Evaluation and Optimization of Cultural Perception of Coastal Greenway Landscape Based on Structural Equation Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
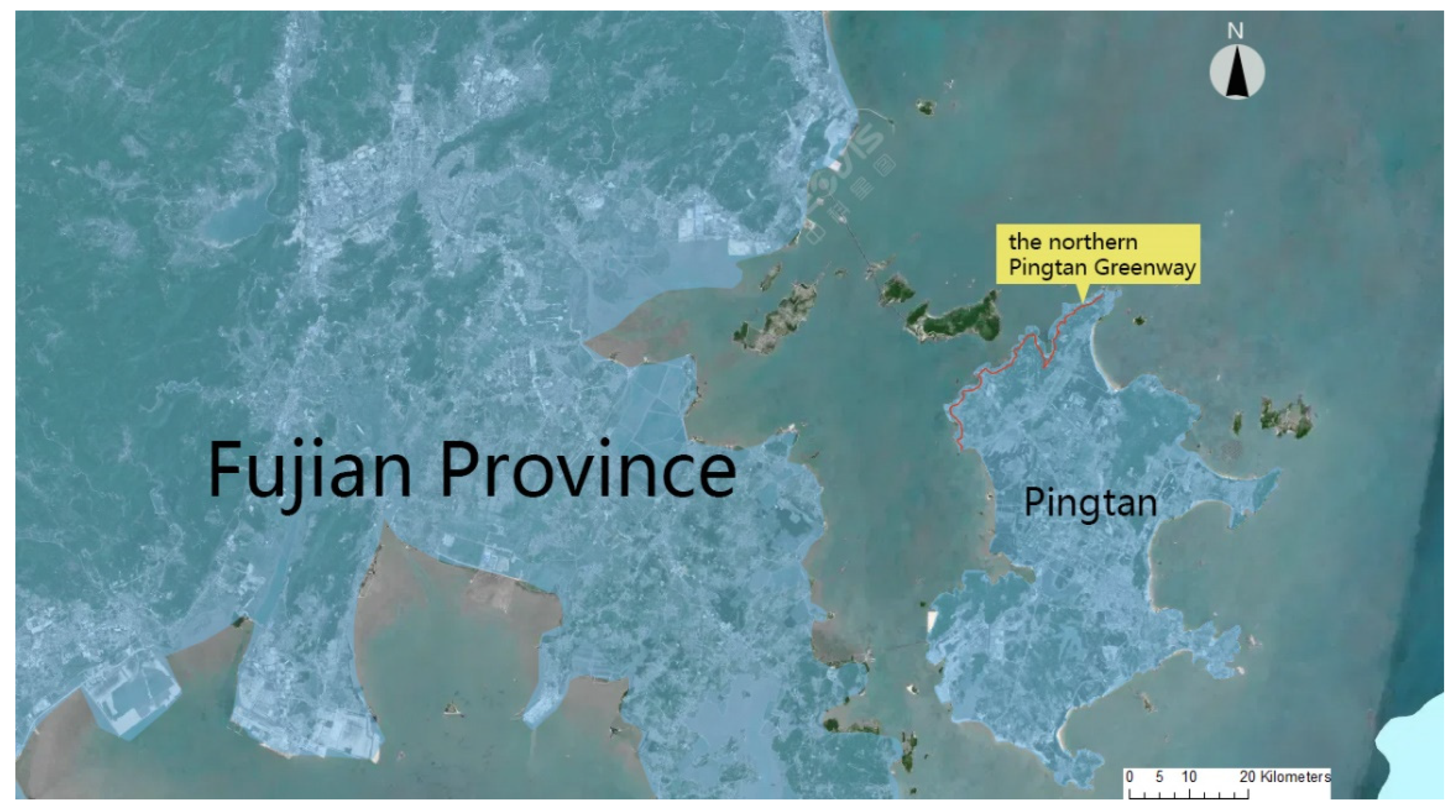
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Structural Equation Modeling
2.2.1. Influence Factors
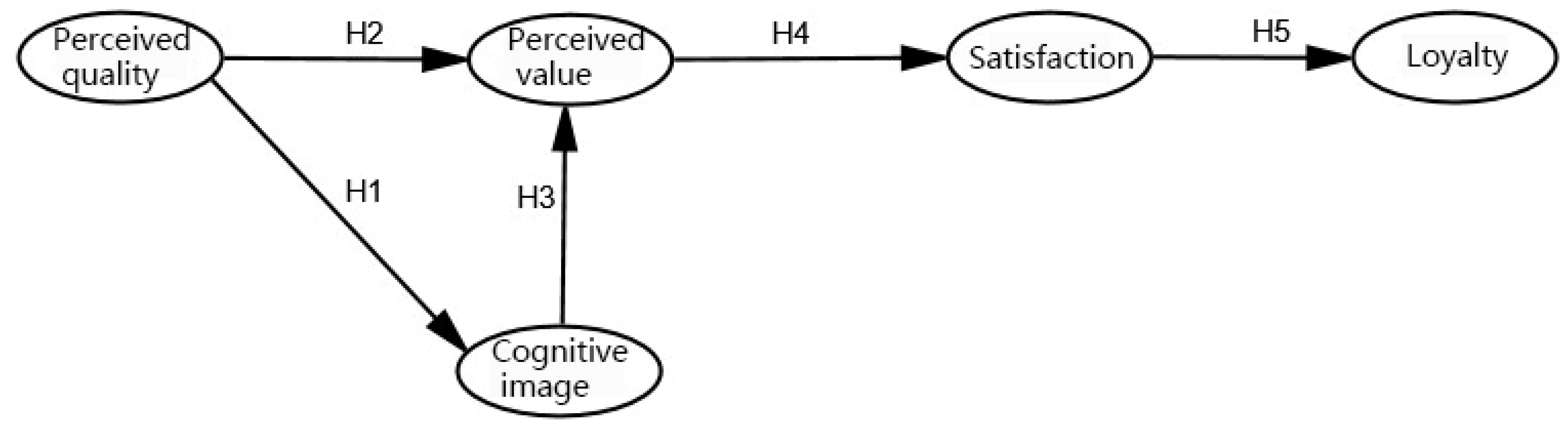
2.2.2. Cultural Experience Satisfaction Model
2.3. Questionnaire Design
2.4. Questionnaire Survey
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Effect of Demographic Characteristics on Perceived Cultural Quality
3.2.1. Gender Factor
3.2.2. Age Factor
3.2.3. Education Factor
3.3. Measurement Model Analysis
3.3.1. Reliability and Validity Analysis
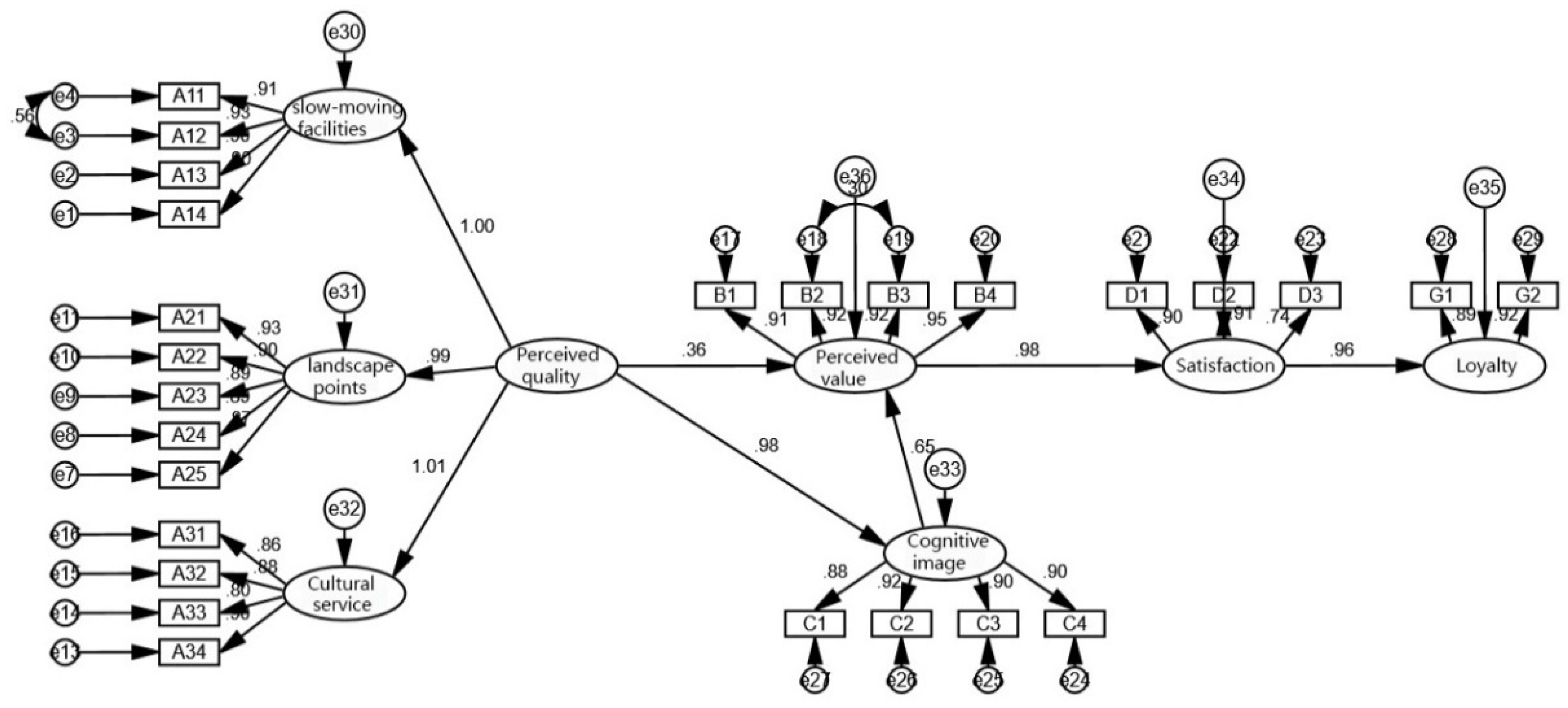
3.3.2. Structural Equation Model Goodness-of-Fit Analysis
3.3.3. Path Hypothesis Testing
4. Discussion
4.1. Perceived Quality, Perceived Value and Cognitive Image
4.2. Perceived Value, Satisfaction and Loyalty
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurdoglu, O.; Kurdoglu, B.C. Determining Recreational, Scenic, and Historical-Cultural Potentials of Landscape Features along a Segment of the Ancient Silk Road Using Factor Analyzing. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabos, J.G. Greenway Planning in the United States: Its Origins and Recent Case Studies. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, A. Greenways as Vehicles for Expression. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1995, 33, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buergi, M.; Verburg, P.H.; Kuemmerle, T.; Plieninger, T. Analyzing Dynamics and Values of Cultural Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 2077–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, T.; de Aguiar, F.B.; Curado, M.J. The Alto Douro Wine Region Greenway. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A. Urban Greenways: Operationalizing Design Syntax and Integrating Mathematics and Science in Design. Front. Archit. Res. 2015, 4, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, S.J.; Larson, L.R.; Shafer, C.S.; Hallo, J.C.; Fernandez, M. Greenway Use and Preferences in Diverse Urban Communities: Implications for Trail Design and Management. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 172, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppido, S.; Ragozino, S. Abandoned Railways, Renewed Pathways: Opportunities for Accessing Landscapes. In New Metropolitan Perspectives: The Integrated Approach of Urban Sustainable Development; Bevilacqua, C., Calabro, F., Spina, L.D., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 11, pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toccolini, A.; Fumagalli, N.; Senes, G. Greenways Planning in Italy: The Lambro River Valley Greenways System. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 76, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowarik, I. The “Green Belt Berlin”: Establishing a Greenway Where the Berlin Wall Once Stood by Integrating Ecological, Social and Cultural Approaches. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 184, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppert, M.; Bahn, B.; Bergmeier, E.; Deutsch, M.; Epperlein, K.; Hallmann, C.; Mueller, A.; Platz, T.V.; Reeh, T.; Stueck, H.; et al. The Saale-Unstrut Cultural Landscape Corridor. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, C.R.; Chen, M.; Chen, P.C. Rural Greenway Planning and Design Based on Maximizing the Value of Native Resources--Taking the Ten-Mile Fruit Corridor Greenway in Jiangjia Town as an Example. China Gard. 2020, 36, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunel, M.C.; Erkut, B. Cultural Tourism in Istanbul: The Mediation Effect of Tourist Experience and Satisfaction on the Relationship between Involvement and Recommendation Intention. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2015, 4, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lin, B.; Chen, W. Research on the Perception of Red Cultural Landscape Based on Structural Equation Model. China Gard. 2022, 38, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultman, M.; Skarmeas, D.; Oghazi, P.; Beheshti, H.M. Achieving Tourist Loyalty Through Destination Personality, Satisfaction, and Identification. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 2227–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.C.; Xie, P.F.; Tsai, M.C. Perceptions of Attractiveness for Salt Heritage Tourism: A Tourist Perspective. Tour. Manag. 2015, 51, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramseook-Munhurrun, P.; Seebaluck, V.N.; Naidoo, P. Examining the Structural Relationships of Destination Image, Perceived Value, Tourist Satisfaction and Loyalty: Case of Mauritius. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 175, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.; Chen, S.-H.; Lee, H.-T.; Tsai, T.-H. Exploring Destination Resources and Competitiveness–A Comparative Analysis of Tourists’ Perceptions and Satisfaction Toward an Island of Taiwan. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2016, 119, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, R. Cultural Tourism in Small-Island States: Contradictions and Ambiguities. In Island Tourism and Sustainable Development; Praeger Publishers: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, W.S.; Ding, Z.Y. Product Development of Coastal Greenway Tourism. Tour. Overv. (Second Half Mon.) 2013, 16, 153–155. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, C. Study on the Optimization Strategy of Coastal Mountain Greenway Based on the Concept of Urban Double Repair; Dalian University of Technology: Dalian, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.F.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.F. A Preliminary Study on the Construction of Tourism-Oriented Island Greenway Network. Art Des. 2018, 2, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.F. Planning and design of Pingtan Northern Greenway. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2019, 19, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.C.; Tian, M. Landscape Design of Historical and Cultural Park from the Perspective of Cultural Perception--Tan Lun’s Tomb Historical and Cultural Park Landscape Design as an Example. Archit. Cult. 2021, 3, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martin, M.; Fagerholm, N.; Bieling, C.; Gounaridis, D.; Kizos, T.; Printsmann, A.; Muller, M.; Lieskovsky, J.; Plieninger, T. Participatory Mapping of Landscape Values in a Pan-European Perspective. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 2133–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.Y.; Gao, Y. Analysis of Factors and Mechanisms Influencing Visitor Satisfaction in Garden Expositions—An Empirical Study Based on Structural Equation Modeling. China Gard. 2016, 32, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.-S.; Um, S.-H.; Lee, T.J. Perceived Restorativeness of Visits to Cultural Heritage Sites. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2016, 21, 1046–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartanto, D.; Brien, A.; Primiana, I.; Wibisono, N.; Triyuni, N.N. Tourist Loyalty in Creative Tourism: The Role of Experience Quality, Value, Satisfaction, and Motivation. Curr. Issues Tour. 2020, 23, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriade, A.; Schofield, P. An Examination of the Role of Service Quality and Perceived Value in Visitor Attraction Experience. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2019, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C. A Review of Research Results on the Application of Structural Equation Modeling Theory. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2014, 33, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Scudo, K.Z. The Greenways of Pavia: Innovations in Italian Landscape Planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 76, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishmanova, M.V. Cultural Tourism in Cultural Corridors, Itineraries, Areas and Cores Networked. In Heritage as an Alternative Driver for Sustainable Development and Economic Recovery in South East Europe-Project See/B/0016/4.3/X Sagittarius; Vasile, V., Ed.; Elsevier Science BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 188, pp. 