The Usefulness of the Application of Compression Therapy among Lipedema Patients-Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Intervention
2.3. Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Circumfernce, BMI, WHR, Body Weight
3.3. Symptom Severity
3.4. Quality of Life
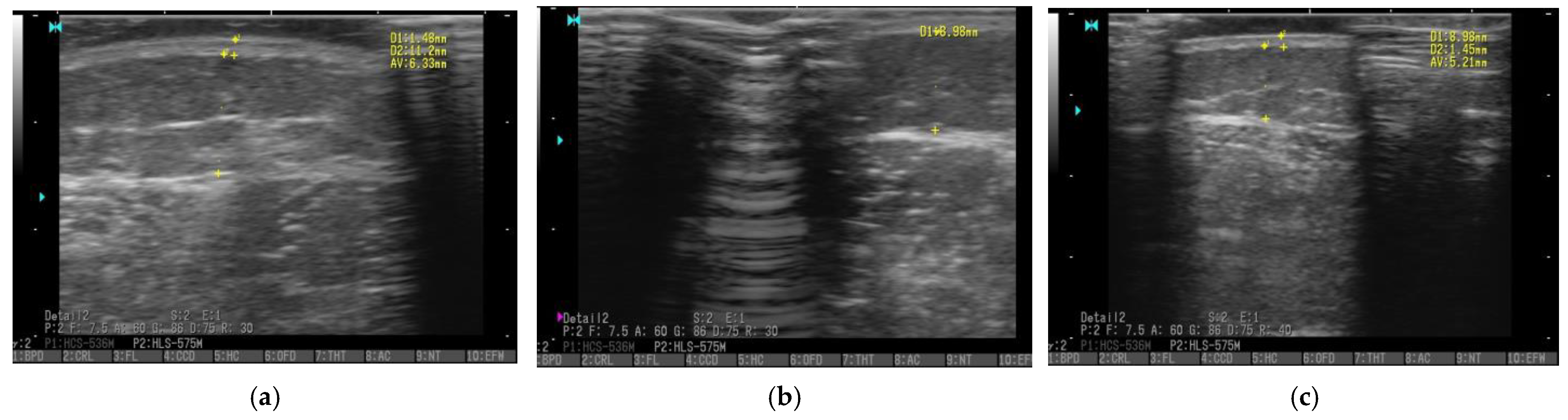
3.5. Ultrasonography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wold, L.E.; Hines JR, E.A.; Allen, E.V. Lipedema of the legs: A syndrome characterized by fat legs and edema. Ann. Intern. Med. 1951, 34, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forner-Cordero, I.; Szolnoky, G.; Forner-Cordero, A.; Kemény, L. Lipedema: An overview of its clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of the disproportional fatty deposition syndrome–systematic review. Clin. Obes. 2012, 2, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, K.; Chava, Y.; Te, C.H.T.; Mirkovskaya, L.; Bharhagava, A. Lipedema Fat and Signs and Symptoms of Illness, Increase with Advancing Stage. Arch. Med. 2015, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bertsch, T.; Erbacher, G.; Elwell, R. Lipoedema: A paradigm shift and consensus. J. Wound Care 2020, 29, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosman, J. Lipoedema: Poor knowledge, neglect or disinterest? J. Lymphoedema 2011, 6, 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Buso, G.; Depairon, M.; Tomson, D.; Raffoul, W.; Vettor, R.; Mazzolai, L. Lipedema: A Call to Action! Obesity 2019, 27, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, K.L.; Kahn, L.A.; Iker, E.; Ehrlich, C.; Wright, T.; McHutchison, L.; Schwartz, J.; Sleigh, M.; Donahue, P.M.C.; Lisson, K.H. Standard of care for lipedema in the United States. Phlebology 2021, 36, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbacher, G.; Bertsch, T. Lipoedema and Pain: What is the role of the psyche?–Results of a pilot study with 150 patients with Lipoedema. Phlebologie 2020, 49, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, A.W.; Kappos, E.A. Lipedema: Diagnostic and management challenges. Int. J. Womens Health 2016, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, A.H.; Sharpe, P.; Gordon, K.D.; Brice, G.; Ostergaard, P.; Jeffery, S.; Mortimer, P.S. Lipedema: An inherited condition. