Influence of Manure as a Complex Mixture on Soil Sorption of Pharmaceuticals—Studies with Selected Chemical Components of Manure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
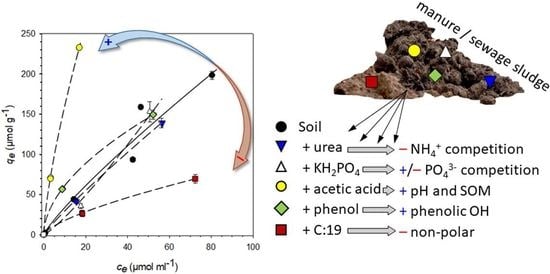
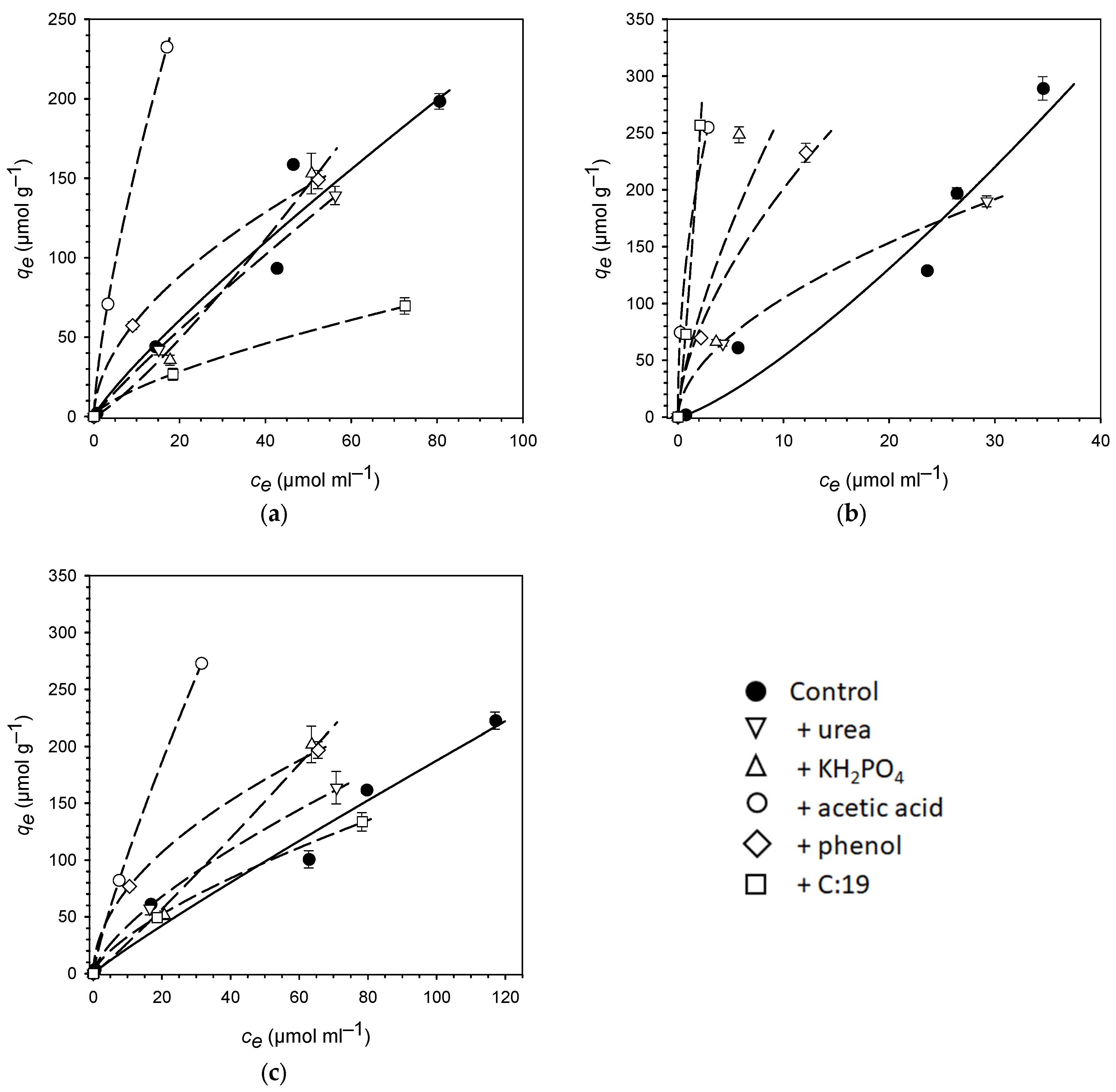
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kleemann, A.; Engel, J.; Kutscher, B.; Reichert, D. Pharmaceutical Substances. In Syntheses, Patents and Applications of the Most Relevant APIs, 5th ed.; Georg Thieme Verlag KG: Stuttgart, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Langhammer, J.P.; Führ, F.; Büning-Pfaue, H. Verbleib von Sulfonamid-Rückständen aus der Gülle in Boden und Nutzpflanze. Lebensmittelchemie 1990, 44, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Thiele, S. Adsorption of the antibiotic pharmaceutical compound sulfapyridine by a long-term differently fertilized loess Chernozem. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2000, 163, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolls, J. Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3397–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamscher, G.; Sczesny, S.; Höper, H.; Nau, H. Determination of persistent tetracycline residues in soil fertilized with liquid manure by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Nors Nielsen, S.; Lanzky, P.F.; Ingerslev, F.; Holten Lützhøft, H.C.; Jørgensen, S.E. Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—A review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 357–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B.A. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Liu, W. Occurrence, fate, and ecotoxicity of antibiotics in agro-ecosystems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, K.; Xu, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Jones, D.L.; Zou, J. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in agricultural soils: A systematic analysis. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 847–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Natasha; Bibi, I.; Sarwar, T.; Shah, A.H.; Niazi, N.K. A review of environmental contamination and health risk assessment of wastewater use for crop irrigation with a focus on low and high-income countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejías, C.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in sewage sludge and soil: A review on their distribution and environmental risk assessment. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 30, e00125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, L.; Tanunchai, B.; Glaser, B. Antibiotics residues in pig slurry and manure and its environmental contamination potential. A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Huang, D.; Du, L.; Song, B.; Yin, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, R.; Huang, H.; Zeng, G. Antibiotic resistance in soil-plant systems: A review of the source, dissemination, influence factors, and potential exposure risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Barra Caracciolo, A. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, K.J.; Reyes, A.; Wang, B.; Selleck, E.M.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Dantas, G. The shared antibiotic resistome of soil bacteria and human pathogens. Science 2012, 337, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedje, J.M.; Wang, F.; Manaia, C.M.; Virta, M.; Sheng, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, T.; Topp, E. Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Human-Impacted Environment: A One Health Perspective. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, X. What happens when pharmaceuticals meet colloids. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 2100–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirardini, A.; Grillini, V.; Verlicchi, P. A review of the occurrence of selected micropollutants and microorganisms in different raw and treated manure—Environmental risk due to antibiotics after application to soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasho, R.P.; Cho, J.Y. Veterinary antibiotics in animal waste, its distribution in soil and uptake by plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlicchi, P.; Zambello, E. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in untreated and treated sewage sludge: Occurrence and environmental risk in the case of application on soil—A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 750–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Kakarla, D.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M.; Yoon, Y.-E.; Lee, Y.B. Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) contamination as a global agro-ecological issue: A critical view. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riviere, J.E. Comparative Pharmacokinetics: Principles, Techniques and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Thiele-Bruhn, S. Environmental risks from mixtures of antibiotic pharmaceuticals in soils—A literature review. In UBA Texte; UBA: Dessau, Germany, 2019; Volume 32, p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick, D.R.; Chen, S. Agriculture, Hydrology and Water Quality-Manures. In Agriculture, Hydrology and Water Quality; Haygarth, P.M., Jarvis, S.C., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 57–82. [Google Scholar]
- Leenheer, J.A.; Rostad, C.E. Fractionation and characterization of organic matter in wastewater from a swine waste-retention basin. In Scientific Investigations Report 2004–5217; U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2004; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Pagliari, P.H.; Waldrip, H.M. Applied and environmental chemistry of animal manure: A review. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 779–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, M.O.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Eckhardt, K.U.; Leinweber, P. Composition of organic matter in particle size fractionated pig slurry. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5736–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senesi, N.; Xing, B.; Huang, P.M. Biophysico-Chemical Processes Involving Natural Nonliving Organic Matter in Environmental Systems; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 876. [Google Scholar]
- Peltre, C.; Gregorich, E.G.; Bruun, S.; Jensen, L.S.; Magid, J. Repeated application of organic waste affects soil organic matter composition: Evidence from thermal analysis, FTIR-PAS, amino sugars and lignin biomarkers. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambier, P.; Pot, V.; Mercier, V.; Michaud, A.; Benoit, P.; Revallier, A.; Houot, S. Impact of long-term organic residue recycling in agriculture on soil solution composition and trace metal leaching in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nightingale, J.; Carter, L.; Sinclair, C.J.; Rooney, P.; Kay, P. Influence of manure application method on veterinary medicine losses to water. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 334, 117361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navon, R.; Hernandez-Ruiz, S.; Chorover, J.; Chefetz, B. Interactions of carbamazepine in soil: Effects of dissolved organic matter. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Guo, X.; Xu, J.; Hao, L.; Kong, D.; Gao, S. Sorption and transport of five sulfonamide antibiotics in agricultural soil and soil–manure systems. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2015, 50, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabauty, F.; Pot, V.; Bourdat-Deschamps, M.; Bernet, N.; Labat, C.; Benoit, P. Transport of organic contaminants in subsoil horizons and effects of dissolved organic matter related to organic waste recycling practices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6907–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Seo, Y.; Essington, M.E. Sorption and transport of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soil—A laboratory study. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, M.; Stamm, C.; Waul, C.; Singer, H.; Müller, S.R. Surface runoff and transport of sulfonamide antibiotics and tracers on manured grassland. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgman, O.; Chefetz, B. Combined effects of biosolids application and irrigation with reclaimed wastewater on transport of pharmaceutical compounds in arable soils. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3431–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadegesin, L.A.; Tang, X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, J. Transport of Veterinary Antibiotics in Farmland Soil: Effects of Dissolved Organic Matter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albero, B.; Tadeo, J.L.; Escario, M.; Miguel, E.; Pérez, R.A. Persistence and availability of veterinary antibiotics in soil and soil-manure systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, N.; Li, B.; Bi, E. Roles of hydrophobic and hydrophilic fractions of dissolved organic matter in sorption of ketoprofen to biochars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31486–31496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leek, A.B.G.; Hayes, E.T.; Curran, T.P.; Callan, J.J.; Beattie, V.E.; Dodd, V.A.; O’Doherty, J.V. The influence of manure composition on emissions of odour and ammonia from finishing pigs fed different concentrations of dietary crude protein. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3431–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Leytem, A.B. Phosphorus compounds in sequential extracts of animal manures: Chemical speciation and a novel fractionation procedure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6101–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, B.J.; Trabue, S.L.; Andersen, D.S.; van Weelden, M.B.; Pepple, L.M. Dietary composition and particle size effects on swine manure characteristics and gas emissions. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.P.; Rahman, S.; Borhan, M.S.; Engel, C. The effect of feeding high fat diet to beef cattle on manure composition and gaseous emission from a feedlot pen surface. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Fadel, J.G.; Zhang, R.; El-Mashad, H.M.; Ying, Y.; Rumsey, T. Evaluation of sample preservation methods for poultry manure. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, X.; Thiele-Bruhn, S. Interaction of pig manure-derived dissolved organic matter with soil affects sorption of sulfadiazine, caffeine and atenolol pharmaceuticals. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4299–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, U. Differenzierung der Eisenoxide des Bodens durch photochemische Extraktion mit saurer Ammoniumoxalat-Lösung. Z. Pflanz. Düngung Bodenkd. 1964, 105, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, P.; Lamshöft, M.; Zühlke, S.; Spiteller, M. Sorption and desorption of sulfadiazine in soil and soil-manure systems. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Test No. 106: Adsorption—Desorption Using a Batch Equilibrium Method; OECD: Paris, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ngigi, A.N.; Ok, Y.S.; Thiele-Bruhn, S. Biochar affects the dissipation of antibiotics and abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in pig manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lim, S.; Han, M.; Cho, J. Sorption characteristics of oxytetracycline, amoxicillin, and sulfathiazole in two different soil types. Geoderma 2012, 185–186, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filep, T.; Szabó, L.; Kondor, A.C.; Jakab, G.; Szalai, Z. Evaluation of the effect of the intrinsic chemical properties of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) on sorption behaviour in soils and goethite. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiecak, A.; Sassine, L.; Boy-Roura, M.; Elsner, M.; Mas-Pla, J.; La Salle, C.L.; Stumpp, C. Sorption properties and behaviour at laboratory scale of selected pharmaceuticals using batch experiments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 225, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, G.; Jorquera, M.; Demanet, R.; Elgueta, S.; Briceño, G.; Mora, M.L. Urea fertilizer and pH influence on sorption process of flumetsulam and MCPA acidic herbicides in a volcanic soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.B.; Yu, X.Q.; Xu, B.L.; Peng, D.; Guo, X.T. Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products on soil and soil components: Influencing factors and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Diva, R.A.; Vasudevan, D.; Mackay, A.A. Trends in soil sorption coefficients within common antimicrobial families. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pedersen, J.A. Sorption of sulfonamide antimicrobial agents to humic acid-clay complexes. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L. Soil Physical Chemistry; CRC Press: Boka Ratoon, FL, USA, 1999; Volume 2, p. 409. [Google Scholar]
- Ngigi, A.N.; Ok, Y.S.; Thiele-Bruhn, S. Biochar-mediated sorption of antibiotics in pig manure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Gypser, S.; Leinweber, P.; Freese, D.; Kühn, O. Infrared spectroscopic characterization of phosphate binding at the goethite-water interface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 4421–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Seibicke, T.; Schulten, H.R.; Leinweber, P. Sorption of sulfonamide pharmaceutical antibiotics on whole soils and particle-size fractions. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guet, T.; Hsini, I.; Labanowski, J.; Mondamert, L. Sorption of selected pharmaceuticals by a river sediment: Role and mechanisms of sediment or Aldrich humic substances. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14532–14543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, S.; Zanetti, M.C. Sorption of phenols: Influence of groundwater pH and of soil organic carbon content. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 5, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Pan, B.; Liang, N.; Chang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Xing, B. Reactive mineral removal relative to soil organic matter heterogeneity and implications for organic contaminant sorption. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Conte, P.; Trivellone, E.; van Lagen, B. Reduced heterogeneity of a lignite humic acid by preparative HPSEC following interaction with an organic acid. Characterization of size-separates by Pyr-GC-MS and H-1-NMR spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haham, H.; Oren, A.; Chefetz, B. Insight into the role of dissolved organic matter in sorption of sulfapyridine by semiarid soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11870–11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, C.; Harter, T.; Radke, M. Effects of pH and manure on transport of sulfonamide antibiotics in soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielmeyer, A.; Höper, H.; Hamscher, G. Long-term monitoring of sulfonamide leaching from manure amended soil into groundwater. Chemosphere 2017, 177, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D.; Bi, E.P.; Chen, H.H. Effects of dissolved humic acid on fluoroquinolones sorption and retention to kaolinite. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 178, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Arenz-Leufen, M.G.; Jacques, D.; Lichtner, P.; Engelhardt, I. Impact of manure-related DOM on sulfonamide transport in arable soils. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2016, 192, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | Molecular | CAS Number | Molar Mass | pKa | KOW a | Water Solubility | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | (g·mol−1) | 1 | 2 | (mg·L−1) | |||
