Utility of Electroencephalograms for Enhancing Clinical Care and Rehabilitation of Children with Acquired Brain Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Utility of EEG Monitoring During Rehabilitation
2.1. Using EEG to Monitor and Predict Epilepsy After TBI
2.2. Using EEGs as Prognostic Markers in Assessing Rehabilitative Potential in TBI Patients
2.3. Using EEG to Evaluate Cognitive Dysfunction
2.4. Using EEGs to Monitor Psychiatric Disorders After TBI
3. Using EEGs During the Rehabilitation of Motor Disability Due to ABI
Brain–Computer Interface (BCI)
4. Applicability of EEG Monitoring for Pediatric Rehabilitation of TBI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coulter, I.C.; Forsyth, R.J. Paediatric traumatic brain injury. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popernack, M.L.; Gray, N.; Reuter-Rice, K. Moderate-to-Severe Traumatic Brain Injury in Children: Complications and Rehabilitation Strategies. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2015, 29, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, Z.M.; Karelina, K. Lifelong consequences of brain injuries during development: From risk to resilience. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 55, 100793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Königs, M.; Heij, H.A.; van der Sluijs, J.A.; Vermeulen, R.J.; Goslings, J.C.; Luitse, J.S.; Poll-Thé, B.T.; Beelen, A.; van der Wees, M.; Kemps, R.J.; et al. Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury and Attention Deficit. Pediatrics 2015, 136, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Max, J.E.; Schachar, R.J.; Levin, H.S.; Ewing-Cobbs, L.; Chapman, S.B.; Dennis, M.; Saunders, A.; Landis, J. Predictors of secondary attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents 6 to 24 months after traumatic brain injury. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2005, 44, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Fur, C.; Câmara-Costa, H.; Francillette, L.; Opatowski, M.; Toure, H.; Brugel, D.; Laurent-Vannier, A.; Meyer, P.; Watier, L.; Dellatolas, G.; et al. Executive functions and attention 7 years after severe childhood traumatic brain injury: Results of the Traumatisme Grave de l’Enfant (TGE) cohort. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 63, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, K.A.; Schmidt, A.T.; Hanten, G.R.; Levin, H.S. Executive dysfunction in children and adolescents with behavior disorders and traumatic brain injury. Child Neuropsychol. 2020, 26, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narad, M.E.; Kennelly, M.; Zhang, N.; Wade, S.L.; Yeates, K.O.; Taylor, H.G.; Epstein, J.N.; Kurowski, B.G. Secondary Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents 5 to 10 Years After Traumatic Brain Injury. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachar, R.J.; Park, L.S.; Dennis, M. Mental Health Implications of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) in Children and Youth. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2015, 24, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti, G.M.; Guerriero, R.M.; Press, C.A. Review of Noninvasive Neuromonitoring Modalities in Children II: EEG, qEEG. Neurocrit. Care 2023, 39, 618–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnato, S.; Boccagni, C.; Prestandrea, C.; Sant’Angelo, A.; Castiglione, A.; Galardi, G. Prognostic value of standard EEG in traumatic and non-traumatic disorders of consciousness following coma. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuwer, M. Assessment of digital EEG, quantitative EEG, and EEG brain mapping: Report of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society. Neurology 1997, 49, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, H.L.; Poole, J.H.; Guillory, S.B.; Salerno, R.M.; Leskin, G.; Sigford, B. Persistent problems after traumatic brain injury: The need for long-term follow-up and coordinated care. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2006, 43, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amico, F.; Koberda, J.L. Quantitative Electroencephalography Objectivity and Reliability in the Diagnosis and Management of Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2023, 54, 15500594231202265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio, F.; La Porta, F.; Petrone, V.; Battaglia, S.; Orlandi, S.; Ippolito, G.; Romei, V.; Piperno, R.; Lullini, G. Accuracy of EEG Biomarkers in the Detection of Clinical Outcome in Disorders of Consciousness after Severe Acquired Brain Injury: Preliminary Results of a Pilot Study Using a Machine Learning Approach. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, A.; Pauli, R.; Banellis, L.; Sokoliuk, R.; Hayton, T.; Sturman, S.; Veenith, T.; Yakoub, K.M.; Belli, A.; Chennu, S.; et al. The prognostic value of resting-state EEG in acute post-traumatic unresponsive states. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engemann, D.A.; Raimondo, F.; King, J.R.; Rohaut, B.; Louppe, G.; Faugeras, F.; Annen, J.; Cassol, H.; Gosseries, O.; Fernandez-Slezak, D.; et al. Robust EEG-based cross-site and cross-protocol classification of states of consciousness. Brain 2018, 141, 3179–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennu, S.; Annen, J.; Wannez, S.; Thibaut, A.; Chatelle, C.; Cassol, H.; Martens, G.; Schnakers, C.; Gosseries, O.; Menon, D.; et al. Brain networks predict metabolism, diagnosis and prognosis at the bedside in disorders of consciousness. Brain 2017, 140, 2120–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pease, M.; Gupta, K.; Moshé, S.L.; Correa, D.J.; Galanopoulou, A.S.; Okonkwo, D.O.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Shutter, L.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Castellano, J.F. Insights into epileptogenesis from post-traumatic epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, D.H. Epilepsy after head injury: An overview. Epilepsia 2009, 50 (Suppl. 2), 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.H.; Goodkin, H.P.; Giza, C.C. Early Posttraumatic Seizures in the Pediatric Population. J. Child Neurol. 2016, 31, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strazzer, S.; Pozzi, M.; Avantaggiato, P.; Zanotta, N.; Epifanio, R.; Beretta, E.; Formica, F.; Locatelli, F.; Galbiati, S.; Clementi, E.; et al. Late Post-traumatic Epilepsy in Children and Young Adults: Impropriety of Long-Term Antiepileptic Prophylaxis and Risks in Tapering. Paediatr. Drugs 2016, 18, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Yu, X.; Ou, S.; Liu, X.; Yuan, J.; Huang, H.; Yang, J.; He, L.; Chen, Y. Risk factors for posttraumatic epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 67, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, V.R.; Parko, K.L. Clinical approach to posttraumatic epilepsy. Semin. Neurol. 2015, 35, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pease, M.; Elmer, J.; Shahabadi, A.Z.; Mallela, A.N.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, J.F.; Sexton, D.; Barot, N.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.A.; Shutter, L.; Okonkwo, D.O.; et al. Predicting posttraumatic epilepsy using admission electroencephalography after severe traumatic brain injury. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Boyle, E.J.; Wu, A.C.; Cole, A.J.; Staley, K.J.; Zafar, S.; Cash, S.S.; Westover, M.B. Epileptiform activity in traumatic brain injury predicts post-traumatic epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Ge, W.; Jing, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Doherty, D.; Herman, A.; Kaleem, S.; Ding, K.; Osman, G.; et al. Quantitative epileptiform burden and electroencephalography background features predict post-traumatic epilepsy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
