Abstract
Heavy metals pollution of water resources is an emerging concern worldwide and seeks immediate attention. Date palm waste was transformed into biochar (BC), which was further modified through Fe-intercalation for the production of magnetic biochar (Fe-BC) in this study. The produced BC and Fe-BC were analyzed for chemical, proximate, surface, and elemental composition. The efficiency of the produced adsorbents to decontaminate the water from Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions was investigated through kinetics and an isotherm adsorption batch trial. Kinetics adsorption data fit well with the pseudo-second order and power function model, while equilibrium data were described well with the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms. The maximum adsorption capacity as shown by the Langmuir model was the highest for Fe-BC for both Cd2+ (48.44 mg g−1) and Pb2+ (475.14 mg g−1), compared with that of BC (26.78 mg g−1 Cd2+ and 160.07 mg g−1 Pb2+). Both materials showed higher removal of Pb (36.34% and 99.90% on BC and Fe-BC, respectively) as compared with Cd (5.23% and 12.28% on BC and Fe-BC, respectively) from a binary solution. Overall, Fe-BC was more efficient in adsorbing both of the studied metals from contaminated water. The application of Fe-BC resulted in 89% higher adsorption of Cd2+ and 197% higher adsorption of Pb2+ from aqueous media as compared to BC. Kinetics and isotherm models as well as SEM–EDS analysis of the post-adsorption adsorbents suggested multiple adsorption mechanisms including chemisorption, pore-diffusion, and electrostatic interactions.
1. Introduction
The demand for fresh and clean water resources is increasing rapidly due to the prompt increase in global population [1]. It is reported that gross per-capita water availability may be reduced significantly by 2050, as the global water requirement is increasing annually [2]. In developing countries, water pollution is one of the major problems, as in these countries people do not have the resources to treat the contaminated water and use it for drinking purposes. It was reported by the World Health Organization (WHO) that about 844 million people cannot drink water which could be safe for drinking purposes, whereas 230 million of the population devote 30 min in a single day to collect drinkable water from improved sources including boreholes, piped water, rainwater, and packed water [3]. The failure in consistency in access to clean drinking water causes an increase in diseases such as diarrhea, which leads to the death of about 1.6 million people each year, and among these deaths, 90% includes children under the age of 5 years [4]. Moreover, the water quality of the resources is depleting quickly because of different kinds of inorganic and organic pollutants, which are being released from various anthropogenic activities. Moreover, natural resources are also contributing to this pollution. Human beings are being influenced by the polluted water through various approaches, including exposure to toxic chemicals which are being used to irrigate the plants. More than 700 inorganic and organic pollutants have been investigated in the water [5], and from these contaminants, heavy metals are considered to be more hazardous due to their toxic nature and persistency [6]. In the present era, industrialization and urbanization have contributed to an increase in adding heavy metals to the environment. Heavy metals contaminate the water through different activities, including mining, metal plating, tanneries, batteries, painting, and fertilizers [7]. These heavy metals are toxic and can reside in the environment for a long time as they are non-degradable. Among the most toxic heavy metals, cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) are of critical importance due to their wide range of applications such in fertilizer, pesticide, cosmetics, batteries, and other industries. Exposure to Pb and Cd may cause serious toxicological issues by affecting the skin, brain, pancreas, liver, and myocardium. Pb poses serious health risks to humans, such as encephalopathy, anemia, hepatitis, and nephritic syndrome [8].
Several techniques have been previously introduced by researchers for the treatment of wastewater, such as oxidation, catalytic degradation, membrane-filtration, solvent extraction, ion exchange, microbial degradation, and steam stripping [9,10,11]. However, the majority of these techniques need high electricity and more resources, which makes them very expensive to use, and therefore there is a need to develop alternative methods that should not only be cost-effective but also easily available and ready-to-use. Adsorption is a common technology worldwide as it is economic and easy. Biomass-derived biochar is considered an excellent adsorbent to adsorb the heavy metals from water and soil. Biochar (BC) is a black carbonaceous material, which is produced by biomass pyrolysis under limited-to-no oxygen supply [12]. In recent times, biochar has gained the world’s attention for various environmental and agricultural applications [13,14,15]. Due to its functional groups, high surface area, porous structure and net negative charges, BC can be used for the removal of numerous inorganic and organic pollutants [16]. However, BC cannot always perform well due to its heterogeneous structure and properties. It was reported that unmodified BC does not perform at the maximum level due to its low anti-interference capability and low adsorption capacity [17]. On the other hand, BC contains positive and negative charges at the same time; therefore, it makes the BC incapable of adsorbing anionic contaminants [18]. To overcome these limitations, scientists are paying attention to BC modification for targeted applications.
