Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2-Altered Urothelial Carcinoma: Clinical and Genomic Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. EPAS1 Expression in UC Cancer Cell Lines
3.2. EPAS1 Genomic Alterations in UC Patients
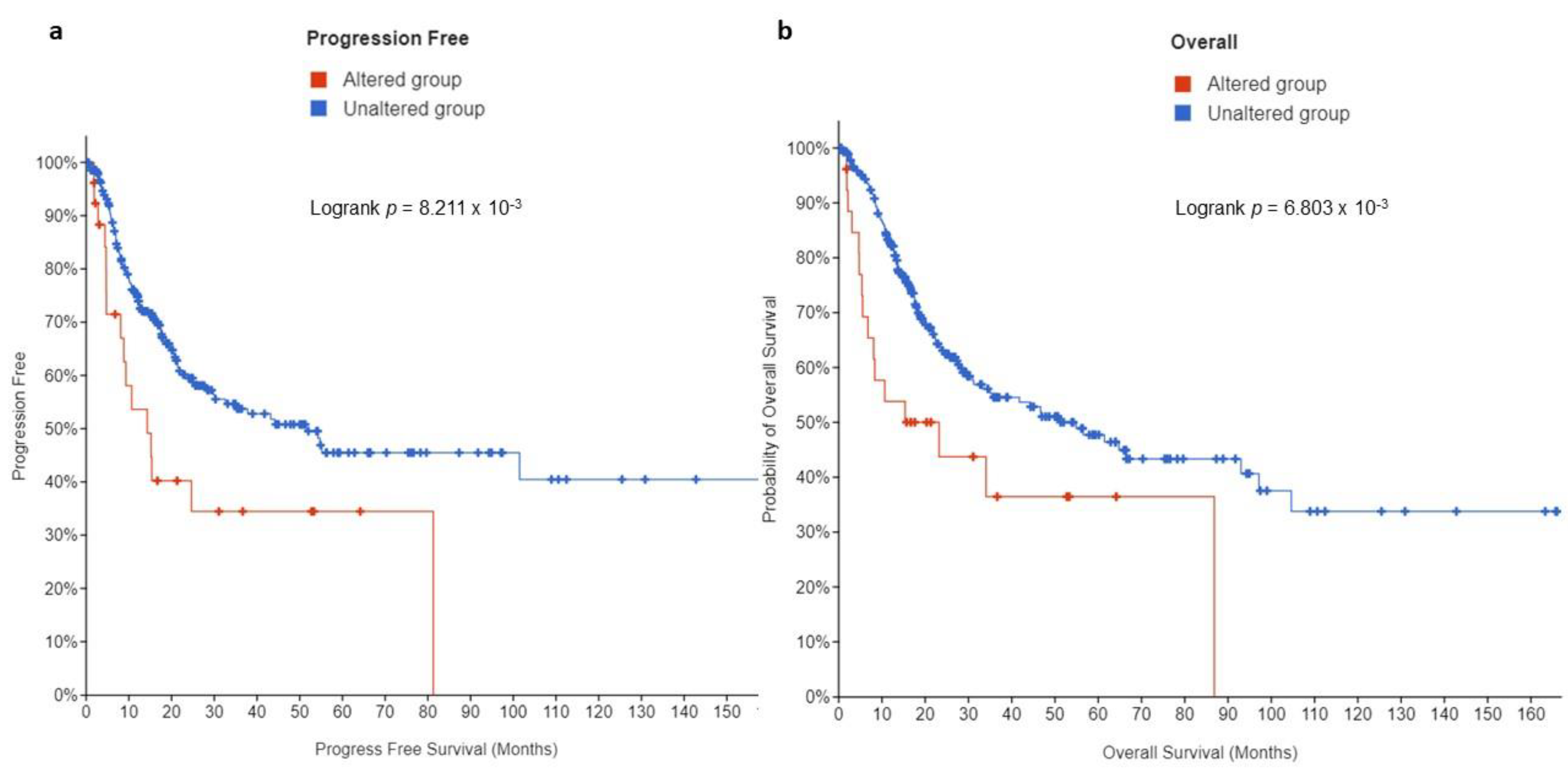
3.3. Prognostic Value of EPAS1 Alterations in UC Patients
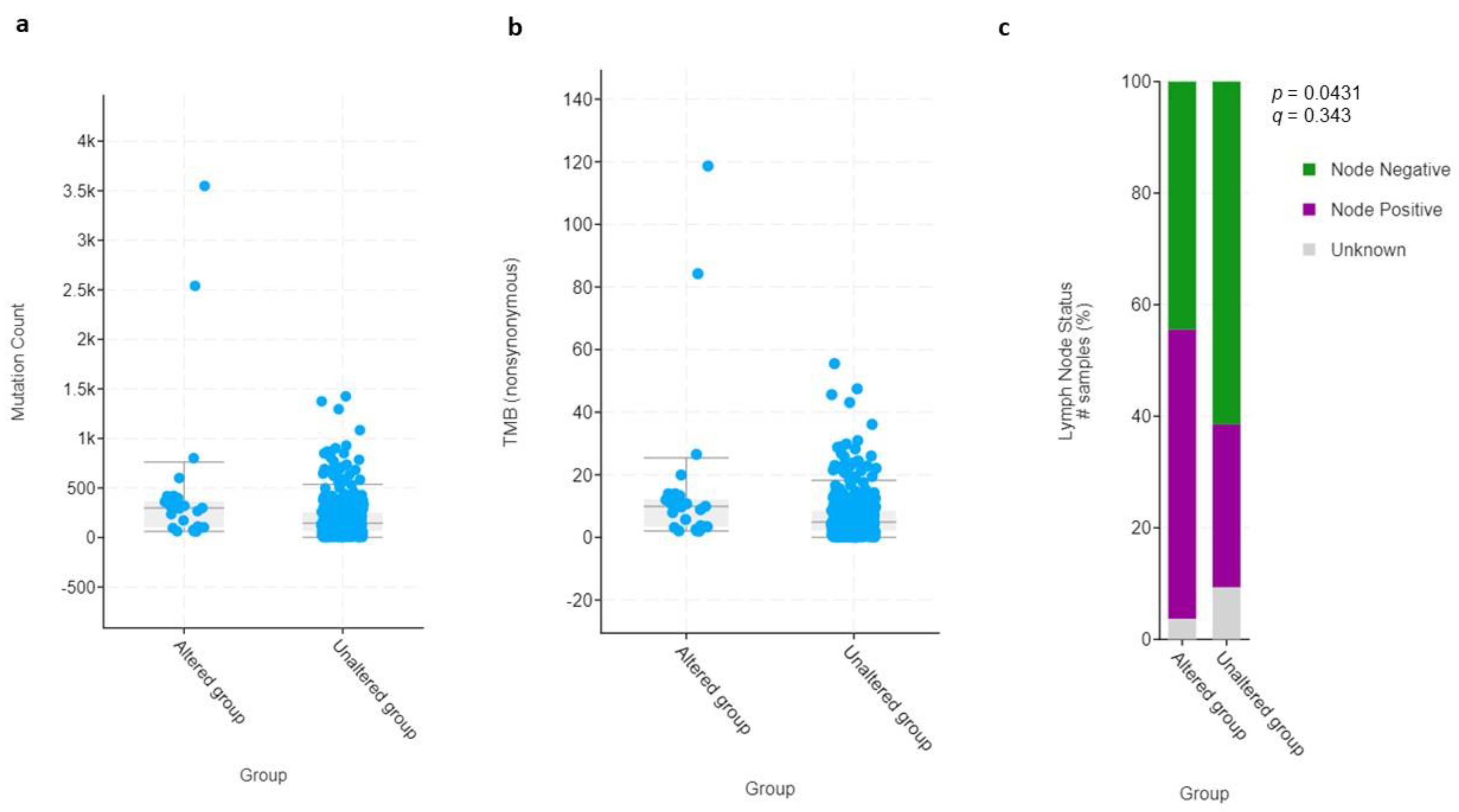
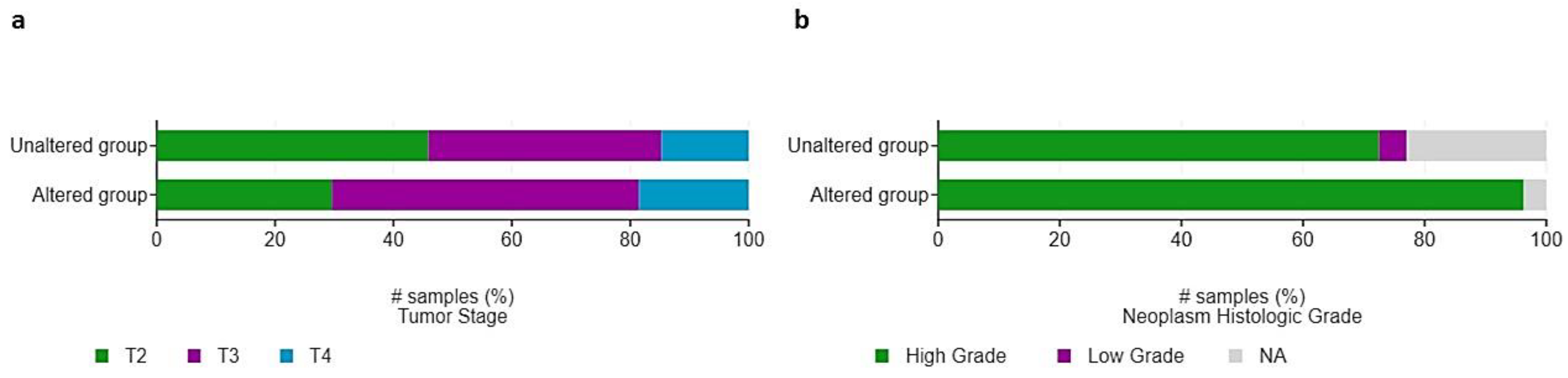
3.4. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of HIF-2-Altered UC
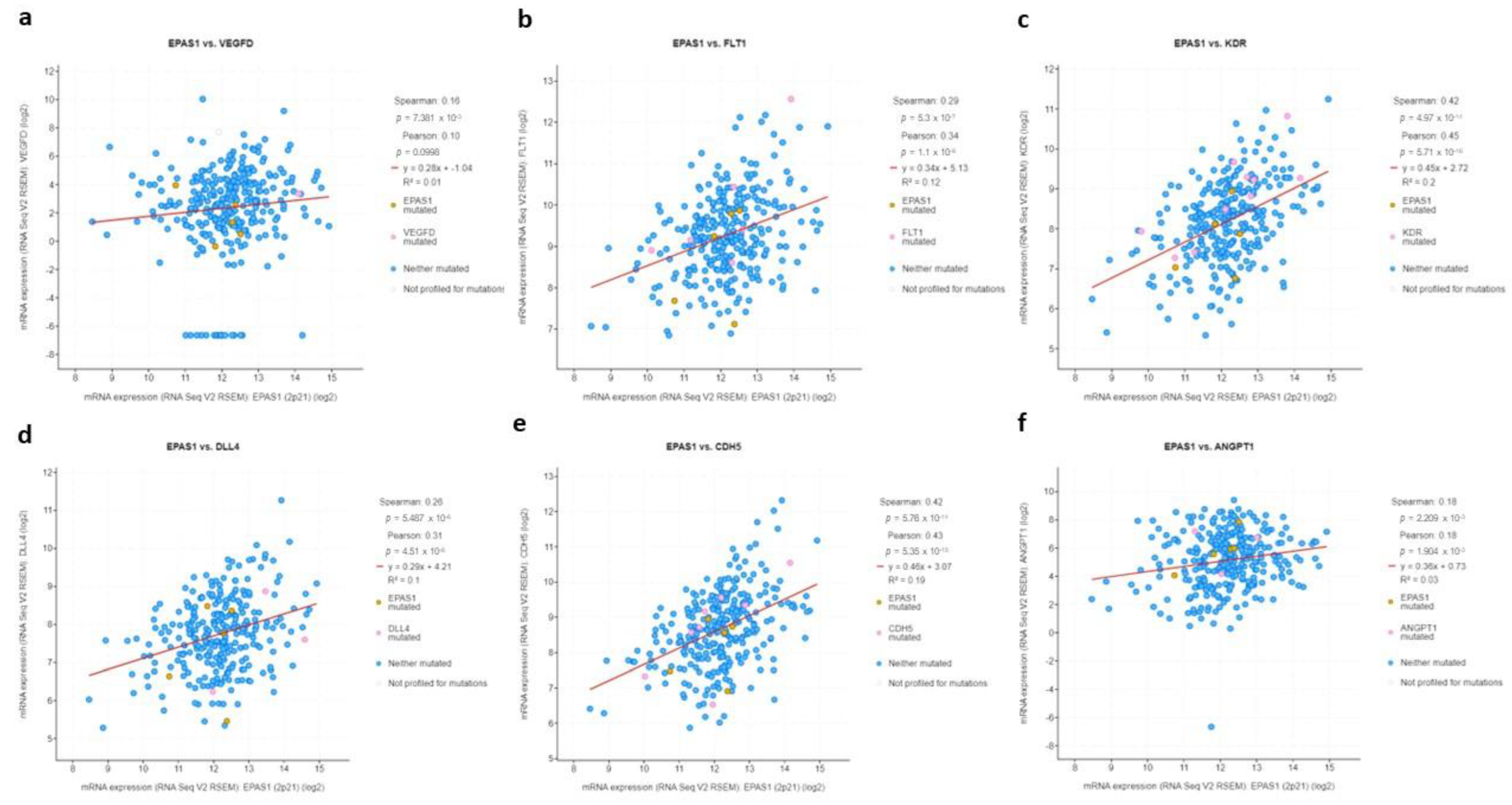
3.5. EPAS1 Is Directly Associated with Expression of HIF-2-Target Genes
3.6. EPAS1 Is Associated with Expression of Immune Suppression Genes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellmunt, J.; de Wit, R.; Vaughn, D.J.; Fradet, Y.; Lee, J.L.; Fong, L.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Climent, M.A.; Petrylak, D.P.; Choueiri, T.K.; et al. Pembrolizumab as Second-Line Therapy for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Durán, I.; van der Heijden, M.S.; Loriot, Y.; Vogelzang, N.J.; De Giorgi, U.; Oudard, S.; Retz, M.M.; Castellano, D.; Bamias, A.; et al. Atezolizumab versus chemotherapy in patients with platinum-treated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (IMvigor211): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.E.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Balar, A.V.; McGregor, B.A.; Heath, E.I.; Yu, E.Y.; Galsky, M.D.; Hahn, N.M.; Gartner, E.M.; Pinelli, J.M.; et al. Pivotal Trial of Enfortumab Vedotin in Urothelial Carcinoma after Platinum and Anti-Programmed Death 1/Programmed Death Ligand 1 Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2592–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Rosenberg, J.E.; Sonpavde, G.P.; Loriot, Y.; Durán, I.; Lee, J.L.; Matsubara, N.; Vulsteke, C.; Castellano, D.; Wu, C.; et al. Enfortumab Vedotin in Previously Treated Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loriot, Y.; Necchi, A.; Park, S.H.; Garcia-Donas, J.; Huddart, R.; Burgess, E.; Fleming, M.; Rezazadeh, A.; Mellado, B.; Varlamov, S.; et al. Erdafitinib in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoropoulos, V.E.; Lazaris, A.C.; Sofras, F.; Gerzelis, I.; Tsoukala, V.; Ghikonti, I.; Manikas, K.; Kastriotis, I. