Evaluation of the Performance of Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Malaria Diagnosis and Mapping of Different Plasmodium Species in Mali
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
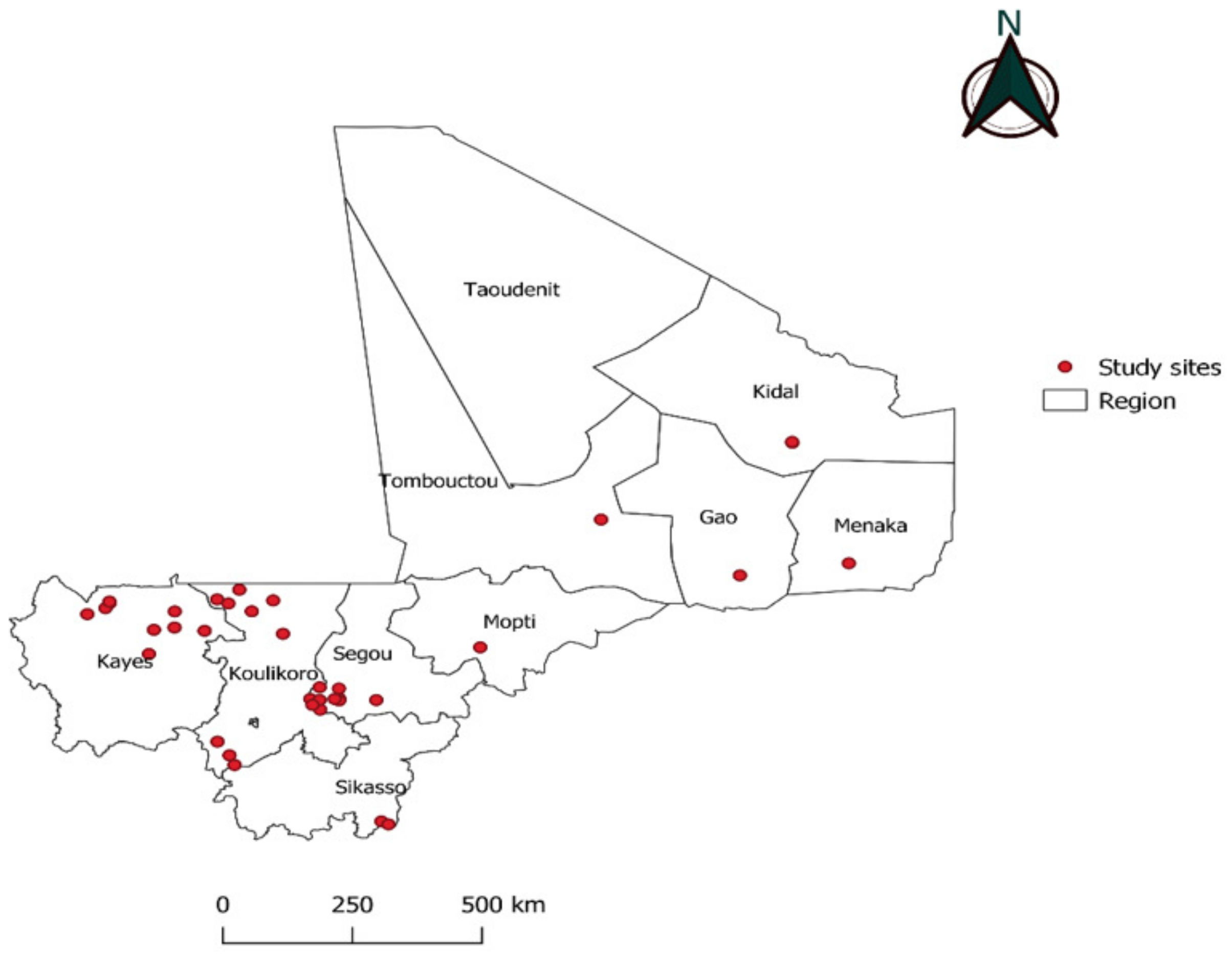
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Study Design
2.2.1. Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT)
2.2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2.3. DNA Extraction Technique
2.2.4. Plasmodium Species Detection by qPCR
2.2.5. Case Definition
2.3. Data Analyses
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Messaging: World Malaria Report 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/WHO-UCN-GMP-2022.07 (accessed on 5 March 2023).