Recently, the modification of BC with foreign material via physical, biological, and chemical treatments has gained much attention as it improves the physiochemical characteristic of BC and increases its efficacy for targeted applications [19]. Additionally, different techniques have been employed by the researchers to modify BC, such as treatment with steam, gas, acids, alkali, oxidants, and microwaves [20]. For instance, Zhou et al. [21] modified BC with chitosan and observed an improvement in surface functional groups, which in turn resulted in the higher removal of Pb2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+ heavy metals. Similarly, Bakshi et al. [22] modified BC with hematite to fabricate zero-valent iron-BC composites and demonstrated an excellent removal capacity for arsenic. BC modification with iron has demonstrated an excellent performance for the removal of pollutants from the environment; however, it is challenging to separate BC particles from the liquid–solid phase due to their small size. Therefore, magnetic-BC composites are more conducive and efficient for contaminant removal; however, most of the methods to synthesize magnetic-BC are complicated. Moreover, there is a possibility for magnetic particles to occupy the adsorption sites of BC. Thus, new techniques are needed to design highly efficient magnetic-BC for heavy metals removal from the environment. By keeping in view the whole scenario, the innovative solution to this problem is to develop magnetic biochar composites. Magnetic biochar composites have been gaining worldwide attention in the last few decades because of their excellent adsorption capacity and magnetic separation technique [23]. Therefore, date palm tree waste was pyrolyzed to produce biochar, which was then modified to synthesize magnetic biochar in this study. The efficacy of the produced pristine and Fe-modified biochars to remove Cd2+ and Pb2+ from contaminated aqueous solution was investigated in batch-type sorption experiments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochar Production
Local agricultural farms in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia were visited, and wastes from date palm tree pruning was collected. The collected waste was thoroughly washed with tap water followed by deionized water to get rid of any soil or dust particles, and then exposed to direct sunlight and dried in air. The petiole bases (fronds) were separated from the waste and cut into smaller pieces. Smaller-sized date palm waste (DFS) was pyrolyzed in a furnace. The DFS was placed in stainless steel boxes and placed into a furnace for pyrolysis at 550 °C for 180 min in an oven under limited oxygen supply. After the completion of pyrolysis, the box was cooled down, and the resultant biochar (BC) was weighed, grinded, and passed through a 2 mm sieve. The yield of the BC was calculated as below:
2.2. Biochar Modification
The resultant BC was modified to synthetize Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC) by using the previously reported method of Zhang et al. [24]. Specifically, a solution containing 2.92 g of Fe2(SO4)3 or 7.30 g of FeSO47H2O (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) was prepared in deionized water. In another flask, 10 g of synthesized BC was added slowly into 200 mL of deionized water under continuous stirring. The suspension was sonicated for 30 min and then stirred for 1 h for complete homogenization. The BC suspension was then added into the Fe3+/Fe2+ mixture slowly under continuous stirring, and the pH of this suspension was adjusted to 10 by the drop-wise addition of NaOH (Fisher Scientific Co., Springfield, NJ, USA). This mixture was put on a stirrer and stirred for 2 h and then allowed to sit for 24 h at ambient temperature (23 ± 2 °C). After that, the solid material was separated from the liquid–solution phase, washed several times using deionized water, dried in a vacuum oven, and labelled as Fe-BC.
2.3. Characterization
The produced Fe-BC and pristine BC were subjected for proximate and chemical analysis. The proximate properties were analyzed by following the standard protocols [25]. The pH was analyzed in a 1:10 ratio suspension, while cation exchange capacity (CEC) of the materials was determined through the procedure reported by Richard [26]. Functional groups were estimated by analyzing the samples on FTIR (Bruker Optics, Inc., Ettlingen, Germany), whereas the mineral composition was analyzed with the help of MAXima_X XRD-7000 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The pore size and surface area of the adsorbents were measured with the help of TriStar II 3020, Micromeritics (USA). Surface morphology qualitative elemental composition were analyzed by a scanning electron microscope attached with EDS. The contents of hydrogen (H), carbon (C), sulfur (S), and nitrogen (N) in the samples were analyzed with the help of the CHNS-O analyzer (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA), whereas the contents of oxygen (O) were estimated by the difference method as shown in Equation (2).
O (%) = 100 − [C (%) + H (%) + N (%) + S (%) + ash (%)]
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
The efficacy of BC and Fe-BC to adsorb Cd2+ and Pb2+ from contaminated water was investigated via adsorption batch experiments. Briefly, the exact weight of Pb(NO3)2 or Cd(NO3)2·4H2O (LobaChemie, Mumbai, India) was dissolved in deionized water to obtain a stock solution containing 1000 mg L−1 of Cd2+ or Pb2+. After complete dissolution, serial dilution was carried out to prepare the metal-containing solutions with various initial concentrations of Cd2+ or Pb2+. Thereafter, the pH of the solutions was adjusted to 5.0 with the help of diluted NaOH or HNO3. These metal-containing solutions were then subjected to kinetics and isotherm batch experiments. Specifically, 30 mL of the metal-containing solution was taken and 1 g L−1 adsorbent was added. This mixture was put on the shaker for a specific period of time (0–1440 min) at 150 rpm. All the trials were replicated three times, and control treatments (without any adsorbent) were also included. After a specific time interval, the solution was filtered with Whatman-42 filter papers and the left-over concentrations of Cd2+ or Pb2+ in the solutions were measured with the help of an ICP-OES (PerkinElmer Optima 4300 DV, USA).
The amount of Cd2+ or Pb2+ adsorbed on the adsorbent can be calculated by following Equation (3):
where Qt is the amount of adsorbate (mg g−1) at time t, C0 and Ct are initial concentration and remaining adsorbate after the adsorption process (mg L−1), respectively, V represents volume (L), and m represents the mass of the adsorbent (g).
Kinetics adsorption trials were conducted by using the initial concentration of 100 mg L−1 of Cd2+ or Pb2+, and an initial pH of 5.0. At pH 5, Cd2+ or Pb2+ ions are mobile and soluble in aqueous solution. Different time intervals such as 0, 15, 30, 60, 120, 180, 300, 480 and 720 and 140 min were used in the kinetics experiments. To perform the isotherm adsorption experiments, various initial concentrations of Pb2+ (0, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400, and 600 mg L−1) and Cd2+ (0, 5, 10, 30, 60, and 100 mg L−1) with an initial pH of 5.0 were used. The equilibrium studies were conducted for 1440 min of equilibrium time.
