Early Detection and Monitoring of Gastrointestinal Infections Using Syndromic Surveillance: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
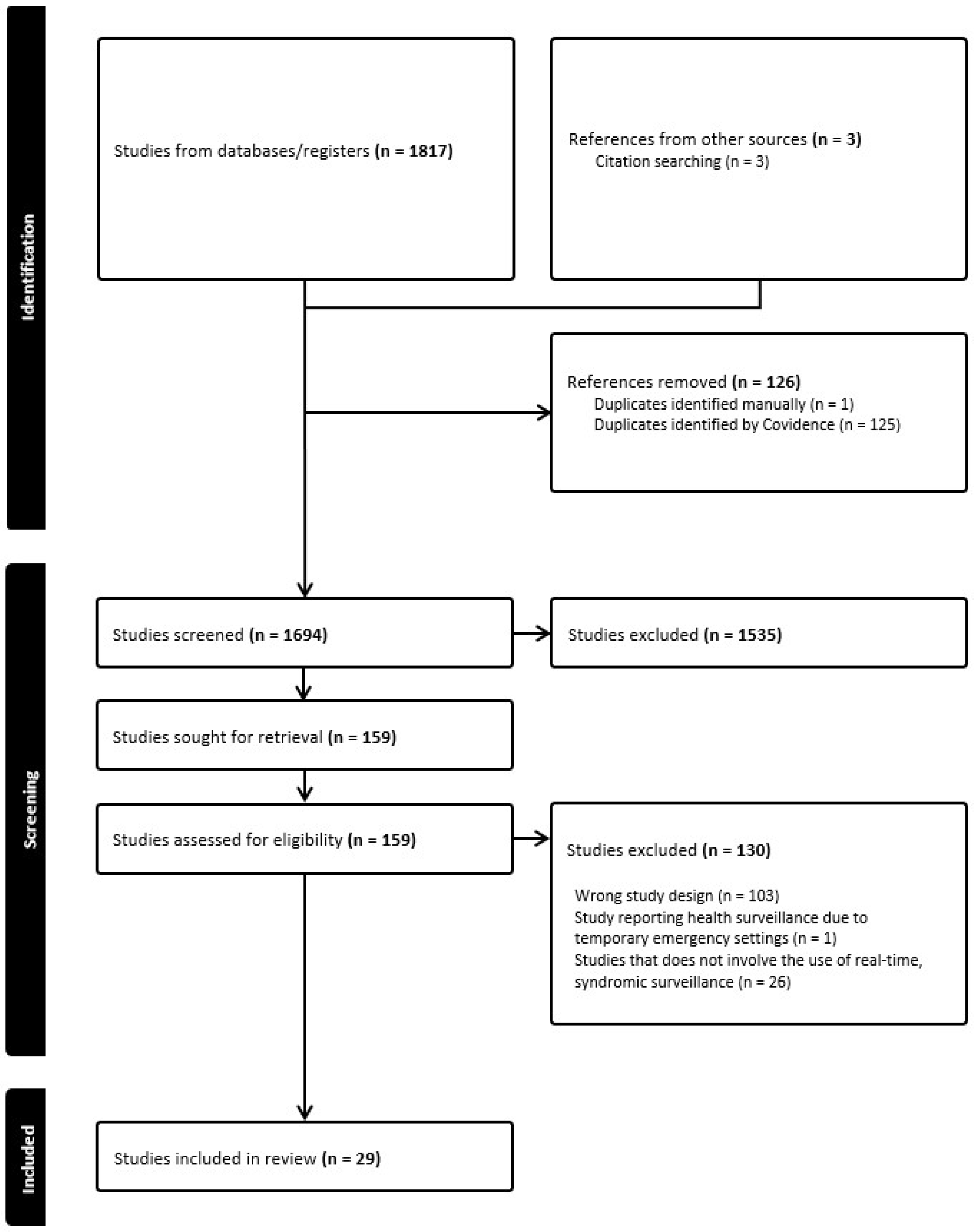
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Summary of the Syndromic Surveillance Systems
