Mosses in Urban Environments as Passive Biofilters and Organisms Impacted by Asbestos-Contaminated Habitats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
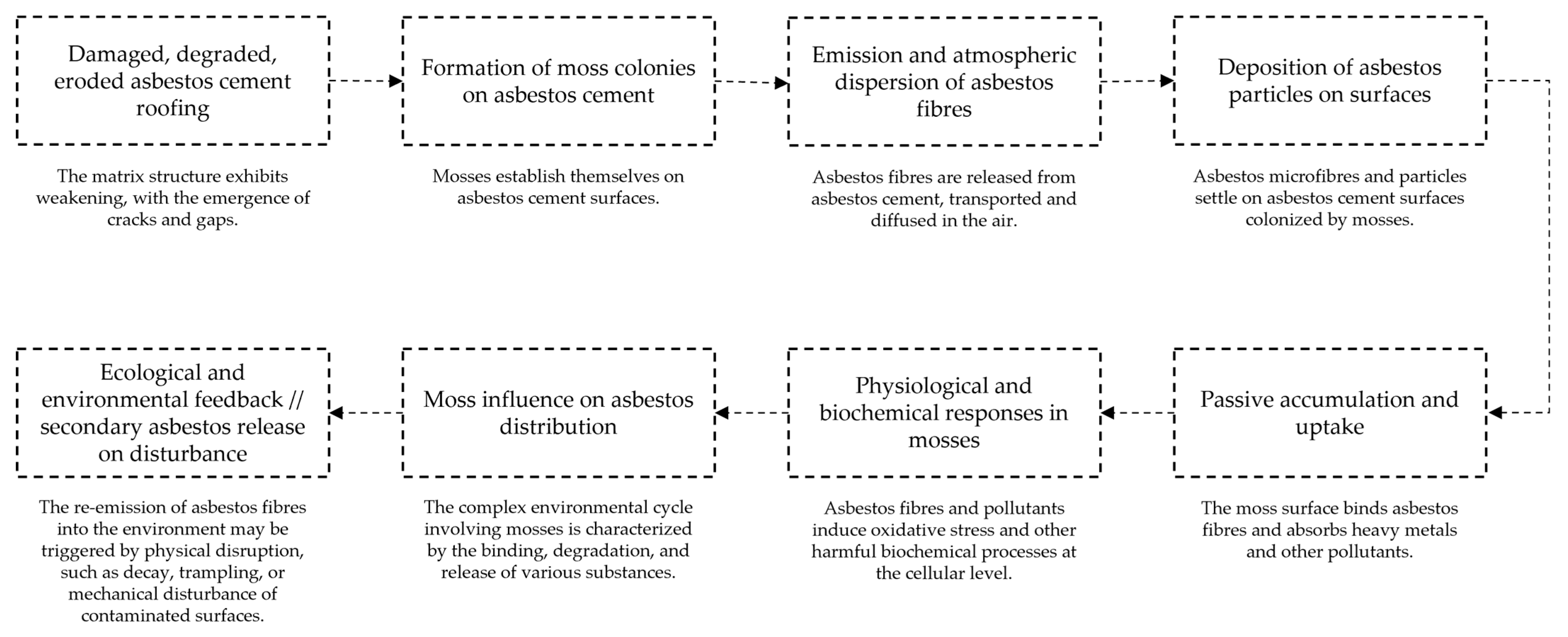
2. Urban Ecological Fate of Asbestos
3. Bryophytes as Early Colonisers and Indicators of Pollution
4. Moss–Asbestos Interactions and Physiological Effects
5. Implications for Urban Ecology and Asbestos Risk Management
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martínez, D.E.V.; Saba, M.; Gil, L.K.T. Assessment of asbestos-cement roof distribution and prioritized intervention approaches through hyperspectral imaging. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, L.K.T.; Valdelamar Martínez, D.; Franco, K.B.; Arrieta Pastrana, A.; Saba, M. Mapping roof coverings of asbestos-cement, the first step to control the technical condition/threat and establish priorities for replacement in developing countries. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curado, A.; Nunes, L.J.R.; Carvalho, A.; Abrantes, J.; Lima, E.; Tomé, M. The Use of Asbestos and Its Consequences: An Assessment of Environmental Impacts and Public Health Risks. Fibers 2024, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E.; Júnior, J.J.T.; Vieira, A.S. Is asbestos still a problem in the world? A current review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusiorowski, R.; Gerle, A.; Kujawa, M.; Antonovič, V.; Boris, R. Structural Characterisation of End-of-Life Cement–Asbestos Materials from Lithuania. Fibers 2024, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durczak, K.; Pyzalski, M.; Brylewski, T.; Juszczyk, M.; Leśniak, A.; Libura, M.; Ustinovičius, L.; Vaišnoras, M. Modern Methods of Asbestos Waste Management as Innovative Solutions for Recycling and Sustainable Cement Production. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadas, P.; Dainius, M.; Edvinas, K.; Linas, K.; Maksim, K.; Axel, Z. Comparative characterization of particle emissions from asbestos and non-asbestos cement roof slates. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 2295–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Yuen, M.L. Public health risks from asbestos cement roofing. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2022, 65, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouharoun, S.; Leklou, N.; Mounanga, P. Use of asbestos-free fiber-cement waste as a partial substitute of Portland cement in mortar. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitzel, R.L.; Sayler, S.K.; Demond, A.H.; D’Arcy, H.; Garabrant, D.H.; Franzblau, A. Measurement of asbestos emissions associated with demolition of abandoned residential dwellings. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 722, 137891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, T.-A.; Belluso, E.; Vigliaturo, R.; Gieré, R.; Emmett, E.A.; Testa, J.R.; Steinhorn, G.; Wallis, S.L. Asbestos and Other Hazardous Fibrous Minerals: Potential Exposure Pathways and Associated Health Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, A. Recent progress and perspectives on the mechanisms underlying Asbestos toxicity. Genes Environ. 2021, 43, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtieri, A.F. Bridging the gap between toxicity and carcinogenicity of mineral fibres by connecting the fibre crystal-chemical and physical parameters to the key characteristics of cancer. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 2, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansová, Š.; Jansa, Z.; Nedvědová, L.; Minár, J. Identification of asbestos fibres from soil sediments in the Pilsen region of the Czech Republic and the impact of these minerals on the health of the local population. Mater. Sci. 2024, 239, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Castro, M.; Montero-Acosta, M.; Saba, M. A critical review of asbestos concentrations in water and air, according to exposure sources. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardelli, F.; Giacobbe, C.; Ballirano, P.; Borelli, V.; Di Benedetto, F.; Montegrossi, G.; Bellis, D.; Pacella, A. Closing the knowledge gap on the composition of the asbestos bodies. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 5039–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Xie, W.; Ding, D.; Kong, L.; Jiang, D.; Long, T.; Deng, S. Asbestos-Environment Pollution Characteristics and Health-Risk Assessment in Typical Asbestos-Mining Area. Toxics 2023, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, S.L.; Emmett, E.A.; Hardy, R.; Casper, B.B.; Blanchon, D.J.; Testa, J.R.; Menges, C.W.; Gonneau, C.; Jerolmack, D.J.; Seiphoori, A.; et al. Challenging Global Waste Management—Bioremediation to Detoxify Asbestos. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangioudakis Khatib, G.; Collins, J.; Otness, P.; Goode, J.; Tomley, S.; Franklin, P.; Ross, J. Australia’s Ongoing Challenge of Legacy Asbestos in the Built Environment: A Review of Contemporary Asbestos Exposure Risks. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuniewski, S.; Rogowska, W.; Łozowicka, B.; Iwaniuk, P. Plants, Microorganisms and Their Metabolites in Supporting Asbestos Detoxification—A Biological Perspective in Asbestos Treatment. Materials 2024, 17, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aszalósné Balogh, R.; Matus, G.; Lőkös, L.; Adorján, B.; Freytag, C.; Mészáros, I.; Oláh, V.; Szűcs, P.; Erzberger, P.; Farkas, E. Cryptogamic communities on flatroofs in the city of Debrecen (East Hungary). Biol. Futur. 2023, 74, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Bhatt, P. Editorial: Environmental pollutants in agroecosystem: Toxicity, mechanism, and remediation. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1208405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Hramco, C.; Chaligava, O.; Yushin, N.; Grozdov, D.; Vergel, K.; Duca, G. Accumulation of Potentially Toxic Elements in Mosses Collected in the Republic of Moldova. Plants 2021, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świsłowski, P.; Nowak, A.; Wacławek, S.; Silvestri, D.; Rajfur, M. Bioaccumulation of Trace Elements from Aqueous Solutions by Selected Terrestrial Moss Species. Biology 2022, 11, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Roy, M. Global ambient air quality monitoring: Can mosses help? A systematic meta-analysis of literature about passive moss biomonitoring. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 5735–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.; Pakravan, H.R.; Pacheco-Torgal, F. Assessment of the Durability Performance of Fiber-Cement Sheets. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, M.B.; de Brito, J.; Martins, I.M.; Silvestre, J.D. Toxicity of cement-based materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 588, 042067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavašnik, J.; Šestan, A.; Škapin, S. Degradation of asbestos—Reinforced water supply cement pipes after a long-term operation. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervik, T.; Eriksen Hammer, S.; Graff, P. Mobilization of asbestos fibers by weathering of a corrugated asbestos cement roof. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2021, 18, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaonga, C.C.; Kosamu, I.B.M.; Utembe, W.R. A Review of Metal Levels in Urban Dust, Their Methods of Determination, and Risk Assessment. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguh, C.E.; Obiwulu, E.N.O.; Umezinwa, O.J.; Ameh, S.E.; Ugwu, C.V.; Sheshi, I.M. Ecosystem and Ecological Services; Need for Biodiversity Conservation-A Critical Review. Asian J. Biol. 2021, 111, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohmeier, B.R.; Huntington, J.C.; Bunker, K.L.; Sanchez, M.S.; Allison, K.; Lee, R.J. What is asbestos and why is it important? Challenges of defining and characterizing asbestos. Int. Geol. Rev. 2010, 52, 801–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghino, S.; Turci, F.; Tomatis, M.; Girlanda, M.; Fubini, B.; Perotto, S. Weathering of chrysotile asbestos by the serpentine rock-inhabiting fungus Verticillium leptobactrum. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobbe, C.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Zoboli, A.; Lassinantti Gualtieri, M.; Bonasoni, P.; Moliterni, A.; Corriero, N.; Altomare, A.; Wright, J.; Gualtieri, A.F. Crystal structure determination of a lifelong biopersistent asbestos fibre using single-crystal synchrotron X-ray micro-diffraction. IUCrJ 2021, 8, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Inam, M.A.; Zam, S.Z.; Park, D.R.; Yeom, I.T. Assessment of Key Environmental Factors Influencing the Sedimentation and Aggregation Behavior of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Aquatic Environment. Water 2018, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Baalousha, M.; Chen, J.; Chaudry, Q.; Von der Kammer, F.