Correction: Duan, Y.; Li, S. Effects of Plant Communities on Human Physiological Recovery and Emotional Reactions: A Comparative Onsite Survey and Photo Elicitation Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 721
1. Figure Legend
2. Table Legends
- Table 9. Effects of professional background and perception method.
- Table 10. Effects of gender and plant community type on physiological and psychological indicators.
- Table 11. Effects of professional background and plant community type on physiological and psychological indicators.
3. Errors in Figures
4. Errors in Tables
5. Text Correction
- Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Northwest A&F University.
- Informed Consent Statement: The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University Ethics Committee. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Reference
- Duan, Y.; Li, S. Effects of Plant Communities on Human Physiological Recovery and Emotional Reactions: A Comparative Onsite Survey and Photo Elicitation Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
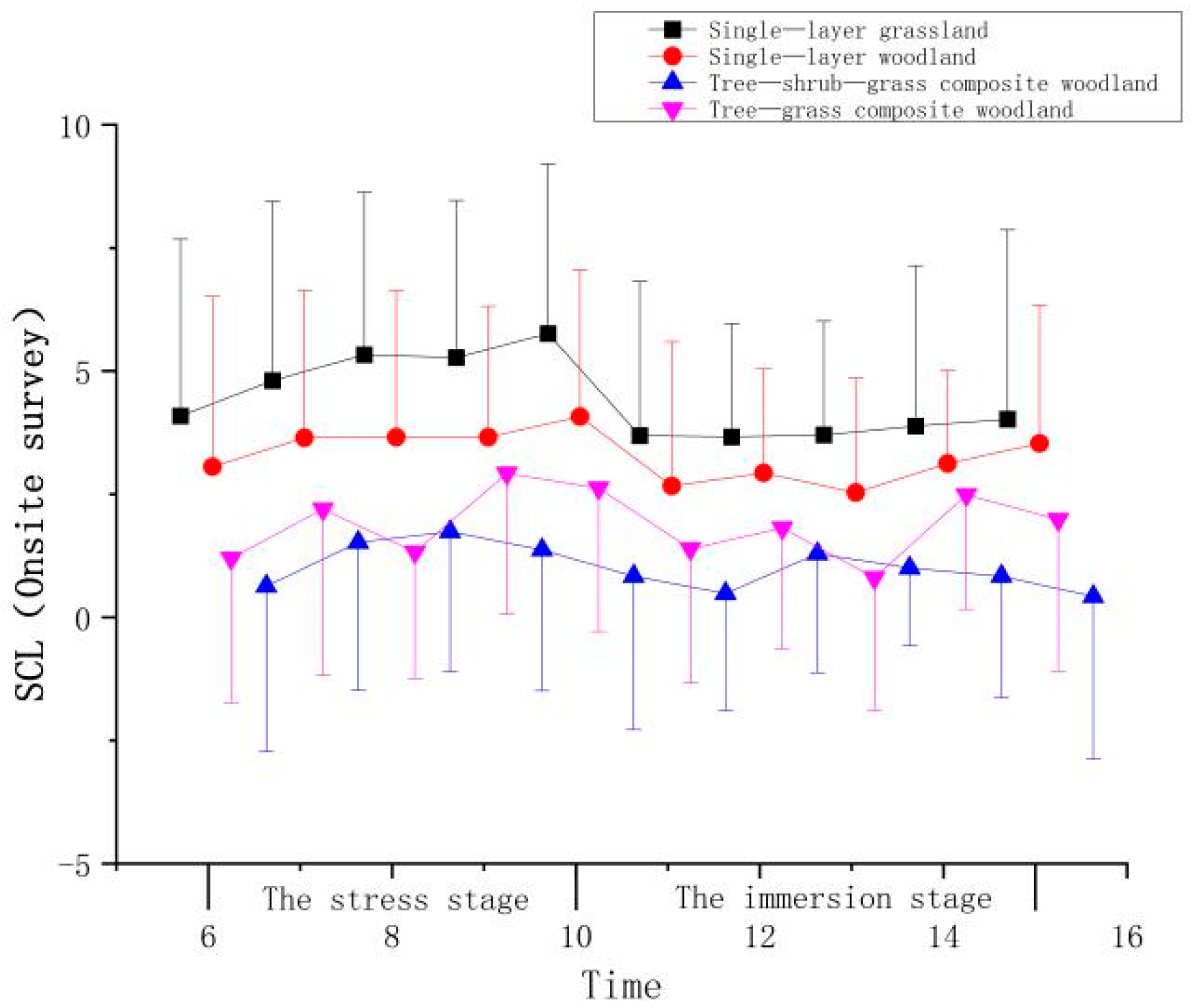
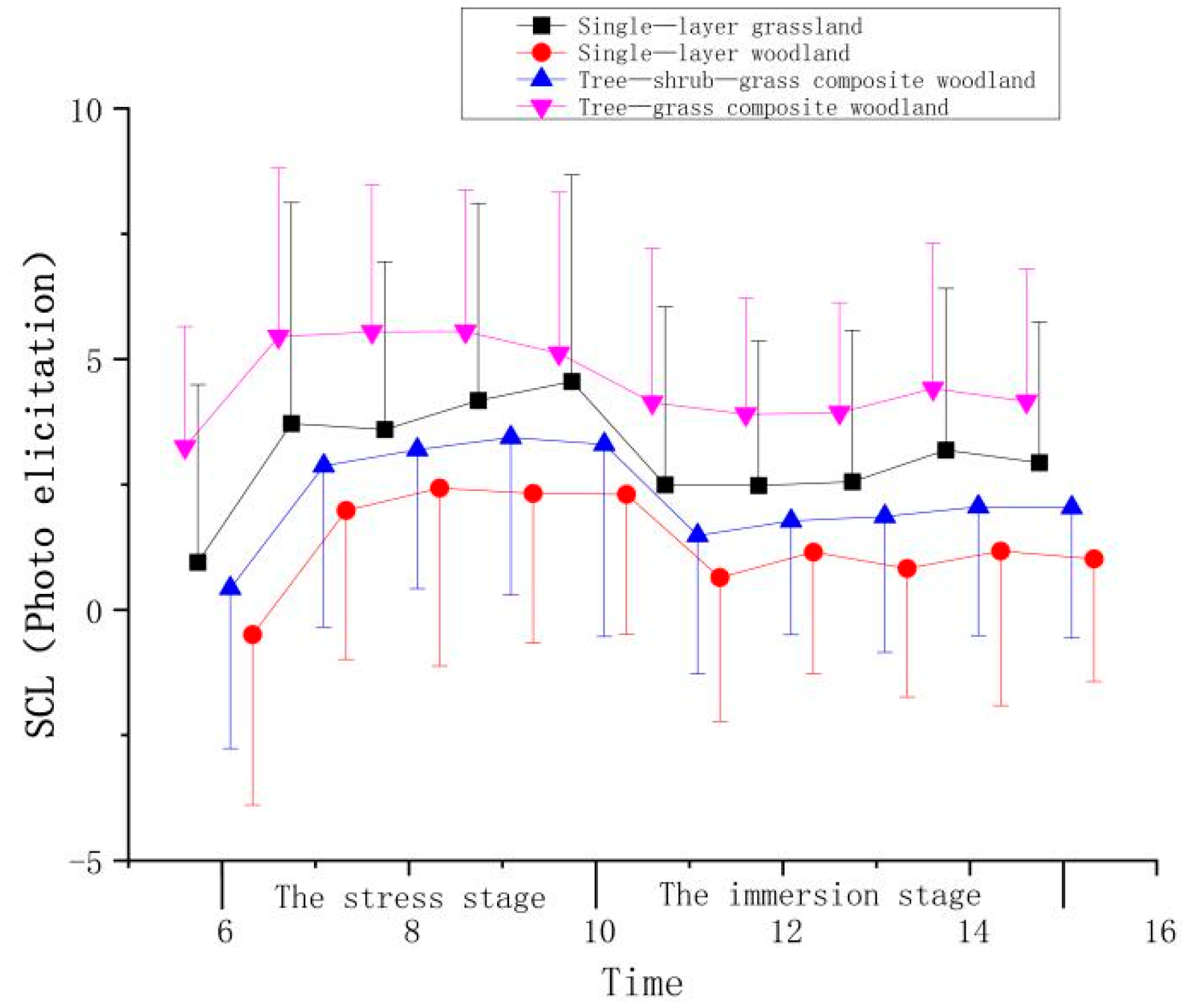
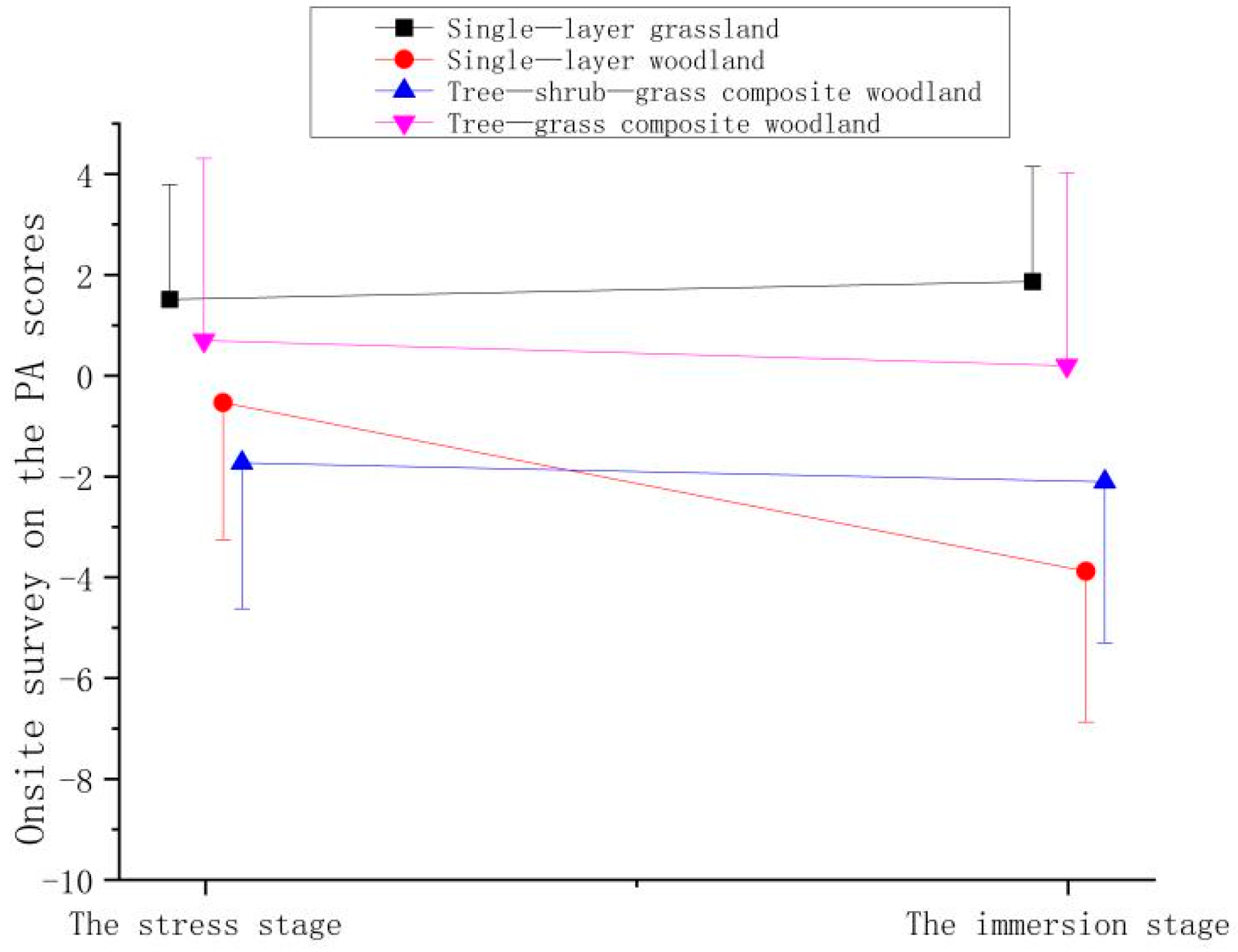
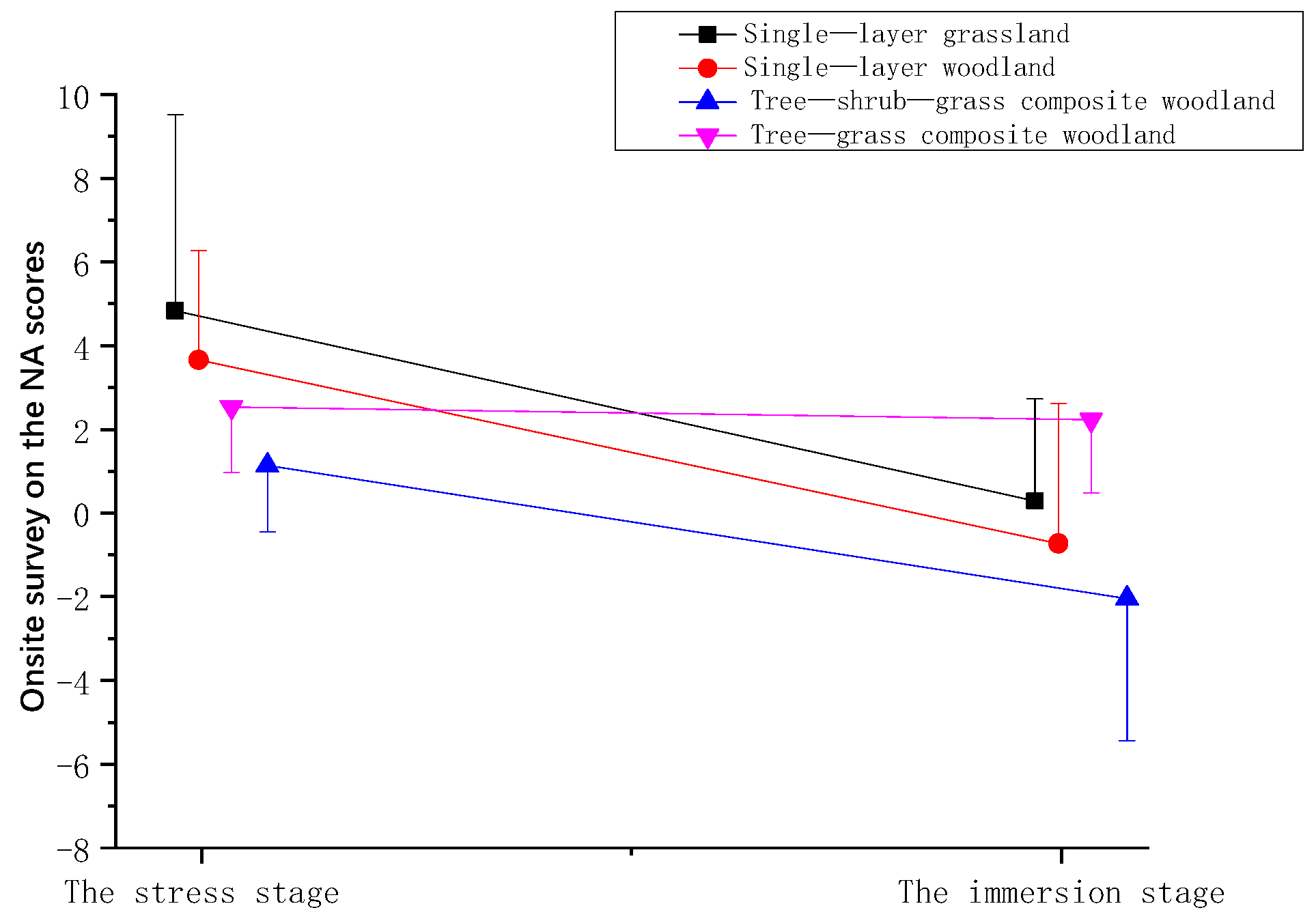
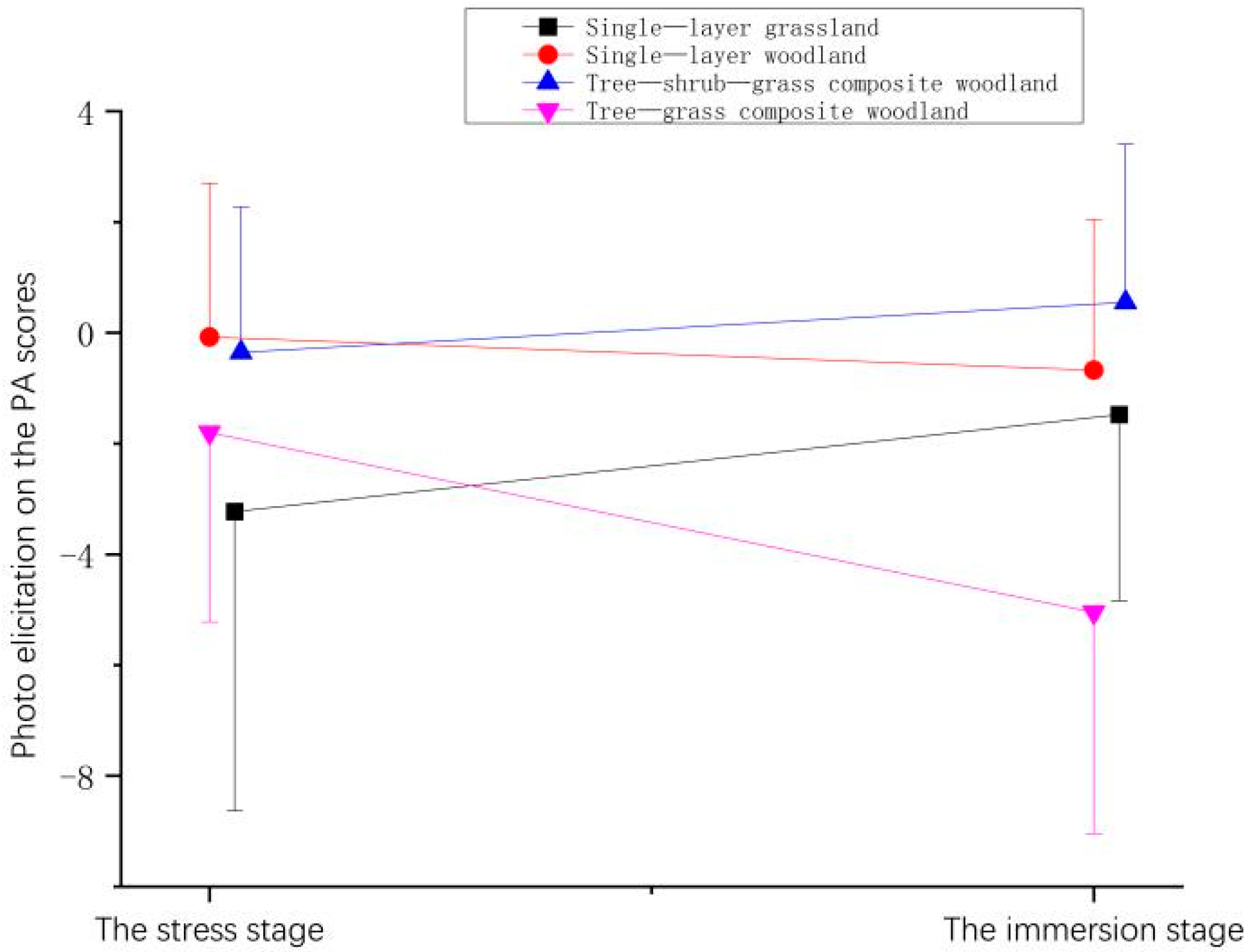
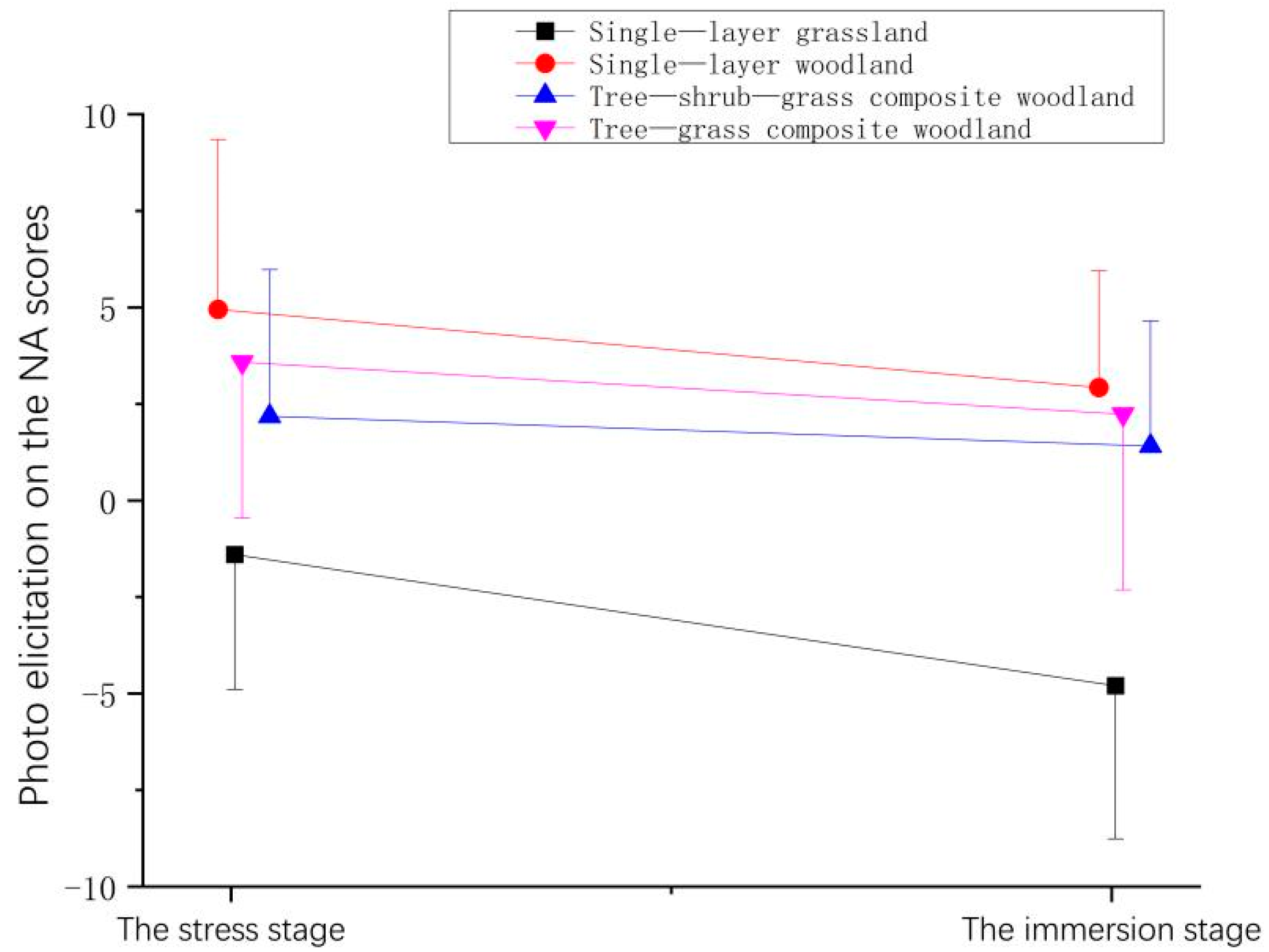
| Stage | Time | Mean ± (SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer Grassland | Single-Layer Woodland | Tree–Shrub–Grass Composite Woodland | Tree–Grass Composite Woodland | ||
| The stress stage | 6 | 1.83 ± 3.59 | 1.29 ± 3.45 | 0.57 ± 3.36 | 0.73 ± 2.93 |
| 7 | 2.55 ± 3.63 | 1.88 ± 3.00 | 1.46 ± 3.06 | 1.73 ± 3.39 | |
| 8 | 3.08 ± 3.30 | 1.89 ± 2.97 | 1.68 ± 2.85 | 0.86 ± 2.57 | |
