Abstract
Suicide research is directed at understanding social, economic, and biological causes of suicide thoughts and behaviors. (1) Background: Worldwide, certain countries have high suicide mortality rates (SMRs) compared to others. Age-standardized suicide mortality rates (SMRs) published by the World Health Organization (WHO) plus numerous bibliographic records of the Web of Science (WoS) database provide resources to understand these disparities between countries and regions. (2) Methods: Hierarchical clustering was applied to age-standardized suicide mortality rates per 100,000 population from 2000–2019. Keywords of country-specific suicide-related publications collected from WoS were analyzed by network and association rule mining. Keyword embedding was carried out using a recurrent neural network. (3) Results: Countries with similar SMR trends formed naturally distinct groups of high, medium, and low suicide mortality rates. Major themes in suicide research worldwide are depression, mental disorders, youth suicide, euthanasia, hopelessness, loneliness, unemployment, and drugs. Prominent themes differentiating countries and regions include: alcohol in post-Soviet countries; HIV/AIDS in Sub-Saharan Africa, war veterans and PTSD in the Middle East, students in East Asia, and many others. (4) Conclusion: Countries naturally group into high, medium, and low SMR categories characterized by different keyword-informed themes. The compiled dataset and presented methodology enable enrichment of analytical results by bibliographic data where observed results are difficult to interpret.
1. Introduction
The suicide mortality rate (SMR) worldwide from 2000–2019 diminished in the majority of countries. However, in some countries such as the US, Mexico, Brazil, Paraguay, and others, the SMR was increasing. These trends are evidenced by the statistical crude and age-standardized suicide mortality rate data available from the World Health Organization (WHO) [1] and also World Bank World Development Indicator (WDI) SMR data [2]. The period of 2000–2019 was before the COVID-19 pandemic that might have affected the SMRs and interpretations.
The World Health Organization indicates [3] that more than 700,000 people per year kill themselves. But even more attempt it [4,5,6,7]. In particular, suicide among young populations [8,9,10] has become a global public health concern. A reduction of suicide mortality rate by one third by 2030 is one of the global goals of the WHO Member States.
There are multitudes of publications addressing this type of preventable death in various contexts. For the current study we collected 19,000 bibliographic records published from 2000–2019 having a suicide keyword either in the keywords or article title or abstract. This number of records shows the magnitude of research devoted to this field and efforts to develop prevention strategies [11,12,13]. It would be impossible to review and cite all publications. However, through the analysis of keywords it is possible to understand directions that are the focus of suicide research.
Epidemiological studies show that mental disorders, depression, and addictions are major risk factors of suicide [4,14,15]. Socioeconomic factors, unemployment rates, access to the internet, unhealthy lifestyle, and mental illness in urbanized areas all negatively affect suicide mortality rates [16,17,18] while increased literacy is strongly positively correlated with help seeking and a lower risk of suicidal ideation [19,20]. Economic downturns, increasing loneliness, and sleep disturbances are other factors increasing suicide rates [12,21,22] while restriction of access to the lethal means had driven concurrent fall in SMR worldwide [23]
Studies performed during various periods of time in different groups of countries reveal significant regional disparities in suicide mortality rates [24,25]. The incidence of suicide varies more than ten-fold between countries, being especially high in Eastern Europe and very low in the Middle East [13,24]. This disparity of suicide incidence between countries and regions is very interesting and merits more study.
Studying the differences and similarities of suicide incidence dynamics (SMR) and literature between countries may provide a better understanding of what makes some societies more prone or protective regarding suicide. Country- or region-specific cultural identity or geography may influence either susceptibility or resilience to suicide. Factors associated with suicidal ideation may have different causes in different regions and countries and may need to be addressed differently through prevention strategies. Reasons leading to the development of depression risk factors might be different in different regions. For example, unemployment in European or East Asian countries may be a serious risk factor for depression but not in Sub-Saharan Africa. In Sub-Saharan Africa, having an infectious disease may be a bigger problem and a risk factor for depression than in Europe.
We attempted to identify and systematically describe groups of countries similar in their SMR dynamics across different geographical regions: Europe and Central Asia, East Asia and the Pacific, South Asia, the Middle East and North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, North America, and Latin America and the Caribbean. To do so we first used unsupervised machine learning to group countries by similarity in their SMR dynamics from 200–2019. Subsequently, we performed analysis of keywords using the Web of Science database bibliographic records on articles published from 2000–2019 associated with suicide and each particular country.
The main goal of this study was to highlight common and specific suicide-related contexts in groups of countries similar in their SMR dynamics across geographic regions. We believe that the analysis and data collected by our study will be useful for practitioners developing suicide prevention strategies and ways to increase literacy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Suicide Mortality Rate Dataset
The World Health Organization age-standardized suicide mortality rate per 100,000 population for the period 2000–2019 of 183 countries with no missing values was downloaded for this study [1]. SMR analysis between regions and in time has to be age-standardized since age structures can vary significantly between populations. Over time, the age composition of populations changes due to factors such as aging, birth rates, and migration. Age standardization allows for accurate tracking of mortality trends over time, distinguishing true changes in mortality risk from changes in population age structure and allows unbiased comparisons of SMR between countries and regions. The downloaded dataset was prepared as SMR time series in which each row represents a country and each column represents year.gender (females as yyyy.f, males as yyyy.m, and both genders as yyyy.b) (see data availability statement for availability). Corresponding crude SMR analysis data related to this study are available from Zenodo [26] for reference.
2.2. Web of Science (WoS) Bibliographic Records and Keywords
Bibliographic records from the Web of Science bibliographic database [27] were available for download for 158 out of 183 countries in the WHO dataset. For each country from the WHO dataset a search was performed in WoS for articles published from 2000–2019 with the query “country name” and “suicide” for the topic, meaning that both words must appear in the title or keywords or abstract. Full bibliographic records were downloaded for each country. The extended and author keywords were extracted and saved in separate files for each country/article, resulting in a training dataset of keywords in which each article is represented by a separate file containing one line of text with keywords separated by spaces and labeled by the country name (available from [28]). Some keywords are phrases, for example, “children left behind”.
2.3. Clustering
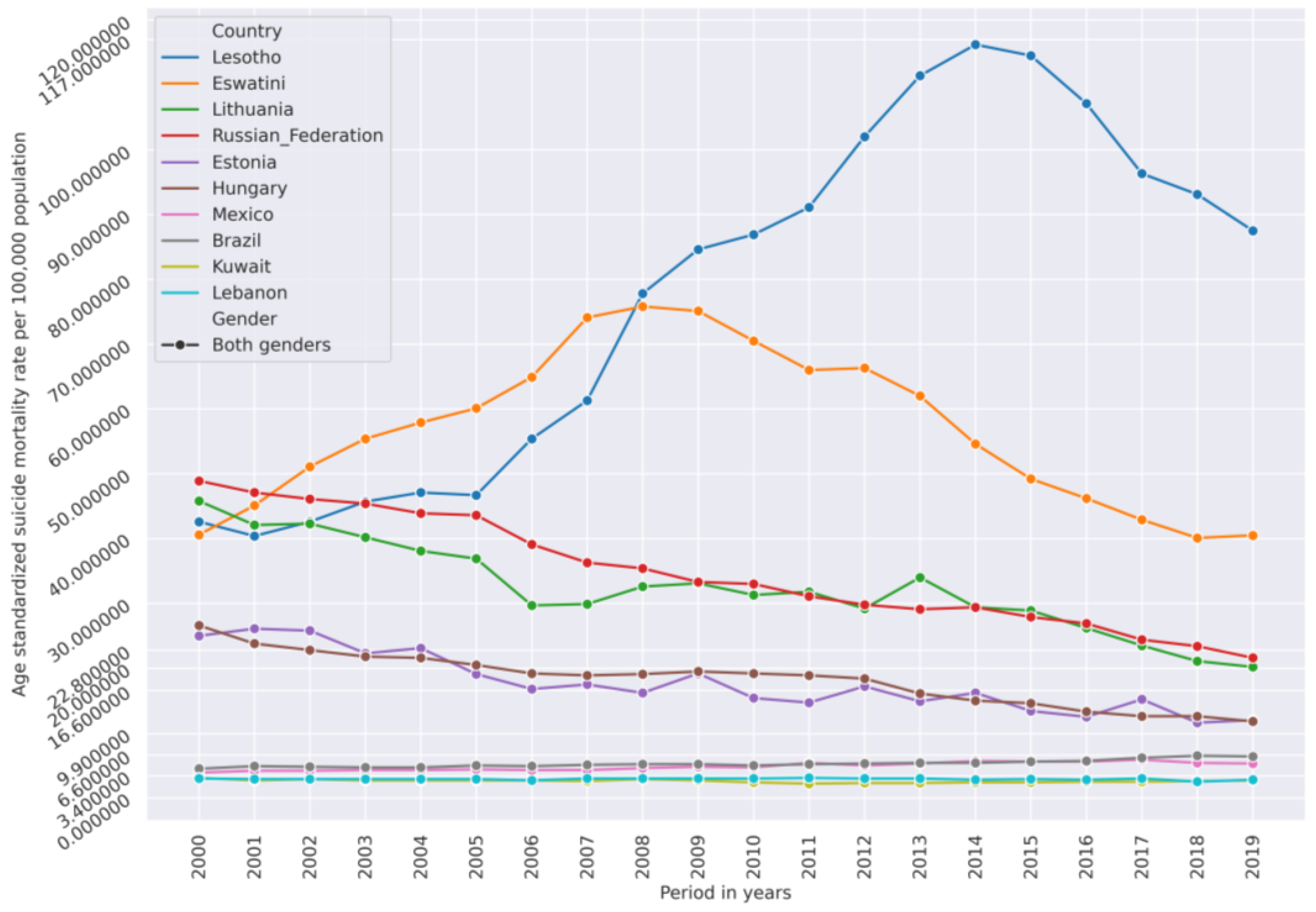
Groups of certain countries have very similar suicide mortality rate (SMR) dynamic trends from 2000 to 2019 which allowed us to use unsupervised agglomerative clustering to cluster their SMR time series. Figure 1 represents age-standardized SMRs per 100,000 population time series of both genders in different countries. This figure is to illustrate the similarity of SMR dynamics in some countries.
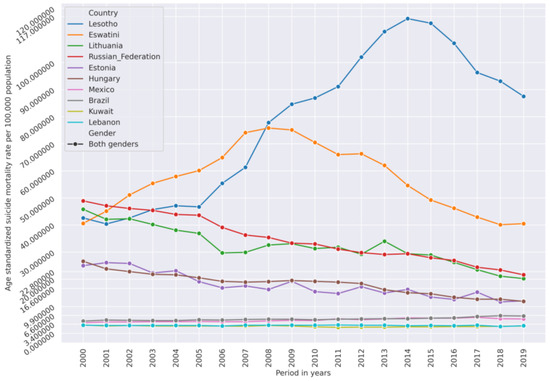
Figure 1.
Age-standardized suicide mortality rate (SMR) in selected countries from 2000–2019 showing similarity of SMR levels and trends in selected countries: Estonia is similar to Hungary, Lithuania is similar to Russian Federation, Brazil is similar to Mexico, and Lebanon is similar to Kuwait. The lower y-axis ticks represent the 10th (3.4), the 30th (6.6), the 50th (9.9) (median), the 80th (16.6), and the 90th (22.8) percentiles of the SMR across all countries. Some countries, such as Lesotho and Eswatini, have an SMR in most of the years from 2009–2019 which is considered high compared to other countries. On the other hand, the countries in which SMR in most of the years from 2000–2019 was below the value of the 10th or 20th percentile can be considered low-SMR countries compared to the other countries.
The suicide mortality rate time series for each country comprising rates of both genders from 2000–2019 were clustered using hierarchical clustering with Euclidean distance and Ward linkage as implemented in the Orange data mining tool [29]. The rationale for this choice is that Euclidean distance metric is widely used to measure time series similarity. If the time series are very similar in magnitude and trend, then there will be a small distance between them in the Euclidean sense. In Ward linkage in the agglomerative clustering procedure, a pair of clusters is chosen to merge such that there is a minimum increase in total within-cluster variance after the merge. In this way, the most similar SMR time series will be grouped together in the initial stages of the algorithm. Grouping at the lowest level naturally will put together SMR time series that have very similar SMR magnitude and dynamics.
Agglomerative clustering does not determine the number of clusters automatically. An optimal number of clusters is determined from the length of dendrogram branches that represent distances between the clusters. The resulting clustering was assessed by silhouette scores measuring how well a country belongs to its cluster. Different similarity metrics and linkage algorithms were attempted. The agglomerative hierarchical clustering using Euclidean distance and Ward linkage produced the best subdivision of countries into clusters with the highest silhouette scores.
2.4. Quantification of Countries into High-, Medium-, and Low-Suicide-Mortality-Rate Groups
No hard threshold exists in determining what is considered a high, medium, or low SMR. This categorization has to be performed using a data-driven comparative approach. In our study, we labeled a country as having a low, medium, or high SMR based on percentiles of age-standardized suicide mortality rate values available for all 183 countries and all years from 2000–2019. We computed each 10th percentile from all SMR values and established SMR intervals spanning from low to high. Table 1 shows intervals and interpretations for each bin.

Table 1.
Percentile intervals of age-standardized suicide mortality rate corresponding to SMR categories spanning from low to high.
Regarding intervals, 30% of SMR values are placed into low (low, low medium, and Low high) intervals, 40% of SMR values into medium (ML, M, M, and MH) intervals, and 30% of SMR values into high (HL, HM, and H) intervals. Although this subdivision of SMR is somewhat arbitrary and fixed for the years 2000–2019, it helps to generalize based on the statistical properties of the dataset. Having established intervals, each country is quantified as having a low, medium, or high SMR by counting how many years were in each SMR bin. The final category of country SMR is assigned based on the counts in each group of intervals: high, medium, or low. Country quantification into categories was performed by in a semi-supervised way using curation. A quantification example for Estonia (SMR is shown in Figure 1) is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Example of quantification and labeling of Estonia’s SMR category.
Estonia’s SMR over the period of 20 years was high for 16 of them. Therefore, Estonia can be labeled as a high-SMR country compared to other countries. If a country does not have a very clear unimodal distribution of SMR, such as Estonia, then it is given a composite label of major modes of the SMR distribution. Table 3 represents an example for Qatar.

Table 3.
Example of quantification and labeling of Qatar’s SMR category.
