Abstract
The high incidence of changes in the lipid profile in the world population is supported by the adoption of a lifestyle with numerous risk factors. Dyslipidemia, the main alteration in the lipid profile, is characterized by increased concentrations of total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TG), and decreased concentration of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). These modifications in lipid metabolism are particularities of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and one of the main risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), one of the main causes of death in the world. Macroalgae have a high percentage of dietary fiber, and a low percentage of lipids. Carrageenans, long-chain polysaccharides extracted from red macroalgae, are present in several foods, such as jelly. Chemically, they present several structures with different applications and purposes in the cosmetic, food, and pharmaceutical industries. The bioactive potential of carrageenans has demonstrated potential in the reduction of the levels of parameters of the lipid profile, being able to be an alternative in the reversion of MetS and, consequently, in the prevention and treatment of CVD. This review article aims to compile, evaluate, and reflect on the effect of carrageenans on lipid profile markers (TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C), relating them to MetS and CVD.
1. Introduction
Technological evolution has led to efficient and qualified progress, with a strong impact on the institutional and social environments [1], promoting a change in life and time management. The lack of time for meals is reflected in the proliferation of fast food [2]. Professional evolution, on the other hand, favors a sedentary lifestyle. The social pressure related to the prestige of the worker led to increased productivity but also to the detriment of health [3]. As a result, pathologies such as alterations in the lipid profile, metabolic syndrome (MS), and cardiovascular diseases (CVD) arise [4].
The balance of the lipid profile is sensitive to dietary and behavioral changes and is easily modified. Lipid profile variations are characterized by the deregulation of one or more parameters: total cholesterol (TC); high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C); low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C); or triglycerides (TG). The most common alteration is an increase in TC, called hypercholesterolemia. Two of the main factors in the high number of variations in the lipid profile are sedentary habits and the abandonment of healthier and nutritionally balanced diets [4,5,6]. About 38% of American adults have high cholesterol (total blood cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL). Too much cholesterol increases the risk of heart disease and stroke, two of the leading causes of death in the United States. Based on this value, we can evaluate that 22.7% of the population has one of the main risk factors for the development of MetS and CVD [7,8,9]. A sedentary lifestyle and a poor diet favor changes in the lipid profile, the development of hypertension, weight gain and increase in abdominal circumference, as well as insulin resistance, characteristic factors of MetS [6]. Due to the complexity of MetS, different criteria allow its diagnosis, such as those defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP), and the International Diabetes Federation (IDF). The multiplicity of criteria makes it difficult to uniformly characterize, monitor, and unify the information [8]. Considering the limitations, calculating a worldwide incidence rate has become a complex task. However, according to US statistics, it was possible to relate the incidence rate of diabetes to the incidence rate of MetS, revealing that the incidence of MetS is approximately three times higher than that presented by diabetes [7,9]. Thus, it is estimated that about a quarter of the world population is affected by MetS [7]. Given that MetS is closely related to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular events, reversing this condition is essential [10]. The increased prevalence of changes in lipid profile and MetS, coupled with risk behaviors such as smoking and sedentary lifestyle, promote an increase in the incidence rate of CVD to levels of concern [10]. A high percentage (31%) of the number of deaths worldwide is caused by cardiovascular events, which have become a serious epidemiological problem, and the need to promote preventive habits is emerging [11]. In this group of pathologies, we can find stroke and myocardial infarction, which represent 85% of the total events [8,12]. The very high impact that these pathologies represent on society and the health of the populations, favors the investment of researchers in the problem [12,13,14]. The inefficiency of pharmacological treatment and of awareness/promotion campaigns leads to the search for more appealing and effective alternatives. The need for more appealing treatments and prevention that can be easily integrated into everyday life has led to the emergence of the concept of Functional Foods, which is based on combining food with direct benefits to the individual’s health [15,16].
The bioactivity of several polysaccharides which can be found in macroalgae is known and the ease of their integration in food reinforces the action in the prevention and treatment of various pathologies [17,18,19]. It should be noted that carrageenans, linear sulfated polysaccharides present in red algae, are already approved by the European Union as a food additive and described in the literature as having multiple benefits for human health. The need to objectively assess the potential of carrageenans in the prevention and rebalance of lipid profile and body mass index parameters constitutes a research target [17]. In this way, an efficient and beneficial action of carrageenans was detected in terms of lipid profile parameters, in MetS and, consequently, in the potential risk of developing cardiovascular events [20,21,22]. This review is focused on researching and analyzing published information on this broad and specific topic.
2. Metabolic Syndrome
MetS is considered a multifactorial disorder with changes in lipid and glucose metabolism [23], in association with abdominal obesity, weight gain, dyslipidemia, hypertension and insulin resistance [7,24]. The main risk in the development of MetS is abdominal obesity and susceptibility to other risk factors [25]. The increased consumption of fast food, high in fat and low in fiber, and the reduction in physical activity, due to the greater availability of means of transport, induces the adoption of a more sedentary lifestyle, enhancing the development of the aforementioned pathologies [7]. The progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus often evolves to a more advanced state of MetS, which may be associated with complications in therapy [25]. MetS is one of the risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes and CVD [7,25,26]. Dietary changes including functional food components constitute an essential approach [27].