The regeneration trials of Fe-BC and BC were conducted using 0.2 M HCl up to 4 cycles. The initial concentrations for Cd2+ and Pb2+ in regeneration studies were 100 and 600 mg L−1, respectively. Briefly, Cd2+- or Pb2+-loaded adsorbents were washed with deionized water to remove surplus metal, and dried in an oven at 60 °C. Thereafter, the dried adsorbents loaded with Cd2+ or Pb2+ were suspended into 30 mL of 0.2 M HCl solution and shaken for 1440 min at 150 rpm. Then, the solutions were separated from the adsorbent and subjected to Cd2+ and Pb2+ analyses by ICP-OES, while the adsorbents were washed with deionized water, dried, and subjected to another cycle of adsorption–desorption.
Different kinetics as well as isotherm models were applied to investigate the adsorption process of Cd2+ or Pb2+ by BC and Fe-BC.
The pseudo-first-order kinetic model was applied as shown in Equation (4).
where k’1 and qe stand for rate constants and adsorption capacity (mg g−1), respectively.
The pseudo-second order was applied as shown in Equation (5).
where k2 are the pseudo-second-order rate constants.
Elovich kinetics were applied as shown in Equation (6).
where α stands for initial adsorption in mg g−1 min−1, and β represents the Elovich rate constant.
The expression of the intraparticle diffusion kinetics model is shown in Equation (7).
where c represents the intraparticle diffusion constant and kid stands for the apparent diffusion rate constant [(mg g−1)0.5].
The non-linear form of the Freundlich isotherm is shown in Equation (8).
where n and KF represent adsorption intensity and the Freundlich isotherm constant (mg g−1) (L mg−1)n, respectively.
The non-linear form of the Langmuir isotherm is expressed in Equation (9).
where QL is the maximum adsorption capacity (mg g−1), and KL is the Langmuir isotherm constant (L mg−1).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. This Adsorbent Characterization
Some of the chemical and proximate analyses of DFS, BC, and Fe-BC are shown in Table 1. The results found that the pH of the DFS was noted less in comparison to BC and Fe-BC. After pyrolyzing the material, the pH was increased to 9.26 in BC from 6.78 in DFS. The exclusion of acidic groups and condensation of alkali salts could have resulted in pH increment [27]. DFS showed the lowest CEC (54.78 cmol kg−1), which was increased by 15% (63.19 cmol kg−1) in BC and up to 87% in Fe-BC (81.74 cmol kg−1). The highest CEC of Fe-BC than that of BC could be due to the presence of Fe-particles. Results showed that Fe contents in BC were 0.12%, while in Fe-BC they were 19.05%, respectively. The produced BC showed 35.47% of the yield and 1.02% moisture contents, whereas DFS and Fe-BC showed 3.21% and 2.08% of moisture contents, respectively. DFS showed the highest volatile matter (62.88%), which reduced almost 4-fold in BC and 4.7-fold in Fe-BC. On the contrary, the ash contents increased from 15.45% in DFS to 25.98% in BC and 51.03% in Fe-BC. Likewise, the resident matter was increased with the pyrolysis process from 18.51% in DFS to 56.79% in BC and 33.49% in Fe-BC. However, the lower resident matter contents of Fe-BC than BC could be due to the presence of Fe-particles in Fe-BC, which might have been confused with ash contents [18]. Higher ash contents in BC materials as compared to DFS could be due to the formation of some mineral compounds due to the thermalization process [28].

Table 1.
Some chemical and proximate analyses of date palm waste (DFS), biochar (BC), and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC).
Table 2 presents the surface area and elemental contents of the produced adsorbents. It was noted that the C contents were enhanced from 41.82% in DFS to 68.82% in BC and 72.98% in Fe-BC. In contrast, O, N, and H were decreased with the pyrolysis process due to dehydration and depolymerization [29]. However, H contents in Fe-BC were higher than pristine BC, which could be due to H-bonding of Fe with the biochar surface. Fe-BC represented the highest Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area (119.82 m2 g−1), while BC and DFS showed the lowest (68.49 and 2.28 m2 g−1, respectively). Likewise, Fe-BC showed the lowest pore size (4.72 nm) as compared to BC (9.18 nm) and DFS (31.71 nm). The highest surface area of Fe-BC may be because of the existence of Fe-particles, while the lower pore size could be due to aromaticity and the loss of volatile matter (as shown in Table 1) [27].

Table 2.
Elemental composition and surface characteristics of date palm waste (DFS), biochar (BC), and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC).
The functional groups’ composition was observed with the help of an FTIR, and the results are shown in Figure 1. A band representing O–H stretching was observed between 3300–3500 cm−1 in DFS, which was removed with pyrolysis in BC, while it appeared again in Fe-BC spectra. This band was probably associated with moisture contents in the sample [18,27]. A band with large intensity was seen at 1050–1100 cm−1 in DFS and BC, while its intensity was significantly reduced in Fe-BC. This band was due to the existence of C–O–C stretching of polysaccharide cellulose [27]. A small band at 3450 cm−1 in Fe-BC was proof for the presence of Fe-particles (ferrioxyhydroxide (FeOOH)) in this composite material as these bands represent OH stretching vibrations [30]. Similarly, a band around 874 cm−1 in Fe-BC could be due to the presence of Fe particles. Likewise, the mineralogical composition of the produced amendments as assessed by XRD analysis is shown in Figure 2. The presence of mellite was witnessed in DFS at 21.48° 2θ, but it was removed during pyrolysis and could not be seen in BC and Fe-BC. The same happened with calcite mineral (29.21° 2θ; JCPDS: 47-1743), which was substantially reduced in BC and Fe-BC as compared to DFS. Akin to FTIR, the presence of the Fe particles was also witnessed by the XRD results of Fe-BC by observing a peak at 44.21 and 63.25° 2θ (JCPDS 00-001-1267). Likewise, a peak representing hematite (JCPDS Card No. 01-073-0603) was found at 35.54° 2θ in the Fe-BC material. These results represent significant variations in chemical, proximate, morphological, and structural properties of DFS, and the produced BC and Fe-BC. Moreover, the successful enrichment of Fe into biochar was also noticed.