| Pharmaceutical active compounds (PhACs) | |||||||
| Sulfadiazine |  | 68-35-9 | 250.30 | 1.57 b | 6.50 b | 0.812 b | 2000 |
| Atenolol | 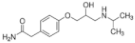 | 29122-68-7 | 266.34 | 9.60 c | 1.445 d | 429 | |
| Caffeine | 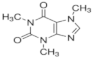 | 58-08-2 | 194.19 | 0.40 c | 10.4 c | 0.851 c | 21,600 |
| Model compounds (manure constituents) e | |||||||
| Urea | CO(NH2)2 | 57-13-6 | 60.06 | 0.18 | 0.008 | 5.45 × 105 | |
| Monopotassium phosphate | KH2PO4 | 7778-77-0 | 136.09 | 2.15 | 6.82 | - | 2.22 × 105 |
| Acetic acid | CH3COOH | 64-19-7 | 60.05 | 4.76 | −0.17 | 4.76 × 105 | |
| Phenol | C6H5OH | 108-95-2 | 94.11 | 9.99 | 28.84 | 8.28 × 104 | |
| Nonadecanoic acid C:19 | C18H37COOH | 646-30-0 | 298.50 | 4.78 | 2.75×108 | 0.002 | |
| Control | +Urea | +KH2PO4 | +Acetic Acid | +Phenol | +C:19 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC (mg·g−1) | 11.57 | 11.63 | 11.57 | 11.78 | 11.93 | 12.71 |
| pH | 4.98 | 4.90 | 4.40 | 2.56 | 4.49 | 4.46 |
| PhAC | Isotherm Parameter | Control | +Urea | +KH2PO4 | +Acetic Acid | +Phenol | +C:19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfadia | Kf | 4.66 | 3.71 | 1.39 | 31.1 | 17.5 | 3.56 |
| zine | n | 0.86 | 0.90 | 1.19 | 0.71 | 0.54 | 0.69 |
| R2 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| SE | 2.41 | 1.15 | 1.43 | 3.85 | 2.55 | 1.26 | |
| Kd | 3.36 | 2.94 | 2.15 | 15.9 | 6.08 | 1.76 | |
| KOC | 290 | 253 | 186 | 1350 | 510 | 138 | |
| Atenolol | Kf | 2.79 | 29.6 | 55.1 | 155 | 50.0 | 107 |
| n | 1.28 | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.48 | 0.61 | 1.16 | |
| R2 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.97 | |
| SE | 2.47 | 4.28 | 24.3 | 2.47 | 2.37 | 0.18 | |
| Kd | 5.38 | 10.5 | 27.1 | 46.6 | 20.1 | 154 | |
| KOC | 465 | 902 | 2340 | 3950 | 1690 | 12,100 | |
| Caffeine | Kf | 2.65 | 8.63 | 2.29 | 15.3 | 23.0 | 6.71 |
| n | 0.93 | 0.69 | 1.07 | 0.84 | 0.51 | 0.69 | |
| R2 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| SE | 1.37 | 3.98 | 2.05 | 1.99 | 3.17 | 1.76 | |
| Kd | 2.23 | 4.21 | 2.71 | 10.5 | 7.50 | 3.25 | |
| KOC | 193 | 362 | 234 | 888 | 629 | 256 |
| Sulfadiazine | Atenolol | Caffeine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC a | r | −0.164 | 0.942 | −0.049 |
| p | 0.756 | 0.005 | 0.927 | |
| SOC b | r | 0.518 | 0.366 | 0.785 |
| p | 0.371 | 0.544 | 0.116 | |
| pH a | r | −0.918 | −0.181 | −0.827 |
| p | 0.010 | 0.732 | 0.042 | |
| pH c | r | 0.034 | −0.501 | −0.274 |
| p | 0.957 | 0.390 | 0.655 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Zhang, W. Influence of Manure as a Complex Mixture on Soil Sorption of Pharmaceuticals—Studies with Selected Chemical Components of Manure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20126154
Thiele-Bruhn S, Zhang W. Influence of Manure as a Complex Mixture on Soil Sorption of Pharmaceuticals—Studies with Selected Chemical Components of Manure. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(12):6154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20126154
Chicago/Turabian StyleThiele-Bruhn, Sören, and Wei Zhang. 2023. "Influence of Manure as a Complex Mixture on Soil Sorption of Pharmaceuticals—Studies with Selected Chemical Components of Manure" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 12: 6154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20126154
APA StyleThiele-Bruhn, S., & Zhang, W. (2023). Influence of Manure as a Complex Mixture on Soil Sorption of Pharmaceuticals—Studies with Selected Chemical Components of Manure. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(12), 6154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20126154