The Impact of Non-Acoustic Factors on Chinese Community Response to Noise: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
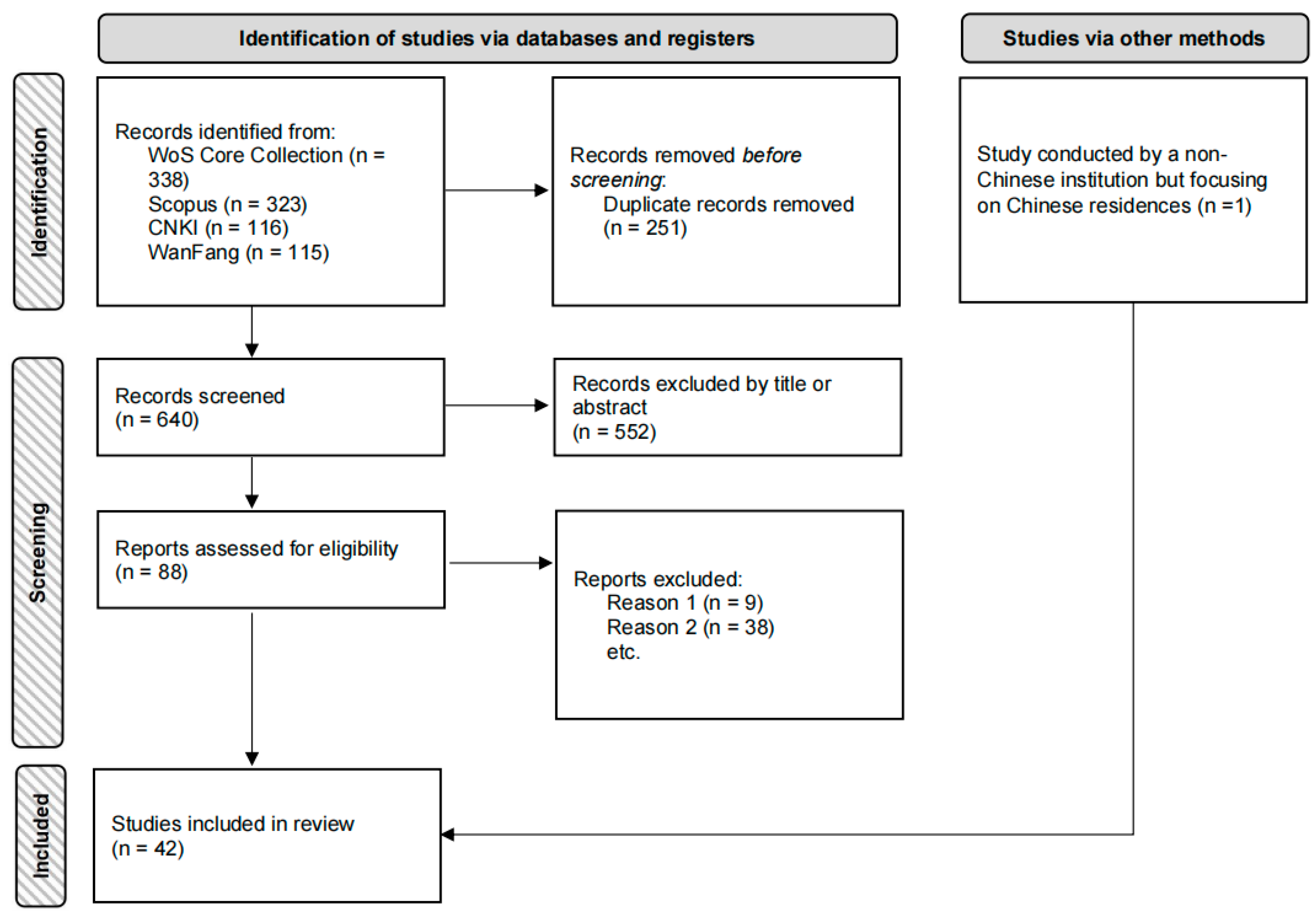
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Exclusion and Inclusion Criteria
3. Results
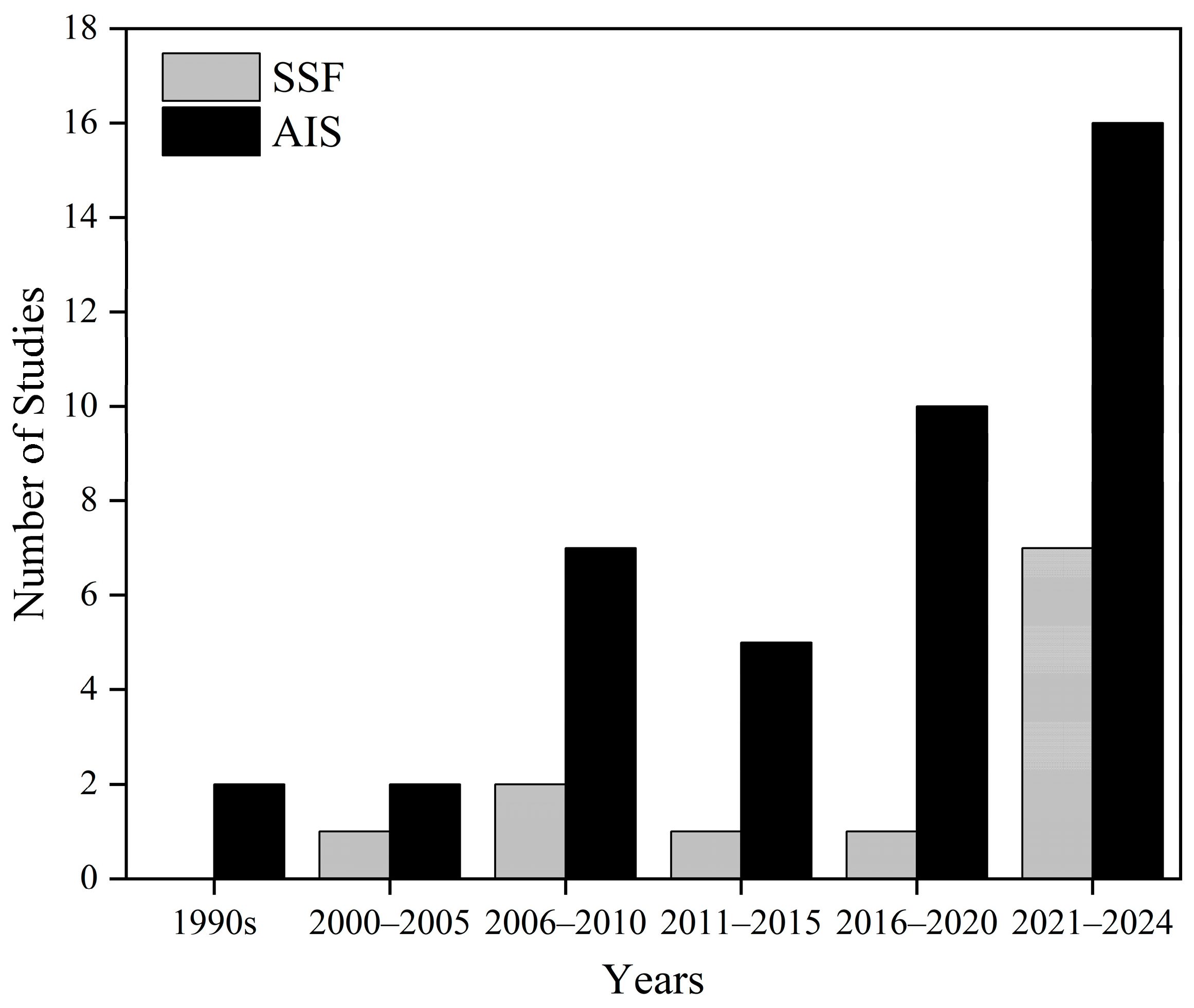
3.1. Overall Research Trends
3.2. Effects of Non-Acoustic Factors
3.2.1. The Impact of Attitudinal Factors on Noise Annoyance
3.2.2. The Impact of Demographic Factors on Noise Annoyance
3.2.3. The Impact of Situational Factors on Noise Annoyance
4. Discussion
- (1)
- Exploration of interactions between certain factors
- (2)
- Interaction between non-acoustic factors and noise types
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The effects of non-acoustic factors on Chinese residents are significant, with the trends for factors such as noise sensitivity, attitude to noise source, health status, perceived quality of the living environment, and education level influencing the Chinese community response to noise having been basically clarified. However, the influence of the remaining factors and the unique influences of various non-acoustic factors await further quantitative analysis.
