The Synergistic Effect of Topographic Factors and Vegetation Indices on the Underground Coal Mine Utilizing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
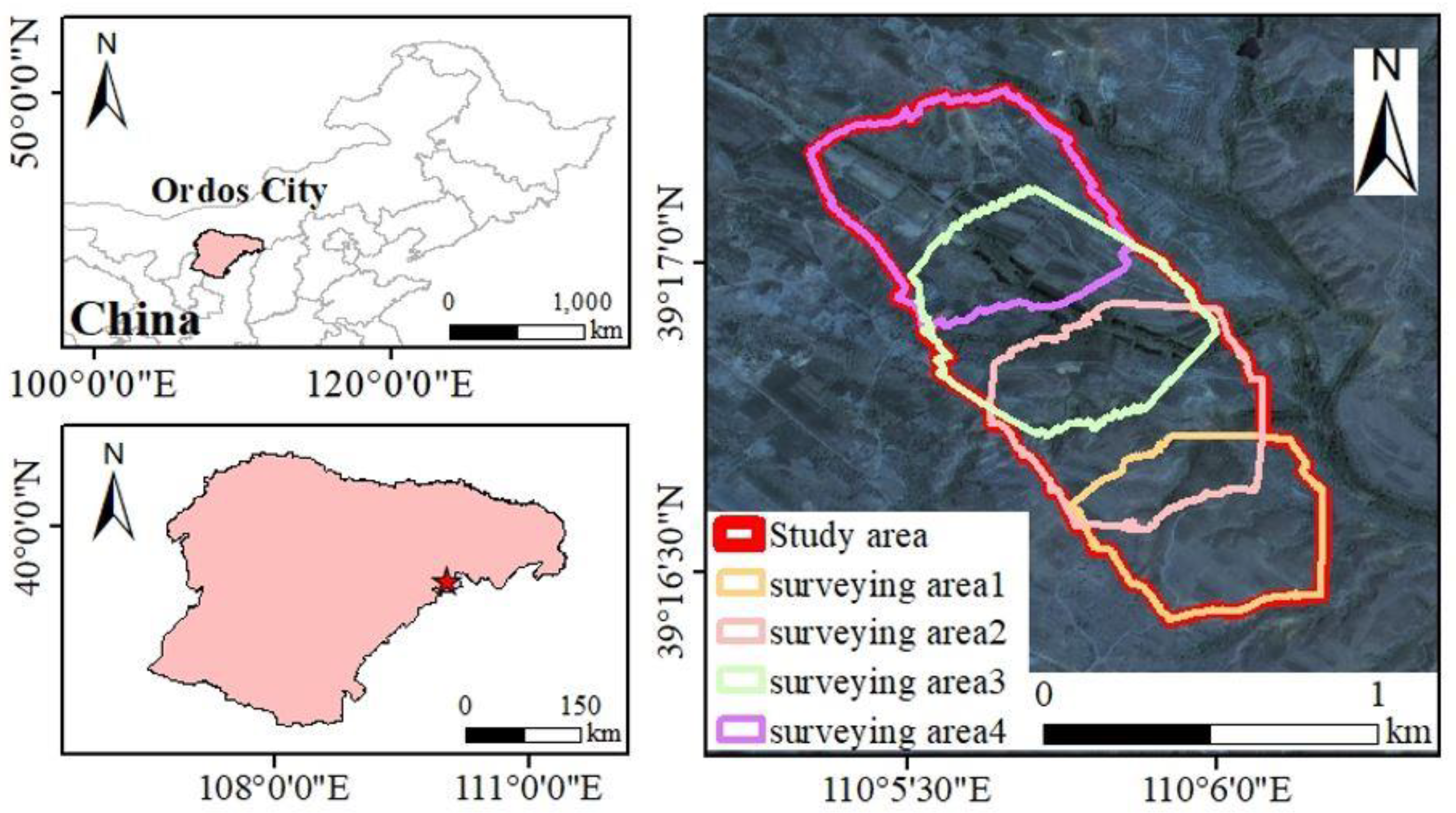
2.1. Study Area
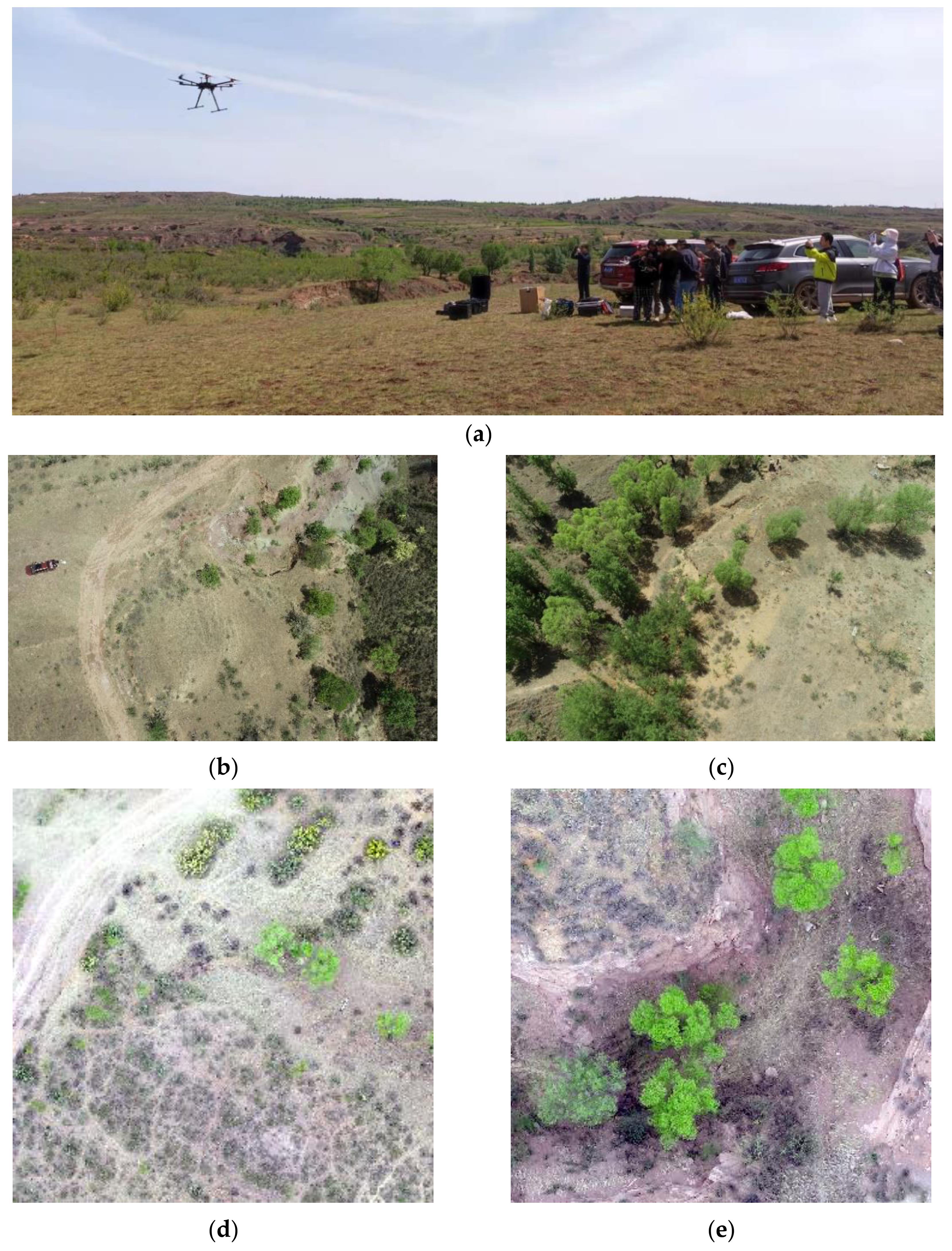
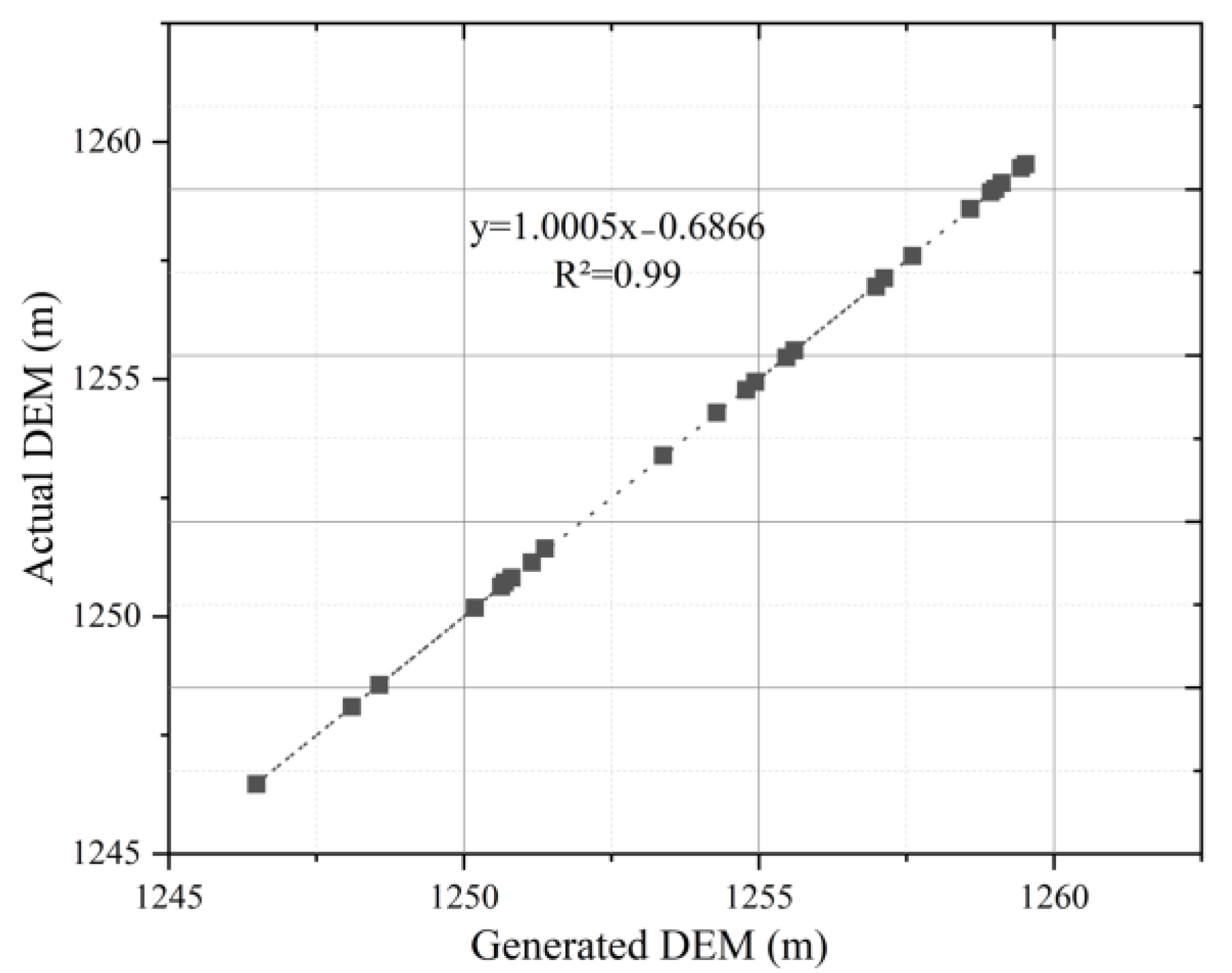
2.2. Datasets
3. Methods
3.1. Calculation of NDVI
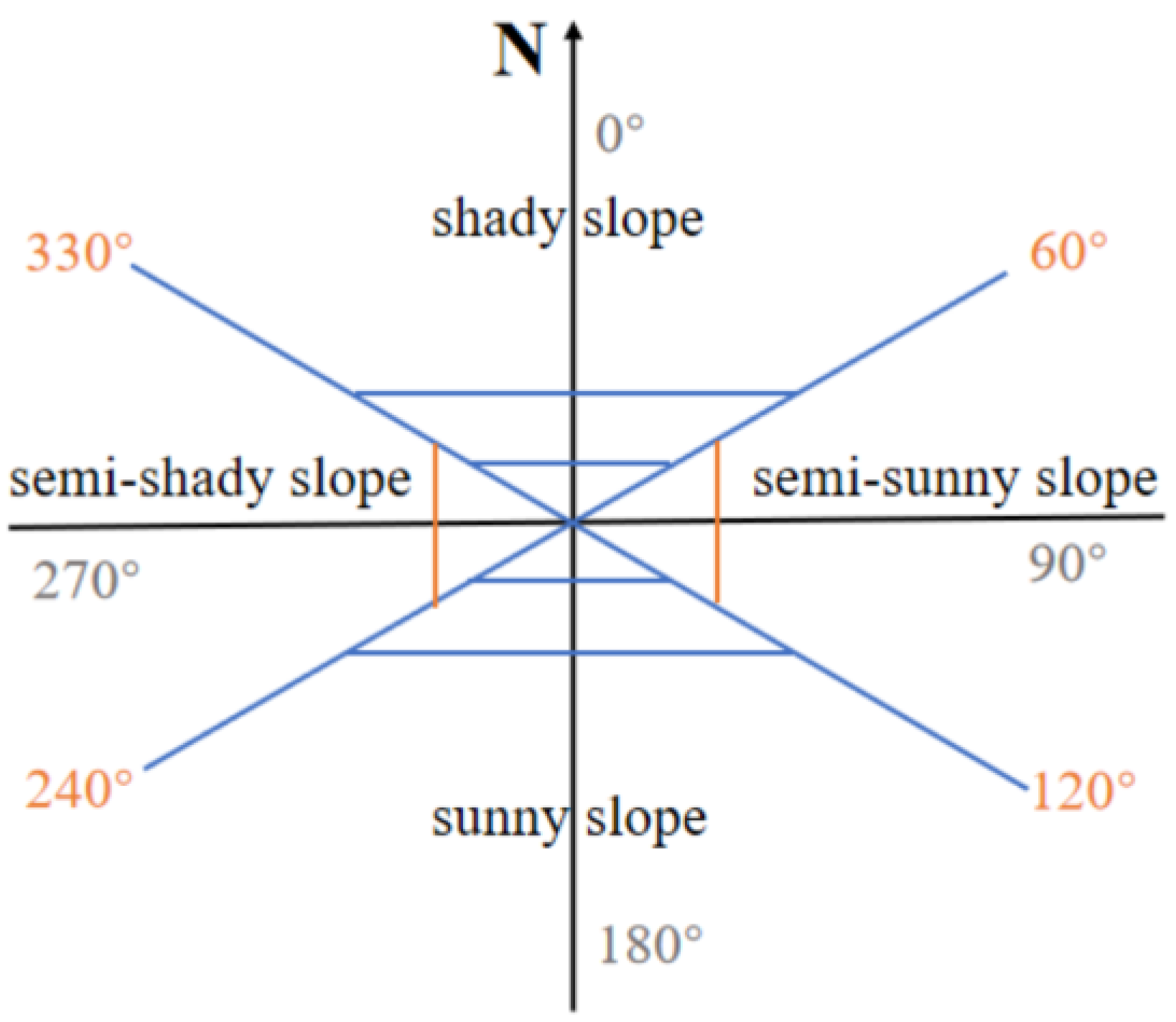
3.2. Calculation of Slope and Aspect
4. Results
4.1. Map of the Vegetation and the Topographic Factors
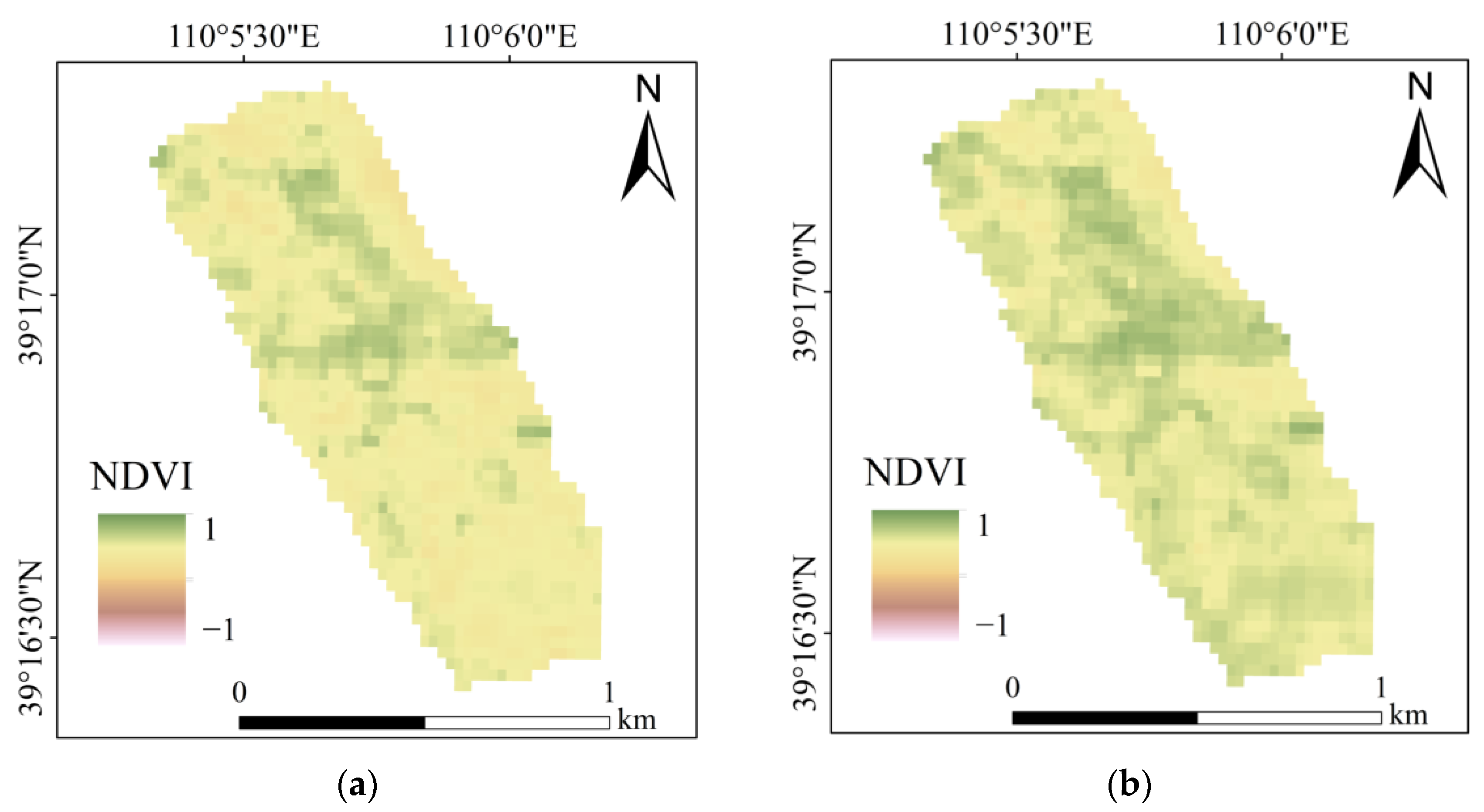
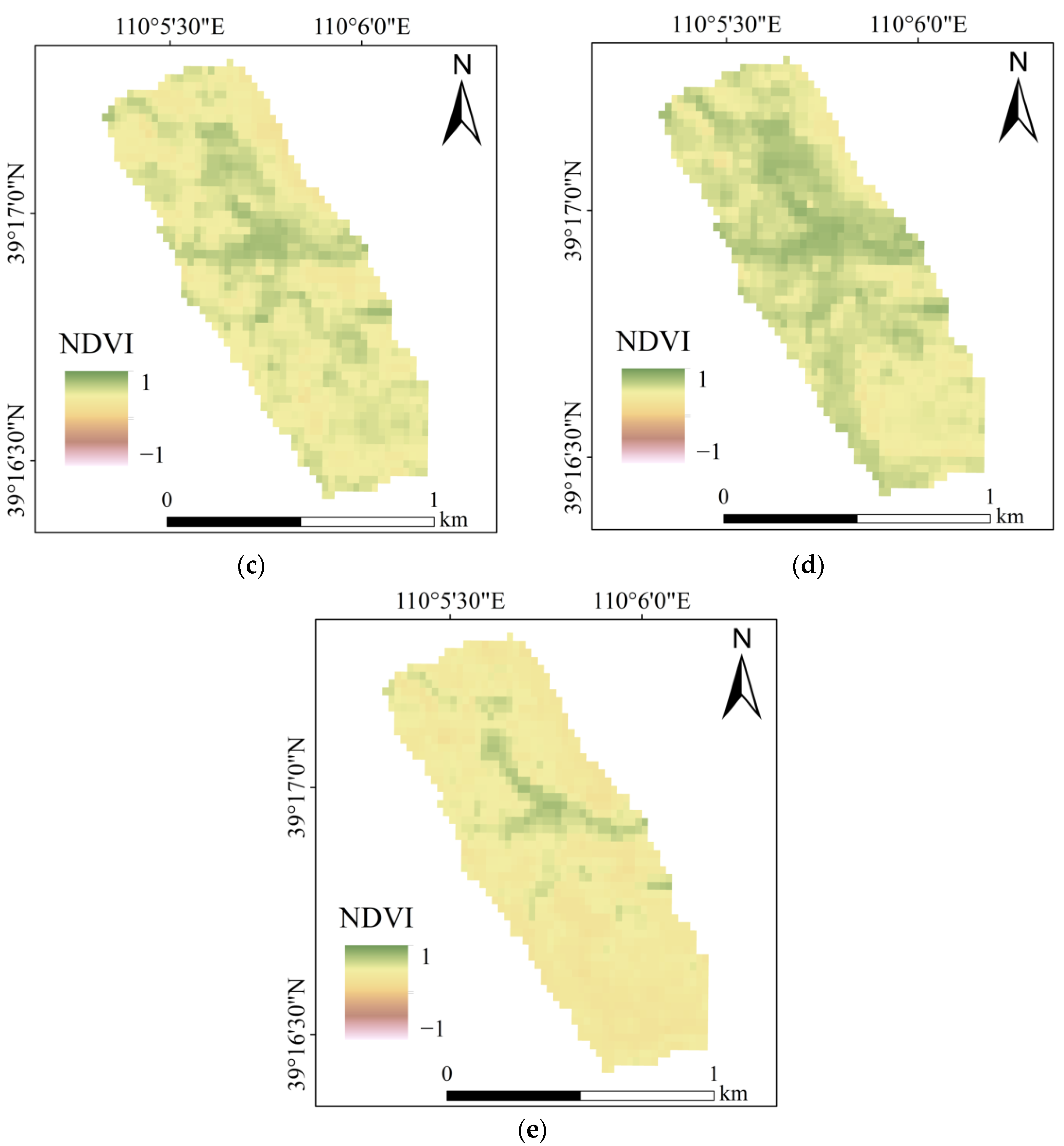
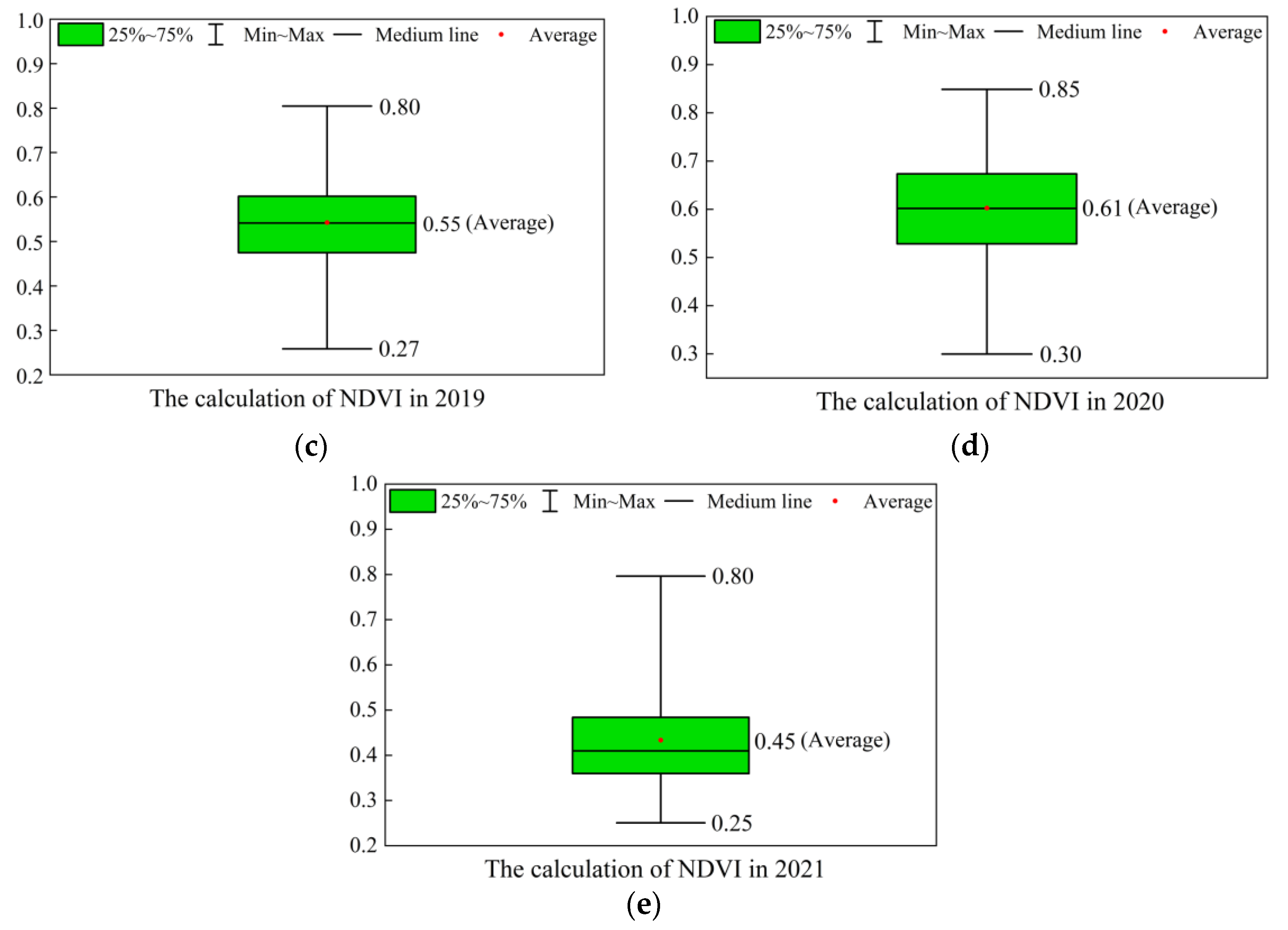
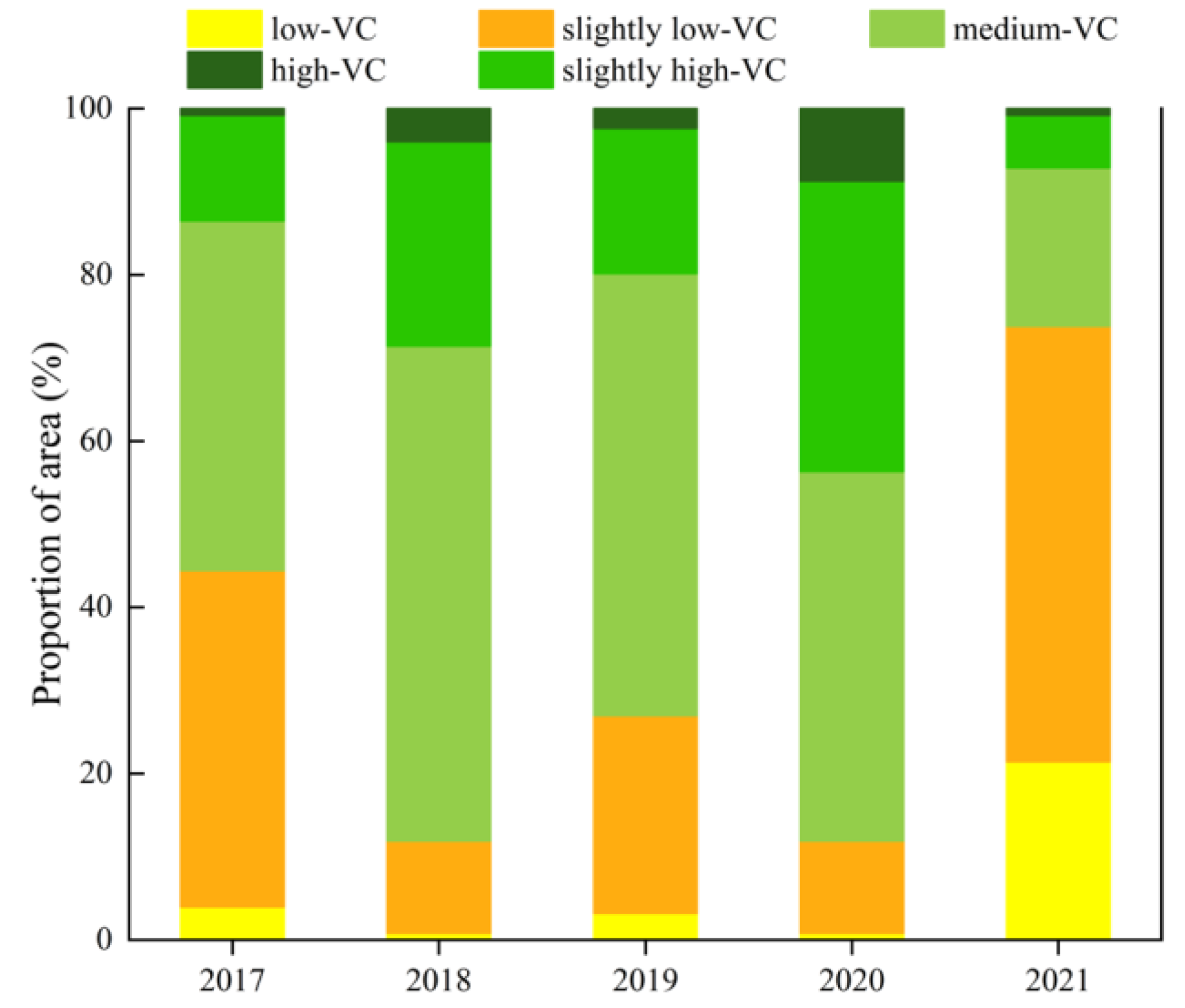
4.1.1. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of NDVI
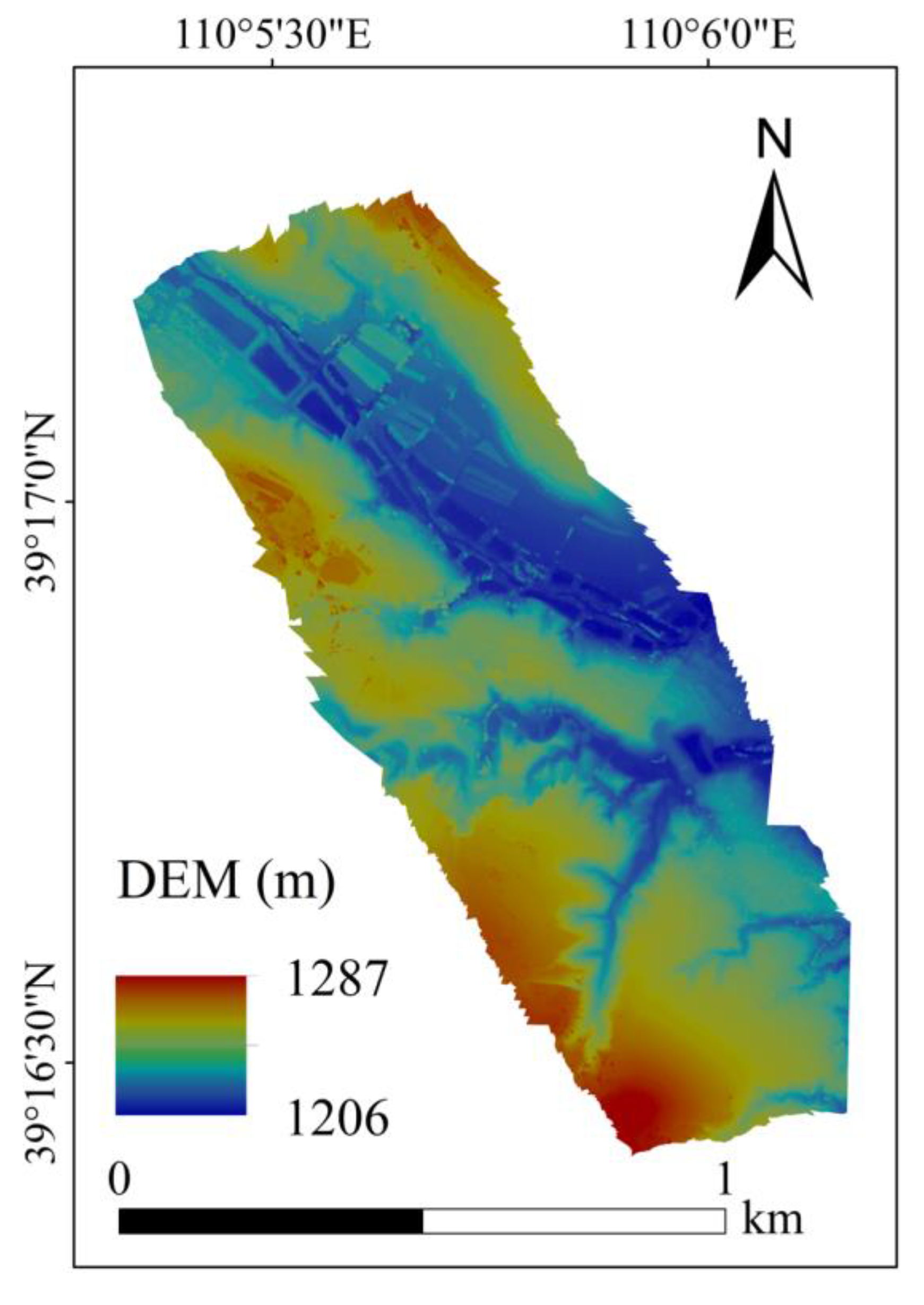
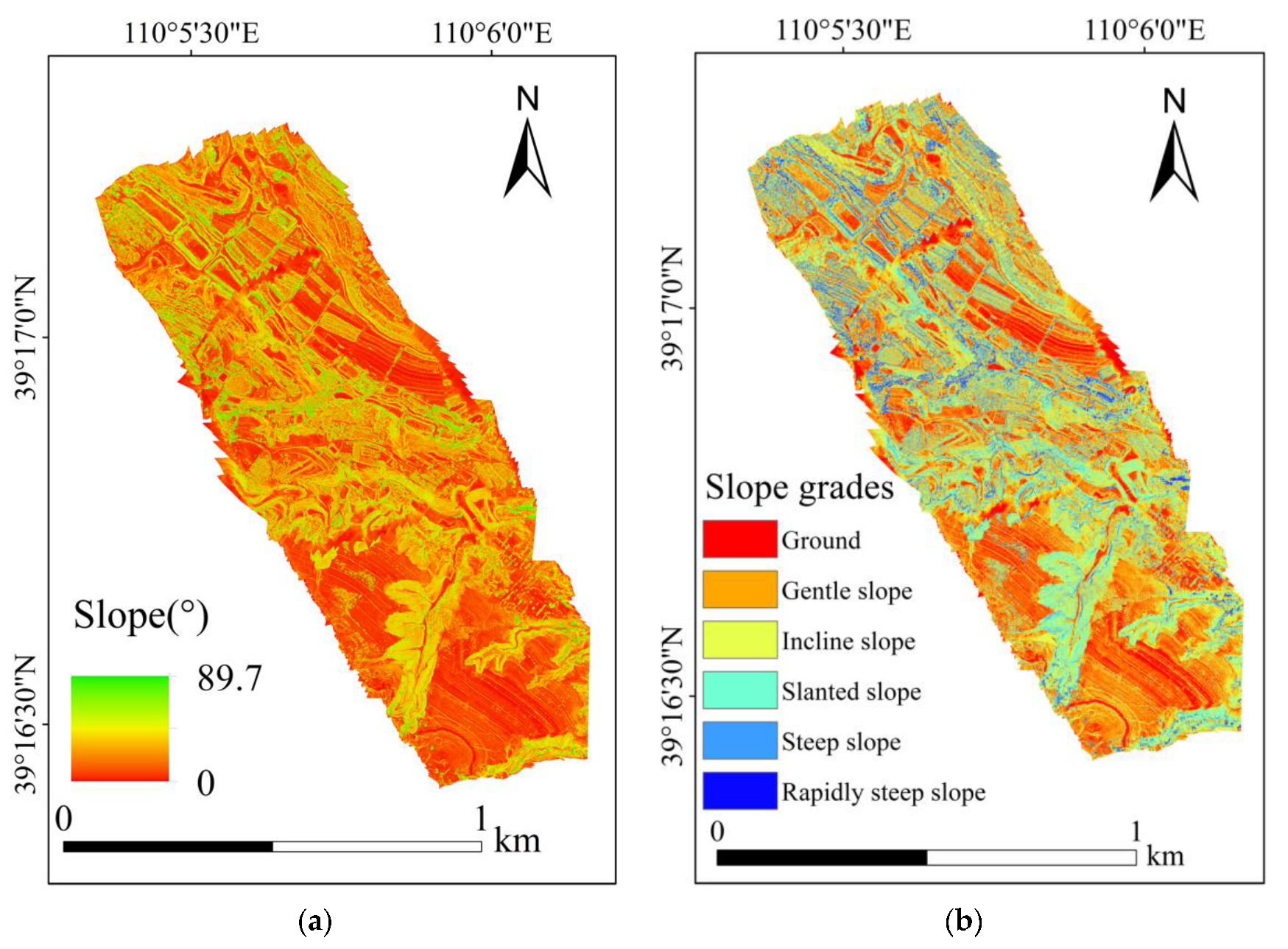
4.1.2. Map of the Topographic Factors
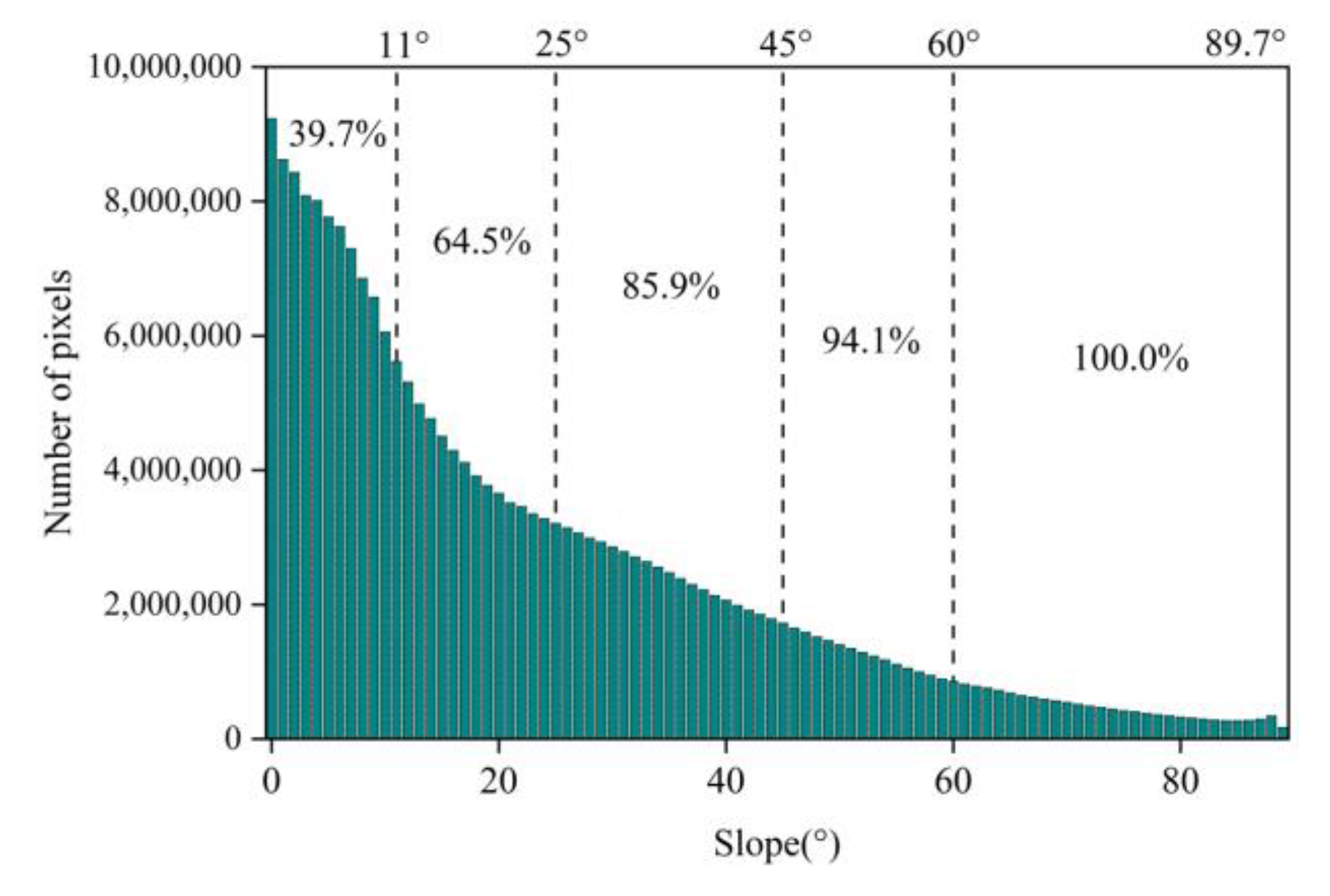
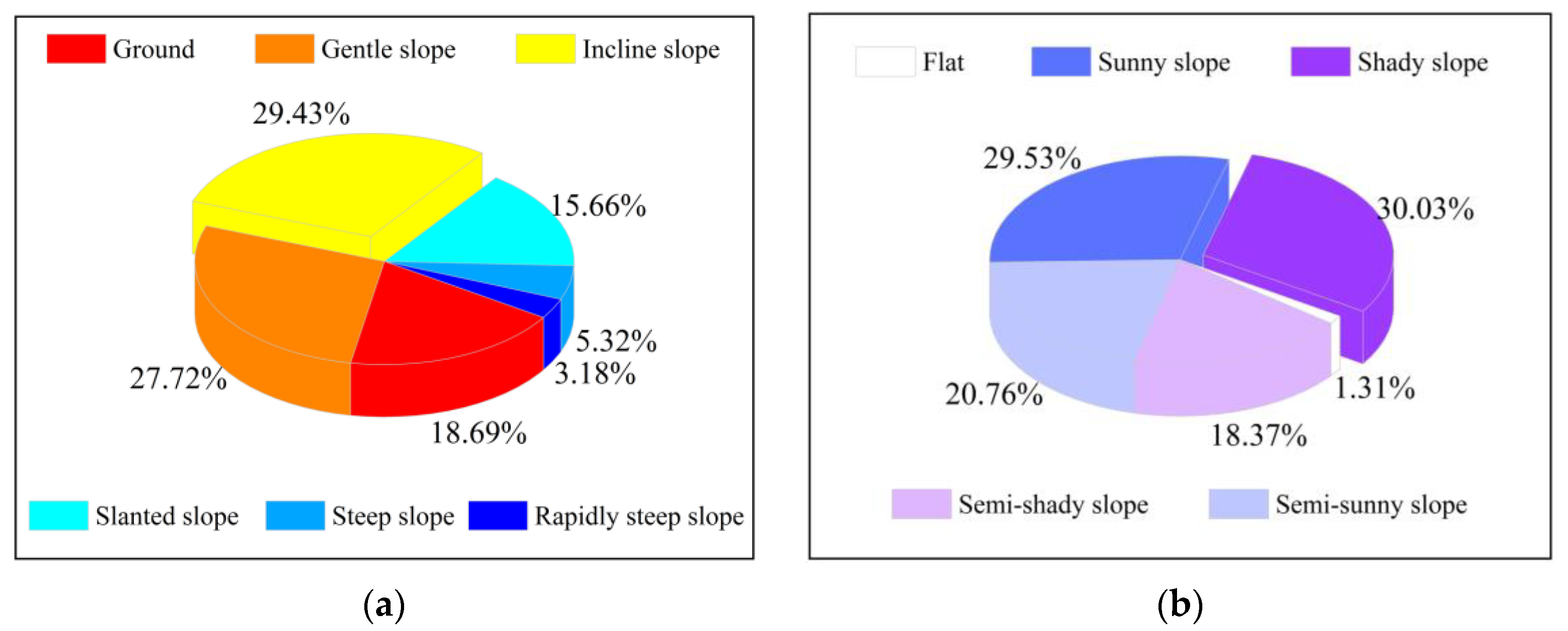
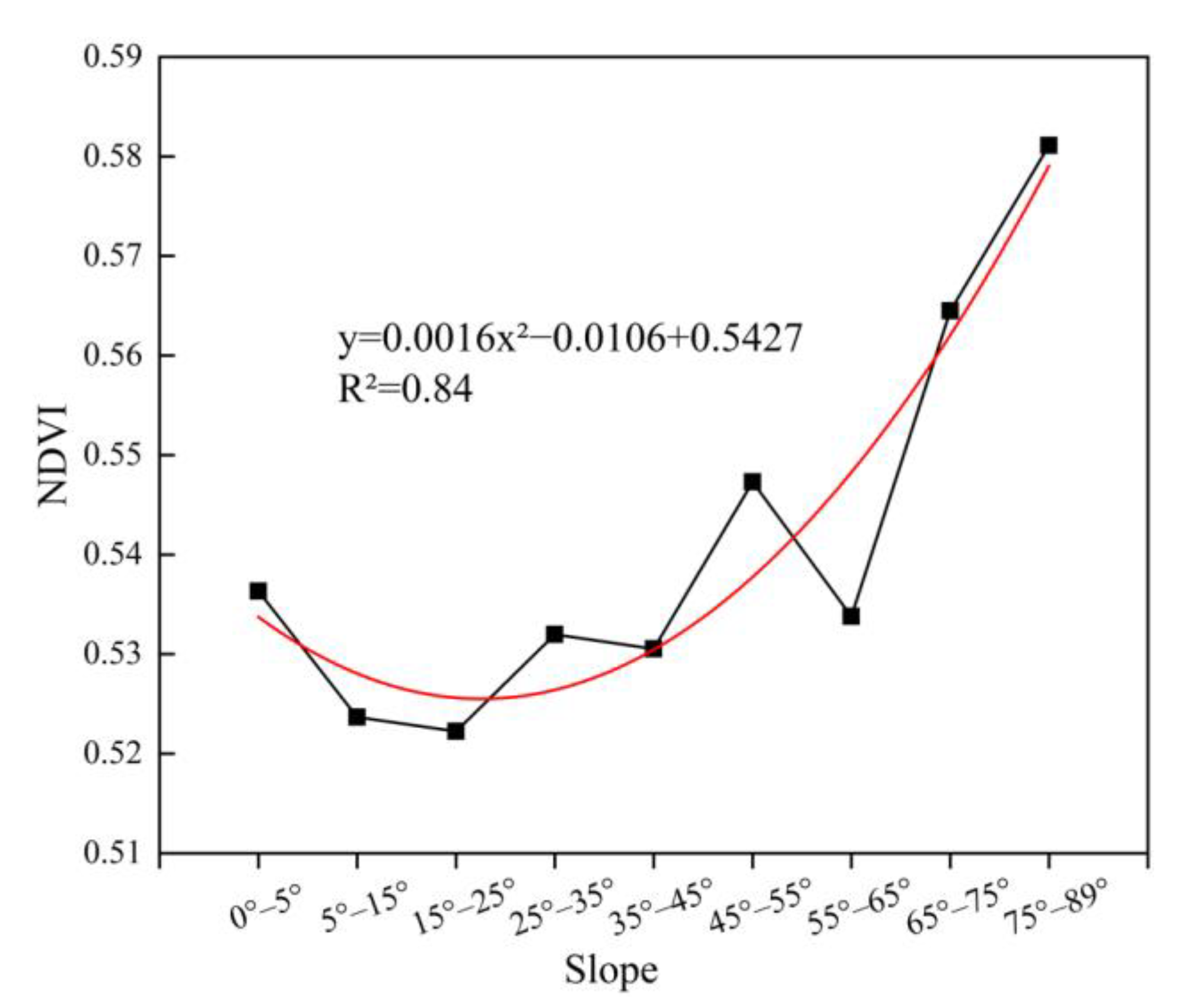
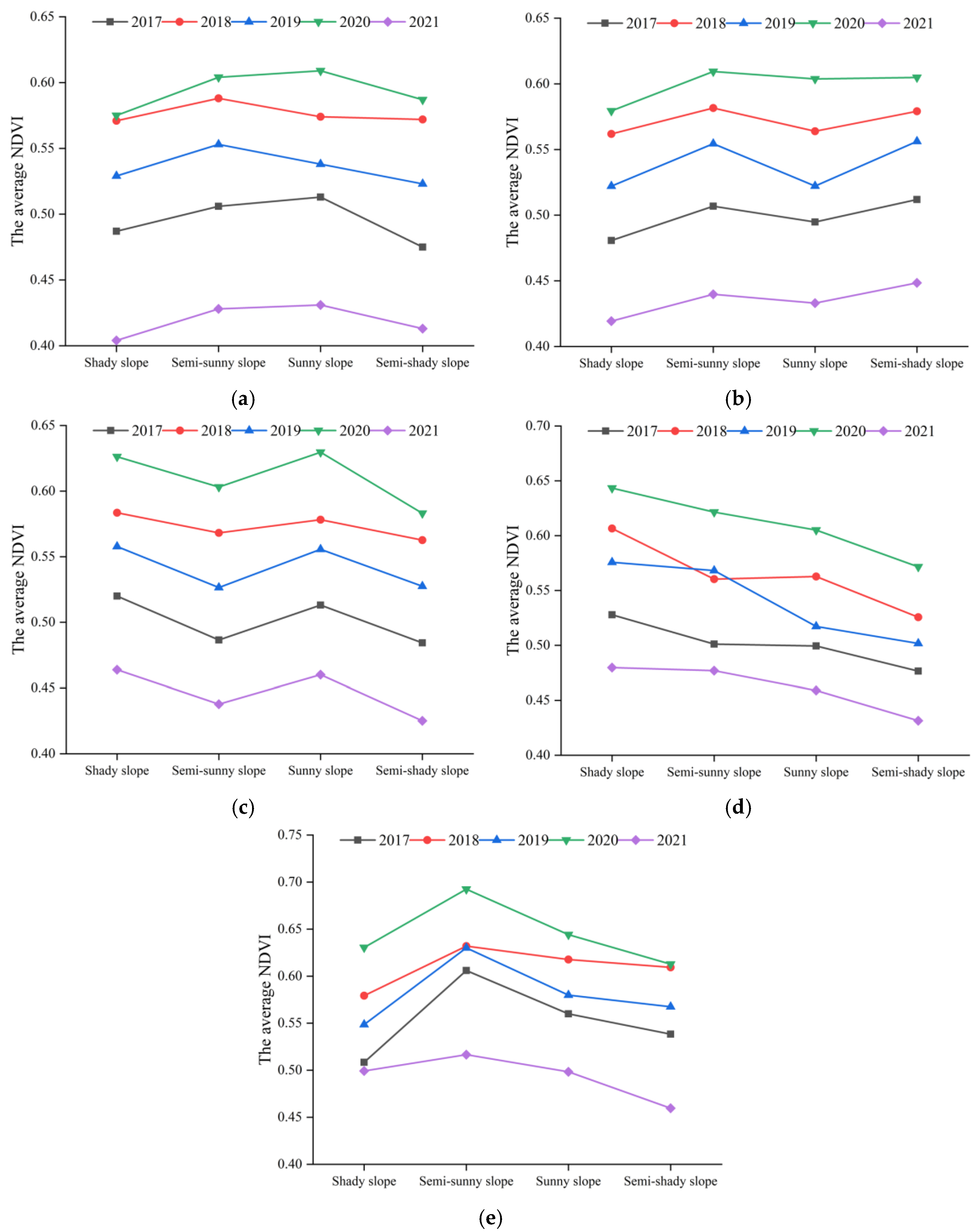
4.2. Influence of Slope on Vegetation
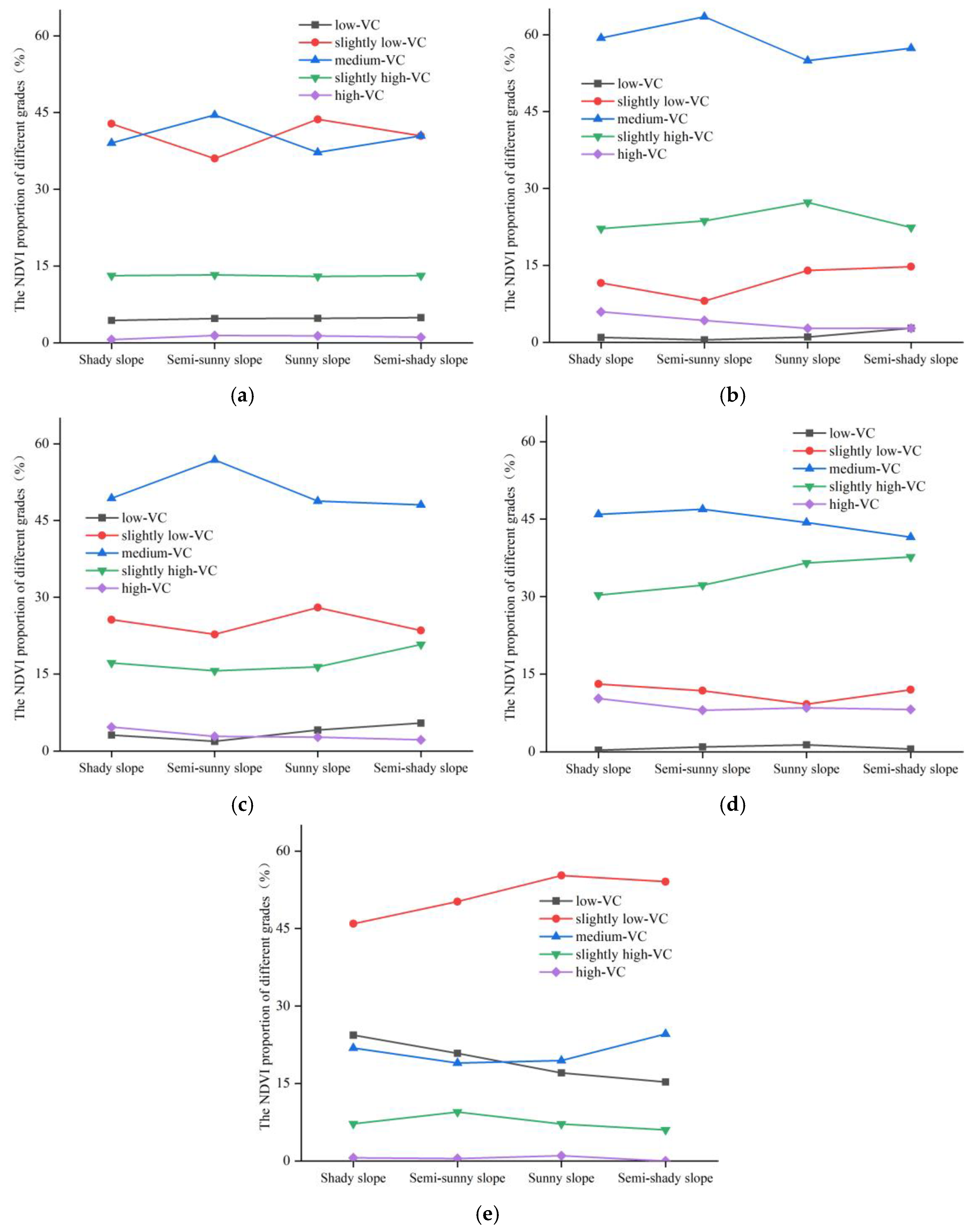
4.3. Influence of Aspect on Vegetation
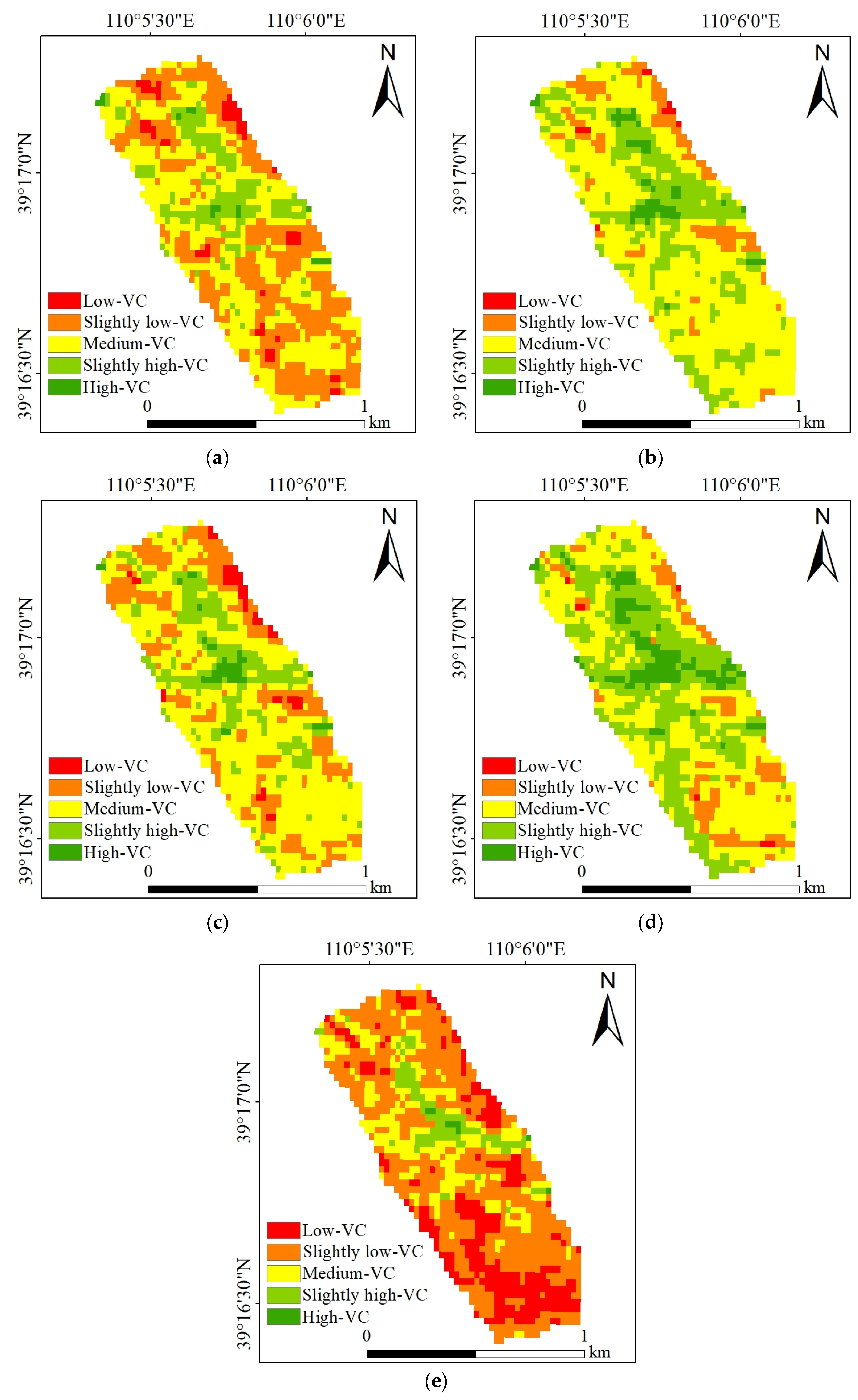
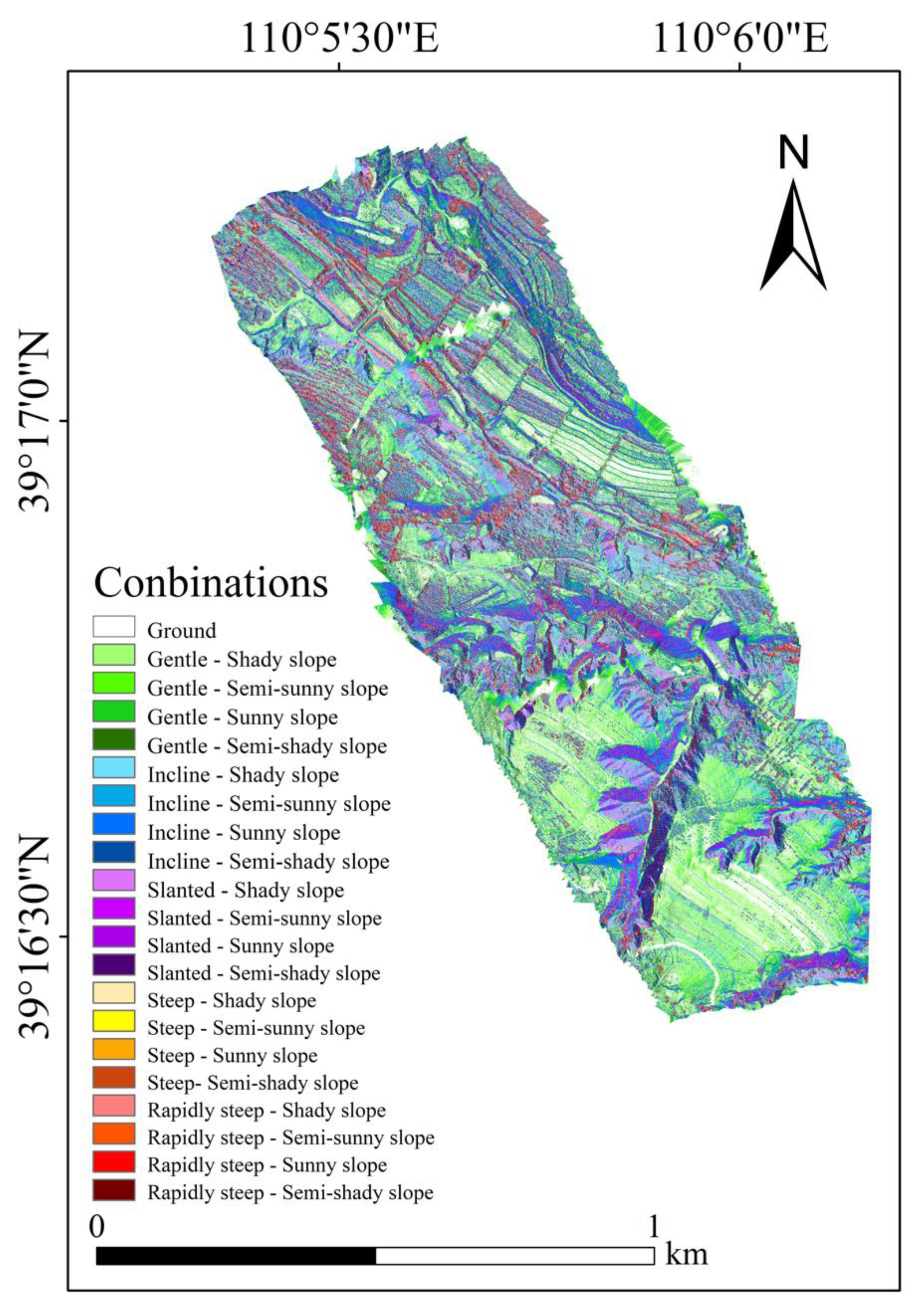
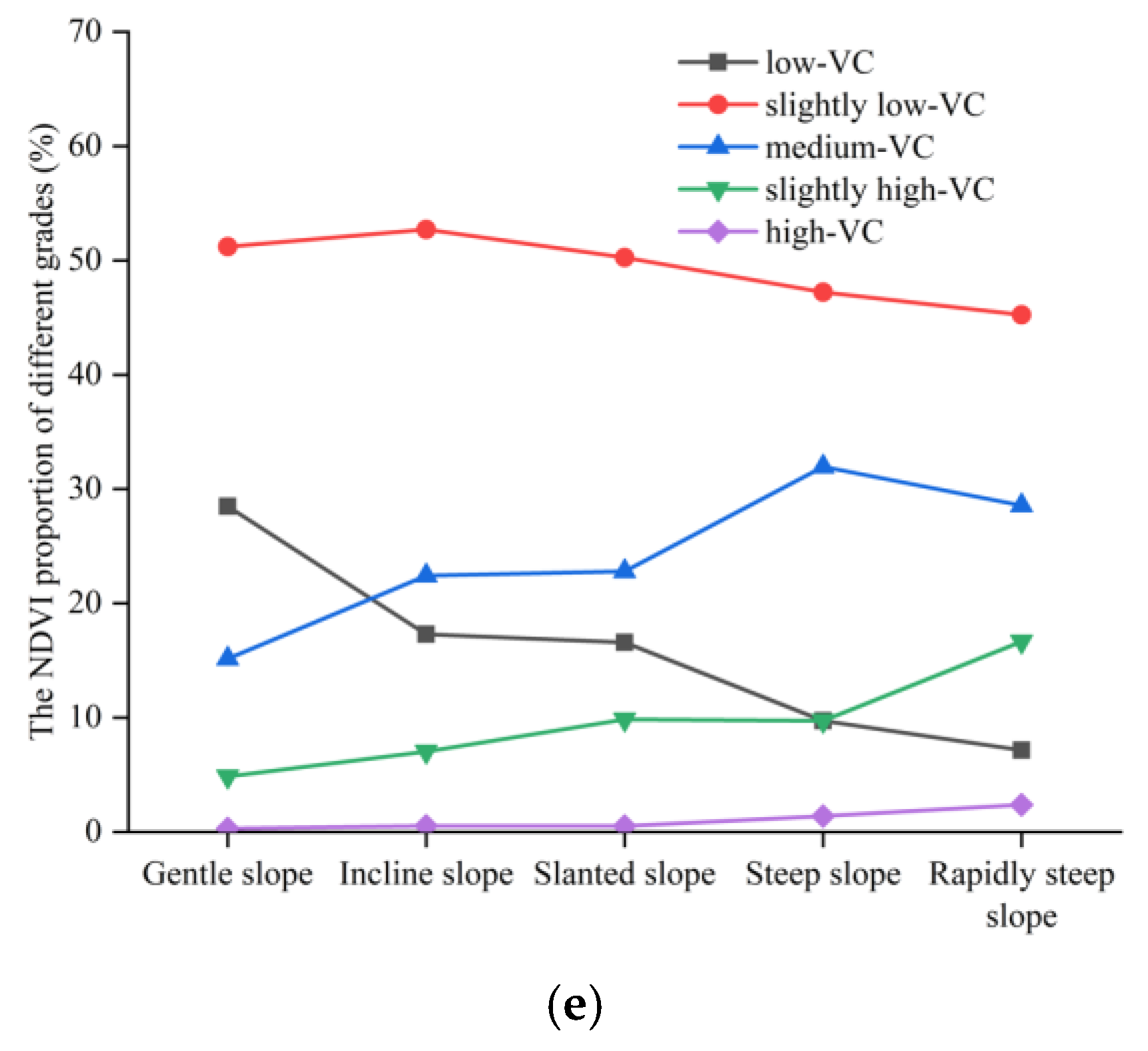
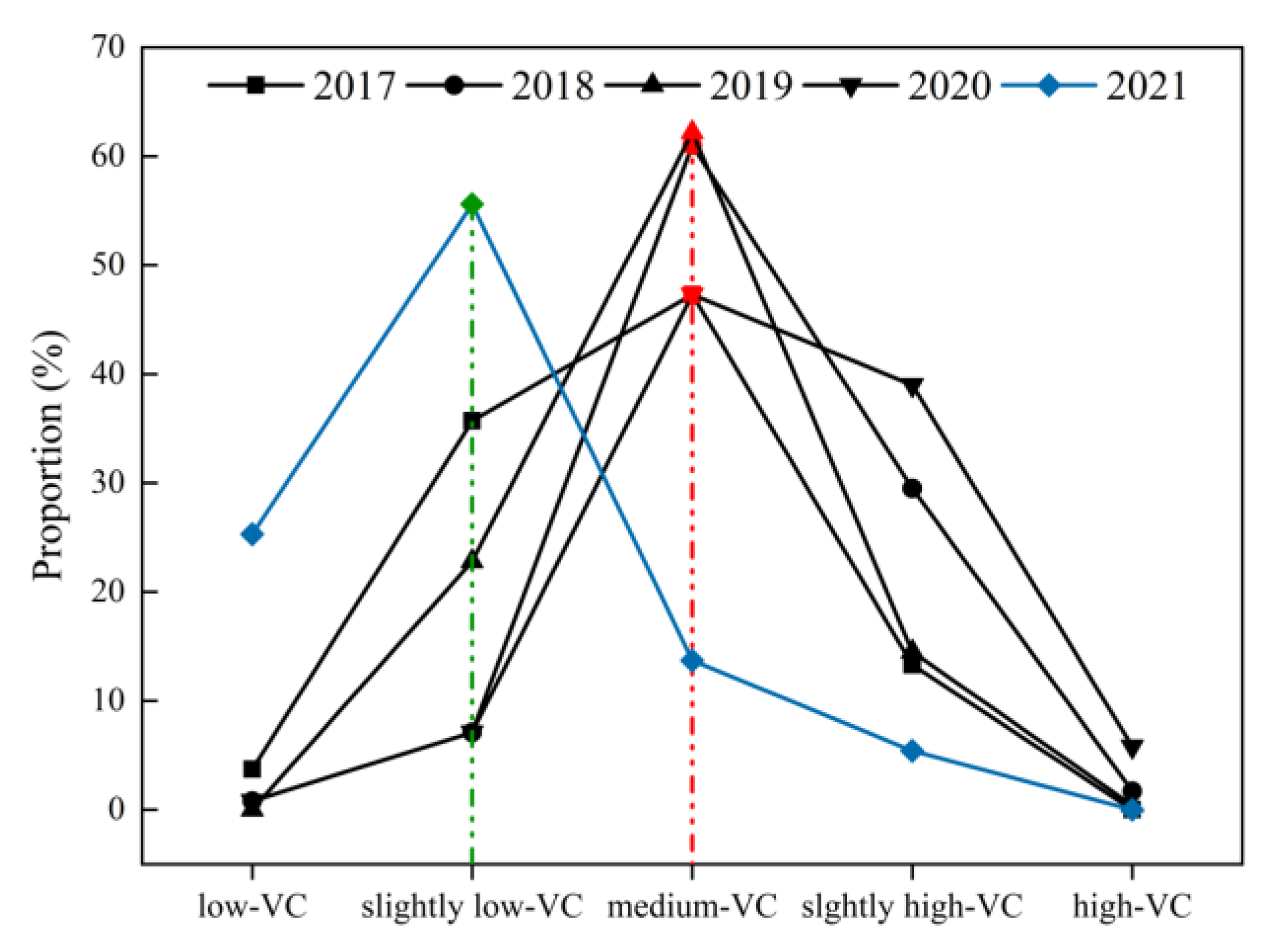
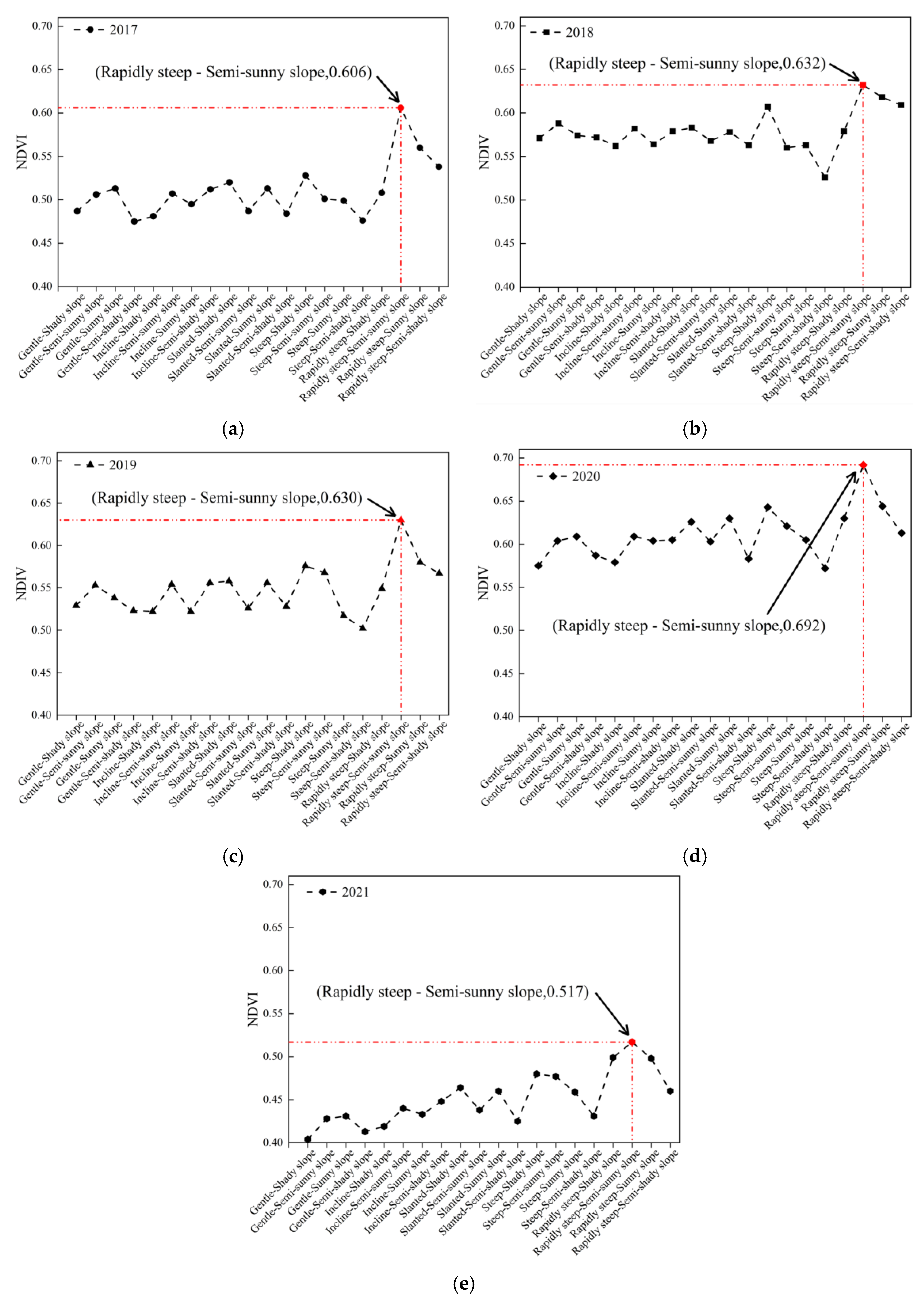
4.4. The NDVI Cover under 21 Types of Combinations
4.4.1. Vegetation Cover on “Ground”