Qatar’s SMR was in the medium low (ML) interval eight times, in the low medium (LM) interval six times, and in the low high (LH) interval six times, fluctuating time on the boundary between medium and low. Therefore, Qatar can be labeled as a medium-low-SMR country. If SMR spans all low, medium, and high intervals, which is rare, then that country is assumed to have a medium wide-spectrum SMR. See the data availability statement for the quantification of SMR of all countries. Clusters obtained in the agglomerative clustering procedure carry the label of the majority of countries. The labeling is rather qualitative, however, it helps to generalize and assess each country’s SMR with respect to the other countries.
2.5. Analysis of Keyword Co-Occurrences Using VOSviewer
Visualization of Similarities viewer (VOSviewer) is a software package used to visualize bibliometric networks. It can be used to find groupings of items linked together by frequent co-occurrences in a subset of articles [30,31]. We analyzed networks of frequent keyword co-occurrences of WoS records to identify semantically distinct leading themes originating from the network of semantically linked keywords in each cluster of countries. Distinction between the themes is achieved by Louvain clustering of network nodes (keywords) by optimizing modularity of the network where a module is a strongly interconnected group of keywords within a group separate from other groups. These modules of keywords highlight different dominant topics existing in analyzed records. Aiming to restrict the number of keywords to a perceptually manageable size, for each analyzed cluster only 35 to 50 top linked keywords were selected to derive the dominant semantically differing topics.
Dominant topics were identified for clusters of high-, medium-, and low-SMR countries in each geographic region, taking only the most significant 5 to 10 representative keywords describing each dominant topic (cluster in VOSviewer terminology). The significance of the keyword in the dominant topic was determined by the frequency of occurrence of this keyword and the number of total links that it formed with other keywords. General, not informative, keywords such as suicide, mortality, risk, epidemiology, prevalence, prevention, health, behavior, suicidal risk, ideation, and similar were omitted. The chosen keywords were used as keyword annotations of high-, medium-, and low-SMR country clusters in tables summarizing countries in each geographical region.
2.6. Association Rule Mining
The association rule mining method identifies item sets frequently occurring together in the records. This method is widely used to analyze market transactions data in order to derive rules informing about customer buying preferences. It can be applied to any type of record of items including keywords of sets of articles. We used the Python Mlxtend library to perform association rule mining of frequent keyword sets [32].
2.7. Network Visualization
Cytoscape software [33] was used to visualize and analyze relationships between frequent keywords in sets of articles associated with geographic regions.
2.8. Deep Learning
Analysis of word neighborhoods using proximity between the word embedding vectors is a very useful technique in exploring and understanding semantic relationships between subsets of words representing specific contexts. The target context of this study was suicide. A recurrent neural network with a word embedding layer was trained to discriminate between 158 countries utilizing TensorFlow and Keras deep learning libraries [34] (pp. 309–363). A single training data point consisted of the keywords assigned to a single article. Each country that had at least one associated article was a class, and in total there were 158 countries/classes that had at least one associated article. The word embedding layer was set to 300 dimensions (used as default in most state-of-the-art word embedding learning algorithms). Training data preprocessing consisted of the creation of a vocabulary including all keywords and conversion of keywords into a numerical representation using their indexes in the vocabulary. A bidirectional long short-term memory (LSTM) layer was used in the network to learn from keyword sequences. The intended use of this network was to derive word embedding vectors that can be explored further including available analysis tools in the TensorFlow embedding projector [35].
2.9. Data Analytics Software
Data analysis and visualizations were carried out by the Orange data mining tool v 3.36.2 [29] and custom Python scripts.
3. Results
3.1. Summary Statistics of Suicide Mortality Rates
Summary statistics of age-standardized suicide mortality rate (SMR) in all 183 countries of all years during the period 2000–2019 show its main intervals of variation. The overall summary statistics for males and females and both genders in all countries and all years from 2000 to 2019 are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Summary statistics of age-standardized SMR per 100,000 population in 183 countries from 2000–2019.
The 3rd quartile of the SMR from 2000–2019 shows that for both genders it was below 14.9 per 100,000 and this value can be considered as a conditional threshold separating low and medium SMR from high SMR during that time period. The summary statistics also indicate that the SMR in females is almost three-fold lower than the SMR in males overall during that period. The fact that females have a much lower SMR than males is already known.
3.2. Clustering of Countries into Groups of Similar SMR Magnitude and Dynamics
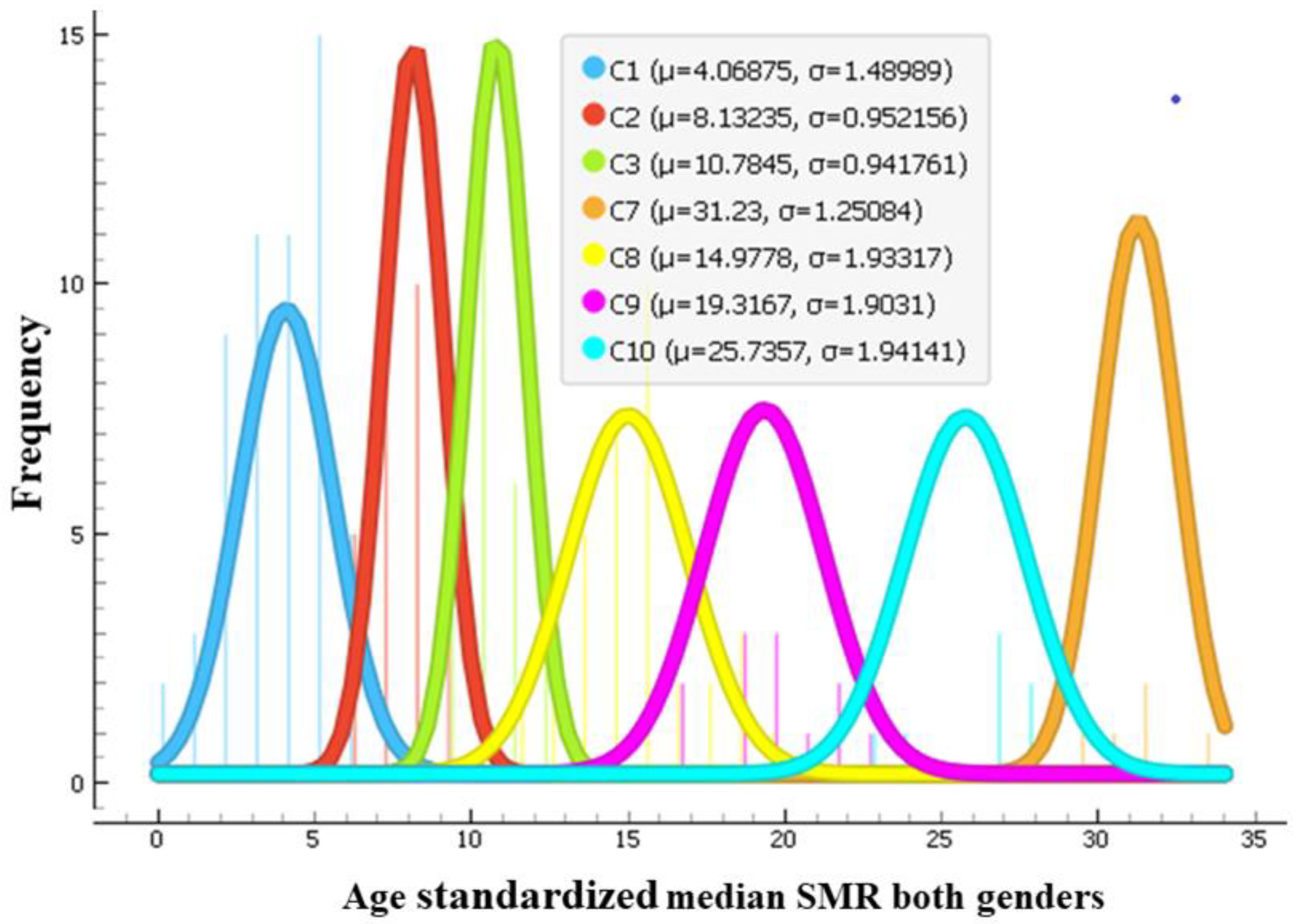
Using age-standardized SMR time series from 2000–2019 of both genders as feature vectors, the 183 countries were clustered by an unsupervised agglomerative hierarchical Ward linkage clustering procedure with Euclidean distance as similarity as implemented in the Orange data mining tool. Based on the height of dendrogram branches, the 10 clusters seemed optimal, since increasing a number of clusters beyond 10 produced many clusters containing a single element. The cluster dendrogram is presented in Supplementary Figure S1. Time series of SMRs in Lesotho and Eswatini (also known as Swaziland) were very different from the rest (see Figure 1). These countries formed clusters of one element. Guyana and Kiribati also formed a cluster of two elements. The median silhouette score of the clustering is 0.435, 1st quartile is 0.257, and 3rd quartile is 0.528, which indicates a fair clustering. However, 12 countries had low scores. Clusters with smaller number of elements were more homogeneous. Clusters with a high number of countries were more variable. Countries close on the dendrogram had very close SMR dynamics, but similarity decreased with the distance between countries on the dendrogram within the assigned cluster. The cluster silhouette plot is presented in Supplementary Figure S2. Nevertheless, the resulting clusters comprised countries generally similar by their SMR magnitude and dynamics from 2000–2019. The median values of age-standardized SMR from 2000–2019 of each country were calculated. Figure 2 shows histograms of those median values in each cluster (except clusters with one or two elements). These histograms are approximated by the normal distribution. In this way, Figure 2 illustrates how far apart the cluster centroids are by the magnitude of median SMRs of countries grouped into these clusters.
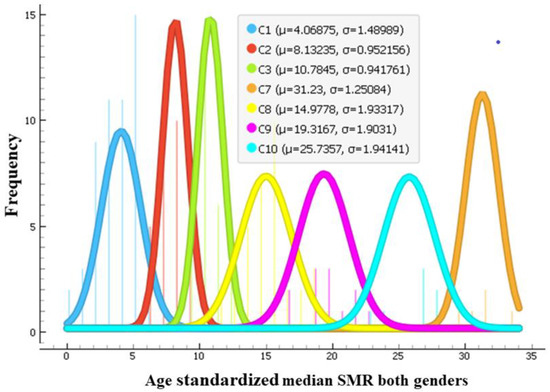
Figure 2.
Histograms approximated by normal distribution of age-standardized median SMR values in countries from 2000–2019 in each cluster. Clusters with one or two elements are omitted. Legend shows parameters of the approximation by normal distribution—values of the centroids of median SMR of the countries grouped into each cluster and a standard deviation.
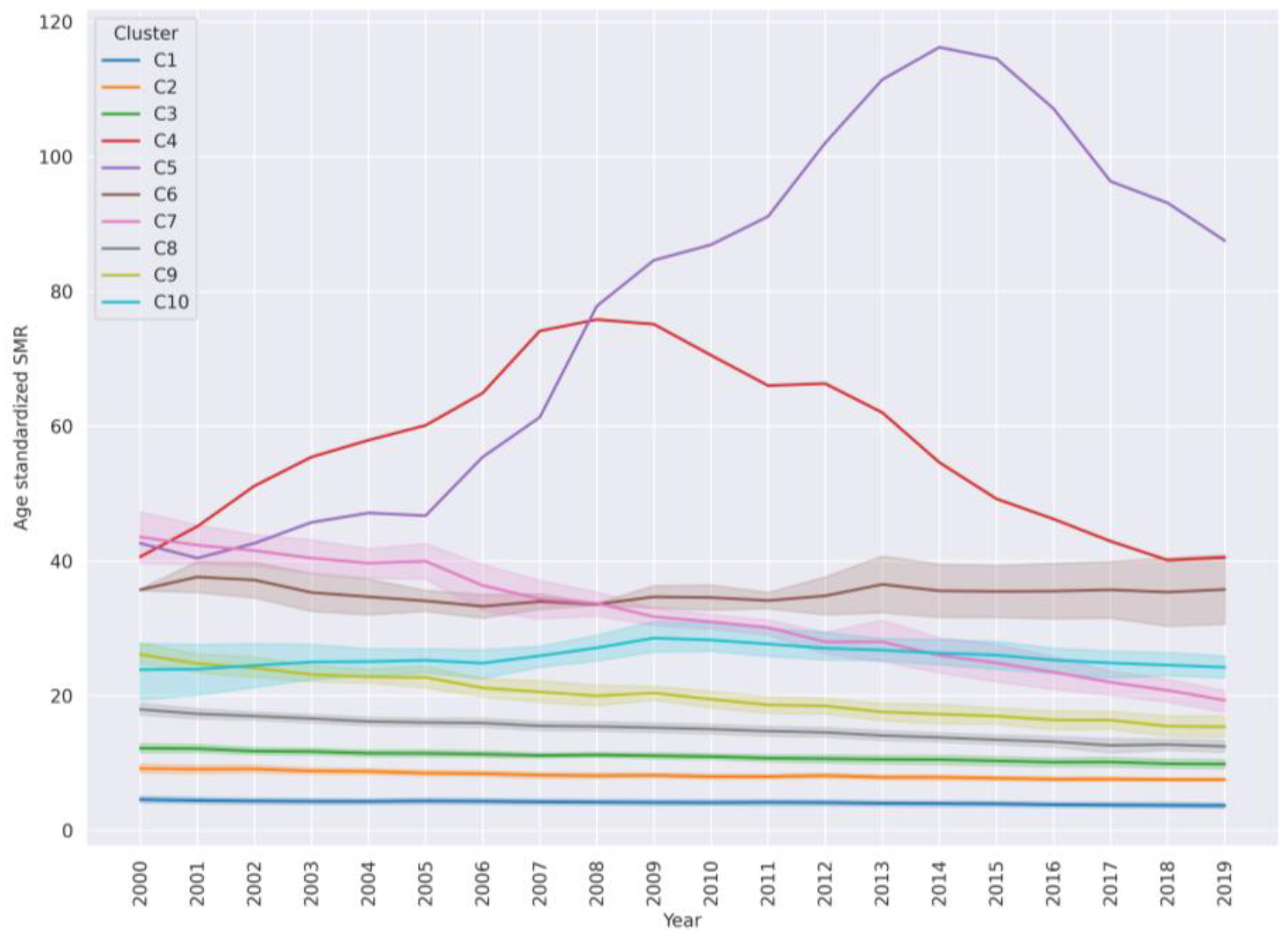
In order to discuss clusters in a generalized manner, countries from clusters were labeled as low, medium, or high (or composite) SMR as described in the Materials and Methods. The dynamic of SMR in clusters from 2000–2019 is represented by Figure 3. For each cluster the mean SMR of countries in the cluster is represented by a line. The shadow around the mean represents the confidence interval for the SMR values for each year from 2000–2019. Very-high-SMR clusters are: Eswatini—C4, Lesotho—C5, Kiribati and Guyana—C6, Belarus, Lithuania, Russian Federation, Kazakhstan, and Botswana—C7. High-SMR clusters are C9, comprising 12 countries, and C10, comprising 7 countries. The rest are low- and medium-SMR country clusters. Cluster C8 with 36 countries is in between a high and medium SMR. In this cluster, the SMR was variable during the period 2000–2019. Cluster C2 with 34 countries and C3 with 29 countries fall into the medium-SMR interval with a total median SMR ~10 (Table 4). Finally, cluster C1 with 56 countries comprises low-SMR countries.
