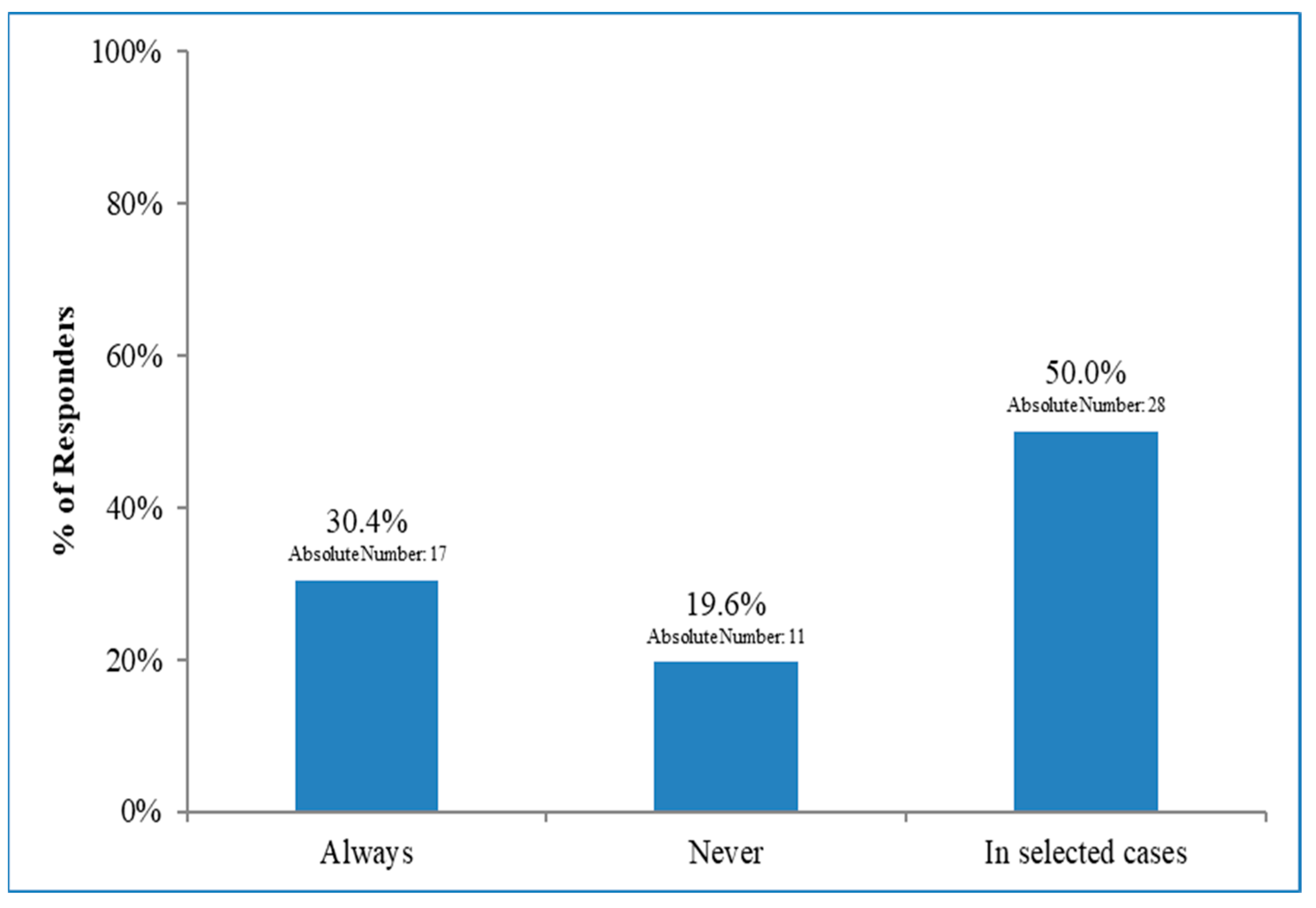
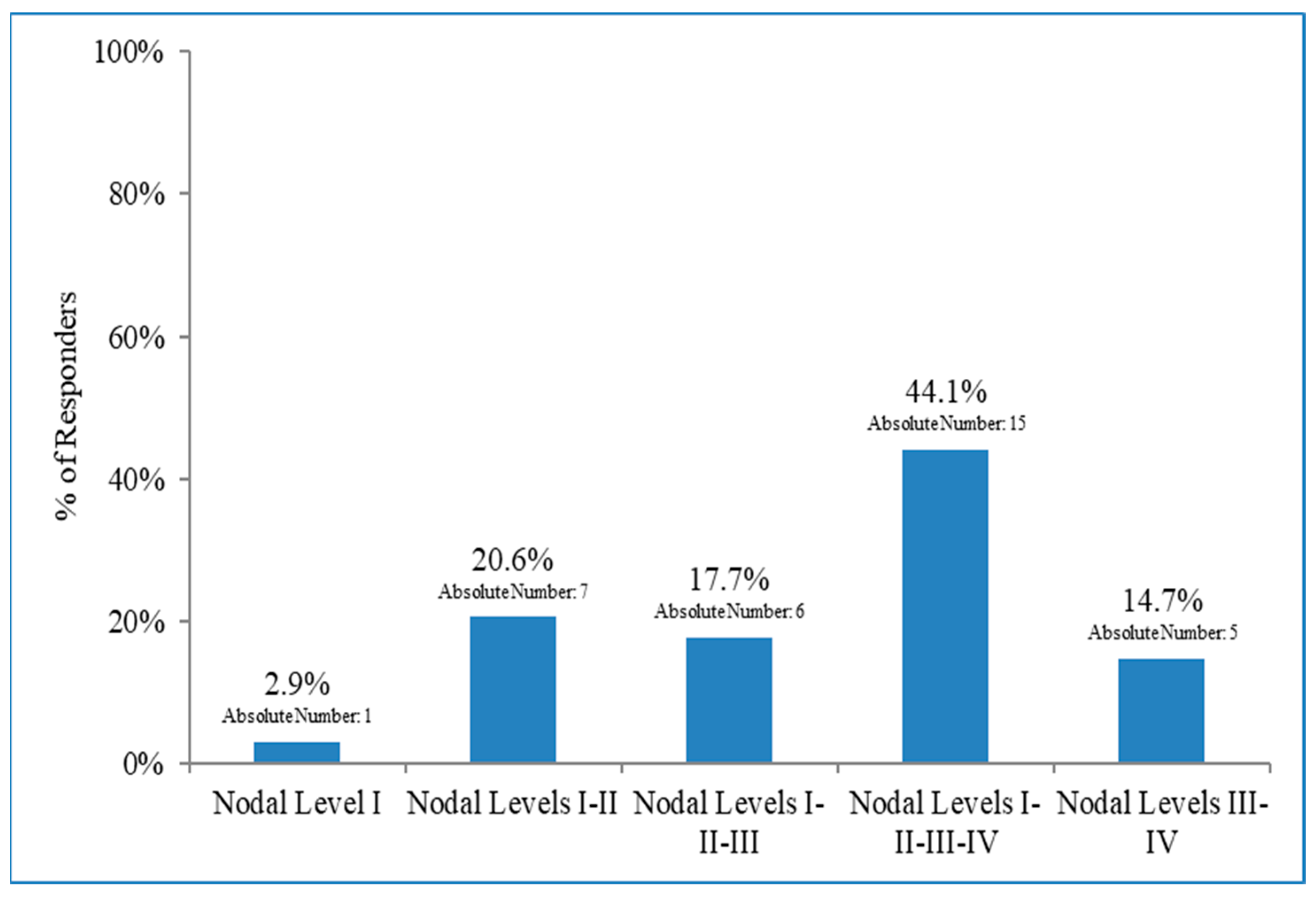
3.3. Lymph Node Irradiation in Patients with Early Breast Cancer and 1–2 Macrometastases after BLS Who Did Not Undergo Axillary Dissection
3.4. Dosimetric Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, B.; Anderson, S.; Bryant, J.; Margolese, R.G.; Deutsch, M.; Fisher, E.R.; Jeong, J.H.; Wolmark, N. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 34, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleissig, A.; Fallowfield, L.J.; Langridge, C.I.; Johnson, L.; Newcombe, R.G.; Dixon, J.M.; Kissin, M.; Mansel, R.E. Post-operative arm morbidity and quality of life. Results of the ALMANAC randomised trial comparing sentinel node biopsy with standard axillary treatment in the management of patients with early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006, 9, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krag, D.N.; Anderson, S.J.; Julian, T.B.; Brown, A.M.; Harlow, S.P.; Costantino, J.P.; Ashikaga, T.; Weaver, D.L.; Mamounas, E.P.; Jalovec, L.M.; et al. Sentinel-lymph node resection compared with conventional axillary lymph-node dissection in clinically node-negative patients with breast cancer: Overall survival findings from the NSABP-B32 randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnim, A.C.; Griffith, K.A.; Sabel, M.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Cimmino, V.M.; Diehl, K.M.; Lucas, P.C.; Snyder, M.L.; Chang, A.E.; Newman, L.A. Clinicopathologic features of metastasis in nonsentinel lymph nodes of breast carcinoma patients. Cancer 2003, 98, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldas, C.; Aparicio, S.A. The molecular outlook. Nature 2002, 415, 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, A.E.; Ballman, K.V.; McCall, L.; Beitsch, P.D.; Brennan, M.B.; Kelemen, P.R.; Ollila, D.W.; Hansen, N.M.; Whitworth, P.W.; Blumencranz, P.W.; et al. Effect of Axillary Dissection vs No Axillary Dissection on 10-Year Overall Survival Among Women With Invasive Breast Cancer and Sentinel Node Metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donker, M.; van Tienhoven, G.; Straver, M.E.; Meijnen, P.; van de Velde, C.J.; Mansel, R.E.; Cataliotti, L.; Westenberg, A.H.; Klinkenbijl, J.H.; Orzalesi, L.; et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, S.A.L.; Donker, M.; Poncet, C.; Sauvé, N.; Straver, M.E.