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Lead, J.; Nickel, C.; Quik, J.T.K.; Renker, M.; et al. A Review of the Properties and Processes Determining the Fate of Engineered Nanomaterials in the Aquatic Environment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 2084–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, A.-K.; Apler, A.; Frogner-Kockum, P.; Göransson, G.; Snowball, I.; Wiberg, K.; Josefsson, S. Dispersal of persistent organic pollutants from fiber-contaminated sediments: Biotic and abiotic pathways. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1852–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avataneo, C.; Capella, S.; Luiso, M.; Marangoni, G.; Lasagna, M.; De Luca, D.A.; Bergamini, M.; Belluso, E.; Turci, F. Waterborne asbestos: Good practices for surface waters analyses. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visonà, S.D.; Villani, S.; Manzoni, F.; Chen, Y.; Ardissino, G.; Russo, F.; Moretti, M.; Javan, G.T.; Osculati, A. Impact of Asbestos on Public Health: A Retrospective Study on a Series of Subjects with Occupational and Non-Occupational Exposure to Asbestos during the Activity of Fibronit Plant (Broni, Italy). J. Public Health Res. 2018, 7, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, D.J.; Larson, T.C.; Pfau, J.C.; Gavett, S.H.; Shukla, A.; Miller, A.; Hines, R. Current Research and Opportunities to Address Environmental Asbestos Exposures. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, A194–A197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Negi, A.; Bhattacharya, B.; Dey, T.; Mitra, P.; Preetam, S.; Kumar, L.; Kar, S.; Das, S.S.; Iqbal, D.; et al. Nanotheranostics to target antibiotic-resistant bacteria: Strategies and applications. OpenNano 2023, 11, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.C.; Rodenburg, U.; Leite, R.R.; Korthals, G.W.; Pover, J.; Koerten, H.; Kuramae, E.E.; Bodelier, P.L. Exploring microbial diversity and interactions for asbestos modifying properties. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 951, 175577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, T.-A.; Wallis, S.; Doyle, E.; de Lange, P.; Steinhorn, G.; Vigliaturo, R.; Belluso, E.; Blanchon, D. A Preliminary Investigation into the Degradation of Asbestos Fibres in Soils, Rocks and Building Materials Associated with Naturally Occurring Biofilms. Minerals 2024, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Gama, J.T. The Role of Soils in Sustainability, Climate Change, and Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities. Ecologies 2023, 4, 552–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, J.; Simon, J.; Rennenberg, H. Soil Respiration and Soil Organic Matter Decomposition in Response to Climate Change. Dev. Environ. Sci. 2013, 13, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishy, M.N.; Shemonty, N.A.; Fatema, S.I.; Mahbub, S.; Mim, E.L.; Raisa, M.B.; Anik, A.H. Unravelling the effects of climate change on the soil-plant-atmosphere interactions: A critical review. Soil Environ. Health 2025, 3, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Cao, B.; Zou, G.; et al. Ecological risk of microplastic toxicity to earthworms in soil: A bibliometric analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1126847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, Z.; Szigeti, C.; Czédli, H.M. “Green” Tram Tracks for the Sustainability of the Urban Environment. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2023, 107, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.T.J.; Arif, I.; Marchetti, F.; Munshi-South, J.; Ness, R.W.; Szulkin, M.; Verrelli, B.C.; Yauk, C.L.; Anstett, D.N.; Booth, W.; et al. Effects of urban-induced mutations on ecology, evolution and health. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 8, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glime, J.M. Roles of Bryophytes in Forest Sustainability—Positive or Negative? Sustainability 2024, 16, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschall, M. Ecophysiology of bryophytes in a changing environment. Acta Biol. Plant. Agriensis 2017, 5, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, L.; Djakovic, N.; Lang, I. Is a Combination of Metals More Toxic to Mosses Than a Single Metal? Plants 2023, 12, 3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollery, R.; Bowie, M.H.; Dickinson, N.M. The ecological importance of moss ground cover in dry shrubland restoration within an irrigated agricultural landscape matrix. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Liu, F.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Luo, X.; Liu, R. The Pioneering Role of Bryophytes in Ecological Restoration of Manganese Waste Residue Areas, Southwestern China. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 9969253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, A.A. Nature and paragenesis of asbestos minerals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1977, 286, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.; Johnson, M.; Liu, Y.; Wilding, N.; Hedderson, T.A.; Wickett, N.; Goffinet, B. Evolutionary dynamism in bryophytes: Phylogenomic inferences confirm rapid radiation in the moss family Funariaceae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 120, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morajkar, S.; Hegde, S. Biodiversity, richness and spatial distribution of extant Pteridophytes in Kudremukh National Park, Western Ghats, India. Plant Sci. Today 2021, 8, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilunga wa Ilunga, E.; Mahy, G.; Piqueray, J.; Séleck, M.; Shutcha, M.N.; Meerts, P.; Faucon, M.-P. Plant functional traits as a promising tool for the ecological restoration of degraded tropical metal-rich habitats and revegetation of metal-rich bare soils: A case study in copper vegetation of Katanga, DRC. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriuso, F.; Urbano, B. Green Roofs and Walls Design Intended to Mitigate Climate Change in Urban Areas across All Continents. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero-Longo, S.E.; Castelli, D.; Fubini, B.; Piervittori, R. Lichens on asbestos–cement roofs: Bioweathering and biocovering effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera-Castro, A.V.; Flexas, J. Desiccation tolerance in bryophytes relates to elasticity but is independent of cell wall thickness and photosynthesis. Physiol. Plant. 2022, 174, e13661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsch, M.; Guex, I.; Todorov, H.; Heiman, C.M.; Vacheron, J.; Vorholt, J.A.; Keel, C.; van der Meer, J.R. Fragmented micro-growth habitats present opportunities for alternative competitive outcomes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, M.S.; Ullah, H.; Faruk, O.; Simon, E.; Czédli, H. Role of Microplastics in Global Warming and Climate Change: A. Review. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Lázár, I.; Szabó, S.; Tóthmérész, B.; Abriha-Molnár, V.É.; Czédli, H.; Simon, E. Decreased Mobility During the COVID-19 Pandemic Period Considerably Improved Air Quality in Debrecen City, Hungary. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Quan, Q.; Gan, Y.; Dong, J.; Fang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Effects of heavy metals on microbial communities in sediments and establishment of bioindicators based on microbial taxa and function for environmental monitoring and management. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 749, 141555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, A. A systematic review on biomonitoring using lichen as the biological indicator: A decade of practices, progress and challenges. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, L.; Bandoni, E.; Sanità di Toppi, L. Lichens and Mosses as Biomonitors of Indoor Pollution. Biology 2023, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, M.S.; Hoque, M.I.; Siddique, M.d.N.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Baranyai, E.; Sajtos, Z.F.; Dönczo, B.; Aib, H.; Kader, A.; Simon, E.; et al. Elemental analysis in the scales of commercially important coastal fishes and their connections with fish feeding habits and habitats. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1546313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, M.S.; Czédli, H.; Hoque, M.I.; Rahman, M.M.; Anwar, A.; Uddin, A.H.M.M.; Hasan, S.; Bibi, D.; Tóthmérész, B.; Magura, T.; et al. Accumulation of Microplastics and Potentially Toxic Elements in Plant Leaves Along an Urbanization Gradient in Bangladesh. Toxics 2024, 12, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aib, H.; Czegeny, I.; Benhizia, R.; Czédli, H.M. Evaluating the Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants in the Northern Hungarian Plains Using Physicochemical and Microbiological Parameters. Water 2024, 16, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aib, H.; Czédli, H.; Baranyai, E.; Sajtos, Z.; Döncző, B.; Parvez, M.S.; Berta, C.; Varga, Z.; Benhizia, R.; Nyeste, K. Fish Scales as a Non-Invasive Method for Monitoring Trace and Macroelement Pollution. Biology 2025, 14, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásquez, C.; Calva, J.; Morocho, R.; Donoso, D.A.; Benítez, Á. Bryophyte Communities along a Tropical Urban River Respond to Heavy Metal and Arsenic Pollution. Water 2019, 11, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejcman, M.; Müllerová, V.; Vondráčková, S.; Száková, J.; Tlustoš, P. Establishment of Bryum argenteum and concentrations of elements in its biomass on soils contaminated by As, Cd, Pb and Zn. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świsłowski, P.; Nowak, A.; Wacławek, S.; Ziembik, Z.; Rajfur, M. Is Active Moss Biomonitoring Comparable to Air Filter Standard Sampling? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez, Á.; Armijos, L.; Calva, J. Monitoring Air Quality with Transplanted Bryophytes in a Neotropical Andean City. Life 2021, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero-Longo, S.E.; Siniscalco, C.; Piervittori, R. Plant and lichen colonization in an asbestos mine: Spontaneous bioattenuation limits air dispersion of fibres. Plant Biosyst.-Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2006, 140, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciorek, T.; Stebel, A.; Jankowska-Błaszczuk, M.; Wojciechowska, A. Bryophyte Species Diversity in Human-Influenced Habitats Within Protected Areas—A Case Study from the Świętokrzyski National Park in Poland. Herzogia 2016, 29, 668–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świsłowski, P.; Hrabák, P.; Wacławek, S.; Liskova, K.; Antos, V.; Rajfur, M.; Ząbkowska-Wacławek, M. The Application of Active Biomonitoring with the Use of Mosses to Identify Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in an Atmospheric Aerosol. Molecules 2021, 26, 7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghori, N.-H.; Ghori, T.; Hayat, M.Q.; Imadi, S.R.; Gul, A.; Altay, V.; Ozturk, M. Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shahrani, M.; Heales, S.; Hargreaves, I.; Orford, M. Oxidative Stress: Mechanistic Insights into Inherited Mitochondrial Disorders and Parkinson’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ding, Y.; Mokhberdoran, F.; Xie, Y. Heavy Metal Stress and Some Mechanisms of Plant Defense Response. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 756120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rola, K.; Plášek, V. The Utility of Ground Bryophytes in the Assessment of Soil Condition in Heavy Metal-Polluted Grasslands. Plants 2022, 11, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polishchuk, A.I.; Antonyak, H.L. Accumulation of heavy metals and antioxidant defense system in the gametophyte of Didymodon rigidulus Hedw. in areas with high traffic loads. Stud. Biol. 2021, 15, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelko, Z.; Korez, R. Presented at the 7th FEB International Scientific Conference: Strengthening Resilience by Sustainable Economy and Business—Towards the SDGs, Univerzitetna Založba Univerze v Mariboru, Maribor, Slovenia, 16 May 2023. [CrossRef]
