Prolonged Exposure to Antiretroviral Therapy and Risk of Developing Hypertension Among HIV-Infected Clinic Attendees: A Pilot Study in Rural Eastern Cape Province, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Research
- n: Number of events required;
- Z1−α/2: Z-value for significance level (e.g., 1.96 for 5%);
- Z1−β: Z-value for desired power (e.g., 0.84 for 80%);
- HR: Hazard Ratio to detect;
- p: Proportion of individuals in the treatment/exposure group.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | American College of Cardiology |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| ART | Anti-retroviral therapy |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CD4 | Cluster of differentiation 4 |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| NCD | Non-communicable diseases |
| NHLS | National Health Laboratory Services |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SSA | Sub-Saharan Africa |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| NRTI | Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor |
| NNRTI | Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor |
| TDT | Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate |
| 3TC | Lamivudine |
| FTC | Emtricitabine |
| EFV | Efavirenz |
| NVP | Nevirapine |
| d4T | Stavudine |
References
- UNAIDS. Fact Sheet—World AIDS Day 2019 Geneva: Global HIV Statistics. 2019. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/UNAIDS_FactSheet_en.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- The Global HIV/AIDS Epidemic. The Global HIV/AIDS Epidemic USA: KFF. 2019. Available online: https://www.kff.org/global-health-policy/fact-sheet/the-global-hiv-aids-epidemic/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Kooij, K.W.; Zhang, W.; Trigg, J.; Cunningham, N.; Budu, M.O.; Marziali, M.E.; Lima, V.D.; Salters, K.A.; Barrios, R.; Montaner, J.S.G.; et al. Life expectancy and mortality among males and females with HIV in British Columbia in 1996–2020: A population-based cohort study. Lancet Public Health 2025, 10, e228–e236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appiedu-Addo, S.N.A.; Appeaning, M.; Magomere, E.; Ansa, G.A.; Bonney, E.Y.; Quashie, P.K. The urgent need for newer drugs in routine HIV treatment in Africa: The case of Ghana. Front. Epidemiol. 2025, 5, 1523109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyo, R.C.; Sigwadhi, L.N.; Carries, S.; Mkhwanazi, Z.; Bhana, A.; Bruno, D.; Davids, E.L.; Van Hout, M.C.; Govindasamy, D. Health-related quality of life among people living with HIV in the era of universal test and treat results from a cross-sectional study in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. HIV Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 25, 2298094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigna, J.J.; Ndoadoumgue, A.L.; Nansseu, J.R.; Tochie, J.N.; Nyaga, U.F.; Nkeck, J.R.; Foka, A.J.; Kaze, A.D.; Noubiap, J.J. Global burden of hypertension among people living with HIV in the era of increased life expectancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzudie, A.; Hoover, D.; Kim, H.Y.; Ajeh, R.; Adedimeji, A.; Shi, Q.; Pefura Yone, W.; Nsame Nforniwe, D.; Thompson Njie, K.; Pascal Kengne, A. Hypertension among people living with HIV/AIDS in Cameroon: A cross-sectional analysis from Central Africa International Epidemiology Databases to Evaluate AIDS. