Chirurgische Untersuchungen aus den 50er Jahren zeigten, dass eine renale Sympathektomie zu einer Senkung des Blutdrucks und der erhöhten Mortalität bei Hypertonikern führt. Basierend auf diesem Konzept wurde die perkutane, katheterbasierte Nierennervenablation mit Radiofrequenzenergie entwickelt. Nach anfänglichem Enthusiasmus enttäuschte die grosse, shamkontrollierte Symplicity-HTN-3-Studie, und die Methode wurde fast verlassen, bis sich zeigte, dass in dieser Untersuchung die Nierenablation bei ⅔ der Patienten nicht sachgemäss durchgeführt worden war. Neuere Studien mit dem Spiralkatheter und Radiofrequenz-energie und dem Ultraschall-Ballonkatheter belegen nun die antihypertensive Wirksamkeit der Methode bei Hypertonikern mit oder ohne Antihypertensiva
Proof of Concept
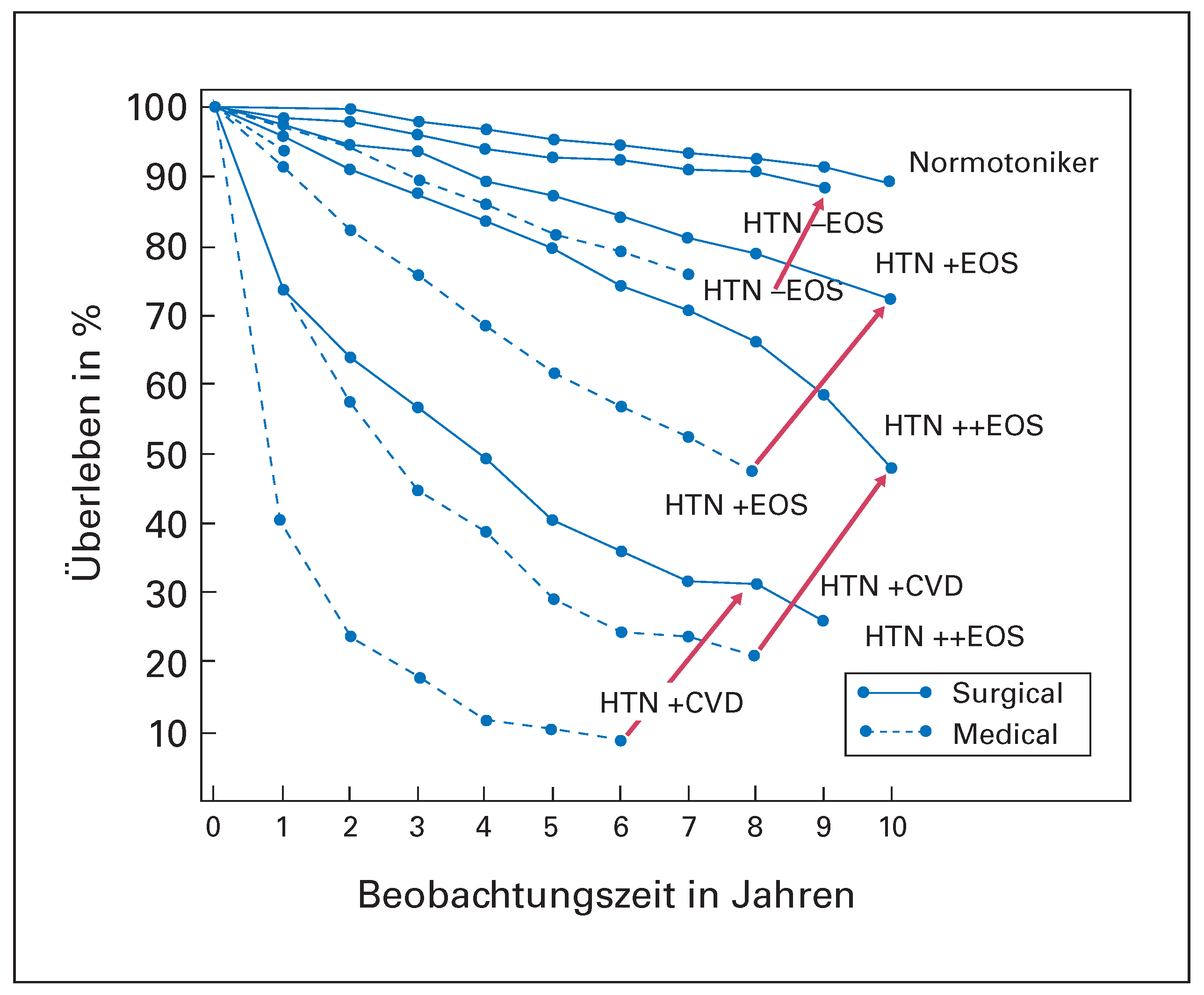
Anfang der 50er Jahre haben die Chirurgen aufgrund der pathophysiologischen Beziehung zwischen gerade erst besser verstandenem sympathischem Nervensystem und Blutdruck eine Untersuchung an damals unbehandelbaren Hypertonikern durchgeführt, in der sie chirurgisch den Sympathikus durchtrennten und damit den Blutdruck senken konnten. Bedeutend an dieser 1953 im Journal of the American Medical Association erschienenen Studie ist die Tatsache, dass vor allem bei Patienten mit schwerer Hypertonie, das heisst solchen mit Endorganschäden oder bereits bekannter koronarer Herzkrankheit, Hirnschlag oder Infarkt die Sterblichkeit massiv gesenkt werden konnte (Figure 1) [1]. Die Beobachtungsdauer von 6 bis 10 Jahren in den verschiedenen Gruppen unterstrich weiter die klinische Bedeutung dieser Beobachtung. Mit der Entwicklung von Antihypertensiva in den 50er bis 70er Jahren des letzten Jahrhunderts wurde diese zwar wirksame, aber doch invasive und nicht komplikationsfreie chirurgische Behandlung der Hypertonie verlassen. Dennoch zeigten diese Untersuchungen, dass der Sympathikus beim hohen Blutdruck eine wichtige Rolle spielt und dass eine Hemmung des vegetativen Nervensystems nicht nur den Blutdruck senkt, sondern auch das Überleben von Hypertonikern verbessert.
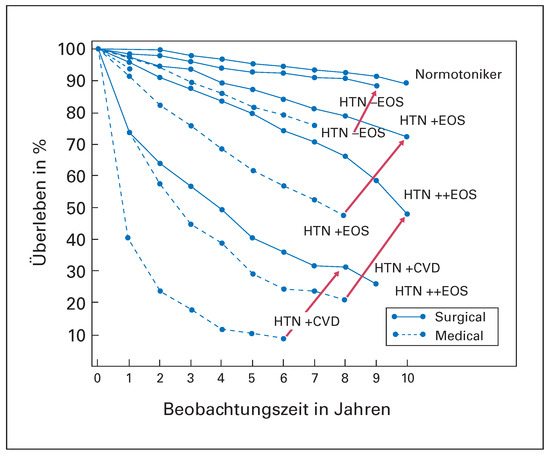
Figure 1.
Wirkung einer chirurgischen Sympathektomie der Niereninnervation bei Hypertonie: Dargestellt ist das Überleben nach mehreren Jahren in der medikamentös bzw. chirurgisch behandelten Gruppe (modifiziert aus: Luscher TF, Mahfoud F. Renal nerve ablation after SYMPLICITY HTN-3: confused at the higher level? Eur Heart J. 2014;35(26):1706–11; Nachdruck mit Genehmigung; nach [1]). CVD = cardiovascular disease; EOS = Endorganschaden; HTN = Hypertonie.