- Sandhi, A.; Landberg, T.; Greger, M. Phytofiltration of arsenic by aquatic moss (Warnstorfia fluitans). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallen-Cooper, M.; Graae, B.J.; Cornwell, W.K. Lichens buffer tundra microclimate more than the expanding shrub Betula nana. Ann. Bot. 2021, 128, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boquete, M.T.; Lang, I.; Weidinger, M.; Richards, C.L.; Alonso, C. Patterns and mechanisms of heavy metal accumulation and tolerance in two terrestrial moss species with contrasting habitat specialization. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 182, 104336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.R.; Ihiawakrim, D.; Regis, R.; Geoffroy, V.A. Efficiency of pyoverdines in iron removal from flocking asbestos waste: An innovative bacterial bioremediation strategy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutnar, L.; Kermavnar, J.; Sabovljević, M.S. Bryophyte diversity, composition and functional traits in relation to bedrock and tree species composition in close-to-nature managed forests. Eur. J. For. Res. 2023, 142, 865–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitt, D.H.; House, M.; Glaeser, L.C. The role of microhabitat for bryophyte establishment in reclamation of boreal wetlands. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 31, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macher, G.Z.; Szigeti, C. The Role of the Circular Economy in the Labour Market and Employment Rate in the European Union. In Proceedings of the 8th FEB International Scientific Conference. Challenges in the Turbulent Economic Environment and Organizations’ Sustainable Development, Maribor, Slovenia, 21 May 2024; University of Maribor Press: Maribor, Slovenia, 2024; pp. 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żołnierz, L.; Fudali, E.; Szymanowski, M. Epiphytic Bryophytes in an Urban Landscape: Which Factors Determine Their Distribution, Species Richness, and Diversity? A Case Study in Wroclaw, Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; John, P.J.; Ledwani, L. Microbial siderophores an envisaged tool for asbestos bioremediation—A microcosm approach. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 3110–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieille, B.; Albert, I.; Leblond, S.; Couvidat, F.; Parent, É.; Meyer, C. Are Grimmia Mosses Good Biomonitors for Urban Atmospheric Metallic Pollution? Preliminary Evidence from a French Case Study on Cadmium. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarova, M.; Grifoni, L.; Aherne, J.; Loppi, S. Comparison of Lichens and Mosses as Biomonitors of Airborne Microplastics. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.R.; Geoffroy, V.A. A Review of Asbestos Bioweathering by Siderophore-Producing Pseudomonas: A Potential Strategy of Bioremediation. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvallot, V.; Baeza-Squiban, A.; Boland, S.; Marano, F. Activation of Transcription Factors by Diesel Exhaust Particles in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells In Vitro. Inhal. Toxicol. 2000, 12, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Chang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T. Advances in transport and toxicity of nanoparticles in plants. J. Nanobiotechnology 2023, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolski, G.J.; Sadowska, B.; Fol, M.; Podsędek, A.; Kajszczak, D.; Kobylińska, A. Cytotoxicity, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of mosses obtained from open habitats. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, A.; Canali, G.; Favero-Longo, S.E.; Loppi, S. Accumulation and Phytotoxicity of Two Commercial Biocides in the Lichen Evernia prunastri and the Moss Brachythecium sp. Stresses 2021, 1, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkodie, E.K.; Jiang, L.; Li, K.; Yang, J.; Guo, Z.; Shi, J.; Deng, Y.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H.; Liang, Y.; et al. A review on the bioleaching of toxic metal(loid)s from contaminated soil: Insight into the mechanism of action and the role of influencing factors. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1049277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, S.R.; Valdés, B. Influence of Washing on Metal Concentrations in Leaf Tissue. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2004, 35, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, A.F.; Lusvardi, G.; Zoboli, A.