- (2)
- Interactions among various factors deserve close attention. The interactions between non-acoustic factors, as well as those between non-acoustic factors and sound source types, have been reflected in some studies. These may be significant for explaining the effects of non-acoustic factors and merit further research.
- (3)
- Compared to international studies, research on non-acoustic factors in China is relatively limited in quantity and unevenly distributed, which is insufficient to support further quantitative analysis or a detailed exploration of the underlying mechanisms. Therefore, more studies are necessary to support the future rationalization of noise policies and national standards in China.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Annual Report on Prevention and Control of Noise Pollution in China; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Muzet, A. Environmental Noise, Sleep and Health. Sleep Med. Rev. 2007, 11, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minichilli, F.; Gorini, F.; Ascari, E.; Bianchi, F.; Coi, A.; Fredianelli, L.; Licitra, G.; Manzoli, F.; Mezzasalma, L.; Cori, L. Annoyance Judgment and Measurements of Environmental Noise: A Focus on Italian Secondary Schools. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.; Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, Y.; He, L. The Relationship between Urban Combined Traffic Noise and Annoyance: An Investigation in Dalian, North of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babisch, W.; Beule, B.; Schust, M.; Kersten, N.; Ising, H. Traffic Noise and Risk of Myocardial Infarction. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahad, O.; Bayo Jimenez, M.T.; Kuntic, M.; Frenis, K.; Steven, S.; Daiber, A.; Münzel, T. Cerebral Consequences of Environmental Noise Exposure. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahad, O.; Prochaska, J.H.; Daiber, A.; Münzel, T. Environmental Noise-Induced Effects on Stress Hormones, Oxidative Stress, and Vascular Dysfunction: Key Factors in the Relationship between Cerebrocardiovascular and Psychological Disorders. Oxidative Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 4623109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahad, O.; Beutel, M.; Gilan, D.; Chalabi, J.; Schuster, A.; Gianicolo, E.; Lackner, K.; Lieb, K.; Galle, P.; Wild, P.; et al. Noise Annoyance and Risk of Prevalent and Incident Atrial Fibrillation—A Sex-Specific Analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1061328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Kang, J.; Ma, H. Evaluation of Healthy Indoor Acoustic Environments in Residential Buildings by the Occupants: A Mixed-Method Approach. Build. Environ. 2023, 246, 110950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skagerstrand, Å.; Köbler, S.; Stenfelt, S. Loudness and Annoyance of Disturbing Sounds–Perception by Normal Hearing Subjects. Int. J. Audiol. 2017, 56, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, T. Synthesis of Social Surveys on Noise Annoyance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1978, 64, 377–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y. Adjustment on Subjective Annoyance of Low Frequency Noise by Adding Additional Sound. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 5707–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X. Annoyance Response to Low Frequency Noise with Tonal Components: A Case Study on Transformer Noise. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 91, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohstrom, E.; Barregård, L.; Andersson, E.; Skånberg, A.; Svensson, H.; Angerheim, P. Annoyance Due to Single and Combined Sound Exposure from Railway and Road Traffic. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 2642–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.M. Transportation Noise Reference Book; Butterworth: London, UK; Boston, UK, 1987; ISBN 978-0-408-01446-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fields, J. Effect of Personal and Situational Variables on Noise Annoyance in Residential Areas. J. Acoust. Soc. Am.-J. Acoust. Soc. Amer. 1993, 93, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, R.F.S. Community Response to Noise: A Review of Factors Influencing the Relationship between Noise Exposure and Reaction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1988, 83, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis-Favre, C.; Premat, E.; Aubrée, D. D Aubree Noise and Its Effects–A Review on Qualitative Aspects of Sound. Part II: Noise and Annoyance. ACTA Acust. United Acust. 2005, 91, 626–642. [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo, H.E.; McRobie, E.; Stansfeld, S.; Hansell, A.L. Annoyance and Other Reaction Measures to Changes in Noise Exposure—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 435–436, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, H.; Vos, H. Demographic and Attitudinal Factor That Modify Annoyance from Transportation Noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am.