Sympathikus und Blutdruck
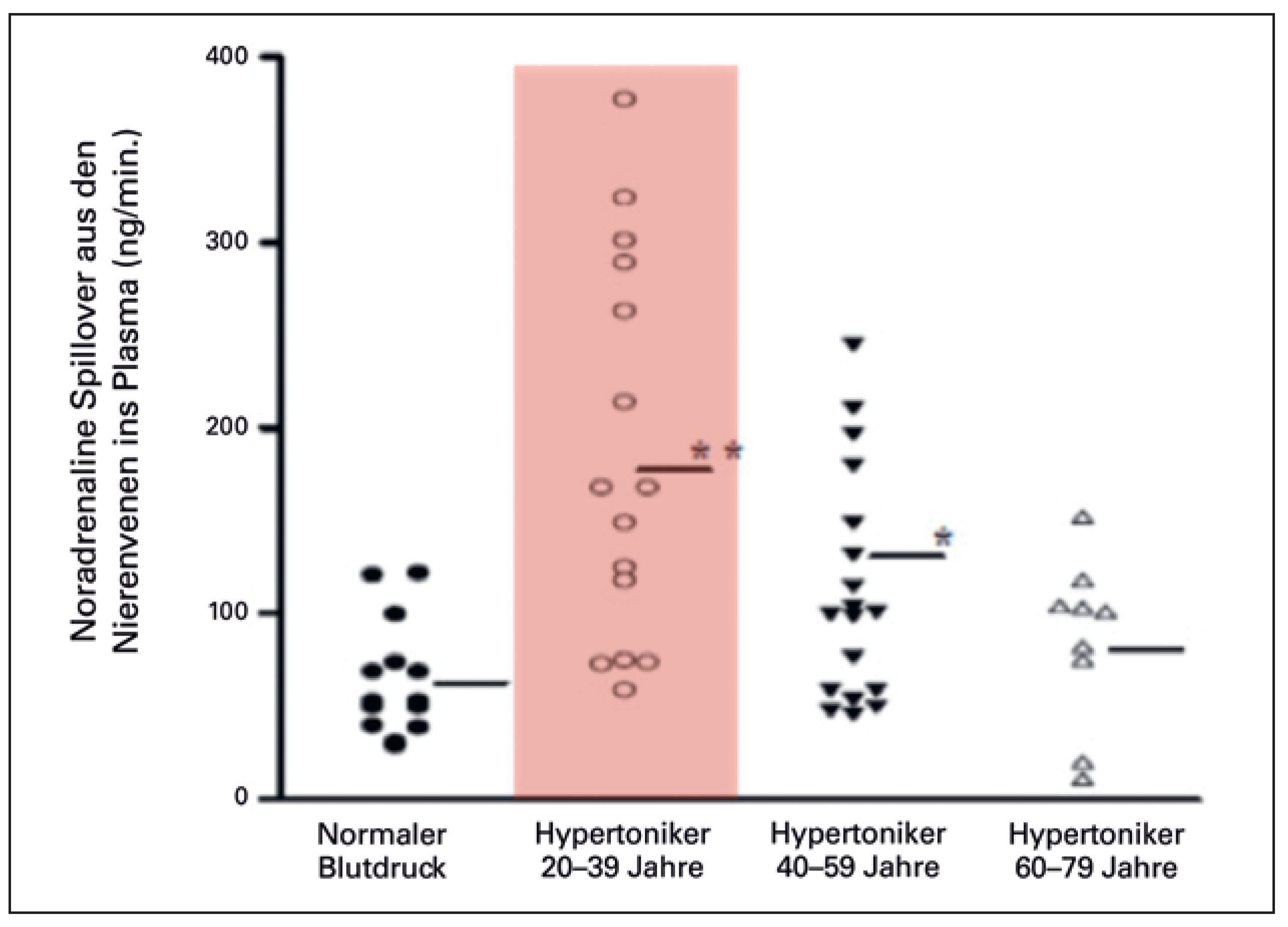
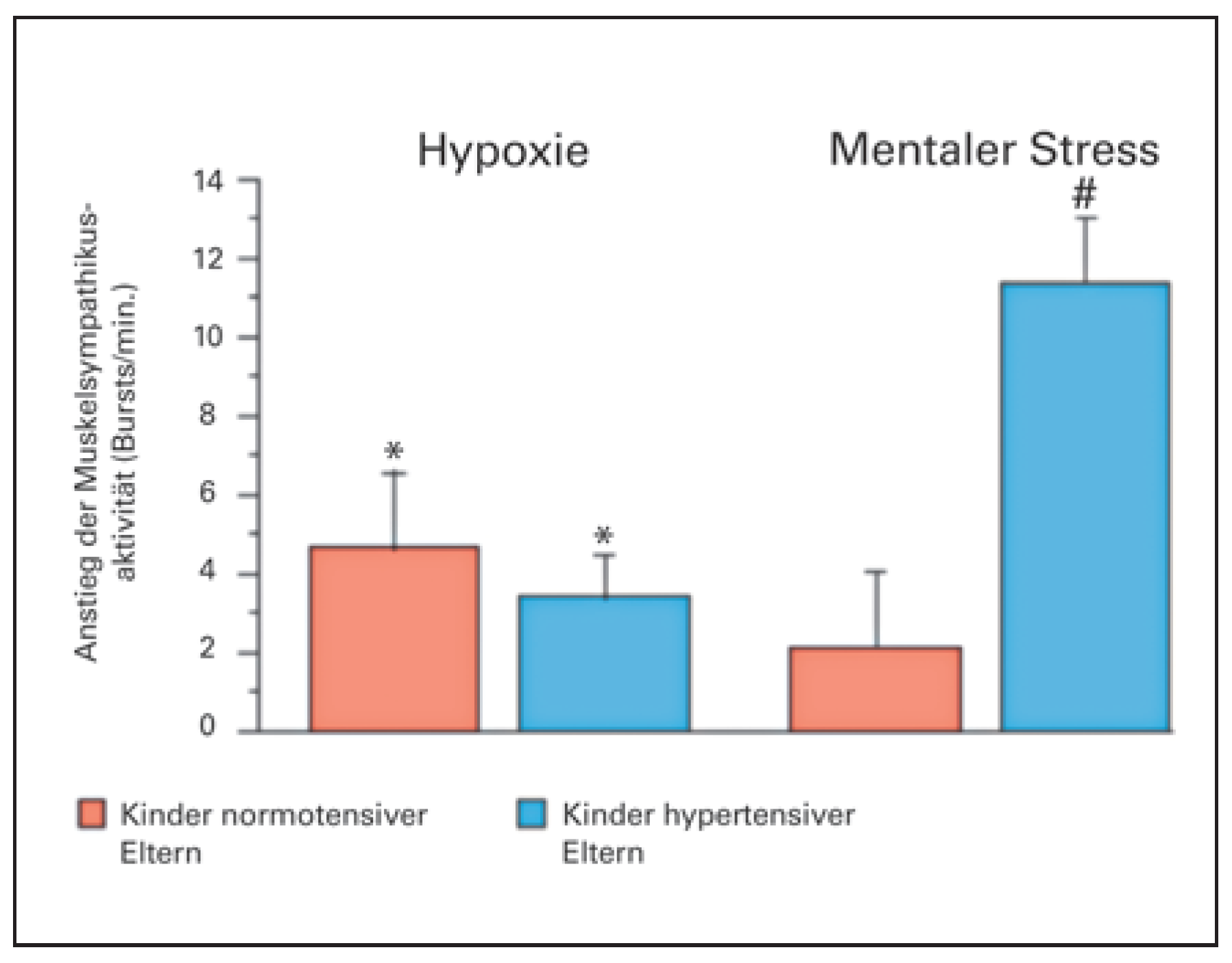
Die Idee der Chirurgen wurde Anfang dieses Jahrhunderts von der australischen Forschungsgruppe um Murray Esler in Melbourne aufgegriffen [2]. Murray Esler hatte in überzeugenden klinischen Untersuchungen gezeigt, dass die Aktivierung des Sympathikus, gemessen mittels Norepinephin-Spill-over in den Nierenvenen, vor allem bei jungen Hypertonikern massiv erhöht ist (Figure 2) [3]. Gleichzeitig konnten wir bei Kindern von Hypertonikern nachweisen, dass bei einer genetischen Veranlagung für hohen Blutdruck in jungen Jahren die Sympathikusaktivierung in Ruhe zwar normal ist, aber unter mentalem Stress massiv ansteigt (Figure 3) [4,5]. Damals haben wir die Hypothese aufgestellt, dass die repetitive Sympathikusaktivie-rung bei Kindern von Hypertonikern möglicherweise für die langfristige Erhöhung des Blutdrucks über die Lebenszeit von Bedeutung ist.