2.1. Lipid Profile and Metabolism
Lipid profile and metabolism are key players in the development of MetS. The assessment of the lipid profile is supported by the serum concentrations of: TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, and TG. TC represents the quantification of all cholesterol fractions present in the sample. The cholesterol molecule is important in the body, constituting its main steroid. It is present in all cell membranes, in the formation of essential bile acids in the processes of absorption and synthesis of steroid hormones, among others. It can be endogenous, when synthesized in the body, or exogenous, if absorbed through food intake. Endogenous steroids can also be reabsorbed via the gastrointestinal tract through the absorption of bile acids and consequent reuse of cholesterol [28]. HDL-C is a small and dense lipoprotein with a high content of apoproteins (50%—Apo AI, AII, C, among others) which in the cell binds to specific receptors releasing cholesterol sterols, essential for proper cell functioning. In LDL-C, only 20 to 25% of its constitution is apoprotein, whose main function is the transport of cholesterol and TG from food [28,29]. TG are the main lipid components present in food. In the gastrointestinal tract, they are hydrolyzed into fatty acids, absorbed by the intestinal wall, transported to adipocytes and stored as an energy reserve [28,30]. The lipid profile is one of the main processes for monitoring MetS and classifying the potential risk of developing CVD. This assessment makes it possible to detect disorders in the lipid profile originating from genetic and/or dietary factors. The most frequent are defined as dyslipidemia when it involves changes in lipoproteins, lipids, or apoproteins; hyperlipemic, if CT and/or TG are elevated; and hypercholesterolemia, when only the CT concentration is increased [28].
2.2. Cardiovascular Diseases
The increasing level of disorders in MetS is intertwined with the increased risk for the development of CVD, representing a heterogeneous group of pathologies that affect the circulatory system, blood vessels and the heart. They constitute the main cause of death in the world, representing 31% of all deaths, characterizing themselves as an epidemiological problem [11]. Risk factors are divided into modifiable and non-modifiable, with changes in the lipid profile (hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia), diabetes, high blood pressure, overweight and obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption and sedentary lifestyle being modifiable ones, while age, sex and genetic factors are considered non-modifiable risk factors. Alterations in the lipid profile are very relevant and currently essential in the monitoring and prevention of CVD [12,13]. Dysregulation of the lipid profile is characterized by an increase in the concentration of one or more lipid fractions in circulation, favoring deposition in blood vessels and promoting the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. The first description of the relationship between cholesterol and atherosclerotic plaques was reported in 1904 by Félix Jacob Marchand, who demonstrated that cholesterol is the main component of atherosclerotic plaques and the basis of the entire process [29]. Atherosclerotic plaques result from the deposition of cholesterol ester on the walls of blood vessels by LDL-C and then give rise to an inflammatory reaction. The main way to prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques is based on eliminating modifiable risk factors and adopting healthy habits, especially in terms of food and physical exercise [29]. The diseases in this group with the greatest impact on the health of populations are pathologies of the coronary arteries (myocardial infarction) and of the cerebral arteries (CVA), representing 85% of all deaths caused by CVD [12,13,29].
3. Carrageenans
Carrageenans are phycocolloids present in macroalgae, which are aquatic photosynthetic organisms with a high percentage of vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, and traces of lipids [18]. These are a health benefit as they are rich in essential omegas and polyunsaturated fatty acids [17,18,31]. Carrageenans are a component of the cell wall and intercellular spaces of several species of red algae, being extracted especially from Chondrus crispus [19,32]. One of the first references to the use of carrageenan occurred in Carragheen, in the South of Ireland, where Chondrus crispus extracts were used in the confection of home cough and cold treatments [33]. Classified as linear sulfated polysaccharides, chemically, the carrageenans consist of repeated units of disaccharides [34,35]. The various types existing in nature (xi—ξ, theta—θ, beta—β, mu—μ, and nu—ν) make most chains hybrid rather than simple. In industry, three types are usually extracted, the kappa (κ)-, the iota (ι)- and the lambda (λ)-carrageenans [32,34,36]. The alkaline method is the most common extraction process and, in this case, the precursors μ- and ν-carrageenan lead to the formation of the types κ- and ι-carrageenan, respectively (Figure 1) [37].
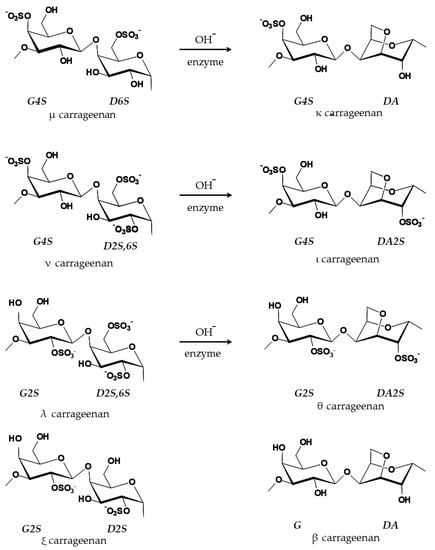
Figure 1.
Idealized units of the main types of carrageenan (adapted from Pereira and van de Velde [37]).
