Abstract
Background: Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) affect approximately 15% of diabetic patients and are the leading cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputations worldwide. This study examines trends in DFU management, predictors of major amputation and in-hospital mortality, and the impact of comorbidities on outcomes. Methods: Using the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) database (2016–2019), we analyzed non-elective admissions of DFU patients categorized into four treatment groups: no surgery, debridement, minor amputation, and major amputation (below-knee or above-knee). Statistical analyses identified factors associated with major amputation and mortality. Results: A significant increase in minor amputations and debridement was observed between 2016 and 2019, while the number of major amputations declined (p < 0.001). Comorbidities varied significantly by treatment type, with dyslipidemia (49.4–51.0%), chronic kidney disease (30.1–44.2%), and hypertension (32.9–47.0%) being the most prevalent (p < 0.001). Major amputation was associated with the highest rate of in-hospital mortality (1.00%) and the longest hospital stay (11.2 days) (p < 0.001). Logistic regression identified sepsis (OR = 4.9, 95% CI: 4.3–5.6), stroke (OR = 3, 95% CI: 2.1–5.5), and pulmonary embolism (OR = 3.7, 95% CI: 2–6) as key predictors of major amputation, while myocardial infarction (OR = 956, 95% CI: 319–2857) and sepsis (OR = 25, 95% CI: 20–29) were the strongest predictors of mortality (p < 0.001). Conclusions: These findings underscore the impact of comorbidities on DFU outcomes and emphasize the need for early intervention to reduce severe complications. Future research should focus on optimizing management strategies for high-risk patients to improve clinical and surgical outcomes.
1. Introduction
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are a severe and increasingly prevalent complication of diabetes mellitus, affecting an estimated 19% to 34% of individuals with diabetes during their lifetime. In the United States alone, approximately 1.6 million new DFU cases are diagnosed each year [1,2,3]. DFUs represent the leading cause of non-traumatic lower-extremity amputations and are associated with significant morbidity, prolonged hospital stays, and elevated healthcare expenditure [2,3,4,5].
The prognosis for patients with DFUs remains poor. Recent studies report a five-year mortality rate ranging from 30% to 56.6%, depending on ulcer severity and associated complications—rates that exceed those observed in many malignancies [3,6,7]. These data highlight the urgent need for timely prevention, risk stratification, and multidisciplinary care strategies.
The progression of DFUs is often exacerbated by systemic comorbidities such as sepsis, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease (CKD) [5,8,9,10]. Among these comorbidities, CKD has been particularly linked to adverse outcomes and increased in-hospital mortality [11,12]. Early identification and proactive management of these underlying conditions are vital to reducing the risk of severe complications, including limb loss and death [9,13,14,15].
Surgical management of DFUs encompasses a spectrum of procedures, ranging from conservative debridement to more invasive interventions such as minor (e.g., toe) and major (e.g., below-knee or above-knee) amputations. Debridement aims to remove devitalized tissue and promote wound healing, whereas amputations are reserved for more advanced cases with extensive infection or tissue necrosis [10,14,15,16,17,18]. Clinical severity and comorbidity burden often dictate the chosen intervention, with more extensive procedures correlating with longer hospital stays, higher healthcare costs, and increased in-hospital mortality [5,8,16].
In recent years, national data have shown a shift in DFU management trends: while the rates of debridement and minor amputations have increased, major amputation rates have declined, particularly between 2009 and 2015 [6]. This change may reflect improvements in early detection and clinical decision-making. Nevertheless, population-level predictors of major amputation and mortality in DFU patients remain inadequately defined.
Major amputation and in-hospital mortality are critical outcome measures in DFU care due to their strong associations with permanent disability, diminished quality of life, and substantial economic burden. Identifying clinical predictors of these outcomes is essential for optimizing risk stratification, guiding treatment decisions, and allocating healthcare resources more effectively.
The aims of this study are as follows: (1) to assess national trends in DFU management between 2016 and 2019; (2) to evaluate the distribution of comorbidities across treatment modalities; and (3) to identify independent predictors of major amputation and in-hospital mortality. We hypothesize that specific clinical variables—including sepsis, CKD, and cardiovascular events—are independently associated with an increased risk of these adverse outcomes.