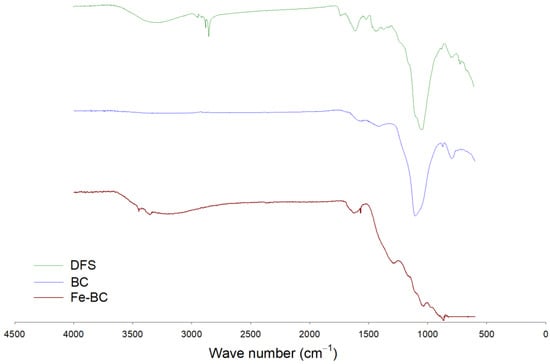
Figure 1.
FTIR analysis of date palm waste (DFS), date palm waste biochar (BC), and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC).
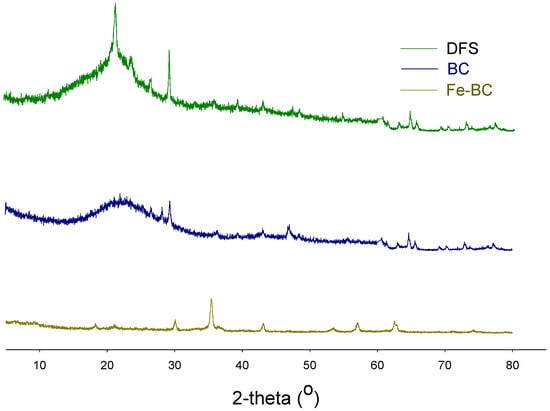
Figure 2.
X-ray diffraction analysis of date palm waste (DFS), date palm waste biochar (BC), and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC).
3.2. Kinetic Adsorption of Cd2+ or Pb2+
The performance of the produced BC and Fe-modified BC to adsorb Cd2+ or Pb2+ from contaminated water was assessed in batch-type adsorption experiments. The effect of contact time on the adsorption of Cd2+ or Pb2+ onto the adsorbents is shown in Figure 3. The adsorption of Cd2+ or Pb2+ followed three phases, i.e., rapid, relatively slower, and equilibrium. A relatively quicker adsorption for both of the metals was seen during the first 200 min due to the accessibility of plentiful adsorption sites, followed by a relatively slow adsorption and eventually equilibrium stage. Overall, the adsorption of Pb2+ was higher than Cd2+ onto both of the adsorbents. This is because Pb2+ contains a negative logarithm of hydrolysis constant (7.71), which is less than that of Cd2+ (10.1) and helps Pb2+ to be adsorbed easily via surface complexation [31]. The Fe-BC exhibited a higher adsorption capacity compared with the pristine BC.
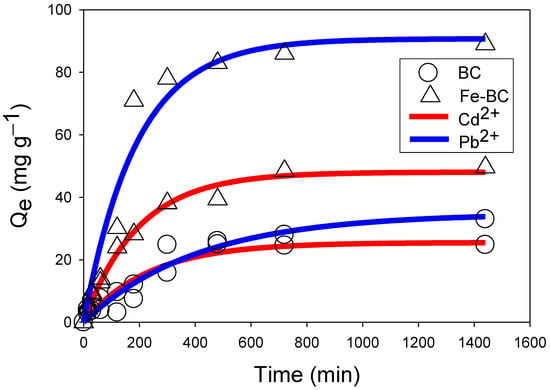
Figure 3.
Effect of contact time on the adsorption of cadmium (Cd2+) and lead (Pb2+) on date palm waste biochar (BC) and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC).
The adsorption data were subjected to different kinetics models. The kinetics parameters and coefficient of correlation (R2) are presented in Table 3. The results showed that the pseudo-second order fit well with the adsorption data for both of the studied metals (R2 = 0.93–0.98), followed by power function (R2 = 0.85–0.98). However, other models were marginally fit to the adsorption data (R2 = 0.93–0.98). The initial sorption rates (h) as presented by the pseudo-second order were highest for Fe-BC for the adsorption of Cd2+ (0.39 mg g−1 m−1) and Pb2+ (0.52 mg g−1 m−1), while pristine BC showed the lowest h for both Cd2+ and Pb2+ (0.23 and 0.08 mg g−1 m−1, respectively). Moreover, the pseudo-second order presented that the highest adsorption capacity was higher for Fe-BC both for the adsorption of Pb2+ (105.49 mg g−1) and Cd2+ (54.49 mg g−1) in comparison to the maximum adsorption capacity of BC for Pb2+ (45.89 mg g−1) and Cd2+ (27.12 mg g−1).

Table 3.
Parameters obtained from kinetic models for cadmium (Cd2+) and lead (Pb2+) adsorption on date palm waste biochar (BC) and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC).