-J. Acoust. Soc. Amer. 1999, 105, 3336–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Yano, T.; Björkman, M.; Rylander, R. Comparison of Community Response to Road Traffic Noise in Japan and Sweden—Part I: Outline of Surveys and Dose-Response Relationships. J. Sound Vib.-J. Sound Vib. 2002, 250, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, C.; Ragettli, M.; Brink, M.; Olaniyan, T.; Baatjies, R.; Saucy, A.; Vienneau, D.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Dalvie, M.; Röösli, M. Comparison of Sensitivity and Annoyance to Road Traffic and Community Noise between a South African and a Swiss Population Sample. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.L.; Lam, K.C.; van Kamp, I. Quantification of the Exposure and Effects of Road Traffic Noise in a Dense Asian City: A Comparison with Western Cities. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated Guidance and Exemplars for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.; Yao, Y.; Chen, C.; Lin, Q.; Li, Z. An Experiment Study on the Identification of Noise Sensitive Individuals and the Influence of Noise Sensitivity on Perceived Annoyance. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 185, 108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, X.; Shi, D.; Wang, P. A Field Study of Train-Interior Noise Using Objective Measurements and Subjective Perceptions. Transp. Res. Part D-Transp. Environ. 2024, 134, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; Han, T.; Wu, J. Effects of Noise Type and Noise Sensitivity on Working Memory and Noise Annoyance. Noise Health 2022, 24, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.; Chan, P.; Chan, T.; Au, W.; Hui, W. Annoyance Response to Mixed Transportation Noise in Hong Kong. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, H. Investigation of Chinese Residents’ Community Response to High-Speed Railway Noise. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 172, 107615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Di, G.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X. Community Survey on Noise Impacts Induced by 2MW Wind Turbines in China. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2016, 35, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.; Au, W. Human Response to a Step Change in Noise Exposure Following the Opening of a New Railway Extension in Hong Kong. ACTA Acust. United Acust. 2008, 94, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xiong, W.; Yang, C. Developing Multivariate Models for Predicting the Level of Dissatisfaction Due to a Specific Metro Noise Masked with Four Specific Water Sounds. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 200, 109082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L. The Multi-Dimensional Perceptions of Office Staff and Non-Office Staff about Metro Noise in Commercial Spaces. ACTA Acust. 2022, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.; Lam, K. The Effects of Information Bias and Riding Frequency on Noise Annoyance to a New Railway Extension in Hong Kong. Transp. Res. Part D-Transp. Environ. 2008, 13, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Kwan, M.; Su, L.; Lu, J. Geographic Ecological Momentary Assessment (GEMA) of Environmental Noise Annoyance: The Influence of Activity Context and the Daily Acoustic Environment. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2020, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaotu, L. Analysis of the Acoustical Environment of Urban Dwellings. Appl. Acoust. 1990, 29, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hui, M. Effects of Environment Noise on Children’s Short-Term Memory and Attention Stability. Acta Acust. 2018, 43, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, H. The Effects of Environmental Noise on Children’s Cognitive Performance and Annoyance. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 198, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Huang, W. Soundscape and Subjective Factors Affecting Residents’ Evaluation of Aircraft Noise in the Communities under Flight Routes. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1197820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, N.; Liu, B. Effect of Water Sound Masking on Perception of the Industrial Noise. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 150, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, T.; Chau, C.; Tang, S.; Xu, J. Developing a Multivariate Model for Predicting the Noise Annoyance Responses Due to Combined Water Sound and Road Traffic Noise Exposure. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 127, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan Liang; Hao Xiaying; Chen Kean A Social Survey on the Community Annoyance with Urban Road Traffic Noise. J. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 28, 300–307.