The gelling capacity of carrageenans results from the interaction between galactose monomers and water molecules in solution. The tendency of the carrageenans to form hydrogen bridges between 2 carbons leads to the formation of a helical chain. This structure induces the ability to form gels, being responsible for the hydrocolloid characteristics of the carrageenans [32,38]. The discovery of the gelling, thickening, and emulsifying/stabilizing action in aqueous solutions, coupled with its inability to alter the color and taste of the solution, made the use of carrageenan very frequent [19,39]. The low cost, the ease of optimization, and the maintenance of the appearance and taste/smell of the solution have allowed the wide use of carrageenans in many industrial areas, namely in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries, in industrial suspensions and paints, among many others [18,33,40]. Its use as a food additive is approved by the European Union, and it is represented on food labels by code E407 [39,41].
3.1. Carrageenans for Human Consumption
Food grade carrageenans are polysaccharides where molecular weight is greater than 100 kDa [42,43]. In this case, there are three types of carrageenans normally commercialized to the food industry: κ-carrageenan, which forms rigid gels with syneresis; ι-carrageenan, which is characterized by producing elastic and soft gels; and, finally, λ-carrageenan, which gives origin to viscous solutions without gelling [44].
Carrageenans are applied to food products in doses below 1 g/L and they are authorized by the Joint Committee of the Food and Agriculture Organization and the World Health Organization, except in baby formulas [39]. The acceptable daily intake for carrageenan is estimated to be between 20 and 200 mg/day [45]. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has set a provisional acceptable daily intake of 75 mg per kilogram of body weight [46].
The FDA has determined that the concentration of carrageenans currently used in processed food products in the United States of America is safe (in commercial products that contain carrageenans), and that no upper limit would have to be established. The FDA only requires that the used carrageenan has between 20 and 40% of sulfated content and that it is mostly galactose and anhydro-galactose monomers [47].
In gastric digestion trials, carrageenans have had mixed results. Some studies have demonstrated the hydrolysis of the molecule in whole or in part [48,49,50]. In other studies, carrageenans, after digestion, were not hydrolyzed similarly to other phycocolloids (e.g., alginate) and were considered safe for human consumption [42,51,52,53]. Thus, the degradation or not of carrageenans is essential to determine the level of risk to human health, since the degraded molecule is harmful by potentiating the inflammatory effect [42,48,54,55].
Carrageenans in the Food Industry: Concept and Future Road
Carrageenans are the most widely used seaweed-derived food hydrocolloid for textural functionality, particularly in dairy products, jellies and confectionery, and cooked processed meat products. Carrageenans have the fourth largest share of the global food texture market (in terms of value), trailing starches, gelatin, and pectin. Hydrocolloids are commonly used in food products to improve appearance (e.g., creaminess, homogeneity) and organoleptic qualities (e.g., mouthfeel, juiciness); to promote easy-to-use application (e.g., pourability, spread-ability); to impart processing benefits, such as freeze–thaw stability, slice-ability, retaining freshness, and increasing shelf life; and to increase yields. As a result, producers benefit from a variety of technical and cost advantages. As the food industry rises to the challenge of meeting global targets for the reduction of "unhealthy" ingredients, such as salt (sodium), sugar, and fat, hydrocolloids are finding increased application in the formulation of healthier foods [56].
Carrageenan is mainly used in dried powder formula, which is blended with the other ingredients, mainly liquids, so as to not add another ingredient to the final products. However, water can be applied to create a carrageenan solution before the mixture. Additionally, carrageenans’ powder can be blended with other ingredients (for example, sugar) to help on the processing: blending carrageenans with sugar can help with dispersion as well as standardization, such as in a chocolate milk grade with a specific gel strength and functionality. Legally, any diluents must be listed in the product specification; however, if the ingredient is present as a byproduct of processing, such as KCl in gel press kappa, no declaration is required. Carrageenans work best in neutral environments, such as milk systems, but certain types can tolerate more acidic conditions as long as milk proteins are not present. The ability to gel in milk, salt, and water systems; viscosity (water); milk reactivity; ash content; and mesh profile are some of the physical measurements commonly used to quantify carrageenans’ performance [57].
Due to the change of mindset to a vegetarian trend, carrageenans are exploited to create products which are similar to their animal-based counterparts, such as puddings, types of bread, jelly, ham, creams and yogurt-similar products. Being a hot topic for vegan food industry to create new products without animal-based ingredients, carrageenans are a great option to be explored, due to being used at a low concentration (for example, they are applied between 0.01 and 1% in the final product), being simple to operate with, and helping with quality control [57].
3.2. Carrageenans in Human Health
The evidence that the ingestion of macroalgae is beneficial for human health has led to the discovery of the high potential of several sulfated polysaccharides present in algae [58]. In particular, the potential of carrageenans in the prevention of pathologies and promotion of human health [59,60]. The multiple health benefits are associated with its characteristics: antioxidant; antitumor, blocking the interactions between the tumor cells and the basal membrane and inhibiting the proliferation of tumor cells [18]; antilipidemic [58]; anticoagulant, prolonging clotting time by inhibiting thrombin activity [18,33]; antifungal; immunosuppressant; and antiviral, preventing the entry of the virus into the cell [33].