| 9 | 3.02 ± 3.18 | 1.89 ± 2.65 | 1.31 ± 2.86 | 2.45 ± 2.86 | |
| 10 | 3.51 ± 3.44 | 2.30 ± 2.97 | 0.77 ± 3.11 | 2.16 ± 2.92 | |
| The immersion stage | 11 | 1.44 ± 3.13 | 0.90 ± 2.93 | 0.42 ± 2.39 | 0.92 ± 2.73 |
| 12 | 1.41 ± 2.29 | 1.16 ± 2.12 | 1.23 ± 2.42 | 1.35 ± 2.46 | |
| 13 | 1.45 ± 2.31 | 0.77 ± 2.32 | 0.94 ± 1.58 | 0.33 ± 2.69 | |
| 14 | 1.63 ± 3.25 | 1.36 ± 1.88 | 0.77 ± 2.47 | 2.02 ± 2.34 | |
| 15 | 1.77 ± 3.84 | 1.76 ± 2.81 | 0.36 ± 3.30 | 1.52 ± 3.08 | |
| Stage | Time | Mean ± (SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer Grassland | Single-Layer Woodland | Tree–Shrub–Grass Composite Woodland | Tree–Grass Composite Woodland | ||
| The stress stage | 6 | 0.20 ± 3.54 | −0.11 ± 3.40 | 0.01 ± 3.19 | 0.48 ± 2.40 |
| 7 | 2.97 ± 4.40 | 2.37 ± 2.97 | 2.46 ± 3.22 | 2.68 ± 3.36 | |