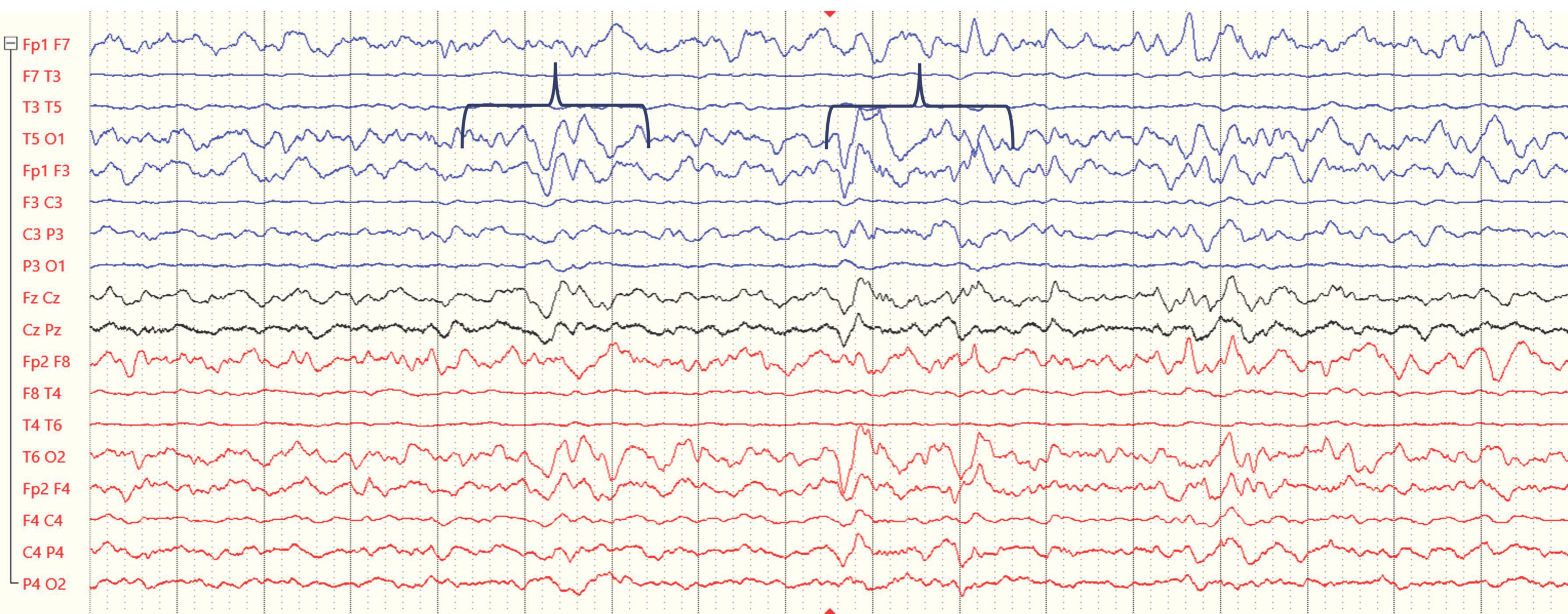
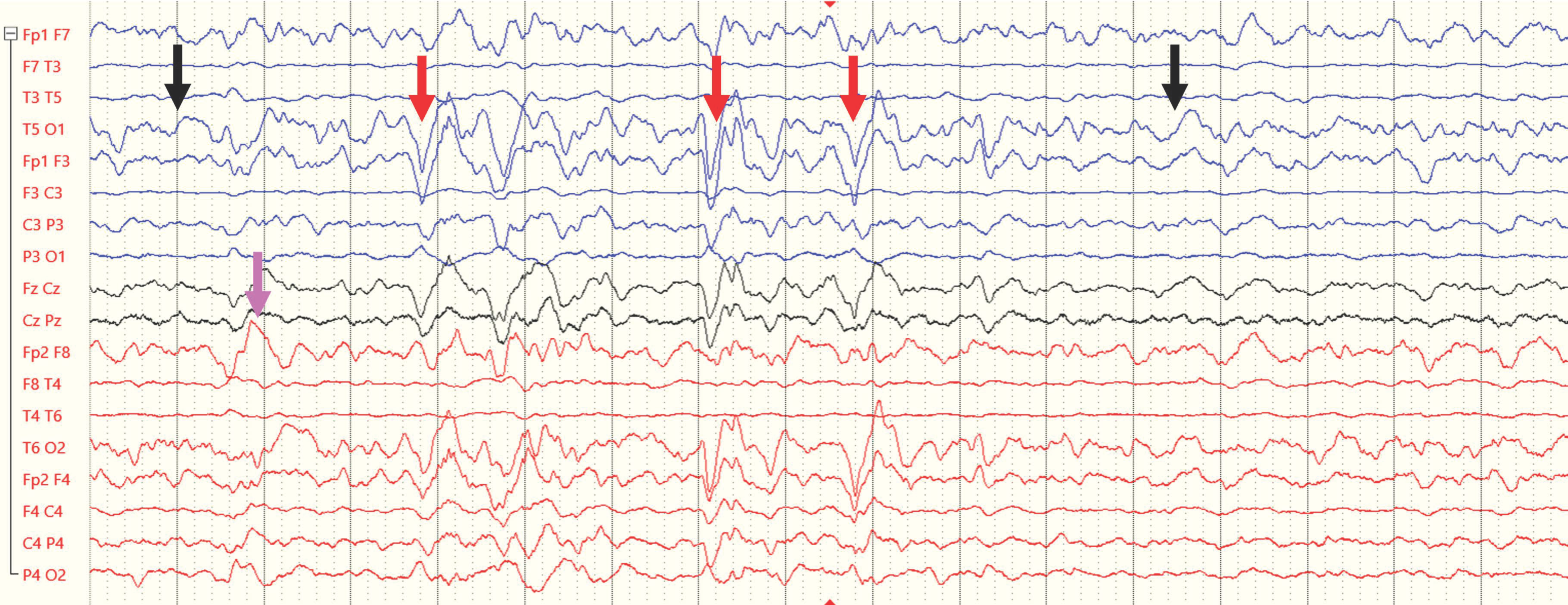
- Guerriero, R.M.; Morrissey, M.J.; Loe, M.; Reznikov, J.; Binkley, M.M.; Ganniger, A.; Griffith, J.L.; Khanmohammadi, S.; Rudock, R.; Guilliams, K.P.; et al. Macroperiodic Oscillations Are Associated With Seizures Following Acquired Brain Injury in Young Children. J. Clin. Neurophysiol 2022, 39, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Manley, G.T.; Abrams, M.; Åkerlund, C.; Andelic, N.; Aries, M.; Bashford, T.; Bell, M.J.; Bodien, Y.G.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Progress and challenges in prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 1004–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouthon, A.L.; Meyer-Heim, A.; Kurth, S.; Ringli, M.; Pugin, F.; van Hedel, H.J.A.; Huber, R. High-Density Electroencephalographic Recordings During Sleep in Children and Adolescents With Acquired Brain Injury. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2017, 31, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhao, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, D. Role of Quantitative EEG and EEG Reactivity in Traumatic Brain Injury. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2022, 53, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandsmark, D.K.; Kumar, M.A.; Woodward, C.S.; Schmitt, S.E.; Park, S.; Lim, M.M. Sleep Features on Continuous Electroencephalography Predict Rehabilitation Outcomes After Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2016, 31, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liuzzi, P.; Grippo, A.; Campagnini, S.; Scarpino, M.; Draghi, F.; Romoli, A.; Bahia, H.; Sterpu, R.; Maiorelli, A.; Macchi, C.; et al. Merging Clinical and EEG Biomarkers in an Elastic-Net Regression for Disorder of Consciousness Prognosis Prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon-Carrion, J.; Martin-Rodriguez, J.F.; Damas-Lopez, J.; Barroso y Martin, J.M.; Dominguez-Morales, M.R. Delta-alpha ratio correlates with level of recovery after neurorehabilitation in patients with acquired brain injury. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarà, M.; Pistoia, F. Complexity loss in physiological time series of patients in a vegetative state. Nonlinear Dyn. Psychol. Life Sci. 2010, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fingelkurts, A.A.; Fingelkurts, A.A.; Bagnato, S.; Boccagni, C.; Galardi, G. Life or death: Prognostic value of a resting EEG with regards to survival in patients in vegetative and minimally conscious states. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolonen, A.; Särkelä, M.O.K.; Takala, R.S.K.; Katila, A.; Frantzén, J.; Posti, J.P.; Müller, M.; van Gils, M.; Tenovuo, O. Quantitative EEG Parameters for Prediction of Outcome in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Development Study. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2018, 49, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingelkurts, A.A.; Fingelkurts, A.A.; Bagnato, S.; Boccagni, C.; Galardi, G. Long-term (six years) clinical outcome discrimination of patients in the vegetative state could be achieved based on the operational architectonics EEG analysis: A pilot feasibility study. Open Neuroimaging J. 2016, 10, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, J.; Crone, J.S.; Johnson, M.A.; Lutkenhoff, E.S.; Spivak, N.M.; Dell’Italia, J.; Hipp, J.F.; Shrestha, V.; Ruiz Tejeda, J.E.; Real, C.; et al. Neural oscillations track recovery of consciousness in acute traumatic brain injury patients. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 1804–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballanti, S.; Campagnini, S.; Liuzzi, P.; Hakiki, B.; Scarpino, M.; Macchi, C.; Oddo, C.M.; Carrozza, M.C.; Grippo, A.; Mannini, A. EEG-based methods for recovery prognosis of patients with disorders of consciousness: A systematic review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 144, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, M.J.; Hendrickx, M.D.; Powell-Jones, A.; Bryan-Hancock, C. A Systematic Review of Cognitive Functioning After Traumatic Brain Injury in Individuals Aged 10–30 Years. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2020, 33, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Watson, W.; Caliendo, E.; Nowak, S.; Schiff, N.D.; Shah, S.A.; Hill, N.J. Objective neurophysiologic markers of cognition after pediatric brain injury. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.A.; Lowder, R.J.; Kuceyeski, A. Quantitative multimodal imaging in traumatic brain injuries producing impaired cognition. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.; Thorstensen, J.R.; Ho, J.M.; Ashley, D.P.; Iyer, K.K.; Barlow, K.M. Attention Please! Unravelling the Link Between Brain Network Connectivity and Cognitive Attention Following Acquired Brain Injury: A Systematic Review of Structural and Functional Measures. Brain Connect. 2024, 14, 4–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.S.; Motes, M.; Afkhami-Rohani, B.; Adhikari, A.; LoBue, C.; Kraut, M.; Cullum, C.M.; Hart, J., Jr. Verbal retrieval deficits due to traumatic brain injury are associated with changes in event related potentials during a Go-NoGo task. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2024, 163, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbilsen, N.; Kotz, S.A.; Rosso, M.; Leman, M.; Triccas, L.T.; Feys, P.; Moumdjian, L. Auditory attention measured by EEG in neurological populations: Systematic review of literature and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.M.; Elbogen, E.B.; Johnson, J.L.; Hamer, R.M.; Belger, A. Event related potentials indexing the influence of emotion on cognitive processing in veterans with comorbid post-traumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.J.; Farrer, T.J.; Clayson, P.E. Cognitive control in mild traumatic brain injury: Conflict monitoring and conflict adaptation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2011, 82, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, R.W.; Walker, R.A.; Gerson, I.; Geisler, F.H. EEG discriminant analyses of mild head trauma. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1989, 73, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, K.E. The electrophysiological effects of a brain injury on auditory memory functioning: The QEEG correlates of impaired memory. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2003, 18, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmonico, R.L.; Tucker, L.Y.; Theodore, B.R.; Camicia, M.; Filanosky, C.; Haarbauer-Krupa, J. Mild Traumatic Brain Injuries and Risk for Affective and Behavioral Disorders. Pediatrics 2024, 153, e2023062340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esterov, D.; Witkowski, J.; McCall, D.M.; Weaver, A.L.; Brown, A.W. Long-Term Risk for Mood and Anxiety Disorders After Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury: A Population-Based, Birth Cohort Analysis. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2023, 38, E212–E222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.; Ford, T.J.; Karl, A.; Reynolds, S.; Limond, J.; Adlam, A.R. Mood Disorders in Young People With Acquired Brain Injury: An Integrated Model. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 835897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberté Durish, C.; Pereverseff, R.S.; Yeates, K.O. Depression and Depressive Symptoms in Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury: A Scoping Review. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2018, 33, E18–E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.; Sugden-Lingard, S.; Brunsdon, R.; Benson, S. Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children with an Early History of Paediatric Acquired Brain Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Turner, R.C.; Nguyen, L.; Motwani, K.; Swatek, M.; Lucke-Wold, B.P. Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury and Autism: Elucidating Shared Mechanisms. Behav. Neurol. 2016, 2016, 8781725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, H.T.; Clark, A.; Holubkov, R.; Ewing-Cobbs, L. Longitudinal Developmental Outcomes of Infants and Toddlers With Traumatic Brain Injury. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2251195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuckols, C.C. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, (DSM–5), 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Font-Clos, F.; Spelta, B.; D’Agostino, A.; Donati, F.; Sarasso, S.; Canevini, M.P.; Zapperi, S.; La Porta, C.A.M. Information Optimized Multilayer Network Representation of High Density Electroencephalogram Recordings. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2021, 1, 746118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shor, O.; Glik, A.; Yaniv-Rosenfeld, A.; Valevski, A.; Weizman, A.; Khrennikov, A.; Benninger, F. EEG p-adic quantum potential accurately identifies depression, schizophrenia and cognitive decline. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livint Popa, L.; Dragos, H.; Pantelemon, C.; Verisezan Rosu, O.; Strilciuc, S. The Role of Quantitative EEG in the Diagnosis of Neuropsychiatric Disorders. J. Med. Life. 2020, 13, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newson, J.J.; Thiagarajan, T.C. EEG Frequency Bands in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review of Resting State Studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevignard, M.; Câmara-Costa, H.; Dellatolas, G. Pediatric traumatic brain injury and abusive head trauma. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 173, 451–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vidal, J.J. Toward direct brain-computer communication. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 1973, 2, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbaumer, N.; Ghanayim, N.; Hinterberger, T.; Iversen, I.; Kotchoubey, B.; Kübler, A.; Perelmouter, J.; Taub, E.; Flor, H. A spelling device for the paralysed. Nature 1999, 398, 297–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaide-Aguirre, R.; Warschausky, S.; Brown, D.; Aref, A.; Huggins, J. Asynchronous brain-computer interface for cognitive assessment in people with cerebral palsy. J. Neural Eng. 2017, 14, 066001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, Y.; Vaughan, T.M.; McCane, L.; Allison, B.Z.; Wolpaw, J.R.; Krusienski, D.J. An exploration of BCI performance variations in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using longitudinal EEG data. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 056031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, M.A.; Nicolelis, M.A. Brain-machine interfaces: From basic science to neuroprostheses and neurorehabilitation. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 767–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Baumert, M. Intra-and inter-subject variability in EEG-based sensorimotor brain computer interface: A review. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vourvopoulos, A.; Pardo, O.M.; Lefebvre, S.; Neureither, M.; Saldana, D.; Jahng, E.; Liew, S.L. Effects of a brain-computer interface with virtual reality (VR) neurofeedback: A pilot study in chronic stroke patients. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Wang, Y.-K.; King, J.-T.; Lin, C.-T. Extended interaction with a BCI video game changes resting-state brain activity. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2020, 12, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Jo, S. A low-cost EEG system-based hybrid brain-computer interface for humanoid robot navigation and recognition. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spataro, R.; Chella, A.; Allison, B.; Giardina, M.; Sorbello, R.; Tramonte, S.; Guger, C.; La Bella, V. Reaching and grasping a glass of water by locked-in ALS patients through a BCI-controlled humanoid robot. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jadavji, Z.; Zewdie, E.; Kirton, A. Evaluating if children can use simple brain computer interfaces. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadavji, Z.; Zewdie, E.; Kelly, D.; Kinney-Lang, E.; Robu, I.; Kirton, A. Establishing a clinical brain-computer interface program for children with severe neurological disabilities. Cureus 2022, 14, e26215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrden, A.; Chau, T. Effects of user mental state on EEG-BCI performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skola, F.; Tinkov’a, S.; Liarokapis, F. Progressive Training for motor imagery brain-computer interfaces using gamification and virtual reality embodiment. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccilli, B. Exploring new horizons: Emerging therapeutic strategies for pediatric stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 374, 114701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Mamun, K.A.; Ahmed, K.; Mostafa, R.; Naik, G.R.; Darvishi, S.; Khandoker, A.H.; Baumert, M. Progress in Brain Computer Interface: Challenges and Opportunities. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 578875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, F.; Xu, T.; Yin, H.; Chen, P.; Yue, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; He, Y.; et al. Brain-Controlled Wheelchair Review: From Wet Electrode to Dry Electrode, from Single Modal to Hybrid Modal, from Synchronous to Asynchronous. IEEE Access. 2021, 9, 55920–55938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.H.; Lerner, J.T.; Matsumoto, J.H.; Madikians, A.; Yudovin, S.; Valino, H.; McArthur, D.L.; Wu, J.Y.; Leung, M.; Buxey, F.; et al. Subclinical early posttraumatic seizures detected by continuous EEG monitoring in a consecutive pediatric cohort. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewarie, P.K.; Beernink, T.M.; Eertman-Meyer, C.J.; Cornet, A.D.; Beishuizen, A.; van Putten, M.J.; Tjepkema-Cloostermans, M.C. Early EEG monitoring predicts clinical outcome in patients with moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. NeuroImage Clin. 2023, 37, 103350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Politi, K.; Weiss, P.L.; Givony, K.; Zion Golumbic, E. Utility of Electroencephalograms for Enhancing Clinical Care and Rehabilitation of Children with Acquired Brain Injury. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21111466
Politi K, Weiss PL, Givony K, Zion Golumbic E. Utility of Electroencephalograms for Enhancing Clinical Care and Rehabilitation of Children with Acquired Brain Injury. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2024; 21(11):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21111466
Chicago/Turabian StylePoliti, Keren, Patrice L. Weiss, Kfir Givony, and Elana Zion Golumbic. 2024. "Utility of Electroencephalograms for Enhancing Clinical Care and Rehabilitation of Children with Acquired Brain Injury" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 21, no. 11: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21111466
APA StylePoliti, K., Weiss, P. L., Givony, K., & Zion Golumbic, E. (2024). Utility of Electroencephalograms for Enhancing Clinical Care and Rehabilitation of Children with Acquired Brain Injury. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 21(11), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21111466





_Weiss.png)