The best fitness of the pseudo-second order model for Pb2+ and Cd2+ adsorption on the Fe-BC and BC suggests the occurrence of the chemisorption mechanism (Reddy and Lee, 2014). Followed by the pseudo-second order model, the power function model presented the R2 values 0.98–0.97 for Cd2+ adsorption and 0.85–0.95 for Pb2+ adsorption. The rate coefficient (kf) values of the power function model were higher for Fe-BC (0.70 mg g−1 m−1) and BC (0.52 mg g−1 m−1) for Pb2+ adsorption as compared with Cd2+ adsorption (0.58 and 0.46 mg g−1 m−1 for Fe-BC and BC, respectively). The rate constants (b) of the power function model were found as 0.13 for both the adsorbents for Cd2+ adsorption, while it was found as 0.10 and 0.02 for BC and Fe-BC, respectively, for Pb2+ sorption. The suitability of the power function model proposed the occurrence of homogenous chemisorption adsorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+ onto the produced adsorbents, which is also in agreement with fitness of the pseudo-second order [32]. Overall, the rate coefficients of the kinetics models were higher for Fe-BC than pristine BC, suggesting better adsorption of these metals onto Fe-BC. Moreover, the marginal fitness of the intraparticle diffusion model advocated that pore diffusion has also aided the adsorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+ onto BC and Fe-BC. Overall, Fe-BC was found to be a more efficient adsorbent for the removal of Cd2+ and Pb2+ from the contaminated aqueous media.
3.3. Equilibrium Adsorption of Cd2+ or Pb2+
Isotherm models including Freundlich and Langmuir were applied on Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions adsorption data, and the constructed isotherms are shown in Figure 4. From the applied isotherm models, initially a quicker adsorption was observed with lower initial concentrations of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions, indicating the presence of abundant free active sites for adsorption, subsequently making L-type isotherm curves. However, at the later stage, with increasing the initial concentrations of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions, the adsorption sites were occupied with Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions and the curves moved to the right, showing a slower adsorption and ultimately leading to the equilibrium stage. Overall, the adsorption capacity of Fe-BC was far greater compared with BC in adsorbing both of the studied metals. On the other hand, both of the adsorbents showed a higher affinity towards Pb2+ adsorption, and removed almost all of the Pb2+ at 100 mg L−1. Therefore, the produced adsorbents remained more efficient in removing Pb2+ compared with Cd2+ ions from contaminated water.
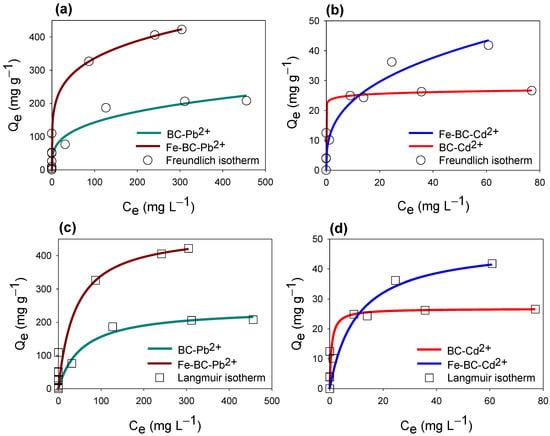
Figure 4.
Isotherm curves for Freundlich (a,b) and Langmuir (c,d) models’ fittings for cadmium (Cd2+) and lead (Pb2+) adsorption on date palm waste biochar (BC) and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC).
The parameters presented by the isotherm curve fittings are presented in Table 4. Both of the applied models fit best with the Pb2+ adsorption, whereas Cd2+ adsorption data were only fit best with the Langmuir isotherm as is indicated by the R2. The maximum adsorption capacity estimated by the Langmuir model (QL) was highest for Fe-BC for adsorbing both of the metals. Overall, the maximum adsorption capacities for Pb2+ were higher than for Cd2+. QL for Pb2+ adsorption onto BC and Fe-BC was 160.07 and 475.14 mg g−1, respectively, while it was 26.78 and 48.44 mg g−1 for Cd2+ adsorption, respectively. Likewise, the Freundlich isotherm predicted KF values were higher for Fe-BC for the adsorption of both metals (23.30 and 129.06 L g−1 for Cd2+ and Pb2+, respectively) as compared to the pristine BC (10.56 and 36.66 L g−1, for Cd2+ and Pb2+, respectively). The 1/n values presented by the Freundlich isotherm for Pb2+ adsorption were found as 0.207 for Fe-BC and 0.295 for BC, while these values were 0.345 for BC and 0.031 for Fe-BC in the case of Cd2+ adsorption. These results indicated that 1/n values for both of adsorbents for Cd2+ and Pb2+ adsorption were less than 1, suggesting that the adsorption was satisfactory at initial lower concentration because of surface loading. Moreover, 1/n values for Fe-BC were lower than pristine BC for both of the models, suggesting more favorable adsorption onto Fe-BC than unmodified BC [18]. The fitness of both isotherm models indicated the involvement of both monolayer and multilayer adsorption mechanisms. Overall, the higher adsorption of Pb2+ onto both of the adsorbents could partially be due to diffusion into the pores as well [33]. The high surface area and pore structure of Fe-BC could have adsorbed Cd2+ and Pb2+ by pore diffusion and physical adsorption [34]. Moreover, ion exchange and electrostatic interactions can also affect the adsorption of metals onto the BC surface [35,36]. The higher adsorption capacity of Fe-BC for both of the studied metals could be due to the presence of Fe2O3/Fe3O4 in this material, which were uniformly distributed on the surface of the adsorbent. Therefore, the adsorption of metals by Fe-BC could be due to a collective effect of complexation, electrostatic attraction, diffusion, and ion exchange, which supported the maximum adsorption of metals, whereas this phenomenon was not possible with pristine BC. Moreover, regeneration studies showed that Cd2+ and Pb2+ removal efficiencies of Fe-BC were 29.58% and 45.31% after 4 cycles, respectively, which was lower than that of BC (38.13% and 53.38%, respectively). Reduction in Fe-BC efficiency could be due to oxidation and dissociation of Fe particles [18]. The maximum adsorption capacities of different magnetic BCs for Cd2+ and Pb2+ have been compared and enlisted in Table 5. It can be seen that the maximum adsorption capacity of Fe-BC for Cd2+ and Pb2+ in current study was much higher than various previously tested magnetic BCs in the literature. Hence, these results suggested that Fe-BC was an effective, robust, and sustainable adsorbent for removing Cd2+ and Pb2+ from the contaminated water.