3.2. Type of Syndromic Surveillance Systems
3.3. Quality of Included Studies
3.4. Patient Public Involvement Reporting
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings of This Study
4.2. How Does This Compare to Others?
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Diarrhoeal Disease Collaborators. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoea in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Your Digestive System and How It Works. 2022. Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/digestive-system-how-it-works (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- UK Health Security Agency. National Norovirus and Rotavirus Surveillance Report. 2024. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/national-norovirus-and-rotavirus-surveillance-reports-2023-to-2024-season/national-norovirus-and-rotavirus-report-week-3-report-data-up-to-week-1-7-january-2024 (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Tam, C.C.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Viviani, L.; Dodds, J.P.; Evans, M.R.; Hunter, P.R.; Gray, J.J.; Letley, L.H.; Rait, G.; Tompkins, D.S.; et al. Longitudinal study of infectious intestinal disease in the UK (IID2 study): Incidence in the community and presenting to general practice. Gut 2011, 61, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Chen, H.; Zeng, D. Syndromic surveillance systems. Annu. Rev. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 425–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbey, R.A.; Harcourt, S.; Pebody, R.; Zambon, M.; Hutchison, J.; Rutter, J.; Thomas, H.; Smith, G.; Elliot, A.J. The burden of seasonal respiratory infections on a national telehealth service in England. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Todkill, D.; Elliot, A.J.; Morbey, R.; Harris, J.; Hawker, J.; Edeghere, O.; Smith, G.E. What is the utility of using syndromic surveillance systems during large subnational infectious gastrointestinal disease outbreaks? An observational study using case studies from the past 5 years in England. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bounoure, F.; Mouly, D.; Beaudeau, P.; Bentayeb, M.; Chesneau, J.; Jones, G.; Skiba, M.; Lahiani-Skiba, M.; Galey, C. Syndromic surveillance of acute gastroenteritis using the French health insurance database: Discriminatory algorithm and drug prescription practices evaluations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedire, O.; Elliot, A.; Hughes, H.; Love, N. Early Detection and Monitoring of Seasonal GI Activity Using Syndromic Surveillance: A Systematic Review. PROSPERO 2022 CRD42022321839. 2022. Available online: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42022321839 (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Veritas Health Innovation. Covidence. 2022. Available online: www.covidence.org (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Lockwood, C.; Munn, Z.; Porritt, K. Qualitative research synthesis. Int. J. Evid.-Based Health 2015, 13, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, H.E.; Elliot, A.J.; Hughes, T.C.; Hungerford, D.; Morbey, R.A.; Smith, G.E.; Vivancos, R.; O’brien, S.J. Using emergency department syndromic surveillance to investigate the impact of a national vaccination program: A retrospective observational study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loveridge, P.; Cooper, D.; Elliot, A.; Harris, J.; Gray, J.; Large, S.; Regan, M.; Smith, G.; Lopman, B. Vomiting calls to NHS Direct provide an early warning of norovirus outbreaks in hospitals. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 74, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.; Hippisley-Cox, J.; Harcourt, S.; Heaps, M.; Painter, M.; Porter, A.; Pringle, M. Developing a national primary care-based early warning system for health protection—A surveillance tool for the future? Analysis of routinely collected data. J. Public Health 2006, 29, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balter, S.; Weiss, D.; Hanson, H.; Reddy, V.; Das, D.; Heffernan, R. Three years of emergency department gastrointestinal syndromic surveillance in New York City: What have we found? MMWR Sppl. 2005, 54, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Heffernan, R.; Mostashari, F.; Das, D.; Karpati, A.; Kulldorff, M.; Weiss, D. Syndromic Surveillance in Public Health Practice, New York City. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, V.A.; Silverman, M.E.; Cochrane, D.G.; Eskin, B.; Ohman-Strickland, P.; Rothman, J.; Allegra, J.R. Biosurveillance of ED visits for gastroenteritis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2007, 25, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.K.; Huang, J.; Abrams, A.M.; Gilliss, D.; Reed, M.; Platt, R.; Huang, S.S.; Kulldorff, M. Gastrointestinal Disease Outbreak Detection Using Multiple Data Streams from Electronic Medical Records. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.R.; Lopman, B.A.; Konty, K.J.; Mathes, R.W.; Papadouka, V.; Ternier, A.; Zucker, J.R.; Simonsen, L.; Grenfell, B.T.; Pitzer, V.E. Surveillance data confirm multiyear predictions of rotavirus dynamics in New York City. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax0586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hripcsak, G.; Soulakis, N.D.; Li, L.; Morrison, F.P.; Lai, A.M.; Friedman, C.; Calman, N.S.; Mostashari, F. Syndromic surveillance using ambulatory electronic health records. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2009, 16, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.V.; Magruder, S.; Snyder, M. Comparison of office visit and nurse advice hotline data for syndromic surveillance--Baltimore-Washington, D.C., metropolitan area. MMWR Sppl. 2004, 53, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, A.L.; Harris, J.P.; Vivancos, R.; O’brien, S.J. Can cases and outbreaks of norovirus in children provide an early warning of seasonal norovirus infection: An analysis of nine seasons of surveillance data in England UK. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armistead, I.; Tran, A.; White, A.E.; Wilson, E.; Walter, E.J.S. Trends in outpatient medical-care seeking for acute gastroenteritis during the COVID-19 pandemic, 2020. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, N.K.; Elliot, A.J.; Chalmers, R.M.; Douglas, A.; Gharbia, S.; McCormick, J.; Hughes, H.; Morbey, R.; Oliver, I.; Vivancos, R.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on gastrointestinal infection trends in England, February–July 2020. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e050469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrikova, N.; Harris, J.P.; Douglas, A.; E Hughes, H.; Iturriza-Gomara, M.; Vivancos, R.; Elliot, A.J.; A Cunliffe, N.; E Clough, H. Predicting norovirus in England using existing and emerging syndromic data: Infodemiology study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e37540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brottet, E.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.; Rachou, E.; Polycarpe, D.; Ristor, B.; Larrieu, S.; Filleul, L. Sentinel physician's network in Reunion Island: A tool for infectious diseases surveillance. Med. Mal. Infect. 2015, 45, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillère, N.; Vilain, P.; Brottet, E.; Kaplon, J.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Polycarpe, D.; Filleul, L. A major outbreak of gastroenteritis in Réunion Island in 2012: First identification of G12 rotavirus on the Island. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delespierre, T.; Josseran, L. Issues in building a nursing home syndromic surveillance system with textmining: Longitudinal observational study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2018, 4, e9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamand, C.; Larrieu, S.; Couvy, F.; Jouves, B.; Josseran, L.; Filleul, L. Validation of a syndromic surveillance system using a general practitioner house calls network, Bordeaux, France. Eurosurveillance 2008, 13, 18905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelstein, M.; Wallensten, A.; Zetterqvist, I.; Hulth, A. Detecting the norovirus season in Sweden using search engine data—Meeting the needs of hospital infection control teams. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, Y.; Kurita, J.; Nagasu, N.; Sugawara, T.; Ohkusa, Y. Infection control in nursery schools and schools using a school absenteeism surveillance system. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2019, 247, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Chae, S.; Jung, S.; Choi, W.; Han, M.; Yoo, C.; Lee, D. Trends in acute viral gastroenteritis among children aged ≤5 years through the national surveillance system in South Korea, 2013–2019. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 4875–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Choi, B.Y.; Park, B. Trends for syndromic surveillance of norovirus in emergency department data based on chief complaints. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, jiad437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisavanh, A.; Horrigue, I.; Debin, M.; Turbelin, C.; Kengne-Kuetche, C.; Nassany, O.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Silva, N.J.-D.; Pontais, I.; de Valk, H.; et al. Epidemiology of acute gastroenteritis in France from November 2019–August 2021, in light of reported adherence to COVID-19 barrier measures. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucaccioni, H.; Machado, R.S. Burden and trends of severe rotavirus infections and all-cause acute gastroenteritis hospital episodes in children under five years old in mainland Portugal. Acta Med. Port. 2021, 34, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.; Lim, K.S. Analysis of the Korean emergency department syndromic surveillance system: Mass type acute diarrheal syndrome. Health Inform. Res. 2010, 16, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Enserink, R.M.; Wijngaard, C.v.D.; Bruijning-Verhagen, P.M.; van Asten, L.; Mughini-Gras, L.D.; Duizer, E.; Kortbeek, T.; Scholts, R.M.; Nagelkerke, N.; Smit, H.A.; et al. Gastroenteritis attributable to 16 enteropathogens in children attending day care significant effects of rotavirus, norovirus, astrovirus, Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstel, L.; Rodrigo, M.P.; Adiego, B.; Luquero, F.J.; Revillo, M.J.; Castillo, F.J.; Barrasa, A.; Valenciano, M. Is Rotavirus contributing to an increase of diarrhoea in a region of Spain? Epidemiol. Infect. 2009, 137, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajita, E.; Luarca, M.Z.; Wu, H.; Hwang, B.; Mascola, L. Harnessing syndromic surveillance emergency department data to monitor health impacts during the 2015 Special Olympics World Games. Public Health Rep. 2017, 132, 99S–105S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enserink, R.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Duizer, E.; Kortbeek, T.; VAN Pelt, W. Risk factors for gastroenteritis in child day care. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 2707–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchaal, P.; Parker, S.; Meganath, K.; Landry, L.; Aramini, J. Evaluation of a national pharmacy-based syndromic surveillance system. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2015, 41, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyllestad, S.; Iversen, A.; MacDonald, E.; Amato, E.; Borge, B.S.; Bøe, A.; Sandvin, A.; Brandal, L.T.; Lyngstad, T.M.; Naseer, U.; et al. Large waterborne Campylobacter outbreak: Use of multiple approaches to investigate contamination of the drinking water supply system, Norway, June 2019. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000011–2000026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Huang, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Jiang, H.; Yang, A.C. Predicting norovirus in the United States using google trends: Infodemiology study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e24554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisrat, H.; Manyazewal, T.; Fekadu, A. Mobile health-supported active syndrome surveillance for COVID-19 early case finding in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Comparative study. Interact. J. Med. Res. 2023, 12, e43492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author/Year | Syndromic Surveillance Data Source | Country | Syndromic Surveillance System(s) Capable of Early Detection of GI Infections | GI Infection Symptoms Monitored | PPI 1 Reporting | Quality of Included Studies 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armistead 2022 [23] | Electronic medical record | United States | Yes | Acute gastroenteritis | No | High |
| Ahn 2010 [36] | ED 3 | Korea | Yes | Acute diarrhoea, acute rash symptoms, acute haemorrhagic fever symptoms | No | High |