It is thought that the interaction of carrageenans in the digestive process is the basis of its modulating action on the lipid profile [18,61]. Physically, the carrageenan, when reaching the intestinal tract, causes an increase in the volume and viscosity of the enteric content [62]. This phenomenon decreases the availability of the food cake to enzymatic action, thus having direct implications on the efficiency of digestion [62]. The chemical structure also confers the ability to interact with cholesterol in the capture and excretion of bile salts. It can also seize cholesterol and consequently prevent its emulsifying action and subsequent absorption. It also has the ability to inhibit lipase. The combination of all its capacities in the gastrointestinal tract induces a decrease in the cholesterol absorption [55,63,64]. The decrease in the absorption of exogenous cholesterol coupled with the decrease in the reuse of bile salts promotes the need for a new synthesis of bile salts in the body [65,66]. This is achieved by mobilizing TG from the energy reserves to restore cholesterol levels [67,68]. The potential of carrageenan comes from its ability to maintain the balance of the lipid profile, performed by the ability to decrease the absorption of exogenous cholesterol and consequent promotion of the synthesis of endogenous cholesterol [69].
4. The Potential of the Carrageenans in the Prevention of MetS
Considering the bioactive and beneficial characteristics of carrageenans and the current expansion of MetS and CVD, either by type of diet or by sedentary lifestyle, the researchers tried to understand if there is evidence of a relationship between carrageenans and MetS and CVD. It was found that when a diet supplemented with carrageenans is applied, in general, a decrease in body weight is detected [7,24]. In contrast, in the study of Bhattacharyya and collaborators conducted in 2015, the administration of 1% of carrageenan through water for 44 weeks showed an increase in body weight, and, regarding the lipid profile, there were higher values in the concentrations of TC, LDL-C, and TG [21]. According to Wanyonyi and coauthors, the potential of carrageenans, present in Kappaphycus alvarezii, with preventive effect on MetS is positive. A reduction in body weight, fat mass, waist circumference and blood pressure were shown in their results, although these were not statistically significant [70]. The work by Chin et al. aimed to evaluate the anti-obesity metabolism of K. alvarezii and, for this purpose, they tested the consumption of various forms of carrageenan. To promote obesity in C57BL/6J mice, the researchers applied a high-fat rodent diet (HFD) with 45% kcal of energy from fat, given for 10 weeks. After 6 weeks, the HFD diet was supplemented with 5% K. alvarezii (T), 5% native κ-carrageenan (CGN), extracted from seaweed, and the remaining 5% sans-carrageenan fraction (SCGN, which represents residues from carrageenan processing) [71]. During the experimental period, body weight was monitored regularly, showing a reduction. Regarding fat mass, when comparing the three groups with supplementation in relation to the model group (high-fat diet) there was a decrease in fat mass. It should be noted that the group with SCGN supplementation showed more significant results [71]. Additionally, the works of Du Preez et al. showed a decrease in body weight, systolic blood pressure and hepatic and abdominal fat mass, in addition to other plasma parameters, such as transaminase activity and TC, when 5% of Sarconema filiforme (Rhodophyta) were added to the diet, regardless of the type of diet applied. For the study, the researchers organized a protocol applied for 16 weeks to 4 groups of male Wistar rats. One group was fed a diet rich in carbohydrates and fats; one group maintained the characteristics of this diet but was supplemented with 5% of S. filiforme in the last 8 weeks; another group was fed with corn starch; and the last group was supplemented with 5% of S. filiforme in the last 8 weeks, besides having the corn starch diet. Rats on a diet rich in carbohydrates and fats had hypertension, dyslipidemia, obesity, fatty liver, glucose intolerance, and increased collagen deposition in the left ventricle. Supplementation improved MetS symptoms [22].
4.1. The Potential of Carrageenans in the Prevention of CVD
An extension of MetS may be CVD, and the consumption of carrageenans may be a preventive factor. The relationship between the alteration of the lipid profile and the development of CVD has led to the investigation of alternative ways of regulating the lipid profile. The hypothesis of the biopotential of carrageenans emerged as a possibility in the promotion and development of studies to evaluate the impact of carrageenan ingestion on the lipid profile of patients with CVD, carrying out studies in animal models and even in humans.
4.2. Studies Carried Out in Animal Models
After analysis of the studies carried out on a non-human animal model, it was found that all of them recorded a significant reduction in the serum concentration of TC [22,72,73]. Most studies have selected the male Wistar rats as a model (8-week-old male C57BL/6J mice [21]; 8-week-old male Wistar rats [22]; 9-week-old male Wistar rats [70]; 8-week-old male C57BL/6J mice [71]; two of the works developed in Wistar rats did not provide the age and sex of the rats [72,74]; male Sprague Dawley rats [75]). In addition, a study was conducted on chicks [73]. The work developed with chicks, with one day of life, had as objective to verify the effect of the ingestion of fermented carrageenans [73,76], described by Hasanuddin et al. [73], in different concentrations (2.5, 5, 7.5 and 10%) during 5 weeks. At the end of the experimental period, they found that the higher the concentration of carrageenans ingested, the greater the reduction in TC, LDL-C, TG and increase in HDL-C levels, with statistically significant results [73].