Research Questions
What are the trends in DFU management, how do comorbidities influence treatment choices, and what are the key predictors of major amputation and in-hospital mortality?
2. Methods
2.1. Dataset Acquisition and Inclusion Criteria
This study utilized data extracted from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database, the largest publicly available all-payer inpatient care database in the United States. The dataset covered the period from 1 January 2016 to 31 December 2019. The study included all patients who presented to U.S. hospitals with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), focusing on non-elective admissions. Patients were categorized into four groups based on the type of treatment they received: no surgery, debridement (soft tissue surgery), minor amputation (various ICD-10 codes for minor amputations), and major amputation (specifically below-knee amputation (BKA) or above-knee amputation (AKA).
2.2. Statistical Analyses
Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 26 and MATLAB 2024, with a significance threshold set at a p-value of less than 0.05. Comorbidities were identified and validated through a comprehensive review of patient-specific ICD-10 codes. Various statistical tests, including logistic regression modeling, were performed to visualize annual trends, discern significant predictors, and derive key statistical insights. Microsoft Excel was employed for data visualization purposes.
Variables were selected for inclusion in multivariate models based on clinical relevance and statistical significance (p < 0.05) in univariate analyses. Feature selection was performed using backward stepwise logistic regression to identify independent predictors. Model validation was conducted through internal cross-validation using random subsets of the dataset, and goodness-of-fit was assessed using Hosmer–Lemeshow tests and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
2.3. Outcome Measures
The primary outcome measures included the incidence of major amputation and in-hospital mortality among patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Secondary outcomes included the length of hospital stay and total hospital charges. The study also assessed the prevalence of postoperative complications and comorbidities across different treatment groups.
2.4. Ethical Considerations
The study was conducted under exemption status granted by the institutional review board, and the requirement for informed consent was waived due to the de-identified nature of the NIS dataset.
3. Results
Table 1 provides a detailed overview of the demographic and baseline characteristics of diabetic foot ulcer patients, categorized by the type of procedure they received. The data highlight notable differences in age, gender, payer type, and racial distribution among patients undergoing no surgery, debridement, minor amputation, and major amputation. These differences are statistically significant and underscore the varying profiles of patients based on their treatment options.

Table 1.
Demographic and baseline characteristics of diabetic foot ulcer patients by type of procedure.
3.1. Annual Distribution of Procedures for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Patients
Figure 1 illustrates the annual trends in the types of procedures performed for diabetic foot ulcer patients from 2016 to 2019. The data demonstrate a significant increase in the percentage of patients undergoing debridement, while the percentage of those receiving major amputations has decreased over time. Both trends are statistically significant, with p-values of less than 0.001.
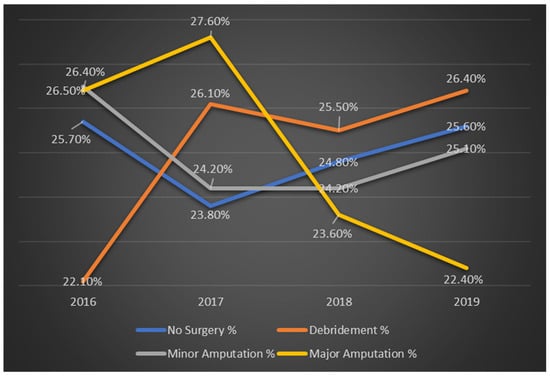
Figure 1.
Trends in procedure types for diabetic foot ulcer patients by year in %.
3.2. Distribution of Comorbidities by Procedure Type
Table 2 displays the prevalence of various comorbidities among diabetic foot ulcer patients based on the type of procedure they underwent. Key observations include that dyslipidemia is most common across all groups, with the highest prevalence among patients undergoing minor amputation. Chronic kidney disease shows a significant increase with the severity of the procedure, peaking in major amputation cases. Hypertension and chronic lung disease are more prevalent in patients who have not undergone surgery. Obstructive sleep apnea and neoplasms are less common but still exhibit significant differences across the treatment groups. Osteoporosis and Parkinson‘s disease are rare and do not show significant statistical differences.