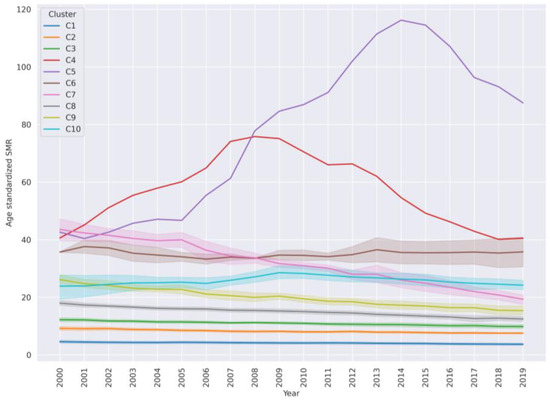
Figure 3.
Overall average trends of suicide mortality rate dynamics (with confidence intervals) in each cluster. Cluster C4 is Eswatini, cluster C5 is Lesotho and cluster C6 contains Kiribati and Guyana. Other clusters have at least 5 countries.
In the majority of countries, the SMR over the years is trending downwards. In high-SMR countries (C7 and C9), the downward slope is steep and the SMR changes are quite synchronous. These clusters have many countries from the former USSR. During the first decade from 2000–2010 the SMR overall was higher than in the following decade in many countries. The code to plot and explore these trends is available as a Jupyter notebook [28]. In the following, each cluster will be discussed in turn.
3.3. Characteristics of High-, Medium-, and Low-SMR Country Clusters
3.3.1. High- and Mixed-High-and-Medium-Suicide-Mortality-Rate Country Clusters
High-SMR country clusters have a small size compared to other clusters. Clusters subdivided by geographical region are shown in Table 5. The majority of high-SMR countries from 2000–2019 had an SMR above the 3rd quartile (14.9) of the total SMR. The trends in SMR in high-SMR country clusters are shown in Figure 4. Countries with the highest SMR were from the former USSR and Sub-Saharan Africa. Overall, SMR was declining, while it was fluctuating in African countries and it was increasing in Guyana. In African countries and South Korea, the SMR had increasing trend from 2007–2009. Out of 24 high-SMR countries, 19 are the least developed and developing regions (United Nations list). In countries from C7, the SMR was declining more rapidly than in countries from C9.

Table 5.
High-SMR country clusters stratified by geographic regions, C4, C5, C6, C7, C9, C10.
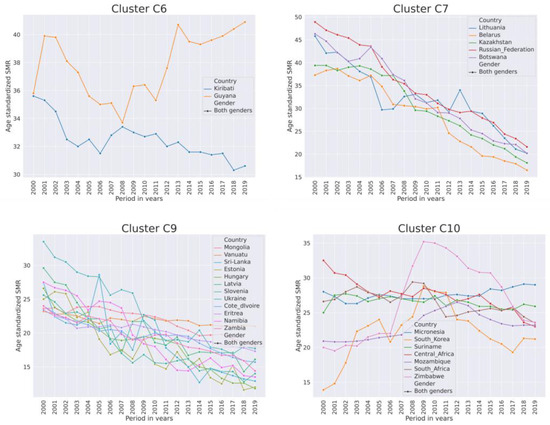
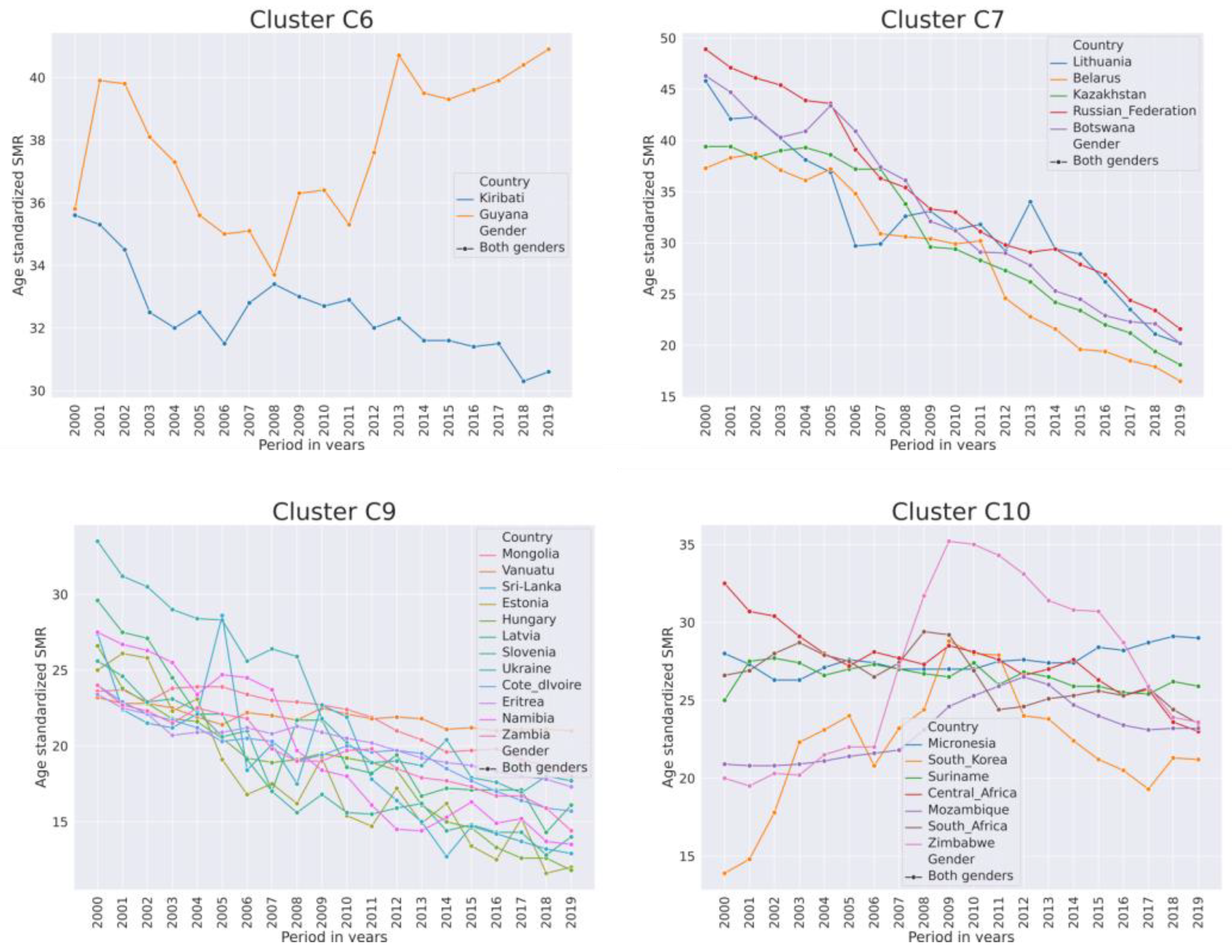
Figure 4.
Trends of SMR per 100,000 population of both genders from 2000–2019 in high-SMR country clusters C6, C7, C9, C10.
In Guyana, which had a very high SMR trending upwards, family dysfunction, child maltreatment, and alcoholism were identified as factors affecting the SMR [36].
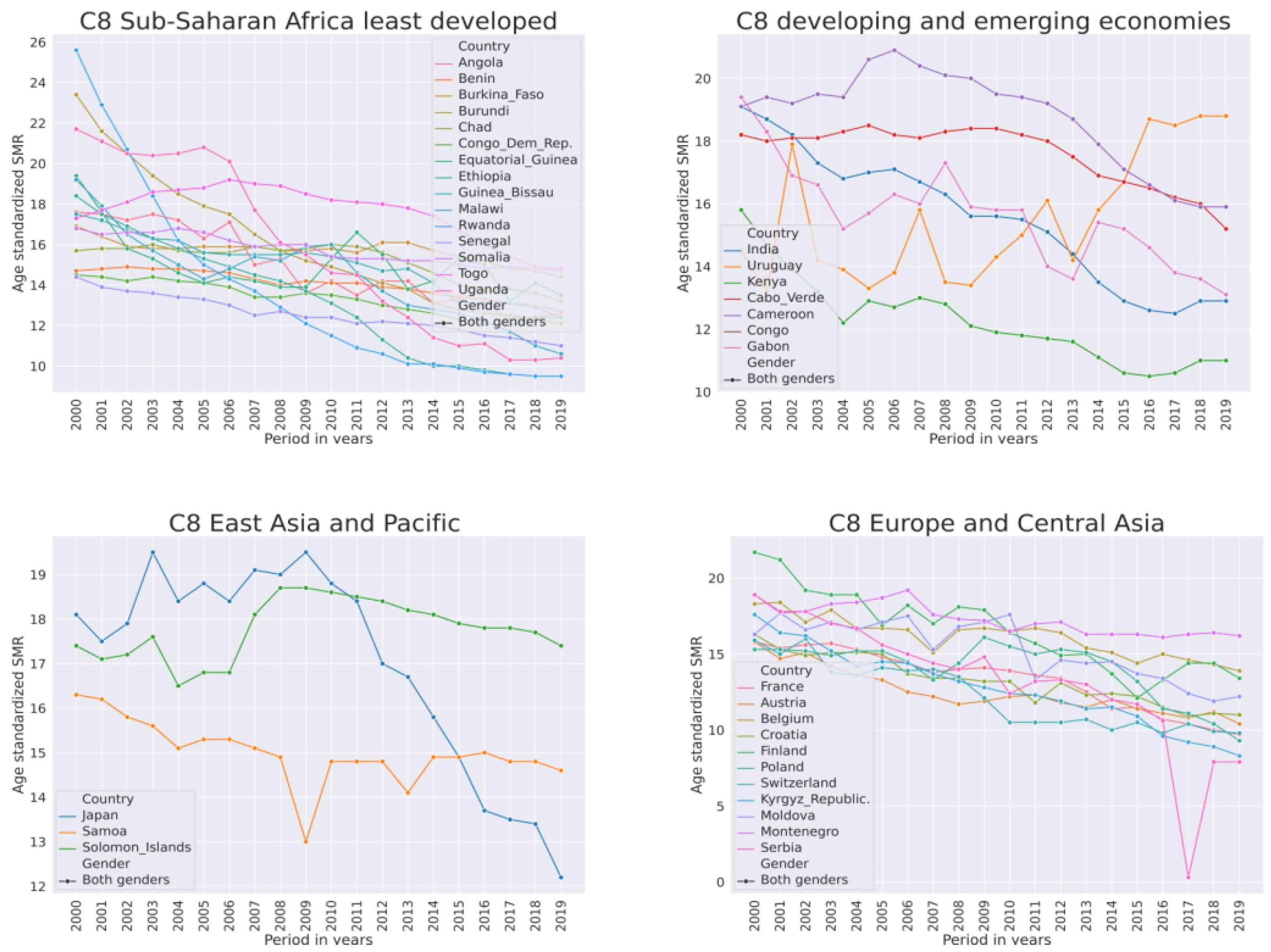
Another group of countries that had an SMR between high and medium (cluster C8) is presented in Table 6. This group comprises 36 countries, 20 of which are Sub-Saharan Africa countries.

Table 6.
Mixed medium- and high-SMR country cluster stratified by geographic region, C8 (N = 36).
Countries from Sub-Saharan Africa in this cluster are from the least developed (United Nations list) or developing regions. European countries in this cluster are developed economies and other emerging economies. The SMR dynamics in countries of this cluster are shown in Figure 5.
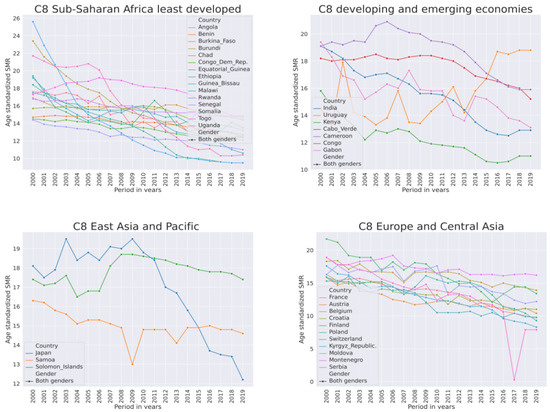
Figure 5.
Dynamics of suicide mortality rate per 100,000 population from 2000–2019 for both genders of countries in cluster C8 that had a mix of high and medium SMR.
The least developed and developed European countries in this cluster had similar magnitudes of SMR. In these countries, the SMR was declining from 2000–2019. The decline was more rapid in Sub-Saharan countries than in European ones. In Sub-Saharan Africa, the most rapid decline was in Rwanda and Uganda from an SMR of 26 and 22 in 2000 to 10 in 2019. Of all countries, only in Uruguay did the SMR rise (Figure 5 top right panel “C8 developing and emerging economies”). A quick review of the literature associated with African countries revealed frequent themes of community support, women’s health, terrorism, and psychological autopsy. Psychological autopsy is a suicide research method and was mostly associated with Uganda. Another quick review of the literature associated with developed European countries revealed euthanasia as a leading theme.
3.3.2. Medium-SMR Country Clusters
Medium-SMR countries comprise a total of 63 countries in two clusters: C2 and C3, in which C3 is characterized by a higher SMR. Medium-SMR countries from C2 and C3 are shown in Table 7. Medium-SMR countries are the largest group and are not localized in any geographical region. In this group, there are 14 countries from Sub-Saharan Africa and countries from South and East Asia that were in war conflicts.

Table 7.
Medium-SMR country clusters stratified by geographic regions in C2 and C3, total Ncountries = 63 countries.
