Effects of Aquatic Exercises for Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A 12-Week Intervention in a Quasi-Experimental Study with Pain as a Mediator of Depression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Anthropometrics Measurement
2.2.2. Physical Fitness
2.2.3. Pain
2.2.4. Depression
2.2.5. Physical Activity
2.2.6. Intervention
2.2.7. Data Analysis
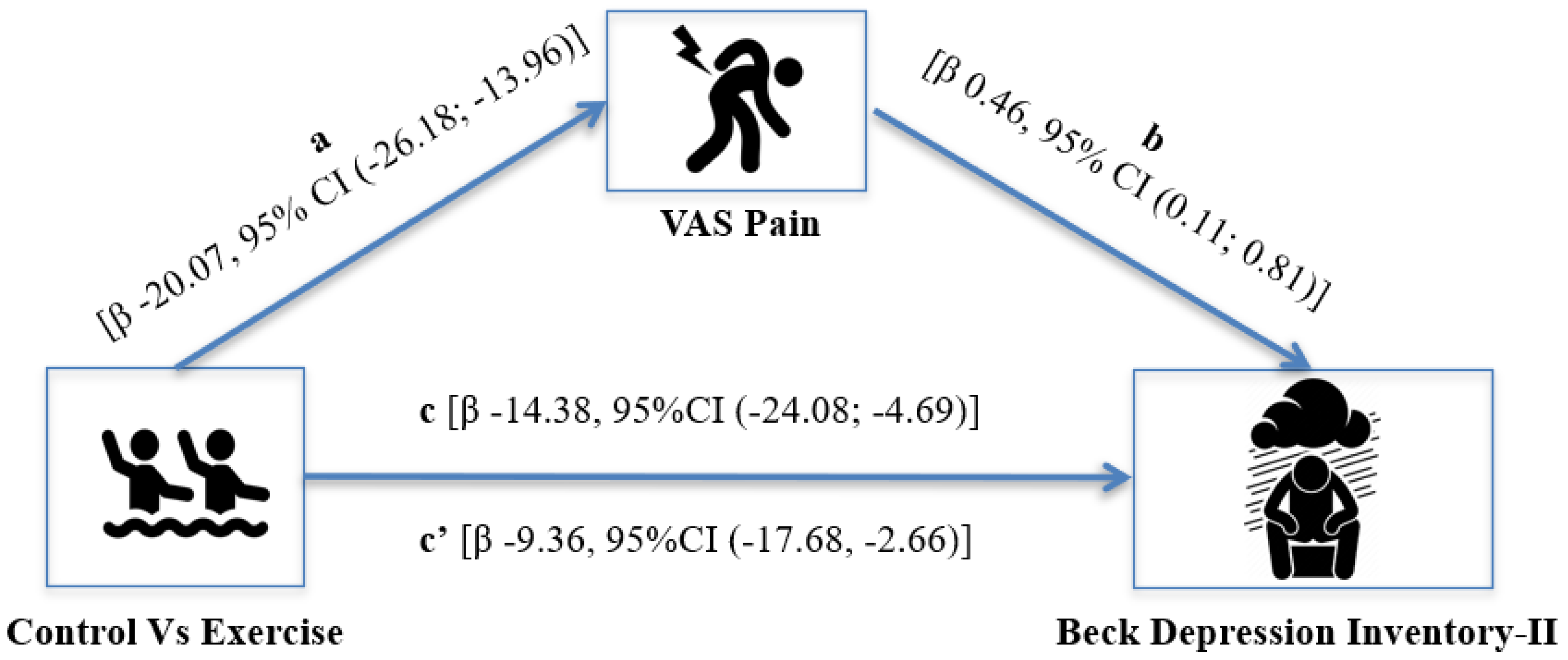
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, D.L.; Wolfe, F.; Huizinga, T.W.J. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Woude, D.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Toes, R.E.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Thomson, W.; Worthington, J.; Van Der Helm-Van Mil, A.H.M.; De Vries, R.R.P. Quantitative Heritability of Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody-Positive and Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody-Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Esquide, V.; Sanmartí, R. Tobacco and Other Environmental Risk Factors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Reumatol. Clínica (Engl. Ed.) 2012, 8, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlens, C.; Hergens, M.P.; Grunewald, J.; Ekbom, A.; Eklund, A.; Höglund, C.O.; Askling, J. Smoking, Use of Moist Snuff, and Risk of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, K.; Nossent, J.; Preen, D.; Keen, H.; Inderjeeth, C. The Global Prevalence of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis Based on a Systematic Review. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyden, S.D.; Hossain, I.N.; Wohlfahrt, A.; Lee, Y.C. Non-Inflammatory Causes of Pain in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Pok, L.S.L.; Ng, C.M.; Yahya, F.; Sockalingam, S.; Tee, Y.C.; Raja, J. Fatigue and Associated Factors in a Multi-Ethnic Cohort of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xu, A.; Gao, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X. The Effect of Physical Exercise on Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2021, 77, 506–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamioka, H.; Tsutani, K.; Okuizumi, H.; Mutoh, Y.; Ohta, M.; Handa, S.; Okada, S.; Kitayuguchi, J.; Kamada, M.; Shiozawa, N.; et al. Effectiveness of Aquatic Exercise and Balneotherapy: A Summary of Systematic Reviews Based on Randomized Controlled Trials of Water Immersion Therapies. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrado, L.N.; Mendonça, M.L.M.; Budib, M.B.; Oliveira-Junior, S.A.; Martinez, P.F. Effectiveness of Aquatic Exercise in the Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis: Systematic Review. Rheumatol. Int. 2022, 42, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, G.A.; Kelley, K.S.; Hootman, J.M. Effects of Exercise on Depression in Adults with Arthritis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickens, C.; McGowan, L.; Clark-Carter, D.; Creed, F. Depression in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review of the Literature with Meta-Analysis. Psychosom. Med. 2002, 64, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.V.; Abner, T.S.; Sluka, K.A. Does Exercise Increase or Decrease pain? Central Mechanisms Underlying These Two Phenomena. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4141–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluka, K.A.; Law, L.F.; Bement, M.H. Exercise-Induced Pain and Analgesia? Underlying Mechanisms and Clinical Translation. Pain 2018, 159, S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.M.; Kamper, S.J.; Maher, C.G.; Latimer, J.; Ferreira, M.L.; Nicholas, M.K. Symptoms of Depression and Stress Mediate the Effect of Pain on Disability. Pain 2011, 152, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seekatz, B.; Meng, K.; Faller, H. Depressivity as Mediator in the Fear-Avoidance Model: A Path Analysis Investigation of Patients with Chronic Back Pain. Schmerz 2013, 27, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. The Link between Depression and Chronic Pain: Neural Mechanisms in the Brain. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 9724371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerurkar, L.; Siebert, S.; McInnes, I.B.; Cavanagh, J. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Depression: An Inflammatory Perspective. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.J.; Rikli, R.E.; Beam, W.C. A 30-s Chair-Stand Test as a Measure of Lower Body. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2013, 70, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Podsiadlo, D.; Richardson, S. The Timed "Up & Go": A Test of Basic Functional Mobility for Frail Elderly Persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawker, G.A.; Mian, S.; Kendzerska, T.; French, M. Measures of Adult Pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2011, 63, S240–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, R.C.; Gonçalves, B. The Portuguese Version of the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II). Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2011, 27, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sember, V.; Meh, K.; Sorić, M.; Jurak, G.; Starc, G.; Rocha, P. Validity and Reliability of International Physical Activity Questionnaires for Adults across EU Countries: Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenhard, W.; Lenhard, A. Computation of Effect Sizes; ResearchGate: Online, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, A.M.; Hopkins, W.G. Making Meaningful Inferences About Magnitudes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2006, 1, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 1462534651. [Google Scholar]
- Dickens, C.; Jackson, J.; Tomenson, B.; Hay, E.; Creed, F. Association of Depression and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Psychosomatics 2003, 44, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, E.C.J.; Thomas, V.N.; Wilson-Barnet, J. Patient Experiences of Anxiety, Depression and Acute Pain after Surgery: A Longitudinal Perspective. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2005, 42, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilderink, P.H.; Burger, H.; Deeg, D.J.; Beekman, A.T.; Oude Voshaar, R.C. The Temporal Relation between Pain and Depression: Results from the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. Psychosom. Med. 2012, 74, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, L.; Manders, T.; Wang, J. Neuroplasticity Underlying the Comorbidity of Pain and Depression. Neural Plast. 2015, 2015, 504691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varallo, G.; Giusti, E.M.; Scarpina, F.; Cattivelli, R.; Capodaglio, P.; Castelnuovo, G. The Association of Kinesiophobia and Pain Catastrophizing with Pain-Related Disability and Pain Intensity in Obesity and Chronic Lower-Back Pain. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzakpasu, F.Q.S.; Carver, A.; Brakenridge, C.J.; Cicuttini, F.; Urquhart, D.M.; Owen, N.; Dunstan, D.W. Musculoskeletal Pain and Sedentary Behaviour in Occupational and Non-Occupational Settings: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021 2021, 18, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholich, S.L.; Hallner, D.; Wittenberg, R.H.; Hasenbring, M.I.; Rusu, A.C. The Relationship between Pain, Disability, Quality of Life and Cognitive-Behavioural Factors in Chronic Back Pain. Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.S.; Lewis, G.N.; Rice, D.A.; Mcnair, P.J. Is Motor Cortical Excitability Altered in People with Chronic Pain? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovsky, Y.; Sprecher, E.; Sinai, A. Motor Corticospinal Excitability: A Novel Facet of Pain Modulation? Pain Rep. 2019, 4, e725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridle, C.; Spanjers, K.; Patel, S.; Atherton, N.M.; Lamb, S.E. Effect of Exercise on Depression Severity in Older People: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 201, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, A.C.Y.; Wong, T.W.L.; Lee, P.H. Effect of Low-Intensity Exercise on Physical and Cognitive Health in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Sports Med.-Open 2015, 1, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.J.; Belza, B.; Elaine Thompson, F.; Whitney, J.D.; Bennett, K. Effects of Aquatic Exercise on Flexibility, Strength and Aerobic Fitness in Adults with Osteoarthritis of the Hip or Knee. J. Adv. Nurs. 2007, 57, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Control Group | Exercise Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 23 | n = 21 | ||
| Age, years | 56.2 ± 10.8 | 56.7 ± 11.2 | 0.892 |
| Weight, kg | 69.7 ± 9.5 | 69.1 ± 7.7 | 0.826 |
| Height, m | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 0.330 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.9 ± 3.5 | 27.1 ± 3.2 | 0.399 |
| Baseline | Changes | Quantitative Chances as % | Clinical Inference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG (n = 23) | EG (n = 21) | Δ% (95%CI) | ES (95%CI) | Harmful | Trivial | Beneficial | ||
| Physical Fitness | ||||||||
| Upper body strength (kg/kg) | 0.23 ± 0.09 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 10.9 (7.0 to 15.0) | 0.27 (0.17 to 0.36) | 0 | 2 | 98 | very likely |
| Lower body power (W·kg−1) | 2.11 ± 0.56 | 2.20 ± 0.75 | 4.0 (1.2 to 6.8) | 0.12 (0.04 to 0.20) | 3 | 97 | 0 | very likely |
| Upper body mobility (cm) | −7.22 ± 7.30 | −6.29 ± 8.92 | 8.9 (−10.7 to 32.8) | 0.12 (−0.15 to 0.39) | 1 | 72 | 27 | possibly |
| Lower body mobility (cm) | −1.04 ± 2.87 | −1.95 ± 4.46 | 6.5 (−8.8 to 24.6) | 0.11 (−0.16 to 0.39) | 1 | 73 | 26 | possibly |
| Agility/dynamic balance (s) | 6.47 ± 1.67 | 5.95 ± 1.67 | 4.8 (2.2 to 7.4) | 0.18 (0.08 to 0.27) | 0 | 70 | 30 | possibly |
| Pain | 4.83 ± 0.83 | 4.48 ± 0.60 | −23.4 (−28.9 to −17.5) | 1.72 (1.24 to 2.21) | 0 | 0 | 100 | most likely |
| Depression | 16.91 ± 10.97 | 15.38 ± 10.26 | −25.7 (−32.9 to −17.8) | 0.45 (0.30 to 0.60) | 0 | 0 | 100 | most likely |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez-Sousa, M.A.; Pedro, J.; Carrasco-Zahinos, R.; Raimundo, A.; Parraca, J.A.; Tomas-Carus, P. Effects of Aquatic Exercises for Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A 12-Week Intervention in a Quasi-Experimental Study with Pain as a Mediator of Depression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105872
Perez-Sousa MA, Pedro J, Carrasco-Zahinos R, Raimundo A, Parraca JA, Tomas-Carus P. Effects of Aquatic Exercises for Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A 12-Week Intervention in a Quasi-Experimental Study with Pain as a Mediator of Depression. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(10):5872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105872
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez-Sousa, Miguel A., Jéssica Pedro, Rocio Carrasco-Zahinos, Armando Raimundo, Jose A. Parraca, and Pablo Tomas-Carus. 2023. "Effects of Aquatic Exercises for Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A 12-Week Intervention in a Quasi-Experimental Study with Pain as a Mediator of Depression" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 10: 5872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105872
APA StylePerez-Sousa, M. A., Pedro, J., Carrasco-Zahinos, R., Raimundo, A., Parraca, J. A., & Tomas-Carus, P. (2023). Effects of Aquatic Exercises for Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A 12-Week Intervention in a Quasi-Experimental Study with Pain as a Mediator of Depression. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(10), 5872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105872








