Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws: An Attempted Demonstration of the Use of Co-Word Analysis to List Main Similar Pathologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
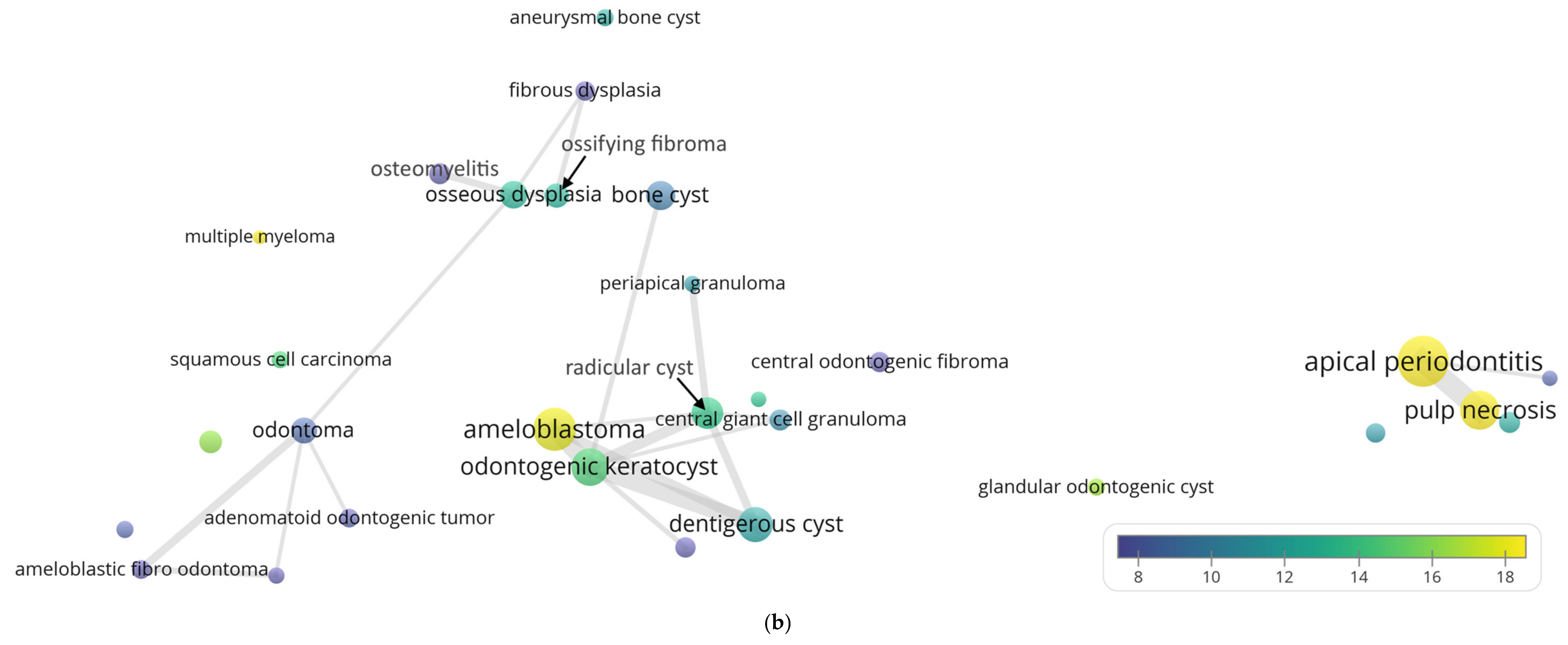
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Wong, N.S.M. Medial Sigmoid Depression of the Mandibular Ramus as a Lesion-Mimicking Anatomical Variation: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.; Montalvao, C.; Tanaka, R.; Kawai, T.; Bornstein, M.M. The use and performance of artificial intelligence applications in dental and maxillofacial radiology: A systematic review. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2020, 49, 20190107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Tanaka, R.; Bornstein, M.M. Current applications, opportunities, and limitations of AI for 3D imaging in dental research and practice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Mozos, I. The innovative and sustainable use of dental panoramic radiographs for the detection of osteoporosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Bornstein, M.M.; Jung, R.E.; Ferrari, M.; Waltimo, T.; Zitzmann, N.U. Recent trends and future direction of dental research in the digital era. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Z.X.; Yeo, K.A.; Sharma, V.K.; Leung, G.K.; McIntyre, R.S.; Guerrero, A.; Lu, B.; Lam, C.C.S.F.; Tran, B.X.; Nguyen, L.H.; et al. Prevalence of burnout in medical and surgical residents: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whaites, E.; Drage, N. Essentials of Dental Radiography and Radiology; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Takata, T.; Slooweg, P. WHO classification of odontogenic and maxillofacial bone tumours. In WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumour, 4th ed.; El-Naggar, A., Chan, J.K.C., Grandis, J.R., Takata, T., Slootweg, P.J., Eds.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 204–260. [Google Scholar]
- Koivisto, T.; Bowles, W.R.; Rohrer, M. Frequency and distribution of radiolucent jaw lesions: A retrospective analysis of 9723 cases. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becconsall-Ryan, K.; Tong, D.; Love, R. Radiolucent inflammatory jaw lesions: A twenty-year analysis. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 43, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A. Diagnosing the most common odontogenic cystic and osseous lesions of the jaws for the practicing pathologist. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, S96–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyosawa, S.; Yuki, M.; Kishino, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Ueda, T.; Murakami, S.; Konishi, E.; Iida, S.; Kogo, M.; Komori, T. Ossifying fibroma vs fibrous dysplasia of the jaw: Molecular and immunological characterization. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Júnior, O.; Borba, A.M.; Alves, C.A.F.; de Gouveia, M.M.; Deboni, M.C.Z.; da Graça Naclério-Homem, M. Reclassification and treatment of odontogenic keratocysts: A cohort study. Braz. Oral Res. 2017, 31, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariji, Y.; Morita, M.; Katsumata, A.; Sugita, Y.; Naitoh, M.; Goto, M.; Izumi, M.; Kise, Y.; Shimozato, K.; Kurita, K. Imaging features contributing to the diagnosis of ameloblastomas and keratocystic odontogenic tumours: Logistic regression analysis. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2011, 40, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikinheimo, K.; Kurppa, K.; Laiho, A.; Peltonen, S.; Berdal, A.; Bouattour, A.A.; Ruhin, B.; Catón, J.; Thesleff, I.; Leivo, I. Early dental epithelial transcription factors distinguish ameloblastoma from keratocystic odontogenic tumor. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Fan, X.; Su, L.; Wang, Z. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of unicystic odontogenic tumors for differentiation of unicystic ameloblastomas from keratocystic odontogenic tumors. Korean J. Radiol. 2018, 19, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, T.A.; Batista, A.C.; Mendonça, E.F.; Leles, C.R.; Fukada, S.; Cunha, F.Q. Comparative expression of RANK, RANKL, and OPG in keratocystic odontogenic tumors, ameloblastomas, and dentigerous cysts. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2008, 105, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVilliers, P.; Liu, H.; Suggs, C.; Simmons, D.; Daly, B.; Zhang, S.; Raubenheimer, E.; Larsson, Å.; Wright, T. Calretinin expression in the differential diagnosis of human ameloblastoma and keratocystic odontogenic tumor. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2008, 32, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaragiri, S.K.; Chawda, J.; Gill, S.; Odedra, S.; Parmar, G. Calretinin expression in unicystic ameloblastoma: An aid in differential diagnosis. J. Oral Biosci. 2010, 52, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eida, S.; Hotokezaka, Y.; Katayama, I.; Ichikawa, Y.; Tashiro, S.; Sumi, T.; Sumi, M.; Nakamura, T. Apparent diffusion coefficient-based differentiation of cystic lesions of the mandible. Oral Radiol. 2012, 28, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.; Van Merkesteyn, J.; Bras, J. Diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis and florid osseous dysplasia. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 1996, 81, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Weathers, D.R.; Waldron, C.A. Distinguishing features of focal cemento-osseous dysplasia and cemento-ossifying fibromas: II. A clinical and radiologic spectrum of 316 cases. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 1997, 84, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Weathers, D.R.; Waldron, C.A. Distinguishing features of focal cemento-osseous dysplasias and cemento-ossifying fibromas: I. A pathologic spectrum of 316 cases. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 1997, 84, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Yang, J.H.; Jo, S.Y.; Kim, B.C.; Lee, J.; Lee, W. Giant complex odontoma in the posterior mandible: A case report and literature review. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2018, 48, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattarataratip, E.; Pholjaroen, C.; Tiranon, P. A clinicopathologic analysis of 207 cases of benign fibro-osseous lesions of the jaws. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 22, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avril, L.; Lombardi, T.; Ailianou, A.; Burkhardt, K.; Varoquaux, A.; Scolozzi, P.; Becker, M. Radiolucent lesions of the mandible: A pattern-based approach to diagnosis. Insights Into Imaging 2014, 5, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariji, Y.; Yanashita, Y.; Kutsuna, S.; Muramatsu, C.; Fukuda, M.; Kise, Y.; Nozawa, M.; Kuwada, C.; Fujita, H.; Katsumata, A. Automatic detection and classification of radiolucent lesions in the mandible on panoramic radiographs using a deep learning object detection technique. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 128, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, H.; Zhai, G.; Han, J. Differential diagnosis of ameloblastoma and odontogenic keratocyst by machine learning of panoramic radiographs. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poedjiastoeti, W.; Suebnukarn, S. Application of convolutional neural network in the diagnosis of jaw tumors. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2018, 24, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.G.; de Oliveira, I.A.; Consolaro, A. The mechanism: How dental resorptions occur in ameloblastoma. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2019, 24, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, H.; Baharvand, M.; Rahmani, S.; Jafari, S.; Parvaei, P. Radiolucent rim as a possible diagnostic aid for differentiating jaw lesions. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2015, 45, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huumonen, S.; Ørstavik, D. Radiological aspects of apical periodontitis. Endod. Top. 2002, 1, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Goto, T.K.; Leung, W.K. The changing landscape of neuroscience research, 2006–2015: A bibliometric study. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; El-Tawil, O.S.; Bungǎu, S.G.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Atanasov, A.G. Antioxidants: Scientific literature landscape analysis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8278454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D. Lesions of the jaws presenting as radiolucencies on cone-beam CT. Clin. Radiol. 