- Cai, J.; Kwan, M.; Kan, Z.; Huang, J. Perceiving Noise in Daily Life: How Real-Time Sound Characteristics Affect Personal Momentary Noise Annoyance in Various Activity Microenvironments and Times of Day. Health Place 2023, 83, 103053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Dong, N. The Effects of Rating Scales and Individual Characteristics on Perceived Annoyance in Laboratory Listening Tests. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 202, 109137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, J. Influencing Factors Identification and Prediction of Noise Annoyance-A Case Study on Substation Noise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chau, C.; Tse, M.; Tang, S. On the Study of the Effects of Sea Views, Greenery Views and Personal Characteristics on Noise Annoyance Perception at Homes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 2131–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei Baoxiang; Gu Shechao An Investigation on the Effects of Train Noise on the Health of the Residents Living beside the Railway. J. Environ. Health 1997, 14, 25–27. [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Huang, Y. An Investigation of the Age Effect on Acoustical Annoyance Developed from Data of Previous Studies. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 192, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Dong, Y.; Cai, J. Experimental Study on Annoyance of Duration Time for Aircraft Flyover Noise. Noise Vib. Control 2015, 35, 121–125, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, M. Study of Natural Sound Mixed Masking on Low Frequency Acoustic Environment in Community. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 46, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Zou, C. Noise Annoyance and Vibration Perception Assessment on Passengers during Train Operation in Guangzhou Metro. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 4246–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tang, F.; Huang, Z.; Wang, G. High-Speed Maglev Noise Impacts on Residents: A Case Study in Shanghai. Transp. Res. Part D-Transp. Environ. 2007, 12, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tan, L.; Liu, X.; Fang, F.; Zhao, W. Investigation of Environmental Noise Perception of Residents in Lu’an City. J. Environ. Health 2007, 24, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Long, T.; Yang, J. Traffic Noise Investigation and Risk Factor Analysis in Haikou. J. Hainan Med. Univ. 2011, 17, 416–419. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.; Geng, X.; Tang, F. Investigation on Health Impact of Noise Created by House Decoration in Residential Quarters. J. Environ. Health 2002, 19, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, L.; Di, G. The Influence of the Visibility of the Source on the Subjective Annoyance Due to Its Noise. Appl. Acoust. 2003, 64, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; De Coensel, B.; Sanchez, G.; Van Renterghem, T.; Botteldooren, D. Effect of Interaction between Attention Focusing Capability and Visual Factors on Road Traffic Noise Annoyance. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 134, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.; Zhao, C.; Lin, Q.; Fan, M. Study on Annoyance and Sleep Disturbance Induced by Combined Noises from Road Traffic and Viaduct Rail Transit. Acoust. Aust. 2019, 47, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.M. A Comparison of Models to Predict Annoyance Reactions from Mixed Sources. J. Sound Vib. 1982, 81, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, H.; Oudshoorn, C. Annoyance from Transportation Noise: Relationships with Exposure Metrics DNL and DENL and Their Confidence Intervals. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, J.M.; Walker, J.G. Comparing the Relationships between Noise Level and Annoyance in Different Surveys: A Railway Noise vs. Aircraft and Road Traffic Comparison. J. Sound Vib. 1982, 81, 51–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Attitudinal Factors | Demographic Factors | Situation Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Noise sensitivity (20) | Gender (23) | Visibility of the source (3) |