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okyere, J.; Ayebeng, C.; Owusu, B.A.; Dickson, K.S. Prevalence and factors associated with hypertension among older people living with HIV in South Africa. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gafane-Matemane, L.F.; Craig, A.; Kruger, R.; Alaofin, O.S.; Ware, L.J.; Jones, E.S.; Kengne, A.P. Hypertension in sub-Saharan Africa: The current profile, recent advances, gaps, and priorities. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2025, 39, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Perel, P.; Mensah, G.A.; Ezzati, M. Global epidemiology, health burden and effective interventions for elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 785–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartey, E.T.; Tetteh, R.A.; Anto, F.; Sarfo, B.; Kudzi, W.; Adanu, R.M. Risk of hypertension in adult patients on antiretroviral therapy: A propensity score matching analysis. Health Sci. Investig. J. 2023, 4, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandakly, E.; Moudgil, R.; Holman, K. Cardiovascular disease in people living with HIV: Risk assessment and management. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2025, 92, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Perez-Guzman, P.; Hoyer, A.; Brinks, R.; Gregg, E.; Althoff, K.N.; Justice, A.C.; Reiss, P.; Gregson, S.; Smit, M. Association between HIV infection and hypertension: A global systematic review and meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Hirigo, A.T.; Yilma, D.; Astatkie, A.; Debebe, Z. The association between dolutegravir-based a3tiretrovirals and high blood pressure among adults with HIV in southern Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, 20499361241306942. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mugisha, N.; Ghanem, L.; Komi, O.A.; Noureddine, R.; Shariff, S.; Wojtara, M.; Nanehkeran, M.M.; Uwishema, O. Addressing Cardiometabolic Challenges in HIV: Insights, Impact, and Best Practices for Optimal Management—A Narrative Review. Health Sci. Rep. 2025, 8, e70727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derick, K.I.; Khan, Z. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, control of hypertension, and availability of hypertension services for patients living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 2023, 15, e37422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.; Moore, T.J.; Long, D.M.; Burkholder, G.A.; Willig, A.; Wyatt, C.; Heath, S.; Muntner, P.; Overton, E.T. Risk factors for incident hypertension within 1 year of initiating antiretroviral therapy among people with HIV. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2022, 38, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuro, U.; Oladimeji, K.E.; Pulido-Estrada, G.A.; Apalata, T.R. Risk factors attributable to hypertension among HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy in selected rural districts of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mivumbi, J.P.; Gbadamosi, M.A. Hypertension Prevalence and Associated Factors in HIV Positive omen at Kicukiro, Kigali, Rwanda: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. medRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bailin, S.S.; Koethe, J.R.; Rebeiro, P.F. The pathogenesis of obesity in people living with HIV. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2024, 19, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanfair, R.; Cheever, L.; Mermin, J. September 18 Is National HIV/AIDS and Aging Awareness Day CDC Encourages People Aged 50 or Older to Get Tested for HIV at a Glance; National Center for HIV, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and Tuberculosis Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.; Chan, Y.K.; Mocumbi, A.O.; Ojji, D.B.; Waite, L.; Beilby, J.; Codde, J.; Dobe, I.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.N.; Damasceno, A.; et al. Hypertension among people living with human immunodeficiency virus in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdela, A.A.; Yifter, H.; Reja, A.; Shewaamare, A.; Ofotokun, I.; Degu, W.A. Prevalence and risk factors of metabolic syndrome in Ethiopia: Describing an emerging outbreak in HIV clinics of the sub-Saharan Africa–a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e069637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Karama, M.; Kamiya, Y. HIV infection, and overweight and hypertension: A cross-sectional study of HIV-infected adults in Western Kenya. Trop. Med. Health 2020, 48, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaviz, K.I.; Patel, S.A.; Siedner, M.J.; Goss, C.W.; Gumede, S.B.; Johnson, L.C.; Ordóñez, C.E.; Laxy, M.; Klipstein-Grobusch, K.; Heine, M.; et al. Integrating hypertension detection and management in HIV care in South Africa: Protocol for a stepped-wedged cluster randomized effectiveness-implementation hybrid trial. Implement. Sci. Commun. 2024, 5, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spach, D.H. National HIV Curriculum. Adverse Effects of Antiretroviral Medications. 2025. Available online: https://www.hiv.uw.edu/go/antiretroviral-therapy/adverse-effects/core-concept/all?utm_source (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Denu, M.K.; Revoori, R.; Buadu, M.A.E.; Oladele, O.; Berko, K.P. Hypertension among persons living with HIV/AIDS and its association with HIV-related health factors. AIDS Res. Ther. 2024, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Statistics 2023. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/gho-documents/world-health-statistic-reports/2023/world-health-statistics-2023_20230519_.