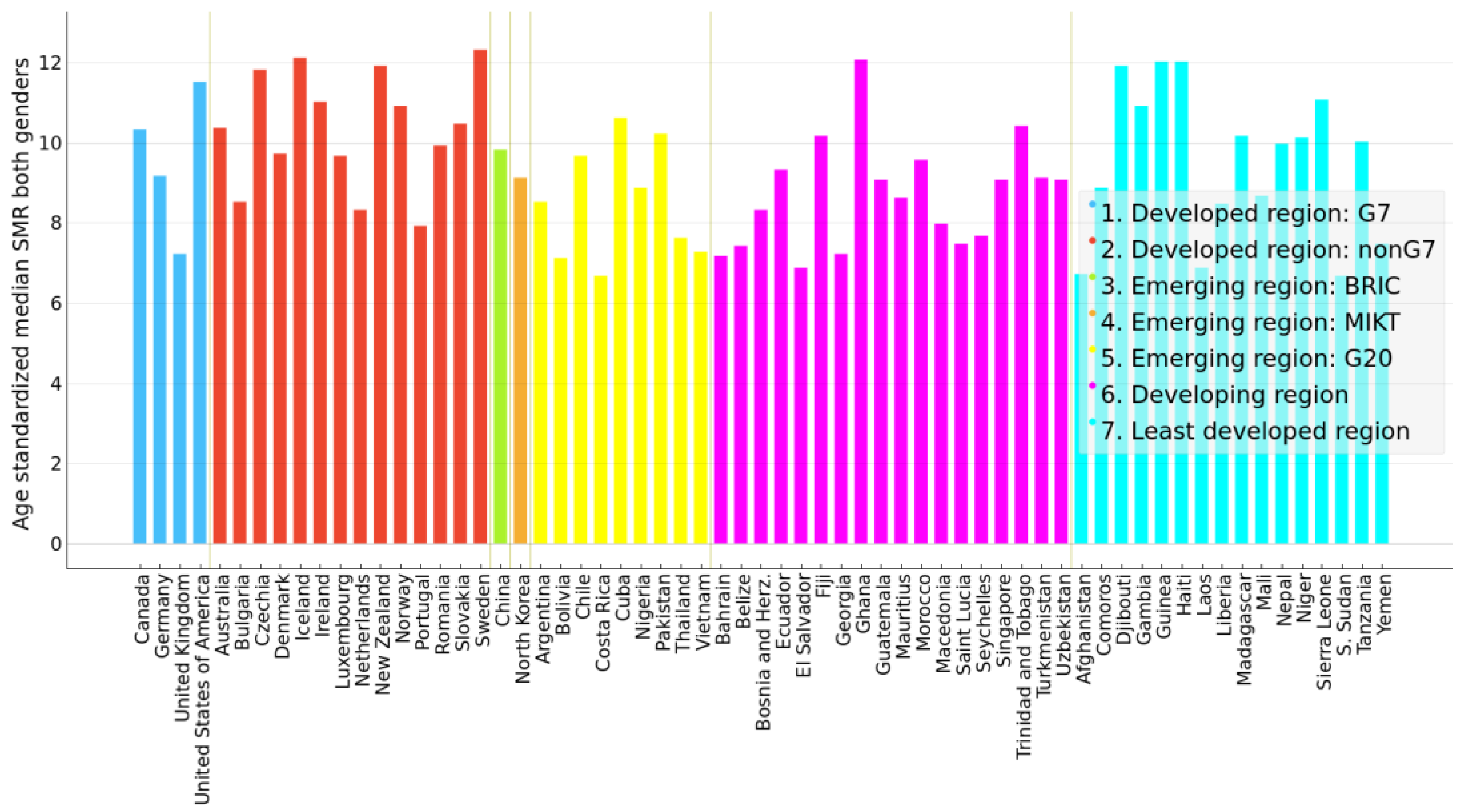
This group of countries is also a mix of economies, as shown in Figure 6. There does not seem to be a correspondence between economy and magnitude of SMR in this group. While more high-SMR countries had the least developed and developing economies, in the medium-SMR group all economies are represented rather proportionally. Figure 7 shows SMR trends in selected countries.
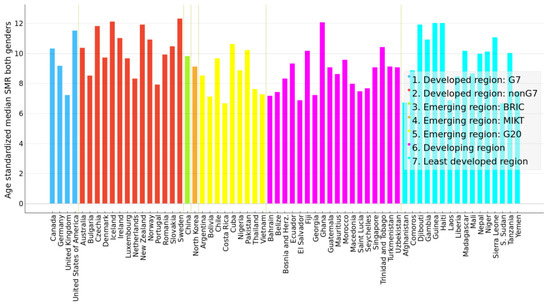
Figure 6.
Bar plot of median suicide mortality rate per 100,000 population of years 2000–2019 for both genders marked by economy for medium-SMR countries in clusters C2 and C3.
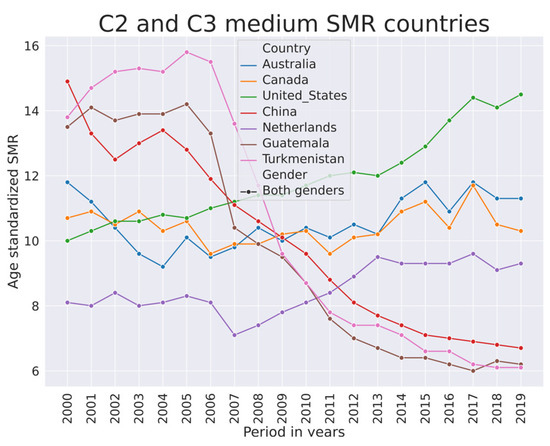
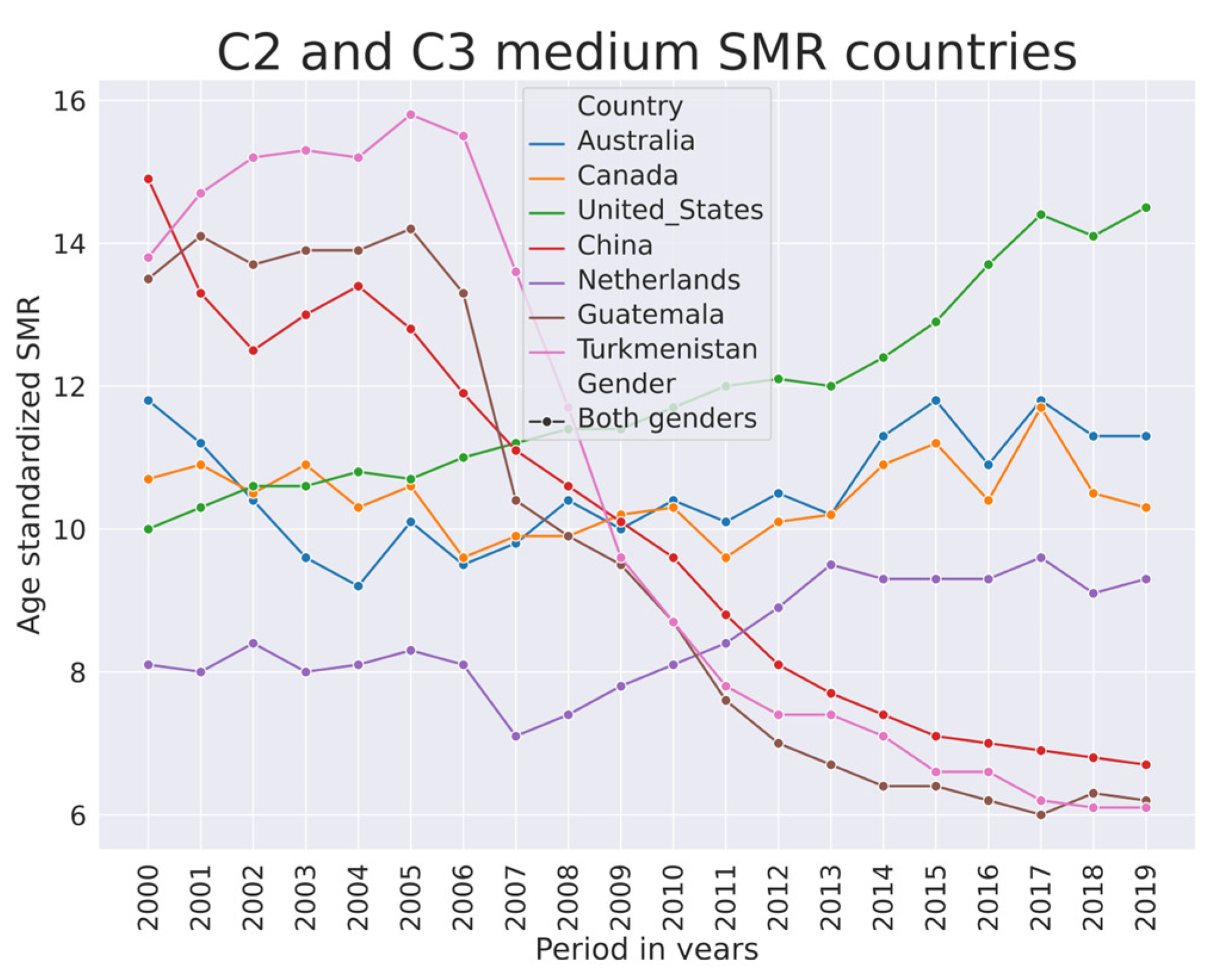
Figure 7.
SMR trends in selected countries from clusters C2 and C3.
The median SMR from 2000–2019 is higher in European developed economies. Overall, the SMR is trending down in this group of countries as well. The Netherlands (Figure 7) and Portugal (data in [1]) have fluctuating SMR that did not decline as rapidly as in other European developed countries. In Australia and Canada, the SMR was trending downwards from 2002–2012, but afterwards it started trending upwards. In the US, the SMR was increasing. In China, it was rapidly decreasing. Figure 7 also depicts SMR dynamics in Turkmenistan and Guatemala. This is an illustration of synchronicity of SMR in two countries that geographically are far apart.
In the literature associated with C2 and C3 countries, various heterogeneous topics emerged. Mostly, they were depression, mental disorders, addictions, euthanasia, euthanasia law, sedation, war, veterans, and unemployment.
3.3.3. Low-Suicide-Mortality-Rate Country Clusters
Low-suicide-mortality-rate countries from cluster C1 are shown in Table 8. This is the largest single cluster comprising 56 countries.

Table 8.
Low-SMR country clusters stratified by geographic regions, C1, N = 56 countries.
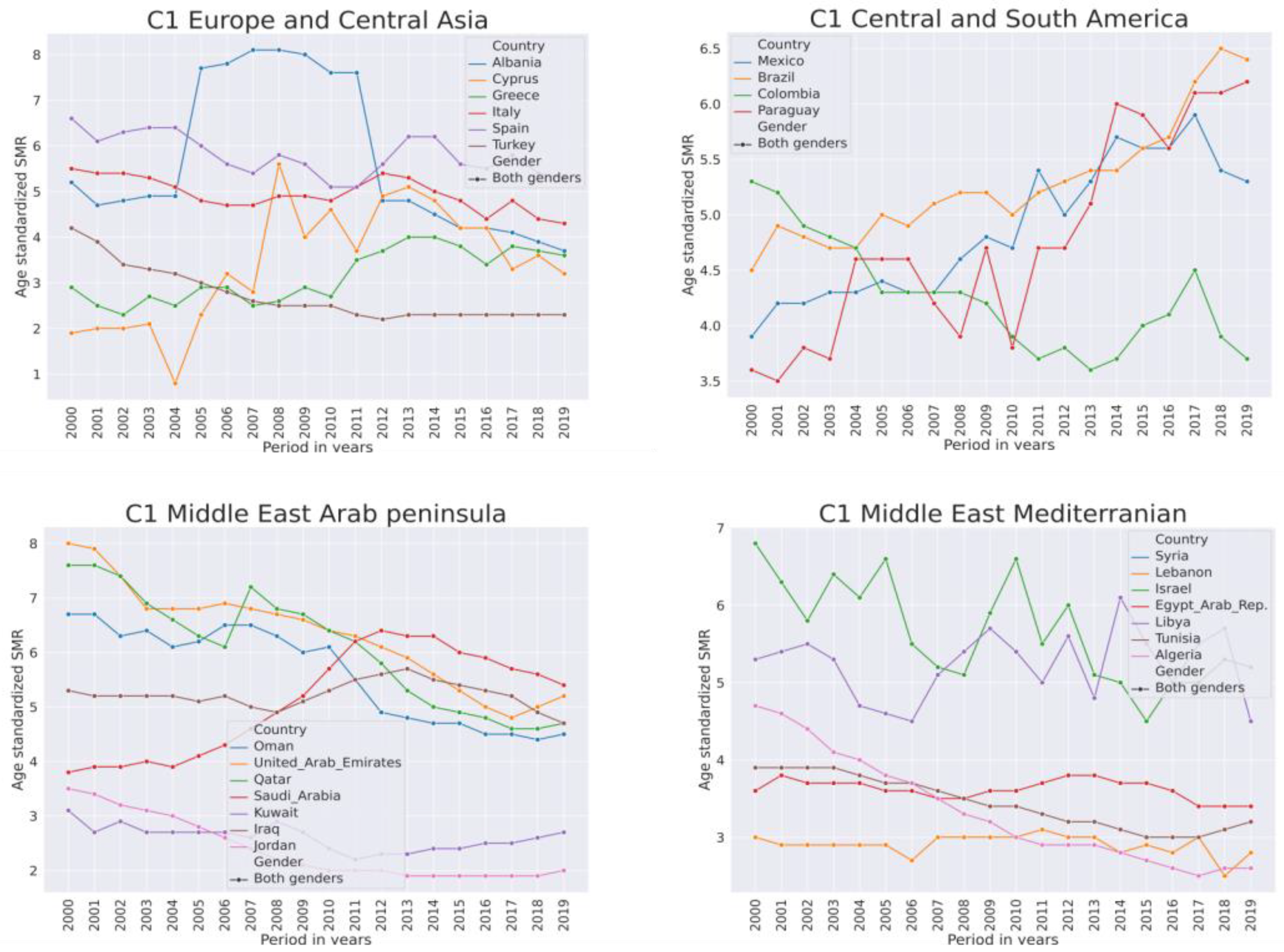
The largest proportion of countries in this group are from the Middle East and North Africa and also from Latin America and the Caribbean region. In the majority of countries, but not in all, in this cluster their SMR frrom 2000–2019 was below the first SMR quartile (SMR < 5.6). Countries in C1 from the Eurasian continent are situated around the Mediterranean Sea. Figure 8 shows SMR trends in several selected countries from C1.
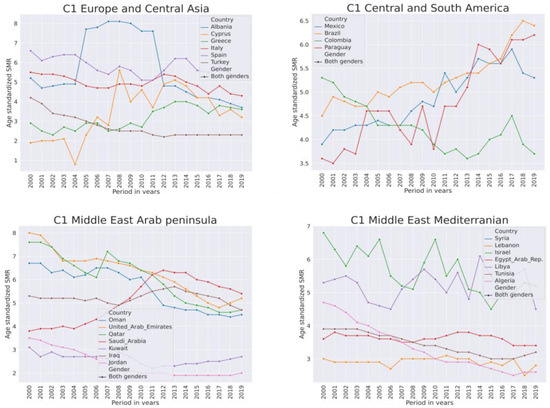
Figure 8.