4.4.2. Vegetation Cover under 20 Combinations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, B.; Ranjtih, P.G.; Choi, S.K.; Khandelwal, M. Geological and geotechnical aspects of underground coal mining methods within Australia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Deng, X.Y.; He, T.T.; Chen, W.Q. Mapping Annual Land Disturbance and Reclamation in a Surface Coal Mining Region Using Google Earth Engine and the LandTrendr Algorithm: A Case Study of the Shengli Coalfield in Inner Mongolia, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, K.; Wu, X.T.; Bai, L.; Zhao, J.G.; Zheng, X.H. Effects of underground coal mining on soil spatial water content distribution and plant growth type in northwest China. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18688–18698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vico, G.; Porporato, A. Probabilistic description of topographic slope and aspect. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, P.; Beven, K.; Chevallier, P.; Planchon, O. The prediction of hillslope flow paths for distributed hydrological modelling using digital terrain models. Hydrol. Process. 1991, 5, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Yan, F. Vegetation Growth Status and Topographic Effects in Frozen Soil Regions on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.R.; Zhang, W.J.; Yang, S.Q.; Zhu, M.K.; Kan, S.S.; Chen, J.; Ai, X.Y.; Ai, Y.W. Topographic aspect affects the vegetation restoration and artificial soil quality of rock-cut slopes restored by external-soil spray seeding. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.F. Derivation of leaf-area index from quality of light on the forest floor. Ecology 1969, 50, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. In Proceedings of the Third Earth Resources Technology Satellite ERTS Symposium, Volume I: Technical Presentations, NASA SP–351, Washington, DC, USA, 1 January 1974; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.R.; Liu, H.Q.; Batchily, K.; Vanleeuwen, W. A comparison of vegetation indices over a global set of TM images for EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, N.S.; Lechner, A.; Fletcher, A.; Erskine, P.; Mulligan, D.; Bai, Z.K. SPOTing long-term changes in vegetation over short-term variability. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2012, 28, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, N.S.; Li, W.W.; Gu, X.W.; Liu, Y.H. Biomass estimation for semiarid vegetation and mine rehabilitation using Worldview-3 and Sentinel-1 SAR imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.D.; Yang, X.R.; Yu, Y.J.; Shu, Y.; Che, D.F. Investigation of vegetation changes in different mining areas in Liaoning Province, China, using multisource remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Erskine, P.D.; Lechner, A.M.; Mulligan, D.; Zhang, S.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Detecting the dynamics of vegetation disturbance and recovery in surface mining area via Landsat imagery and LandTrendr algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.X.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, S.L.; An, S.; Hou, H.P.; Hua, Y.F.; Chen, F.Y. Tracking the land use/land cover change in an area with underground mining and reforestation via continuous Landsat classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, L.Z.D.; Xulu, S. Monitoring mining disturbance and restoration over RBM site in South Africa using LandTrendr algorithm and Landsat data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, T.T.