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Sun, S.; Zhou, S.; Huang, Q.; Sun, J. The unique relationship between body mass index and metabolic syndrome in AIDS patients. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, J.O.; Leyden, W.A.; Alexeeff, S.; Lea, A.N.; Hechter, R.C.; Hu, H.; Marcus, J.L.; Pitts, L.; Yuan, Q.; Towner, W.J.; et al. Changes in body mass index over time in people with and without HIV infection. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 11, p. ofad611. [Google Scholar]
- Fryar, C.D.; Kit, B.; Carroll, M.D.; Afful, J. Hypertension Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control Among Adults Ages 18 and Older: United States, August 2021—August 2023. In NCHS Data Briefs; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Demissie, B.M.; Girmaw, F.; Amena, N.; Ashagrie, G. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and associated factors among patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Ethiopia, 2023: Asystematic review and meta analysis. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, Z.; Ayoobi, F.; Jalali, Z.; Bidaki, R.; Lotfi, M.A.; Esmaeili-Nadimi, A.; Khalili, P. Metabolic syndrome: A population-based study of prevalence and risk factors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global HIV Programme. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/hiv/treatment/advanced-hiv-disease (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Ren, Q.W.; Teng, T.H.K.; Ouwerkerk, W.; Tse, Y.K.; Tsang, C.T.W.; Wu, M.Z.; Tse, H.-F.; Voors, A.A.; Tromp, J.; Lam, C.S.P.; et al. Triglyceride levels and its association with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular outcomes among patients with heart failure. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.S.; Newby, L.K.; Arnold, S.V.; Bittner, V.; Brewer, L.C.; Demeter, S.H.; Dixon, D.L.; Fearon, W.F.; Hess, B.; Johnson, H.M.; et al. 2023 AHA/ACC/ACCP/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline for the management of patients with chronic coronary disease: A report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 833–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwarisiima, D.; Atukunda, M.; Owaraganise, A.; Chamie, G.; Clark, T.; Kabami, J.; Jain, V.; Byonanebye, D.; Mwangwa, F.; Balzer, L.B.; et al. Hypertension control in integrated HIV and chronic disease clinics in Uganda in the SEARCH study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, M.D.; Ayieko, J.; Owaraganise, A.; Sim, N.; Balzer, L.B.; Kabami, J.; Atukunda, M.; Opel, F.J.; Wafula, E.; Nyabuti, M.; et al. Effect of a patient-centered hypertension delivery strategy on all-cause mortality: Secondary analysis of SEARCH, a community-randomized trial in rural Kenya and Uganda. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkuemah, M. The Epidemiology of Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDS) and NCD Risk Factors in Adolescents & Youth Living with HIV in Cape Town, South Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, L.; Mu, Z. Effects of different weight loss dietary interventions on body mass index and glucose and lipid metabolism in obese patients. Medicine 2023, 102, e33254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banović Fuentes, J.; Beara, I.; Torović, L. Regulatory Compliance of Health Claims on Omega-3 Fatty Acid Food Supplements. Foods 2024, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, M.; Wilsgaard, T.; Grimsgaard, S.; Hopstock, L.A.; Hansson, P. Associations between postprandial triglyceride concentrations and sex, age, and body mass index: Cross-sectional analyses from the Tromsø study 2015–2016. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1158383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Fukui, S.; Shinozaki, T.; Asano, T.; Yoshida, T.; Aoki, J.; Mizuno, A. Lipid profiles after changes in alcohol consumption among adults undergoing annual checkups. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e250583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, S.; Jian, W.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, H. Triglyceride-glucose index predicts adverse cardiovascular events in patients with H-type hypertension combined with coronary heart disease: A retrospective cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirigo, A.T.; Yilma, D.; Astatkie, A.; Debebe, Z. Prevalence and Determinants of Metabolic Syndrome among Adults Living with HIV on First-Line Antiretroviral Treatment in Southern Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2025, 16, 20406223251346289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Code | Components (Drugs) | Full Names | Drug Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1T3E | Tenofovir + Lamivudine + Efavirenz | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) + Lamivudine (3TC) + Efavirenz (EFV) | NRTI + NRTI + NNRTI |
| 1TFE | Tenofovir + Emtricitabine + Efavirenz | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) + Emtricitabine (FTC) + Efavirenz (EFV) | NRTI + NRTI + NNRTI |
| 1S3E | Stavudine + Lamivudine + Efavirenz | Stavudine (d4T) + Lamivudine (3TC) + Efavirenz (EFV) | NRTI + NRTI + NNRTI |
| 1S3N | Stavudine + Lamivudine + Nevirapine | Stavudine (d4T) + Lamivudine (3TC) + Nevirapine (NVP) | NRTI + NRTI + NNRTI |
| 1T3N | Tenofovir + Lamivudine + Nevirapine | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) + Lamivudine (3TC) + Nevirapine (NVP) | NRTI + NRTI + NNRTI |
| Variables of Interest | Total N (%) | Blood Pressure | Chi-Square | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | High | ||||
| Non-modifiable risk factors: | |||||
| Age, years | 4.58 | 0.032 | |||
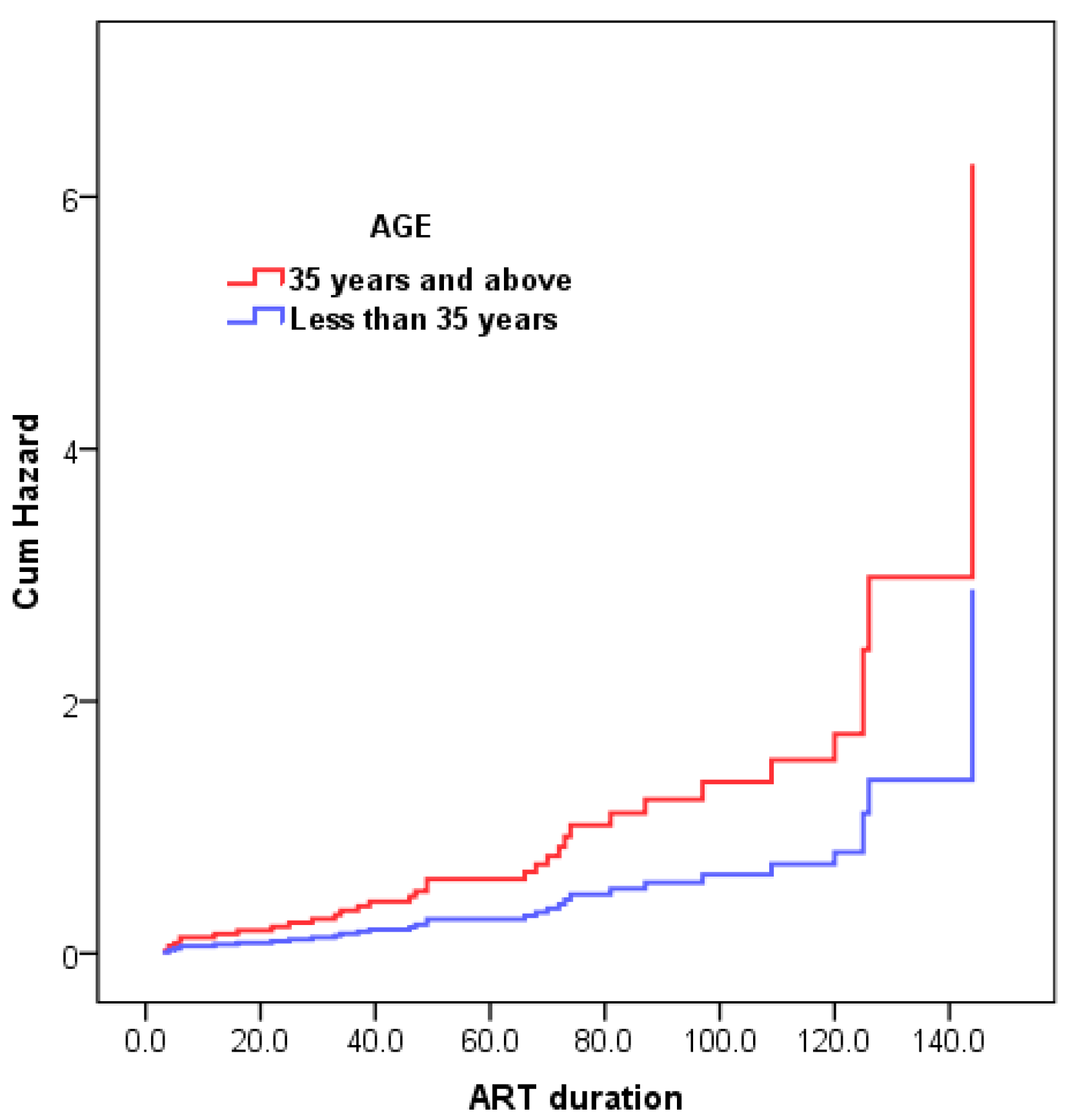
| <35 | 32 (45.71%) | 24/32 (75%) | 8/32 (25%) | ||
| ≥35 | 38 (54.29%) | 19/38 (50%) | 19/38 (70.4%) | ||
| Gender | 2.29 | 0.130 | |||
| Male | 11 (15.70%) | 9/11 (81.8%) | 2/11 (18.2%) | ||