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Lassinantti Gualtieri, M. Biodurability and release of metals during the dissolution of chrysotile, crocidolite and fibrous erionite. Environ. Res. 2019, 171, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, Z.; Fernández, J.; Real, C.; Carballeira, A.; Aboal, J. Influence of the physicochemical characteristics of pollutants on their uptake in moss. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 102, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedoh, O.P.; Compant, S.; Doty, S.L.; Santoyo, G.; Glick, B.R.; Babalola, O.O. Root colonizing microbes associated with notable abiotic stress of global food and cash crops. Plant Stress 2025, 15, 100714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.K.; Pandey, N.; Meena, R.P.; Rai, S.P. Biotechnological strategies for enhancing heavy metal tolerance in neglected and underutilized legume crops: A comprehensive review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero-Longo, S.E.; Girlanda, M.; Honegger, R.; Fubini, B.; Piervittori, R. Interactions of sterile-cultured lichen-forming ascomycetes with asbestos fibres. Mycol. Res. 2007, 111, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, A.K.; Ahmad, I.; Musthapa, M.S.; Ansari, F.A.; Rahman, Q. Environmental Contamination of Chrysotile Asbestos and Its Toxic Effects on Growth and Physiological and Biochemical Parameters of Lemna gibba. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 47, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, A.K.; Ahmad, I.; Musthapa, M.S.; Ansari, F.A. Environmental Contamination of Chrysotile Asbestos and Its Toxic Effects on Antioxidative System of Lemna gibba. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 52, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genga, A.; Mattana, M.; Coraggio, I.; Locatelli, F.; Piffanelli, P.; Consonni, R. Plant Metabolomics: A Characterisation of Plant Responses to Abiotic Stresses. Abiotic Stress in Plants—Mechanisms and Adaptations; InTech: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraire-Velázquez, S.; Emmanuel, V. Abiotic Stress in Plants and Metabolic Responses. Abiotic Stress—Plant Responses and Applications in Agriculture, InTech: London, UK, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Ares, A.; Fernández, J.A.; Carballeira, A.; Aboal, J.R. Towards the methodological optimization of the moss bag technique in terms of contaminants concentrations and replicability values. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, D.J.; Guirado, E.; Reich, P.B.; Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Berdugo, M.; Sáez-Sandino, T.; Blanco-Pastor, J.L.; Tedersoo, L.; Plaza, C.; Ding, J.; et al. The global contribution of soil mosses to ecosystem services. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziemska, M.; Mazur, Z.; Bes, A.; Majewski, G.; Gusiatin, Z.M.; Brtnicky, M. Using Mosses as Bioindicators of Potentially Toxic Element Contamination in Ecologically Valuable Areas Located in the Vicinity of a Road: A Case Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baczewska-Dąbrowska, A.H.; Gworek, B.; Dmuchowski, W. The Use of Mosses in Biomonitoring of Air Pollution in the Terrestrial Environment: A Review. Environ. Prot. Nat. Resour. 2023, 34, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, F.; Rao, D.N. A review of the literature on Bryophytes with respect to air pollution. Bull. Société Bot. Fr. 1974, 121, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanek, A.; de Baro, M.E.Z.; Newman, P. Biophilic streets: A design framework for creating multiple urban benefits. Sustain. Earth 2020, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S. Nature in the Urban Context: Renaturalisation as an Important Dimension of Urban Resilience and Planning. Módulo Arquit. Cuc. 2021, 26, 161–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.D.; Kiers, E.T.; Anthony, M.A.; Kiers, A.H. Supporting urban greenspace with microbial symbiosis. Plants People Planet 2024, 6, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, F.; Sorrentino, M.C.; Cascone, E.; Iuliano, M.; De Tommaso, G.; Granata, A.; Giordano, S.; Spagnuolo, V. Biomonitoring of Airborne Microplastic Deposition in Semi-Natural and Rural Sites Using the Moss Hypnum cupressiforme. Plants 2023, 12, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, A.C.; Lanzer, R.; Bordin, J.; Schäfer, A.; Wasum, R. Mosses as indicators of atmospheric metal deposition in an industrial area of southern Brazil. Acta Bot. Bras. 2012, 26, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haughian, S.R.; Lundholm, J.L. Mosses for minimalist green roofs: A preliminary study of the effects of rooftop exposure, species selection, and lab-grown vs. wild-harvested propagule sources. Nat.