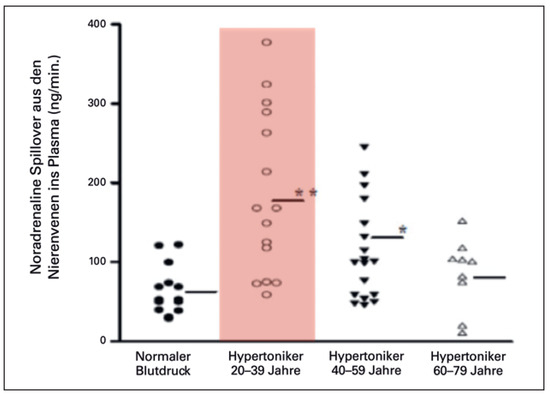
Figure 2.
Noradrenalin-Spillover aus den Nierenvenen mit radioaktiv markiertem Noradrenalin bei Patienten mit normalen Blutdruck (links) sowie drei Gruppen mit Hypertonie verschiedenen Alters (modifiziert aus: Luscher TF, Mahfoud F. Renal nerve ablation after SYMPLICITY HTN-3: confused at the higher level? Eur Heart J. 2014;35(26):1706–11; Nachdruck mit Genehmigung; nach [3]).
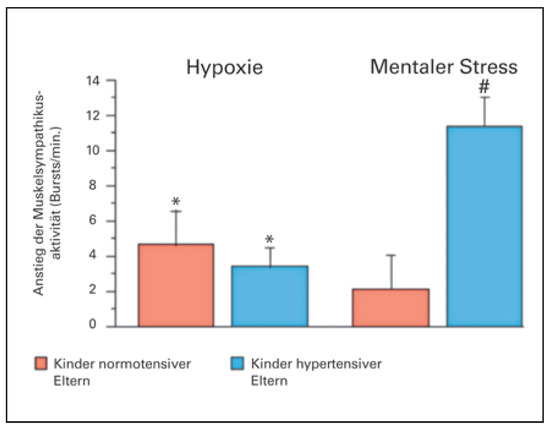
Figure 3.
Symypathikus-Aktivierung durch Hypoxie (Atmen von Stickstoff; links) oder durch einen mentalen Rechen-stresstest (rechts). Bei Kindern von Hypotonikern bzw. Normotonikern (modifiziert aus: Noll G, Wenzel RR, Schneider M, Oesch V, Binggeli C, Shaw S, Weidmann P, Luscher TF. Increased activation of sympathetic nervous system and endothelin by mental stress in normotensive offspring of hypertensive parents. Circulation. 1996;93(5):866–9. Website: https://www.ahajournals.org/journal/circ; Nachdruck mit Genehmigung).
Sympatholytische Antihypertensiva
Auch einige Antihypertensiva interferieren mit dem Sympathikus: Reserpin, das im zentralen Nervensystem und im postganglionären Sympathikus zu einer Abnahme der Katecholaminkonzentration führt, war kombiniert mit einem Diuretikum das erste Antihypertensivum, das in den paradigmatischen Trials von Edward Fries nicht nur den Blutdruck senkte, sondern auch die Mortalität reduzierte [6,7].
Der alpha-2-adrenerge Rezeptoragonist Clonidin hemmt im Mittelhirn, den Basalganglien und den peripheren Nerven die Freisetzung von Noradrenalin, wird jedoch trotz seiner guten antihypertensiven Wirksamkeit aufgrund verschiedener Nebenwirkungen kaum mehr verwendet [8].
Der selektive I1-imidazolin-Agonsist Moxonidin reduziert die direkt gemessene Muskelsympathikusaktivität im Nervus peronaeus [9], die Plasma-Noradrenalin- und Adrenalin-Spiegel und den Blutdruck, sowohl unter Ruhebedingungen als auch unter mentalem Stress [10]. Eine klinische Outcome-Studie mit Moxonidin wurde nicht durchgeführt; allerdings ergab die MOXCON-Studie bei Patienten mit Herzinsuffizienz überraschenderweise trotz Senkung der Katecholaminspiegel im Blut eine erhöhte Mortalität in der Aktivgruppe [11]. Die Ursachen für diesen Befund blieben unklar.
Methyldopa ist eine weiteres Antihypertensivum, das mit dem Sympathikus, als False Transmitter, mit der Synthese des Neuotransmitters Noradrenalin interferiert und so den Blutdruck senkt. Aufgrund seiner breiten Wirkung im sympathischen Nervensystem ist Methyldopa mit einer Reihe von Nebenwirkungen verbunden, was seine Verwendbarkeit, ausser aufgrund seiner fehlenden Teratogenität bei Schwangerschahs-hypertonie [12], stark eingeschränkt hat.
Betablocker sind ebenfalls Antihypertensiva, die wenigstens teilweise den Blutdruck über eine Aktivierung der sympathischen Betarezeptoren in den juxtaglome-rulären Zellen hemmen und die Reninproduktion vermindern. Bei Patienten mit Herzinsuffizienz hemmt der nicht-selektive Betablocker Carvedilol, aber nicht der selektive β1-Rezeptor-Antagonist Metoprolol die Sympa-thikusaktivität [13].
Betablocker gehören auch in den neusten ESC-Guide-lines zu den fünf Antihypertensiva mit in Plazebo-kont-rollierten Studien nachgewiesener Reduktion kardio-vaskulärer Ereignisse [14].
Warum lernen wir von diesen Daten so wenig für die Nierennervenablation? Weil diese Medikamente nicht selektiv den Nierensympathikus beeinflussen und weil die allermeisten Patienten 2–3 Antihypertensiva einnehmen und einige davon, insbesondere die Kalzi-umantagonisten, den Sympathikus markant stimulieren [15,16,17], was die Wirkung der Sympathikolytika zumindest teilweise auLebt.
