Lipid-Lowering Therapies and Liver Enzymes
Summary
Introduction
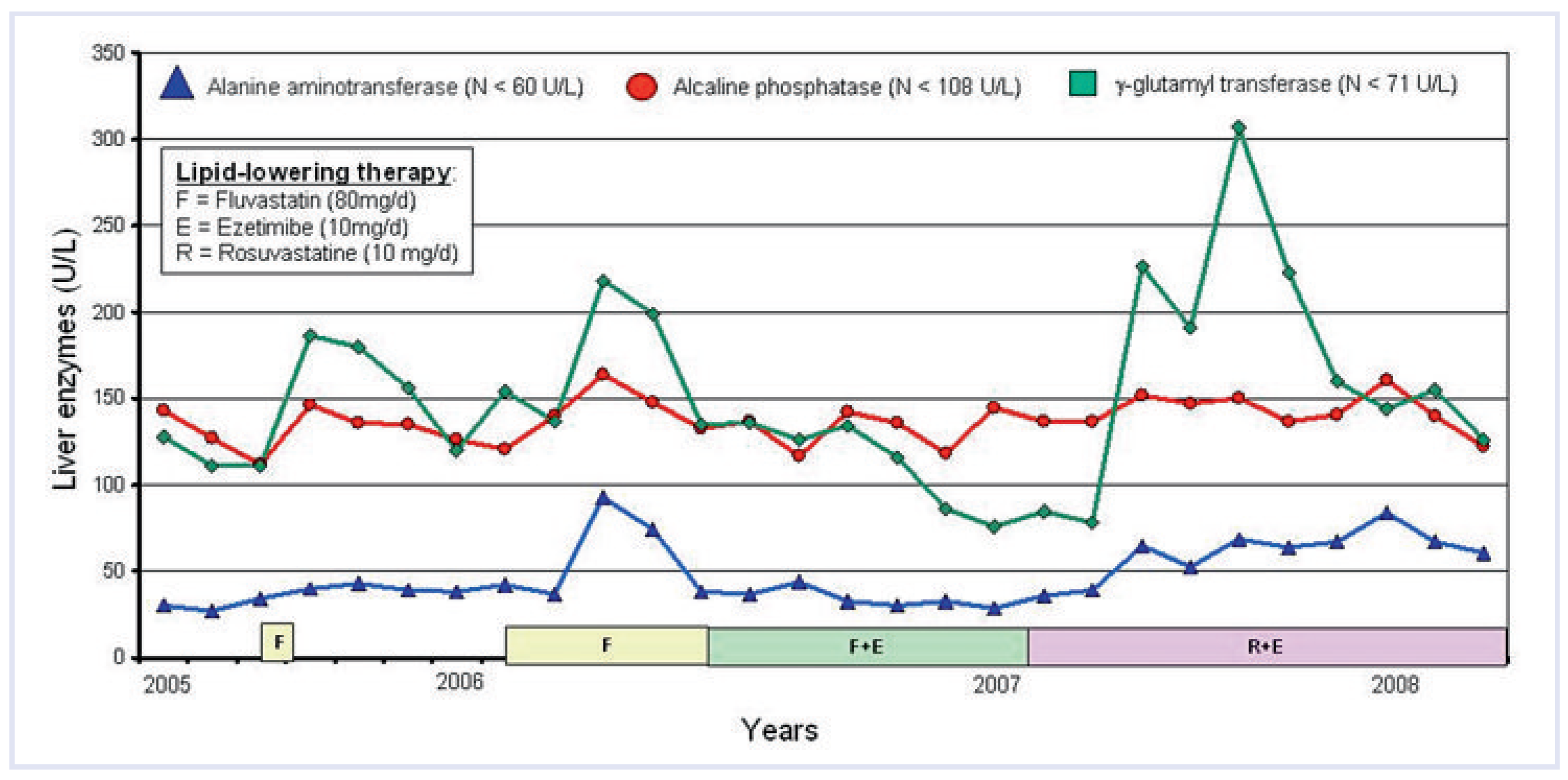
Clinical case
Treatment of dyslipidaemia and liver tests
HMGCoA reductase inhibitors (statins)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
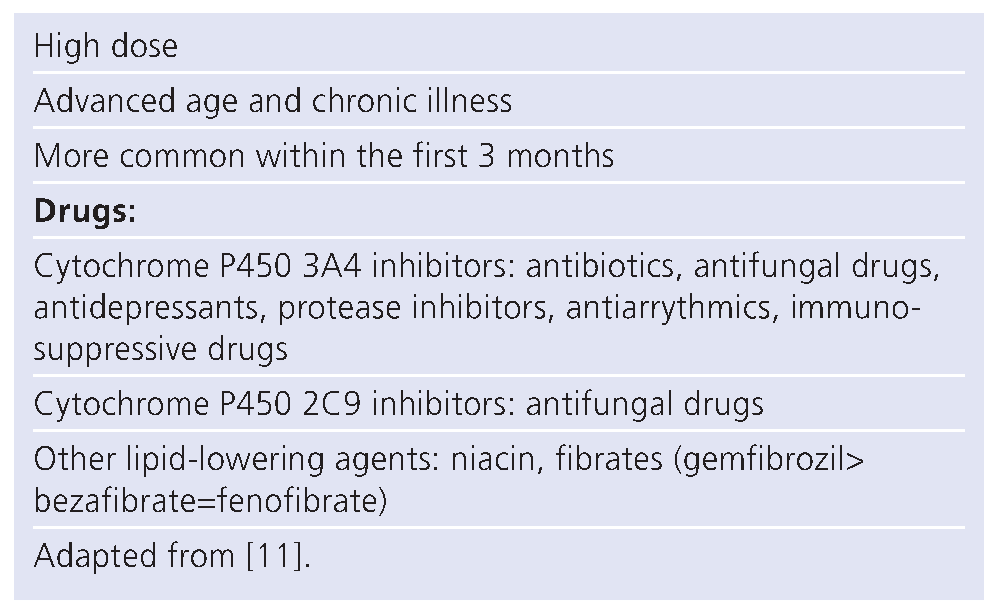
Risk factors for adverse effects of lipid-lowering agents
Statin dose
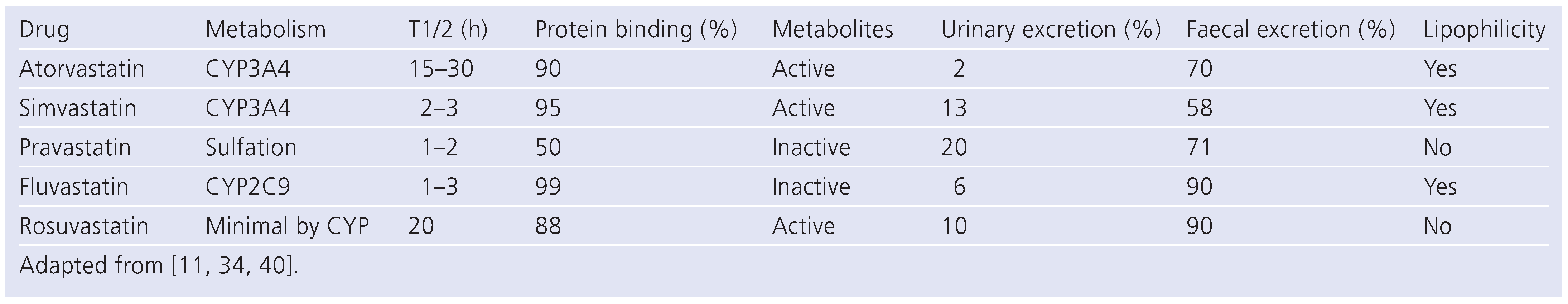
Hydrophilicity
Drug interaction (Table 4)
 |
Differences between lipid-lowering agents for effects on liver
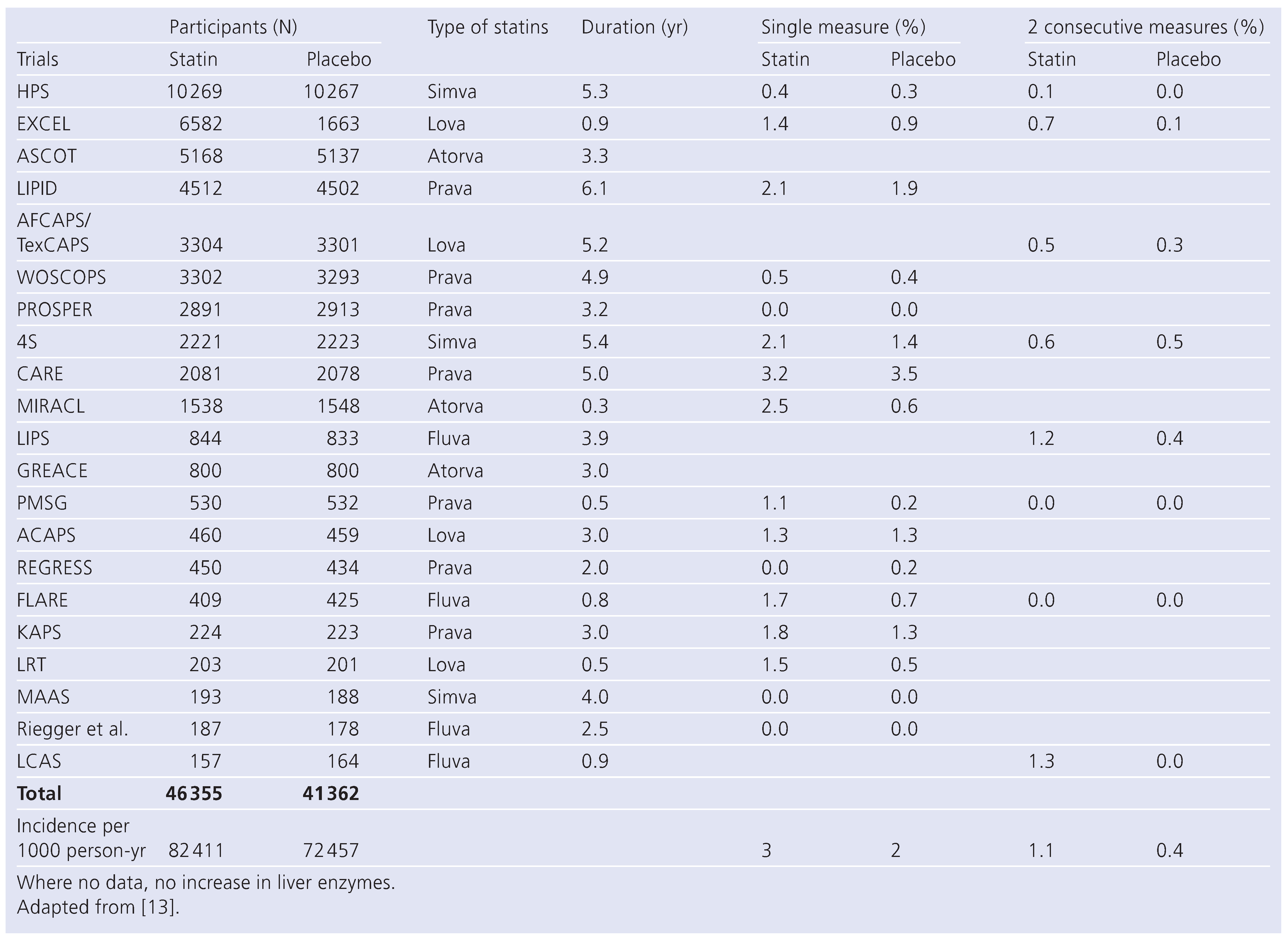
Statins
Niacin
Fibrates
Ezetimibe
Combinations
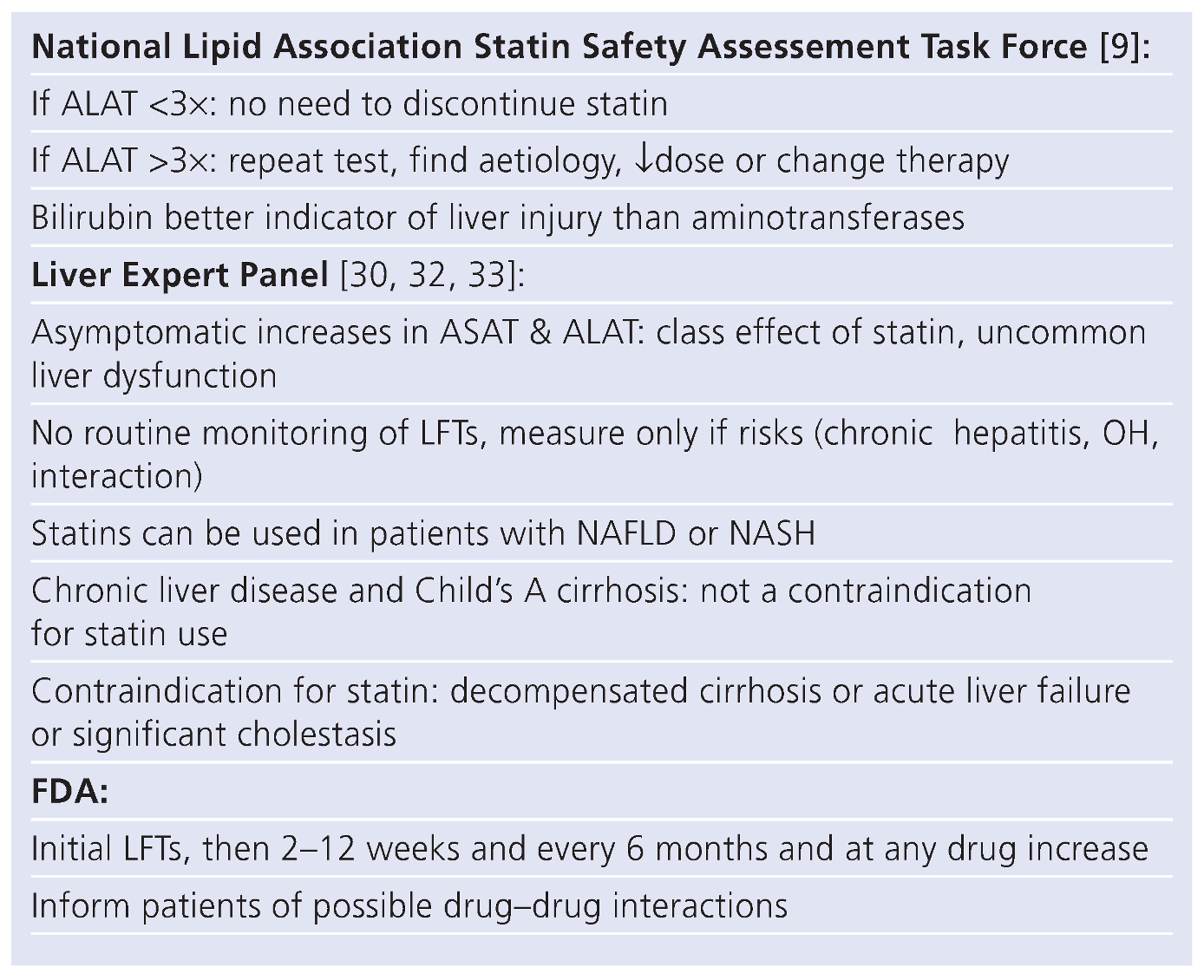
When to measure liver function tests?
Use of statins in chronic liver disease
Back to the case
Conclusion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anonymous. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: The Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet 1994, 344, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; et al. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, A.; et al. New insights into the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of statins. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 84, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, R.H.; et al. Expanded Clinical Evaluation of Lovastatin (EXCEL) study results: Two-year efficacy and safety follow-up. Am. J. Cardiol. 1994, 74, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppalanchi, R.; Chalasani, N. Statins for hyperlipidemia in patients with chronicliverdisease: Aretheysafe? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006, 4, 838–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnman, N.; Hultcrantz, R. Lipid lowering medication and hepatotoxicity. J. Intern. Med. 2001, 250, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Schiano, T.D. Review article: Drug hepatotoxicity. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 1135–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettsch, W.G.; et al. Results from a rosuvastatin historical cohort study in more than 45,000 Dutch statin users, a PHARMO study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2006, 15, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenney, J.M.; et al. Final conclusions and recommendations of the National Lipid Association Statin Safety Assessment Task Force. Am J Cardiol. 2006, 97, 89C–94C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.H.; Byrne, C.D. Current treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellosta, S.; Paoletti, R.; Corsini, A. Safety of statins: Focus on clinical pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Circulation 2004, 109 (Suppl. 1), III50–III57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, K.M.; et al. Impact of statin dosing intensity on transaminase and creatine kinase. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.; Rudnicka, A.R. Statin safety: A systematic review. Am J Cardiol. 2006, 97, 52C–60C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.; et al. Comparative safety of atorvastatin 80 mg versus 10 mg derived from analysis of 49 completed trials in 14,236 patients. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsheikh-Ali, A.A.; et al. Effect of the magnitude of lipid lowering on risk of elevated liver enzymes, rhabdomyolysis, and cancer: Insights from large randomized statin trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, T.A. Statin safety: Lessons from new drug applications for marketed statins. Am J Cardiol. 2006, 97, 44C–51C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, T.A. Comparative pharmacokinetic interaction profiles of pravastatin, simvastatin, and atorvastatin when coadministered with cytochrome P450 inhibitors. Am J Cardiol. 2004, 94, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdaas, H.; et al. Effect of fluvastatin on cardiac outcomes in renal transplant recipients: A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.D.; Clarkson, P.; Karas, R.H. Statin-associated myopathy. JAMA 2003, 289, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T.A.; et al. Safety considerations with gastrointestinally active lipidlowering drugs. Am J Cardiol. 2007, 99, 47C–55C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodis, H.N. Acute hepatic failure associated with the use of low-dose sustained-release niacin. JAMA 1990, 264, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, J.R.; Bays, H.E. Safety considerations with niacin therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2007, 99, 22C–31C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Diego Lorenzo, A.; et al. Cholestatic hepatitis caused by gemfibrozil. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2001, 93, 610–611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.Y.; et al. Fenofibrate-induced acute cholestatic hepatitis. J. Chin. MedAssoc. 2004, 67, 245–247. [Google Scholar]
- Stolk, M.F.; et al. Severe hepatic side effects of ezetimibe. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Fernandez, J.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ezetimibe co-administered with ongoing atorvastatin therapy in achieving low-density lipoprotein goal in patients with hypercholesterolemia and coronary heart disease. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2005, 59, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shek, A.; Ferrill, M.J. Statin-fibrate combination therapy. Ann. Pharmacother. 2001, 35, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cziraky, M.J.; et al. Statin safety: An assessment using an administrative claims database. Am J Cardiol. 2006, 97, 61C–68C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keech, A.; et al. Effects of long-term fenofibrate therapy on cardiovascular events in 9795 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the FIELD study): Randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.E.; Anania, F.A.; Chalasani, N. An assessment of statin safety by hepatologists. Am J Cardiol. 2006, 97, 77C–81C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/.
- Bradford, R.H.; et al. Expanded Clinical Evaluation of Lovastatin (EXCEL) study results. I. Efficacy in modifying plasma lipoproteins and adverse event profile in 8245 patients with moderate hypercholesterolemia. Arch. Intern. Med. 1991, 151, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotto, A.M., Jr. Safety and statin therapy: Reconsidering the risks and benefits. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, R.H. Drug treatment of lipid disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorashadi, S.; Hasson, N.K.; Cheung, R.C. Incidence of statin hepatotoxicity in patients with hepatitis C. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 902–907; quiz 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of high-dose pravastatin in hypercholesterolemic patients with well-compensated chronic liver disease: Results of a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; et al. Patients with elevated liver enzymes are not at higher risk for statin hepatotoxicity. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, E.F.; Georgescu, M. Therapeutic options in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Are all agents alike? Results of a preliminary study. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2007, 16, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N. Statins and hepatotoxicity: Focus on patients with fatty liver. Hepatology 2005, 41, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.; Feely, J. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic drug interactions with HMG-CoAreductase inhibitors. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 343–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 |
 |
 |
 |
© 2009 by the author. Attribution-Non-Commercial-NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Stoll, D.; Darioli, R.; Rodondi, N. Lipid-Lowering Therapies and Liver Enzymes. Cardiovasc. Med. 2009, 12, 239. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2009.01446
Stoll D, Darioli R, Rodondi N. Lipid-Lowering Therapies and Liver Enzymes. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2009; 12(9):239. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2009.01446
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoll, Delphine, Roger Darioli, and Nicolas Rodondi. 2009. "Lipid-Lowering Therapies and Liver Enzymes" Cardiovascular Medicine 12, no. 9: 239. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2009.01446
APA StyleStoll, D., Darioli, R., & Rodondi, N. (2009). Lipid-Lowering Therapies and Liver Enzymes. Cardiovascular Medicine, 12(9), 239. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2009.01446