Table 2.
Prevalence of comorbidities by procedure type for diabetic foot ulcer patients.
3.3. Trends in Postoperative Complications Across Different Treatment Modalities for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Table 3 shows the incidence of postoperative complications associated with different treatment modalities for diabetic foot ulcers. The data reveal that acute kidney injury is significantly more common in patients undergoing major amputation compared to those receiving no surgery or debridement. Sepsis and stroke are notably rare but exhibit significantly higher rates among major amputation patients. Urinary tract infection and deep vein thrombosis also show statistically significant differences, with higher incidence in patients who underwent more invasive procedures. Pneumonia and ileus are less frequent but still significantly more common in those undergoing major amputation.

Table 3.
Postoperative complications by procedure type in DFU patients.
3.4. Outcomes by Treatment Modality for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Table 4 details the postoperative outcomes associated with different treatment modalities for diabetic foot ulcers. Mortality rates during hospitalization show a clear increase with the severity of treatment, with major amputations associated with a significantly higher mortality rate of 1.00%, compared to just 0.10% for patients receiving no surgery (p < 0.001). The length of hospital stay escalates with more invasive treatments. Patients who underwent major amputations had the longest average stay of 11.2 days, while those with no surgery had the shortest stay of 4.4 days (p < 0.001). Total hospital charges follow the same trend, with major amputations resulting in the highest average costs of USD 100,616, compared to USD 34,752 for patients with no surgery (p < 0.001).

Table 4.
Clinical outcomes of DFU patients by treatment modality.
3.5. Multivariate Predictors of Major Amputation
Figure 2 illustrates the odds ratios (OR) for various predictors of major amputation in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. The odds ratio quantifies the odds of a particular outcome (major amputation) occurring with the presence of a specific predictor variable compared to the absence of that predictor. The predictors with the highest odds ratios include sepsis (OR = 4.877, 95% CI: 4.256 to 5.588), stroke (OR = 3.411, 95% CI: 2.109 to 5.518), and pulmonary embolism (PE) (OR = 3.701, 95% CI: 2.113 to 6.48). This indicates that these conditions are strongly associated with an increased likelihood of major amputation. Other predictors include dementia (OR = 1.763, 95% CI: 1.511 to 2.056) and neoplasms (OR = 1.502, 95% CI: 1.235 to 1.828), which also show significant associations with major amputation. Peripheral vascular disease (OR = 1.496, 95% CI: 1.365 to 1.64) and pneumonia (OR = 1.614, 95% CI: 1.302 to 2.00) are also significant predictors.
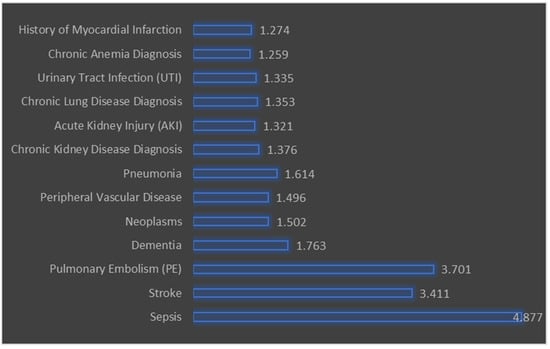
Figure 2.
Multivariate predictors of major amputation in diabetic foot ulcers.
All predictors listed have a p-value of less than 0.001, indicating that they are statistically significant predictors of major amputation.
3.6. Multivariate Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality
Table 5 presents the OR for various predictors of mortality among patients with DFUs. All predictors listed have a p-value of less than 0.001, indicating a high level of statistical significance.

Table 5.
Multivariate predictors of in-hospital mortality in diabetic foot ulcer patients.