Die perkutane Nierennervenablation
Aufgrund der zentralen Rolle der Niere in der Langzeit-regulation des Blutdrucks und der Nebenwirkungen einer unselektiven Sympathikusblockade war es naheliegend zu versuchen, selektiv die sympathischen Nerven, die sich in der Nähe und um die Nierenarterien befinden, mittels einer katheterbasierten Technologie zu zerstören. Radiofrequenzenergie wurde bereits erfolgreich bei Patienten mit Rhythmusstörungen wie AV-Reentry, WPW-Syndrom oder später Vorhoffiimmern erfolgreich eingesetzt. Und in der Tat zeigten erste Proof-of-Concept-Studien, dass die Nierennerve-nablation mit Radiofrequenzenergie bei Patienten mit hohem Blutdruck die Sympathikusaktivierung in Nervus peroneus wie auch die Katecholaminspiegel und zuletzt den Blutdruck senkt [18].
Eine erste grössere Registerstudie bestätigte die initialen Befunde an wenigen Patienten in einem grösseren Kollektiv [19]. In der Folge wurde eine randomisierte prospektive, allerdings nicht Sham-kontrollierte Studie durchgeführt und bestätigte vollumfänglich die initialen Registerdaten mit einem beeindrucken Blutdruckbfall von 32/12 mm Hg bei den behandelten Patienten [20]. Besonders beeindruckend war damals die Tatsache, dass die Wirkung der Nierennerven-ablation nicht unmittelbar einsetzte, sondern dass sich der Blutdruck langsam über Wochen bis 6 Monate später, in den Follow-up-Studien bis über 3 Jahre, um 32/14 mm Hg senkte [21].
Hype und Ernüchterung
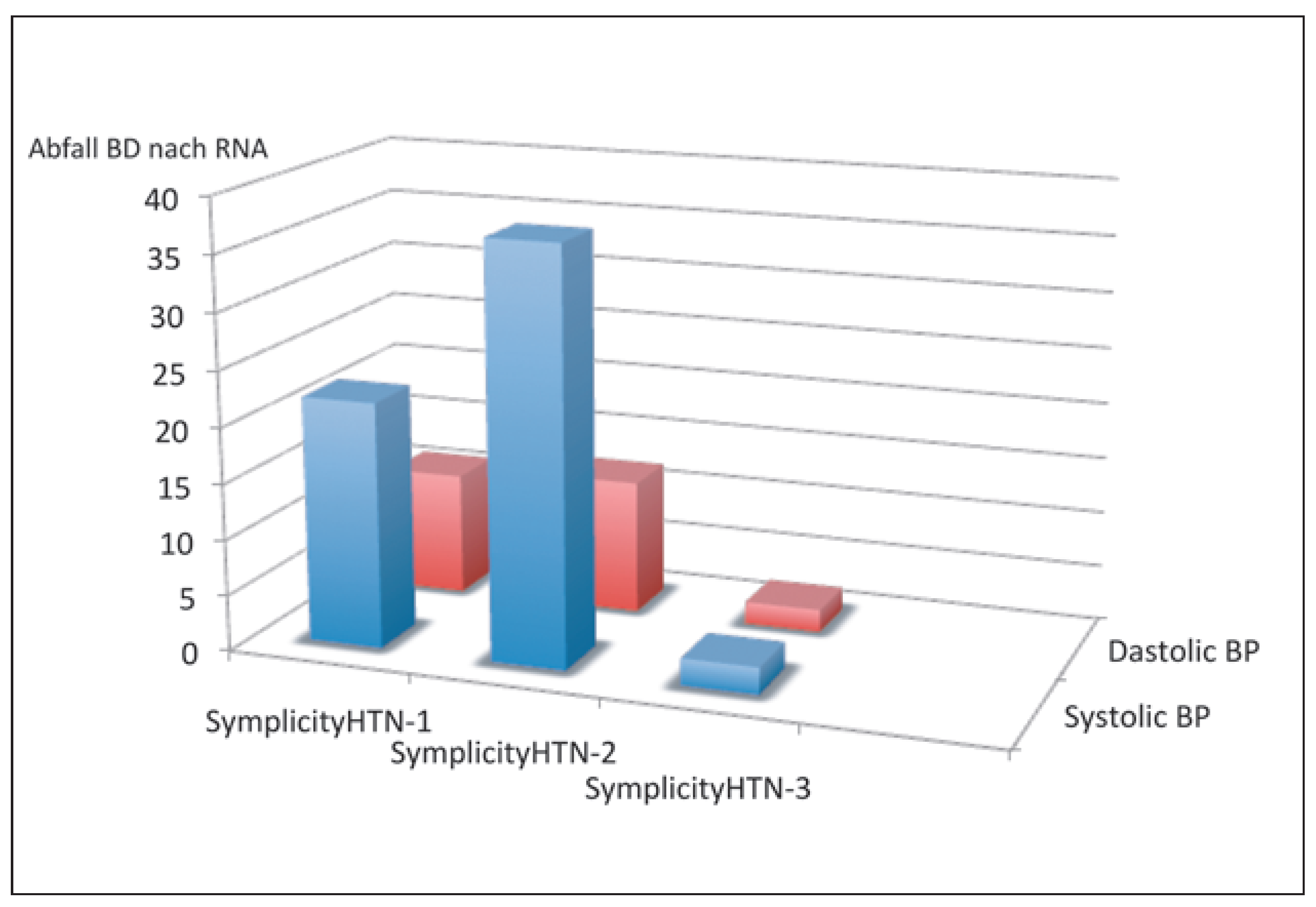
Nach dem Hype kam alsbald die Ernüchterung durch die Publikation von SIMPLICITY HTN-3 im Jahre 2014 im New England Journal of Medicine (Figure 4) [22]. Diese rigoros geplante doppelblinde Sham-kontrollierte Studie an 535 Patienten mit therapieresistenter Hypertonie und im Mittel 5 Antihypertensiva konnte entgegen allen Erwartungen keinerlei Wirksamkeit der Nierennervenablation nachgewiesen werden. Das Medienecho war entsprechend und Patientenzuweisungen gingen auf ein Minimum zurück.
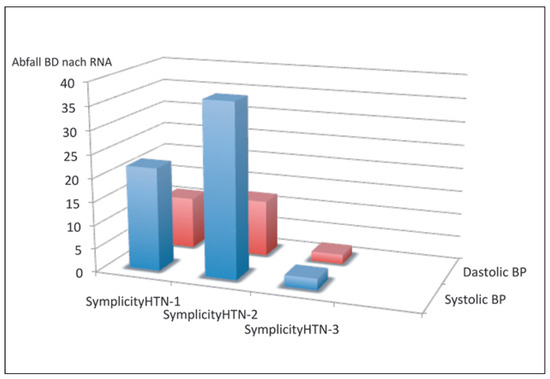
Figure 4.
Blutdrucksenkung durch eine Nierennervenablation mit dem Symplicity Single Elektrode Nierennerven Ablationskatheter in einem Register (SYMPLICITY HTN-1), sowie in zwei randomisieren Studien mit Sham-Kontrolle (SYMPLICITY HTN-3 bzw. SYMPLICITY HTN-2) (aus: Luscher TF, Mahfoud F. Renal nerve ablation after SYMPLIC-ITY HTN-3: confused at the higher level? Eur Heart J. 2014;35(26):1706–11; Nachdruck mit Genehmigung).
Die Studie wurde anschliessend intensiv in der Literatur diskutiert und auch hehig kritisiert [23,24]. So wurde die Tatsache, dass die meisten Patienten bereits 5–6 Medikamente bei der Randomisierung eingenommen hatten und die Therapie bei zwei Dritteln der Patienten während der Studie geändert wurde, ebenso kritisiert wie die Tatsache, dass zwei Drittel der Patienten radiologisch nachweisbar nur wenige Ablationen erhalten hatten.