| Female | 59 (84.30%) | 34/59 (57.6%) | 25/59 (42.4%) | ||
| Modifiable risk factors: | |||||
| Alcohol consumption | |||||
| Yes | 26 (37.1%) | 15/26 (57.7%) | 11/26 (42.3%) | 0.24 | 0.621 |
| No | 44 (62.9%) | 28/44 (63.6%) | 16/44 (36.%) | ||
| Cigarette smoking | 0.41 | 0.521 | |||
| Yes | 13 (18.6%) | 9/13 (20.9%) | 4/13 (30.8%) | ||
| No | 57 (81.4%) | 34/57 (59.1%) | 23/57 (40.4%) | ||
| History of type 2 diabetes mellitus | 0.16 | 0.686 | |||
| Yes | 4 (6.2%) | 3/4 (75.0%) | 1/4 (25.0%) | ||
| No | 61 (93.8%) | 39/61 (63.9%) | 22/61 (36.1%) | ||
| Body mass index | 9.74 | 0.008 | |||
| Normal | 29 (41.4%) | 24/29 (82.8%) | 5/29 (17.2%) | ||
| Overweight | 20 (28.6%) | 10/20 (50.0%) | 10/20 (50%) | ||
| Obesity | 21 (30%) | 9/21 (42.9%) | 12/21 (57.1%) | ||
| Variables of Interest | Total N (%) | Blood Pressure | Chi-Square | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | High | ||||
| Lipid profile: | |||||
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 2.32 | 0.128 | |||
| Desirable | 60 (93.8%) | 38/60 (63.3%) | 22/60 (36.7%) | ||
| High | 4 (6.3%) | 1/4 (25.0%) | 3/4 (75%) | ||
| LDL, mmol/L | 1.60 | 0.205 | |||
| Desirable | 45 (97.8%) | 28/45 (62.2%) | 17/45 (37.8)% | ||
| High | 1 (2.2%) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) | ||
| HDL, mmol/L | 1.44 | 0.230 | |||
| Desirable | 45 (70.3%) | 26/45 (57.8%) | 19/45 (42.2%) | ||
| Low | 19 (29.7%) | 14/19 (35%) | 5/19 (20.8%) | ||
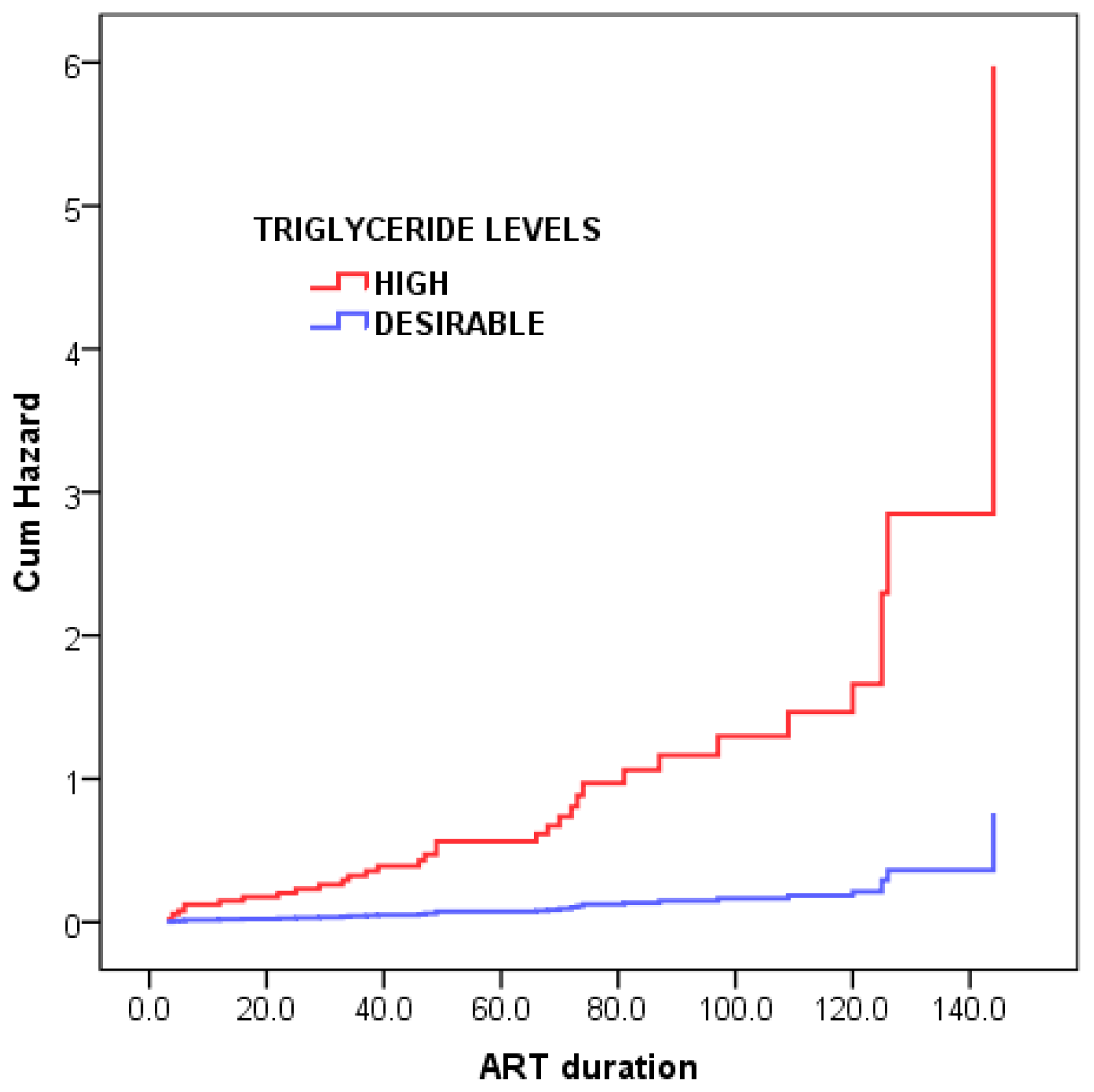
| Triglyceride, mmol/L | 13.15 | 0.0002 | |||
| Desirable | 46 (82.1%) | 33/46 (77.1%) | 13/46 (28.3%) | ||
| High | 10 (17.9%) | 1/10 (10.0%) | 9/10 (90.0%) | ||
| Ratio total cholesterol/HDL | 2.83 | 0.024 | |||
| <4 | 56 (88.9%) | 36/56 (64.3%) | 20/56 (83.3%) | ||
| 4–6 | 6 (9.5%) | 2/6 (33.3%) | 4/6 (66.7%) | ||
| >6 | 1/1 (1.6%) | 1/1 (100%) | 0/1 (0%) | ||
| Blood glucose tests | |||||
| Random blood glucose, mmol/L | 0.64 | 0.424 | |||
| Normal | 69 (98.6%) | 42/69 (60.9%) | 27/69 (39.1%) | ||
| Abnormal | 1 (1.4%) | 1/1 (100%) | 0/1 (0%) | ||
| Glycated Hb, mmol/L | 3.40 | 0.065 | |||
| Normal | 48 (68.6%) | 26/48 (60.5%) | 22/48 (81.5%) | ||
| Abnormal | 22 (31.4%) | 17/22 (77.3%) | 5/22 (22.72%) | ||
| Coagulation disorders | |||||
| D-dimmer | 1.58 | 0.208 | |||
| Positive | 30 (46.2%) | 16/30 (53.3%) | 14/30 (46.6%) | ||
| Negative | 35 (53.8%) | 24/35 (68.5%) | 11/35 (31.4%) | ||
| Metabolic syndrome | |||||
| MS by NCEP | 3.07 | 0.080 | |||
| Present | 31 (44.3%) | 15/31 (48.4%) | 16/31 (51.6%) | ||
| Absent | 39 (55.7%) | 28/39 (71.7%) | 11/39 (28.2%) | ||
| MS by IDF | 1.58 | 0.209 | |||
| Present | 31 (44.3%) | 16/31 (51.6%) | 15/31 (48.4%) | ||
| Absent | 39 (55.7%) | 27/39 (69.2%) | 12/39 (30.8%) | ||
| HIV-associated risk factors | |||||
| WHO staging at ART initiation | 1.96 | 0.58 | |||
| Stage 1 | 34 (49.3%) | 20/34 (58.8%) | 14/34 (41.2%) | ||
| Stage 2 | 15 (21.7%) | 8/15 (53.3%) | 7/15 (46.7%) | ||
| Stage 3 | 18 (26.1%) | 12/18 (66.7%) | 6/18 (33.3%) | ||