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Mansel, R.E.; Blanken, C.; Orzalesi, L.; Klinkenbijl, J.H.G.; et al. Radiotherapy or Surgery of the Axilla After a Positive Sentinel Node in Breast Cancer: 10-Year Results of the Randomized Controlled EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sávolt, Á.; Péley, G.; Polgár, C.; Udvarhelyi, N.; Rubovszky, G.; Kovács, E.; Győrffy, B.; Kásler, M.; Mátrai, Z. Eight-year follow up result of the OTOASOR trial: The Optimal Treatment Of the Axilla—Surgery Or Radiotherapy after positive sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer: A randomized, single centre, phase III, non-inferiority trial. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Etienne, C.A.; Ferrari, A.; Della Valle, A.; Lucioni, M.; Ferraris, E.; Di Giulio, G.; Squillace, L.; Bonzano, E.; Lasagna, A.; Rizzo, G.; et al. Management of the axilla in patients with breast cancer and positive sentinel lymph node biopsy: An evidence-based update in a European breast center. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, G.H.; Somerfield, M.R.; Bosserman, L.D.; Perkins, C.L.; Weaver, D.L.; Giuliano, A.E. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with early-stage breast cancer: American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Breast Cancer. 2022. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/category_1 (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Tinterri, C.; Gentile, D.; Gatzemeier, W.; Sagona, A.; Barbieri, E.; Testori, A.; Errico, V.; Bottini, A.; Marrazzo, E.; Dani, C.; et al. SINODAR-ONE Collaborative Group. Preservation of Axillary Lymph Nodes Compared with Complete Dissection in T1-2 Breast Cancer Patients Presenting One or Two Metastatic Sentinel Lymph Nodes: The SINODAR-ONE Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5732–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Mann, G.B.; Fallowfield, L.; Duley, L.; Reed, M.; Dodwell, D.; Coleman, R.E.; Fakis, A.; Newcombe, R.; Jenkins, V.; et al. POSNOC Trialists. POSNOC-POsitive Sentinel NOde: Adjuvant therapy alone versus adjuvant therapy plus Clearance or axillary radiotherapy: A randomised controlled trial of axillary treatment in women with early-stage breast cancer who have metastases in one or two sentinel nodes. BMJ Open 2021, 11, 11:1–11:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelgren, M.; Sackey, H.; Wengström, Y.; Johansson, K.; Ahlgren, J.; Andersson, Y.; Bergkvist, L.; Frisell, J.; Lundstedt, D.; Rydén, L.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes one year after positive sentinel lymph node biopsy with or without axillary lymph node dissection in the randomized SENOMAC trial. Breast 2022, 63, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roozendaal, L.M.; de Wilt, J.H.; van Dalen, T.; van der Hage, J.A.; Strobbe, L.J.; Boersma, L.J.; Linn, S.C.; Lobbes, M.B.; Poortmans, P.M.