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha expression correlates with angiogenesis and unfavorable prognosis in bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2004, 46, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palit, V.; Phillips, R.M.; Puri, R.; Shah, T.; Bibby, M.C. Expression of HIF-1alpha and Glut-1 in human bladder cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 14, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Nanzhang, U.; Xiao, J.; Wu, H.; Ding, K. Hypoxia-Induced Autophagy Enhances Cisplatin Resistance in Human Bladder Cancer Cells by Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 8887437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, M.; Huang, F.W.; Jané-Valbuena, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Lo, C.C.; McDonald, E.R., 3rd; Barretina, J.; Gelfand, E.T.; Bielski, C.M.; Li, H.; et al. Next-generation characterization of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. Nature 2019, 569, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.; Fujiyama, C.; Blanche, C.; Moore, J.W.; Fuggle, S.; Cranston, D.; Bicknell, R.; Harris, A.L. Relation of vascular endothelial growth factor production to expression and regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha in human bladder tumors and cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Befani, C.; Liakos, P. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha in angiogenesis. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 9087–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.J.; Wang, L.Y.; Chodosh, L.A.; Keith, B.; Simon, M.C. Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in hypoxic gene regulation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 9361–9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathomas, R.; Lorch, A.; Bruins, H.M.; Compérat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Fietkau, R.; Gakis, G.; Hernández, V.; Espinós, E.L.; et al. The 2021 Updated European