| Stage 4 | 2 (2.9%) | 2/2 (100%) | 0/2 (0%) | ||
| Current HIV viral load, copies/mL | 1.00 | 0.32 | |||
| Detectable | 39 (58.2%) | 22/39 (56.4%) | 17/39 (43.6%) | ||
| Undetectable | 28 (41.8%) | 20/28 (71.4%) | 8/28 (28.6%) | ||
| Level of immunosuppression | 0.38 | 0.943 | |||
| Severe | 4 (6%) | 3/4 (75.0%) | 1/4 (25.0%) | ||
| Advanced | 10 (14.9%) | 6/10 (60.0%) | 4/10 (40.0%) | ||
| Mild | 7 (10.4%) | 4/7 (57.1%) | 3/7 (42.8%) | ||
| Normal | 46 (68.7%) | 29/46 (63.0%) | 17/46 (36.9%) | ||
| ART-associated risk factors | |||||
| Initial ART regiments ** | 2.14 | 0.71 | |||
| 1T3E | 25 (35.7%) | 15/25 (60.0%) | 10/25 (40.0%) | ||
| 1TFE | 33 (47.1%) | 20/33 (60.9%) | 13/33 (39.4%) | ||
| 1S3E | 3 (4.3%) | 3/3 (100%) | 0/3 (0%) | ||
| 1S3N | 5 (7.1%) | 3/5 (60.0%) | 2/5 (40.0%) | ||
| 1T3N | 4 (5.7%) | 2/4 (50.0%) | 2/4 (50.0%) | ||
| Current ART regiments | 6.02 | 0.019 | |||
| 1T3E | 16 (23.2%) | 10/16 (62.5%) | 6/16 (37.5%) | ||
| 1TFE | 48 (69.6%) | 30/48 (62.5%) | 18/48 (37.5%) | ||
| 1S3E | 2 (2.9%) | 2/2 (100.0%) | 0/2 (0%) | ||
| 1S3N | 1 (1.4%) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100.0%) | ||
| 1T3N | 2 (2.9%) | 0/2 (0%) | 2/2 (100%) | ||
| ART duration, years | 0.20 | 0.91 | |||
| <5 years | 36 (51.4%) | 23/36 (63.5%) | 13/36 (36.1%) | ||
| 5–10 years | 24 (34.3%) | 14/24 (58.3%) | 10/24 (41.7%) | ||
| >10 years | 10 (14.3%) | 6/10 (60.0%) | 4/10 (40.0%) | ||
| Risk Factors | Hazard Ratio (HR) (95% CI for HR) | B-Coefficient | SE | Wald Chi-Square | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, Years | 2.169 (1.035–4.546) | 0.774 | 0.378 | 4.206 | 0.04 * |
| Triglyceride, mmol/L | 7.855 (1.037–59.469) | 2.061 | 1.033 | 3.982 | 0.046 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apalata, T.; Tsuro, U.; Akapo, O.O. Prolonged Exposure to Antiretroviral Therapy and Risk of Developing Hypertension Among HIV-Infected Clinic Attendees: A Pilot Study in Rural Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22091397
Apalata T, Tsuro U, Akapo OO. Prolonged Exposure to Antiretroviral Therapy and Risk of Developing Hypertension Among HIV-Infected Clinic Attendees: A Pilot Study in Rural Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(9):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22091397
Chicago/Turabian StyleApalata, Teke, Urgent Tsuro, and Olufunmilayo Olukemi Akapo. 2025. "Prolonged Exposure to Antiretroviral Therapy and Risk of Developing Hypertension Among HIV-Infected Clinic Attendees: A Pilot Study in Rural Eastern Cape Province, South Africa" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 9: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22091397
APA StyleApalata, T., Tsuro, U., & Akapo, O. O. (2025). Prolonged Exposure to Antiretroviral Therapy and Risk of Developing Hypertension Among HIV-Infected Clinic Attendees: A Pilot Study in Rural Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(9), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22091397







