Percutaneous Ablation of Hepatic Tumors at the Hepatocaval Confluence Using Irreversible Electroporation: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. IRE Procedure
2.3. Assessment of Treatment Response and Patient Follow-Up
2.4. Outcome Measures and Statistical Analysis
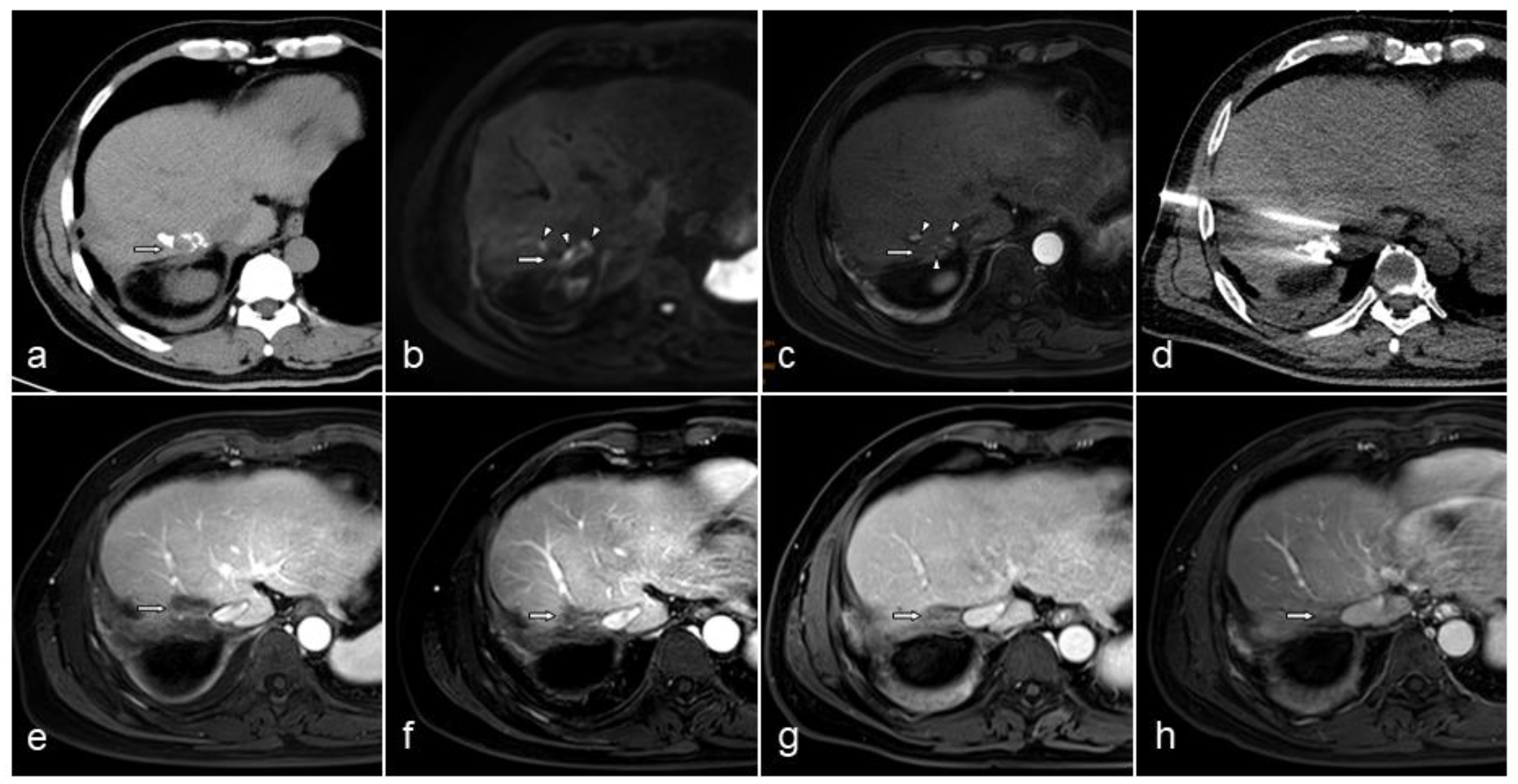
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dou, L.; Yu, Z.P.; Yang, H.Y.; Ran, J.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, X.P. Personalized stepwise vascular control during complex hepatectomy involving hepatocaval confluence. ANZ J. Surg. 2018, 88, E606–E609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.S.; Yu, N.C.; Raman, S.S.; Limanond, P.; Lassman, C.; Murray, K.; Tong, M.J.; Amado, R.G.; Busuttil, R.W. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: Treatment success as defined by histologic examination of the explanted liver. Radiology 2005, 234, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.S.; Raman, S.S.; Vodopich, D.J.; Wang, M.; Sayre, J.; Lassman, C. Effect of vessel size on creation of hepatic radiofrequency lesions in pigs: Assessment of the “heat sink” effect. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 178, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Shiina, S.; Tateishi, R.; Arano, T.; Uchino, K.; Enooku, K.; Goto, E.; Nakagawa, H.; Masuzaki, R.; Asaoka, Y.; et al. Intrahepatic bile duct dilatation after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Impact on patient’s prognosis. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccomandi, P.; Lapergola, A.; Longo, F.; Schena, E.; Quero, G. Thermal ablation of pancreatic cancer: A systematic literature review of clinical practice and pre-clinical studies. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 35, 398–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aujla, A.K.; Averbukh, L.D.; Gill, G.; Swales, C. Hepatic Artery Thrombosis: A Rare Complication of Microwave Ablation in Hepatocelluar Carcinoma. Cureus 2020, 12, e6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Rhim, H.; Park, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, D.; Lim, H.K. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas adjacent to the gallbladder with internally cooled electrodes: Assessment of safety and therapeutic efficacy. Korean J. Radiol. 2009, 10, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hsieh, M.F.; Chen, C.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Chou, C.T. Hemobilia after CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: Frequency, risk factors, and clinical significance. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lyu, C.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chang, T.T.; Rubinsky, B. Molecular and histological study on the effects of non-thermal irreversible electroporation on the liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, L.J.; Chapiro, J.; Hamm, B.; Gebauer, B.; Collettini, F. Irreversible Electroporation in Interventional Oncology: Where We Stand and Where We Go. Fortschr. Geb. Rontgenstrahlen Nukl. 2016, 188, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Velázquez, P.; Clavien, P.A. The role of the irreversible electroporation in the hepato-pancreatico-biliary surgery. Cir. Esp. 2017, 95, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Feng, Z.; Chen, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, C. A fundamental theoretical study on the different effect of electroporation on tumor blood vessels and normal blood vessels. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 144, 108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringel-Scaia, V.M.; Beitel-White, N.; Lorenzo, M.F.; Brock, R.M.; Huie, K.E.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.; Eden, K.; McDaniel, D.K.; Verbridge, S.S.; Rossmeisl, J.H., Jr.; et al. High-frequency irreversible electroporation is an effective tumor ablation strategy that induces immunologic cell death and promotes systemic anti-tumor immunity. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.J.; Xu, K.; Wang, P.F.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.L. Histological analysis of human pancreatic carcinoma following irreversible electroporation in a nude mouse model. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2018, 10, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distelmaier, M.; Barabasch, A.; Heil, P.; Kraemer, N.A.; Isfort, P.; Keil, S.; Kuhl, C.K.; Bruners, P. Midterm Safety and Efficacy of Irreversible Electroporation of Malignant Liver Tumors Located Close to Major Portal or Hepatic Veins. Radiology 2017, 285, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, Y.; Sun, T.; Cao, Y.; Yan, L.; Zhang, W.; Ouyang, T.; Zheng, C. The efficacy of radiofrequency ablation versus cryoablation in the treatment of single hepatocellular carcinoma: A population-based study. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 3715–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.A.; van Veldhuisen, E.; Agnass, P.; Crezee, J.; Dijk, F.; Verheij, J.; van Gulik, T.M.; Meijerink, M.R.; Vroomen, L.G.; van Lienden, K.P.; et al. Time-Dependent Impact of Irreversible Electroporation on Pancreas, Liver, Blood Vessels and Nerves: A Systematic Review of Experimental Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.G.; Bhattacharya, R.; Yeh, M.M.; Padia, S.A. Irreversible Electroporation Can Effectively Ablate Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Complete Pathologic Necrosis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.H.; Martin, R.C.G., 2nd. Cardiac synchronization and arrhythmia during irreversible electroporation. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 122, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Froud, T.; Lo, K.; Barbery, K.J.; Perez-Rojas, E.; Yrizarry, J. Pain analysis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Irreversible electroporation versus radiofrequency ablation-initial observations. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiani, N.; Philips, P.; Scoggins, C.R.; McMasters, K.M.; Potts, M.H.; Martin, R.C. Evaluation of tolerability and efficacy of irreversible electroporation (IRE) in treatment of Child-Pugh B (7/8) hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Off. J. Int. Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc. 2016, 18, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillström, D.; Beermann, M.; Engstrand, J.; Freedman, J.; Nilsson, H. Initial experience with irreversible electroporation of liver tumours. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2019, 6, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafeld, S.; Wong, J.J.; Kibriya, N.; Stenberg, B.; Manas, D.; Bassett, P.; Aslam, T.; Evans, J.; Littler, P. Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) of Hepatic Malignancy: A Bi-institutional Analysis of Safety and Outcomes. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Lin, X.; Li, S. Comparison of Survival Between Irreversible Electroporation Followed by Chemotherapy and Chemotherapy Alone for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, R.C.; Goldman, D.A.; D’Angelica, M.I.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Allen, P.J.; Balachandran, V.P.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Kingham, T.P. Recurrence patterns following irreversible electroporation for hepatic malignancies. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Eresen, A.; Shangguan, J.; Ma, Q.; Yaghmai, V.; Zhang, Z. Irreversible electroporation ablation overcomes tumor-associated immunosuppression to improve the efficacy of DC vaccination in a mice model of pancreatic cancer. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1875638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbach, B.J.; O’Flanagan, S.D.; Shao, Q.; Young, K.M.; Slaughter, J.R.; Rollins, M.R.; Street, T.J.L.; Granger, V.E.; Beura, L.K.; Azarin, S.M.; et al. Irreversible electroporation augments checkpoint immunotherapy in prostate cancer and promotes tumor antigen-specific tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wen, X.; Tian, L.; Li, T.; Xu, C.; Wen, X.; Melancon, M.P.; Gupta, S.; Shen, B.; Peng, W.; et al. Irreversible electroporation reverses resistance to immune checkpoint blockade in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaggar, M.; Lin, M.; Mesmar, A.; Liang, S.; Qaid, A.; Xu, K.; Chen, J.; Niu, L.; Yin, Z. Allogenic Natural Killer Cell Immunotherapy Combined with Irreversible Electroporation for Stage IV Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Survival Outcome. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, J.T.; Mittra, A.; Song, T.J.; Cavnar, M.; Jun, K.; Carson, J.; Gholami, S.; Haddad, D.; Gaujoux, S.; Monette, S.; et al. Irreversible electroporation facilitates gene transfer of a GM-CSF plasmid with a local and systemic response. Surgery 2013, 154, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, J.T.; Wong, J.; Mittra, A.; Carpenter, S.; Haddad, D.; Carson, J.; Jayaraman, S.; Monette, S.; Solomon, S.B.; Ezell, P.; et al. Irreversible electroporation is a surgical ablation technique that enhances gene transfer. Surgery 2011, 150, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasivisvanathan, V.; Thapar, A.; Oskrochi, Y.; Picard, J.; Leen, E.L. Irreversible electroporation for focal ablation at the porta hepatis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 35, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingham, T.P.; Karkar, A.M.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Allen, P.J.; Dematteo, R.P.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Solomon, S.B.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Fong, Y. Ablation of perivascular hepatic malignant tumors with irreversible electroporation. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2012, 215, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridouani, F.; Ghosn, M.; Cornelis, F.; Petre, E.N.; Hsu, M.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Kingham, P.T.; Solomon, S.B.; Srimathveeravalli, G. Ablation Zone Involution of Liver Tumors Is Faster in Patients Treated with Irreversible Electroporation Than Microwave Ablation. Medicina 2021, 57, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.L.; Mangu, P.B.; Choti, M.A.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Dodd, G.D., 3rd; Dorfman, G.S.; Eng, C.; Fong, Y.; Giusti, A.F.; Lu, D.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology 2009 clinical evidence review on radiofrequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seror, O.; N’Kontchou, G.; Muhammad, M.; Barrucand, C.; Tin Tin Htar, M.; Assaban, M.; Haddar, D.; Trinchet, J.C.; Beaugrand, M.; Sellier, N. The impact of large vessel proximity on effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: A controlled study. J. De Radiol. 2007, 88, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.S.; Raman, S.S.; Limanond, P.; Aziz, D.; Economou, J.; Busuttil, R.; Sayre, J. Influence of large peritumoral vessels on outcome of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 14, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komorizono, Y.; Oketani, M.; Sako, K.; Yamasaki, N.; Shibatou, T.; Maeda, M.; Kohara, K.; Shigenobu, S.; Ishibashi, K.; Arima, T. Risk factors for local recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma tumors after a single session, single application of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Cancer 2003, 97, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, R.; Ellis, S.; Hayes, D.; Narayanan, G.; Martin, R.C., 2nd. Safety and early efficacy of irreversible electroporation for hepatic tumors in proximity to vital structures. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, C.; Beyer, L.P.; Pregler, B.; Dollinger, M.; Trabold, B.; Schlitt, H.J.; Jung, E.M.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Percutaneous Ablation of Hepatic Tumors Using Irreversible Electroporation: A Prospective Safety and Midterm Efficacy Study in 34 Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silk, M.T.; Wimmer, T.; Lee, K.S.; Srimathveeravalli, G.; Brown, K.T.; Kingham, P.T.; Fong, Y.; Durack, J.C.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Solomon, S.B. Percutaneous ablation of peribiliary tumors with irreversible electroporation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessen, C.; Igl, J.; Pregler, B.; Beyer, L.; Noeva, E.; Dollinger, M.; Schreyer, A.G.; Jung, E.M.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Factors associated with short-term local recurrence of liver cancer after percutaneous ablation using irreversible electroporation: A prospective single-center study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Data |
|---|---|
| Total patient, n | 21 |
| Median follow-up, d, median (range) | 313 (25–1786) |
| Tumors treated per patient, n, median (range) | 1 (1–5) |
| Age, y, median (range) | 58 (41–83) |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Male | 16 (76.2%) |
| Female | 5 (23.8%) |
| BMI (kg/m2), median (range) | 22.9 (15.6–26.0) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 3 (14.3%) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 11 (52.4%) |
| Heart disease, n (%) | 4 (19.0%) |
| Cirrhosis, n (%) | 9 (42.9%) |
| Child-Pugh class | |
| A | 20 (95.2%) |
| B | 1 (4.8%) |
| C | 0 (0.0%) |
| Variable | Data |
|---|---|
| Tumor size | |
| Median maximum diameter, cm (range) | 1.81 (1.31–4.04) |
| 1.01–2.00 cm, n (%) | 12 (57.1%) |
| 2.01–3.00 cm, n (%) | 5 (23.8%) |
| ≥3.01 cm, n (%) | 4 (19.1%) |
| Location of tumor, n (%) | |
| Segments 2 | 1 (4.8%) |
| Segments 4a | 2 (9.5%) |
| Segments 7 | 7 (33.3%) |
| Segments 8 | 8 (38.1%) |
| Junctional region of segments | 3 (14.3%, 2 × (S4a + S8), 1 × (S7 + S8)) |
| Distance from the hepatocaval confluence, cm | |
| Median distance (range) | 0.50 (0.10–1.72) |
| ≤0.50, n (%) | 11 (52.4%) |
| 0.50–1.00, n (%) | 4 (19.0%) |
| 1.01–2.00, n (%) | 6 (28.6%) |
| Distance from the major hepatic vein, cm | |
| Median distance (range) | 0.15 (0.10–0.45) |
| Lesions distant from the hepatocaval confluence | |
| Yes, n (%), median (range) | 8 (38.1%), 1.5 (1–4) |
| None, n (%) | 13 (61.9%) |
| Primary tumor types | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma, n (%) | 9 (42.9%) |
| Cholangiocarcinoma, n (%) | 2 (9.5%) |
| Intestinal cancer, n (%) | 4 (19.1%) |
| Gastric carcinoma, n (%) | 3 (14.3%) |
| Pancreatic carcinoma, n (%) | 3 (14.3%) |
| Variable | Data |
|---|---|
| Treated tumors, n | 38 |
| Lesions at the hepatocaval confluence, n, patients, n (%) | 21, 21 (100%) |
| Lesions distant from the hepatocaval confluence, n, patients, n (%) | 17, 8 (38.1%) |
| Procedures, n | 21 |
| Number of electrodes, median (range) | 4 (2–4) |
| 2, n (%) | 8 (38.1%) |
| 3, n (%) | 2 (9.5%) |
| 4, n (%) | 11 (52.4%) |
| Exposure length of electrodes (cm), median (range) | 2.25 (1.5–3) |
| Spacing (cm), median (range) | 1.9 (1.5–2.2) |
| Electrode replacement | |
| Pull-back technique, n (%) | 14 (66.7%) |
| Electrode replacement, n (%) | 6 (28.6%) |
| IRE ablation size | |
| Median largest diameter, cm (range) | 3.87 (2.85–6.55) |
| 2.01–3.00, n (%) | 2 (9.5%) |
| 3.01–4.00, n (%) | 10 (47.6%) |
| 4.01–5.00, n (%) | 5 (23.8%) |
| ≥5.01, n (%) | 4 (19.0%) |
| IRE ablation size/tumor size, median (range) | 2.83 (1.4–3.2) |
| Patients with lesions distant from the hepatocaval confluence receiving IRE, n (%) | 4 (19.0%, 6 lesions) |