Association of Urology Guidelines on Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, N.; Shao, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, X. Multi-omics Perspective on the Tumor Microenvironment based on PD-L1 and CD8 T-Cell Infiltration in Urothelial Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.D.; Vlachostergios, P.J.; Bhinder, B.; Liu, W.; Li, K.; Moss, T.J.; Bareja, R.; Park, K.; Tavassoli, P.; Cyrta, J.; et al. Upper tract urothelial carcinoma has a luminal-papillary T-cell depleted contexture and activated FGFR3 signaling. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Kageyama, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Hyochi, N.; Kawakami, S.; Kihara, K. Positive expression of HIF-2alpha/EPAS1 in invasive bladder cancer. Urology 2002, 59, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onita, T.; Ji, P.G.; Xuan, J.W.; Sakai, H.; Kanetake, H.; Maxwell, P.H.; Fong, G.H.; Gabril, M.Y.; Moussa, M.; Chin, J.L. Hypoxia-induced, perinecrotic expression of endothelial Per-ARNT-Sim domain protein-1/hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha correlates with tumor progression, vascularization, and focal macrophage infiltration in bladder cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 471–480. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, F.; Kageyama, Y.; Kawakami, S.; Fujii, Y.; Hyochi, N.; Ando, N.; Takizawa, T.; Saito, K.; Iwai, A.; Masuda, H.; et al. Prognostic significance of endothelial Per-Arnt-sim domain protein 1/hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha expression in a subset of tumor associated macrophages in invasive bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Fakih, M.; Lopez, J.; Shah, M.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Nakagawa, K.; Chung, H.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Lopez-Martin, J.A.