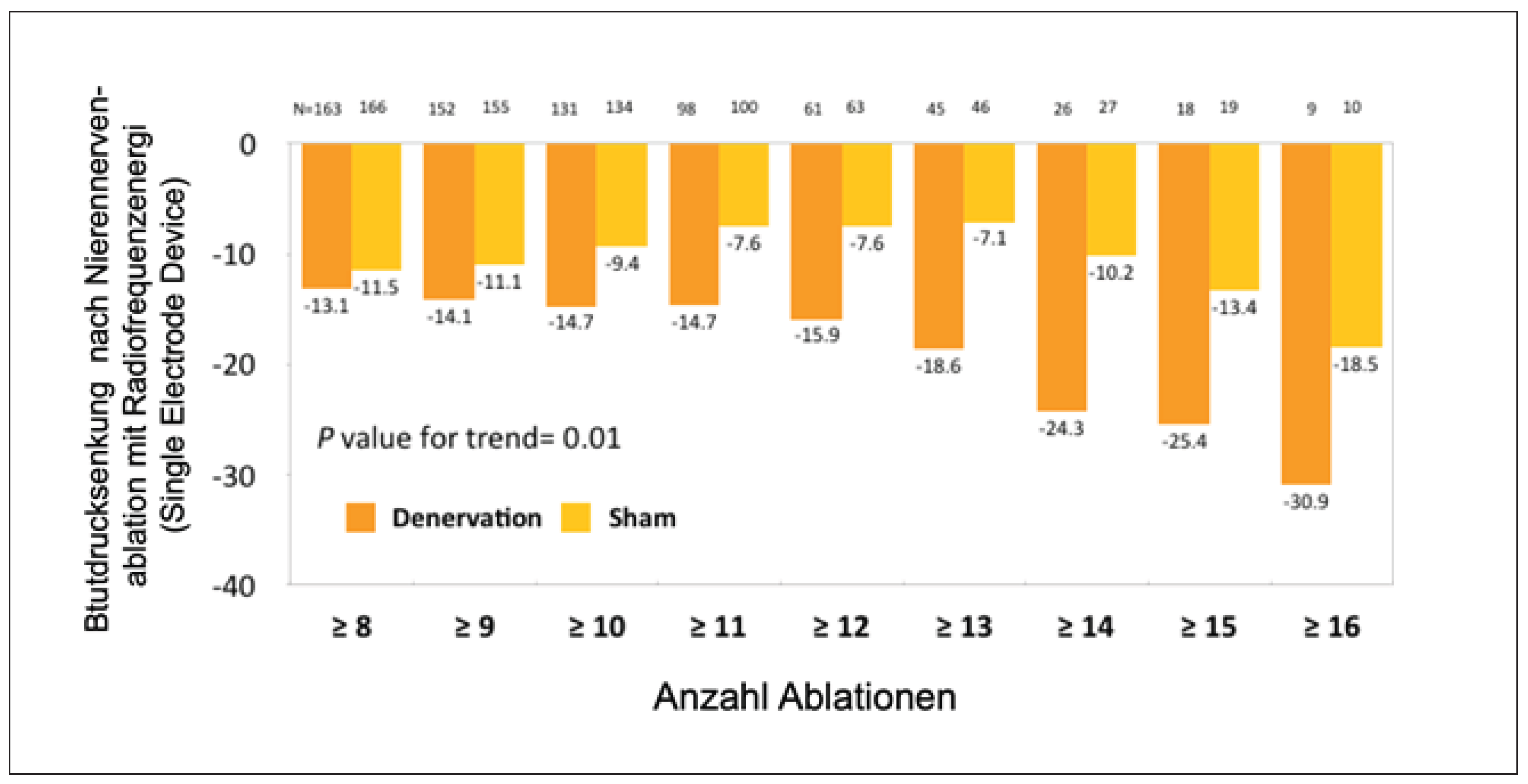
Entsprechend zeigte eine Subanalyse im European Heart Journal durch David Kandzari, dass sich bei Patienten, die 12–16 Ablationen an den Nierenarterien halten haben, doch eine signifikante Blutdrucksenkung nachweisen liess (Figure 5) [25]. Dennoch dauerte es lange, bis neue Studien durchgeführt wurden.
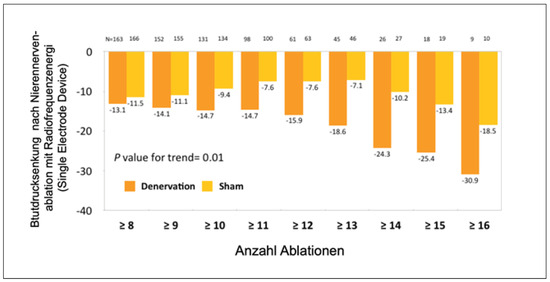
Figure 5.
Subanalyse der SYMPLICITY HTN-3 Studie entsprechend der Anzahl der durchgeführten Radiofrequenzablation in beiden Nierenarterien bei Patienten mit schwerer Hypertonie. Dargestellt ist die dosisabhängige Beziehung zwischen der Anzahl von Ablationen und der Senkung des systolischen Blutdrucks. Gleiche Ergebnisse wurden im diastolischen Bereich erhoben.
Die PRAGUE-15-Studie zeigte immerhin bei 106 Patienten mit unkontrollierter Hypertonie eine vergleichbare Wirkung der Nierennervenablation wie eine intensivierte antihypertensive Therapie [26]. Die DENTER HTN-Studie durch Michel Aziz et al. in Frankreich dokumentierte, allerdings ohne Sham-Kontrolle, erneut eine Wirksamkeit der Nierennervenabtlation sowohl im 24-Stunden-Blutdruck wie im Visitenblutdruck [27]. Doch auch diese Studie wurde aufgrund der mangelnden Sham-Kontrolle kritisiert und von der FDA nicht akzeptiert. Auch recht grosse internationale und schweizerische Registerdaten wiesen auf die Wirksamkeit der Nierennervenablation hin [28,29], konnten aber weder die Registrationsbehörden noch die Hypertensiologen überzeugen.
