Expression of IRAK1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Its Clinical Significance, and Docking Characteristics with Selected Natural Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pan-Cancer, Gene Alteration and Survival Analyses
2.2. Analysis of IRAK1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Associations with Clinicopathological Parameters
2.3. Immunohistochemistry Experiments on Liver Tissues from Clinical Specimens
2.4. Molecular Docking Study
3. Results
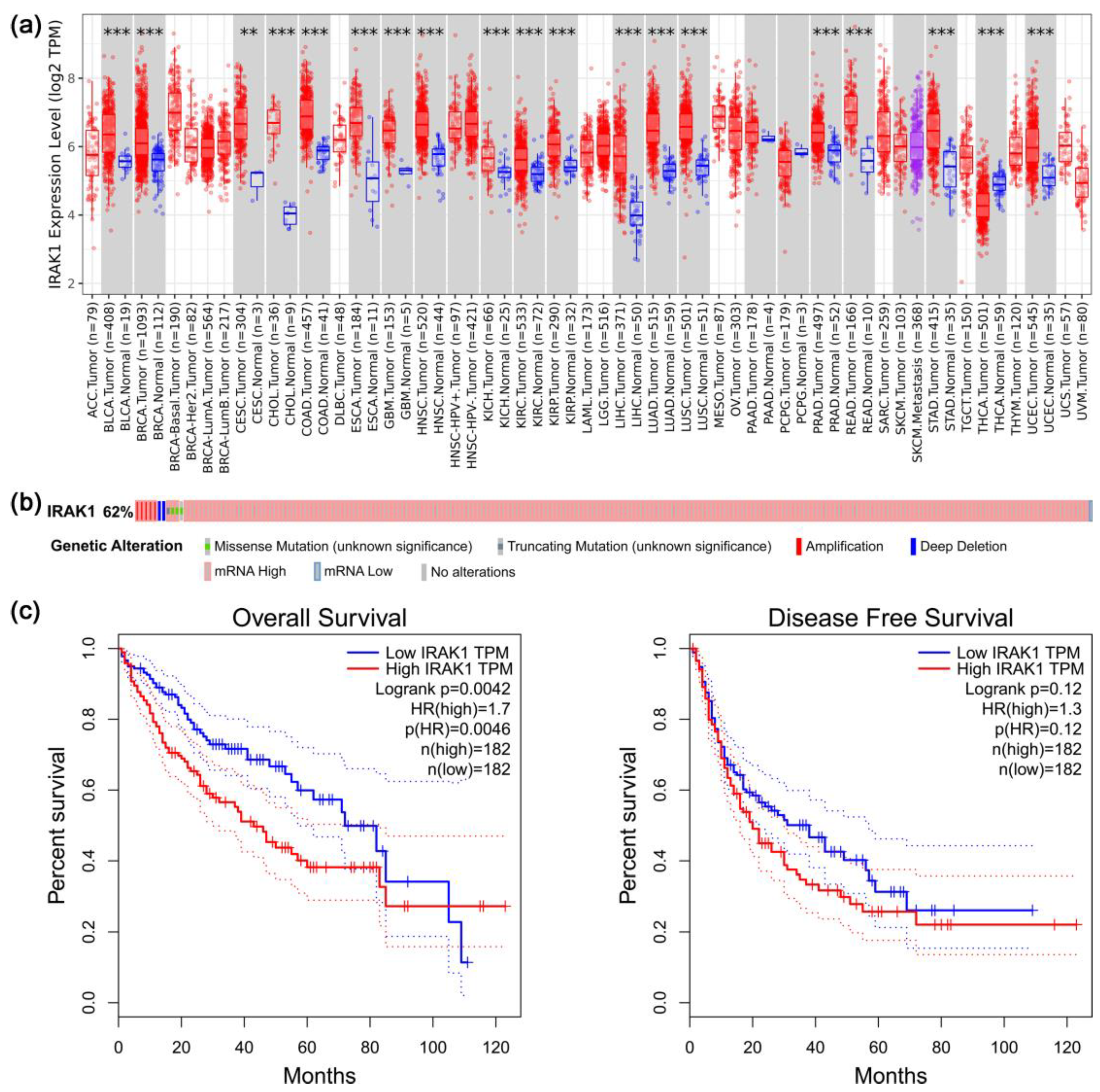
3.1. Results of Pan-Cancer, Gene Alteration, and Survival Analyses Regarding IRAK1
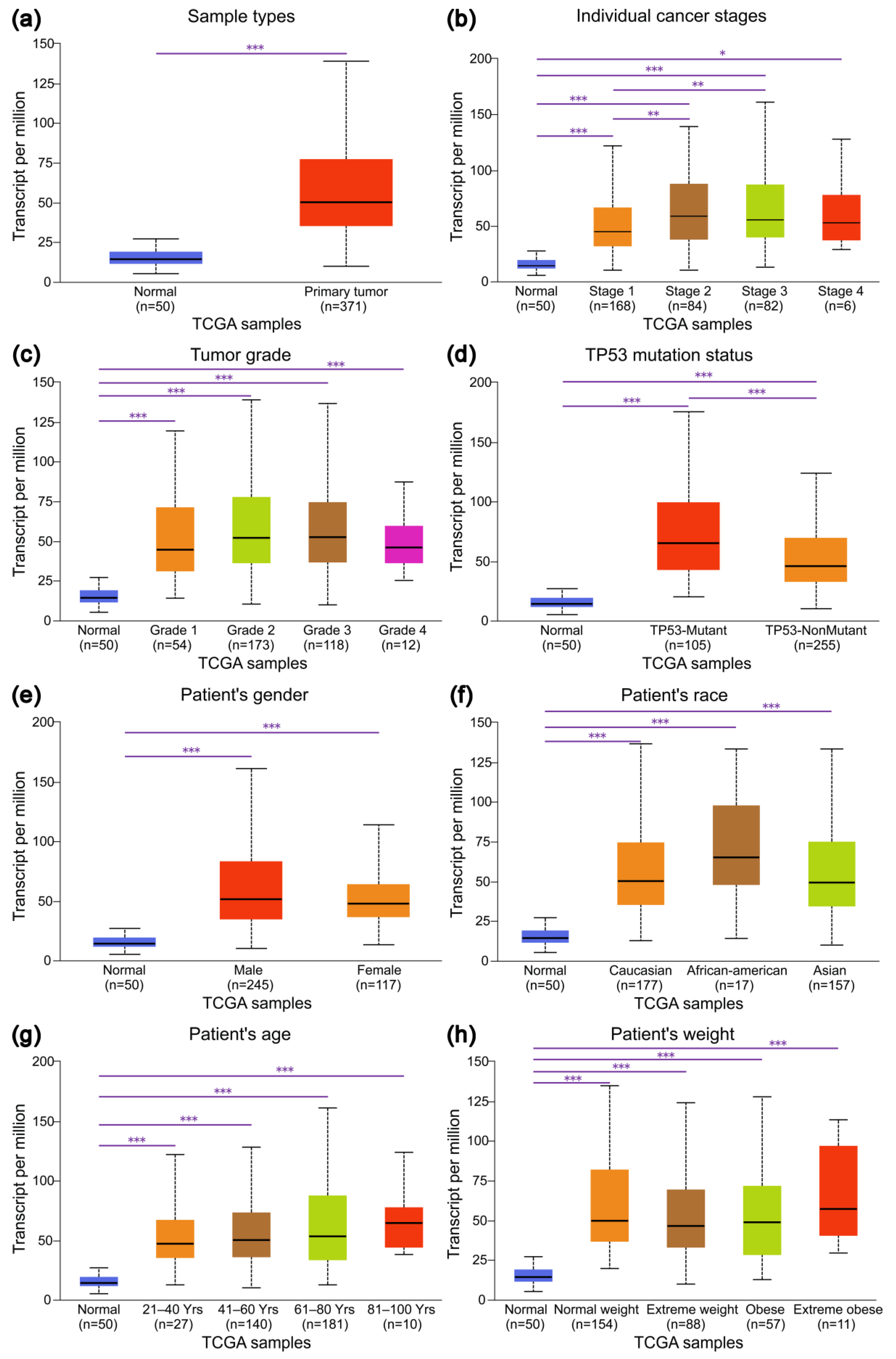
3.2. Expression Profiles of IRAK1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Their Associations with Clinicopathological Parameters
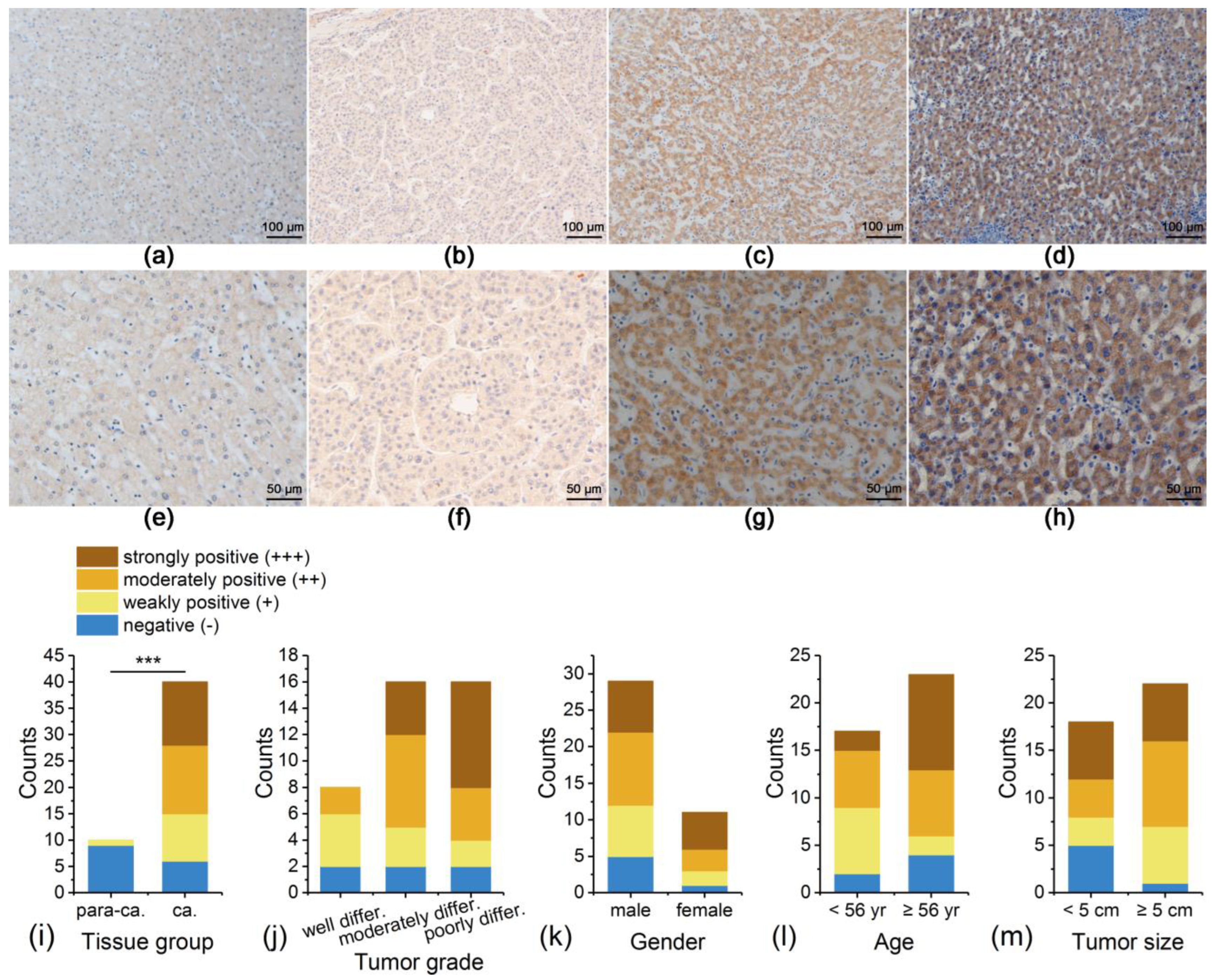
3.3. IRAK1 Expression in Liver Tissues of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Experimentally Detected by Immunohistochemistry
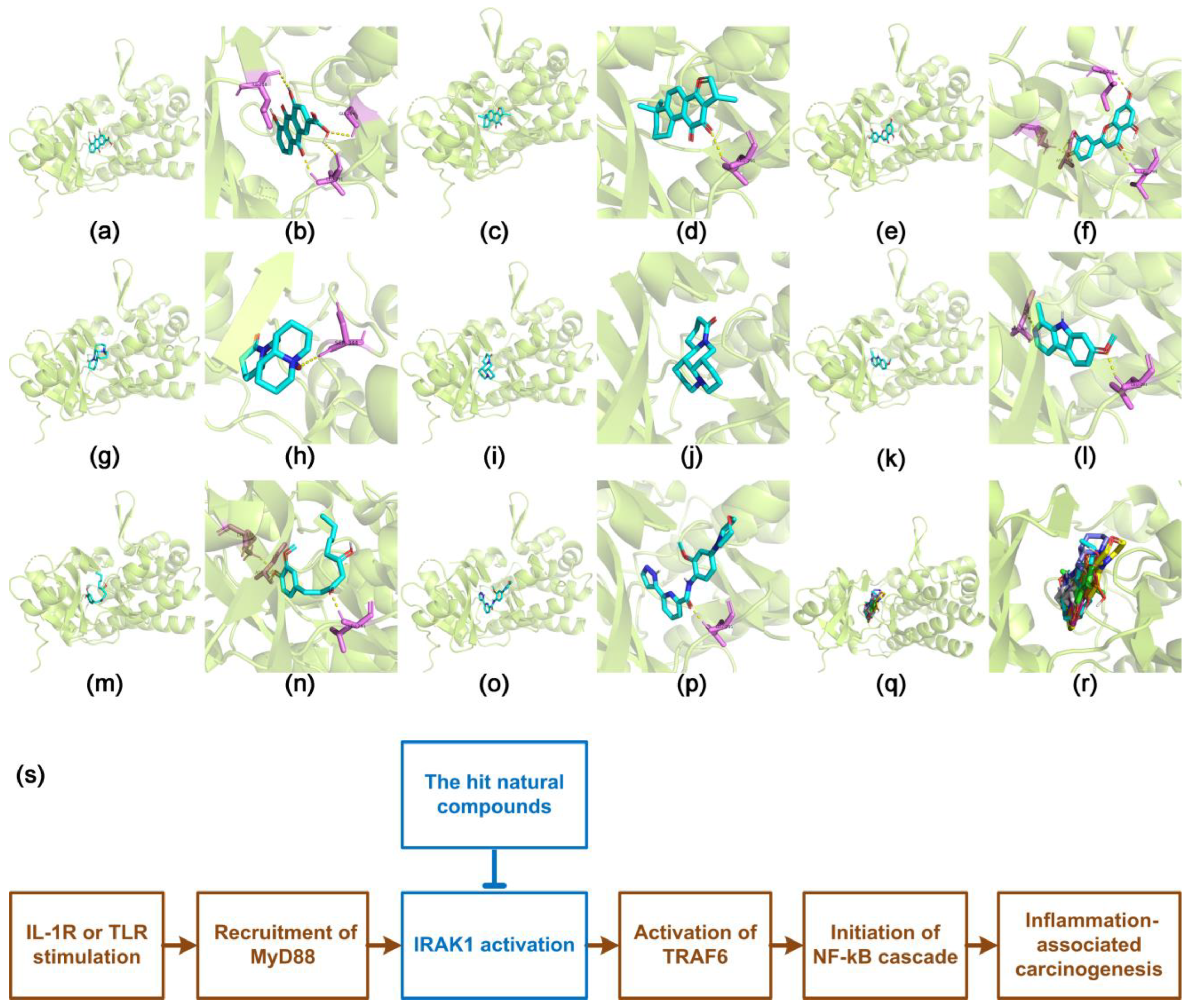
3.4. Docking Characteristics of IRAK1 with Selected Natural Compounds
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderaro, J.; Ziol, M.; Paradis, V.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Molecular and histological correlations in liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib, W.H.; Daoud, S.; Mahmod, A.I.; Hamed, R.A.; Awajan, D.; Abuarab, S.F.; Odeh, L.H.; Khater, S.; Al Kury, L.T. Plants as a Source of Anticancer Agents: From Bench to Bedside. Molecules 2022, 27, 4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovoli, F.; Ielasi, L.; Casadei-Gardini, A.; Granito, A.; Foschi, F.G.; Rovesti, G.; Negrini, G.; Orsi, G.; Renzulli, M.; Piscaglia, F. Management of adverse events with tailored sorafenib dosing