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; et al. Association of tumour mutational burden with outcomes in patients with advanced solid tumours treated with pembrolizumab: Prospective biomarker analysis of the multicohort, open-label, phase 2 KEYNOTE-158 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Lv, J.; Xu, X.; Yu, W.; Zhou, M.; Yue, L. Pan-cancer analysis of ARID family members as novel biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimwell, N.J.; Bryan, R.T.; Wei, W.; James, N.D.; Cheng, K.K.; Zeegers, M.P.; Johnson, P.J.; Martin, A.; Ward, D.G. Combined proteome and transcriptome analyses for the discovery of urinary biomarkers for urothelial carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Xie, F.; Wang, L.; Liang, Z.; Li, D.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Qi, X.; Yang, X.; et al. Evaluating the biological functions of the prognostic genes identified by the Pathology Atlas in bladder cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lv, D.; Wu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Jiang, D. Identification and validation of a novel signature for prediction the prognosis and immunotherapy benefit in bladder cancer. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.M.; Wang, Z.; Mott, S.L.; Dupuy, A.J.; Weiner, G.J. A Genetic Screen to Identify Gain- and Loss-of-Function Modifications that Enhance T-cell Infiltration into Tumors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Lin, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, W. Identification of chloride intracellular channels as prognostic factors correlated with immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma using bioinformatics analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e27739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, Z.; Jin, Z.; Li, X.; Yuan, C. Sortilin 1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Migration by Regulating Immune Cell Infiltration. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 6509028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, G.; Wu, L.; Yao, Y.; Shen, X.; Hou, Z.; et al. LncRNA IFITM4P promotes immune escape by up-regulating PD-L1 via dual mechanism in oral carcinogenesis. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 1564–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonangeli, F.; Natalini, A.; Garassino, M.C.; Sica, A.; Santoni, A.; Di Rosa, F. Regulation of PD-L1 Expression by NF-κB in Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 584626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, J.; Brave, M.H.; Weinstock, C.; Mehta, G.U.; Bradford, D.; Gittleman, H.; Bloomquist, E.W.; Charlab, R.; Hamed, S.S.; Miller, C.P.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Belzutifan for von Hippel-Lindau disease associated tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 38037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia Garcia, C.J.; Huang, Y.; Fuentes, N.R.; Turner, M.C.; Monberg, M.E.; Lin, D.; Nguyen, N.D.; Fujimoto, T.N.; Zhao, J.; Lee, J.J.; et al. Stromal HIF2 Regulates Immune Suppression in the Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 2018–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boumelhem, B.B.; Fraser, S.T.; Assinder, S.J. Differentiation of Urothelium from Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells in Chemically Defined Conditions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2029, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; He, M.; Zhao, L.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Han, L.; Wei, B.; Ye, D.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. A novel HIF-2α targeted inhibitor suppresses hypoxia-induced breast cancer stemness via SOD2-mtROS-PDI/GPR78-UPRER axis. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 1769–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.C.O.B.; Vijaya Kumar, A.; Kumar Katakam, S.; Cocola, C.; Pelucchi, P.; Graf, M.; Kiesel, L.; Reinbold, R.; Pavão, M.S.G.; Greve, B.; et al. The Heparan Sulfate Sulfotransferases HS2ST1 and HS3ST2 Are Novel Regulators of Breast Cancer Stem-Cell Properties. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 559554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, S.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J. Physiological and pathological functions of βB2-crystallins in multiple organs: A systematic review. Aging 2021, 13, 15674–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Cheong, J.H.; Im, J.Y.; Ban, H.S.