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2010, 152, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpertz, U. Lipedema—Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment Options. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Int. 2021, 118, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Langendoen, S.I.; Habbema, L.; Nijsten, T.E.C.; Neumann, H.A.M. Lipoedema: From clinical presentation to therapy. A review of the literature. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.-T.; von Lukowicz, D.; Lossagk, K.; Aitzetmueller, M.; Moog, P.; Cerny, M.; Erne, H.; Schmauss, D.; Duscher, D.; Machens, H.-G. New Insights on Lipedema: The Enigmatic Disease of the Peripheral Fat. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeijn, J.R.M.; de Rooij, M.J.M.; Janssen, L.; Martens, H. Exploration of Patient Characteristics and Quality of Life in Patients with Lipoedema Using a Survey. Dermatol. Ther. 2018, 8, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescenzi, R.; Mahany, H.B.; Lants, S.K.; Wang, P.; Donahue, M.J.; Marton, A.; Titze, J.; Donahue, P.M.C.; Beckman, J.A. Tissue Sodium Content is Elevated in the Skin and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Women with Lipedema. Obesity 2018, 26, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, H.; Karadag, A.S.; Wollina, U. Cause and management of lipedema-associated pain. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 34, e14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucker, C.; Schmidt-Lucke, J.-A.; Litmathe, J. Hämatomneigung bei Lipödem: Kutane Genese oder Gerinnungsdefekt? Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2021, 171, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, C.; Juuso, P.; Olsson, M. Women’s experiences of living with lipedema. Health Care Women Int. 2021, 43, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwińska, M.; Ostrowska, P.; Hansdorfer-Korzon, R. Lipoedema as a Social Problem. A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, J.E.; Białaszek, W.; Gabriel, M. Quality