Health Literacy in People with Type 1 Diabetes: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Search Methods: Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Study Assessment and Eligibility
2.5. Selection Process Strategy
2.6. Data Items and Data Extraction
2.7. Synthesis of Results
2.8. Risk of Bias
3. Results
3.1. Selection Process
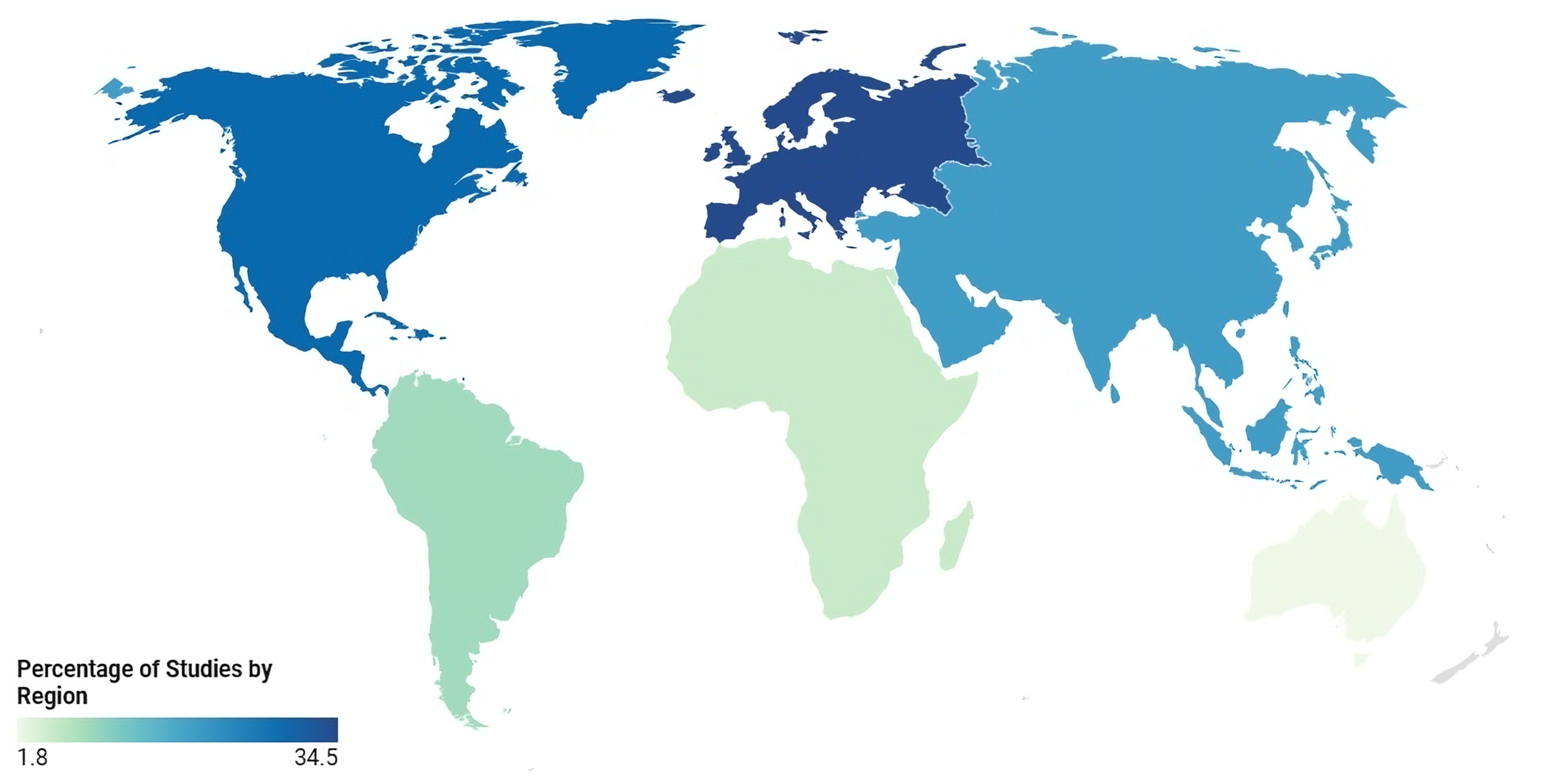
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Records
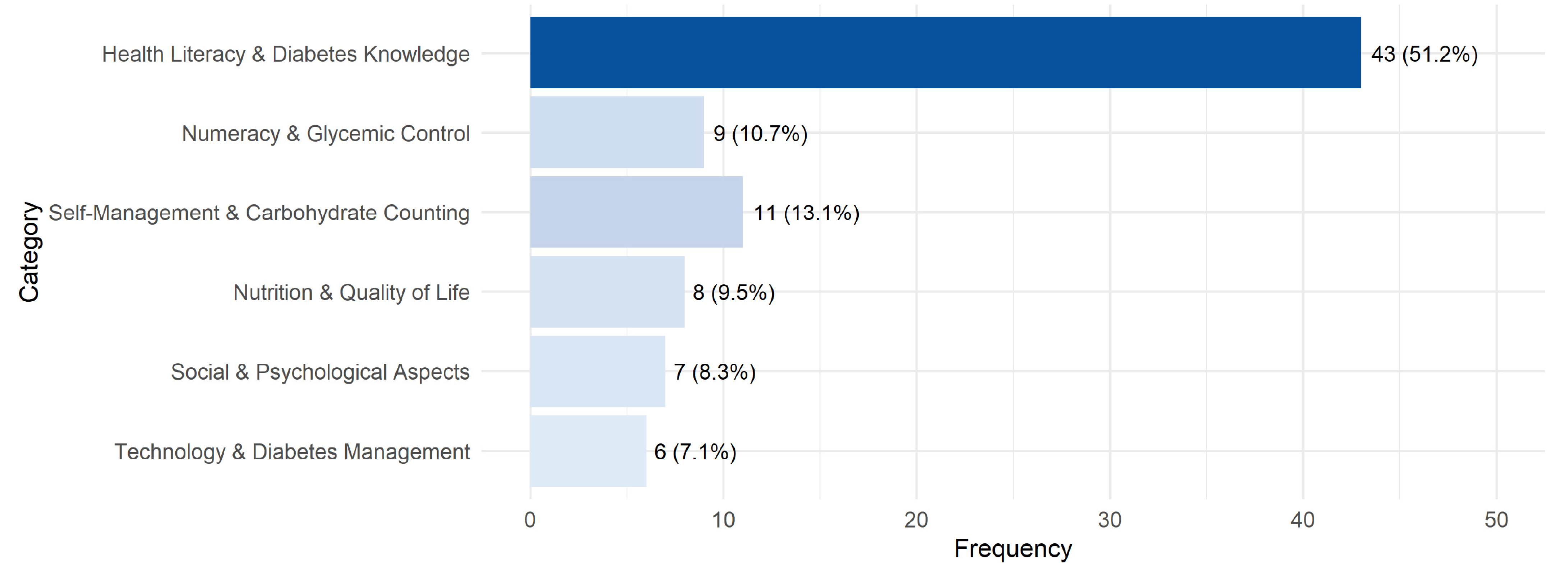
3.3. RQ1 Concepts Related to Health Literacy
3.4. RQ2 Factors Influence Health Literacy in People with Type 1 Diabetes
3.4.1. Individual Factors: Experience, Education, and Numeracy
3.4.2. Cognitive and Functional Impairments
3.4.3. Social and Psychological Factors
3.4.4. Disease Management and Dietary Knowledge
3.4.5. Socio-Demographic Disparities and Comorbidities
3.4.6. Age-Stratified Analysis of Health Literacy, Numeracy, and Diabetes Management
3.5. RQ3 Relationships Between HL and Health Outcomes
3.5.1. Impact of HL on Glycemic Control and Self-Management
3.5.2. The Role of HL in Disease Outcomes and Technology Use
3.5.3. Disparities in HL and Disease Outcomes
3.5.4. HL and Clinical Outcomes
3.5.5. HL, Perceived Competence, and Adherence
3.6. RQ4 Implications for Nursing Practice
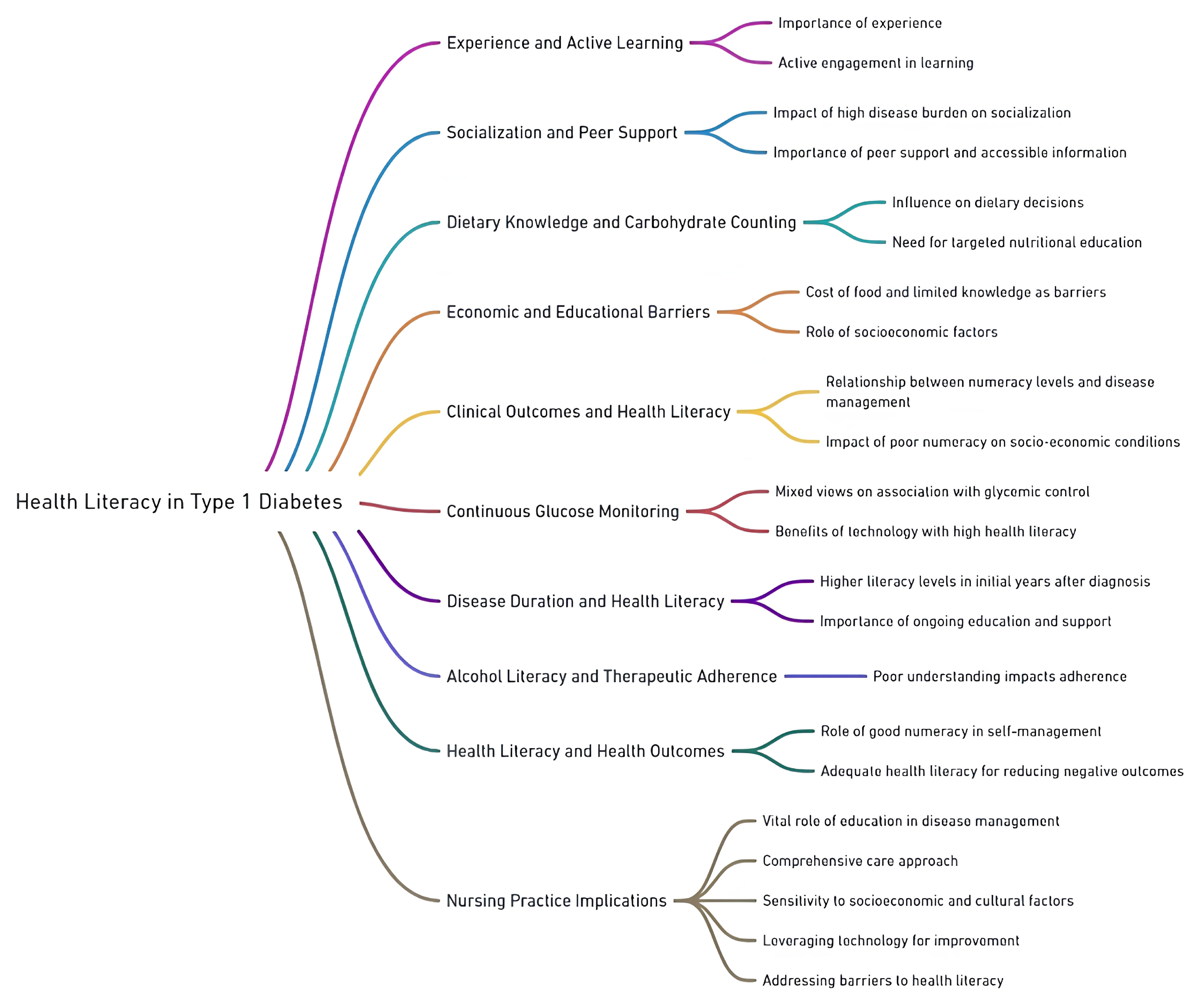
3.7. Main Concepts: Mind Map of the Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acronym | Extended Form |
| T1DM | Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| HL | Health Literacy |
| HLQ | Health Literacy Questionnaire |
| s-TOFHLA | Test of Functional Health Literacy in Adults—Short Form |
| NVS | Newest Vital Sign |
| DNT-15 | 15-Item Diabetes Numeracy Test |
| REALM | Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy in Medicine |
| DMQ | Diabetes Mathematical Questionnaire |
| FHL | Functional Health Literacy |
| IADLs | Instrumental Activities of Daily Living |
| CGM | Continuous Glucose Monitoring |
| PCC | Population, Concept, and Context (JBI Framework) |
| PRISMA-ScR | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews |
| JBI | Joanna Briggs Institute |
References
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas Tenth Edition 2021. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Ogle, G.D.; Wang, F.; Gregory, G.A.; Maniam, J. Type 1 Diabetes Estimates in Children and Adults. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/resources/idf-diabetes-atlas-reports/type-1-diabetes-estimates-in-children-and-adults/ (accessed on 13 January 2024).
- Xu, X.Y.; Leung, A.Y.M.; Chau, P.H. Health Literacy, Self- Efficacy, and Associated Factors among Patients with Diabetes. Health Lit. Res. Pract. 2018, 2, e67–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, D.C.; Barry, S.; Wagner, D.V.; Speight, J.; Choudhary, P.; Harris, M.A. Distal Technologies and Type 1 Diabetes Management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlebowy, D.O. The Complexity of Diabetes Self-Care. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2021, 43, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotidis, P.; Kalokairinou, A.; Tzavara, C.; Michailidou, A.; Velonaki, V.S. Health Literacy, Self-Efficacy and Glycemic Control in Patients with Diabetes Type 2 in a Greek Population. Cureus 2024, 16, e55691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, D.A.; Nordin, A.; Johansson, U.B.; Nilsson, J. eHealth Literacy and Its Association with Demographic Factors, Disease-Specific Factors, and Well-Being among Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Cross-Sectional Survey Study. JMIR Diabetes 2025, 