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, K.C.; Paik, S.; et al. PI3K/AKT/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Vestigial-Like 1 Which Predicts Poor Prognosis and Enhances Malignant Phenotype in Gastric Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yi, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, X. Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals SH3TC2 as an Oncogene for Colorectal Cancer and Promotes Tumorigenesis via the MAPK Pathway. Cancers 2022, 14, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Ishii, A.; Watanabe, M.; Fujitani, N.; Sugeo, A.; Gotoh, S.; Ohta, T.; Hiyoshi, M.; Matsuzaki, H.; et al. A brain-specific Grb2-associated regulator of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) (GAREM) subtype, GAREM2, contributes to neurite outgrowth of neuroblastoma cells by regulating Erk signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 29934–29942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, M.; Lapierre, M.; Cavailles, V.; Mokdad-Gargouri, R. Expression and role of nuclear receptor coregulators in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4480–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, H.; Matsuhisa, K.; Saito, A.; Kanemoto, S.; Asada, R.; Hino, K.; Takai, T.; Cui, M.; Cui, X.; Kaneko, M.; et al. Promotion of Cancer Cell Proliferation by Cleaved and Secreted Luminal Domains of ER Stress Transducer BBF2H7. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Tan, C.; Zhao, P. Expression and prognostic significance of EPAS-1 in renal clear cell carcinoma. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2021, 92, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jarman, E.J.; Ward, C.; Turnbull, A.K.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Meehan, J.; Xintaropoulou, C.; Sims, A.H.; Langdon, S.P. HER2 regulates HIF-2α and drives an increased hypoxic response in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskiizmir, G.; Çalıbaşı Koçal, G.; Uysal, T.; Ellidokuz, H.; Başpınar, Y. Serum hypoxia-inducible factor-2: A candidate prognostic biomarker for laryngeal cancer. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2021, 46, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.; Kuo, C.C.; Tu, H.F.; Yang, C.C. The prognosis outcome of oral squamous cell carcinoma using HIF-2α. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2017, 80, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangoura, G.; Liu, Z.S.; Qian, Q.; Jiang, C.Q.; Yang, G.F.; Jing, S. Prognostic significance of HIF-2alpha/EPAS1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 3176–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
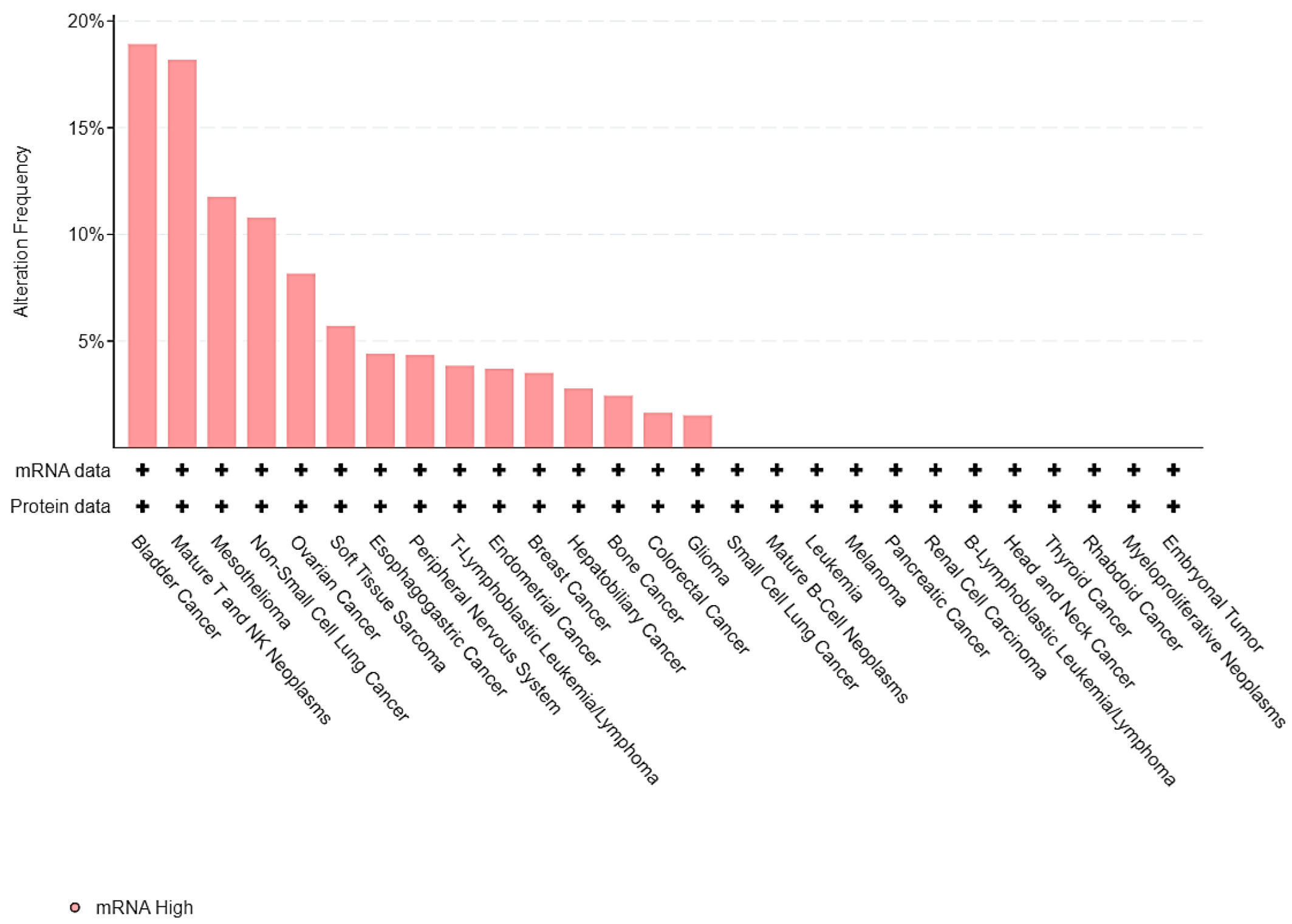
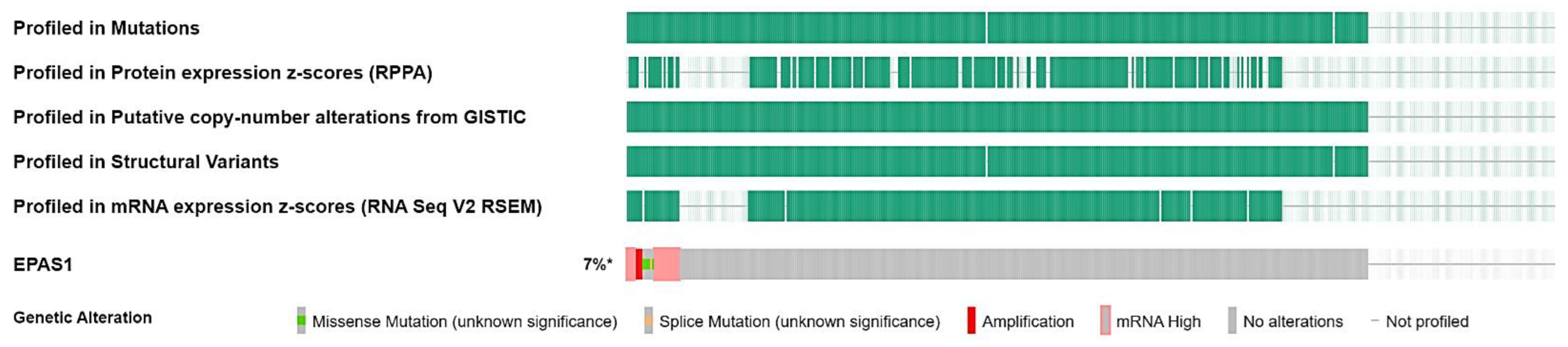
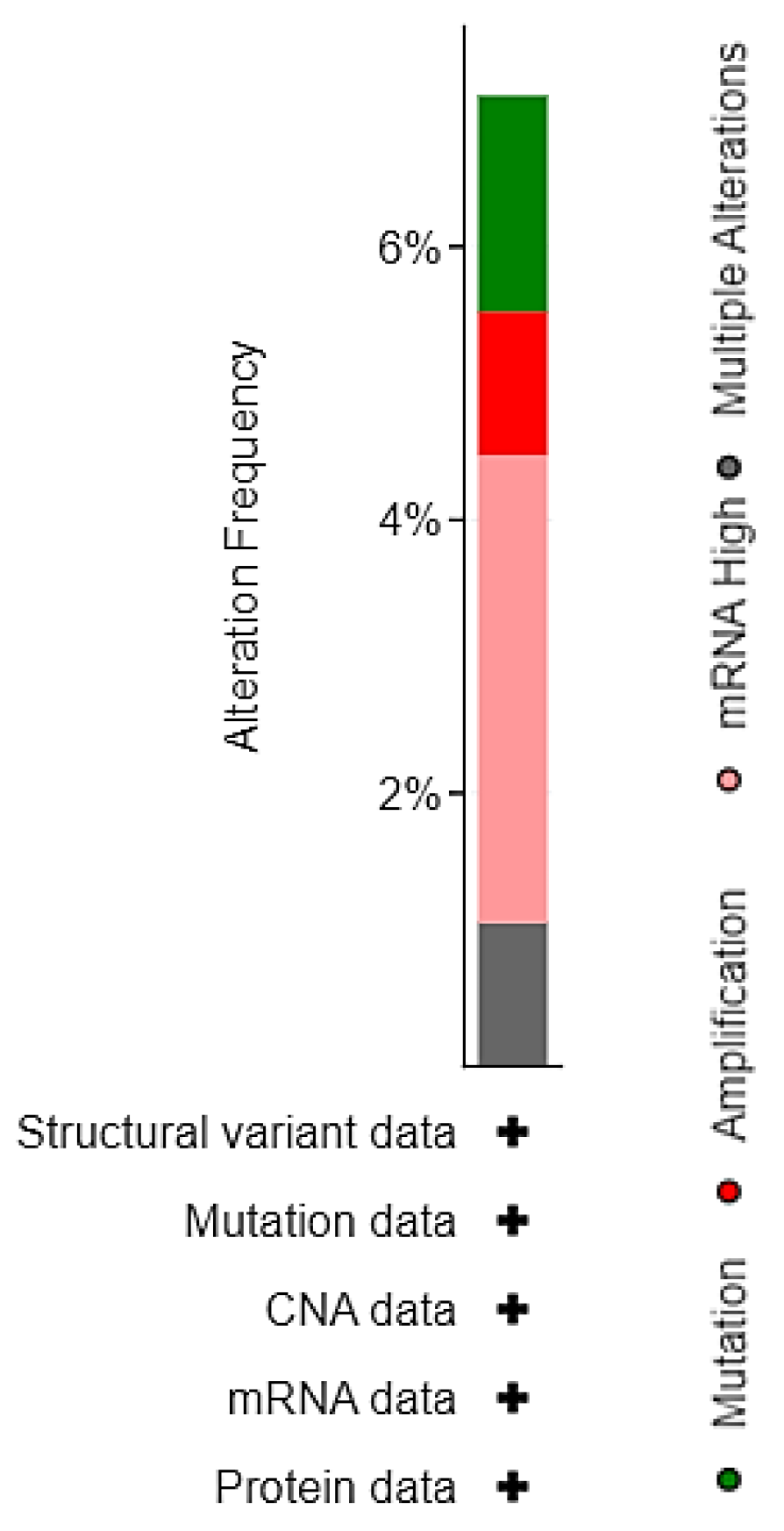
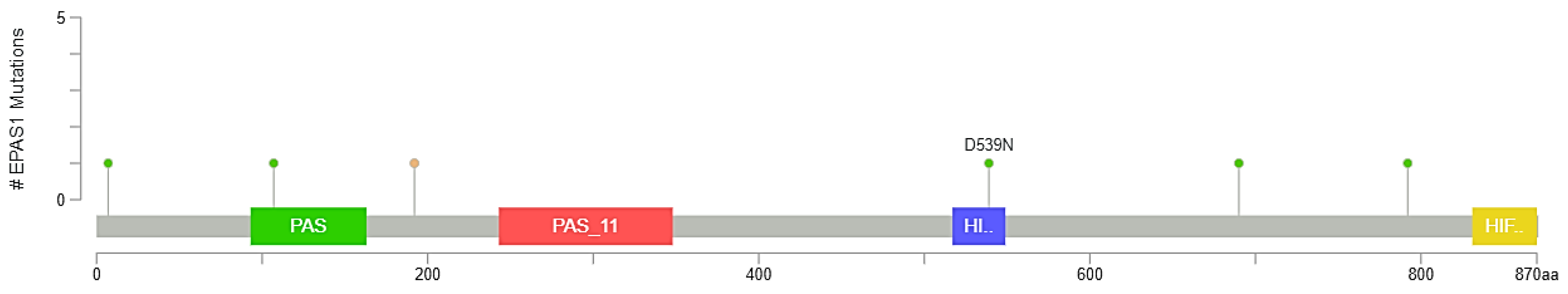

| Sample ID | Protein Change | Mutation Type | Allele Freq (T) | # Mut in Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSKCC-0450_NR | D539N | Missense | NA | 61 |
| TCGA-DK-A1A5-01 | R690Q | Missense | 0.25 | 236 |
| TCGA-E5-A4TZ-01 | D107N | Missense | 0.16 | 420 |
| TCGA-FD-A5BV-01 | K7R | Missense | 0.35 | 111 |
| TCGA-S5-A6DX-01 | X192_splice | Splice | 0.27 | 600 |
| TCGA-UY-A78N-01 | G792R | Missense | 0.22 | 267 |
| Gene | Cytoband | μ in Altered Group | μ in Unaltered Group | σ in Altered Group | σ in Unaltered Group | Log Ratio | p-Value | q-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGLL1 | Xq26.3 | 11.01 | 9.07 | 1.4 | 2.85 | 1.94 | 2.8 × 10−7 | 6.996 × 10−4 |
| UPK2 | 11q23.3 | 12.59 | 9.78 | 2.44 | 4.23 | 2.8 | 6.397 × 10−6 | 7.116 × 10−3 |
| EPAS1 | 2p21 | 13.4 | 12.04 | 1.31 | 0.91 | 1.35 | 1.979 × 10−5 | 0.0152 |
| GPR78 | 4p16.1 | 5.77 | 3.92 | 1.77 | 2.81 | 1.85 | 2.527 × 10−5 | 0.0158 |
| SPINT1 | 15q15.1 | 13.35 | 12.6 | 0.73 | 1.1 | 0.74 | 3.785 × 10−5 | 0.0205 |
| HS3ST2 | 16p12.2 | 4.72 | 3.42 | 1.3 | 1.89 | 1.3 | 4.418 × 10−5 | 0.0233 |
| SH3TC2 | 5q32 | 8.3 | 7.49 | 0.79 | 1.7 | 0.81 | 6.16 × 10−5 | 0.0268 |
| GAREM1 | 18q12.1 | 8.61 | 7.85 | 0.78 | 1.3 | 0.76 | 7.524 × 10−5 | 0.0284 |
| AAK1 | 2p13.3 | 10.46 | 9.99 | 0.51 | 0.56 | 0.47 | 8.999 × 10−5 | 0.0328 |
| NCOA1 | 2p23.3 | 10.51 | 9.99 | 0.57 | 0.65 | 0.53 | 9.475 × 10−5 | 0.0339 |