2016, 71, 972–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Orhan, I.E.; Horbanczuk, O.K.; Barreca, D.; Battino, M.; Belwal, T.; Bishayee, A.; Daglia, M.; Devkota, H.P.; et al. Resveratrol, a popular dietary supplement for human and animal health: Quantitative research literature analysis—A review. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2019, 37, 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, A.W.K. The Usage of the Terms Mandibular Canal, Inferior Alveolar Canal, and Inferior Dental Canal in the Academia: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Morphol. 2021, 39, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, K. Humour of gene names lost in translation to patients. Nature 2006, 439, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysooriya, M.; Soria, M.; Kasu, M.S.; Ziemann, M. Gene name errors: Lessons not learned. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, P.; Herbort, C.P.; Hedayatfar, A.; Tugal-Tutkun, I.; Cimino, L.; Urzua, C.A.; Papasavvas, I.; Takeuchi, M.; Lages, V. “White dot syndromes”, an inappropriate and outdated misnomer. Int. Ophthalmol. 2021, 42, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Features or Parameters | Reference |
|---|---|
| Ameloblastoma as compared to OKC | |
| Bone expansion in buccolingual dimension and absence of high-density areas on CT | [14] |
| Early dental epithelial markers were differentially overexpressed in ameloblastoma, whereas squamous epithelial differentiation markers were the most differentially overexpressed genes in OKC | [15] |
| Higher ADC level in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging | [16] |
| Ameloblastoma as compared to dentigerous cyst | |
| RANK-positive and RANKL-positive cells | [17] |
| Ameloblastoma as compared to dentigerous cyst and OKC | |
| Higher number of RANK-positive than OPG-positive cells. Opposite is true for the latter two pathologies. | [17] |
| Positive calretinin staining | [18,19] |
| Ameloblastoma as compared to radicular cyst and OKC | |
| Higher ADC level in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging | [20] |
| Osseous dysplasia as compared to osteomyelitis | |
| Presence of fibroblastic stroma with bone and cementum-like structures | [21] |
| Osseous dysplasia as compared to ossifying fibroma | |
| More commonly in close proximity with tooth apices or previous tooth extraction sites | [22] |
| Less frequently possesses a well-defined border | [22] |
| The former often contains cavernous-like vascularity associated with bone trabeculae and frequent hemorrhage, whereas the latter usually shows more cells arranged in a storiform pattern | [23] |
| Osseous dysplasia as compared to odontoma | |
| Occurring in older patients (over 30 years of age) and related to the root | [24] |
| Osseous dysplasia as compared to fibrous dysplasia and ossifying fibroma | |
| The former one is usually symptomless, whereas the latter two present painless swelling | [25] |
| The former one contains woven bone, whereas the latter two contain a mixture of woven bone and cementum-like materials | [25] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeung, A.W.K. Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws: An Attempted Demonstration of the Use of Co-Word Analysis to List Main Similar Pathologies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19041933
Yeung AWK. Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws: An Attempted Demonstration of the Use of Co-Word Analysis to List Main Similar Pathologies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(4):1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19041933
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeung, Andy Wai Kan. 2022. "Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws: An Attempted Demonstration of the Use of Co-Word Analysis to List Main Similar Pathologies" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 4: 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19041933
APA StyleYeung, A. W. K. (2022). Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws: An Attempted Demonstration of the Use of Co-Word Analysis to List Main Similar Pathologies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4), 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19041933