| Attitude to noise source (6) | Age * (20) | Time spent at home (1) |
| Perceived quality of theliving environment (5) | Education level (7) | Time at home (1) |
| Activity during exposure (3) | Occupation (7) | Sound proofing |
| Fear (1) | Health condition (6) | Dwelling orientation |
| Health effect | Use of the noise source (4) | |
| Income (4) | ||
| Marital situation (3) | ||
| Ownership of a house (3) | ||
| History of noise exposure (3) | ||
| Length of residence (1) | ||
| Dependency on the noise source (1) | ||
| No. of people in the household | ||
| Social status | ||
| Size of household | ||
| Type of home |
| Research | Definition of Attitude to Noise Source | Categories |
|---|---|---|
| Lam et al., 2008 [31] AND Lam et al., 2009 [28] | Comparing railway and road traffic, do you agree that railway/road traffic is comfortable AND convenient AND environmentally friendly AND noisy AND safe | Comprehensive attitude |
| Song et al., 2016 [30] | Attitudes towards wind turbines’ visual impact on the landscape AND general opinions on wind turbines | |
| Zhang et al., 2021 [29] | Considering high-speed railway safer OR expressing more support for high-speed rail construction | |
| Wang et al., 2022 [33] | Metro noise attitude: 1 as “not at all”, 5 as “extremely noisy” | Single impact |
| Wang et al., 2022 [32] | Do you agree that you are a person who strongly hates metro noise? |
| Research | Type of Noise | Conclusions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leung et al., 2017 [41] | Water sounds and road traffic noise | Females experience higher levels of annoyance | \ |
| Wang et al., 2022 [32] | Water sounds and metro noise | \ | |
| Qu et al., 2023 [39] | Aircraft noise | \ | |
| Yan et al., 2009 [42] | Road traffic noise | \ | |
| Wang et al., 2022 [33] | Metro noise | \ | |
| Cai et al., 2023 [43] | Environmental noise | Males experience higher levels of annoyance | Tracking daily activities |
| Zhang et al., 2022 [38] | Road traffic noise, white noise, low-frequency noise | Focus on children | |
| Zhang et al., 2018 [37] | Road traffic noise, white noise, air conditioner noise | Focus on children | |
| Cai et al., 2019 [40] | Water sounds and industrial noise | Relief from annoyance was greater for female participants | \ |
| Factor | Research | Study Area | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Education level | Qu et al., 2023 [39] | Three communities | Individuals with lower education levels tend to experience higher levels of annoyance |
| Di et al., 2022 [45] | Laboratory experiment | Individuals with higher education levels tend to experience higher levels of annoyance | |
| Li et al., 2012 [46] | Single community | ||
| Zhang et al., 2020 [35] | Single community | ||
| Chen et al., 2007 [52] | Four different sites | ||
| Income | Qu et al., 2023 [39] | Three communities | Low-income groups tend to experience higher levels of annoyance |
| Cai et al., 2023 [43] | Two communities with different environments | ||
| Di et al., 2022 [45] | Laboratory experiment | High-income groups tend to experience higher levels of annoyance | |
| Zhang et al., 2020 [35] | Single community |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, C. The Impact of Non-Acoustic Factors on Chinese Community Response to Noise: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22040651
Wang W, Ma H, Wang C. The Impact of Non-Acoustic Factors on Chinese Community Response to Noise: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(4):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22040651
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenkai, Hui Ma, and Chao Wang. 2025. "The Impact of Non-Acoustic Factors on Chinese Community Response to Noise: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 4: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22040651
APA StyleWang, W., Ma, H., & Wang, C. (2025). The Impact of Non-Acoustic Factors on Chinese Community Response to Noise: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(4), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22040651








