Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients with AAI Pacemakers for Sick Sinus Syndrome: System Upgrades and Changes in Wenckebach Block Point Behaviour
Abstract
- 1
- AAI Pacemaker with atrial sensing, atrial pacing and inhibition mode
- 2
- DDD Pacemaker with atrial and ventricular sensing, atrial and ventricular pacing and inhibition as well as triggered mode.
Methods
Results
Discussion
Main findings
- 3
- VVI Pacemaker with ventricular sensing, ventricular pacing and inhibition mode
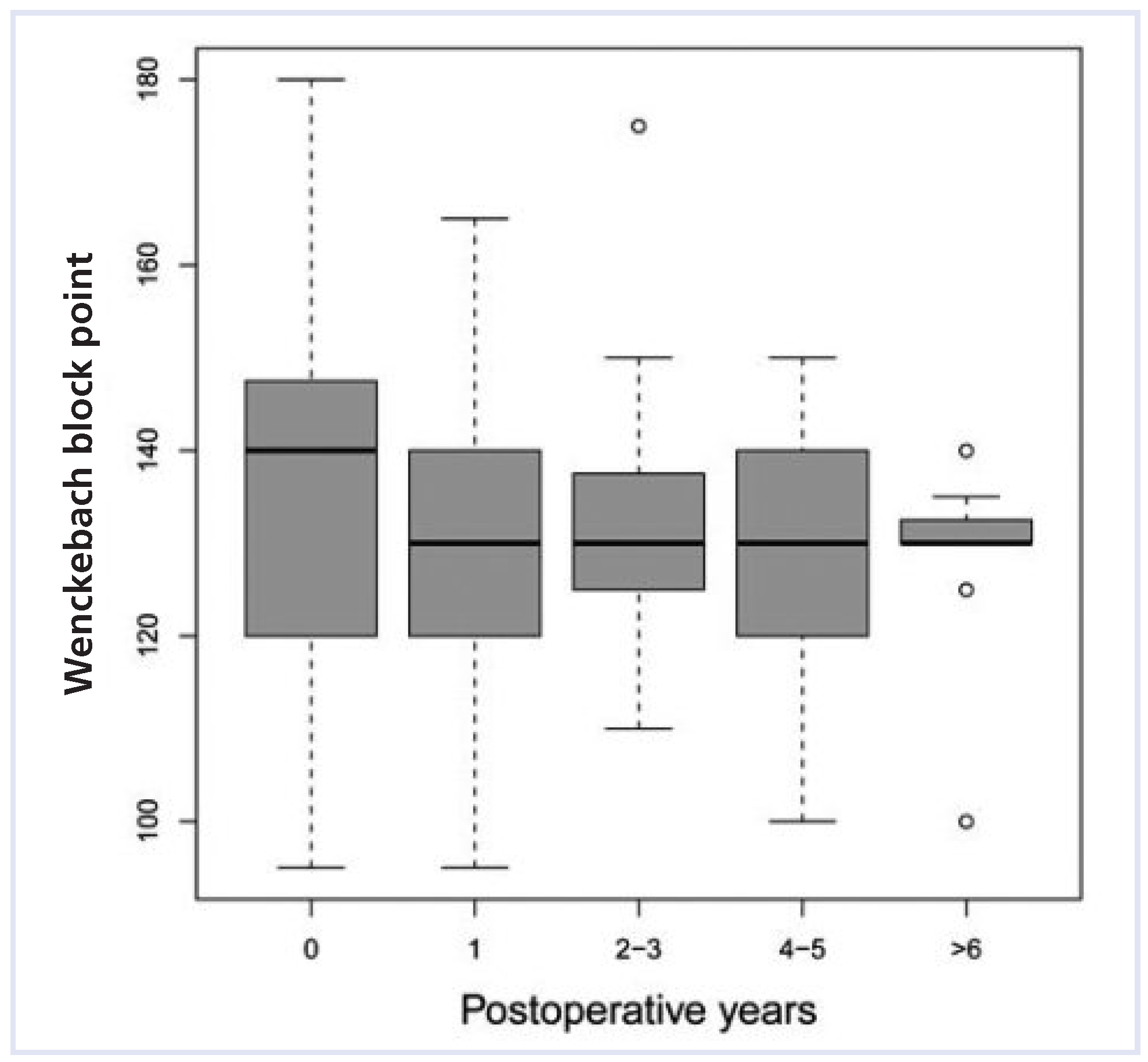
Wenckebach block point behaviour over time
Upgrade rate
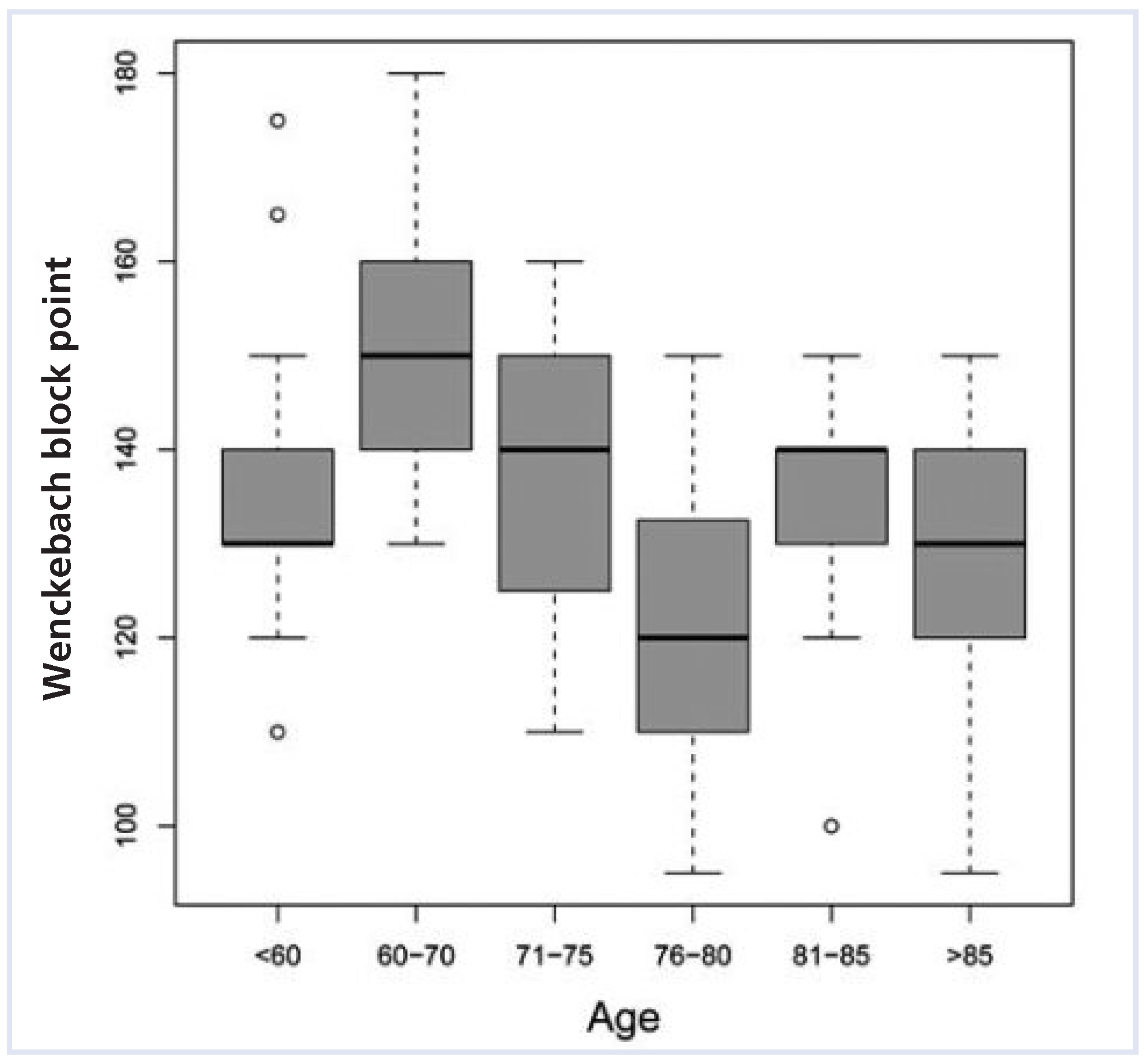
Predictors for occurrence of AV block during follow-up
Funding/potential competing interests
References
- Epstein, A.E.; DiMarco, J.P.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Estes, N.A., 3rd.; Freedman, R.A.; Gettes, L.S.; et al. ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 Guidelines for Device-Based Therapy of Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the ACC/AHA/NASPE 2002 Guideline Update for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices): developed in collaboration with the American Association for Thoracic Surgery and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation 2008, 117, e350–e408. [Google Scholar]
- Lemke, B.; Nowak, B.; Pfeiffer, D. Leitlinien zur Herzschrittmachertherapie. Z Kardiol. 2005, 94, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, H.R.; Nielsen, J.C.; Thomsen, P.E.; Thuesen, L.; Mortensen, P.T.; Vesterlund, T.; et al. Long-term follow-up of patients from a randomised trial of atrial versus ventricular pacing for sick-sinus syndrome. Lancet 1997, 350, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertsen, A.E.; Nielsen, J.C. Selecting the appropriate pacing mode for patients with sick sinus syndrome: evidence from randomized clinical trials. Card Electrophysiol Rev. 2003, 7, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.O.; Bank, A.J.; Nsah, E.; Koullick, M.; Zeng, Q.C.; Hettrick, D.; et al. Minimizing ventricular pacing to reduce atrial fibrillation in sinusnode disease. N Engl J Med. 2007, 357, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masumoto, H.; Ueda, Y.; Kato, R.; Usui, A.; Maseki, T.; Takagi, Y.; et al. Longterm clinical performance of AAI pacing in patients with sick sinus syndrome: a comparison with dual-chamber pacing. Europace 2004, 6, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, H.J.; Gammage, M.D.; Griffith, M.J. AAI pacing for sick sinus syndrome: first choice on all counts. Heart 1998, 80, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, K.W.; Connelly, D.T.; Charles, R.G. Single chamber atrial pacing: an underused and cost-effective pacing modality in sinus node disease. Heart 1998, 80, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, I.G.; Armstrong, G.P.; Stewart, J.T.; Hood, M.A.; Smith, W.M. Atrial pacing should be used more frequently in sinus node disease. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2005, 28, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, H.R.; Nielsen, J.C.; Thomsen, P.E.; Thuesen, L.; Vesterlund, T.; Pedersen, A.K.; et al. Atrioventricular conduction during long-term followup of patients with sick sinus syndrome. Circulation 1998, 98, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenqvist, M.; Obel, I.W. Atrial pacing and the risk for AV block: is there a time for change in attitude? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1989, 12, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- http://www.pacemaker.ch/de/statistik/statistik_2008.asp (downloaded on 31st October 2009).
- Connolly, S.J.; Kerr, C.R.; Gent, M.; Roberts, R.S.; Yusuf, S.; Gillis, A.M.; et al. Effects of physiologic pacing versus ventricular pacing on the risk of stroke and death due to cardiovascular causes. Canadian Trial of Physiologic Pacing Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2000, 342, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J.C.; Kristensen, L.; Andersen, H.R.; Mortensen, P.T.; Pedersen, O.L.; Pedersen, A.K. A randomized comparison of atrial and dual-chamber pacing in 177 consecutive patients with sick sinus syndrome: echocardiographic and clinical outcome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003, 42, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkoff, B.L.; Cook, J.R.; Epstein, A.E.; Greene, H.L.; Hallstrom, A.P.; Hsia, H.; et al. Dual-chamber pacing or ventricular backup pacing in patients with an implantable defibrillator: the Dual Chamber and VVI Implantable Defibrillator (DAVID) Trial. JAMA 2002, 288, 3115–3123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santini, M.; Alexidou, G.; Ansalone, G.; Cacciatore, G.; Cini, R.; Turitto, G. Relation of prognosis in sick sinus syndrome to age, conduction defects and modes of permanent cardiac pacing. Am J Cardiol. 