of life, its factors, and sociodemographic characteristics of Polish women with lipedema. BMC Womens Health 2021, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, J.E.; Białaszek, W.; Ostaszewski, P.; Smidt, T. Depression and appearance-related distress in functioning with lipedema. Psychol. Health Med. 2018, 23, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A. Understanding the challenges of lipoedema. J. Community Nurs. 2018, 32, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Fetzer, A. Specialist approaches to managing lipoedema. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2016, 21, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertsch, T. Compression garments for pain management, comfort and freedom of movement in lipoedema patients: Clinical benefits of JOBST® Confidence. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2022, 27, S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paling, I.; Macintyre, L. Survey of lipoedema symptoms and experience with compression garments. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2020, 25, S17–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwińska, M.; Teodorczyk, J.; Hansdorfer-Korzon, R. A Scoping Review of Available Tools in Measurement of the Effectiveness of Conservative Treatment in Lipoedema. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szél, E.; Kemény, L.; Groma, G.; Szolnoky, G. Pathophysiological dilemmas of lipedema. Med. Hypotheses 2014, 83, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Gao, J.; Ogawa, R. Mechanobiology and mechanotherapy of adipose tissue-effect of mechanical force on fat tissue engineering. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2015, 3, e578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipoedema UK Big Survey 2014 Research Report. 2016. Available online: https://www.lipoedema.