- OMS. World Health Organization World Malaria Report 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 322. ISBN 978-92-4-004049-6. [Google Scholar]
- DHIS 2, Https://Mali.Dhis2.Org/Dhis/Dhis-Web-Dashboard/#/. Available online: https://dhis2.org/?s=dashboard (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Doumbo, O.; Koita, O.; Traore, S.F.; Sangare, O.; Coulibaly, A.; Robert, V.; Soula, G.; Quilici, M.; Toure, Y.T. Les Aspects Parasitologiques de l’épidémiologie du Paludisme dans le Sahara Malien|GHDx. Available online: https://ghdx.healthdata.org/record/les-aspects-parasitologiques-de-lépidémiologie-du-paludisme-dans-le-sahara-malien (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Bernabeu, M.; Gomez-Perez, G.P.; Sissoko, S.; Niambélé, M.B.; Haibala, A.A.; Sanz, A.; Théra, M.A.; Fernandez-Becerra, C.; Traoré, K.; Alonso, P.L.; et al. Plasmodium Vivax Malaria in Mali: A Study from Three Different Regions. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koita, O.A.; Sangaré, L.; Sango, H.A.; Dao, S.; Keita, N.; Maiga, M.; Mounkoro, M.; Fané, Z.; Maiga, A.S.; Traoré, K.; et al. Effect of Seasonality and Ecological Factors on the Prevalence of the Four Malaria Parasite Species in Northern Mali. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 2012, 367160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institut National de La Statistique (INSTAT) Enquête Demographique et de Santé. Available online: https://www.instat-mali.org/laravel-filemanager/files/shares/pub/eds6-18_pub.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Enquête sur les Indicateurs du Paludisme au Mali en 2021. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjLzob8xKSEAxWxoa8BHZR1BGkQFnoECBQQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.instat-mali.org%2Flaravel-filemanager%2Ffiles%2Fshares%2Feq%2Find-cle-eipm21_eq.pdf&usg=AOvVaw2PKEu18HcIp4HEJAIc3eAg&opi=89978449 (accessed on 22 September 2022).
- Conférence Ministérielle sur le Paludisme (1992; Amsterdam). Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiL-92gxaSEAxVrh68BHU0dChQQFnoECBkQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fapps.who.int%2Firis%2Fbitstream%2Fhandle%2F10665%2F199385%2FWHA46_7_fre.pdf%3Fsequence%3D1&usg=AOvVaw3JeyAU0V6uzobwZthxE1N7&opi=89978449 (accessed on 14 September 2022).
- WHO_CDS_RBM_2000.25.pdf.https://iris.who.int/bitstream/hadle/10665/66745/WHO_CDS_RBM_2000.25.pdf;sequence=1 National Malaria Control Program Mali Annual Activity Report 2022; p 1–38. Available online: https://p2p.kemkes.go.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/FINAL_231123_Layout_Malaria_Bahasa-Inggris_compressed.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Bell, D.; Wongsrichanalai, C.; Barnwell, J.W. Ensuring Quality and Access for Malaria Diagnosis: How Can It Be Achieved? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, S7–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohfeld, L.; Kangombe-Ngwenya, T.; Winters, A.M.; Chisha, Z.; Hamainza, B.; Kamuliwo, M.; Miller, J.M.; Burns, M.; Bridges, D.J. A Qualitative Review of Implementer Perceptions of the National Community-Level Malaria Surveillance System in Southern Province, Zambia. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randriatsarafara, F.M.; Mandrosovololona, V.; Andrianirinarison, J.C.; Rakotondrandriana, A.N.; Randrianarivo-Solofoniaina, A.E.; Ratsimbasoa, A.; de Dieu Marie Rakotomanga, J. Adherence of private sector providers to uncomplicated malaria management policy in Madagascar. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2019, 32, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouatcho, J.C.; Goldring, J.P.D. Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests: Challenges and Prospects. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozycki, C.T.; Umulisa, N.; Rulisa, S.; Mwikarago, E.I.; Musabyimana, J.P.; Habimana, J.P.; Karema, C.; Krogstad, D.J. False-Negative Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests in Rwanda: Impact of Plasmodium falciparum Isolates Lacking Hrp2 and Declining Malaria Transmission. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMorrow, M.L.; Aidoo, M.; Kachur, S.P. Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests in Elimination Settings—Can They Find the Last Parasite? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motshoge, T.; Ababio, G.K.; Aleksenko, L.; Read, J.; Peloewetse, E.; Loeto, M.; Mosweunyane, T.; Moakofhi, K.; Ntebele, D.S.; Chihanga, S.; et al. Molecular Evidence of High Rates of Asymptomatic P. vivax Infection and Very Low P. falciparum Malaria in Botswana. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feleke, S.M.; Gidey, B.; Mohammed, H.; Nega, D.; Dillu, D.; Haile, M.; Solomon, H.; Parr, J.B.; Tollera, G.; Tasew, G.; et al. Field Performance of Plasmodium falciparum Lactate Dehydrogenase Rapid Diagnostic Tests during a Large Histidine-Rich Protein 2 Deletion Survey in Ethiopia. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Choi, L.; Johnson, S.; Takwoingi, Y. Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Plasmodium vivax Malaria in Endemic Countries. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 11, CD013218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltha, J.; Gillet, P.; Jacobs, J. Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests in Endemic Settings. Clin Microbiol Infect 2013, 19, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mens, P.F.; Schoone, G.J.; Kager, P.A.; Schallig, H.D. Detection and Identification of Human Plasmodium Species with Real-Time Quantitative Nucleic Acid Sequence-Based Amplification. Malar. J. 2006, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snounou, G.; Viriyakosol, S.; Zhu, X.P.; Jarra, W.; Pinheiro, L.; do Rosario, V.E.; Thaithong, S.; Brown, K.N. High Sensitivity of Detection of Human Malaria Parasites by the Use of Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1993, 61, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OMS. Stratégie Technique Mondiale de lutte contre le Paludisme 2016–2030. 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/fr/publications-detail/9789240031357 (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Mady, C.; Cissoko, M.; Sagara, I.; Landier, J.; Guindo, A.; Sanogo, V.; Coulibaly, O.; Dembélé, P.; Dieng, S.; Stephane, C.; et al. Optimising Malaria Control Interventions in Mali Based on Epidemiological Surveillance and Rainfall Data. 2022. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1235012/v1 (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- DNA Extraction: Preparing Rapid Diagnostic Tests. Available online: https://www.wwarn.org/tools-resources/procedures/dna-extraction-preparing-rapid-diagnostic-tests (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Sazed, S.A.; Kibria, M.G.; Alam, M.S. An Optimized Real-Time qPCR Method for the Effective Detection of Human Malaria Infections. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodio, A. Interactions Entre les Communautés Bactériennes et Fongiques Intestinales et le Paludisme et des Pathogènes Entériques Eucaryotes Chez des Enfants au Pays Dogon (Mali). Ph.D. Thesis, Aix-Marseille, Marseille, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- JavaStat—2-Way Contingency Table Analysis. Available online: https://statpages.info/ctab2x2.html (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Un Coefficient D’accord Pour les Échelles Nominales—Jacob Cohen. 1960. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/001316446002000104?journalCode=epma (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Dynamique de L’infection Palustre Dans Une Etude de Cohorte D’enfant à Bandiagara, Mali. Available online: https://www.bibliosante.ml/handle/123456789/4085 (accessed on 19 February 2022).