The data show that myocardial infarction (MI) has an exceptionally high odds ratio of 955.978, suggesting an extremely elevated likelihood of death associated with this condition. Similarly, respiratory failure and sepsis also exhibit very high odds ratios of 44.068 and 25.025, respectively, reflecting their substantial impact on mortality. Stroke and pneumonia have somewhat lower but still notable odds ratios of 7.447 and 4.167, indicating their significant roles in predicting death. Additionally, urinary tract infection (UTI) and osteoporosis diagnosis have moderate odds ratios of 3.041 and 2.754, respectively, suggesting that while these conditions are significant predictors, their impact on mortality is less pronounced compared to the conditions with higher odds ratios. Finally, dementia and chronic anemia diagnosis have the lowest odds ratios among the significant predictors, at 1.808 and 1.794, respectively, though they still represent important factors associated with increased mortality.
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
The primary finding of this study is that while the absolute number of major amputations in DFU management has not significantly changed, the use of minor amputations and debridement has increased over time. This shift may reflect improvements in early detection and localized interventions that help prevent disease progression to more severe forms requiring major limb loss. Similar trends have been reported in prior nationwide analyses, including the study by Armstrong et al., who noted increased use of limb-sparing procedures over the past decade [6,13].
The severity of surgical intervention strongly correlates with poor outcomes. However, an important question remains: are these adverse outcomes driven by the severity of comorbidities, the invasiveness of the intervention itself, or a combination of both? Our data show that patients undergoing major amputations are significantly more likely to experience complications such as urinary tract infections, pneumonia, ileus, and deep vein thrombosis—findings that align with prior studies highlighting the elevated risks of prolonged immobilization and systemic infection in these patients [10,12].
Cardiovascular disease appears to play a central role in the prognosis of DFU patients. Dyslipidemia—an established component of metabolic syndrome—was the most prevalent comorbidity across all treatment groups, emphasizing the need for aggressive systemic disease management [4,6,13,18,19]. CKD, both acute and chronic, was most prevalent among patients requiring major amputations. This finding reinforces the bidirectional relationship between renal dysfunction and poor wound healing in diabetics, as shown in previous studies [20,21,22,23,24].
Of particular note, myocardial infarction (MI) emerged as the strongest independent predictor of in-hospital mortality (OR = 956). Although this figure is statistically accurate based on our model, we acknowledge that such an elevated odds ratio may reflect model instability due to low counts in the non-MI comparison group or collinearity between MI and other high-risk features, such as sepsis or multi-organ failure. Similar findings have been reported in critical care cohorts, where acute MI significantly increases inpatient mortality risk [21]. We have now added a cautionary note regarding this result in both the Abstract and Discussion to clarify its interpretation.
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is well established as a major driver of DFU severity, delayed wound healing, and limb loss. While we agree with its clinical importance, the coding of PAD within the NIS database is inconsistent across hospitals and often underreported. For this reason, PAD was excluded from our final regression models.
Our findings are consistent with studies such as those by Zhang et al. and Apelqvist et al., which emphasize the importance of multidisciplinary care and early vascular assessment in reducing amputation rates [22]. The elevated risks associated with sepsis, pulmonary embolism, and stroke—classified in our study as complications rather than comorbidities—highlight the urgency of early medical intervention and aggressive infection control.
Caregivers should anticipate higher mortality rates, longer hospital stays, and increased healthcare costs with more invasive interventions. This information is essential for shared decision-making, helping both patients and clinicians weigh the benefits and risks of available treatment strategies. For instance, Ndip et al. demonstrated that the presence of CKD significantly increases mortality in amputee patients with DFUs, further emphasizing the importance of preoperative optimization [24,25,26,27].
Finally, while this study identifies several independent predictors of poor outcomes, it does not fully elucidate the complex pathways leading to these endpoints. The observed decline in major amputations may not solely reflect improved clinical practice—it could also be influenced by changing hospital admission patterns, coding practices, or demographic shifts. Future research should incorporate longitudinal designs and patient-reported outcome measures to better assess long-term recovery and quality of life.