Trends of suicide mortality rate per 100,000 population in years 2000–2019 for both genders in low-SMR countries from cluster C1.
In this cluster, the SMR trends in the developed European countries are stable but tended to increase in Greece. In the Middle East and North Africa, the SMR in general was declining. It was fluctuating in Israel and Libya. It jumped in Saudi Arabia from 2006–2011. In Central and South America, in general, the SMR was variable but declining. However, in the emerging economies of Brazil, Mexico, and Paraguay, the SMR is increasing. In South Asian and Sub-Saharan African regions, the SMR was decreasing in this group, except Bangladesh and Malaysia were trending up slightly in the last years. In the literature associated with low-SMR countries the most frequent topic was war.
3.3.4. Increasing SMR
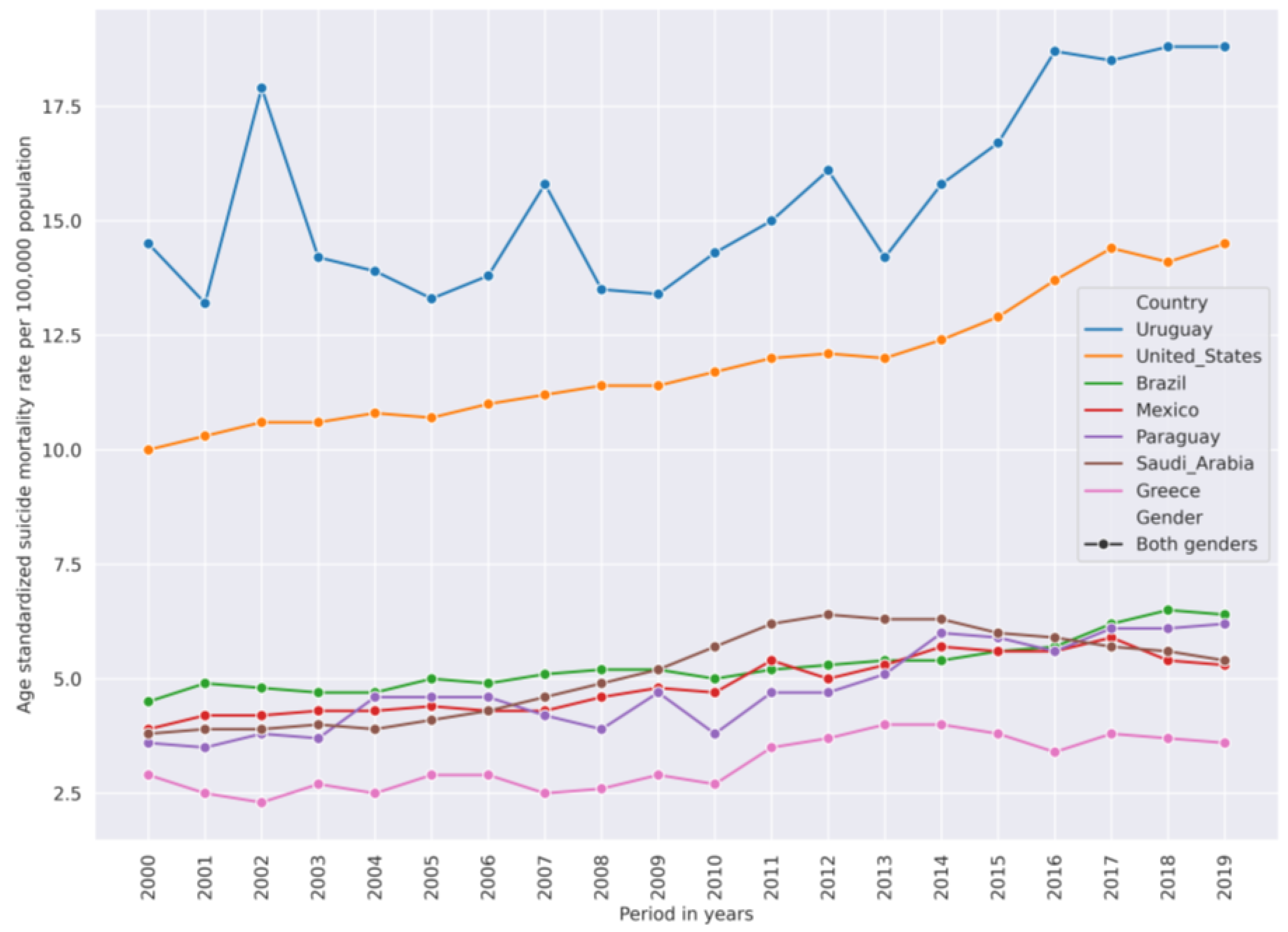
The overall suicide mortality rate was declining from 2000–2019 but not in all countries. In the US, the SMR was going up: in 2000 it was 10 per 100,000 population, but in 2019 it increased up to 14. Figure 9 shows countries with increasing SMR.
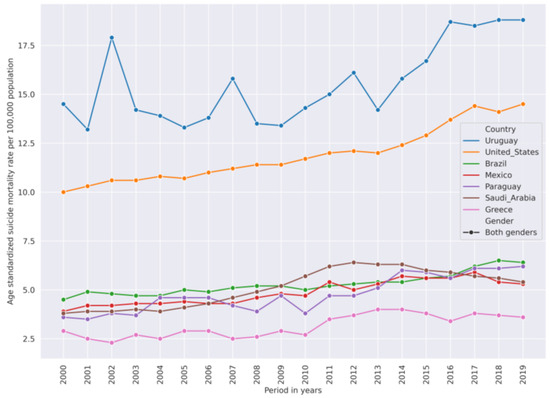
Figure 9.
Countries that have increasing SMR trend from 2000–2019. Uruguay comes from a high-SMR cluster. United States is from a medium-SMR cluster. Other countries are from a low-SMR cluster.
3.4. Results of Association Rule Mining
A quick analysis of the literature associated with the countries in high-, medium-, and low-SMR groups showed similar themes repeating in all groups of countries. We could not discern specific topics in suicide research attributable to the groups of countries or regions without a more detailed analysis. We further investigated themes frequent across geographical regions by performing association rule mining on keywords in articles associated with individual countries in each geographic region.
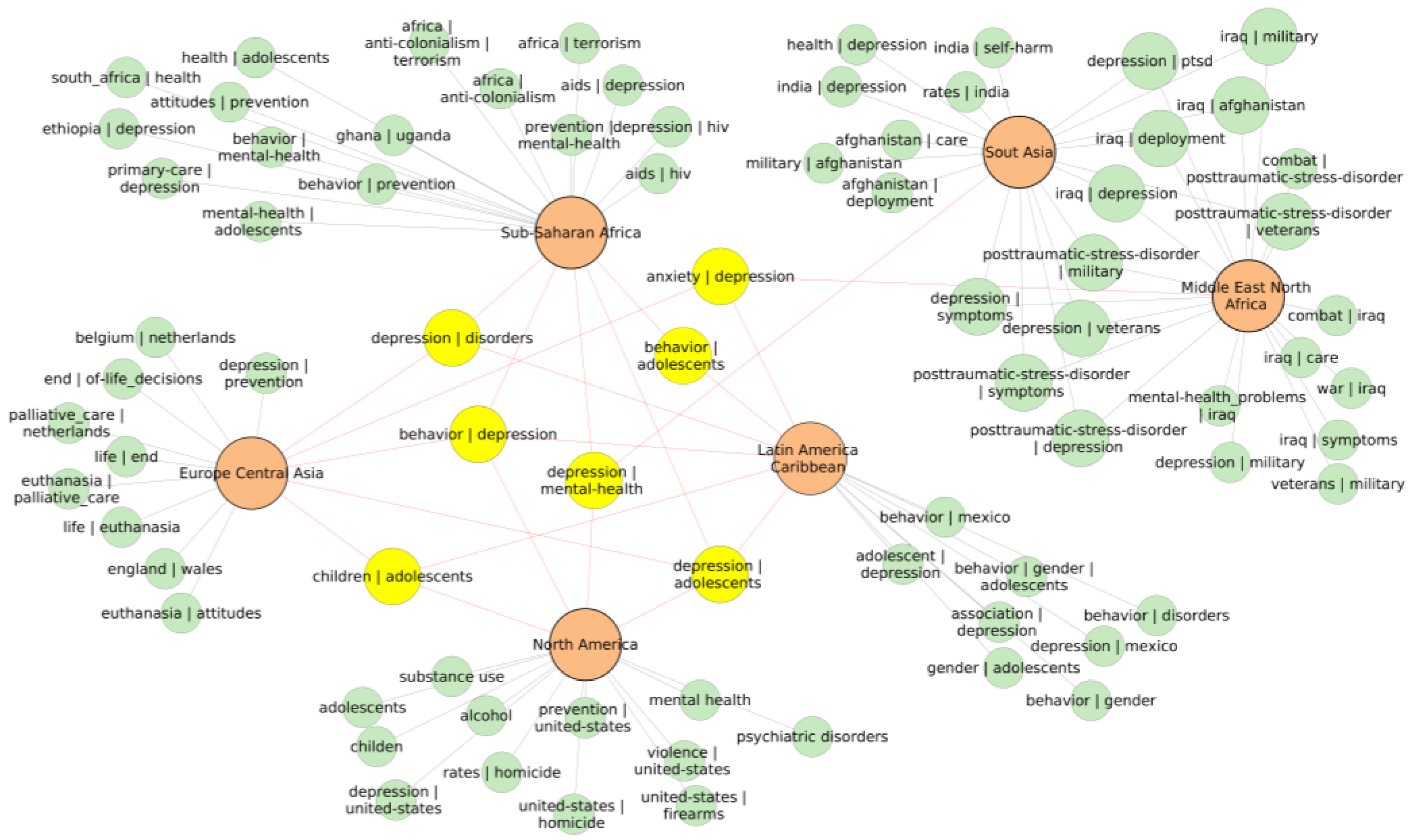
Association rule mining helps to identify items frequently occurring together in a collection of records. Mostly, it is used in marketing to identify products frequently bought together [32]. Here, the record was represented by a list of keywords associated with one article associated with one country. Collections of the records consisted of records of all countries in the particular geographic region. Frequent combinations of phrases were extracted from the collections of the records. The top 15 phrase combinations with highest support were selected. Values of support were different for each region since they depend on the number of records. Therefore, the selection was based on a fixed number of the top-ranking phrase combinations. From the selected phrases, the repetitive and uninformative frequent phrases containing suicide, mortality, prevalence, and similar were filtered out. From the selected phrases, a network was created in which nodes consisted of regions and the phrases. The purpose was to identify and visualize themes connecting the regions and the specific themes. The simplified pruned network is shown in Figure 10. We limited the number of nodes to only the most frequent phrases to make the network manageable.
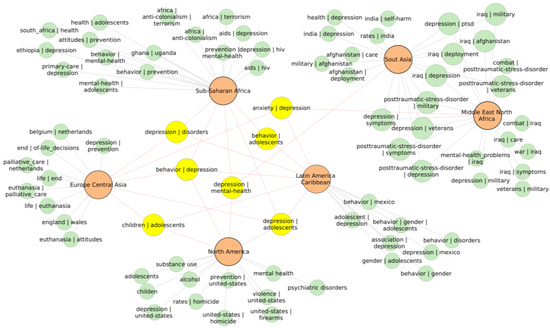
Figure 10.
Network representation of the top 15 most frequent keywords and phrases (item sets) resulting from association rule mining algorithm applied on keywords of articles associated with countries in each geographical region. Highlighted are the most frequent phrases common between the regions. Depression emerges as the central theme in all regions.
Overarching themes connecting all regions were depression and adolescents. The term “depression” frequently occurred with other phrases such as behavior, disorders, anxiety, mental health, and also adolescents. This analysis revealed contexts frequently researched in suicide literature together with depression.
Each geographical region, however, had its own very frequent specific themes. In Sub-Saharan Africa, the themes were HIV/AIDS, anticolonialism, terrorism, mental health, Ghana, Uganda, and Ethiopia. In Europe and Central Asia, the prevailing theme was euthanasia, Netherlands, and Belgium. In North America, the most frequent topics were related to substance use and violence. In Latin America and the Caribbean, the most frequent topics were adolescents and gender. In the Middle East, North Africa, and South Asia, the themes were related to war, military, and post-traumatic stress disorder. In South Asia, India and self-harm were frequent. Such simple analysis of frequent phrases in articles associated with suicide and a particular country allowed us to highlight themes that are common and also specific themes that gained more attention in different geographical regions. The themes identified by association rule mining were in good correspondence with themes found by VOSviewer that will be discussed in the following section.
Association rule mining revealed the most frequent and common themes of interest in the context of suicide in different regions. The source for this analysis was a textual corpus of keywords of ~24,000 expressions originating from bibliographic records of 19,000 articles. Frequent combinations of phrases revealed a few dominant themes associated with each geographic region. To refine these results in groups of high-, medium-, and low-SMR countries in a geographic region, we analyzed subsets of bibliographic records associated with those groups of countries using the VOSviewer tool. In addition, we explored frequent keyword occurrences repeating across multiple countries in the group as well as frequent keywords specific to only one particular country.
3.5. Descriptive Analysis of High-, Medium-, and Low-SMR Country Clusters Across Geographic Regions Using Visualization of Similarities Viewer (VOSviewer) Tool and Frequent Keyword Occurrences
To perform VOSviewer analysis [30] we used Web of Science database bibliographic records of 19,000 articles published from 2000–2019. Selection criteria were such that the term suicide and a country name had to be in the title or keywords or abstract. Among those selected, the US had the most associated articles published during that period—3563. Ireland was in second place—1258 articles. In third place was Australia—1070 articles. Other countries that had many associated articles were China—896, Japan—770, Canada—730, the Netherlands—639, India—570, Sweden—558, and Germany—462 articles. The number of associated articles does not correlate with the suicide mortality rate across countries. However, European countries were in a higher suicide mortality rate bracket compared to Middle Eastern countries and, statistically, had more associated articles compared to the low-SMR Middle Eastern countries.
In this section, we summarize details about each geographic region with regard to groups of high-, medium-, and low-SMR countries in this region. We annotated clusters of countries using top keywords inferred by VOSviewer and reviewed and summarized the most frequent keywords repeating across multiple countries in the group. For the most part, keywords repeating across many countries agree with the top keyword annotations derived by VOSviewer. In addition, we summarized country-specific keywords that highlight uniqueness.