- Coulibaly, D.; Rebaudet, S.; Travassos, M.; Tolo, Y.; Laurens, M.; Kone, A.K.; Traore, K.; Guindo, A.; Diarra, I.; Niangaly, A.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Malaria within a Transmission Season in Bandiagara, Mali. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; Njie, F.; Cairns, M.; Bojang, K.; Coulibaly, S.O.; Kayentao, K.; Abubakar, I.; Akor, F.; Mohammed, K.; Bationo, R.; et al. Non-Falciparum Malaria Infections in Pregnant Women in West Africa. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, F.; Dembele, L.; Diarra, B.; Sogore, F.; Marin-Menendez, A.; Goita, S.; Haidara, A.S.; Barre, Y.N.; Sangare, C.P.O.; Kone, A.; et al. The Prevalence of Human Plasmodium Species during Peak Transmission Seasons from 2016 to 2021 in the Rural Commune of Ntjiba, Mali. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiam-Ong, S. Malarial Nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2003, 23, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickse, R.G.; Adeniyi, A.; Edington, G.M.; Glasgow, E.F.; White, R.H.; Houba, V. Quartan Malarial Nephrotic Syndrome. Collaborative Clinicopathological Study in Nigerian Children. Lancet 1972, 1, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, S.; Douglas, N.M.; Lampah, D.A.; Simpson, J.A.; Kenangalem, E.; Sugiarto, P.; Anstey, N.M.; Poespoprodjo, J.R.; Price, R.N. Plasmodium malariae Infection Associated with a High Burden of Anemia: A Hospital-Based Surveillance Study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, F.; Djonor, S.K.; Ayin, C.T.-M.; Adu, G.A.; Sarfo, B.; Nortey, P.; Akuffo, K.O.; Danso-Appiah, A. Burden of Malaria in Children under Five and Caregivers’ Health-Seeking Behaviour for Malaria-Related Symptoms in Artisanal Mining Communities in Ghana. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Cullen, K.A.; Kachur, S.P.; Arguin, P.M.; Baird, J.K. Severe Morbidity and Mortality Risk from Malaria in the United States, 1985–2011. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2014, 1, ofu034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, W.E.; Jeffery, G.M. Plasmodium Malariae: Parasite and Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, D.A. Malaria Pathogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a025569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutledge, G.G.; Böhme, U.; Sanders, M.; Reid, A.J.; Cotton, J.A.; Maiga-Ascofare, O.; Djimdé, A.A.; Apinjoh, T.O.; Amenga-Etego, L.; Manske, M.; et al. Plasmodium Malariae and P. Ovale Genomes Provide Insights into Malaria Parasite Evolution. Nature 2017, 542, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebben, K.; Yirampo, S.; Coulibaly, D.; Koné, A.K.; Laurens, M.B.; Stucke, E.M.; Dembélé, A.; Tolo, Y.; Traoré, K.; Niangaly, A.; et al. Malian Children Infected with Plasmodium Ovale and Plasmodium falciparum Display Very Similar Gene Expression Profiles. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0010802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguike, M.C.; Betson, M.; Burke, M.; Nolder, D.; Stothard, J.R.; Kleinschmidt, I.; Proietti, C.; Bousema, T.; Ndounga, M.; Tanabe, K.; et al. Plasmodium Ovale Curtisi and Plasmodium Ovale Wallikeri Circulate Simultaneously in African Communities. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.A.; Burrows, J.N.; Manyando, C.; van Huijsduijnen, R.H.; Van Voorhis, W.C.; Wells, T.N.C. Malaria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forney, J.R.; Magill, A.J.; Wongsrichanalai, C.; Sirichaisinthop, J.; Bautista, C.T.; Heppner, D.G.; Miller, R.S.; Ockenhouse, C.F.; Gubanov, A.; Shafer, R.; et al. Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Devices: Performance Characteristics of the ParaSight F Device Determined in a Multisite Field Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2884–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Sharrock, W.W.; Bain, L.M.; Gray, K.-A.; Bobogare, A.; Boaz, L.; Lilley, K.; Krause, D.; Vallely, A.; Johnson, M.-L.; et al. A Large Proportion of Asymptomatic Plasmodium Infections with Low and Sub-Microscopic Parasite Densities in the Low Transmission Setting of Temotu Province, Solomon Islands: Challenges for Malaria Diagnostics in an Elimination Setting. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiáñez-Vendrell, X.; Skjefte, M.; Sikka, R.; Gupta, H. Factors Affecting the Performance of HRP2-Based Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltha, J.; Gillet, P.; Cnops, L.; van den Ende, J.; van Esbroeck, M.; Jacobs, J. Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests: Plasmodium falciparum Infections with High Parasite Densities May Generate False Positive Plasmodium vivax pLDH Lines. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briolant, S.; Pradines, B.; Basco, L.K. Place de la primaquine dans la lutte contre le paludisme en Afrique francophone. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2017, 110, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Target Species | Primers and Probes | Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Plasmodium spp. | VAR ATS-F | CCCATACACAACCAAYTGGA |
| VAR ATS-R | TTCGCACATATCTCTATGTCTATCT | |
| Var ATS-Probe | FAM-TRTTCCATAAATGGT | |
| Plasmodium falciparum | Pf-F | TAGCATATATTAAAATTGTTGCAG |
| Pf-R | GTTATTCCATGCTGTAGTATTCA | |
| Pf-probe | 6FAM-CGGGTAGTCATGATTGAGTTCATTC | |
| Plasmodium malariae | Pm-F | TAGCATATATTAAAATTGTTGCAG |
| Pm-R | GTTATTCCATGCTGTAGTATTCA | |
| Pm-probe | 6FAM- TGCATGGGAATTTTGTTACTTTGAGT | |
| Plasmodium ovale | Po-F | TAGCATATATTAAAATTGTTGCAG |
| Po-F R | GTTATTCCATGCTGTAGTATTCA | |
| Po-probe | 6VIC- TGCATTCCTTATGCAAAATGTGTTC | |
| Plasmodium vivax | Pv-F | AGCATATATTAAAATTGTTGCAG |
| Pv-R | GTTATTCCATGCTGTAGTATTCA | |
| Pv-probe | 6VIC- CGACTTTGTGCGCATTTTGC |
| Area | Health District | RDT Collection Site | Result | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive N (%) | Negative N (%) | ||||
| Kayes | Diéma | Torodo | 6 (2.2) | 272 (97.8) | 278 |