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zheng, H.Y.; Guo, J.T.; Xie, H.Z.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.C. A New Method for Quantitative Analysis of Driving Factors for Vegetation Coverage Change in Mining Areas: GWDF-ANN. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zheng, H.Y.; Li, J.; Qin, T.T.; Guo, J.T.; Du, M.H. A Method for Identifying the Spatial Range of Mining Disturbance Based on Contribution Quantification and Significance Test. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Wang, H.D.; Cao, Y.G.; Bai, Z.K.; Qin, Q. Effects of soil and topographic factors on vegetation restoration in opencast coal mine dumps located in a loess area. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.H.; Cui, L.L. Vegetation dynamics in the Qinling-Daba Mountains through climate warming with Land-Use policy. Forests 2022, 13, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.L.; Wang, H.L. Spatial relationships between NDVl and topographic factors at multiple scales in a watershed of the Minjiang River, China. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 69, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhu, L.Q. Variations in growing season NDVI and its sensitivity to climate change responses to green development in mountainous areas. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 678450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokarram, M.; Sathyamoorthy, D. Relationship between landform classification and vegetation (case study: Southwest of Fars province, Iran). Open Geosci. 2016, 8, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Ali, M.Z.; Höfle, B. Multi-Parameter Relief Map from High-Resolution DEMs: A Case Study of Mudstone Badland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Dong, P.L.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Shen, J.; Liao, S.B. Geomorphic analysis of Xiadian buried fault zone in Eastern Beijing plain based on SPOT image and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) data. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayatulloh, A.; Chaabani, A.; Zhang, L.F.; Elhag, M. DEM Study on Hydrological Response in Makkah City, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.W.; Shortridge, A.; Lin, S.P.; Wu, J.P. Comparison and validation of SRTM and ASTER GDEM for a subtropical landscape in Southeastern China. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 969–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.L.; Hu, Z.Q. Land damage assessment using maize aboveground biomass estimated from unmanned aerial vehicle in high groundwater level regions affected by underground coal mining. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21666–21679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Sun, B.; Liu, S.M.; Zhang, C.; He, X.; Xu, D.; Tang, W. Identification of mining induced ground fissures using UAV and infrared thermal imager: Temperature variation and fissure evolution. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 180, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, Y. Applications of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Mining from Exploration to Reclamation: A Review. Minerals 2020, 10, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Zhou, D.D.; Hai, C.X.; Yu, Y.H.; Jun, H.; Li, B.Z. Temporal and spatial variation of vegetation in net primary productivity of the Shendong coal mining area, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.L.; Yang, Q.K.; Huang, W.D. Analysis of the spatial and temporal changes of NDVI and its driving factors in the Wei and Jing River Basins. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, S.; Latifi, H.; Khare, S. Vegetation growth analysis of UNESCO World Heritage Hyrcanian Forests using multi-sensor optical remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Y.; Xiao, X.Y.; Shang, L.X.; Huang, X. Study on spatial-temporal dynamic change of vegetation coverage and its influencing factors in blue economic zone of Shandong Peninsula: Taking Qingdao as a case. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 632, 22045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, M.; Toprak, A.; Polat, N. DEM generation with UAV Photogrammetry and accuracy analysis in Sahitler hill. Measurement 2015, 73, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidori, L.; El Hage, M. Digital Elevation Model Quality Assessment Methods: A Critical Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L. Effect of rounding off elevation values on the calculation of aspect and slope from a gridded digital elevation model. J. Spat. Sci. 2013, 58, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwandana, E.; Kawamura, K.; Sakuno, Y.; Kustiyanto, E.; Raharjo, B. Evaluation of ASTER GDEM2 in comparison with GDEM1, SRTM DEM and Topographic-Map-Derived DEM using inundation area analysis and RTK-dGPS aata. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulighe, G.; Fava, F. DEM extraction from archive aerial photos: Accuracy assessment in areas of complex topography. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 46, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Lin, Q. Effect of DEM mesh size on AnnAGNPS simulation and slope correction. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 179, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; He, L.R.; Xin, Q.; Yang, T.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S. Slope aspect affects the non-structural carbohydrates and C: N: P stoichiometry of Artemisia sacrorum on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena 2017, 152, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.M.; Dong, B.Q.; Qin, T.L.; Liu, S.S.; Zhang, J.W.; Gong, X.F. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of NDVI and its relationship with environmental factors in Huangshui River Basin from 2000 to 2018. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 3043–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Guo, J.T.