3.5.1. Europe and Central Asia
There are 48 countries from the Europe and Central Asia region listed in Table 9. For each country, the first, median, and third quartiles of SMR, the SMR category, the number of bibliographic records associated with the country, and top keyword annotations derived by VOSviewer are presented in the table. Countries from the Europe and Central Asia region predominantly have medium and high SMR except for Turkey, Albania, Cyprus, Greece, Italy, and Spain. The low-SMR European countries are from the Mediterranean region. Western, Eastern, and Northern European countries had rather high SMRs. The former USSR had an especially high SMR compared to the rest. Even though it is decreasing, its magnitude was still above the third quartile of the total SMR of 14.9 per 100,000 population for both genders.

Table 9.
SMR in Europe and Central Asia geographic region.
Frequent keywords associated with Europe and Central Asia point to several themes. The first are euthanasia and assisted suicide. Other frequent themes in many countries comprise mental disorders, parasuicide, and psychiatric disorders. Parasuicide is a form of self-harm in which someone mimics the act of suicide without the intent to kill (MedGen Concept ID: C0595861). Lastly, in many countries, frequent mentions are made to adverse childhood experiences, youth, and social support. Former USSR countries are marked by alcohol consumption and crime. Other keywords repeating across countries are unemployment, economic crisis, financial crisis, hopelessness, elderly, hospitalization, psychological distress, and substance use. There are mentions of seasonality and weather. Economic and financial crisis themes were most frequent in Greece. Euthanasia frequently occurred with the Netherlands and Belgium with no mentions among keywords associated with countries from cluster C7 (Table 9).
Some country-specific unique keywords in relation to suicide were as follows. Belgium—non-voluntary euthanasia and continuous palliative sedation; Hungary—congenital abnormalities and suicide attempt during pregnancy; Slovenia—heroin use and social and economic consequences of gambling; Belarus—alcohol psychosis; Lithuania—relation with authority and cosmic ray; Russian Federation—migrations, migratory politics, depopulation, programs for prevention of suicides among minors, native peoples of Siberia; Ukraine—strategy of eradicating female terrorism; Austria—rugged individualism, film effects; Croatia—heavy metals; Finland—global solar radiation, adolescent parricide; Poland—political protest, exile, Polish Catholicism, Satanism; Serbia—responsible media reporting, invisible victims, code of ethics of Serbian journalists, prison environment, plant toxins; Switzerland—suicide regulation, maintaining hope, unassisted suicide; Bosnia and Herzegovina—emo subculture (lifestyle based on emotional hardcore punk rock music); Denmark—life mission theory, shelters, radicalization awareness; Germany—inpatient suicide; dialectical behavioral therapy for adolescents; Iceland—friendship networks; Ireland—ganciclovir, planned complex suicide, Iowa gambling task, bystander effect; Norway—tension type headache; Portugal—water supply, children depression, drinking water lithium; Romania—intimate partner homicide suicide, children left behind; Sweden—international adoption; Italy—illicit drug overdose; Netherlands—train the trainer, e-learning; United Kingdom—genderqueer, political terrorism, pastoral care; Turkey—shelter, chronotype, authoritarian, incest, mobbing; Armenia—personality peculiarities; Azerbaijan—electronic device; Cyprus—workplace empowerment, colonial policies, goats; Greece—Greek crisis, marital quality, lunar periods, cyclicity, female aborigines.
3.5.2. Sub-Saharan Africa
The Sub-Saharan Africa region has 48 countries that are shown in Table 10. Several African countries, such as Lesotho and Eswatini, had the highest SMR from 2000–2019 and no published articles in relation to suicide. Not many countries in this region had associated publications except of South Africa which had 232 publications. Keywords that did not appear in VOSviewer top keyword annotations but did appear in no less than five countries were anticolonialism and CIA, mentioned in articles associated with Guinea, Cameroon, Congo, Togo, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, and Kenya. In addition to these countries, terrorism was frequently mentioned in articles associated with Mali, Chad, Niger, Nigeria, Ghana, and Kenya. Women and HIV were frequent topics in almost all countries. Other frequent topics were nurses, students, education, disability, injury, alcohol, gender differences, social support, low income, domestic violence, sexual violence, men, and war. Less frequent were mentions of suicide bombing, Boko Haram (jihadist group), corporal punishment, and terms from virology, molecular biology, and plant toxicity.

Table 10.
SMR in Sub-Saharan Africa geographic region.
Some unique country-specific keywords: South Africa—non-fatal suicidal behavior; Zimbabwe—lysosomes, protein crystal structures; Ethiopia—neglected tropical disease, non-filarial elephantiasis; Ghana—funeral rites, moral infraction, disabled women, sleep disruption; Somalia—UN peacekeepers; Uganda—post-conflict northern Uganda, qualitative psychological autopsy, African refugee settlement, women suicide; Guinea—Guinea pig, ototoxicity; Kenya—life questionnaire, emotional loneliness scale, family discord, faith healer; Tanzania—low-income country, school bullying.
3.5.3. Middle East and North Africa
The Middle East and North Africa region has 20 countries shown in Table 11. All countries except a few are low-SMR countries. Three countries had much more articles associated with them than the rest: Iran—259 articles, Iraq—379 articles, and Israel—248 articles. That makes VOSviewer keyword annotations somewhat biased.

Table 11.
SMR in Middle East and North Africa geographic region.
We summarized keywords in this category that repeated in more than three countries and were not highlighted by VOSviewer. The theme of euthanasia had mentions in Israel, Iran, Kuwait, and Malta. Post-traumatic stress disorder was frequent in Egypt, Iraq, Israel, and Lebanon. Conflict and disability were mentioned in association with Yemen, Syria, Libya, Algeria, and Iraq. In addition to the mentioned countries, terrorism was also associated with Morocco. Other group of keywords in Libya, Algeria, Egypt, and Morocco included maternal mortality, maternal and child health, deadly traffic injuries, and non-communicable diseases. Another big group of common shared keywords consisted of suicide terrorism, suicide bombings, childhood sexual abuse, addiction, politics of education, cannabis, pregnancy, use disorders, social media, politics, jihadism, parental death, cross-cultural comparisons, high school students, Gulf War, war, refugees, trauma, stigma, shame, political violence, emergency department, insurgency, and suicide attacks.
Some unique country-specific keywords included: Algeria—agency theory; authoritarian institutions; Egypt—addict, autoaggression; Jordan—seaside resort, contemporary Irish fiction; Kuwait—parental smoking; Lebanon—Syrian crisis, trans feminine; Iran—Khozestan Province, Iranian Kurds; Iraq—focused attention, mass casualty response, Pacific Rim; Israel—Hamas, Second Intifada, Arab, assassinations; Oman—antiepileptic drug; Qatar—Qatari women, suicide scales, menopause; Saudi Arabia—skin disease; Umrah worship, psychology of worship.
3.5.4. East Asia and Pacific
The East Asia and Pacific region has 22 countries shown in Table 12. More countries from this group belong to the low-SMR category than others. Most articles published in relation to suicide were associated with Australia, China, Japan, South Korea, and Vietnam.

Table 12.
SMR in East Asia and Pacific geographic region.
We reviewed keywords that repeated in no less than eight countries in addition to VOSviewer annotations. One keyword that was characteristic to only this region was “community psychiatry”. It appeared in keywords associated with Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, Kiribati, Tonga, Samoa, Papua New Guinea, and Micronesia. Community psychiatry is a study and treatment of individuals with complex mental illness in the community rather than in psychiatric hospitals. Interestingly, the mentioned countries had rather high SMRs. Other frequent common themes related to suicide in this region were: homicide, self-harm, hopelessness, unemployment, social support, psychological autopsy, quality of life, global burden, university students, older adults, migration, physical activity, HIV, gender differences, internet, stress, intimate partner violence, women, students, young people, loneliness, distress, smoking, alcohol, and substance use.
Mentions of country-specific unique keywords: Japan—Mie and Akita prefectures, medical residents, depressive state, electromagnetic field, geomagnetic storm, defeat depression campaign; South Korea—solar radiation, Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (KYRBWS), game addiction; Australia—Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander, remoteness, psychiatric injury, veterinarians, chronic callers; China—psychological strain, negative life event, micro-blog, one child policy, celebrities, strain theory of suicide; Fiji—trauma registry, condoms, social learning theory, motor-vehicle-assisted suicide; North Korea—Cold War, Czechoslovakia, national missile defense, Korean nuclear crisis, US foreign policy, national and extended deterrence, liberal internationalism; Singapore—academic stress, adolescent outpatients, catatonia, train suicide, meaning-centered ethnography; Thailand—Thai adolescents, cardiotoxic ornamental plant species, Bangkok, suicide tree; Indonesia—Islamist, emotional loneliness, terrorism and social media, youth and terrorism, lone wolf terrorism, online radicalization, female jihadist, spiritual messages; Philippines—levodopa equivalent dose, Parkinson disease; Cambodia—women’s health, key somatic complaints, cultural syndromes, alcohol advertising, media exposure; Malaysia—suicide registry, Chrysomya megacephala, human–robot interaction, cyber aggression and victimization; Vietnam—post-service mortality, Vietnam theater veterans, academic pressure, low mood, prisoners of war.
3.5.5. South Asia
The South Asia region has eight countries shown in Table 13. Countries in this region mostly are mix of medium- and low-SMR countries.

Table 13.
SMR in South Asia geographic region.
We summarized keywords repeated in three or more countries, some not captured by VOSviewer. In this group of countries, frequent keywords comprise education, mothers, post-natal depression, inflicted burns, farmers, policy, substance use, anxiety disorders, sleep, psychiatric disorders, religion, family, college, discrimination, culture, global health, interpersonal violence, organophosphates, post-partum depression, developing countries.
In articles associated with Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Sri Lanka, there was a group of keywords including social mechanisms, social networks, martyrdom, culture of martyrdom, axiological rationality, radicalization, jihadism, spirituality, suicide bombers, suicide terrorism, political conflict, civil war, and green revolution.
Keywords that stood in association with Pakistan, India, Afghanistan, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh were “self-immolation” and “young married illiterate women”. These keywords originated from the article “The geographical belt of self-immolation” [37] which discusses the strictly geographically localized phenomenon of self-immolation that is specific to countries in Asia, mostly South Asia.
Country-specific unique keywords: Sri Lanka—yellow oleander, Kataragama, militarization, female militant, food production, suicide-like acts; India—Maharashtra, agrarian crisis, farmer suicides, marginal farmers, Kerala, Jainism; Nepal—Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale, thinking healthy program, mother–child interaction; Pakistan—chemical burn, caliphate, sexual infidelity, divorcee individuals, Sunni–Shia sectarianism; Afghanistan—survey sampling, chronic pain, US army, behavioral activation, symptom clusters, induced traumatic stress; Bangladesh—tetanus, micro-credit, women with disabilities, female garment workers, psychosocial well-being; Bhutan—parental engagement.
3.5.6. Latin America and Caribbean
The Latin America and Caribbean region has 31 countries shown in Table 14. In this region, countries are low- and medium-SMR countries except for Guyana, Suriname, and Uruguay. The SMR in these countries was quite high. Countries in this region did not have many associated publications except Brazil and Mexico. For this region, in addition to VOSviewer annotations, we reviewed keywords that repeated in four or more countries. In high-SMR countries of this region, the most important themes were suicide in young people, middle and high school students, teenagers, depression, and alcohol drinking. Other common themes repeating across countries were mental heath, public health, stressful life events, sexual abuse, smoking, drugs, trauma, spirituality, accidents, risk behaviors, self-esteem, thyroid abnormalities, spectrum disorders, victimization, gender differences, guns, and school.

Table 14.
SMR in Latin America and Caribbean geographic region.
Euthanasia had a few mentions in Chile, Mexico, Uruguay, and Colombia. Obesity and its relationship to depression, mental health, and suicide was studied in Brazil, Mexico, Chile, and Costa Rica. The topic of obesity in the context of suicide also appears in other regions except Sub-Saharan Africa.
Country-specific unique keywords in this region: Guyana—toxic plants, catharsis, mass suicide; Suriname—global health governance, multi-lateral development banks, mercury exposure; Uruguay—cocaine base post, historical evolution; Chile—dangerous behavior, cocaine-related disorders, hidden populations; Cuba—epidemiology descriptive, refractory temporal lobe epilepsy, deaths from epilepsy; Argentina—Maria Ines Krimer, thyroid-stimulating hormone, iodine, mental health policies, sex workers, aggressors, cyberbullying perpetration; Guatemala—school health survey, sexual initiation; Haiti—community health workers, rural Haiti, adolescent depression; Jamaica—sickle cell disease, underachievement, packer syndrome, internalizing distress; Peru—subjective constitution, fatherhood, depressive symptoms, antepartum depressive symptoms; Brazil—the elderly, psychosocial autopsy, suicide among elderly; Colombia—war crimes, sexual dissidence, persons deprived of freedom, unconstitutional state of things, rights of the prisoners, pesticide toxicity; Mexico—international consortium, school population survey, amyloid plaques, addiction, attitude towards institutional authority, child suicide; Nicaragua—family of origin, hospital surveillance, seasonal pattern; Paraguay—scopadulcic acid b, traditional herbal medicines of guanary indio, bone resorption; Venezuela—antibiotics, Aeromonas spp.
3.5.7. North America
The North America region includes the US (3563 articles) and Canada (730 articles) shown in Table 15. Both represent medium-SMR countries. Together, the US and Canada surpass all other countries by the number of articles on suicide. Top-ranking topics by the frequency of mentions in articles associated with both countries comprise depression, euthanasia, mental and psychiatric disorders, adolescents, children, gender, Inuit, substance use, firearms, and violence in general.

Table 15.
SMR in North America geographic region.
It is difficult to comprehensively review very numerous unique keywords associated with North American countries. We mention only a few of the most frequent. For a full list, see the data availability statement. Unique country-specific keywords associated with North American countries: US—non-Hispanic whites, reporting system, mass shootings, youth violence, DSM-IV disorders (mental retardation and intellectual disability disorders), multiple births, households, rampage shootings, decedents; Canada—Nunavut, Metis, home care, CAG repeats, Alberta, marijuana use evidence, British Columbia, narrative research, body donation, aboriginal young people, Edmonton, correctional service of Canada, interpersonal trauma, hospital pharmacists, Dutch program.
3.6. Word Embedding of Suicide-Related Keywords
Having such a large corpus of expressions related to suicide, an exploration of contexts and semantic neighborhoods of keywords of interest is not possible through analysis of just keyword co-occurrences. We attempted to carry out word embedding for all suicide-related keywords that we collected from 19,000 articles. To do that, we trained a recurrent neural network to discriminate countries based on the keywords in the suicide-related articles for a particular country. The main aim of the network training was to derive word embedding vectors rather than classification of countries by keywords.
