Demands for Community Services and Associated Factors among Residents in Smart Communities: A Case Study of Xuzhou City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses
2.1. Different Types of Community Services in Smart Communities
2.2. Factors Influencing Residents’ Demands for Community Services in Smart Communities
2.3. Hypotheses of this Study
3. Method
3.1. Variables and Measures
- A succinct explanation of community services in smart communities and the intention of this survey;
- Respondents’ basic information;
- The measurement of respondents’ demands for community services in smart communities. The question “Are you in need of this type of community service?” was used in the measurement and residents’ responses were measured as a dichotomous variable, with 1 representing a need for this type of community service and 0 otherwise. In light of the literature review, seven categories of community services in smart communities mentioned above were chosen as outcome variables and measured through residents’ responses to the question;
- Factors influencing respondents’ demands for community services in smart communities, including respondents’ sociodemographic characteristics, living characteristics, economic characteristics, and individual attitude characteristics.
3.2. Sampling and Data Collection
3.3. Statistical Model and Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics of the Respondents
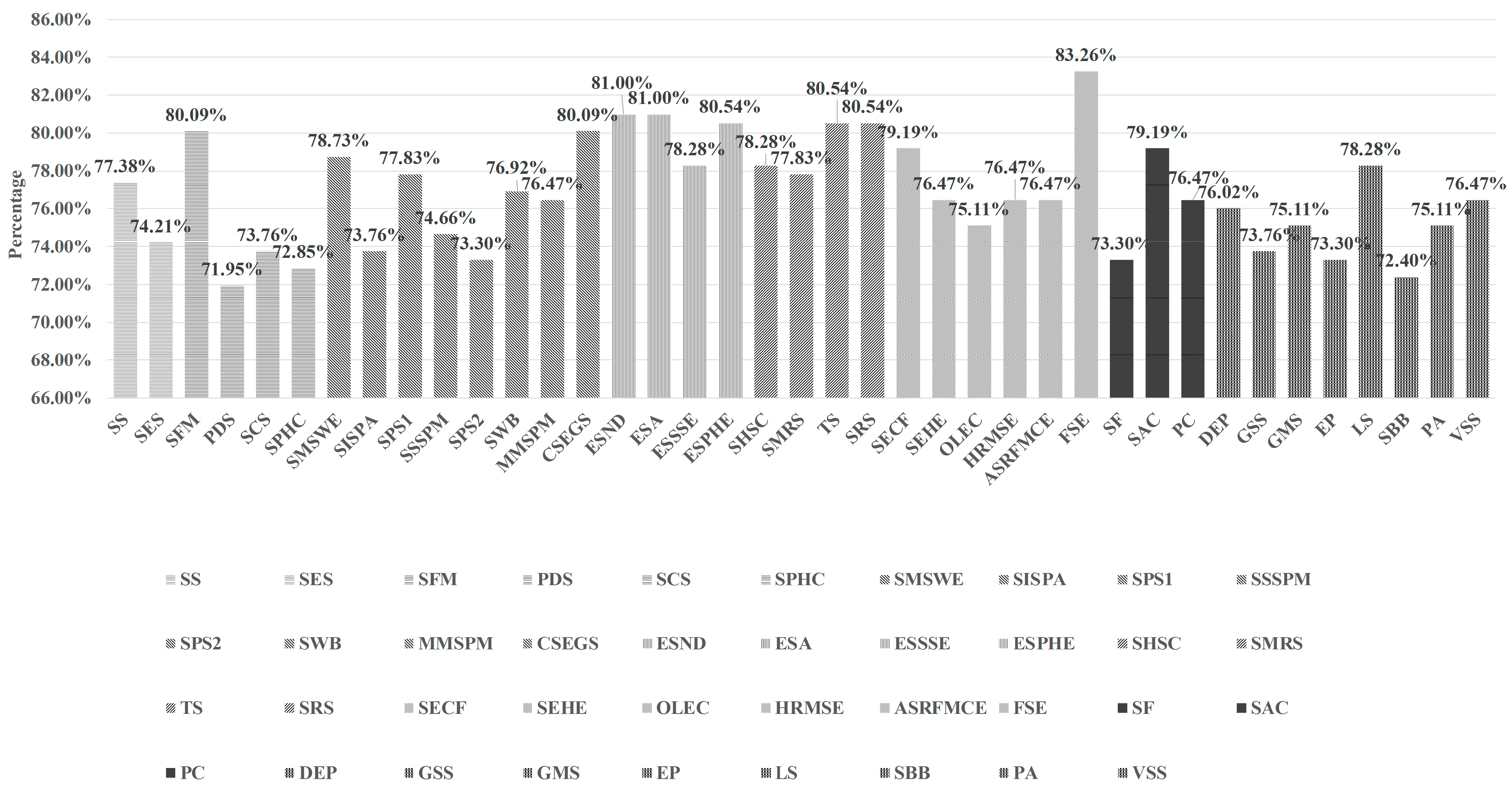
4.2. Residents’ Demands for Community Services in Smart Communities in Xuzhou
4.3. Results of the Binary Logistic Regression Test
4.3.1. Assessment of Model Fit
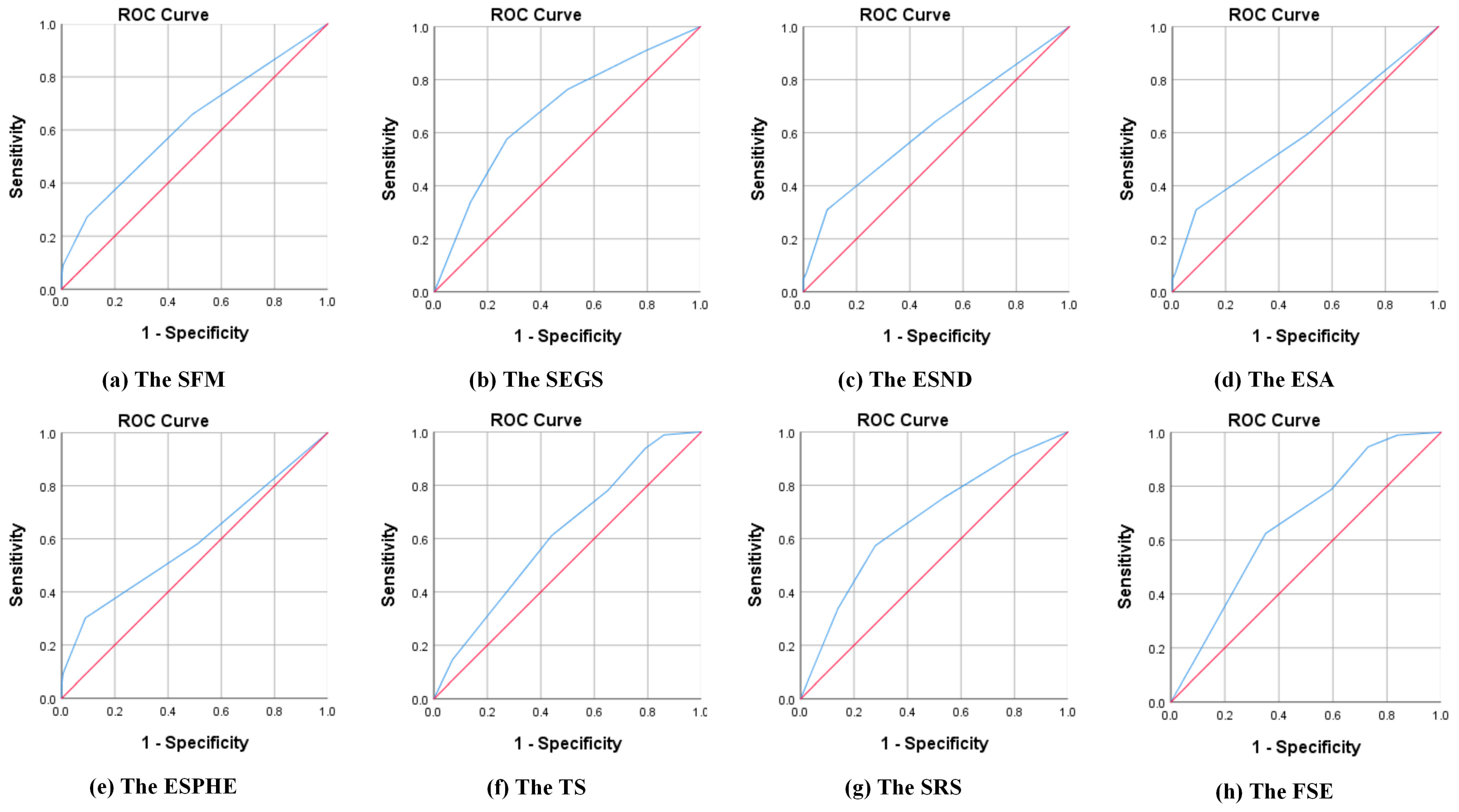
4.3.2. Validation of Predicted Probabilities
4.3.3. Explanation of Coefficients in the Binary Logistic Regression
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SS | Self-service Supermarket |
| SES | Smart E-commerce System |
| SFM | Smart Farmers Market |
| PDS | Package Delivery System |
| SCS | Smart Childcare System |
| SPHC | Service Platform for House Cleaning |
| SMSWE | Smart Management System of Water and Electricity |
| SISPA | Smart Illumination System in Public Area |
| SPS1 | Smart Parking System |
| SSSPM | Smart Security System of Property Management |
| SPS2 | Smart Payment System |
| SWB | Smart Waste Bin |
| MMSPM | Maintenance Management System of Property Management |
| CSEGS | Smart Environmental Greening System |
| ESND | Emergency System of Natural Disaster |
| ESA | Emergency System of Accident |
| ESSSE | Emergency System of Social Security Event |
| ESPHE | Emergency System of Public Health Event |
| SHSC | Smart Healthcare Service Center |
| SMRS | Smart Medical Record System |
| TS | Telemedicine System |
| SRS | Smart Referral System |
| SECF | Smart Elderly Care Facilities |
| SEHE | Smart Elderly Health Examination |
| OLEC | Online Lectures about Elderly Care |
| HRMSE | Health Record Management System of the Elderly |
| ASRFMCE | Appointment System of Regular and Free Medical Consultations for the Elderly |
| FSE | First-aid Service for the Elderly |
| SF | Smart Forum |
| SAC | Smart Activity Center |
| PC | Psychological Counseling |
| DEP | Demand Expression Platform |
| GSS | Government Service System |
| GMS | Grid Management System |
| EP | Employment Platform |
| LS | Legal Service |
| SBB | Smart Bulletin Board |
| PA | Poverty Assistance |
| VSS | Volunteer Service System |
References
- The Smart Community Construction and Operation Guide (2021) Has Been Officially Released. Available online: http://scdrc.sic.gov.cn/News/339/11118.htm (accessed on 8 May 2022). (In Chinese)
- Enayet, A.; Razzaque, M.A.; Hassan, M.M.; Alamri, A.; Fortino, G. A Mobility-Aware Optimal Resource Allocation Architecture for Big Data Task Execution on Mobile Cloud in Smart Cities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Buys, L.; Ioppolo, G.; Sabatini-Marques, J.; Da Costa, E.M.; Yun, J.J. Understanding ‘Smart Cities’: Intertwining Development Drivers with Desired Outcomes in a Multidimensional Framework. Cities 2018, 81, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhan, X. Assessment of social stability risk in the construction of lntelligent community: Based on bow-tie model and bayesian network. J. Shanghai Adm. Inst. 2019, 20, 89–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; He, R. Actors, interest interaction and integration strategy in the construction of smart community: An exploratory study based on grounded theory. J. Gansu Adm. Inst. 2019, 28, 80–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Feng, D. Research hotspot and development trend of smart community informatization construction. Inf. Sci. 2021, 39, 187–193. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Planning Was Divorced from Reality and Construction Stalled. How Can Village Planning Avoid Detours. Available online: https://www.163.com/dy/article/EKSIOC8H05149JLH.html (accessed on 13 August 2022). (In Chinese).
- Farahani, B.; Firouzi, F.; Chang, V.; Badaroglu, M.; Constant, N.; Mankodiya, K. Towards Fog-Driven Iot Ehealth: Promises and Challenges of Lot in Medicine and Healthcare. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 78, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhang, K.; Lin, X.; Shen, X.S. Securing Fog Computing for Internet of Things Applications: Challenges and Solutions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 601–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; McElhannon, J. Future Edge Cloud and Edge Computing for Internet of Things Applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.M.; Gia, T.N.; Negash, B.; Anzanpour, A.; Azimi, I.; Jiang, M.; Liljeberg, P. Exploiting Smart E-Health Gateways at the Edge of Healthcare Internet-of-Things: A Fog Computing Approach. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 78, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, A.S.; Javaid, N.; Javed, M.U.; Almogren, A.; Radwan, A. Blockchain Based Secure Energy Trading with Mutual Verifiable Fairness in a Smart Community. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefpour, A.; Fung, C.; Tam, N.; Kadiyala, K.; Jalali, F.; Niakanlahiji, A.; Kong, J.; Jue, J.P. All One Needs to Know About Fog Computing and Related Edge Computing Paradigms: A Complete Survey. J. Syst. Archit. 2019, 98, 289–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liang, F.; He, X.; Hatcher, W.G.; Lu, C.; Lin, J.; Yang, X. A Survey on the Edge Computing for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 6900–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Ning, Z.; Ngai, E.C.H.; Zhou, L.; Wei, J.; Cheng, J.; Hu, B. Energy-Latency Tradeoff for Energy-Aware Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 2633–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F. The design of rule of law need coordinate with the governance of smart communities. Frontiers 2020, 9, 100–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Qian, Z.; Huang, D.; Zheng, T. The medicine effect and smart community for triggering unknown innovation. Urban Dev. Stud. 2020, 27, 100–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. The future trend of smart community development: From design-based to life-based. Fujian Trib. 2020, 40, 92–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yao, G. Research on the driving factors of service brand value of smart communities based on WSR system methodology. Manag. Rev. 2021, 33, 174–183. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Wang, Q. Smart community: New relations between subjects and new forms of governance. E-Government 2020, 17, 121–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Han, Y. The construction and optimization of smart community in China. Leadersh. Sci. 2020, 36, 122–124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Liu, J.; Ran, X. Research on environmental evaluation of intelligent community based on multi-source big data. J. China Acad. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2021, 16, 270–276. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, Q. Research on collaborative governance mode of information system of ethnic minority smart community based on the hierarchy of needs theory. Libr. Inf. 2020, 41, 86–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Van Cutsem, O.; Dac, D.H.; Boudou, P.; Kayal, M. Cooperative Energy Management of a Community of Smart-Buildings: A Blockchain Approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 117, 105643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zou, F.; Wu, Z.; Gu, W.; Hong, Q.; Booth, C. A Smart Community Energy Management Scheme Considering User Dominated Demand Side Response and P2P Trading. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 114, 105378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Li, D.; Li, L. The Elderly’s Demand for Community-Based Care Services and its Determinants: A Comparison of the Elderly in the Affordable Housing Community and Commercial Housing Community of China. J. Healthc. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1840543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X. Construction of healthy elderly care service system from the perspective of smart community elderly care. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2018, 38, 1743–1745. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Escarce, J.J.; Wozniak, G.D.; Tsipas, S.; Pane, J.D.; Brotherton, S.E.; Yu, H. Effects of the Affordable Care Act Medicaid Expansion On the Distribution of New General Internists Across States. Med. Care 2021, 59, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Jin, C.; Xu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, B. Supply-Demand Matching of Medical Services at a City Level Under the Background of Hierarchical Diagnosis and Treatment-Based On Didi Chuxing Data in Haikou, China. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2022, 22, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, C.; Zheng, S. The Rising and Heterogeneous Demand for Urban Green Space by Chinese Urban Residents: Evidence from Beijing. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 313, 127781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Measuring Spatial Disparity in Accessibility with a Multi-Mode Method Based On Park Green Spaces Classification in Wuhan, China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 94, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Model Construction of Urban Public Sports Service System under the Background of Information Technology. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 5207857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Song, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, W.; Lo, J.T.Y.; Lo, S.M. Comparing the Impacts of Location Attributes On Residents’ Preferences and Residential Values in Compact Cities: A Case Study of Hong Kong. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wen, W.; Han, M.S. Predicting Determinants of Consumers’ Purchase Motivation for Electric Vehicles: An Application of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Model. Energy Policy 2021, 151, 112167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.; Huang, C.; Huang, M.; Chen, C.; Lin, C.; Tang, F. The Association of Sociodemographic Factors and Needs of Haemodialysis Patients According to Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. J. Clin. Nurs. 2019, 28, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.; Takashima, M.; Choi, H.H.; Yang, H.; Tung, V. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Psychological Needs of Tourists: Implications for the Travel and Tourism Industry. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2021, 38, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yuan, B.; Wang, D.; Meng, Q. Motivating Factors On Performance of Primary Care Workers in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e2861911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Guo, J. Development of Smart City Community Service Integrated Management Platform. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2019, 15, 370582068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, R.; Liang, X.; Shen, X.S.; Chen, J.; Lin, X. Smart Community: An Internet of Things Application. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2011, 49, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mital, M.; Pani, A.K.; Damodaran, S.; Ramesh, R. Cloud Based Management and Control System for Smart Communities: A Practical Case Study. Comput. Ind. 2015, 74, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Li, C. Passive Uhf-Rfid Localization Based On the Similarity Measurement of Virtual Reference Tags. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 2926–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattlegger, L. Making Food Manageable—Packaging as a Code of Practice for Work Practices at the Supermarket. J. Contemp. Ethnogr. 2021, 50, 341–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, H.; Skizim, M.; Afaneh, H.; Miele, L.; Sothern, M. Farmers’ Market Utilization among Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program Recipients in New Orleans, Louisiana: Preliminary Findings. Ethn. Dis. 2017, 271, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Huang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zheng, B.; Liu, H. Factors Affecting Smart Community Service Adoption Intention: Affective Community Commitment and Motivation Theory. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2019, 38, 1324–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P. Influencing Factors of Smart Community Service Quality: Evidence from China. Teh. Vjesn. 2021, 28, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H. Design and Implementation of Smart Community Big Data Dynamic Analysis Model Based On Logistic Regression Model. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 4038084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardini, K.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Diallo, O.; Das, A.K.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Kozlov, S.A. A Smart Waste Management Solution Geared Towards Citizens. Sensors 2020, 20, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Wan, X.; Skitmore, M.; Sun, H. An Intelligent Waste Removal System for Smarter Communities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-De-Witt, D.; Carrera, E.V.; Munoz-Romero, S.; Luis Rojo-Alvarez, J. Statistical, Spatial and Temporal Mapping of 911 Emergencies in Ecuador. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yoon, S.; Albert, L.A. An Approximate Hypercube Model for Public Service Systems with Co-Located Servers and Multiple Response. Transp. Res. Part E-Logist. Transp. Rev. 2017, 103, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitron De La Vega, P.; Losi, S.; Martinez, L.S.; Bovell-Ammon, A.; Garg, A.; James, T.; Ewen, A.M.; Stack, M.; DeCarvalho, H.; Sandel, M.; et al. Implementing an Ehr-Based Screening and Referral System to Address Social Determinants of Health in Primary Care. Med. Care 2019, 572, S133–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshmangir, L.; Bazyar, M.; Majdzadeh, R.; Takian, A. So Near, so Far: Four Decades of Health Policy Reforms in Iran, Achievements and Challenges. Arch. Iran. Med. 2019, 22, 592–605. [Google Scholar]
- Alabdulatif, A.; Khalil, I.; Forkan, A.R.M.; Atiquzzaman, M. Real-Time Secure Health Surveillance for Smarter Health Communities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahi, P.K.; Mishra, D.; Singh, T. Medical Education Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic. Indian Pediatr. 2020, 57, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, C.P.; Tempski, P.Z.; Busnardo, F.F.; Martins, M.D.A.; Gemperli, R. Online Learning and COVID-19: A Meta-Synthesis Analysis. Clinics 2020, 75, e2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyal, H.A.; Shuaib, F.; Dauda, M.; Suleiman, A.; Braka, F.; Tegegne, S.G.; Nsubuga, P.; Nomhwange, T.; Yehualashet, Y.G.; Ishaku, S.; et al. Assessment of Unmet Needs to Address Noncompliant Households during Polio Supplemental Immunization Activities in Kaduna State, 2014-2016. BMC Public Health 2018, 184, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, M.; Endo, M.; Yoshino, A. Factors Associated with Access to Health Care among Foreign Residents Living in Aichi Prefecture, Japan: Secondary Data Analysis. Int. J. Equity Health 2021, 20, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Hu, Y.; Yao, G. Smart Community Service Brand Functional Value and Sustainable Brand Relationship-the Mediating Role of Customer Emotional Cognition. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ling, W. Impact of Smart City Planning and Construction on Community Governance under Dynamic Game. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6690648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelstaedt, J.C. The Grid Management System in Contemporary China: Grass-Roots Governance in Social Surveillance and Service Provision. China Inf. 2022, 36, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, L.; Garlick, R.; Johnson, E.; Shaw, P.; Gargano, M. Linkedin(to) Job Opportunities: Experimental Evidence From Job Readiness Training. Am. Econ. J.-Appl. Econ. 2022, 14, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarie, B.; Niblett, A.; Yoon, A.H. How Artificial Intelligence Will Affect the Practice of Law. Univ. Tor. Law J. 2018, 681, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Kim, D.J. The Effect of Unmindfulness on Impulse Purchasing Behaviours in the Context of Online Shopping From a Classical Attitude Theory Perspective. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2021, 16, 3432–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olya, H.G.T.; Alipour, H.; Peyravi, B.; Dalir, S. Tourism Climate Insurance: Implications and Prospects. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2019, 24, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Ko, Y.J.; Hur, Y.; Bang, H.; Kim, T. Exploring Volunteer Engagement in a Mega Sport Events: The Role of Functional Attitudes. Eur. Sport Manag. Q. 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Yuan, J.; Li, L.; Shao, Q.; Zheng, C. Demand for Community-Based Care Services and its Influencing Factors Among the Elderly in Affordable Housing Communities: A Case Study in Nanjing City. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2020, 20, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xiao, W. The ‘Intention to Stay’ of the Floating Migrant Population: A Spatiotemporal Meta-Analysis in Chinese Cities. Popul. Space Place 2022, 28, e2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Hu, C.; Qiu, Y. Residents’ Awareness of Family Doctor Contract Services, Status of Contract with a Family Doctor, and Contract Service Needs in Zhejiang Province, China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, M. Medical Treatment Behaviour of the Elderly Population in Shanghai: Group Features and Influencing Factor Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Ariyo, T. Supply and Demand-Related Decisive Factors in the Utilization of Non-Medical Community Healthcare Services Among Elderly Chinese. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Gu, H.; Shen, T.; Feng, C. The Impact of Micro-Level Influencing Factors on Home Value: A Housing Price-Rent Comparison. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, L.; Huang, J.; Dong, Y.; Li, H. Determinants of Preference for Future Living Arrangement in Disabled Elders: A Cross-Sectional Study of Elderly Residents in Kunshan, China. Psychogeriatrics 2022, 22, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tsung, L. Learning Chinese as a Second Language in China: Positive Emotions and Enjoyment. System 2021, 96, 102410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, C.; Rau, T.; Allroggen, M. The Relationship between a Sense of Security and Psychological Problems in Adolescents Living in Boarding Schools and Youth-Welfare Institutions. Z. Kinder Jugendpsychiatr. Psychother. 2018, 46, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, D.; Kaciak, E.; Thongpapanl, N. Happy at Home, Successful in Competition: The Beneficial Role of Happiness and Entrepreneurial Orientation for Women Entrepreneurs. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2022, 28, 1463–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, K.E.; Robinson, S.R.; Schrag, R.V. Facilitators of Formal Help-Seeking for Adult Survivors of Ipv in the United States: A Systematic Review. Trauma Violence Abus. 2021, 23, 1420–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Approval of the Ministry of Civil Affairs on the Recognition of Beijing Shijingshan District and Other Units as the National Community Governance and Service Innovation Experimental Zones. Available online: http://www.mca.gov.cn/article/gk/wj/201904/20190400016136.shtml (accessed on 6 May 2022). (In Chinese)
- “Smart Community 2.0 Platform” Was Officially Launched in Gulou District, Xuzhou City. Available online: http://mzt.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2020/11/20/art_54981_9581601.html (accessed on 5 May 2022). (In Chinese)