-Based Solut. 2024, 5, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Cirrincione, L.; La Gennusa, M.; Peri, G.; Scaccianoce, G. Green Roofs’ End of Life: A Literature Review. Energies 2023, 16, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelovski, I.; Connolly, J.J.T.; Cole, H.; Garcia-Lamarca, M.; Triguero-Mas, M.; Baró, F.; Martin, N.; Conesa, D.; Shokry, G.; del Pulgar, C.P.; et al. Green gentrification in European and North American cities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J. Ecological information and approaches needed for risk communication dialogs for acute or chronic environmental crises. Risk Anal. 2022, 42, 2408–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, R.; Redding, D.W.; Friant, S.; Jones, K.E. Towards a ‘people and nature’ paradigm for biodiversity and infectious disease. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2025, 380, 20230259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrim, C.; Aherne, J. Moss Bags as Biomonitors of Atmospheric Microplastic Deposition in Urban Environments. Biology 2023, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatim, N.M.; Azman, N.I.A. Moss as Bio-indicator for Air Quality Monitoring at Different Air Quality Environment. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2021, 10, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, M.; Abollino, O.; Conca, R.; Malandrino, M.; Mentasti, E.; Sarzanini, C. The use of mosses as environmental metal pollution indicators. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, Z.; Kézi, C.; Czédli, H. Analysis of Differences Between Levelling Networks in the County of Hajdú-Bihar. Int. J. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2023, 8, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whysner, J.; Covello, V.T.; Kuschner, M.; Rifkind, A.B.; Rozman, K.K.; Trichopoulos, D.; Williams, G. Asbestos in the Air of Public Buildings: A Public Health Risk? Prev. Med. 1994, 23, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Organism Group | Key Advantages | Key Limitations | Relevance to Asbestos Cement Surfaces |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mosses | High surface-area-to-volume ratio, poikilohydric, survive in extreme substrates | Sensitive to desiccation in exposed sites | Frequently colonise asbestos cement, trap fibres |
| Lichens | Long lifespan, good for long-term accumulation studies | Slow growth, sensitive to sulphur and pH extremes | Less common on urban asbestos cement surfaces |
| Algae | Rapid growth, useful for waterborne pollutants | Require moisture/nutrients, less substrate specificity | Rare on dry or vertical asbestos cement surfaces |
| Vascular plants | Structural root systems, visible physiological changes | Limited to well-developed soils, slower colonisation | Rare on intact AC surfaces, more relevant post-weathering |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macher, G.Z.; Beke, D. Mosses in Urban Environments as Passive Biofilters and Organisms Impacted by Asbestos-Contaminated Habitats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22060838
Macher GZ, Beke D. Mosses in Urban Environments as Passive Biofilters and Organisms Impacted by Asbestos-Contaminated Habitats. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(6):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22060838
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacher, Gergely Zoltán, and Dóra Beke. 2025. "Mosses in Urban Environments as Passive Biofilters and Organisms Impacted by Asbestos-Contaminated Habitats" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 6: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22060838
APA StyleMacher, G. Z., & Beke, D. (2025). Mosses in Urban Environments as Passive Biofilters and Organisms Impacted by Asbestos-Contaminated Habitats. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(6), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22060838