| Balter 2005 [15] | ED | United States | Yes (with limitations) | Vomiting, diarrhoea, fever | No | Medium |
| Bounoure 2020 [8] | Electronic medical record | United States | Unclear | Medicalised acute gastroenteritis | No | Low |
| Brottet 2015 [26] | GP | France | Yes | Gastroenteritis, acute diarrhoea | No | Low |
| Caillère 2013 [27] | ED, GP | France | Yes | Acute diarrhoea, gastroenteritis | No | Medium |
| Cho 2021 [32] | Electronic medical record | South Korea | Yes | Diarrhoea, vomiting, abdominal pain, acute gastroenteritis | No | High |
| Delespierre 2018 [28] | Nursing home surveillance | France | Yes | Acute gastroenteritis | No | High |
| Donaldson 2022 [22] | NHS 111 calls | United Kingdom | Yes | Gastroenteritis, vomiting, diarrhoea | No | High |
| Edelstein 2014 [30] | Websök internet-based surveillance | Sweden | Yes | Vomiting, diarrhoea/winter vomiting disease | No | High |
| Enserink 2015 [40] | Children day care surveillance centres | Netherlands | Unclear | Gastroenteritis | No | High |
| Flamand 2008 [29] | GP | France | Yes | Gastrointestinal infections (not specified) | No | High |
| Gerstel 2009 [38] | GP | Spain | Unclear | Diarrhoea | No | Medium |
| Greene 2012 [18] | Electronic medical Records | United States | Yes (only when combined with traditional surveillance system) | Vomiting, gastroenteritis, nausea, diarrhoea | No | Medium |
| Heffernan 2004 [16] | ED | United States | Yes | Fever, diarrhoea, and vomiting | No | Medium |
| Henry 2004 [21] | Nurse advice hotline | United States | Unclear | Fever, gastrointestinal infections (not specified), haemorrhagic | No | Medium |
| Hripcsak 2009 [20] | Ambulatory electronic records | United States | Yes (with limitations) | Diarrhoea, stomach-ache, vomiting | No | Low |
| Hughes 2020 [12] | ED | United Kingdom | Unclear | Gastroenteritis | No | High |
| Kim 2023 [33] | ED | Korea | Yes | Diarrhoea, watery diarrhoea, abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting | No | High |
| Love 2023 [24] | GP, ED, NHS 111 calls | United Kingdom | Yes | Diarrhoea, vomiting, abdominal pain | No | High |
| Loveridge 2010 [13] | NHS Direct calls | United Kingdom | Yes | Diarrhoea, vomiting | No | High |
| Lucaccioni 2021 [35] | Electronic medical record | Portugal | Yes | Acute gastroenteritis | No | Medium |
| Muchaal 2015 [41] | Pharmacy sales | Canada | No | Acute gastrointestinal illness | No | Medium |
| Nisavanh 2022 [34] | ED | France | Yes | Acute gastroenteritis, diarrhoea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bloody diarrhoea, fever, nausea, headache | No | High |
| Olson 2020 [19] | ED | United States | Unclear | Diarrhoea | No | Low |
| Ondrikova 2023 [25] | GP, NHS 111 calls | United Kingdom | Yes | Vomiting, gastroenteritis | No | High |
| Rodriguez 2007 [17] | ED | United States | Unclear | Gastroenteritis | No | Medium |
| Smith 2007 [14] | GP 4 | United Kingdom | No | Vomiting | No | Medium |
| Tanabe 2018 [31] | Nursery school surveillance | Japan | Yes | Diarrhoea, vomiting, fever | No | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adedire, O.; Love, N.K.; Hughes, H.E.; Buchan, I.; Vivancos, R.; Elliot, A.J. Early Detection and Monitoring of Gastrointestinal Infections Using Syndromic Surveillance: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21040489
Adedire O, Love NK, Hughes HE, Buchan I, Vivancos R, Elliot AJ. Early Detection and Monitoring of Gastrointestinal Infections Using Syndromic Surveillance: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2024; 21(4):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21040489
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdedire, Olubusola, Nicola K. Love, Helen E. Hughes, Iain Buchan, Roberto Vivancos, and Alex J. Elliot. 2024. "Early Detection and Monitoring of Gastrointestinal Infections Using Syndromic Surveillance: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 21, no. 4: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21040489
APA StyleAdedire, O., Love, N. K., Hughes, H. E., Buchan, I., Vivancos, R., & Elliot, A. J. (2024). Early Detection and Monitoring of Gastrointestinal Infections Using Syndromic Surveillance: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 21(4), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21040489