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/ (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Atan, T.; Bahar-Özdemir, Y. The Effects of Complete Decongestive Therapy or Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Therapy or Exercise Only in the Treatment of Severe Lipedema: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2021, 19, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, K.L.; Ussery, C.; Eekema, A. Pilot study: Whole body manual subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) therapy improved pain and SAT structure in women with lipedema. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2017, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, M.; Eekema, A.; Ussery, C.; Neuhardt, D.; Garby, K.; Herbst, K.L. Subcutaneous adipose tissue therapy reduces fat by dual X-ray absorptiometry scan and improves tissue structure by ultrasound in women with lipoedema and Dercum disease. Clin. Obes. 2018, 8, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, A.C.M.; Saucedo, D.Z.; Santos, K.D.S.; Benitti, D.A. Ultrasound criteria for lipedema diagnosis. Phlebology 2021, 36, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, T.; Schleinitz, J.; Marshall, M.; Faerber, G. Is the differential diagnosis of lipoedema by means of high-resolution ultrasonography possible. Phlebologie 2018, 47, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
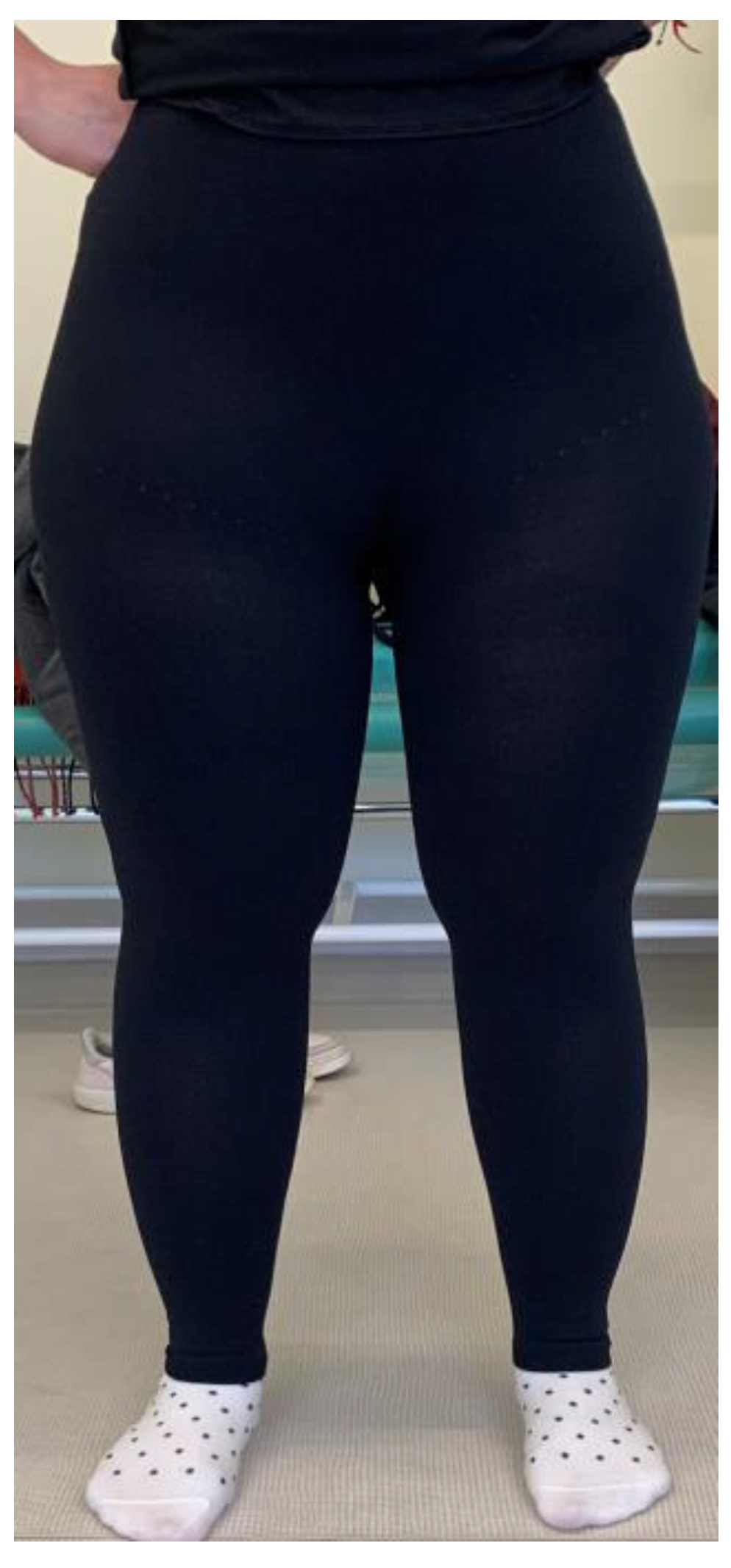

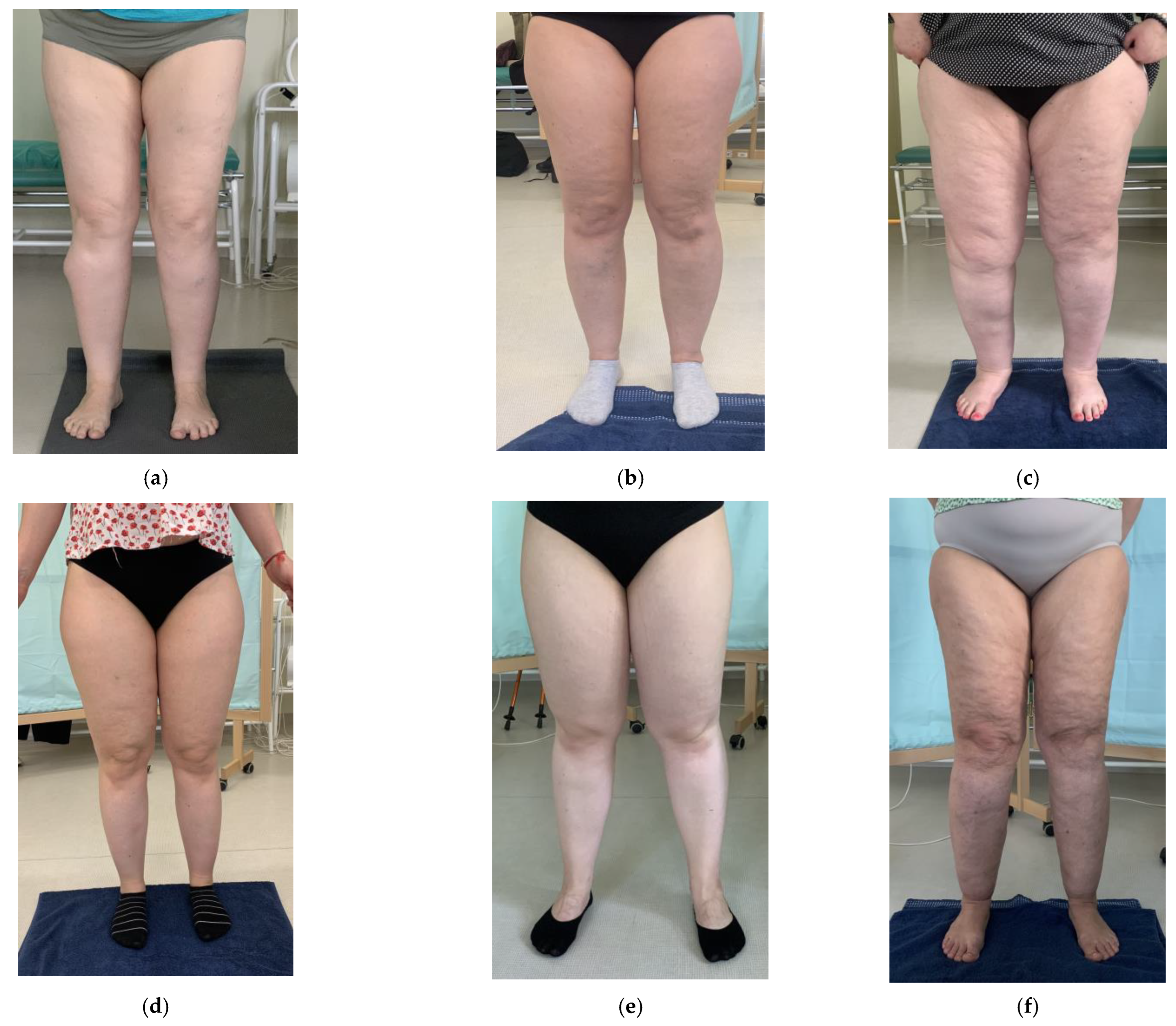
| Feature | Total (n = 6) | Group A (n = 3) | Group B (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 39.7 (12.8) | 48 (4.9) | 31 (12.8) |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 31.35 (8.4) | 34.56 (10.6) | 28.12 (2.83) |
| Body weight (kg), mean (SD) | 90.89 (28.64) | 104 (34.215) | 77.76 (11.19) |
| Previous lipedema diagnosis | |||
| Yes | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| No | 6 (100%) | 3 (100%) | 3 (100%) |
| Lipedema symptoms | |||
| Heaviness in lower extremities | 6 (100%) | 3 (100%) | 3 (100%) |
| Pain at palpation | 5 (83.34%) | 3 (100%) | 2 (66.67%) |
| Disproportion between slimmer trunk and enlarged lower limbs | 5 (83.34%) | 2 (66.67%) | 3 (100%) |
| Easy bruising | 5 (83.34%) | 3 (100%) | 2 (66.67%) |
| Accumulation of fat tissue mostly around legs | 5 (83.34%) | 2 (66.67%) | 3 (100%) |
| Characteristic fat cuffs above the ankles | 4 (66.67%) | 2 (66.67%) | 2 (66.67%) |