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Xiang, W.-N.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X. Incorporating Landscape Diversity into Greenway Alignment Planning. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 35, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, L.Y.; Li, H.H. Exploration of the Design Guidance for the Composite Visual Perception of the Mountain Greenway Landscape Space—Example of the Demonstration Section of the Mountain Greenway in Quanzhou City. China Gard. 2021, 37, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobster, P.H. Perception and Use of a Metropolitan Greenway System for Recreation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1995, 33, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.W. A Greenway Network for Singapore. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 76, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Plieninger, T.; Primdahl, J. A Systematic Comparison of Cultural and Ecological Landscape Corridors in Europe. Land 2019, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conine, A.; Xiang, W.-N.; Young, J.; Whitley, D. Planning for Multi-Purpose Greenways in Concord, North Carolina. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, S.J.; Boley, B.B. Importance-Performance Analysis of Local Resident Greenway Users: Findings from Three Atlanta BeltLine Neighborhoods. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 44, 126426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidlöf-Gunnarsson, A.; Öhrström, E. Noise and Well-Being in Urban Residential Environments: The Potential Role of Perceived Availability to Nearby Green Areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pals, R.; Steg, L.; Siero, F.W.; van der Zee, K.I. Development of the PRCQ: A Measure of Perceived Restorative Characteristics of Zoo Attractions. J. Environ. Psychol. 2009, 29, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, Y.; Gayie, D.J. Island Tourism and Sustainable Development; Praeger: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, S.; Bardwell, L.V.; Slakter, D.B. The Museum as a Restorative Environment. Environ. Behav. 1993, 25, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, Y.F.; Zheng, C.H. Relationship between Tourist Perception and Destination Image, Satisfaction and Loyalty—A Case Study of Xi’an. Tour. Forum 2011, 4, 43–47+53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.Q.; Cui, F.J. The Influence of World Cultural Heritage Sites’ Perception on Tourists’ Satisfaction and Loyalty—The Case of Hangzhou. World Geogr. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar]
| Structure Variables | Source of Observation Indicators |
|---|---|