| Lakamané | 3 (3.4) | 89 (96.7) | 92 | ||
| Lattakaf | 0 (0.0) | 47 (100) | 47 | ||
| Débomassassi | 0 (0.0) | 48 (100) | 48 | ||
| Koungo | 3 (75.0) | 1 (25.0) | 4 | ||
| Lambidou | 0 (0.0) | 13 (100) | 13 | ||
| Diancounté Camara | 3 (6.4) | 44 (93.6) | 47 | ||
| Yélimané | Kodié | 12 (19.0) | 51 (81.0) | 63 | |
| Csréf | 6 (4,1) | 139 (95.9) | 145 | ||
| Dogofry | 0 (0.0) | 23 (100.0) | 23 | ||
| Bandiougoula | 0 (0.0) | 11 (100.0) | 11 | ||
| sub total | 33 (4.3) | 738 (95.7) | 771 | ||
| Koulikoro | Nara | Bagoini | 0 (0.0) | 50 (100.0) | 50 |
| Mourdiah | 5 (7.4) | 68 (100.0) | 73 | ||
| Kassakaré | 4 (12.1) | 29 (87.9) | 33 | ||
| Alasso | 7 (20.0) | 28 (80.0) | 35 | ||
| Tiapato | 3 (14.3) | 18 (85.7) | 21 | ||
| Waourou | (0.0) | 13 (100.0) | 13 | ||
| Kangaba | Naréna | 2 (1.6) | 126 (98.4) | 128 | |
| Cscom Central | 14 (28.0) | 36 (72.0) | 50 | ||
| Séléfougou | 0 (0.0) | 30 (100.0) | 30 | ||
| sub total | 35 (8.1) | 398 (91.9) | 433 | ||
| Sikasso | Kadiolo | Cscom central | 110 (59.5) | 75 (40.5) | 185 |
| Kebeni | 12 (16.4) | 69 (85.2) | 81 | ||
| Zégoua | 28 (38.9) | 44 (61.1) | 72 | ||
| sub total | 150 (44.4) | 188 (55.6) | 338 | ||
| Segou | Barouéli | Cscom Central | 5 (41.7) | 7 (58.3) | 12 |
| Dioforogo | 13 (65.0) | 7 (35.0) | 20 | ||
| Tamani | 7 (35.0) | 13 (65.0) | 20 | ||
| NGara | 16 (80.0) | 4 (20.0) | 20 | ||
| Tigui | 20 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 20 | ||
| Bananido | 7 (50.0) | 7 (50.0) | 14 | ||
| N’Gossola | 5 (31.2) | 11(68.8) | 16 | ||
| Nianzana | 20 (66.7) | 10 (33.3) | 30 | ||
| Yerebougou | 16 (80.0) | 4 (20.0) | 20 | ||
| C.S. Réf. | 8 (6.2) | 122 (93.8) | 130 | ||
| Ndjila | 10 (50.0) | 10 (50.0) | 20 | ||
| sub total | 127 (39.4) | 195 (60.6) | 322 | ||
| Mopti | Mopti | Soufouroulaye | 79 (34.3) | 151 (65.7) | 230 |
| Fatoma | 0 (0.0) | 35 (100.0) | 35 | ||
| Sévaré II | 136 (91.9) | 12 (8.1) | 148 | ||
| sub total | 215 (52.1) | 198 (47.9) | 413 | ||
| Tombouctou | Gourma Rharous | 400 (66.9) | 198 (33.1) | 598 | |
| Gao | Gao | C.S. Réf. d’Ansongo | 30 (13.4) | 194 (86.6) | 224 |
| Menaka | Menaka | Menaka | 21 (36.8) | 36 (63.2) | 57 |
| Kidal | Kidal | Cscom d’Aliou | 9 (14.3) | 54 (85.7) | 63 |
| C.S. Réf. de Kidal | 20 (14.3) | 120 (85.7) | 140 | ||
| sub total | 29 (14.3) | 174 (85.7) | 203 | ||
| Total | 1019 (30.5) | 2319 (69.5) | 3338 | ||
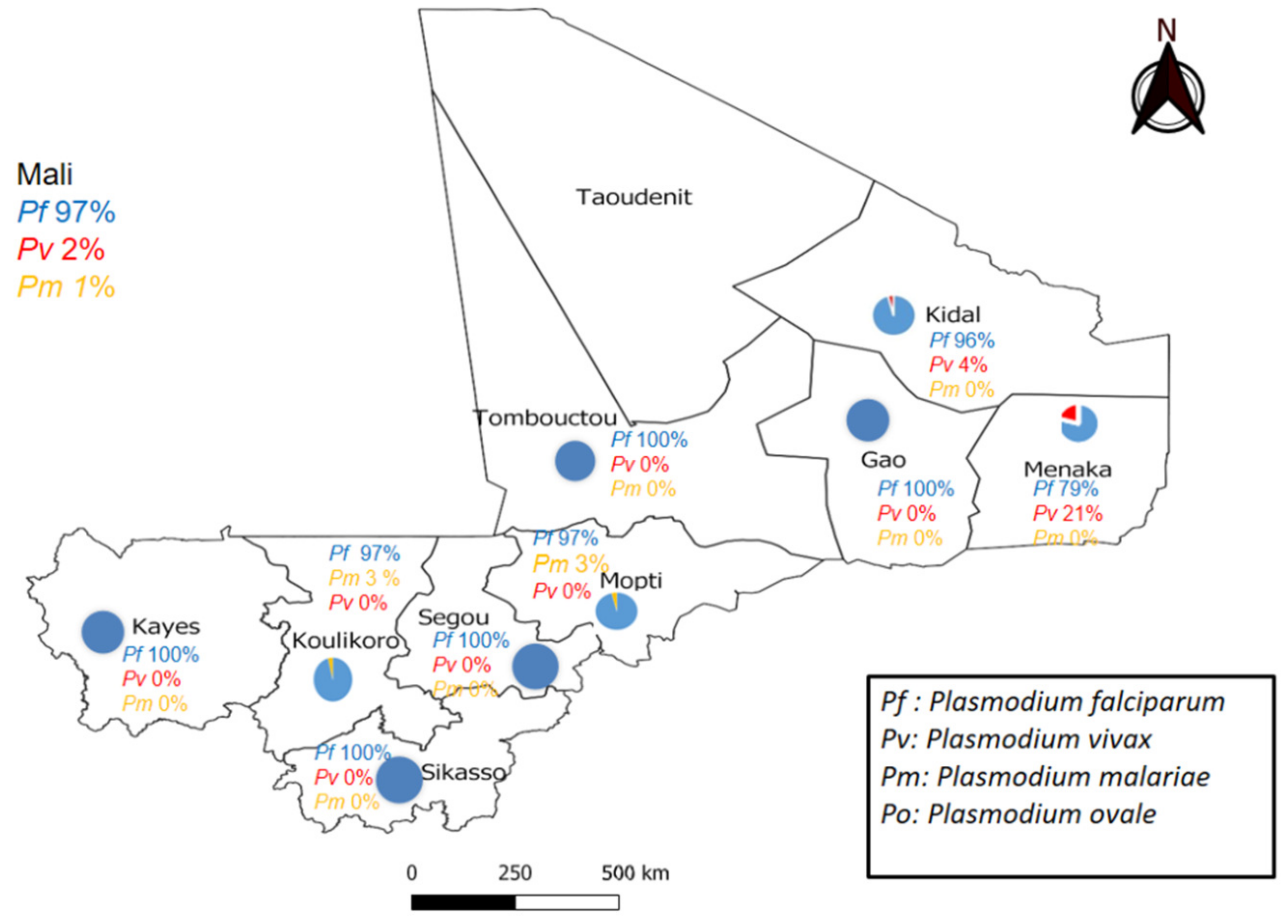
| Regions | P. falciparum | P. vivax | P. malariae | P. ovale | P. falciparum + P. malariae | P. falciparum + P. vivax | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | N | % | n | % | N | % | n | % | ||
| Kayes | 33 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 |
| Koulikoro | 28 | 96.6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0 | 29 |
| Sikasso | 30 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| Ségou | 42 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 42 |
| Mopti | 33 | 97.1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 34 |