Table 4.
Non-linear parameters of isotherm models for cadmium (Cd2+) and lead (Pb2+) adsorption on date palm waste biochar (BC) and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC).

Table 5.
Maximum adsorption capacities of different magnetic biochars for cadmium and lead from aqueous media.
3.4. Adsorption Mechanism
The impacts of the coexisting metals ions (Pb2+ and Cd2+) on adsorption capacity are shown in Figure 5a. The binary adsorption system affected the adsorption of both the coexisting metals, and demonstrated the competitive effect of Pb2+ and Cd2+ on the removal of each other. As presented in Figure 5a, Pb2+ adsorption was far greater than Cd2+ on both Fe-BC and BC. The pristine BC could remove 5.23% of Cd2+ and36.34% of Pb2+ from a binary solution containing 100 mg L−1 of both of aforementioned metals. Similarly, Fe-BC proved to be an excellent adsorbent by removing 99.90% of Pb2+ and only 12.28% of Cd2+ from the binary solution. These results suggest more adsorption of Pb2+ as compared to Cd2+. It could be stated that a complexation interaction may have occurred between the metals in the binary system. Multiple mechanisms were involved in the sorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ on the Fe-BC and pristine BC, including electrostatic interaction, ion exchange, surface complexation, chemical sorption, and intraparticle diffusion [34]. The higher adsorption of Pb2+ could be due to its bigger ionic size (Cd2+ = 1.03 Å and Pb2+ = 1.32 Å), which may create the Pb2+ aquo-cation, ultimately attracting the adsorption sites in vicinity and stabilizing the adsorbate [42]. Moreover, the hydrated radius (4.01 Å) and negative log of hydrolysis (7.71) of Pb2+ is less than that of Cd2+ (4.26 Å and 10.1, respectively) which might have favored its adsorption to the adsorbent [43]. Hence, Pb2+ exhibited the competitive adsorption advantage over Cd2+.
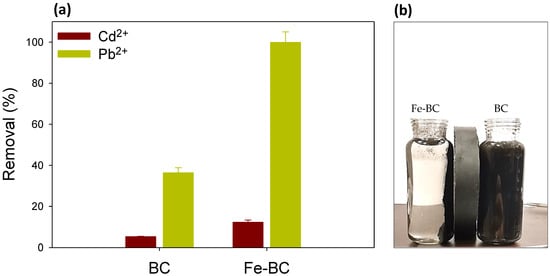
Figure 5.
(a) Competitive removal of cadmium (Cd2+) and lead (Pb2+) ions from binary solution on date palm waste biochar (BC) and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC), (b) attraction of BC and Fe-BC materials to the applied magnetic force.
The solution’s pH is one of the critical factors influencing the adsorption process and competition of metals ions for the adsorption sites. The net surface charge as well as the type of speciation of the metal is highly dependent on the solution pH. It has been reported previously that metals such as Pb2+ and Cd2+ exist in ionic form below pH 7.0, and thus, can easily be adsorbed on the adsorbent through electrostatic interactions and binding on surface functional groups [44]. Generally, at lower pH levels, H+ is bounded with functional groups present on the surface of the adsorbent, subsequently attracting metals ions for adsorption. A further increase in pH may result in deprotonation, consequently making surface functional groups adsorption sites for metal ions [45]. In the current study, the pH of the solution for both BC and Fe-BC remained below 7.0 (initial pH 5 was used) as shown in Figure 6. Further, the pH in the Fe-BC-metal suspensions was lower than BC-metal suspension. Therefore, the lower pH levels of the adsorbent–adsorbate suspension suggested the adsorption chemical adsorption electrostatic interactions were involved in the adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ on BC and Fe-BC. These results are in agreement with the results of isotherm and kinetic model simulations. The kinetic adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ suggested the involvement of chemisorption and pore diffusion of metals, while the results of isotherm models suggested the presence of both the monolayer and multilayer adsorption of metals on the heterogeneous surface of the adsorbents. The adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ on the produced adsorbents was further confirmed by SEM–EDS analysis (Figure 7). The pristine BC has 0.19% of Fe contents, which were increased to 32.27% within magnetic BC (Fe-BC). The EDS results revealed that the pristine BC and Fe-BC have no Pb2+ or Cd2+. However, after the adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from the contaminated water, BC showed 3.59% of Pb2+ and 4.59% of Cd2+, while Fe-BC showed 5.24% of Pb2+ and 5.66% of Cd2+. The presence of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in higher amounts after the adsorption trials is indication for the successful adsorption of these metals on BC and Fe-BC. Further, the higher adsorption of metals onto Fe-BC than that of BC is obvious with the higher weight percentages of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Fe-BC after adsorption trials. The reduction in Fe contents from 32.27% in Fe-BC to 27.43% in Cd2+-loaded Fe-BC and 10.12% in Pb2+-loaded Fe-BC suggested the leaching of Fe-particles during the adsorption trials, which might have resulted in reducing the adsorption capacity of these adsorbents after four cycles of regeneration compared with BC. On the contrary, Fe-BC showed a higher recovery under applied magnetic field compared with BC (Figure 5b), which suggests the higher potential of Fe-BC for regeneration and repeated application. However, even with the reduced activity of Fe-BC after four regenerations, its Pb2+ and Cd2+ removal efficiency was relatively higher than most of the previously reported magnetic biochars. Therefore, modification of BC with Fe could be used as an excellent adsorbent for the removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from contaminated water on a sustainable basis.