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, Y.C. Unmixing the coupling influence from driving factors on vegetation changes considering spatio-temporal heterogeneity in mining areas: A case study in Xilinhot, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.L.; Yang, Q.K.; Zhang, H. Temporal and spatial variation of NDVI and its driving factors in Qinling Mountain. Water 2021, 13, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.W.; Wei, X.C.; Zhou, X.; Cai, M.Y.; Xu, Y.X. Vegetation coverage change and its response to topography in a typical karst region: The Lianjiang River Basin in Southwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Li, F.; Guo, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, C. The Synergistic Effect of Topographic Factors and Vegetation Indices on the Underground Coal Mine Utilizing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043759
Li Q, Li F, Guo J, Guo L, Wang S, Zhang Y, Li M, Zhang C. The Synergistic Effect of Topographic Factors and Vegetation Indices on the Underground Coal Mine Utilizing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043759
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Quansheng, Feiyue Li, Junting Guo, Li Guo, Shanshan Wang, Yaping Zhang, Mengyuan Li, and Chengye Zhang. 2023. "The Synergistic Effect of Topographic Factors and Vegetation Indices on the Underground Coal Mine Utilizing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043759
APA StyleLi, Q., Li, F., Guo, J., Guo, L., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Li, M., & Zhang, C. (2023). The Synergistic Effect of Topographic Factors and Vegetation Indices on the Underground Coal Mine Utilizing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043759






