The Accumulation and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin in Southern China and Their Threatening on Water Security
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
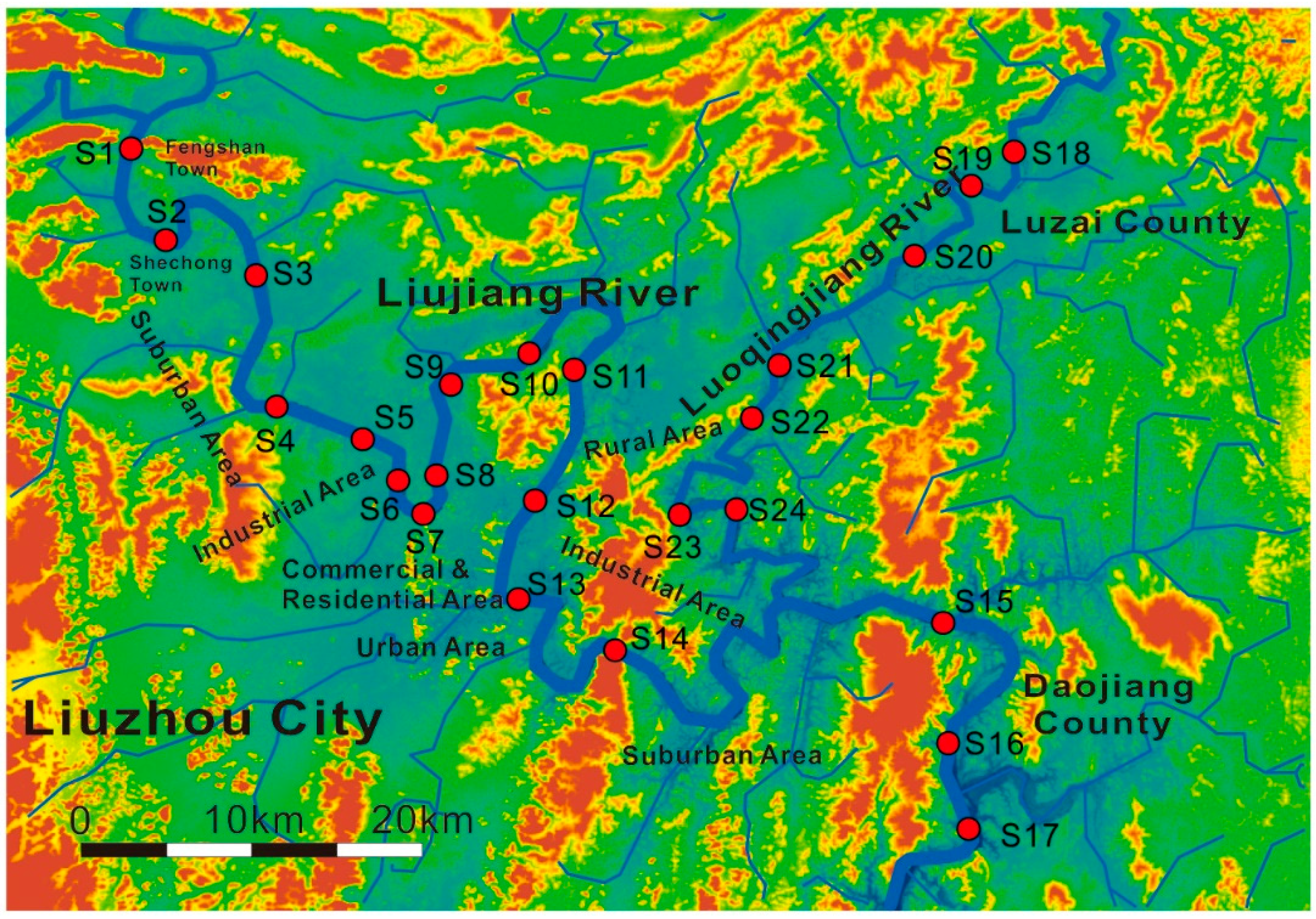
2.1. The Description of Study Area and Field Sampling
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ecological Risk Assessment Method
3. Results and Discussion
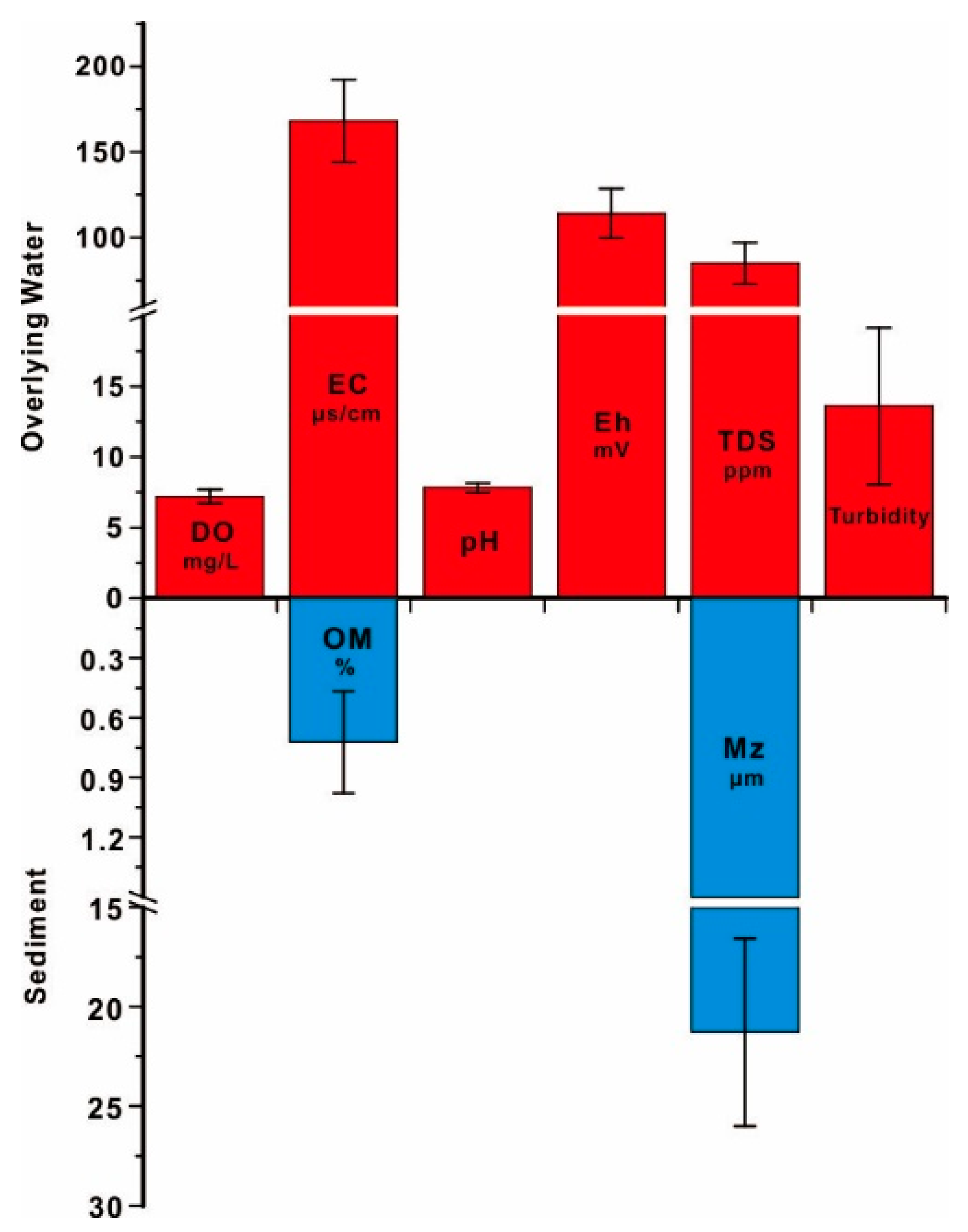
3.1. The Variations of Water Chemistry in the Surface Water
3.2. The Distribution of Particle Size in Surface Sediments
3.3. The Distribution of HMs in Surface Water and Sediments
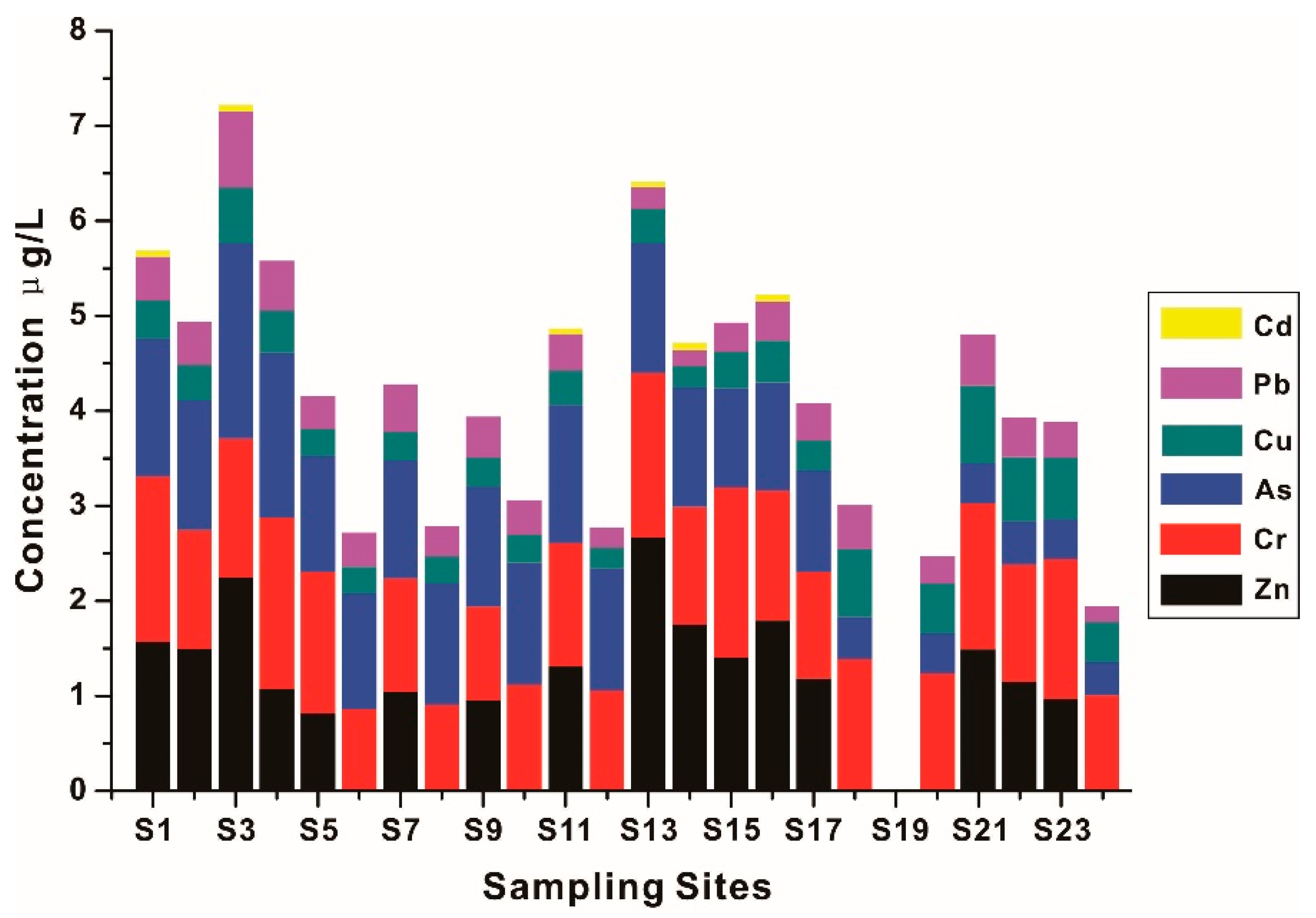
3.3.1. The Distribution of HMs in Surface Water
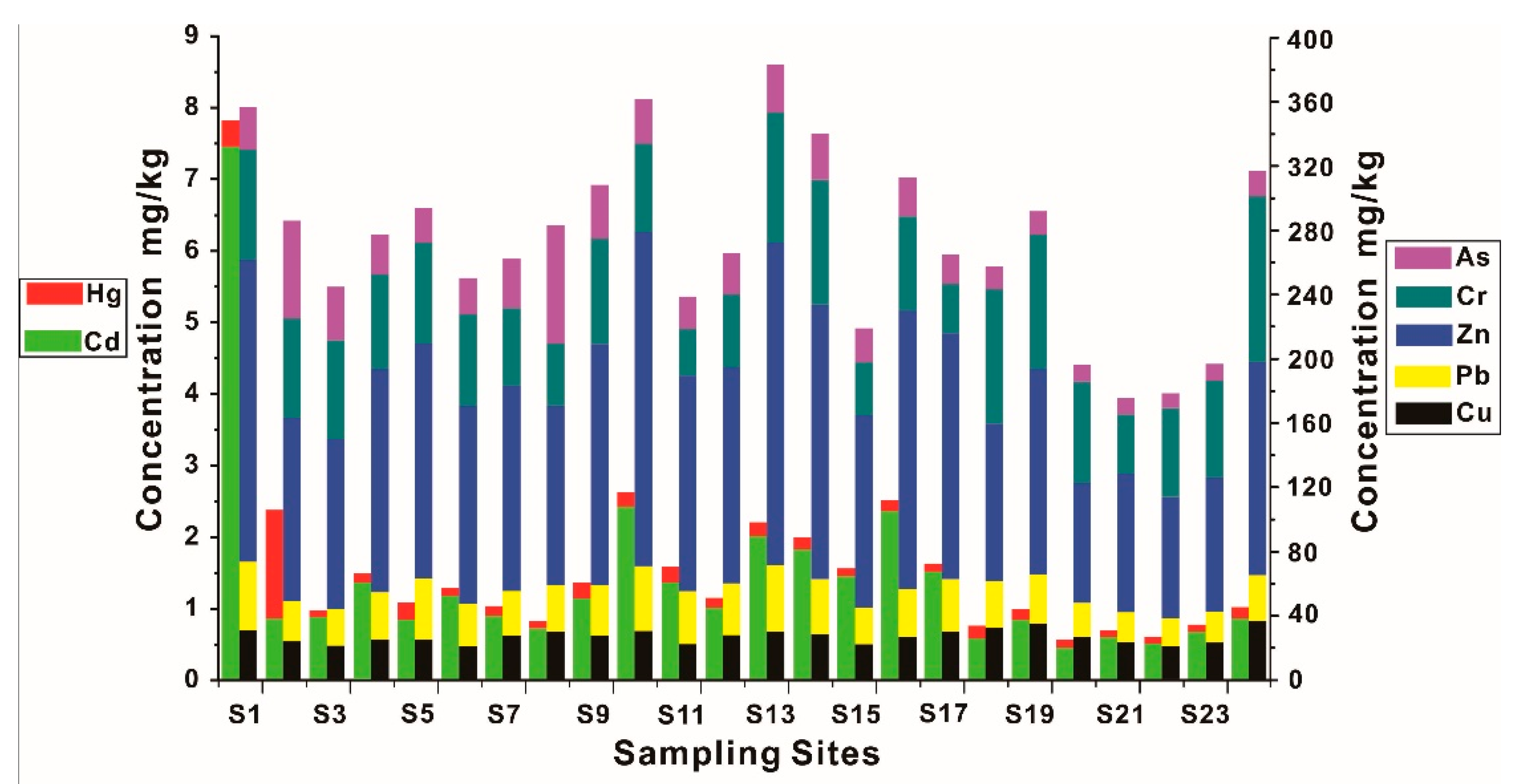
3.3.2. The Distribution of HMs in Sediments
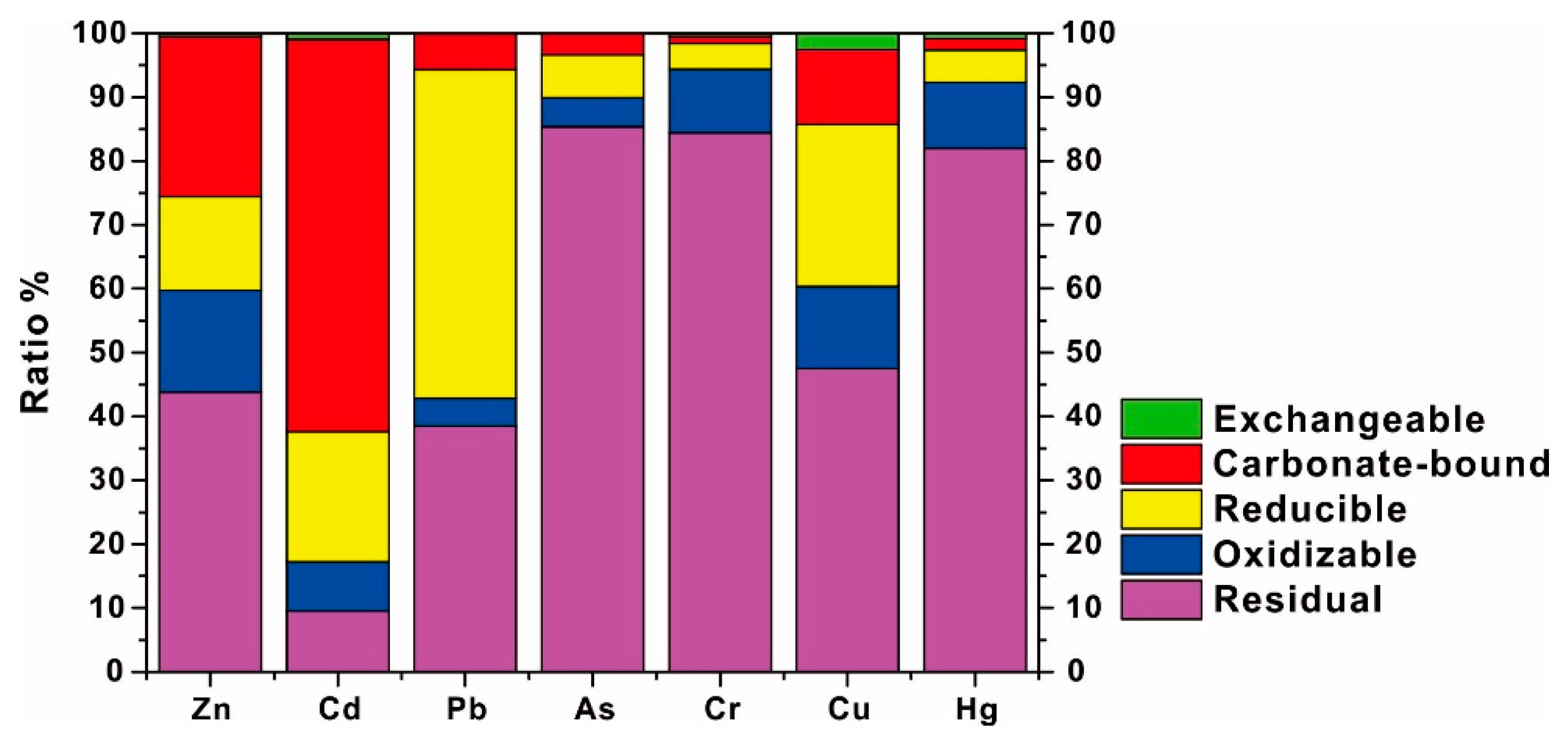
3.3.3. The Speciation of HMs in Sediments
3.4. Accumulation Mechanism of HMs in Surface Sediments of Liujiang River Basin
3.4.1. The Existing Forms of HMs in Surface Water
3.4.2. Impact Factors of the Accumulation of HMs in Surface Sediments
3.4.3. Controlling Factors on HM Speciation in Surface Sediments