| Cultural perception of slow-moving facilities (A1) | Cultural expression of pavement paving [5,8,9,10,11,12,31,32] (A11) |
| Cultural expression of signage and interpretation system [5,8,9,10,11,12,31,32] (A12) | |
| Cultural expression of leisure facilities [5,8,9,10,11,12,31,32] (A13) | |
| Cultural expression of landscape vignettes [5,8,9,10,11,12,31,32] (A14) | |
| Cultural perception of landscape design (A2) | Distribution of viewpoints [6,9] (A21) |
| Regional characteristics of ancient villages [33] (A22) | |
| Viewpoint geographical appreciation perspective [34] (A23) | |
| View the regional cultural atmosphere of the site [6,9] (A24) | |
| Native plant landscape creation [35] (A25) | |
| Cultural service quality (A3) | Greenway Cultural Activities enrichment [8,36,37] (A31) |
| Types of transportation to reach various cultural attractions on the greenway [38] (A32) | |
| Distribution of food and beverage on the greenway [39] (A33) | |
| Enthusiasm of local residents (A34) | |
| Perceived value (B) | Relieve fatigue from work and study [22,39,40] (B1) |
| Increase experience, knowledge [22,39,40] (B2) | |
| Emotional relief [22,39,40] (B3) | |
| Rejuvenation [22,39,40] (B4) | |
| Cognitive image (C) | The connotation of traditional culture of the island [14,41,42] (C1) |
| The infectious power of traditional culture of the island [14,41,42] (C2) | |
| The perception of traditional culture of the islands [14,41,42] (C3) | |
| The specificity of the traditional culture of the island [14,41,42] (C4) | |
| Satisfaction (D) | Very satisfied overall [14,27,42] (D1) |
| Very satisfied compared to the ideal island culture [14,27,42] (D2) | |
| The sense of cultural belonging I get here is what I need [14,27,42] (D3) | |
| Loyalty (G) | Willingness to revisit [27,28,29] (G1) |
| Willing to actively recommend this place [27,28,29] (G2) |
| Variables | Frequency | Percentage | Cumulative Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 205 | 49.20% | 49.20% |
| Female | 212 | 50.80% | 100.00% | |
| Age | <18 years old | 13 | 3.10% | 3.10% |
| 18–40 years old | 340 | 81.60% | 84.70% | |
| Over 40 years old | 64 | 15.30% | 100.00% | |
| Academic qualifications | High school and below | 91 | 21.80% | 21.80% |
| College | 88 | 21.10% | 42.90% | |
| Bachelor’s degree and above | 238 | 57.10% | 100.00% | |
| Place of origin | Foreign visitors | 172 | 41.20% | 41.20% |
| Local residents | 245 | 58.80% | 100.00% |
| Dependent Variable | Gender | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Mean Difference | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of cultural perception | Female | 4.08 | 0.374 | 0.11 | 2.707 * | 0.016 |
| Male | 3.97 | 0.398 |