| Patients with lesions distant from the hepatocaval confluence receiving thermal ablation, n (%) | 4 (19.0%, 11 lesions) |
| Variable | Data |
|---|---|
| CIRSE grade | |
| 1 | |
| Fever, n (%) | 3 (14.3%) |
| Pain, n (%) | 2 (9.5%, 1 × Grade 2, 1 × Grade 3) |
| 2 | |
| Hydrothorax, n (%) | 11 (52.4%) |
| Seroperitoneum, n (%) | 5 (23.8%) |
| 3 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 |
| Variable | Patient Number, n (%) | Recurrence, n (%) | Recurrence without This Treatment, n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prior treatments | |||
| Hepatic resection, n (%) | 6 (28.6%) | 2 (33.3%) | 7 (46.7%) |
| Systemic chemotherapy, n (%) | 8 (38.1%) | 3 (37.5%) | 6 (46.2%) |
| Hepatic arterial therapy, n (%) | 8 (38.1%) | 4 (50%) | 5 (38.5%) |
| Radiofrequency ablation OR Microwave ablation, n (%) | 6 (28.6%) | 4 (66.7%) | 5 (33.3%) |
| TKI Targeted Therapies, n (%) | 5 (23.8) | 4 (80%) | 5 (29.4%) |
| Immunotherapy, n (%) | 1 (4.8%) | 1 (100%) | 8 (40%) |
| Three-dimensional conformal radiation, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | - | - |
| Postoperative treatments | |||
| Systemic chemotherapy | 8 (38.1%) | 5 (62.5%) | 4 (30.8%) |
| Hepatic arterial therapy (TACE) | 1 (4.8%) | 1 (100%) | 8 (40%) |
| TKI Targeted Therapies | 5 (23.8%) | 4 (80%) | 5 (31.2%) |
| Immunotherapy | 5 (23.8%) | 1 (20%) | 8 (50%) |
| Radiofrequency ablation | 1 (4.8%) | 1 (100%) | 8 (40%) |
| Hepatic resection | 0 (0.0%) | - | - |
| Three-dimensional conformal radiation | 0 (0.0%) | - | - |
| Variable | Data |
|---|---|
| Postcaval status | |
| Vein patent | 21 (100%) |
| Postcava occluded | 0 (0.0%) |
| Hepatic vein status | |
| Vein patent | 20 (95.2%) |
| Vein occluded | 1 (4.8%) |
| Bile duct status | |
| Bile duct patent | 20 (95.2%) |
| Bile duct occluded | 1 (4.8%) |
| Ablation size at 1 mo to postoperative size, median (range) | 0.68 (0.50–0.84) |
| Ablation size at 3 mo to postoperative size, median (range) | 0.49 (0.27–0.61) |
| Ablation size at 6 mo to postoperative size, median (range) | 0.38 (0.25–0.59) |
| Progression-free survival (d), median (range) | 121 (25–566) |
| Death, n (%), survival time (d), median (range) | 4 (19.0%), 451.5 (25–716) |
| Disease persistence/recurrence | |
| Local recurrence, n (%), time to recurrence (d) | 1 (4.8%), 176 |
| Distant recurrence, n (%), time to recurrence (d), median (range) | 8 (38.1%), 127 (32–566) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Huang, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Ding, X.; et al. Percutaneous Ablation of Hepatic Tumors at the Hepatocaval Confluence Using Irreversible Electroporation: A Preliminary Study. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3950-3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29060316
Li T, Huang W, Wu Z, Wang Y, Wang Q, Wang Z, Liu Q, Liu J, Wang S, Ding X, et al. Percutaneous Ablation of Hepatic Tumors at the Hepatocaval Confluence Using Irreversible Electroporation: A Preliminary Study. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(6):3950-3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29060316
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tiankuan, Wei Huang, Zhiyuan Wu, Yong Wang, Qingbing Wang, Ziyin Wang, Qin Liu, Jingjing Liu, Shenjie Wang, Xiaoyi Ding, and et al. 2022. "Percutaneous Ablation of Hepatic Tumors at the Hepatocaval Confluence Using Irreversible Electroporation: A Preliminary Study" Current Oncology 29, no. 6: 3950-3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29060316
APA StyleLi, T., Huang, W., Wu, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, Z., Liu, Q., Liu, J., Wang, S., Ding, X., & Wang, Z. (2022). Percutaneous Ablation of Hepatic Tumors at the Hepatocaval Confluence Using Irreversible Electroporation: A Preliminary Study. Current Oncology, 29(6), 3950-3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29060316