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
This study benefits from the use of a large, nationally representative dataset spanning multiple years, which provides robust insights into DFU trends, surgical outcomes, and hospital-level care patterns across the United States. However, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, the use of administrative data restricts access to detailed clinical information, such as ulcer severity, laboratory values, glycemic control, or outpatient treatment history. Additionally, the NIS does not provide long-term follow-up or patient-reported outcomes, which are essential for assessing the sustained impact of interventions.
Second, while comorbidities and complications were identified using ICD-10 codes, these diagnoses were not validated against medical records [28,29,30,31]. This introduces the potential for misclassification or coding inaccuracies. Third, the cross-sectional design of the dataset precludes any inference of causality between predictors and outcomes [28,29,30,31].
Furthermore, the NIS does not capture important contextual variables such as quality of care, hospital-specific practices, or socioeconomic status. These unmeasured factors may influence treatment decisions and outcomes, leading to residual confounding. For instance, patients from underserved communities or hospitals with limited resources may experience delays in diagnosis or differences in clinical management.
Despite these limitations, our study offers valuable national-level evidence and identifies high-risk profiles that can inform future prospective studies. Future research should aim to validate these findings in clinical cohorts and incorporate longitudinal data to better assess causality and long-term outcomes.
5. Conclusions
This nationwide analysis identifies sepsis, stroke, and pulmonary embolism as the strongest independent predictors of major amputation, while myocardial infarction, sepsis, and respiratory failure are the most powerful predictors of in-hospital mortality in DFU patients. These findings reinforce the critical need for early detection and aggressive management of systemic complications in DFU care.
These findings underscore the importance of early intervention and the careful management of comorbidities to mitigate severe outcomes. Further research is warranted to explore strategies for optimizing care and improving long-term outcomes in patients with DFUs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.B. and D.M.; writing—original draft, D.M. and L.B.Z.; writing—review and editing, L.B.Z. and M.M.; supervision, Y.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted under the exemption status granted by the Carmel medical Center review board.
Informed Consent Statement
The requirement for informed consent was waived due to the de-identified nature of the NIS dataset.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
List of Abbreviations (A–Z):
| AKA | Above-Knee Amputation |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| BKA | Below-Knee Amputation |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| DFU | Diabetic Foot Ulcer |
| DVT | Deep Vein Thrombosis |
| HMO | Health Maintenance Organization |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision |
| LOS | Length of Stay |
| MI | Myocardial Infarction |
| NIS | National Inpatient Sample |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PAD | Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| PE | Pulmonary Embolism |
| UTI | Urinary Tract Infection |
References
- Adams, C.A., Jr.; Deitch, E.A. Diabetic foot infections. In Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented; Zuckschwerdt: Munich, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, D.G.; Boulton, A.J.; Bus, S.A. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Berendt, A.R.; Cornia, P.B.; Pile, J.C.; Peters, E.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Deery, H.G.; Embil, J.M.; Joseph, W.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; et al. 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, e132–e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownrigg, J.R.; Davey, J.; Holt, P.J.; Davis, W.A.; Thompson, M.M.; Ray, K.K.; Hinchliffe, R.J. The association of ulceration of the foot with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, C.; Okoloise, M.; Williams, K.; Stern, M.P.; Haffner, S.M. The metabolic syndrome as predictor of type 2 diabetes: The San Antonio heart study. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffcoate, W.J.; Harding, K.G. Diabetic foot ulcers. Lancet 2003, 361, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, C.J.; Libby, G.; Brennan, G.M.; MacAlpine, R.R.; Morris, A.D.; Leese, G.P.; DARTS/MEMO Collaboration. Mortality and hospitalization in patients after amputation: A comparison between patients with and without diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2252–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Chawla, S. Amputation in diabetic patients. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2006, 62, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, B.; Pomposelli, F.; Talmor, D.; Park, K.W. Perioperative and long-term morbidity and mortality after above-knee and below-knee amputations in diabetics and nondiabetics. Anesth. Analg. 