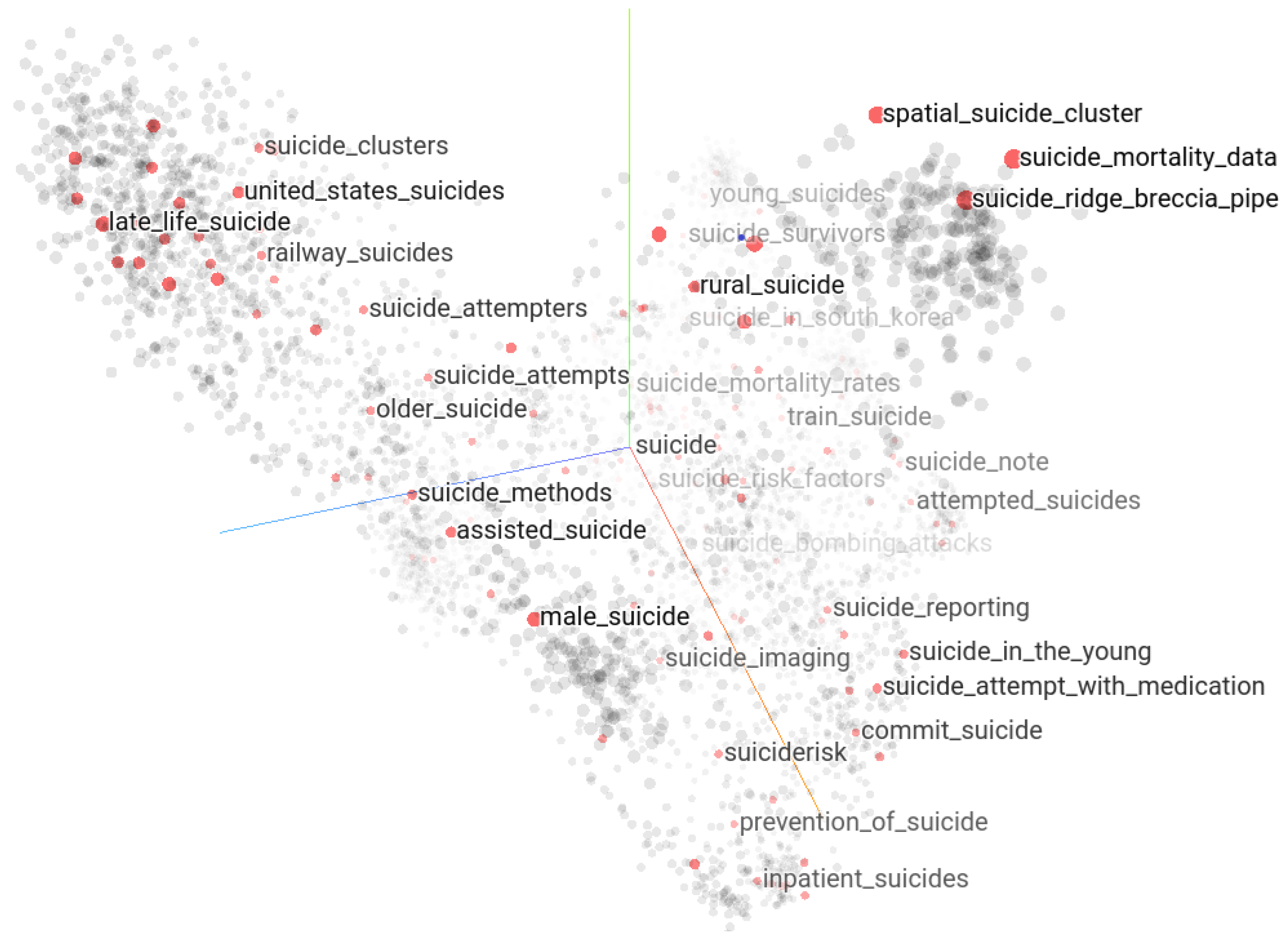
Semantic proximity between keywords in the suicide context can be explored as a neighborhood of the word embedding vectors in their high-dimensional Euclidean space. The keywords whose embedding vectors are close in their original high-dimensional space must be close semantically in that context from which the embedding vectors were derived. The lower-dimensional representation of the word embedding vectors corresponding to the 23,826 suicide-related keywords and expressions in 3D UMAP projection using the Keras embedding projector tool [35] shows a discernible structure presented in Figure 11. The expression “suic” highlights 687 keyword matches of which any matching keyword can be selected to explore its neighborhoods further.
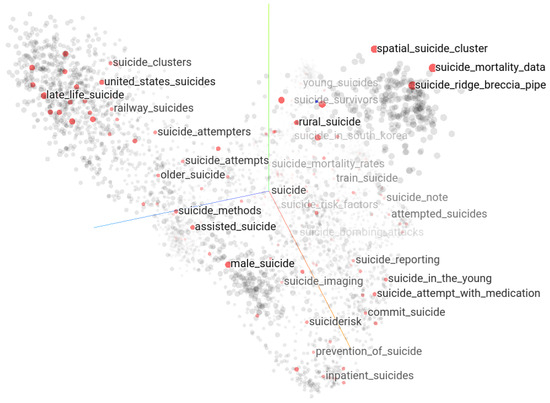
Figure 11.
Suicide vocabulary mapped in Keras embedding projector tool in 3D UMAP projection in which the string “suicide” is highlighted (685 matches).
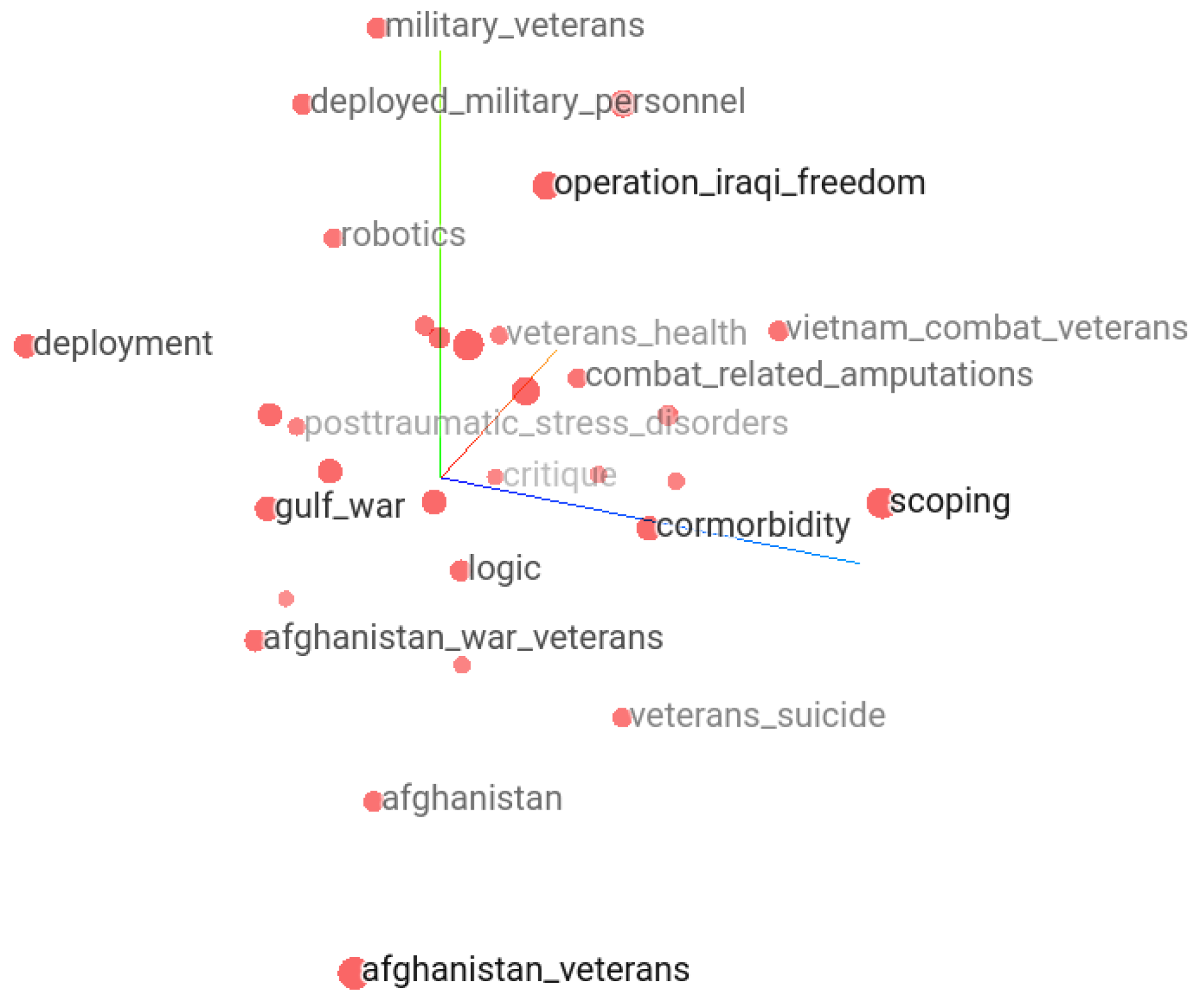
In the following, we attempt to demonstrate how we can ask questions and explore neighborhoods of topics semantically related to the keywords of interest by the help of keyword embedding vectors. Besides the Keras embedding projector, selected groups of keyword embedding vectors can also be explored for proximity by other mappings such as principal component analysis or multi-dimensional scaling. Here, using word embedding vectors, we attempt to demonstrate how a single keyword surrounded by other semantically close keywords helps reasoning. For example, Figure 12 shows the 30 closest keywords to “Afghanistan” in the TensorFlow embedding projector. Each keyword is at a certain distance from “Afghanistan”. In the context of suicide, the “Afghanistan” keyword is surrounded by terms indicating war veterans, veteran suicide, post-traumatic stress disorder, veteran’s health, and combat-related amputations that reflect topics in papers related to Afghanistan and suicide.
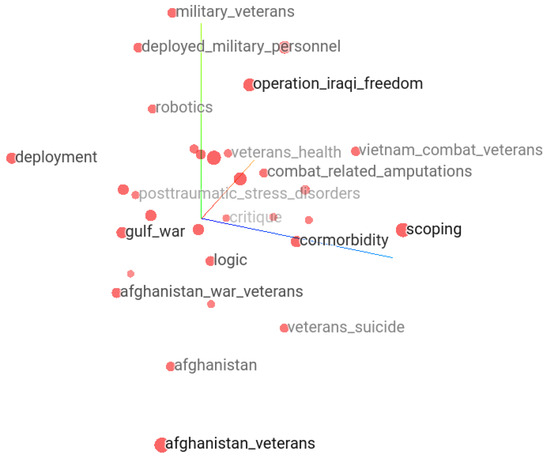
Figure 12.
Closest neighbors of “Afghanistan” keyword are “Afghanistan war veterans”, “Afghanistan veterans”, “veterans’ suicide”.
The most discussed topics on suicide and Afghanistan include war veterans and traumatic health events. Themes from the corpus of keywords and expressions in the context of suicide can be studied using word embedding. It reveals possibly semantically close keywords in the selected topic. For example, similar analysis of “children left behind” showed Balkans, intimate partner homicide suicide, obsessive compulsive symptoms, Groningen Protocol, Perestroika, migrant parents, and weight control behaviors as the closest keywords. The keywords “migrant parents” and/or “intimate partner homicide suicide” semantically relate to “children left behind”.
3.7. How Keyword Analysis and Word Embedding Helps: Use Case about Loneliness
Loneliness is one of the suicide risk factors strongly linked to depression. Using collected keywords, we computed co-occurrences of the term “loneliness” with other keyword phrases in each region. Phrases frequently coming together were aggregated across regions. Some repeating phrases were seen in multiple regions. Nevertheless, there were terms specific to a particular region. Here, we summarize some of the observed regularities.
The most frequent expressions coming together were “suicide” and “loneliness”. This combination was frequently seen in all regions except Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). The combination of “loneliness” and “depression” was also found. The combination of “prevalence” and “loneliness” was frequently seen in all regions except for the Middle East and North Africa (MENA). In the MENA region, appearances of “loneliness” were quite rare compared to other regions.
We may hypothesize that, in in the SSA region, loneliness does not have a strong connection to suicide. The most frequent SSA-region-specific phrases paired with loneliness were child, collective self-esteem, attachment theory, homeless youth, Kampala lifestyle, abuse, and alcohol consumption. Especially frequent in this context were parental neglect, sadness, school-going adolescents, street youth, trading sex, and vulnerable youth. In the North America (NA) region, the frequent contexts in which loneliness was found were minority stress, Aboriginals, social loneliness, parasuicide, perceived burden, poor health, sexual orientation, sleep disturbances, social engagement, thwarted belonging, veterans, ethnicity, eventual suicide, anxiety sensitivity, bariatric surgery, and weight. The contexts of loneliness specific to Europe and Central Asia differed from those previously mentioned and they were mental disorders, older people, poverty, shyness, social factors, social exclusion, social recognition, cyberbullying, cyber victimization, death wishes, impulsivity, and interpersonal relations. The East Asia and Pacific region had the largest number of phrases paired with loneliness. Since there were many, we mention only a few here: migration, Muslim, physical activity, prolonged social withdrawal, public holidays, religion, resilience, self-esteem, substance use, unemployment, and urbanization.
From the observed relationships between phrases frequently occurring and co-occurring in the literature, we gained a practical insight into different topics surrounding loneliness in the context of suicide in different regions. In Sub-Saharan Africa, it points to child abuse, in North America it highlights obesity problems, in Europe it points to social problems and cyberspace, and in East Asia and the Pacific it points to rural life. The code to extract co-occurrences is available on GitHub [28].
Word embedding space exploration of “loneliness” as the closest neighbor gave the semantically close phrase “children left behind”. This phrase was not in the matrix of co-occurrences and word embedding in this case brought into focus a semantically related topic.
4. Discussion
Recent work [38] analyzed the disparity in publishing on suicide across countries by using the Scopus bibliographic database. It revealed the fact that about 78% of articles were published from two regions—Europe and the Americas. From low- and middle-income countries, only China and India were highly published countries. Our collected bibliographical information results from the Web of Science database were in agreement with those findings. We also identified that Australia had many publications on suicide research.
Retrospective analysis of suicide that focused on the causes and determinants of suicide [39,40,41] showed that political factors such as laws restricting access to alcohol and firearms and social welfare expenditures and social factors such as marriage, parenting, and religiousness were found as preventive against suicide, while media coverage of celebrity suicide could have negatively affected vulnerable persons. Economic factors such as unemployment, debt, low income, and economic recessions were identified as strong predictive factors of suicide behavior. Keyword analysis allowed us to notice that economic recession as related to suicide has gained more focus in Greece.