10, e66117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutbeam, D. Health Literacy as a Public Health Goal: A Challenge for Contemporary Health Education and Communication Strategies into the 21st Century. Health Promot. Int. 2000, 15, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, T.A.; Stichler, J.F.; Barton, A.J.; Loan, L.A.; Boyle, D.K.; Allen, P.E. A Concept Analysis of Health Literacy. Nurs. Forum 2019, 54, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofaeono, V.; Tong, K.; Sy, A.; Cassel, K.; Pagano, I.; Ka’opua, L.S.I.; Scanlan, L.; Thompson, L.; Vaofanua, T.; McCutchan, J.B.; et al. Validation of the Short-Test of Functional Health Literacy in Adults for the Samoan Population. Health Lit. Res. Pr. 2022, 6, e247–e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.C.; Long, S.W.; Jackson, R.H.; Mayeaux, E.J.; George, R.B.; Murphy, P.W.; Crouch, M.A. Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy in Medicine: A Shortened Screening Instrument. Fam. Med. 1993, 25, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, K.; Van den Broucke, S.; Pelikan, J.M.; Fullam, J.; Doyle, G.; Slonska, Z.; Kondilis, B.; Stoffels, V.; Osborne, R.H.; Brand, H.; et al. Measuring Health Literacy in Populations: Illuminating the Design and Development Process of the European Health Literacy Survey Questionnaire (HLS-EU-Q). BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levic, M.; Bogavac-Stanojevic, N.; Krajnovic, D. The Instruments Used to Assess Health Literacy and Pharmacotherapy Literacy of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Patients: A Scoping Review. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 747807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.-H.; Kim, C.-J.; Lee, J.; Moon, S.H. Self-Administered Health Literacy Instruments for People with Diabetes: Systematic Review of Measurement Properties. J. Adv. Nurs. 2017, 73, 2035–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H. Health Literacy and Diabetes Self-Care Activities: The Mediating Effect of Knowledge and Patient Activation. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2021, 27, e12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broos, B.; Charleer, S.; Bolsens, N.; Moyson, C.; Mathieu, C.; Gillard, P.; De Block, C. Diabetes Knowledge and Metabolic Control in Type 1 Diabetes Starting with Continuous Glucose Monitoring: FUTURE-PEAK. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e3037–e3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RobatSarpooshi, D.; Mahdizadeh, M.; Alizadeh Siuki, H.; Haddadi, M.; Robatsarpooshi, H.; Peyman, N. The Relationship Between Health Literacy Level and Self-Care Behaviors in Patients with Diabetes. PROM 2020, 11, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, K.; F Reynheim, A.L.; Joensen, L.; Ridderstråle, M.; Kayser, L.; Maindal, H.T.; Osborne, R.H.; Skinner, T.; Willaing, I. Higher Health Literacy Is Associated with Better Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cohort Study among 1399 Danes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2017, 5, e000437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffari-Fam, S.; Lotfi, Y.; Daemi, A.; Babazadeh, T.; Sarbazi, E.; Dargahi-Abbasabad, G.; Abri, H. Impact of Health Literacy and Self-Care Behaviors on Health-Related Quality of Life in Iranians with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohanny, W.; Wu, S.-F.V.; Liu, C.-Y.; Yeh, S.-H.; Tsay, S.-L.; Wang, T.