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.; et al. The value of completion axillary treatment in sentinel node positive breast cancer patients undergoing a mastectomy: A Dutch randomized controlled multicentre trial (BOOG 2013-07). BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciabattoni, A.; Gregucci, F.; De Rose, F.; Falivene, S.; Fozza, A.; Daidone, A.; Morra, A.; Smaniotto, D.; Barbara, R.; Lozza, L.; et al. AIRO Breast Cancer Group Best Clinical Practice 2022 Update. Tumori 2022, 108 (Suppl. S2), 1–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fozza, A.; Giaj-Levra, N.; De Rose, F.; Ippolito, E.; Silipigni, S.; Meduri, B.; Fiorentino, A.; Gregucci, F.; Marino, L.; Di Grazia, A.; et al. Lymph nodal radiotherapy in breast cancer: What are the unresolved issues? Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2021, 21, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenbach, G. Improving the quality of Web surveys: The Checklist for Reporting Results of Internet E-Surveys (CHERRIES). J. Med. Internet Res. 2004, 6, 6:1–6:6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recht, A.; Edge, S.B.; Solin, L.J.; Robinson, D.S.; Estabrook, A.; Fine, R.E.; Fleming, G.F.; Formenti, S.; Hudis, C.; Kirshner, J.J.; et al. Postmastectomy radiotherapy: Clinical practice guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1539–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBCTCG (Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group); McGale, P.; Taylor, C.; Correa, C.; Cutter, D.; Duane, F.; Ewertz, M.; Gray, R.; Mannu, G.; Peto, R.; et al. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 383, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, T.J.; Olivotto, I.A.; Parulekar, W.R.; Ackerman, I.; Chua, B.H.; Nabid, A.; Vallis, K.A.; White, J.R.; Rousseau, P.; Fortin, A.; et al. MA.20 Study Investigators. Regional Nodal Irradiation in Early-Stage Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poortmans, P.M.; Weltens, C.; Fortpied, C.; Kirkove, C.; Peignaux-Casasnovas, K.; Budach, V.; van der Leij, F.; Vonk, E.; Weidner, N.; Rivera, S.; et al. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Radiation Oncology and Breast Cancer Groups. Internal mammary and medial supraclavicular lymph node chain irradiation in stage I-III breast cancer (EORTC 22922/10925): 15-year results of a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borm, K.J.; Oechsner, M.; Düsberg, M.; Buschner, G.; Weber, W.; Combs, S.E.; Duma, M.N. Irradiation of regional lymph node areas in breast cancer—Dose evaluation according to the Z0011, AMAROS, EORTC 10981-22023 and MA-20 field design. Radiother Oncol. 