Socioeconomic factors, unemployment, unhealthy lifestyle, and mental disorders were highlighted [16,17,18] as factors of high risk of suicide. Our study does not provide tools for causal inference. Nevertheless, its data can aid in understanding the wider scope and regional specificity of the risk factors. We demonstrated that regionally specific phrases occurring together with “loneliness” are different for each region. From this, we could hypothesize about factors strongly linked to loneliness in the suicide context in different regions: child neglect emerged in the Sub-Saharan Africa region, obesity in North America (complements unhealthy lifestyle), and social exclusion in Europe. The overall results of our study in a systematic way address suicide research topics and directions that gained the most attention in the literature from 2000–2019 across groups of high-, medium-, and low-SMR countries and geographic regions. For example, HIV/AIDS in the African continent, war-related subjects in the Middle East region, farmer suicides in India, and euthanasia in European countries and North America.
Depression is a central theme in the literature associated with suicide across all countries and all regions, as well as other prevailing topics related to depression such as major depressive disorder, suicide in youth, euthanasia, alcohol usage, hopelessness, loneliness, and unemployment. It is no surprise that genetic, genomic, molecular, and neurochemical underpinnings [42,43,44] and neurobiology of suicide [45] are rapidly evolving areas overlapping significantly with research into molecular mechanisms of depression [46]. Even in this area, keyword embedding may help to discover close semantic neighbors. For example, the SLC6A4 gene (associated with depression) is in close proximity to “Vietnam veterans”, “mental health policies”, and “mushroom”. Specifically, the SLC6A4 gene was investigated in Vietnam veterans suffering from depression and some studies showed that psilocybin present in some mushroom species has antidepressant potential. Indeed, not all proximal terms are meaningful, but some are informative. A search using word embedding has very practical utility. It helps to overcome information explosion if one is looking to make a meaningful inference from tens of thousands of interrelated keywords.
Highlighted country-specific keywords and maps of interconnected keywords may be useful as exploratory tools in the development of prevention strategies. They can help to notice important themes and to understand a target population to adopt better practices. For example, in South Asia there is a phenomenon of self-immolation in young married women that occurs in a strict geographic area [37]. In Iceland, friendship networks have been shown to support peer delinquency [47]. The preventive strategies in both examples may consider factors pertaining to these phenomena.
Text mining in suicide research has been applied to mine articles, social media, and electronic health records and helped to identify risk factors and track trends [48]. In suicide research, document classification and natural language processing are the most widely used methods [49]. Our work differs from conventional text mining applications in that it uses a semi-supervised analysis of keywords in articles in an attempt to reveal differences and similarities between countries and regions with regard to suicide research rather than to design an algorithm to predict the risk of a suicide. As such, results of our work may enrich, complement, and facilitate text mining algorithms aimed at suicide risk prediction from textual data.
Our study has certain limitations. First, there could be errors in statistical data of suicide mortality rates. These data are usually collected from death certificates and in some countries there might be omissions and reported wrong reasons. Second, it is very difficult to establish hard criteria for N in the analysis of the top N keywords and keyword rankings. Usually, the very top keywords are not informative and there is a tradeoff between imposing a limit on the number of top keywords and selecting informative keywords when using VOSviewer and other approaches. Third, there was no reference to the assignment of country into high-, medium-, and low-SMR group. The assignment is data-driven, determined by the limits of summary statistics and tied to the period 2000–2019. If we wanted to include more years and SMR went higher than the existing maximum, or there was a massive drop in SMR in many countries, then the thresholds for high, medium and low would shift.
5. Conclusions
In this exploratory study of the age-standardized suicide mortality rate (SMR) dynamics from 2000–2019 worldwide using machine learning, we grouped countries into high-, medium-, and low-SMR groups and performed detailed analysis of keywords tagging articles on suicide in each country.
Our study made two novel contributions. First, we summarized total SMRs in 183 countries from 2000–2019 statistically and, using data-driven percentile intervals of age-standardized SMR statistical distribution, we grouped countries into high-, medium-, and low-SMR groups across geographic regions. We numerically highlighted some regional differences. MENA countries were found in a low-SMR category compared to others. Former USSR countries and some African countries were found in a high-SMR category. We demonstrated that countries formed naturally different groups in terms of their SMR magnitude and dynamics from 2000–2019. Second, aiming to understand and explain SMR disparities between groups of countries and geographic regions, we collected 19,000 bibliographic records and the analyzed authors and extended keywords of articles associated with suicide and a particular country. The analysis was focused on frequently occurring keywords and their combinations in high-, medium-, and low-SMR country groups and across geographic regions. During this process, we collected a corpus of phrases related to suicide and made word embedding vector representations of these keywords that allowed us to find semantic relationships between keywords to enrich other simpler analyses. To our knowledge, this is a first attempt to create a corpus and subsequently a map of topic relationships for suicide research.
Through keyword analysis, we were able to at least partially address disparities between high-, medium-, and low-suicide-mortality-rate country groups and geographic regions through keyword analysis. In addition, we provided a breakdown of repeating and shared keywords in each group of countries in separate geographic regions. It aimed at understanding what might be common or specific between low-, medium-, and high-suicide-mortality-rate countries across different geographic regions. We used an algorithm to find word embedding vectors and metadata using a corpus of keywords and phrases extracted from suicide-related papers published with reference to a specific country. This allowed us to make logical inferences and analyze the semantic scope in which these keywords were used in the context of suicide.
Amount of research works addressing suicide is vast. We attempted to navigate through it in a systematic way utilizing analysis of keywords. It revealed variety of most frequent themes associated with suicide raising awareness of existing problems that may positively impact prevention and literacy campaigns.
The methodology used in our study can be adopted to perform other similar analysis of different indicator datasets and situations where quantitative analysis revealed objective regularities that are difficult to explain. We advocate using keyword analysis, machine learning, and neural-net-enabled bibliographic text mining to study poorly characterized phenomena.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijerph21091202/s1, Figure S1: Country clusters; Figure S2: Country clusters silhouette plot.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.P. and J.K.; methodology, E.P. and J.K.; software, E.P.; validation, E.P. and J.K.; formal analysis, J.K.; investigation, E.P.; resources, E.P.; data curation, E.P.; writing—original draft preparation, E.P. and J.K.; writing—review and editing, E.P. and J.K.; visualization, E.P. and J.K.; supervision, E.P.; project administration, E.P.; funding acquisition, J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data collected for this study and Python code used to analyze the collected data are publicly available on GitHub [28].
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the reviewers for valuable comments that helped to improve the manuscript very much.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. The Global Health Observatory. Suicide Rates. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators/indicator-details/GHO/age-standardized-suicide-rates-(per-100-000-population) (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- World Bank. DataBank World Development Indicators. Suicide Mortality Rate (per 100,000 Population). Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/reports.aspx?source=2&series=SH.STA.SUIC.P5 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- World Health Organization Suicide Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/suicide (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Aleman, A.; Denys, D. A roadmap for suicide research and prevention. Nature 2014, 509, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.J.; Apter, A.; Bertolote, J.; Beautrais, A.; Currier, D.; Haas, A.; Hegerl, U.; Lonnqvist, J.; Malone, K.; Marusic, A.; et al. Suicide prevention strategies: A systematic review. JAMA 2005, 294, 2064–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalsman, G.; Hawton, K.; Wasserman, D.; van Heeringen, K.; Arensman, E.; Sarchiapone, M.; Carli, V.; Höschl, C.; Barzilay, R.; Balazs, J.; et al. Suicide prevention strategies revisited: 10-year systematic review. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.J.; Michel, C.A.; Auerbach, R.P. Improving suicide prevention through evidence-based strategies: A systematic review. Am. J. Psychiatry 2021, 178, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, D.; Carli, V.; Iosue, M.; Javed, A.; Herrman, H. Suicide prevention in childhood and adolescence: A narrative review of current knowledge on risk and protective factors and effectiveness of interventions. Asia-Pac. Psychiatry 2021, 13, 12452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, C.R.; Kleiman, E.M.; Kellerman, J.; Pollak, O.; Cha, C.B.; Esposito, E.C.; Porter, A.C.; Wyman, P.A.; Boatman, A.E. Annual research review: A meta-analytic review of worldwide suicide rates in adolescents. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatr. 2020, 61, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellví, P.; Lucas-Romero, E.; Miranda-Mendizábal, A.; Parés-Badell, O.; Almenara, J.; Alonso, I.; Blasco, M.J.; Cebrià, A.; Gabilondo, A.; Gili, M.; et al. Longitudinal association between self-injurious thoughts and behaviors and suicidal behavior in adolescents and young adults: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 215, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, G.; Thapa, P.; Mathur, R. The top 100 most cited publications on suicide: A citation analysis. OMEGA J. Death Dying 2023, 302228231189642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Värnik, P. Suicide in the world. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claveria, O. Global economic uncertainty and suicide: Worldwide evidence. Soc. Sci. Med. 2022, 305, 115041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brådvik, L. Suicide risk and mental disorders. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Too, L.; Spittal, M.J.; Bugeja, L.; Reifels, L.; Butterworth, P.; Pirkis, J. The association between mental disorders and suicide: A systematic review and meta-analysis of record linkage studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 259, 302–313. [Google Scholar]
- Lari, M.S.; Sefiddashti, S.E. Socio-economic, health and environmental factors influencing suicide rates: A cross-country study in the Easter Mediterranean region. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2023, 93, 102463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Page, A.; Martin, G.; Taylor, R. Attributable risk of psychiatric and socio-economic factors for suicide from individual-level, population-based studies: A systematic review. Soc. Sci. Med. 2011, 72, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chandler, A. Socioeconomic inequalities of suicide: Sociological and psychological intersections. Eur. J. Soc. Theory 2020, 23, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shannaq, Y.; Aldalaykeh, M. Suicide literacy, suicide stigma, and psychological help seeking attitudes among Arab youth. Curr. Psychol. 2023, 42, 6532–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.-Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, Y.-K.; Li, R.; Sang, X.; Fu, Y.-N.; Gong, X.-J.; Sun, W.-J.; Liu, J.J.-W.; Wong, J.P.-H.; et al. Mental health literacy and suicidal ideation among Chinese college students: The mediating role of depressive symptoms and anxiety symptoms. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 339, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, H.K.; Richardson, D.; Solberg, V.S.H. Identifying important predictors of adolescent suicide ideation, planning, and attempt in low- and middle-income countries. Suicide Life-Threat. Behav. 2023. early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipe, D.; John, A.; Padmanathan, P.; Eyles, E.; Dekel, D.; Higgins, J.P.; Bantjes, J.; Dandona, R.; Macleod-Hall, C.; McGuinness, L.A.; et al. Suicide and self-harm in low-and middle-income countries during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2022, 2, 0000282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.J.; Rizk, M.M. A brain-centric model of suicidal behavior. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 902–916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertuccio, P.; Ameria, A.; Grande, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Costanza, A.; Aguglia, A.; Berardelli, I.; Serafini, G.; Amore, M.; Pompili, M.; et al. Global trends in youth suicide from 1990 to 2020: An analysis of data from the WHO mortality database. Clin. Med. 2024, 70, 102506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lersch, K.M. Exploring the geography of suicide threats and suicide attempts: An application of Risk Terrain Modeling. Soc. Sci. Med. 2020, 249, 112860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranckeviciene, E. Global Suicide Mortality Rates (2000–2019) and Bibliographic Data (v1.0) [Data Set]. Zenodo. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/12267302 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Web of Science Bibliographic Database. Available online: https://www.webofknowledge.com (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Github Repository. Available online: https://github.com/erinijapranckeviciene/idkwdan (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Demsar, J.; Curk, T.; Erjavec, A.; Gorup, C.; Hocevar, T.; Milutinovic, M.; Mozina, M.; Polajnar, M.; Toplak, M.; Staric, A.; et al. Orange: Data Mining Toolbox in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J.; Noyons, E.C.M. A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks. J. Informetr. 2010, 4, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschka, S. MLxtend: Providing machine learning and data science utilities and extensions to Python’s scientific computing stack. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Deep Learning with Python; Simon Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Keras Tensorflow Projector. Available online: https://projector.tensorflow.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Anthony, M.; Groh, C.; Gash, J. Suicide in Guyana: Nurses’ perspectives. J. Forensic Nurs. 2017, 13, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeian, M. The geographical belt of self-immolation. Burns 2017, 43, 896–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, S.Y.; Singh, R.; Singh, K.; Amin, R. Trend and Geographical Distribution of Suicide Research: A Bibliometric Analysis of Three Decades. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2024, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyor, M.; Hawton, K.; Appleyby, L.; Armstrong, G.; Ueda, M.; Gunnell, D.; Kapur, N.; Chang, S.; Arensman, E.; O’Connor, R.C.; et al. The coming global economic downturn and suicide: A call to action. Nat. Ment. Health 2023, 1, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, S. Suicide: A 15-year review of the sociological literature part I: Cultural and economic factors. Suicide Life-Threat. Behav. 2000, 30, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stack, S. Contributing factors to suicide: Political, social, cultural and economic. Prev. Med. 2021, 1, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turecki, G.; Brent, D.A.; Gunnel, D.; O’Connor, R.C.; Oquendo, M.A.; Pirkis, J.; Stanley, B.H. Suicide and suicide risk. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldrini, M.; Xiao, Y.; Sing, T.; Zhu, C.; Jabbi, M.; Pantazopoulos, H.; Gürsoy, G.; Martinowich, K.; Punzi, G.; Vallender, E.J.; et al. Omics approaches to investigate the pathogenesis of suicide. Biol. Psychiatry 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marušič, A. History and geography of suicide: Could genetic risk factors account for the variation in suicide rates? Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2005, 133, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, C.; Mechawar, N.; Turecki, G. Suicide neurobiology. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 89, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strumila, R.; Lengvenyte, A.; Zdanavicius, L.; Badaras, R.; Dlugauskas, E.; Lesinskiene, S.; Matiekus, E.; Marcinkevicius, M.; Venceviciene, L.; Utkus, A.; et al. Higher levels of plasma Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) are associated with lower suicidal ideation in depressed patients compared to controls and suicide attempters, independently from depression severity. Compr. Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2024, 19, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorlindsson, T.; Bernburg, J.G. Durkheim’s theory of social order and deviance: A multi-level test. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 2004, 20, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, J.M.; Kafka, J.M. A critical review of text mining applications for suicide research. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2022, 9, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Lui, C.S. Applying text mining methods to suicide research. Suicide Life-Threat. Behav. 2021, 51, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).