-J. Health Literacy, Self-Efficacy, and Self-Care Behaviors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pr. 2013, 25, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, I.; Cipponeri, E.; Ripa, P.; Magon, A.; Cilluffo, S.; Terzoni, S.; Lusignani, M.; Caruso, R. Literature Trends and Hidden Patterns in Health Literacy Studies among Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes: A Scoping Review Protocol. MethodsX 2024, 13, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, R.; Magon, A.; Baroni, I.; Dellafiore, F.; Arrigoni, C.; Pittella, F.; Ausili, D. Health Literacy in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, I.; Cipponeri, E.; Ripa, P.; Caruso, R. Health Literacy in People with Type 1 Diabetes: A Scoping Review Protocol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping Studies: Towards a Methodological Framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levac, D.; Colquhoun, H.; Brien, K.K.O. Scoping Studies: Advancing the Methodology. Implement. Sci. 2010, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; Mcinerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Update Methodological Guidance for the Conduct of Scoping Reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Godfrey, C.M.; McInerney, P.; Soares, C.B.; Khalil, H.; Parker, D. Methodology for JBI Scoping Reviews. In The Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers’ Manual 2015; Joanna Briggs Institute: North Adelaide, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trochim, W.M. Hindsight Is 20/20: Reflections on the Evolution of Concept Mapping. Eval. Program. Plan. 2017, 60, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, M.; Sheppard, L. Mind Mapping Research Methods. Qual. Quant. 2012, 46, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Godfrey, C.; McInerney, P.; Munn, Z.; Tricco, A.C.; Khalil, H. Chapter 11: Scoping Reviews. In JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; Joanna Briggs Institute: North Adelaide, Australia, 2020; ISBN 978-0-648-84880-6. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Barrera, E.; Duran-Perez, E.G.; Almedavaldes, P.; Mehta, R.; Cuevas-Ramos, D.; Gomezperez, F.J. Impact of Diabetes-Related Numeracy, Diabetes Self-Care Activities and Depression on Metabolic Control in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 2011, 60, A202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marden, S.; Thomas, P.; Lueddeke, J.; Kerr, D.; Knott, J. Numeracy and Literacy Skills and Achieved Glycaemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marden, S.; Thomas, P.W.; Sheppard, Z.A.; Knott, J.; Lueddeke, J.; Kerr, D. Poor Numeracy Skills Are Associated with Glycaemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabet. Med. A J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2012, 29, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosa, F.Y.; Segal, D. Assessing Maths Literacy Skills in Type 1 Diabetic Children and Their Caregivers. J. Endocrinol. Metab. Diabetes South. Afr. 2011, 16, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrakeeva, E.; Romanova, N.; Zalevskaya, A. Poor Numeracy as a Limitating Factor for Type 1 Diabetes Patients on Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2013, 15, A49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, K.D.; Dyson, P.; Sinclair, J.M.A.; Young, A.J.; Lawton, J.M.A.; Holt, R.I.G. Alcohol Health Literacy in Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Web-Based Study Highlights the Extent of the Problem. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2014, 16, A109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, K.D.; Holt, R.I.G.; Lawton, J.; Sinclair, J.M.A.; Young, A.J.; VanDenTol, A.; Dyson, P. Alcohol Health Literacy in Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes and Impact on Diabetes Management. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, P.; Sutcliffe, K.; Curtis, K. Children as Partners with Adults in Their Medical Care. Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatt, G.A.; Valerio, M.A.; Nwankwo, R.; Lucas, S.M.; Funnell, M.M. Health Literacy among Insulin-Taking African Americans: A Need for Tailored Intervention in Clinical Practice. Diabetes Educ. 2014, 40, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, M.; Andrade, L.; Maia, M. I Know, so I Do! Relationship between Literacy and Metabolic Control in Patients with Type i Diabetes. Aten. Primaria 2013, 45, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, C.; Meliker, J.; Floreen Sabino, A. Nutrition Literacy: What Are Young Adults with Type- 1 Diabetes Missing ? Cureus 2023, 15, e39899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghittu, A.; Deiana, G.; Castiglia, E.; Pacifico, A.; Brizzi, P.; Cossu, A.; Castiglia, P.; Dettori, M. Knowledge, Attitudes, and Behaviors towards Proper Nutrition and Lifestyles in Italian Diabetic Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Morais Borges Marques, R.; Rizzo, M.F.; De Carvalho Félix, P.L. Health and Nutritional Literacy of Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzkovitz, A. Food Literacy of Young Canadian Adults Living with Type 1 Diabetes; McGill University: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lappenschaar, T. Is Good Knowledge of Carbohydrates and Numeracy before Starting Continuous Glucose Measurement a Criteria for Succesful Treatment? Pediatr. Diabetes 2012, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruhaim, H.Y.; Almigbal, T.H.; Almutairi, J.S.; Mujammami, M.H.; AlMogbel, T.A.; Alrasheed, A.A.; Al Zahrani, A.M.; Batais, M.A. The Association between Diabetes Numeracy and Diabetes Self-Management among Saudi Adults with Insulin-Treated Diabetes. Saudi Med. J. 2021, 42, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouclaous, C.; Azar, L.; Barmo, N.; Daher, R.; Tabaja, J.; El Hout, G.; Berika, L. Levels and Correlates of Numeracy Skills in Lebanese Adults with Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, U.; Schillinger, D. Does Lower Diabetes-Related Numeracy Lead to Increased Risk for Hypoglycemic Events? Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 149, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuercher, E.; Diatta, I.D.; Burnand, B.; Peytremann-Bridevaux, I. Health Literacy and Quality of Care of Patients with Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Prim. Care Diabetes 2017, 11, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangi, A.; Khan, H.; Junno, A.; Nindwani, R.; Yousuf, M.; Shehanshah, M. Knowledge, Attitude and Practice about Diabetes among Diabetic Patients in Sindh, Pakistan. Rawal Med. J. 2018, 43, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Muniz, L.H.; Gomes, M.B.; Negrato, C.A.; De Campos Calassara, P.; Dias, A.L.N. Health Literacy and Glycemic Control in Patients with Diabetes: A Tertiary Care Center Study in Brazil. In Proceedings of the 22nd Brazilian Diabetes Society Congress, Natal, Brazil, 16–18 October 2019; P135. p. 