| Dependent Variable | I/Year | J/Year | Mean Difference (I-J) | Standard Error | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of cultural perception | <18 years old | 18–40 years old | −0.041 | 0.104 | 0.577 |
| Over 40 years old | 0.335 | 0.111 * | 0.006 | ||
| 18–40 years old | <18 years old | 0.041 | 0.104 | 0.577 | |
| Over 40 years old | 0.376 | 0.055 * | 0.000 | ||
| Over 40 years old | <18 years old | −0.335 | 0.111 * | 0.006 | |
| 18–40 years old | −0.376 | 0.055 * | 0.000 |
| Dependent Variable | P | R | Mean Difference (P-R) | Standard Error | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of cultural perception | High School and below | College | −0.098 | 0.057 | 0.1170 |
| Bachelor’s degree and above | −0.200 | 0.047 * | 0.0002 | ||
| College | High School and below | 0.098 | 0.057 | 0.1170 | |
| Bachelor’s degree and above | −0.103 | 0.048 | 0.0610 | ||
| Bachelor’s degree and above | High School and below | 0.200 | 0.047 * | 0.0002 | |
| College | 0.103 | 0.048 | 0.0610 |
| KMO Sampling Suitability Quantity | Bartlett’s Spherical Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Approximate Cardinality | Degree of Freedom | Significance | |
| 0.984 | 15,977.054 | 325 | 0 |
| Fitting Index | X2/df | GFI | AGFI | RMSEA | RMR | NFI | IFI | TLI | CFI | RFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptation standards | [1,3] | ≥0.8 | ≥0.8 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.10 | ≥0.9 | ≥0.9 | ≥0.9 | ≥0.9 | ≥0.9 |
| Fitted index value | 2.977 | 0.862 | 0.832 | 0.069 | 0.003 | 0.947 | 0.964 | 0.960 | 0.964 | 0.941 |
| Structure Variables | Source of Observation Indicators | Standardized Factor Loadings | CR | AVE | Cronbach’s Alpha Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural perception of slow-moving facilities (A1) | Cultural expression of pavement paving (A11) | 0.907 | 0.951 | 0.828 | 0.955 |
| Cultural expression of signage and interpretation system (A12) | 0.933 | ||||
| Cultural expression of leisure facilities (A13) | 0.902 | ||||
| Cultural expression of landscape vignettes (A14) | 0.897 | ||||
| Cultural perception of landscape design (A2) | Distribution of viewpoints (A21) | 0.929 | 0.953 | 0.801 | 0.953 |
| Regional characteristics of ancient villages (A22) | 0.897 | ||||
| Viewpoint geographical appreciation perspective (A23) | 0.889 | ||||
| View the regional cultural atmosphere of the site (A24) | 0.890 | ||||
| Native plant landscape creation (A25) | 0.869 | ||||
| Cultural service quality (A3) | Greenway Cultural Activities enrichment (A31) | 0.856 | 0.919 | 0.739 | 0.918 |
| Types of transportation to reach various cultural attractions on the greenway (A32) | 0.880 | ||||
| Distribution of food and beverage on the greenway (A33) | 0.803 | ||||
| Enthusiasm of local residents (A34) | 0.896 | ||||