1990, 65, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, M.; Igawa, O.; Yano, A.; Miake, J.; Inoue, Y.; Ogura, K.; et al. Longterm reliability of AAI mode pacing in patients with sinus node dysfunction and low Wenckebach block rate. Europace 2008, 10, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.; Nielsen, J.C.; Pedersen, A.K.; Mortensen, P.T.; Andersen, H.R. AV block and changes in pacing mode during long-term follow-up of 399 consecutive patients with sick sinus syndrome treated with an AAI/ AAIR pacemaker. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2001, 24, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, G.A.; Ward, J.; Ward, D.E.; Camm, A.J. Atrioventricular Wenckebach point and progression to atrioventricular block in sinoatrial disease. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1990, 13, 2054–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2011 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Bussell, H.; Kühne, M.; Osswald, S.; Sticherling, C.; Schaer, B. Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients with AAI Pacemakers for Sick Sinus Syndrome: System Upgrades and Changes in Wenckebach Block Point Behaviour. Cardiovasc. Med. 2011, 14, 148. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2011.01589
Bussell H, Kühne M, Osswald S, Sticherling C, Schaer B. Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients with AAI Pacemakers for Sick Sinus Syndrome: System Upgrades and Changes in Wenckebach Block Point Behaviour. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2011; 14(5):148. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2011.01589
Chicago/Turabian StyleBussell, Hannah, Michael Kühne, Stefan Osswald, Christian Sticherling, and Beat Schaer. 2011. "Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients with AAI Pacemakers for Sick Sinus Syndrome: System Upgrades and Changes in Wenckebach Block Point Behaviour" Cardiovascular Medicine 14, no. 5: 148. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2011.01589
APA StyleBussell, H., Kühne, M., Osswald, S., Sticherling, C., & Schaer, B. (2011). Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients with AAI Pacemakers for Sick Sinus Syndrome: System Upgrades and Changes in Wenckebach Block Point Behaviour. Cardiovascular Medicine, 14(5), 148. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2011.01589