Phoenix steigt aus seiner Asche
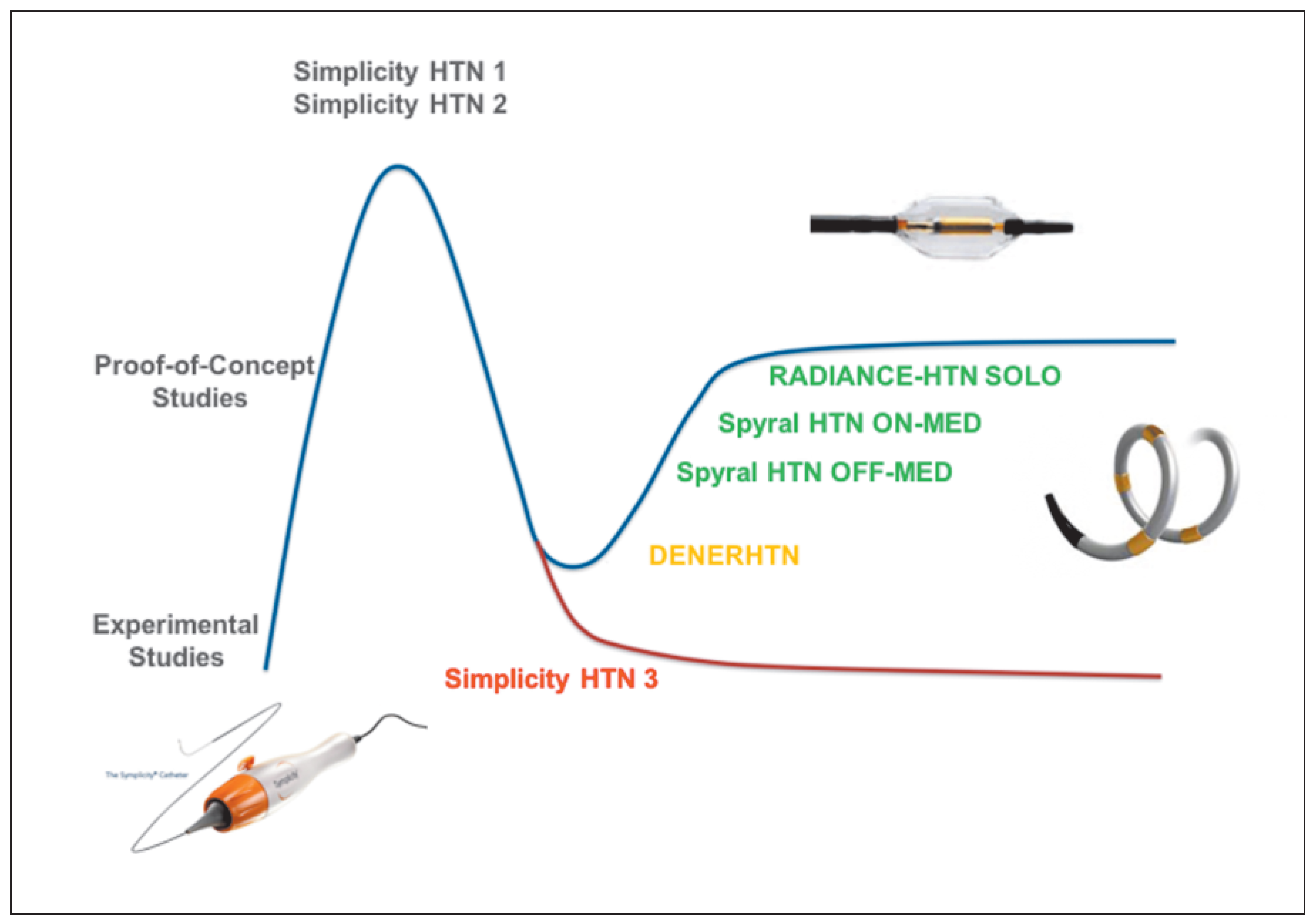
Doch nach dem Hype und der Ernüchterung stieg der Phoenix wieder aus seiner Asche empor (Figure 6): Aufgrund der Probleme mit der Medikamentenstandardi-sierung kam es dann zu einer neuen Studie mit dem neu entwickelten SPYRAL-Ablationskatheter wiederum mit Radiofrequenzenergie (SPYRAL HTN OFF MED Studie) bei unbehandelten Hypertonikern mit einem massiv erhöhten Blutdruck von 160/100 mm Hg [30]. Diese Proof-of-Concept-Studie bei Patienten ohne Antihypertensiva konnte nun zweifelsfrei zeigen, dass die Nierennervenablation den Blutdruck senkt; allerdings war die Wirkung der Intervention geringer als in den ersten Studien vermutet.
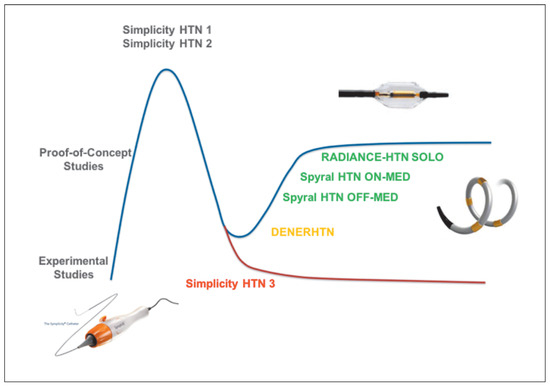
Figure 6.
Die Hype und Ernüchterungskurve in der klinischen Forschung: Nach einer ersten Phase mit überschäumendem Enthusiasmus mit experimentellen und Proof-of-Concept-Studien und anschliessend vielversprechendem Register SYMPLICITY HTN-1 und schliesslich einer ersten randomisierten Studie SYMPLICITY HTN-2 kam es mit der Publikation der SYMPLICITY HTN-3-Studie zu einer massiven Ernüchterung. Die meisten Forscher und Kliniker verliessen diese neue therapeutische Option in Forschung und Klinik. Danach kam es mit den nächsten, meistens Sham-kontrollierten Studien zu einer realistischeren Erholung auf einem tieferen Blutdrucksenkungsniveau.
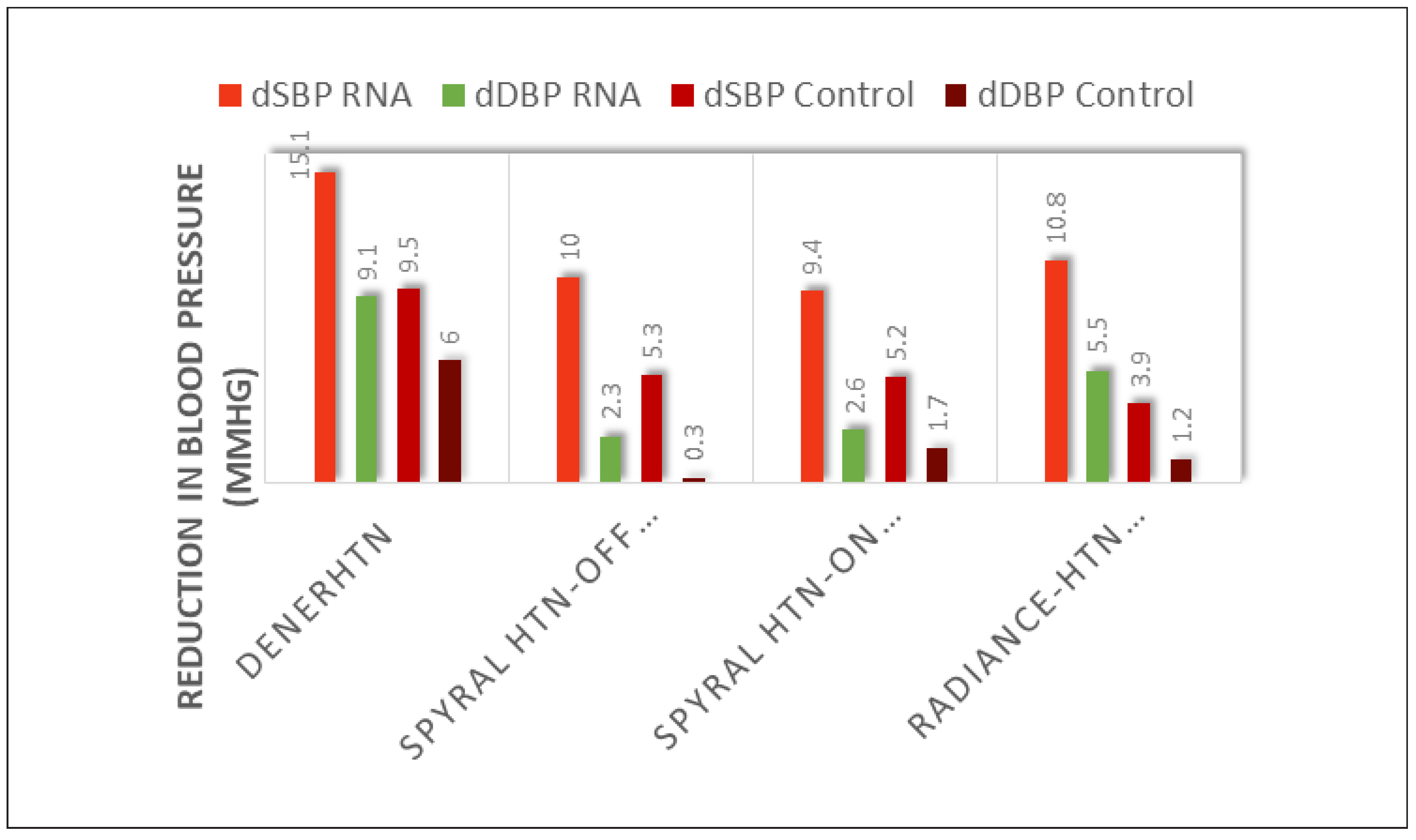
Am EuroPCR 2018 in Paris wurden am 24. Mai 2018 nun zwei zusätzliche Studien vorgestellt und gleichzeitig im Lancet publiziert, nämlich SPYRAL HTN ON MED [30] und die RADIANCE HTN SOLO [31]. Beide Studien, sowohl die erste mit Radiofrequenzenergie wie die zweite mit Ultraschallenergie, konnten erneut die Wirksamkeit der Nierennervenablation nachweisen (Figure 7).