2020, 142, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, S.R.D.; Harbeck, N.; Hegg, R.; Toi, M.; Martin, M.; Shao, Z.M.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Martinez Rodriguez, J.L.; Campone, M.; Hamilton, E.; et al. MonarchE Committee Members and Investigators. Abemaciclib Combined With Endocrine Therapy for the Adjuvant Treatment of HR+, HER2-, Node-Positive, High-Risk, Early Breast Cancer (monarchE). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3987–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkus, E.; Cardoso, M.J.; Kaidar-Person, O.; Łacko, A.; Meattini, I.; Poortmans, P. De-escalation of axillary irradiation for early breast cancer—Has the time come? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 101, 101:1–101:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meattini, I.; De Santis, M.C.; De Rose, F.; Desideri, I.; Franco, P.; Kaidar-Person, O.; Meduri, B.; Pasinetti, N.; Lancellotta, V.; Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Group (COBCG) Investigators. Local Treatment of the Axilla in Early Breast Cancer: So Many Questions, Still Few Answers. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.) 2020, 32, e37–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Years of Experience | <5 | 15.8% (16) * | 5 ≤ x < 10 | 12.9% (13) | ≥10 | 71.3% (72) | ||
| Geographical Distribution | North | 47.5% (48) | Centre | 19.8% (20) | South | 32.7% (33) | ||
| Institution of Work | Academic Hospital | 42.5% (36) | Non-Academic Hospital | 61.5% (62) | Public Hospital | 83.3% (84) | Private Hospital | 16.7% (17) |
| Irradiation Technique | Brachy/IORT | 48.0% (49) | 3DCRT | 94.1% (96) | IMRT/VMAT | 88.2% (90) | Cyber/Tomo/ Protons | 28.4% (29) |
| Pts/y Treated (within each Institution) | <100 | 8.0% (8) | 100 ≤ x < 200 | 24.0% (24) | 200 ≤ x < 500 | 53% (53) | ≥500 | 15.0% (15) |
| Pts/y Treated (by each Respondent) | 10 < x < 50 | 16.0% (16) | 50 ≤ x < 100 | 36.0% (36) | ≥100 | 48% (48) | ||
| Pts Discussed (with the MD Group) | <25% | 2.0% (2) | 25% ≤ x < 50% | 1.0% (1) | 50% ≤ x < 75% | 12.9% (13) | ≥75% | 84.1% (85) |
| OARS | Dose Constraints | Concordance between Respondents |
|---|---|---|
| Ipsilateral Lung | V20Gy < 15% | 15% (4) * |
| V20Gy < 20% | 19% (5) | |
| V8Gy < 30–35% | 15% (4) | |
| V4Gy < 40–50% | 19% (5) | |
| Controlateral Breast | Dmean < 3 Gy | 40% (11) |
| Heart | Dmean < 5 Gy | 38% (10) |
| Dmean < 4 Gy | 26% (7) | |