| Tombouctou | 30 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| Gao | 18 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
| Kidal | 21 | 91.3 | 1 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4.3 | 23 |
| Ménaka | 15 | 78.9 | 4 | 21.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 |
| Total | 251 | 96.9 | 5 | 1.9 | 2 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.4 | 258 |
| Regions | Sensitivity | Specificity | Youden | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kayes | 87.9% [76.9–90.7] | 99.3% [96.9–100] | 0.87 [0.74–0.91] | 0.90 [0.77–0.94] |
| Koulikoro | 96.6% [84.9–99.8] | 98.7% [95.7–98.6] | 0.95 [0.81–0.99] | 0.94 [0.80–0.98] |
| Sikasso | 80.0% [65.3–90.0] | 96.0% [93.1–97.9] | 0.76 [0.58–0.87] | 0.76 [0.58–0.88] |
| Segou | 71.4% [62.7–71.4] | 100% [97.3–100] | 0.71 [0.60–0.71] | 0.79 [0.67–0.79] |
| Mopti | 88.2% [79–88.0] | 100% [98–100] | 0.88 [0.76–0.88] | 0.92 [0.80–0.92] |
| Tombouctou | 93.3% [80.6–98.7] | 97.3% [94.8–98.4] | 0.91 [0.75–0.97] | 0.88 [0.73–0.95] |
| Gao | 94.4% [73.4–99.7] | 92.6% [90.3–93.2] | 0.87 [0.64–0.93] | 0.68 [0.50–0.73] |
| Kidal | 73.9% [54.5–87.8] | 92.3% [89.4–94.4] | 0.66 [0.44–0.82] | 0.60 [0.40–0.74] |
| Ménaka | 78.9% [59.0–92.0] | 84.2% [74.2–90.7] | 0.63 [0.33–0.83] | 0.62 [0.32–0.80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dembélé, P.; Cissoko, M.; Diarra, A.Z.; Doumbia, L.; Koné, A.; Magassa, M.H.; Mehadji, M.; Thera, M.A.; Ranque, S. Evaluation of the Performance of Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Malaria Diagnosis and Mapping of Different Plasmodium Species in Mali. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21020228
Dembélé P, Cissoko M, Diarra AZ, Doumbia L, Koné A, Magassa MH, Mehadji M, Thera MA, Ranque S. Evaluation of the Performance of Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Malaria Diagnosis and Mapping of Different Plasmodium Species in Mali. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2024; 21(2):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21020228
Chicago/Turabian StyleDembélé, Pascal, Mady Cissoko, Adama Zan Diarra, Lassana Doumbia, Aïssata Koné, Mahamadou H. Magassa, Maissane Mehadji, Mahamadou A. Thera, and Stéphane Ranque. 2024. "Evaluation of the Performance of Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Malaria Diagnosis and Mapping of Different Plasmodium Species in Mali" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 21, no. 2: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21020228
APA StyleDembélé, P., Cissoko, M., Diarra, A. Z., Doumbia, L., Koné, A., Magassa, M. H., Mehadji, M., Thera, M. A., & Ranque, S. (2024). Evaluation of the Performance of Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Malaria Diagnosis and Mapping of Different Plasmodium Species in Mali. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 21(2), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21020228