| 8 | 2.85 ± 3.35 | 2.81 ± 3.55 | 2.78 ± 2.78 | 2.78 ± 2.93 | |
| 9 | 3.43 ± 3.93 | 2.71 ± 2.99 | 3.03 ± 3.14 | 2.78 ± 2.83 | |
| 10 | 3.81 ± 4.12 | 2.69 ± 2.80 | 2.89 ± 3.84 | 2.35 ± 3.21 | |
| The immersion stage | 11 | 1.75 ± 3.55 | 1.03 ± 2.87 | 1.07 ± 2.77 | 1.37 ± 3.07 |
| 12 | 1.73 ± 2.88 | 1.54 ± 2.42 | 1.36 ± 2.28 | 1.13 ± 2.31 | |
| 13 | 1.81 ± 3.02 | 1.21 ± 2.57 | 1.45 ± 2.72 | 1.17 ± 2.19 | |
| 14 | 2.44 ± 3.22 | 1.56 ± 3.08 | 1.65 ± 2.57 | 1.65 ± 2.90 | |
| 15 | 2.19 ± 2.81 | 1.40 ± 2.44 | 1.63 ± 2.61 | 1.39 ± 2.64 | |
| Stage | Mean ± (SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer Grassland | Single-Layer Woodland | Tree–Shrub–Grass Composite Woodland | Tree–Grass Composite Woodland | |
| The stress stage | −0.18 ± 2.27 | −0.50 ± 2.72 | −0.80 ± 2.90 | −1.18 ± 3.61 |
| The immersion stage | 0.18 ± 2.28 | −3.85 ± 2.99 | −1.18 ± 3.20 | −1.68 ± 3.83 |