prolongs survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Marinelli, S.; Terzi, E.; Piscaglia, F.; Renzulli, M.; Venerandi, L.; Benevento, F.; Bolondi, L. Metronomic capecitabine as second-line treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma after sorafenib failure. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Forgione, A.; Marinelli, S.; Renzulli, M.; Ielasi, L.; Sansone, V.; Benevento, F.; Piscaglia, F.; Tovoli, F. Experience with regorafenib in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 17562848211016959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovoli, F.; Dadduzio, V.; De Lorenzo, S.; Rimassa, L.; Masi, G.; Iavarone, M.; Marra, F.; Garajova, I.; Brizzi, M.P.; Daniele, B.; et al. Real-Life Clinical Data of Cabozantinib for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2021, 10, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielasi, L.; Sansone, V.; Granito, A.; Benevento, F.; De Lorenzo, S.; Tovoli, F. An update of treatments of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients refractory to sorafenib. Drugs Today 2018, 54, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Seki, E. Inflammation and Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Semin Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 026–042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiao, Q.; Ferrao, R.; Shen, C.; Hatcher, J.M.; Buhrlage, S.J.; Gray, N.S.; Wu, H. Crystal structure of human IRAK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13507–13512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.; Starczynowski, D.T. IRAK1 and IRAK4 as emerging therapeutic targets in hematologic malignancies. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2022, 29, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, C.; Feng, L.; Kadara, H.