- Notice of the Ministry of Civil Affairs on Confirming the Evaluation Results of the National Community Governance and Service Innovation Experimental Zones. Available online: http://www.mca.gov.cn/article/wh/whbq/jsmlsq/cssqzl/202112/20211200038387.shtml (accessed on 6 May 2022). (In Chinese)
- The “Gulou Path” of Smart Community Governance and Service Innovation in Xuzhou. Available online: http://mz.xz.gov.cn/001/001004/20220127/849d3ed2-b53f-4cfe-aa1f-fba5720498bf.html (accessed on 11 October 2022). (In Chinese)
- Jacquerioz, F.; Baggio, S.; Gayet-Ageron, A.; Chappuis, F.; Getaz, L.; Guessous, I.; Kaiser, L.; Vernaz, N.; Yerly, S.; Salamun, J.; et al. Development and Validation of the Outcov Score to Predict the Risk of Hospitalisation Among Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Ambulatory Settings: A Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e44242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courvoisier, D.S.; Combescure, C.; Agoritsas, T.; Gayet-Ageron, A.; Perneger, T.V. Performance of Logistic Regression Modeling: Beyond the Number of Events per Variable, the Role of Data Structure. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittinghoff, E.; McCulloch, C.E. Relaxing the Rule of Ten Events Per Variable in Logistic and Cox Regression. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 165, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, K.J.; Lee, C.; Choi, Y.J.; Han, S. Analysis of Three-Dimensional Imaging Findings and Clinical Symptoms in Patients with Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Beasley, M.; Hatton, N.; Dickinson, P.; Franks, K.; Clarke, K.; Jain, P.; Teo, M.; Murray, P.; Lilley, J. Clinical and Dosimetric Predictors of Radiation Pneumonitis in Early-Stage Lung Cancer Treated with Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (Sabr)—An Analysis of Uk’s Largest Cohort of Lung Sabr Patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 156, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, T.; Han, M.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Diagnostic Utility of Clinical Laboratory Data Determinations for Patients with the Severe COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenssle, H.A.; Fink, C.; Schneiderbauer, R.; Toberer, F.; Buhl, T.; Blum, A.; Kalloo, A.; Hassens, A.B.H.; Thomas, L.; Enk, A.; et al. Man Against Machine: Diagnostic Performance of a Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Network for Dermoscopic Melanoma Recognition in Comparison to 58 Dermatologists. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, L.; Jiang, W.; Fan, G. Effect of Nursing Intervention Based On Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease Interventional Surgery. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 10189–10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Kang, Y.; Lin, C.; Cheng, C.; Suk, F.; Chen, H.; Hsu, C.; Fong, T.; Huang, W. Why Do Pre-Clinical Medical Students Learn Ultrasound? Exploring Learning Motivation through Erg Theory. BMC Med. Educ. 2021, 21, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, R.; De Simone, S.; Vargas, M.; Franco, M. The Other Side of the Crisis: Organizational Flexibility in Balancing COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Health-Care Services. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2022, 22, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, A.D. The Willingness to Receive COVID-19 Vaccine and its Associated Factors: "Vaccination Refusal Could Prolong the War of this Pandemic" a Systematic Review. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2021, 14, 2609–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, L.; Guo, R.; Wang, H.; Cao, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. The Influence of Patient and Hospital Characteristics on Inpatient Satisfaction at Beijing District-Level Hospitals. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2021, 15, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Zhang, S.; Deng, Y.; Liu, F.; Shi, W.; Xie, H.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, J. Willingness-to-Pay and Benefit-Cost Analysis of Ipl for Rosacea Treatment: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2020, 14, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hounsome, N.; Kassahun, M.M.; Ngari, M.; Berkley, J.A.; Kivaya, E.; Njuguna, P.; Fegan, G.; Tamiru, A.; Kelemework, A.; Amberbir, T.