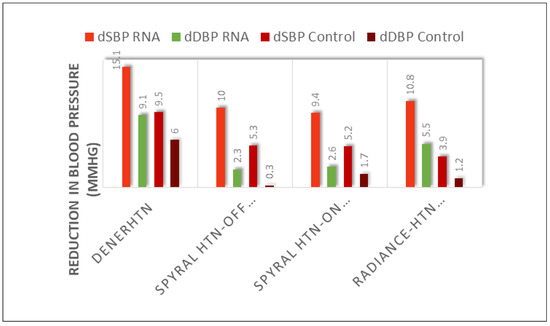
Figure 7.
Senkung des systolischen Blutdrucks in DENERHTN [15] und in den neueren Sham-kontrollierten Studien bei Patienten ohne (Spyral HTN OFF MED [17]) oder mit Antihypertensiva (Spyral HTN ON MED [18]) mit dem neuen Spyral-Radio-frequenzablationskatheter (links und Mitte). Ähnliche Ergebnisse wurden mit Ultraschallenergie erhoben (Radiance SOLO trial; rechts [19]).
Offene Fragen
Somit ist die Nierennervenablation zweifelsfrei eine mögliche antihypertensive Strategie bei gewissen Patienten. Die Fragen, die nun bleiben, sind: (1.) Welche Patientinnen und Patienten sind besonders geeignet für diese Intervention? (2.) Was sind die Langzeitwir-kungen (gibt es eine Reinnervation, gegebenenfalls Nierenarterienstenosen, die zu einer erneuten Blutdruckerhöhung führen könnten)? (3) Führt die Blutdrucksenkung durch die Nierennervenablation zu einer Reduktion kardiovaskulärer Ereignisse und ist sie gegebenenfalls sogar wirksamer als die gegenwärtig verwendeten Medikamente?
Was die Patientenauswahl betrifft, so zeigte sich in verschiedenen Untersuchungen, dass Patienten mitisolierter systolischer Hypertonie für eine Nierennervenablation weniger geeignet sind, da diese Form des Blutdrucks vor allem durch Veränderungen der Elastitizität der Überleitungsgefässe mit Verlust des Windkesseleffekts im Alter bedingt ist.
Weiter scheint die Subanalyse der bisherigen Studien nahezulegen, dass übergewichtige Patienten, die bekanntermassen eine Aktivierung des sympathischen Nervensystems aufweisen [32], etwas besser ansprechen als normalgewichtige Hypertoniker.
Ob die Afro-Amerikaner, die typischerweise eine volumenabhängige Low-Renin-Hypertension aufweisen, weniger gut ansprechen, ist im Moment nicht sicher beantwortbar.
Langzeitergebnisse
Langzeitergebnisse sind nur von der nicht Sham-kontrollierten Simplicity-HTN-2-Studie über 3 Jahre verfügbar [21], während die neueren Studien nur 3–6 Monate Beobachtungszeiten nachweisen können. Die Langzeitergebnisse werden vor allem aus zwei Gründen diskutiert, nämlich (1.) der Möglichkeit einer Reinervation, wie sie bei Patienten nach Herzoder Nierentransplantation in einem gewissen Prozentsatz auhritt [33], und (2.) der Möglichkeit von Nierenarterienstenosen aufgrund der Ablation, vor allem in den kleinen Seitengefässen der Nierenarterien. Beide Möglichkeiten konnten bisher noch nicht ausgeschlossen werden, obgleich bisher die Häufigkeit dieser Komplikationen in kleineren kontrollierten Untersuchungen äusserst gering erscheint [34].
Nierennervenablation und Outcome
Zuletzt ist die Frage zu beantworten, und solche Studien befinden sich im Moment in der Planung, ob eine Nierennervenablation auch kardiovaskuläre Ereignisse wie Hospitalisationen für Hochdruck oder Herzinsuffizienz bzw. Herzinfarkt, Hirnschlag und Tod vermindert. Die Auswertung der letzten beiden oben genannten Studien zeigte eine anhaltende über 24 Stunden gleichmässig nachweisbare Blutdrucksen-kung nach Nierennervenablation. Dies könnte sich gegenüber Medikamenten, vor allem solchen mit kurzer Halbwertszeit, sowie bei Patienten mit schlechter Compliance als Vorteil erweisen. In der Tat konnte kürzlich eine Untersuchung im European Heart Journal zeigen, dass die Visit-to-Visit-Blutdruckveränderung bei Patienten mit einem erhöhten kardiovaskulären Risiko assoziiert ist [35].
Disclosure statement
Der Autor wurde durch Forschungsgrants von Boston Scientific und Medtronic, sowie Educational Grants von St. Jude Medical (nun Abbott Inc.) unterstützt.