Other researchers have tested the action of carrageenans when introduced in association with carbohydrate and/or lipid-enriched diets. In these works, the results presented some dichotomy observed in the two analyzed articles [70,74]. According to Wanyonyi and collaborators, the ingestion of a diet enriched in carbohydrates, lipids and with the introduction of about 5% of algae K. alvarezii, in a period of 8 weeks, showed a tendency for the increase of the TC concentration and a reduction of TG; however, neither alteration was significant [70]. In relation to the study of Xia et al., there was a reduction in the concentration of TC and TG, when, for 30 days, Wistar rats were supplied with 1% of carrageenans (CC), 1% (1% LC) and 3% (3% LC) of low-density carrageenans, obtained through the red alga Eucheuma denticulatum (formerly Eucheuma spinosum, Rhodophyta), along with a high-fat feeding (HC: 3.5% cholesterol, 10% lard, 0.2% propylthiouracil, 0.5% sodium cholate and 5% refined sugar) and also a group with normal powder (NC: 19% fats, 55%, carbohydrates, 22% proteins, 7% ash, and 5% cellulose) [74]. There was, however, greater efficiency in reducing serum concentrations with the ingestion of low molecular weight carrageenans; all results were obtained through comparison with the HC group.
In Du Preez’ and co-authors’ works, the action of carrageenans on the lipid profile was beneficial both when introduced in a diet enriched with carbohydrates and fats, and in a diet with corn starch. It was demonstrated that in both diets there was a statistically significant decrease in the concentrations of TC and TG [22].
Bhattacharyya et al. [21] evaluated the action of carrageenans introduced in water, in male C57BL/6J mice at 8 weeks of age. For this, 1% of non-degraded carrageenans (carrageenan λ and κ; Sigma Chemical Co., St Louis, MO, USA) was added to water for 44 weeks and the mice were divided into two groups (with and without carrageenans). The total sample was subdivided into four groups, control group (standard feeding), CGN group (standard feeding and 1% carrageenans in water), HDF group (high fat feeding) and HDF+CGN group (high fat feeding and 1% carrageenans in water). At the end of the experimental period, the results did not correspond to the expected, with an increase in the concentration of TC, TG and LDL-C [21]. The team of Chin et al. [71] sought to estimate how best to reduce lipid profile levels, with a diet enriched in carbohydrates and supplemented with 5% K. alvarezii (T), 5% native κ-carrageenan (CGN), and the 5% leftover sans-carrageenan fraction (SCGN). The three groups with supplemented diet were analyzed before and after 6 weeks. After the beginning of the diet it was verified, comparatively to the model (carbohydrate enriched diet), a tendency in the decrease of TC, LDL-C, TG, and an increase of HDL-C concentrations. There were only significant results in the HDL-C concentration in the SCGN group [71].
In the study developed by Tsai and collaborators, it was recorded that the time of ingestion of carrageenans can influence the results. This team of researchers observed an increase in TC levels after 32 days of diet enriched with 7% carrageenans and a decrease of the same parameter after 42 days of intake [75]. The work done by Gómez-Ordóñez et al. evaluated the effect of the introduction on the feeding of Wistar rats of 10% of Mastocarpus stellatus (Rhodophyta). After 4 weeks of ingestion, the results were analyzed, comparing the experimental group (feeding with carrageenans) with the control group. A statistically significant decrease in TC and TG concentrations was observed [72]. The results of the studies are compiled in (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of studies carried out in animal and human models.
4.3. Studies Carried Out in Humans
Human studies are still very scarce, perhaps because of the low consumption of algae in the diet of Western populations or even because of the characteristics of the study. However, when analyzing the results obtained in the three published studies, it was observed that the behavior in the TC levels is homogeneous [20,65,77]. In the study of Panlasigui et al. [65], a portion of carrageenans was added to the food prepared and normally eaten by a group of volunteers for 8 weeks. The experimental group ingested 40 g of carrageenans daily. At the end of the experimental period, there was a significant decrease in TC and TG concentrations and an increase, also significant, in HDL-C [65]. Afterwards, Sokolova et al. [20] showed that taking a supplement in the form of capsules containing carrageenans and administered for 20 days to a group of hospitalized patients with cardiovascular events presents benefits in their recovery. After 20 days, a significant decrease in TC and LDL-C concentration was observed; however, a significant increase in TG levels was registered [20]. Most recently, Valado et al. [77] revealed that the daily intake of 100 mL of vegetable jelly, which has carrageenans in its constitution, presents benefits to the regulation of the lipid profile. In the study, two periods of time, 30 and 60 days, were tested. In both it was observed a significant decrease in the concentrations of TC and an increase of TG, without, however, exceeding the reference levels defined [77]. The results are compiled in (Table 1).