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness and Social Outcomes of a Community-Based Treatment for Podoconiosis Lymphoedema in the East Gojjam Zone, Ethiopia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e778010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Lan, C.E. Impacts of Skin Disorders Associated with Facial Discoloration On Quality of Life: Novel Insights Explaining Discordance Between Life Quality Scores and Willingness to Pay. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3053–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goeb, J.; Dillon, A.; Lupi, F.; Tschirley, D. Pesticides: What You Don’t Know Can Hurt You. J. Assoc. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2020, 7, 801–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Henneberry, S.R.; Sun, C.; Nayga, R.M., Jr. Consumer Demand for Genetically Modified Rice in Urban China. J. Agric. Econ. 2018, 69, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan-Pettes, S.R.; Lange, L.L.; Magnuson, K.I. Mobile Phone Access and Preference for Technology-Assisted Aftercare among Low-Income Caregivers of Teens Enrolled in Outpatient Substance Use Treatment: Questionnaire Study. Jmir Mhealth Uhealth 2019, 7, e124079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Ko, J. Factors Associated with Commuter Satisfaction Across Travel Time Ranges. Transp. Res. Part F-Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2019, 66, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mion, S.; Duval, B.; Besnard, T.; Darne, B.; Mouton, C.; Jecker, O.; Labrousse, L.; Remy, A.; Zaouter, C.; Ouattara, A. U-Shaped Relationship Between Pre-Operative Plasma Fibrinogen Levels and Severe Peri-Operative Bleeding in Cardiac Surgery. Eur. J. Anaesth. 2020, 37, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Category | Type | Researchers |
|---|---|---|
| Smart business service | 1. Self-service Supermarket (SS) | [41,42] |
| 2. Smart E-commerce System (SES) | [38] | |
| 3. Smart Farmers Market (SFM) | [43] | |
| 4. Package Delivery System (PDS) | [38] | |
| 5. Smart Childcare System (SCS) | [39] | |
| 6. Service Platform for House Cleaning (SPHC) | [38,40] | |
| Smart property service | 1. Smart Management System of Water and Electricity (SMSWE) | [38,40] |
| 2. Smart Illumination System in Public Area (SISPA) | [38] | |
| 3. Smart Parking System (SPS1) | [38,40] | |
| 4. Smart Security System of Property Management (SSSPM) | [38,39,40,46] | |
| 5. Smart Payment System (SPS2) | [40,44] | |
| 6. Smart Waste Bin (SWB) | [47,48] | |
| 7. Maintenance Management System of Property Management (CMMSPM) | [40] | |
| 8. Smart Environmental Greening System (SEGS) | [39,40,45] | |
| Smart emergency service | 1. Emergency System of Natural Disaster (ESND) | [38,39,45,46] |
| 2. Emergency System of Accident (ESA) | [38,45,46] | |
| 3. Emergency System of Social Security Event (ESSSE) | [49,50] | |
| 4. Emergency System of Public Health Event (ESPHE) | [39] | |
| Smart medical care service | 1. Smart Healthcare Service Center (SHSC) | [45] |
| 2. Smart Medical Record System (SMRS) | [38] | |
| 3. Telemedicine System (TS) | [38] | |
| 4. Smart Referral System (SRS) | [51,52] | |
| Smart elderly care service | 1. Smart Elderly Care Facilities (SECF) | [38,53] |
| 2. Smart Elderly Health Examination (SEHE) | [38] | |
| 3. Online Lectures about Elderly Care (OLEC) | [54,55] | |
| 4. Health Record Management System of the Elderly (HRMSE) | [38] | |
| 5. Appointment System of Regular and Free Medical Consultations for the Elderly (ASRFMCE) | [56,57] | |
| 6. First-aid Service for the Elderly (FSE) | [39] | |
| Smart communication service | 1. Smart Forum (SF) | [39,40,58] |
| 2. Smart Activity Center (SAC) | [39,40,58] | |
| 3. Psychological Counseling (PC) | [45] | |
| Smart government service | 1. Demand Expression Platform (DEP) | [40,58] |
| 2. Government Service System (GSS) | [44] | |
| 3. Grid Management System (GMS) | [60] | |
| 4. Employment Platform (EP) | [61] | |
| 5. Legal Service (LS) | [62] | |
| 6. Smart Bulletin Board (SBB) | [40,44] | |
| 7. Poverty Assistance (PA) | [40] | |