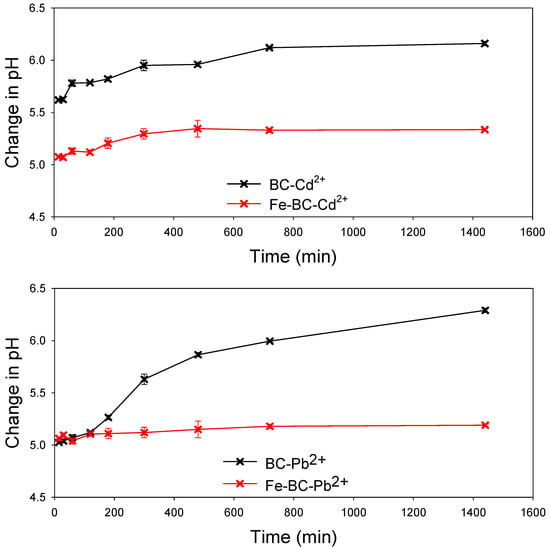
Figure 6.
Changes in solution pH with time for the adsorption of cadmium (Cd2+) and lead (Pb2+) ions on date palm waste biochar (BC) and Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC).
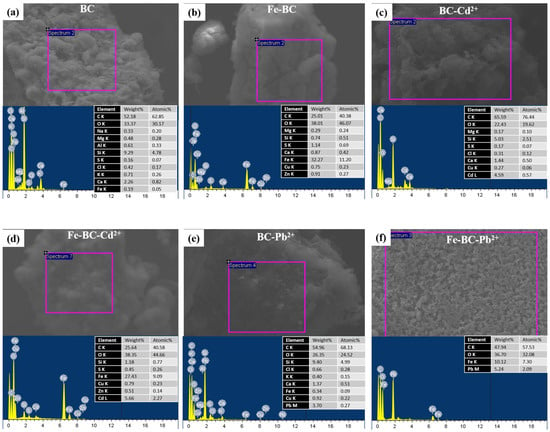
Figure 7.
SEM–EDS analyses for (a) date palm waste biochar (BC), (b) Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC) before the adsorption, and after the (c) adsorption of cadmium (Cd2+) onto BC, (d) adsorption of Cd2+ onto Fe-BC, (e) adsorption of lead (Pb2+) onto BC, and (f) adsorption of Pb2+ onto Fe-BC.
4. Conclusions
Date palm waste was pyrolyzed to produce biochar (BC), which was subsequently modified to produce Fe-modified biochar (Fe-BC). The synthesized adsorbents were analyzed for chemical, structural, and surface properties, and successfully employed for the adsorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+ from the contaminated water. The results of the modeling data showed the best suitability of the adsorption data to the pseudo-second order and power function kinetic models, as well as to the Freundlich and Langmuir isotherm models. The best fitness of the adsorption date to the Freundlich and Langmuir isotherm models suggested the occurrence of mono- and multilayer adsorption. The adsorption of Pb2+ was seven to eight-fold higher than the adsorption of Cd2+ on both of the used adsorbents. Overall, Fe-BC was more efficient in removing both the Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions from the contaminated solution. Fe-BC application adsorbed 89% more Cd2+ and 197% more Pb2+ in comparison to BC, indicating the higher efficacy of Fe-BC towards both Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions. Cd2+- and Pb2+-loaded adsorbents were analyzed with SEM–EDS. The presence of Cd2+ and Pb2+ on the adsorbents was observed in post-adsorption SEM–EDS results, suggesting successful adsorbate–adsorbent bindings. Hence, Cd2+- and Pb2+-contaminated wastewater can effectively be remediated with Fe-modified BC on a sustainable basis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, project administration, writing—original draft preparation, A.G.A. and Z.A.; formal analysis, data curation, supervision, reviewing and editing the manuscript, A.G.A. and Z.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project no. (IFKSURG-2-1168).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Manikandan, S.; Subbaiya, R.; Saravanan, M.; Ponraj, M.; Selvam, M.; Pugazhendhi, A. A critical review of advanced nanotechnology and hybrid membrane based water recycling, reuse, and wastewater treatment processes. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 132867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN-Water. 2018 UN World Water Development Report, Nature-Based Solutions for Water; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- UNICEF; WHO. Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Pandit, A.B.; Kumar, J.K. Clean Water for Developing Countries. Annal. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2015, 6, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I. The Quest for Active Carbon Adsorbent Substitutes: Inexpensive Adsorbents for Toxic Metal Ions Removal from Wastewater. Separ. Purif. Rev. 2010, 39, 95–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Brit. Medic. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Obidul Huq, A.K.; binti Yahya, R. The removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater/aqueous solution using polypyrrole-based adsorbents: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14778–14791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Su, Y.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X. Biosorption of copper (II) and lead (II) from aqueous solutions by nonliving green algae Cladophora fascicularis: Equilibrium, kinetics and environmental effects. Adsorption 2006, 12, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Naeem, S.; Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.R.A.; Al-Wabel, M.I. A critical review on organic micropollutants contamination in wastewater and removal through carbon nanotubes. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Tao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ding, X.; Chu, H. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Gao, B. Removal of Cu, Zn, and Cd from aqueous solutions by the dairy manure-derived biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.; Macdonald, L.M.; Butler, G.; Chirino-Valle, I.; Condron, L.M. Biochar and fertiliser applications influence phosphorus fractionation and wheat yield. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayogo, C.; Jones, J.E.; Baeyens, J.; Bending, G.D. Impact of biochar on mineralisation of C and N from soil and willow litter and its relationship with microbial community biomass and structure. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, J.; Rondon, M.; Molina, D.; Riha, S.J.; Lehmann, J. Maize yield and nutrition during 4 years after biochar application to a Colombian savanna oxisol. Plant Soil 2010, 333, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.H.; Lee, S.M. Magnetic biochar composite: Facile synthesis, characterization, and application for heavy metal removal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 454, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, J.; Yang, L. Engineered Biochar Reclaiming Phosphate from Aqueous Solutions: Mechanisms and Potential Application as a Slow-Release Fertilizer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8700–8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.R.; Rafique, M.I.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Engineered biochar composites with zeolite, silica, and nano-zerovalent iron for the efficient scavenging of chlortetracycline from aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 15136–15152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, Y.S.; Chang, S.X.; Gao, B.; Chung, H.