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.J.; Mehran, R.; Hong, W.K.; Lotan, R.; Wistuba, I.I. Expression of Interleukin-1 Receptor–Associated Kinase-1 in Non–Small Cell Lung Carcinoma and Preneoplastic Lesions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.H.; Gao, L.; Wen, D.Y.; He, Y.; Pang, Y.Y.; Chen, G. Diagnostic and prognostic roles of IRAK1 in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues: An analysis of immunohistochemistry and RNA-sequencing data from the cancer genome atlas. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Qin, X.; Qin, G.; Zheng, X. The role of IRAK1 in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Jiang, J.; Fu, J.; Yu, T.; Wang, B.; Qin, W.; Xu, A.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Targeting interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 for human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.H.; Shah, R.B.; Li, Y.; Arora, A.; Ung, P.M.-U.; Raman, R.; Gorbatenko, A.; Kozono, S.; Zhou, X.Z.; Brechin, V.; et al. An IRAK1–PIN1 signalling axis drives intrinsic tumour resistance to radiation therapy. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.Y.; Lau, E.Y.; Leung, H.-W.; Leung, C.O.-N.; Ho, N.P.; Gurung, S.; Cheng, L.K.; Lin, C.H.; Lo, R.C.-L.; Ma, S.; et al. IRAK1 Augments Cancer Stemness and Drug Resistance via the AP-1/AKR1B10 Signaling Cascade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2332–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoadley, K.A.; Yau, C.; Hinoue, T.; Wolf, D.M.; Lazar, A.J.; Drill, E.; Shen, R.; Taylor, A.M.; Cherniack, A.D.; Thorsson, V.; et al. Cell-of-Origin Patterns Dominate the Molecular Classification of 10,000 Tumors from 33 Types of