| 8. Volunteer Service System (VSS) | [59] |
| Category | Type | Researchers |
|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic characteristics | 1. Gender | [26,67,70] |
| 2. Age | [26,68,69] | |
| 3. Career | [66] | |
| 4. Educational level | [26,66,67,68,69] | |
| 5. Marital status | [68,69] | |
| 6. Health status | [26,66,69,70] | |
| Living characteristics | 1. Living duration | [67] |
| 2. Living status | [26,69] | |
| 3. Housing choice | [71] | |
| Economic characteristics | 1. Monthly income | [26,67,68,69,70] |
| 2. Whether paying social insurance | [69,72] | |
| Individual attitude characteristics | 1. Sense of gain | [73] |
| 2. Sense of safety | [74] | |
| 3. Sense of happiness | [75] | |
| 4. Perception of community services | [70] | |
| 5. Desire for smart community services | [76] |
| Category | Type | Option | Frequency | Percentage (N = 221) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic characteristics | Gender | Male | 109 | 49.32% |
| Female | 112 | 50.68% | ||
| Age | 17 years old and below | 13 | 5.88% | |
| 18–35 years old | 109 | 49.32% | ||
| 36–45 years old | 41 | 18.55% | ||
| 46–69 years old | 58 | 26.24% | ||
| 70 years old and above | 0 | 0.00% | ||
| Career | Civil servant | 14 | 6.33% | |
| Staff of state-owned enterprises and institutions | 62 | 28.05% | ||
| Staff of private and foreign enterprises and institutions | 56 | 25.34% | ||
| Individual industrial and commercial household | 15 | 6.79% | ||
| Freelancer | 21 | 9.50% | ||
| Student | 41 | 18.55% | ||
| Other | 12 | 5.43% | ||
| Educational level | Primary school or below | 8 | 3.62% | |
| Middle school | 12 | 5.43% | ||
| High school and technical secondary school | 34 | 15.38% | ||
| Junior college | 39 | 17.65% | ||
| Bachelor’s degree | 99 | 44.80% | ||
| Master’s degree or above | 29 | 13.12% | ||
| Marital status | Married | 157 | 71.04% | |
| Unmarried | 64 | 28.96% | ||
| Health status | Good | 195 | 88.24% | |
| General | 25 | 11.31% | ||
| Bad | 1 | 0.45% | ||
| Living characteristics | Living duration | Less than 1 year | 23 | 10.41% |
| 1 to 3 years | 44 | 19.91% | ||
| More than 3 years | 154 | 69.68% | ||
| Living status | Living alone | 14 | 6.33% | |
| Not living alone | 207 | 93.67% | ||
| Housing choice | Renter | 28 | 12.67% | |
| House owner | 171 | 77.38% | ||
| Other | 22 | 9.95% | ||
| Economic characteristics | Monthly income | Within 1000 RMB (about 146.69 USD) | 25 | 11.31% |
| 1000–3000 RMB (about 146.69–440.09 USD) | 39 | 17.65% | ||
| 3000–5000 RMB (about 440.09–733.54 USD) | 43 | 19.46% | ||
| 5000–7000 RMB (about 733.54–1026.92 USD) | 48 | 21.72% | ||
| Above 7000 RMB (about 1026.92 USD) | 66 | 29.86% | ||
| Whether paying social insurance | All | 147 | 66.52% | |
| Partly (e.g., only medical insurance) | 50 | 22.62% | ||
| Not at all | 24 | 10.86% | ||
| Individual attitude characteristics | Sense of gain | Mean score of sense of gain | 3.95 | |
| Sense of safety | Mean score of sense of safety | 4.09 | ||
| Sense of happiness | Mean score of sense of happiness | 3.97 | ||
| Perception of community services | Mean score of perception of community services | 3.37 | ||
| Desire for smart community services | Mean score of desire for smart community services | 4.31 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Gu, T.; Wang, C.; Hao, E. Demands for Community Services and Associated Factors among Residents in Smart Communities: A Case Study of Xuzhou City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043750
Chen J, Wang L, Gu T, Wang C, Hao E. Demands for Community Services and Associated Factors among Residents in Smart Communities: A Case Study of Xuzhou City. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043750
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiongxun, Linxiu Wang, Tiantian Gu, Chenyang Wang, and Enyang Hao. 2023. "Demands for Community Services and Associated Factors among Residents in Smart Communities: A Case Study of Xuzhou City" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043750
APA StyleChen, J., Wang, L., Gu, T., Wang, C., & Hao, E. (2023). Demands for Community Services and Associated Factors among Residents in Smart Communities: A Case Study of Xuzhou City. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043750