| CLIC3 | 9q34.3 | 10.15 | 8.25 | 2.06 | 2.54 | 1.9 | 1.105 × 10−4 | 0.0382 |
| ARID5B | 10q21.2 | 10.61 | 10.02 | 0.64 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 1.273 × 10−4 | 0.0404 |
| CREB3L2 | 7q33 | 11.25 | 10.57 | 0.76 | 0.93 | 0.68 | 1.446 × 10−4 | 0.0419 |
| SORT1 | 1p13.3 | 11.18 | 10.55 | 0.69 | 0.94 | 0.63 | 1.528 × 10−4 | 0.0419 |
| SASH1 | 6q24.3-q25.1 | 10.15 | 9.34 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.81 | 1.541 × 10−4 | 0.0419 |
| CRYBG2 | 1p36.11 | 9.72 | 8.66 | 1.19 | 1.74 | 1.06 | 1.86 × 10−4 | 0.0481 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vlachostergios, P.J.; Tamposis, I.A.; Anagnostou, M.; Papathanassiou, M.; Mitrakas, L.; Zachos, I.; Thodou, E.; Samara, M.; Tzortzis, V. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2-Altered Urothelial Carcinoma: Clinical and Genomic Features. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 8638-8649. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110681
Vlachostergios PJ, Tamposis IA, Anagnostou M, Papathanassiou M, Mitrakas L, Zachos I, Thodou E, Samara M, Tzortzis V. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2-Altered Urothelial Carcinoma: Clinical and Genomic Features. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(11):8638-8649. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110681
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlachostergios, Panagiotis J., Ioannis A. Tamposis, Maria Anagnostou, Maria Papathanassiou, Lampros Mitrakas, Ioannis Zachos, Eleni Thodou, Maria Samara, and Vassilios Tzortzis. 2022. "Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2-Altered Urothelial Carcinoma: Clinical and Genomic Features" Current Oncology 29, no. 11: 8638-8649. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110681
APA StyleVlachostergios, P. J., Tamposis, I. A., Anagnostou, M., Papathanassiou, M., Mitrakas, L., Zachos, I., Thodou, E., Samara, M., & Tzortzis, V. (2022). Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2-Altered Urothelial Carcinoma: Clinical and Genomic Features. Current Oncology, 29(11), 8638-8649. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29110681