2005, 100, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, D.P.; Armstrong, D.G.; Dacus, J.B.; Laughlin, T.J.; Morgan, C.B.; Lavery, L.A. The natural history of great toe amputations. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 1997, 36, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Liu, J.; Sun, H. Risk factors for lower extremity amputation in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ndip, A.; Lavery, L.A.; Boulton, A.J. Diabetic foot disease in people with advanced nephropathy and those on renal dialysis. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2010, 10, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prompers, L.; Huijberts, M.; Apelqvist, J.; Jude, E.; Piaggesi, A.; Bakker, K.; Edmonds, M.; Holstein, P.; Jirkovska, A.; Mauricio, D.; et al. High prevalence of ischaemia, infection and serious comorbidity in patients with diabetic foot disease in Europe. Baseline results from the Eurodiale study. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Zha, P.; Bista, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Ran, X.; et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of lower extremity amputation in the diabetic inpatients with foot ulcers. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1144806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thornhill, H.L.; Jones, G.D.; Brodzka, W.; VanBockstaele, P. Bilateral below-knee amputations: Experience with 80 patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1986, 67, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traballesp, M.; Brunelli, S.; Pratesi, L.; Pulcini, M.; Angioni, C.; Paolucci, S. Prognostic factors in rehabilitation of above knee amputees for vascular diseases. Disabil. Rehabil. 1998, 20, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.L.; Nather, A.; Liang, S.; Chang, Z.; Wong, T.T.; Lim, C.T. Clinical outcomes of below knee amputations in diabetic foot patients. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2013, 42, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.W.; Selvin, E. Epidemiology of Peripheral Neuropathy and Lower Extremity Disease in Diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2019, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, S.J.; Lewis, J.D. Above-knee amputation. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1991, 73, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Criqui, M.H.; Aboyans, V. Epidemiology of peripheral artery disease. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1509–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayya, D.; O’Neill, O.; Habib, N.; Moore, J.; Iyer, K.; Huedo-Medina, T.B. Debridement of diabetic foot ulcers: Public health and clinical implications—A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. BMJ Surg. Interv. Health Technol. 2022, 4, e000081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayya, D.; O’Neill, O.J.; Huedo-Medina, T.B.; Habib, N.; Moore, J.; Iyer, K. Debridement of diabetic foot ulcers. Adv. Wound Care 2022, 11, 666–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M. Metabolic Syndrome Update. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 26, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masenga, S.K.; Kabwe, L.S.; Chakulya, M.; Kirabo, A. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Met, R.; Janssen, L.I.; Wille, J.; Langezaal, A.E.; van de Mortel, R.W.; van de Pavoordt, E.D.; de Vries, J.P. Functional results after through-knee and above-knee amputations: Does more length mean better outcome? Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2008, 42, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulik, P.K.; Mtonga, R.; Gill, G.V. Amputation and mortality in new-onset diabetic foot ulcers stratified by etiology. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roon, A.J.; Moore, W.S.; Goldstone, J. Below-knee amputation: A modern approach. Am. J. Surg. 1977, 134, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maman, D.; Mahamid, A.; Finkel, B.; Gan-Or, H.; Fournier, L.; Berkovich, Y.; Behrbalk, E. Comparative evaluation of postoperative outcomes and expenditure between robotic and conventional single-level lumbar fusion surgery: A comprehensive analysis of nationwide inpatient sample data. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 2637–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maman, D.; Laver, L.; Becker, R.; Mahamid, A.; Berkovich, Y. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty reduces postoperative complications and length of stay without increased cost compared to navigation-guided techniques: A national analysis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2025, 33, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maman, D.; Laver, L.; Becker, R.; Takrori, L.A.; Mahamid, A.; Finkel, B.; Gan-Or, H.; Yonai, Y.; Berkovich, Y. Trends and Epidemiology in Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: Reduced Complications and Shorter Hospital Stays. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2025, 32, 3281–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maman, D.; Mahamid, A.; Yonai, Y.; Berkovich, Y. Comparing Complication Rates, Costs, and Length of Stay between Unicompartmental and Total Knee Arthroplasty: Insights from a Big Data Analysis Using the National Inpatient Sample Dataset. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).