| LAD | Dmean < 20–25 Gy | 55% (15) |
| Dmean < 10 Gy | 33% (9) | |
| V40Gy < 1% | 27% (8) | |
| V30Gy < 2% | 22% (6) | |
| Humeral Head | Dmean < 40 Gy | 27% (8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Rose, F.; Colciago, R.R.; Lucidi, S.; La Rocca, E.; Prisco, A.; Bonzano, E.; Meduri, B.; De Santis, M.C.; Dicuonzo, S.; Pasinetti, N.; et al. Axillary Management in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Upfront Surgery: Results from a Nationwide Survey on Behalf of the Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Group (COBCG) and the Breast Cancer Study Group of the Italian Association of Radiotherapy and Clinical Oncology (AIRO). Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 7489-7498. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080542
De Rose F, Colciago RR, Lucidi S, La Rocca E, Prisco A, Bonzano E, Meduri B, De Santis MC, Dicuonzo S, Pasinetti N, et al. Axillary Management in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Upfront Surgery: Results from a Nationwide Survey on Behalf of the Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Group (COBCG) and the Breast Cancer Study Group of the Italian Association of Radiotherapy and Clinical Oncology (AIRO). Current Oncology. 2023; 30(8):7489-7498. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080542
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Rose, Fiorenza, Riccardo Ray Colciago, Sara Lucidi, Eliana La Rocca, Agnese Prisco, Elisabetta Bonzano, Bruno Meduri, Maria Carmen De Santis, Samantha Dicuonzo, Nadia Pasinetti, and et al. 2023. "Axillary Management in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Upfront Surgery: Results from a Nationwide Survey on Behalf of the Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Group (COBCG) and the Breast Cancer Study Group of the Italian Association of Radiotherapy and Clinical Oncology (AIRO)" Current Oncology 30, no. 8: 7489-7498. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080542
APA StyleDe Rose, F., Colciago, R. R., Lucidi, S., La Rocca, E., Prisco, A., Bonzano, E., Meduri, B., De Santis, M. C., Dicuonzo, S., Pasinetti, N., Palumbo, I., Meattini, I., & Franco, P. (2023). Axillary Management in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Upfront Surgery: Results from a Nationwide Survey on Behalf of the Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Group (COBCG) and the Breast Cancer Study Group of the Italian Association of Radiotherapy and Clinical Oncology (AIRO). Current Oncology, 30(8), 7489-7498. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080542