Cancer. Cell 2018, 173, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cohen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W509–W514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Karthikeyan, S.K.; Korla, P.K.; Patel, H.; Shovon, A.R.; Athar, M.; Netto, G.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Kumar, S.; Manne, U.; et al. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 2022, 25, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.V.S.K.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasaikar, S.V.; Straub, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D956–D963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pence, H.E.; Williams, A. ChemSpider: An Online Chemical Information Resource. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.J.; Hinner, M.J. Getting Across the Cell Membrane: An Overview for Small Molecules, Peptides, and Proteins. In Site-Specific Protein Labeling: Methods and Protocols; Gautier, A., Hinner, M.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 29–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, P.; Rohde, B.; Selzer, P. Fast Calculation of Molecular Polar Surface Area as a Sum of Fragment-Based Contributions and Its Application to the Prediction of Drug Transport Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3714–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetterberg, F.R.; MacKinnon, A.; Brimert, T.; Gravelle, L.; Johnsson, R.E.; Kahl-Knutson, B.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J.; Pedersen, A.; Peterson, K.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of the First Highly Effective and Orally Available Galectin-3 Inhibitors for Treatment of Fibrotic Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 12626–12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger LLC. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. 2022. Available online: https://pymol.org/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminf. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiue, E.H.-C.; Wright, K.M.; Douglass, J.; Hwang, M.S.; Mog, B.J.; Pearlman, A.H.; Paul, S.; DiNapoli, S.R.; Konig, M.F.; Wang, Q.; et al. Targeting a neoantigen derived from a common TP53 mutation. Science 2021, 371, eabc8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giriwono, P.E.; Shirakawa, H.; Ohsaki, Y.; Sato, S.; Aoyama, Y.; Ho, H.-J.; Goto, T.; Komai, M. Geranylgeraniol Suppresses the Expression of IRAK1 and TRAF6 to Inhibit NFκB Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Human Macrophage-Like Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Cao, H.; Zhou, H.; Sun, L.; Xue, J.; Li, J.; Bian, Y.; Sun, R.; Dong, S.; Liu, P.; et al. Research Progress on the Antitumor Effects of Rhein: Literature Review. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, S.; De Stefano, A.; Calabrese, C.; Giovannelli, A.; Pieri, M.; Savini, I.; Tesauro, M.; Bernardini, S.; Minieri, M.; Terrinoni, A. Anti-Inflammatory and Active Biological Properties of the Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds Luteolin and Luteolin 7-Glucoside. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-R.; Li, B.; Yan, Z.-Y. Cryptotanshinone: A review of its pharmacology activities and molecular mechanisms. Fitoterapia 2020, 145, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Ohbayashi, S.; Ooka, A.; Yamashita, H.; Motohashi, N.; Kaneko, Y.K.; Kimura, T.; Saito, S.-y.; Ishikawa, T. Harmine suppresses collagen production in hepatic stellate cells by inhibiting DYRK1B. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 600, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ji, W.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Gao, Q.; Su, C. Anti-tumor activities of matrine and oxymatrine: Literature review. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 5111–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafees, S.; Zafaryab, M.; Mehdi, H.S.; Zia, B.; Rizvi, A.M.; Khan, A.M. Anti-Cancer Effect of Gingerol in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, C.; Gu, X.; Li, R. Expression of IRAK1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Its Clinical Significance, and Docking Characteristics with Selected Natural Compounds. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 8904-8916. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110700
Song C, Gu X, Li R. Expression of IRAK1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Its Clinical Significance, and Docking Characteristics with Selected Natural Compounds. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(11):8904-8916. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110700
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Chaoying, Xinyu Gu, and Ruifang Li. 2022. "Expression of IRAK1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Its Clinical Significance, and Docking Characteristics with Selected Natural Compounds" Current Oncology 29, no. 11: 8904-8916. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110700
APA StyleSong, C., Gu, X., & Li, R. (2022). Expression of IRAK1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Its Clinical Significance, and Docking Characteristics with Selected Natural Compounds. Current Oncology, 29(11), 8904-8916. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110700