5. Current and Future Perspectives
From the literature review, it was inferred that the ingestion of carrageenans revealed possible benefits on the lipid profile and on the weight and abdominal perimeter, appearing to be an added value in the prevention of MetS and CVD. The reduced number of specific publications in the area was one of the main limitations of the authors in the development of the theme. Moreover, the lack of uniformity in studies, such as the different algae used; the modes of ingestion of carrageenans: whole algae [22,70], dissolved in water [21], or post extraction [73,74,77]; and the different methodologies used, are key factors in the results’ variability. In human studies, one of the main limitations found are the dietary differences of populations [65,77] and the assurance of diet compliance [20,65], as well as the principles defined by the study. However, despite all the variants, the results showed benefits, indicating the real potential of the carrageenans in the maintenance/regulation of the lipid profile. The time of exposure to diets supplemented with carrageenans seems to be an efficiency factor, because studies that compared the same population at different times, showed a direct relation of improvement, when evaluated the period of ingestion and the action of carrageenans in the regulation of the lipid profile. According to the studies of Chin et al. and Hasanuddin et al., the percentage of carrageenans included as a supplement in the diet does not seem to be very relevant for the efficiency in reducing the parameters evaluated in MetS and rebalancing the lipid profile [71,73]. It should be noted that some studies have promoted changes in the lipid profile and parameters of MetS through the introduction of lipid-rich diets to test the action of carrageenans. Even so, with inadequate alimentary behaviors it was demonstrated the efficacy in rebalancing of the evaluated parameters [22,70,71,74].
In the investigations developed in humans, despite the various ways of inserting carrageenan in the diet, the cultural differences in terms of feeding, the time period used being different, and the different amount of carrageenans supplied, all the works presented a regulatory action on the lipid profile [20,65,77].
Thus, the analysis of all publications presented revealed the high potential of carrageenans on the parameters of lipid profile and MetS, demonstrating a high potential in preventing and reversing harmful changes in the lipid profile and MetS and consequently in reducing the incidence of CVD.
Author Contributions
The authors A.V., M.P., M.A. and J.C. made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study and performed data analysis and interpretation. L.P. was responsible for curating the data and reviewing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financed by national funds through FCT (Foundation for Science and Technology), I.P., within the scope of the projects UIDB/04292/2020 (MARE, Marine and Environmental Sciences Centre), and ARNET Associate Laboratory.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sakurai, R.; Zuchi, J.D. Industrial revolutions to industry 4.0. Interface Tecnol. 2018, 15, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mirosa, M.; Bremer, P. Review of Online Food Delivery Platforms and their Impacts on Sustainability. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, M.H.; Oh, Y.H. Sedentary Lifestyle: Overview of Updated Evidence of Potential Health Risks. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2020, 41, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassi, E.; Pervanidou, P.; Kaltsas, G.; Chrousos, G. Metabolic syndrome: Definitions and controversies. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopčeková, J.; Holovičová, M.; Gažarová, M.; Mrázová, J.; Habánová, M.; Mečiarová, L.; Bronkowska, M. Association between Selected Dietary Habits and Lipid Profiles of Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Dias, N.; Robalo Martins, S.; Belo, A.; Fiúza, M. Characterization of lipid profile in primary health care users in Portugal. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2013, 32, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guembe, M.J.; Fernandez-Lazaro, C.I.; Sayon-Orea, C.; Toledo, E.; Moreno-Iribas, C.; Investigators, R.S. Risk for cardiovascular disease associated with metabolic syndrome and its components: A 13-year prospective study in the RIVANA cohort. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhai, Y.; Zhao, J.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, A.; Li, L.; Huang, T.; Xu, A.; et al. Impact of Metabolic Syndrome and It’s Components on Prognosis in Patients With Cardiovascular Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 704145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO—World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Kruk, M.E.; Gage, A.D.; Arsenault, C.; Jordan, K.; Leslie, H.H.; Roder-DeWan, S.; Adeyi, O.; Barker, P.; Daelmans, B.; Doubova, S.V.; et al. High-quality health systems in the Sustainable Development Goals era: Time for a revolution. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1196–e1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuckler, D. Population causes and consequences of leading chronic diseases: A comparative analysis of prevailing explanations. Milbank Q. 2008, 86, 273–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granato, D.; Barba, F.J.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Cruz, A.G.; Putnik, P. Functional foods: Product development, technological trends, efficacy testing, and safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nystrand, B.T.; Olsen, S.O. Consumers’ attitudes and intentions toward consuming functional foods in Norway. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 80, 103827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.M.; Pereira, O.R.; Seca, A.M.; Pinto, D.C.; Silva, A.M. Seaweeds as Preventive Agents for Cardiovascular Diseases: From Nutrients to Functional Foods. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L. Biological and therapeutic properties of the seaweed polysaccharides. Int. Biol. Rev. 2018, 2, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, V.D.; Maheriya, P.M.; Jani, G.K.; Solanki, H.K. Carrageenan: A natural seaweed polysaccharide and its applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, E.V.; Bogdanovich, L.N.; Ivanova, T.B.; Byankina, A.O.; Kryzhanovskiy, S.P.; Yermak, I.M. Effect of carrageenan food supplement on patients with cardiovascular disease results in normalization of lipid profile and moderate modulation of immunity system markers. PharmaNutrition 2014, 2, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Feferman, L.; Unterman, T.; Tobacman, J.K. Exposure to Common Food Additive Carrageenan Alone Leads to Fasting Hyperglycemia and in Combination with High Fat Diet Exacerbates Glucose Intolerance and Hyperlipidemia without Effect on Weight. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 513429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Preez, R.; Paul, N.; Mouatt, P.; Majzoub, M.E.; Thomas, T.; Panchal, S.K.; Brown, L. Carrageenans from the red seaweed Sarconema filiforme attenuate symptoms of diet-Induced metabolic syndrome in rats. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Chávez, A.; Chávez-Fernández, J.A.; Elizondo-Argueta, S.; González-Tapia, A.; León-Pedroza, J.I.; Ochoa, C. Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease: A Health Challenge. Arch. Med. Res. 2018, 49, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCracken, E.; Monaghan, M.; Sreenivasan, S. Pathophysiology of the metabolic syndrome. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M. Metabolic syndrome: A multiplex cardiovascular risk factor. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, M.P.; Williams, K.; González-Villalpando, C.; Hunt, K.J.; Haffner, S.M. Does the metabolic syndrome improve identification of individuals at risk of type 2 diabetes and/or cardiovascular disease? Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qin, J.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, D.; Li, M.; Qi, Y.; Lan, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Z. Marine Sulfated Polysaccharides: Preventive and Therapeutic Effects on Metabolic Syndrome: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solnica, B.; Sygitowicz, G.; Sitkiewicz, D.; Cybulska, B.; Jóźwiak, J.; Odrowąż-Sypniewska, G.; Banach, M. 2020 Guidelines of the Polish Society of Laboratory Diagnostics (PSLD) and the Polish Lipid Association (PoLA) on laboratory diagnostics of lipid metabolism disorders. Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 16, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zárate, A.; Manuel-Apolinar, L.; Basurto, L.; De la Chesnaye, E.; Saldívar, I. Cholesterol and atherosclerosis. Historical considerations and treatment. Arch. Cardiol. Mex. 2016, 86, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.E.; Hall, M.E.; Guyton, A.C. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; p. 1152. ISBN 9780323597128. [Google Scholar]
- Dousip, A.; Matanjun, P.; Sulaiman, M.R.; Tan, T.S.; Ooi, Y.B.H.; Lim, T.P. Effect of seaweed mixture intake on plasma lipid and antioxidant profile of hyperholesterolaemic rats. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 26, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Soares, F.; Freitas, A.C.; Duarte, A.C.; Ribeiro-Claro, P. Extraction, Characterization, and Use of Carrageenans (Chapter 3). In Industrial Applications of Marine Biopolymers; Sudha, P.N., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2017; pp. 34–89, 626. ISBN 9781498731485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L. Carrageenan: A review. Vet. Med. 2013, 58, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L. Carrageenans: Sources and Extraction Methods, Molecular Structure, Bioactive Properties and Health Effects; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 304. ISBN 978-1-63485-503-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L. Vibrational Spectroscopy of Seaweed Polysaccharides. In Seaweed Polysaccharides—Isolation, Biological and Biomedical Applications; Venkatesan, J., Anil, S., Kim, S.-K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 83–100. ISBN 978-0-12-809816-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usov, A.I. Polysaccharides of the red algae. In Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry; Horton, D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 115–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; van de Velde, F. Portuguese carrageenophytes: Carrageenan composition and geographic distribution of eight species (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanusorn, N.; Thummarungsan, N.; Sangwan, W.; Lerdwijitjarud, W.; Sirivat, A. Influence of carrageenan molecular structures on electromechanical behaviours of poly(3-hexylthiophene)/carrageenan conductive hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 2098–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, M.; Aggett, P.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Filipič, M.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U. Re-evaluation of carrageenan (E 407) and processed Eucheuma seaweed (E 407a) as food additives. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated Seaweed Polysaccharides as Multifunctional Materials in Drug Delivery Applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CREU—Commission Regulation (EU) No 1129/2011 of 11 November 2011. Amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council by Establishing a Union list of Food Additives Text with EEA Relevance. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2011/1129/oj (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- McKim, J.M.; Baas, H.; Rice, G.P.; Willoughby, J.A.; Weiner, M.L.; Blakemore, W. Effects of carrageenan on cell permeability, cytotoxicity, and cytokine gene expression in human intestinal and hepatic cell lines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.M.; Ito, N. A Critical Review of the Toxicological Effects of Carrageenan and Processed Eucheuma Seaweed on the Gastrointestinal Tract. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2002, 32, 413–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, A.H.; Camus, C.; Infante, J.; Neori, A.; Israel, Á.; Hernández-González, M.C.; Pereda, S.V.; Gomez-Pinchetti, J.L.; Golberg, A.; Tadmor-Shalev, N.; et al. Seaweed production: Overview of the global state of exploitation, farming and emerging research activity. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO—World Health Organization. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Eightieth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/204410 (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Weiner, M.L. Food additive carrageenan: Part II: A critical review of carrageenan in vivo safety studies. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 244–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA—US Food & Drug Administration. CFR—Code of Federal Regulations Title 21. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?fr=172.620 (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Borthakur, A.; Dudeja, P.K.; Tobacman, J.K. Carrageenan Reduces Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 (BMP4) and Activates the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Normal Human Colonocytes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobacman, J.K. Review of harmful gastrointestinal effects of carrageenan in animal experiments. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobacman, J.K. Filament disassembly and loss of mammary myoepithelial cells after exposure to lambda-carrageenan. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 2823–2826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weiner, M.L.; McKim, J.M.; Blakemore, W.R. Addendum to Weiner, M.L. (2016) Parameters and Pitfalls to Consider in the Conduct of Food Additive Research, Carrageenan as a Case Study. Food Chemical Toxicology 87, 31–44. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, W.R.; Davis, S.R.; Hroncich, M.M.; Vurma, M. Carrageenan analysis. Part 1: Characterisation of the carrageenan test material and stability in swine-adapted infant formula. Food Addit. Contam. 2014, 31, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakemore, W.R.; Brant, A.F.; Bissland, J.G.; Bissland, N.D. Carrageenan analysis. Part 3: Quantification in swine plasma. Food Addit. Contam. 2014, 31, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsani, B.; De Santis, R.; Perico, V.; Penagini, F.; Pendezza, E.; Dilillo, D.; Bosetti, A.; Zuccotti, G.V.; D’Auria, E. The Role of Carrageenan in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Allergic Reactions: Where Do We Stand? Nutrients 2021, 13, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKim, J.M. Food additive carrageenan: Part I: A critical review of carrageenan in vitro studies, potential pitfalls, and implications for human health and safety. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 211–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, S.; Brooks, M.; Campbell, R.; Philp, K.; Trius, A. The use of carrageenan in food. In Carrageenans: Sources and Extraction Methods, Molecular Structure, Bioactive Properties and Health Effects; Pereira, L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 229–243. ISBN 978-1-63485-503-7. [Google Scholar]
- Leandro, A.; Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Seaweed’s Bioactive Candidate Compounds to Food Industry and Global Food Security. Life 2020, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, T.; Kuriyama, S.; Hozawa, A.; Ohmori, K.; Sato, Y.; Nakaya, N.; Nishino, Y.; Tsubono, Y.; Tsuji, I. Dietary patterns and cardiovascular disease mortality in Japan: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamori, Y.; Miura, A.; Taira, K. Implications from and for food cultures for cardiovascular diseases: Japanese food, particularly Okinawan diets. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 10, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaporozhets, T.; Besednova, N. Prospects for the therapeutic application of sulfated polysaccharides of brown algae in diseases of the cardiovascular system: Review. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvarna, K.S.; Layton, C.; Bancroft, J.D. Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 654. ISBN 9780702050329. [Google Scholar]
- Capuano, E. The behavior of dietary fiber in the gastrointestinal tract determines its physiological effect. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3543–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, H.; Kakinuma, M.; Coury, D.A.; Ohno, H.; Hara, T. Effect of a seaweed mixture on serum lipid level and platelet aggregation in rats. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Fani, A.; Singh, H. Biophysical insights into modulating lipid digestion in food emulsions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2022, 85, 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panlasigui, L.N.; Baello, O.Q.; Dimatangal, J.M.; Dumelod, B.D. Blood cholesterol and lipid-lowering effects of carrageenan on human volunteers. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 12, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Chater, P.I.; Wilcox, M.; Cherry, P.; Herford, A.; Mustar, S.; Wheater, H.; Brownlee, I.; Seal, C.; Pearson, J. Inhibitory activity of extracts of Hebridean brown seaweeds on lipase activity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Onnagawa, M.; Yoshie, Y.; Suzuki, T. Binding of bile salts to soluble and insoluble dietary fibers of seaweeds. Fish. Sci. 2001, 67, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthan, N.R.; Zhu, L.; Pencina, M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Schaefer, E.J.; Lichtenstein, A.H. Sex-specific differences in the predictive value of cholesterol homeostasis markers and 10-year cardiovascular disease event rate in Framingham Offspring Study participants. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e005066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, M.; Miller, C. A diet containing food rich in soluble and insoluble fiber improves glycemic control and reduces hyperlipidemia among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Rev. 2001, 59, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyonyi, S.; du Preez, R.; Brown, L.; Paul, N.A.; Panchal, S.K. Kappaphycus alvarezii as a Food Supplement Prevents Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Rats. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.X.; Mi, Y.; Cao, W.X.; Lim, P.E.; Xue, C.H.; Tang, Q.J. A pilot study on anti-obesity mechanisms of Kappaphycus alvarezii: The role of native kappa-carrageenan and the leftover sans-carrageenan Fraction. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ordonez, E.; Jimenez-Escrig, A.; Ruperez, P. Effect of the red seaweed Mastocarpus stellatus intake on lipid metabolism and antioxidant status in healthy Wistar rats. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuddin, A.; Rusdi; Arief, R. Effects of inclusion of fermented carrageenan by-products in the basal diet of broiler chickens on growth performance, blood profiles and meat composition. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2017, 16, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qiu, X.; Zhong, W. Antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic effects of low-molecular-weight carrageenan in rats. Open Life Sci. 2018, 13, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, A.C.; Elias, J.; Kelley, J.J.; Lin, R.S.; Robson, J.R. Influence of certain dietary fibers on serum and tissue cholesterol levels in rats. J. Nutr. 1976, 106, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuddinrusdi, A. Evaluation of nutritional values of fermented carrageenan by-product of seaweed (Eucheuma cottonii) raw materials. Agrisains 2012, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Valado, A.; Pereira, M.; Caseiro, A.; Figueiredo, J.P.; Loureiro, H.; Almeida, C.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L. Effect of Carrageenans on Vegetable Jelly in Humans with Hypercholesterolemia. Mar. Drugs 2019, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).