References
- Smithwick, R.H.T.J.E. Surgical sympathectomy in hypertension. JAMA. 1953, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Parati, G.; Esler, M. The human sympathetic nervous system: its ­relevance in hypertension and heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2012, 33, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Esler, M.; Lambert, G.; Jennings, G. Increased regional sympathetic nervous activity in human hypertension: causes and consequences. Journal of hypertension Supplement: official journal of the International Society of Hypertension 1990, 8, S53–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noll, G.; Wenzel, R.R.; Schneider, M.; Oesch, V.; Binggeli, C.; Shaw, S.; Weidmann, P.; Luscher, T.F. Increased activation of sympathetic nervous system and endothelin by mental stress in normotensive offspring of hypertensive parents. Circulation. 1996, 93, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieker, L.E.; Hurlimann, D.; Ruschitzka, F.; Corti, R.; Enseleit, F.; Shaw, S.; Hayoz, D.; Deanfield, J.E.; Luscher, T.F.; Noll, G. Mental stress induces prolonged endothelial dysfunction via endothelin-A receptors. Circulation. 2002, 105, 2817–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effects of treatment on morbidity in hypertension. Results in patients with diastolic blood pressures averaging 115 through 129 mm Hg. JAMA. 1967, 202, 1028–1034. [CrossRef]
- Effects of treatment on morbidity in hypertension. II. Results in patients with diastolic blood pressure averaging 90 through 114 mm Hg. JAMA. 1970, 213, 1143–1152. [CrossRef]
- Krieger, E.M.; Drager, L.F.; Giorgi, D.M.A.; Pereira, A.C.; Barreto-Filho, J.A.S.; Nogueira, A.R.; Mill, J.G.; Lotufo, P.A.; Amodeo, C.; Batista, M.C.; et al. Spironolactone Versus Clonidine as a Fourth-Drug Therapy for Resistant Hypertension: The ReHOT Randomized Study (Resistant Hypertension Optimal Treatment). Hypertension. (Dallas, Tex: 1979) 2018, 71, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.R.; Spieker, L.; Qui, S.; Shaw, S.; Luscher, T.F.; Noll, G. I1-imidazoline agonist moxonidine decreases sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in hypertensives. Hypertension. (Dallas, Tex: 1979) 1998, 32, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.R.; Mitchell, A.; Siffert, W.; Buhrmann, S.; Philipp, T.; Schafers, R.F. The I1-imidazoline agonist moxonidine decreases sympathetic tone under physical and mental stress. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004, 57, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, J.N.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Rouleau, J.; Sharpe, N.; Swedberg, K.; Straub, M.; Wiltse, C.; Wright, T.J. Adverse mortality effect of central sympathetic inhibition with sustained-release moxonidine in patients with heart failure (MOXCON). Eur J Heart Fail. 2003, 5, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeltzenbein, M.; Beck, E.; Fietz, A.K.; Wernicke, J.; Zinke, S.; et al. Pregnancy Outcome After First Trimester Use of Methyldopa: A Prospective Cohort Study. Hypertension. 2017, 70, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, E.R.; Kubo, T.; Mak, S.; Al-Hesayen, A.; Schofield, A.; Allan, R.; Kelly, S.; Newton, G.E.; Floras, J.S.; Parker, J.D. Nonselective versus selective beta-adrenergic receptor blockade in congestive heart failure: differential effects on sympathetic activity. Circulation. 2001, 104, 2194–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.R.; Allegranza, G.; Binggeli, C.; Shaw, S.; Weidmann, P.; Luscher, T.F.; Noll, G. Differential activation of cardiac and peripheral sympathetic nervous system by nifedipine: role of pharmacokinetics. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997, 29, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noll, G.; Wenzel, R.R.; Shaw, S.; Luscher, T.F. Calcium antagonists and sympathetic nerve activation: are there differences between classes? Journal of hypertension Supplement: official journal of the International Society of Hypertension 1998, 16, S17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Binggeli, C.; Corti, R.; Sudano, I.; Luscher, T.F.; Noll, G. Effects of chronic calcium channel blockade on sympathetic nerve activity in hypertension. Hypertension. (Dallas, Tex: 1979) 2002, 39, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaich, M.P.; Sobotka, P.A.; Krum, H.; Lambert, E.; Esler, M.D. Renal sympathetic-nerve ablation for uncontrolled hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2009, 361, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krum, H.; Schlaich, M.; Whitbourn, R.; Sobotka, P.A.; Sadowski, J.; Bartus, K.; Kapelak, B.; Walton, A.; Sievert, H.; Thambar, S.; et al. Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension: a multicentre safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet. 2009, 373, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esler, M.D.; Krum, H.; Sobotka, P.A.; Schlaich, M.P.; Schmieder, R.E.; Bohm, M. Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010, 376, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Krum, H.; Schlaich, M.P.; Sobotka, P.A.; Bohm, M.; Mahfoud, F.; Rocha-Singh, K.; Katholi, R.; Esler, M.D. Percutaneous renal denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension: final 3-year report of the Symplicity HTN-1 study. Lancet. 2014, 383, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Kandari, D.E.; O’Neill, W.W.; D’Agostino, R.; Flack, J.M.; Katzen, B.T.; Leon, M.B.; Liu, M.; Mauri, L.; Negoita, M.; et al. A controlled trial of renal denervation for resistant hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2014, 370, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luscher, T.F.; Mahfoud, F. Renal nerve ablation after SYMPLICITY HTN-3: confused at the higher level? Eur Heart J. 2014, 35, 1706–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoud, F.; Luscher, T.F. Renal denervation: symply trapped by complexity? Eur Heart J. 2015, 36, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kandzari, D.E.; Bhatt, D.L.; Brar, S.; Devireddy, C.M.; Esler, M.; Fahy, M.; Flack, J.M.; Katzen, B.T.; Lea, J.; Lee, D.P.; et al. Predictors of blood pressure response in the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial. Eur Heart J. 2015, 36, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosa, J.; Widimsky, P.; Tousek, P.; Petrak, O.; Curila, K.; Waldauf, P.; Bednar, F.; Zelinka, T.; Holaj, R.; Strauch, B.; et al. Randomized comparison of renal denervation versus intensified pharmacotherapy including spironolactone in true-resistant hypertension: six-month results from the Prague-15 study. Hypertension. (Dallas, Tex: 1979) 2015, 65, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azizi, M.; Sapoval, M.; Gosse, P.; Monge, M.; Bobrie, G.; Delsart, P.; Midulla, M.; Mounier-Vehier, C.; Courand, P.Y.; Lantelme, P.; et al. Optimum and stepped care standardised antihypertensive treatment with or without renal denervation for resistant hypertension (DENERHTN): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015, 385, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, M.; Mahfoud, F.; Ukena, C.; Hoppe, U.C.; Narkiewicz, K.; Negoita, M.; Ruilope, L.; Schlaich, M.P.; Schmieder, R.E.; Whitbourn, R.; et al. First report of the Global SYMPLICITY Registry on the effect of renal artery denervation in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Hypertension. (Dallas, Tex: 1979) 2015, 65, 766–774. [Google Scholar]
- Denegri, A.; Naduvathumuriyil, T.; Luscher, T.F.; Sudano, I. Renal nerve ablation reduces blood pressure in resistant hypertension: Long-term clinical outcomes in a single-center experience. J Clin Hypertens. (Greenwich, Conn) 2018, 20, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, R.R.; Mahfoud, F.; Kandzari, D.E.; Kario, K.; Pocock, S.; Weber, M.A.; Ewen, S.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D.; Sharp, A.S.P.; et al. Catheter-based renal denervation in patients with uncontrolled hypertension in the absence of antihypertensive medications (SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED): a randomised, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept trial. Lancet. (London, England) 2017, 390, 2160–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Schmieder, R.E.; Mahfoud, F.; Weber, M.A.; Daemen, J.; Davies, J.; Basile, J.; Kirtane, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Lobo, M.D.; et al. Endovascular ultrasound renal denervation to treat hypertension (RADIANCE-HTN SOLO): a multicentre, international, single-blind, randomised, sham-controlled trial. The Lancet. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, M.E. Obesity-induced hypertension: interaction of neurohumoral and renal mechanisms. Circulation research 2015, 116, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupper, A.; Gewirtz, H.; Kushwaha, S. Reinnervation post-heart transplantation. Eur Heart J. 2018, 39, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, T.; Nahler, A.; Reiter, C.; Schwarz, S.; Gammer, V.; Blessberger, H.; Kammler, J.; Saleh, K.; Grund, M.; Steinwender, C. Frequency of renal artery stenosis after renal denervation in patients with resistant arterial hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 2015, 115, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlum, M.H.; Liestol, K.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Julius, S.; Hua, T.A.; Rothwell, P.M.; Mancia, G.; Parati, G.; Weber, M.A.; Berge, E. Blood pressure variability and risk of cardiovascular events and death in patients with hypertension and different baseline risks. Eur Heart J. 2018. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.