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, B.A.; Ofori-Boateng, P.; Forbes, A.; Doku, D.T. Knowledge of Young People Living with Type 1 Diabetes and Their Caregivers about Its Management. Nurs. Open 2023, 10, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwennesen, N.; Barghadouch, A.; Olesen, K. Health Literacy and Self-Care among Visually Impaired People with Type 1 Diabetes in Denmark. Chronic Illn. 2018, 15, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Olesen, K. Social Inequalities in the Self-Management of Type 1 Diabetes: A Serial Multiple Mediation Analysis. Scand. J. Public. Health 2023, 51, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drown, L.; Adler, A.J.; Schwartz, L.N.; Sichali, J.; Valeta, F.; Boudreaux, C.; Trujillo, C.; Ruderman, T.; Bukhman, G. Living with Type 1 Diabetes in Neno, Malawi: A Qualitative Study of Self-Management and Experiences in Care. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2023, 23, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naef, A.A.N.; Fischbock, N.; Tezcan-Güntekin, H.; Amelung, V.E. Promoting Health Literacy through Digital Health among Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes- Perspectives of Experts and Patients. Gesundheitswesen 2023, 85, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, K.K.; Baranowski, T.; Anderson, B.J.; Bansal, N.; Redondo, M.J. Psychosocial Aspects of Type 1 Diabetes in Latino and Asian-American Youth. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 80, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, I.; Esen, S. Health Literacy and Quality of Life in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Cureus J. Med. Sci. 2020, 12, 10860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broos, B.; Charleer, S.; Bolssens, N.; Moyson, C.; Mathieu, C.; Gillard, P.; De Block, C. Influence of Diabetes Knowledge and Health Literacy on Metabolic Control in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Starting with Flash Glucose Monitoring: Future-Peak Trial. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, A17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan, L.A.; Walsh, S.J.; Shelton, D. Relationships of Illness Representation, Diabetes Knowledge, and Self-Care Behaviour to Glycemic Control in Incarcerated Persons with Diabetes. Int. J. Prison. Health 2016, 12, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chima, C.C.; Abdelaziz, A.; Asuzu, C.; Beech, B.M. Impact of Health Literacy on Medication Engagement among Adults with Diabetes in the United States: A Systematic Review. Diabetes Educ. 2020, 46, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, K. From the Editor’s Desk. Top. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 37, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciano, L.; Camerini, A.-L.; Schulz, P.J. The Role of Health Literacy in Diabetes Knowledge, Self-Care, and Glycemic Control: A Meta-Analysis. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogessie, H.M.; Gebeyehu, M.A.; Kenbaw, M.G.; Tadesse, T.A. Diabetic Health Literacy and Associated Factors among Diabetes Mellitus Patients on Follow up at Public Hospitals, Bale Zone, South East Ethiopia, 2021. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.B.; Muniz, L.H.; Melo, L.G.N.; Pizarro, M.H.; Barros, B.S.V.; Santos, D.C.; Negrato, C.A. Health Literacy and Glycemic Control in Patients with Diabetes: A Tertiary Care Center Study in Brazil. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owusu, B.A.; Ofori-Boateng, P.; Doku, D.T. Coping and Adaptation Strategies among Young Persons Living with Type 1 Diabetes and Their Caregivers: Textual and Photovoice Analyses. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs Early, K. Value of Carbohydrate Counting. BMJ Nutr. Prev. Heal. 2023, 6, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc, B.; Von Oettingen, J.E.; Duperval, R.; Altenor, K.; Joseph, M. 49 Effects of numeracy and literacy on glycemic control and self-perceived efficacy in youth with type 1 diabetes in Haiti. Paediatr. Child Health 2024, 29, e22–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, C.Y.; Cavanaugh, K.; Wallston, K.A.; Rothman, R.L. Self-Efficacy Links Health Literacy and Numeracy to Glycemic Control. J. Health Commun. 2010, 15, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancrainte, L.; Shah, A.S.; Bowers, K.A.; Leyendecker, A.C.; Jones, N.Y. Health Literacyand Quality of Life in Young Adults from the Belgian Crohn’s Disease Registry Compared toType 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 624416. [Google Scholar]
- Turrin, K.B.; Trujillo, J.M. Effects of Diabetes Numeracy on Glycemic Control and Diabetes Self-Management Behaviors in Patients on Insulin Pump Therapy. Diabetes Ther. 2019, 10, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H.; Ogawa, R.; Otsuki, A.; Saito, J.; Yaguchi-Saito, A.; Kuchiba, A.; Fujimori, M.; Fukuda, Y.; Shimazu, T. INFORM Study Group Effect Modification by Geographic Area on the Association between Health Literacy and Self-Rated Health: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Japan. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, D. Poor Numeracy: The Elephant in the Diabetes Technology Room. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaugg, S.D.; Dogbey, G.; Collins, K.; Reynolds, S.; Batista, C.; Brannan, G.; Shubrook, J.H. Diabetes Numeracy and Blood Glucose Control: Association with Type of Diabetes and Source of Care. Clin. Diabetes 2014, 32, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begjani, J.; Hosseini, A.S.S.; Saneifard, H.; Hasanabad, V.R. Social Learning-Based Health Literacy Promotion on the Self Efficacy and Social Anxiety of Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esen, İ.; Demirci, H.; Güçlü, M.; Esen, S.A.; Şimşek, E.E. The Relationship Between Health Literacy, Diabetic Control, and Disease-Specific Complications in Patients withType 1 Diabetes Mellitus. South. Clin. Ist. Euras. 2018, 29, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, E.I.; Pincus, K.J.; Seung, H.; Rochester-Eyeguokan, C.D. Health Literacy of Patients Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2024, 64, 102109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyüboğlu, E.; Schulz, P.J. Do Health Literacy and Patient Empowerment Affect Self-Care Behaviour? A Survey Study among Turkish Patients with Diabetes. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillson, R. Learning and Diabetes. Pr. Diabetes 2016, 33, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi Hassanabad, V.; Begjani, J.; Sadat Hoseini, A.S.; Sanei Fard, H. Relationship between Diabetes Health Literacy, Self-Efficacy and Social Anxiety of Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2024, 209, 111390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhling, M.; Roslon, M.; Arndt, K.; Hess, I.; Kremer, A.; Leibold, K.; Seddiki, R.; Sommer, S.; Landgraf, R.; Kempf, K.; et al. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Health Literacy in Childhood and Adolescence - a 12-Year Follow-Up. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2023, 148, E1–E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seger, M.; Ryan, C.D.; Januszewski, A.S.; Kilov, G.; MacIsaac, R.J.; Ludvigsson, J.; O’Neal, D.N.; Jenkins, A.J. Is It Time to Screen Health Literacy in Diabetes Clinical Practice? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2024, 208, 111117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaytor, N.S.; Riddlesworth, T.D.; Bzdick, S.; Odegard, P.S.; Gray, S.L.; Lock, J.