| Swelling around the ankles | 3 (50%) | 2(66.67%) | 1 (33.34%) |
| Lipedema Stage | |||
| Stage 1 | 2 (33.34%) | 1 (33.34%) | 1 (33.34%) |
| Stage 2 | 3 (50%) | 1 (33.34%) | 2 (66.67%) |
| Stage 3 | 1 (16.67%) | 1 (33.34%) | 0 |
| Previous dieting | |||
| Yes | 4 (66.67%) | 2 (66.67%) | 2 (66.67%) |
| No | 2 (33.34%) | 1 (33.34%) | 1 (33.34%) |
| Declared level of physical activity | |||
| None | 1 (16.67%) | 1 (33.34%) | 0 |
| Low | 1 (16.67%) | 1 (33.34%) | 0 |
| Medium | 4 (66.67%) | 1 (33.34%) | 3 (100%) |
| High | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Feature | Patient 1A | Patient 2A | Patient 3A | Patient 1B | Patient 2B | Patient 3B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) pre-intervention | 114 | 58 | 140 | 69.7 | 70 | 93.6 |
| Weight (kg) after 4 weeks | 117.5 | 58 | 140 | 70.5 | 74 | 93.6 |
| Weight (kg) after 6 weeks | 116.8 | 58.2 | 140.4 | 69.2 | 73.1 | 93.8 |
| BMI pre-intervention | 32.6 | 22.65 | 48.44 | 24.69 | 28.04 | 31.63 |
| BMI after 4 weeks | 33.6 | 22.65 | 48.44 | 24.9 | 29.64 | 31.63 |
| BMI after 6 weeks | 33.4 | 22.73 | 48.58 | 24.5 | 29.28 | 31.7 |
| WHR pre-intervention | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.76 | 0.82 |
| WHR after 4 weeks | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.75 | 0.83 |
| WHR after 6 weeks | 0.8 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.77 | 0.81 |
| P5 (cm) pre intervention | 99 | 72 | 111 | 66 | 79 | 92 |
| P5 (cm) after 4 weeks | 98 | 71 | 111 | 64 | 78 | 93 |
| P5 (cm) after 6 weeks | 97 | 71 | 112 | 66 | 80 | 92 |
| P7 (cm) pre intervention | 118 | 93 | 150 | 103 | 104 | 111 |
| P7 (cm) after 4 weeks | 119 | 94 | 150 | 100 | 104 | 112 |
| P7 (cm) after 4 weeks | 120 | 96 | 150 | 101 | 104 | 113 |
| P8 (cm) pre-intervention | R-65 | R-54 | R-81 | R-63 | R-63 | R-67 |
| L-65 | L-54 | L-80 | L-63 | L-63 | L-67 | |
| P8 (cm) after 4 weeks | R-66 | R-54 | R-84 | R-64 | R-63 | R-66 |
| L-66 | L-54 | L-83 | L-64 | L-63 | L-66 | |
| P8 (cm) after 6 weeks | R-66 | R-54 | R-84 | R-64 | R-63 | R-65 |
| L-66 | L-54 | L-83 | L-64 | L-63 | L-65 | |
| P9 (cm) pre-intervention | R-54.5 | R-47 | R-74 | R-52 | R-53 | R-56 |