-J. SMART biochar technology—A shifting paradigm towards advanced materials and healthcare research. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 4, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, N.L.; Pawar, A. Influence of activation conditions on the physicochemical properties of activated biochar: A review. Biomass Conver. Biorefin. 2020, 12, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Fang, J.; Sun, Y.; Cao, X. Sorption of heavy metals on chitosan-modified biochars and its biological effects. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Banik, C.; Rathke, S.J.; Laird, D.A. Arsenic sorption on zero-valent iron-biochar complexes. Water Res. 2018, 137, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, C. Adsorption of methylene blue onto humic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 435, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Ali, A.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced aqueous Cr (VI) removal using chitosan-modified magnetic biochars derived from bamboo residues. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM D1762-84; Standard Methods for Chemical Analysis of Wood Charcoal. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1989.
- Richard, L.A. Diagnoses and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agriculture Handbook, 60: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.R.; Al-Faraj, A.S.; Abduljabbar, A.S.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Biochar composites with nano zerovalent iron and eggshell powder for nitrate removal from aqueous solution with coexisting chloride ions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 25757–25771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, L. Effects of feedstock type, production method, and pyrolysis temperature on biochar and hydrochar properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Al-Omran, A.; El-Naggar, A.H.; Nadeem, M.; Usman, A.R.A. Pyrolysis temperature induced changes in characteristics and chemical composition of biochar produced from conocarpus wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Misra, V.; Singh, R.P. Synthesis, characterization and role of zero-valent iron nanoparticle in removal of hexavalent chromium from chromium-spiked soil. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 4063–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, J.S.; Heo, J.S.; Delaune, R.D.; Seo, D.C. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto sesame straw biochar in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakaduwa, S.S.; Kumarathilaka, P.; Herath, I.; Ahmad, M.; Al-Wabel, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Usman, A.; Abduljabbar, A.; Vithanage, M. Equilibrium and kinetic mechanisms of woody biochar on aqueous glyphosate removal. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2516–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wei, D.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Yan, L.; Wei, Q.; Du, B.; Xu, W. EDTA functionalized magnetic biochar for Pb (II) removal: Adsorption performance, mechanism and SVM model prediction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.H.; Wang, D.; Wei, Z.S.; Chang, J.S.; Ren, N.Q. Lead removal by a magnetic biochar derived from persulfate-ZVI treated sludge together with one-pot pyrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Oladipo, A.A.; Ahaka, E.O.; Gazi, M. High adsorptive potential of calcined magnetic biochar derived from banana peels for Cu2+, Hg2+, and Zn2+ ions removal in single and ternary systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 31, 31887–31899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedifar, M.; Seyedi, N.; Shafiei, S.; Basij, M. Surface-modified magnetic biochar: Highly efficient adsorbents for removal of Pb(ΙΙ) and Cd(ΙΙ). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 271, 124860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Kumar, H.; Sarswat, A.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Pittman Jr, C.U. Cadmium and lead remediation using magnetic oak wood and oak bark fast pyrolysis bio-chars. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakal, L.; Bingöl, D.; Pohořelý, M.; Hruška, M.; Komárek, M. Geochemical and spectroscopic investigations of Cd and Pb sorption mechanisms on contrasting biochars: Engineering implications. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Kong, L.; Qu, Z.; Li, L.; Shen, G. Magnetic biochar decorated with ZnS nanocrytals for Pb (II) removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, M.W.; Mubarak, N.M.; Sahu, J.N.; Abdullah, E.C. Microwave induced synthesis of magnetic biochar from agricultural biomass for removal of lead and cadmium from wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 45, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.H.; Gao, M.; Qiu, W.; Islam, M.S.; Song, Z. Mechanisms for cadmium adsorption by magnetic biochar composites in an aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Tan, X.; Huang, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, B.; Cai, X. Competitive removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by biochars produced from water hyacinths: Performance and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 7, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.J.; Huang, Q.S.; Wang, C.; Ni, T.Y.; Sun, J.; Wei, W. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals in aqueous solution onto biochar derived from anaerobically digested sludge. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Huang, L.; Yuan, Z.H.; Li, Z.J.; Liu, M.C. Removal of Cd and Pb with biochar made from dairy manure at low temperature. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 1, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, G.; Tan, X.; Huang, B.; Tang, X.; Wang, S.; Hua, Q.; Yan, Z. Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II) onto chitosan-pyromellitic dianhydride modified biochar. J. Colloid Inter. Sci. 2017, 506, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).