-P.; DuBose, S.N.; Beck, R.W. The Relationship between Neuropsychological Assessment, Numeracy, and Functional Status in Older Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2015, 27, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendejas Medina, L.A.; Sousa Albuquerque Brandão, M.G.; Alves Lima, G.; Zanetti, M.L.; Pace, A.E.; Serrano Gallardo, M.P.; Gutierrez Valverde, J.M.; Bessa de Oliveira, B.S.; Teixeira Lima, F.E.; de Souza Teixeira, C.R. Health Literacy and Numeracy in Self-Monitoring of Capillary Glycemia: A Systematic Review of Mixed Methods. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, E.-M.; Vogt, D.; Messer, M.; Hurrelmann, K.; Schaeffer, D. Health Literacy among Different Age Groups in Germany: Results of a Cross-Sectional Survey. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.; Rilstone, S.; Cooper, P.; Oliver, N.S. Type 1 Diabetes in Adults: Supporting Self-Management. BMJ 2016, 352, i998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, W.; Lim, S.; Wu, V. Factors Associated with Glycaemic Control in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Clin. Nurs. 2019, 28, 1433–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, D. Social Determinants, Health Literacy, and Disparities: Intersections and Controversies. Health Lit. Res. Pr. 2021, 5, e234–e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, G.; Whitney, D.; Moon, G. Developing and Applying Geographical Synthetic Estimates of Health Literacy in GP Clinical Systems. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shahzad, F. A Visualized and Scientometric Analysis of Health Literacy Research. Front. Public. Health 2022, 9, 811707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schillinger, D. The Intersections Between Social Determinants of Health, Health Literacy, and Health Disparities. Stud. Health Technol. Inf. 2020, 269, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Orom, H.; Hay, J.L.; Waters, E.A.; Schofield, E.; Li, Y.; Kiviniemi, M.T. Differences in Rural and Urban Health Information Access and Use. J. Rural. Health 2019, 35, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, F.; Biggs, K.; Aldiss, S.K.; O’Neill, P.M.; Clowes, M.; McDonagh, J.; While, A.; Gibson, F. Transition of Care for Adolescents from Paediatric Services to Adult Health Services. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 4, CD009794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, A.T.; Smaldone, A. Components of Interventions That Improve Transitions to Adult Care for Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes. J. Adolesc. Health 2017, 60, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ude, A.O.; De Baca, T.C.; Dixon, S.A.; Arboine, S.-A.; Terry, N.L.; Chung, S.T. Transitioning Care in Youth-Onset Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Scoping Review Protocol Using the Socio-Ecological Model Framework. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e064186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurynski, Y.; Carrigan, A.; Meulenbroeks, I.; Sarkies, M.N.; Dammery, G.; Halim, N.; Lake, R.; Davis, E.; Jones, T.W.; Braithwaite, J. Transition Models of Care for Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2023, 23, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otieno, P.; Agyemang, C.; Wainaina, C.; Igonya, E.K.; Ouedraogo, R.; Wambiya, E.O.A.; Osindo, J.; Asiki, G. Perceived Health System Facilitators and Barriers to Integrated Management of Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes in Kenya: A Qualitative Study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e074274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