| L- 54.5 | L-47.5 | L-73 | L-52 | L-53 | L-56 | |
| P9 (cm) after 4 weeks | R-55.5 | R-47 | R-75 | R-52.5 | R-53 | R-56 |
| L-55.5 | L-46.5 | L-74 | L-53 | L-53 | L-56 | |
| P9 (cm) after 6 weeks | R-56 | R-46.5 | R-75 | R-53 | R-53 | R-56 |
| L-56 | L-46.5 | L-74 | L-53 | L-53 | L-56 | |
| P10 (cm) pre-intervention | R-45 | R-36 | R-58 | R-37 | R-38 | R-45 |
| L-45 | L-36 | L-58 | L-37 | L-38 | L-45 | |
| P10 (cm) after 4 weeks | R-45 | R-36 | R-59 | R-38 | R-38 | R-45 |
| L-45 | L-36 | L-58 | L-38 | L-38 | L-45 | |
| P10 (cm) after 6 weeks | R-45 | R-36.5 | R-59 | R-37 | R-38 | R-45 |
| L-45 | L-36.5 | L-58 | L-37 | L-38 | L-45 | |
| P11 (cm) pre-intervention | R-45.5 | R-38 | R-54 | R-42 | R-42 | R-48 |
| L-45.5 | L-39 | L-54 | L-42 | L-41 | L-48 | |
| P11 (cm) after 4 weeks | R-45 | R-39 | R-54 | R-42 | R-41 | R-48 |
| L-44.5 | L-39 | L-54 | L-42 | L-41 | L-48 | |
| P11 (cm) after 6 weeks | R-46 | R-39 | R-54 | R-42 | R-41 | R-48 |
| L-46 | L-39 | L-55 | L-42 | L-41 | L-48 | |
| P12 (cm) pre-intervention | R-30 | R-28 | R-39 | R-28 | R-28 | R-36 |
| L-30 | L-28 | L-37 | L-28 | L-28 | L-36 | |
| P12 (cm) after 4 weeks | R-30 | R-28 | R-39 | R-28.5 | R-28.5 | R-34 |
| L-30 | L-28 | L-37 | L-29 | L-28 | L-34 | |
| P12 (cm) after 6 weeks | R-30 | R-30 | R-38 | R-27.5 | R-28 | R-35 |
| L-30 | L-30 | L-38 | L-28 | L-28 | L-34.5 | |
| P13 (cm) pre-intervention | R-26 | R-21 | R-26 | R-23 | R-22 | R-24 |
| L-26 | L-21 | L-26 | L-23 | L-22 | L-24 | |
| P13 (cm) after 4 weeks | R-26 | R-21 | R-26 | R-23 | R-22 | R-24 |
| L-26 | L-21 | L-26 | L-23 | L-22 | L-24 | |
| P13 (cm) after 6 weeks | R-26 | R-21 | R-25.5 | R-23 | R-22 | R-24 |
| L-26 | L-21 | L-25.5 | L-23 | L-22 | L-24 |
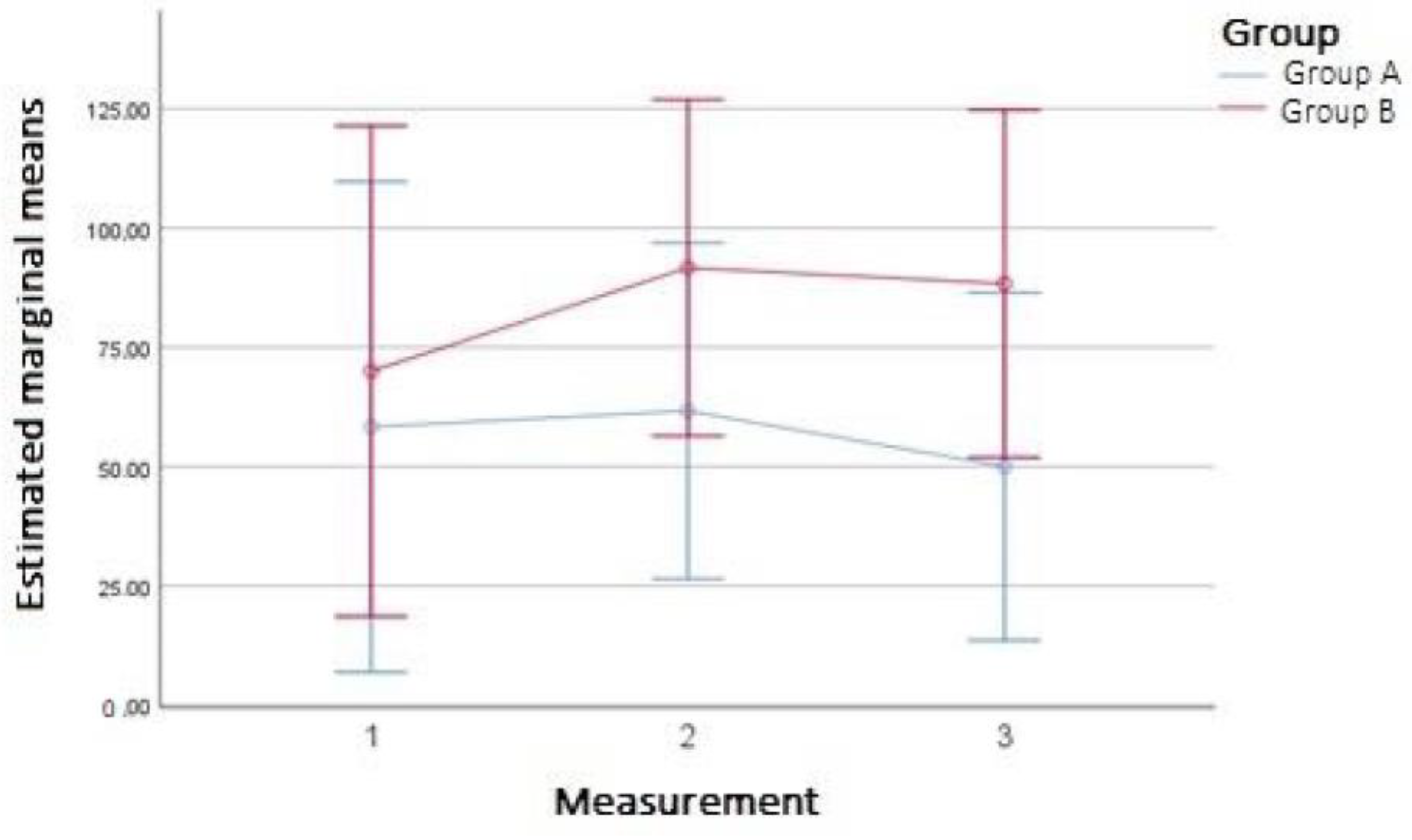
| Outcome Measurement | Measurement Time | Group A | Group B | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain-VAS (0–10) | Pre-intervention | 5.67 | 2.67 | 0.35 | 0.22 | 0.68 |
| After 4 weeks | 5.33 | 3 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 5 | 2.3 | ||||
| Subjective impact on daily functioning (0–10) | Pre-intervention | 5 | 1.67 | 1.0 | 0.078 | 0.058 |