| Perceived value (B) | Relieve fatigue from work and study (B1) | 0.913 | 0.959 | 0.854 | 0.963 |
| Increase experience, knowledge (B2) | 0.919 | ||||
| Emotional relief (B3) | 0.916 | ||||
| Rejuvenation (B4) | 0.947 | ||||
| Cognitive image (C) | The connotation of traditional culture of the island (C1) | 0.880 | 0.945 | 0.810 | 0.944 |
| The infectious power of traditional culture of the island (C2) | 0.921 | ||||
| The perception of traditional culture of the islands (C3) | 0.897 | ||||
| The specificity of the traditional culture of the island (C4) | 0.902 | ||||
| Satisfaction (D) | Very satisfied overall (D1) | 0.897 | 0.889 | 0.730 | 0.872 |
| Very satisfied compared to the ideal island culture (D2) | 0.913 | ||||
| The sense of cultural belonging I get here is what I need (D3) | 0.742 | ||||
| Loyalty (G) | Willingness to revisit (G1) | 0.890 | 0.899 | 0.817 | 0.898 |
| Willing to actively recommend this place (G2) | 0.918 |
| Assumptions | Standardized Path Coefficient | Standard Error | t-Value | p-Value | Hypothesis Testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived quality has a significant positive effect on cognitive image (H1) | 0.98 | 0.035 | 28.24 | *** | Established |
| Perceived quality has a significant positive effect on perceived value (H2) | 0.36 | 0.135 | 2.621 | ** | Established |
| Cognitive image has a significant positive effect on perceived value (H3) | 0.65 | 0.135 | 4.694 | *** | Established |
| Perceived value has a significant positive effect on satisfaction (H4) | 0.98 | 0.035 | 29.017 | *** | Established |
| Satisfaction has a significant positive effect on loyalty (H5) | 0.96 | 0.039 | 25.558 | *** | Established |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, T.; Chen, L. Evaluation and Optimization of Cultural Perception of Coastal Greenway Landscape Based on Structural Equation Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032540
Yang Y, Chen Y, Liu Y, He T, Chen L. Evaluation and Optimization of Cultural Perception of Coastal Greenway Landscape Based on Structural Equation Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(3):2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032540
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yili, Yuxing Chen, Yueyan Liu, Tianyou He, and Lingyan Chen. 2023. "Evaluation and Optimization of Cultural Perception of Coastal Greenway Landscape Based on Structural Equation Model" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 3: 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032540
APA StyleYang, Y., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., He, T., & Chen, L. (2023). Evaluation and Optimization of Cultural Perception of Coastal Greenway Landscape Based on Structural Equation Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032540