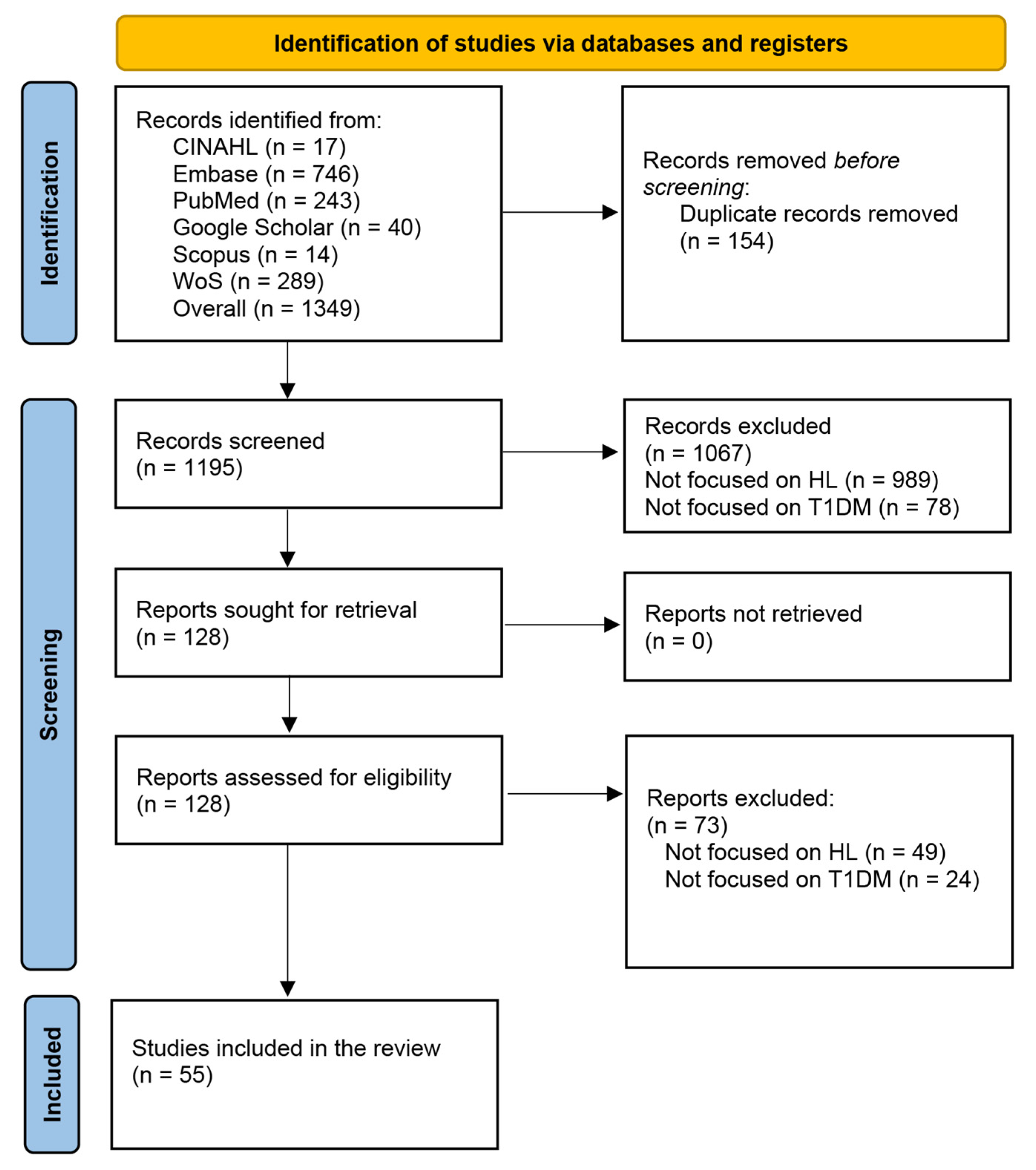
| Count (%) | Reference(s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Years of Publication | |||
| 2005–2014 | 11 (29%) | [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] | |
| 2015–2023 | 27 (71%) | [3,16,18,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68] | |
| Geographic Region | |||
| Africa | 4 (10.5%) | [36,54,57,66] | |
| Asia | 3 (7.9%) | [3,37,52] | |
| Europe | 15 (39.5%) | [16,18,33,34,35,44,47,51,56,58,61,65,69,70,71] | |
| Middle East | 3 (7.9%) | [48,49,60] | |
| North America | 9 (23.7%) | [43,46,50,59,62,63,64,72,73] | |
| South America | 4 (10.5%) | [45,53,67,74] | |
| Country economy | |||
| Lower middle income | 5 (13.1%) | [49,52,57,66,68] | |
| Upper middle income | 6 (15.8%) | [36,45,53,60,74] | |
| High income | 27 (71.1%) | [3,18,33,34,35,37,43,44,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,56,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,69,70,71,72,73] | |
| Journal discipline | |||
| Nursing | 1 (2.6%) | [54] | |
| Other | 37 (97.4%) | [3,18,33,34,35,36,37,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,69,70,71,72,73,74] | |
| Type of publication | |||
| Journal article | 36 (94.7%) | [3,18,33,34,35,36,37,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,65,66,67,69,70,71,72,73,74] | |
| Other | 2 (5.3%) | [50,64] | |
| Study design | |||
| Literature review | 4 (10.5%) | [3,59,63,65] | |
| Observational | 28 (73.7%) | [33,34,35,36,37,43,44,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,56,59,60,61,62,64,65,66,67,69,70,71,73,74] | |
| Qualitative | 4 (10.5%) | [33,54,57,58] | |
| Letters | 1 (2.6%) | [50] | |
| Editorial | 1 (2.6%) | [67] | |
| Extracted Themes | References |
|---|---|
| Experience and Active Learning | [33,57] |
| Socialization and Peer Support | [43,56,58,66] |
| Dietary Knowledge and Carbohydrate Counting | [43,44,45,46,47,54,57] |
| Economic and Educational Barriers | [52,57] |
| Clinical Outcomes and Health Literacy | [3,35,36,45,47,48,49,50,53,56,59,62,63,64,65,67,69,71,72,73,74] |
| Continuous Glucose Monitoring | [16,47,58,61] |
| Disease Duration and Health Literacy | [18,51,57,66] |
| Alcohol Literacy and Therapeutic Adherence | [34,63,70] |
| Health Literacy and Health Outcomes | [3,57,59,60,64,65,72] |
| Nursing Practice Implications | [37,57,66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milani, I.; Cipponeri, E.; Ripa, P.; Magon, A.; Terzoni, S.; Cilluffo, S.; Lusignani, M.; Caruso, R. Health Literacy in People with Type 1 Diabetes: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22060869
Milani I, Cipponeri E, Ripa P, Magon A, Terzoni S, Cilluffo S, Lusignani M, Caruso R. Health Literacy in People with Type 1 Diabetes: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(6):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22060869
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilani, Ilaria, Elisa Cipponeri, Paola Ripa, Arianna Magon, Stefano Terzoni, Silvia Cilluffo, Maura Lusignani, and Rosario Caruso. 2025. "Health Literacy in People with Type 1 Diabetes: A Scoping Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 6: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22060869
APA StyleMilani, I., Cipponeri, E., Ripa, P., Magon, A., Terzoni, S., Cilluffo, S., Lusignani, M., & Caruso, R. (2025). Health Literacy in People with Type 1 Diabetes: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(6), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22060869