| Stage | Mean ± (SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer Grassland | Single-Layer Woodland | Tree–Shrub–Grass Composite Woodland | Tree–Grass Composite Woodland | |
| The stress stage | 3.13 ± 4.68 | 1.83 ± 2.62 | 0.28 ± 1.58 | 0.88 ± 1.56 |
| The immersion stage | −1.4 ± 2.45 | −2.55 ± 3.34 | −2.90 ± 3.40 | 0.58 ± 1.75 |
| Stage | Mean ± (SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer Grassland | Single-Layer Woodland | Tree–Shrub–Grass Composite Woodland | Tree–Grass Composite Woodland | |
| The stress stage | −3.25 ± 5.41 | −0.08 ± 2.77 | −0.38 ± 2.62 | −1.80 ± 3.42 |
| The immersion stage | −1.50 ± 3.36 | −0.68 ± 2.72 | 0.53 ± 2.85 | −5.05 ± 3.99 |
| Stage | Mean ± (SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer Grassland | Single-Layer Woodland | Tree–Shrub–Grass Composite Woodland | Tree–Grass Composite Woodland | |
| The stress stage | −1.35 ± 3.50 | 2.65 ± 4.40 | 1.65 ± 3.79 | 1.58 ± 4.04 |
| The immersion stage | −4.75 ± 3.97 | 0.63 ± 3.03 | 0.88 ± 3.24 | 0.23 ± 4.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, Y.; Li, S. Correction: Duan, Y.; Li, S. Effects of Plant Communities on Human Physiological Recovery and Emotional Reactions: A Comparative Onsite Survey and Photo Elicitation Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 721. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21121636
Duan Y, Li S. Correction: Duan, Y.; Li, S. Effects of Plant Communities on Human Physiological Recovery and Emotional Reactions: A Comparative Onsite Survey and Photo Elicitation Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 721. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2024; 21(12):1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21121636
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Yifan, and Shuhua Li. 2024. "Correction: Duan, Y.; Li, S. Effects of Plant Communities on Human Physiological Recovery and Emotional Reactions: A Comparative Onsite Survey and Photo Elicitation Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 721" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 21, no. 12: 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21121636
APA StyleDuan, Y., & Li, S. (2024). Correction: Duan, Y.; Li, S. Effects of Plant Communities on Human Physiological Recovery and Emotional Reactions: A Comparative Onsite Survey and Photo Elicitation Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 721. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 21(12), 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21121636