| After 4 weeks | 6 | 0.67 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 4.67 | 2 | ||||
| Subjective disproportion between lower and upper body (0–10) | Pre-intervention | 6 | 5.34 | 1.0 | 0.68 | 0.89 |
| After 4 weeks | 6 | 5.34 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 6.34 | 5 | ||||
| Subjective swelling around the ankles (0–10) | Pre-intervention | 5.67 | 4.3 | 0.726 | 0.412 | 0.41 |
| After 4 weeks | 6.3 | 3 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 6 | 2.67 | ||||
| Subjective heaviness in lower extremities (0–10) | Pre-intervention | 6.34 | 5.67 | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.23 |
| After 4 weeks | 7 | 3.67 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 6 | 3 | ||||
| Subjective tendency to bruising (0–10) | Pre-intervention | 5.67 | 5.33 | 0.079 | 0.088 | 0.034 |
| After 4 weeks | 5 | 1.67 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 7 | 1.33 | ||||
| Subjective pain at palpation (0–10) | Pre-intervention | 3.67 | 4.67 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 0.016 |
| After 4 weeks | 4 | 3.33 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 6 | 1.67 | ||||
| Subjective level of accumulation of fat tissue mostly around legs (0–10) | Pre-intervention | 7.67 | 7 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.64 |
| After 4 weeks | 7.33 | 5.3 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 7.33 | 5 |
| Outcome Measurement | Measurement Time | Group A | Group B | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF-36 Physical functioning | Pre-intervention | 58.34 | 70 | 0.083 | 0.263 | 0.061 |
| After 4 weeks | 61.67 | 91.67 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 50 | 88.33 | ||||
| SF-36 Role limitations due to physical health | Pre-intervention | 66.67 | 100 | 0.397 | 0.19 | 0.79 |
| After 4 weeks | 50 | 91.67 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 41.67 | 91.67 | ||||
| SF-36 Role limitations due to emotional health | Pre-intervention | 100 | 88.89 | 0.624 | 0.358 | 0.4 |
| After 4 weeks | 97.22 | 97.22 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 100 | 77.78 | ||||
| SF-36 Energy/fatigue | Pre-intervention | 46.67 | 65 | 0.056 | 0.731 | 0.099 |
| After 4 weeks | 82.5 | 70.3 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 66.67 | 53.33 | ||||
| SF-36 Emotional well-being | Pre-intervention | 72 | 73.34 | 0.19 | 0.157 | 0.23 |
| After 4 weeks | 73.34 | 54.67 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 84 | 66.67 | ||||
| SF-36 Social functioning | Pre-intervention | 79.1 | 91.67 | 0.001 | 0.08 | 0.001 |
| After 4 weeks | 22.5 | 55 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 87.5 | 87.5 | ||||
| SF-36 Pain | Pre-intervention | 34.16 | 75 | 0.56 | 0.14 | 0.18 |
| After 4 weeks | 50 | 69.16 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 26.67 | 75.84 | ||||
| SF-36 General health | Pre-intervention | 28.33 | 44.8 | 0.92 | 0.432 | 0.57 |
| After 4 weeks | 21.67 | 45 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 23.33 | 48.33 | ||||
| SF-36 Total | Pre-intervention | 58.05 | 71.5 | 0.78 | 0.23 | 0.78 |
| After 4 weeks | 58.1 | 75.8 | ||||
| After 6 weeks | 56.6 | 73.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czerwińska, M.; Teodorczyk, J.; Spychała, D.; Hansdorfer-Korzon, R. The Usefulness of the Application of Compression Therapy among Lipedema Patients-Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20020914
Czerwińska M, Teodorczyk J, Spychała D, Hansdorfer-Korzon R. The Usefulness of the Application of Compression Therapy among Lipedema Patients-Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(2):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20020914
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzerwińska, Monika, Jacek Teodorczyk, Dawid Spychała, and Rita Hansdorfer-Korzon. 2023. "The Usefulness of the Application of Compression Therapy among Lipedema Patients-Pilot Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 2: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20020914
APA StyleCzerwińska, M., Teodorczyk, J., Spychała, D., & Hansdorfer-Korzon, R. (2023). The Usefulness of the Application of Compression Therapy among Lipedema Patients-Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20020914