3.4.4. The Conversion and Accumulation of HMs between Sediments and Water
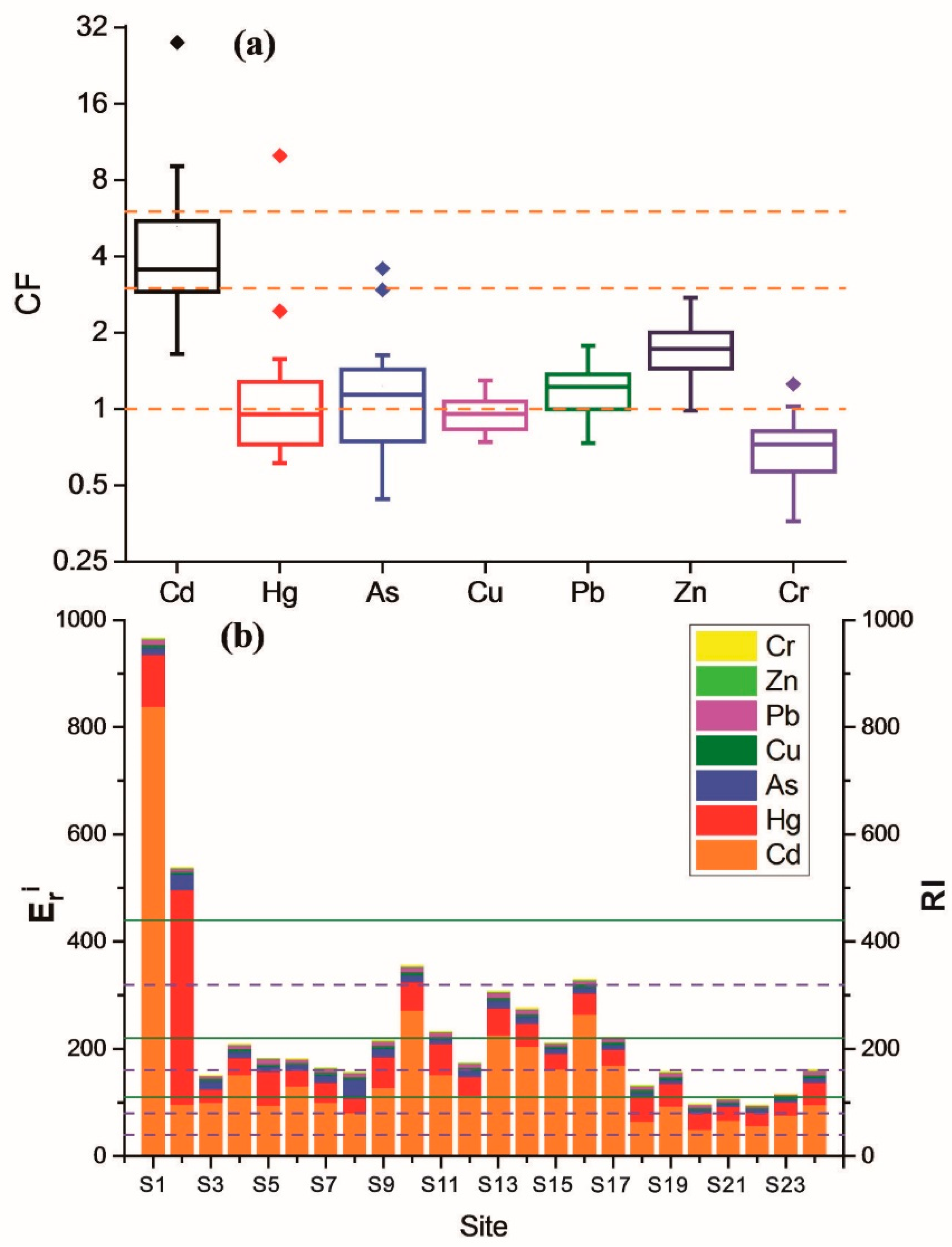
3.5. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of HMs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gashi, F.; Frančišković-Bilinski, S.; Bilinski, H.; Kika, L. Assessment of the effects of urban and industrial development on water and sediment quality of the Drenica River in Kosovo. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, D.; Usero, J.; Morillo, J. Assessment of heavy metals bioavailability and toxicity toward Vibrio fischeri in sediment of the Huelva estuary. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.-Z.; Shi, W.-L.; Meng, X.-Z. Comprehensive risk assessment of heavy metals in lake sediment from public parks in Shanghai. Ecotoxicol Env. Saf. 2014, 102, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Zhao, C.; Luo, Y.; Liu, C.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, D.; An, S.; Zhu, H. Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: Their relations to environmental factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 270, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Tang, X.; Xie, Z.; Liu, L.; Luo, S.; Huang, Q.; Zou, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, J. Analysis and health risk assessment of toxic and essential elements of the wild fish caught by anglers in Liuzhou as a large industrial city of China. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, R.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in freshwater fish in the central and eastern North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bervoets, L.; Blust, R. Metal concentrations in water, sediment and gudgeon (Gobio gobio) from a pollution gradient: Relationship with fish condition factor. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 126, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhou, C. Health Risk Assessment of Metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, Hg, Se) in Angling Fish with Different Lengths Collected from Liuzhou, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosch, A.C.; O’Neill, B.; Sigge, G.O.; Kerwath, S.E.; Hoffmanb, L.C. Heavy metals in marine fish meat and consumer health: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Mamat, Z.; Ye, Q. Sources identification and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Bortala River, Northwest China. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2016, 126, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, T.T. Use of partial dissolution techniques in geochemical exploration. J. Geochem. Explor. 1984, 20, 101–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaray, S.K.; Nayak, B.B.; Lin, S.; Bhatta, D. Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—A case study: Mahanadi basin, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zuo, H.; Tian, M.; Zhang, L.; Meng, J.; Zhou, X.; Min, N.; Chang, X.; Liu, Y. Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, R.A. BCR®-701: A review of 10-years of sequential extraction analyses. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 680, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particular trace elements. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, A.; Fine, P. Sequential Selective Extraction Procedures for the Study of Heavy Metals in Soils, Sediments, and Waste Materials—a Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 365–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.; Tang, W.; Dong, L.; Zhang, W.; Pei, Y. Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Hu, Z.; Fan, D. Accumulation and transformation of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Yangtze River estuary to the East China Sea shelf. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Ju, Y.-R.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. Changes in the total content and speciation patterns of metals in the dredged sediments after ocean dumping: Taiwan continental slope. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 181, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Babu, P.V.R.; Sarma, V.V. A study of lead and cadmium speciation in some estuarine and coastal sediments. Chem. Geol. 2012, 294, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, A.R.; Karbassi, A.R.; Fakhraee, M. Assessing the trace metal pollution in the sediments of Mahshahr Bay, Persian Gulf, via a novel pollution index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillan, D.C.; Pede, A.; Sabbe, K.; Gao, Y.; Leermakers, M.; Baeyens, W.; Cabana, B.L.; Billon, G. Effect of bacterial mineralization of phytoplankton-derived phytodetritus on the release of arsenic, cobalt and manganese from muddy sediments in the Southern North Sea. A microcosm study. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 419, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Tian, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, M. Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient levels on heavy metal contents and fractions in river surface sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, S.; Jalali, M. Effect of heavy metals on pH buffering capacity and solubility of Ca, Mg, K, and P in non-spiked and heavy metal-spiked soils. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, C.A.; Jolley, D.F.; Simpson, S.L. Effect of overlying water pH, dissolved oxygen, salinity and sediment disturbances on metal release and sequestration from metal contaminated marine sediments. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, B.A. Effect Of pH, Ionic Strength, Dissolved Organic Carbon, Time, and Particle Size on Metals Release from Mine Drainage Impacted Streambed Sediments. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, A.; Li, M.; Zhang, X. Effect of pH, Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen, and Flow Rate of Overlying Water on Heavy Metals Release from Storm Sewer Sediments. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 434012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, Z.; Miao, D.; He, X. Effects of heavy metals speciations in sediments on their bioaccumulation in wild fish in rivers in Liuzhou—A typical karst catchment in southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, J.; Yu, S. Heavy Metal Pollution of the Drinking Water Sources in the Liujiang River Basin, and Related Health Risk Assessments. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Miao, X.; Liu, H.; Miao, D. The Variation of Heavy Metals Bioavailability in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin, SW China Associated to Their Speciations and Environmental Fluctuations, a Field Study in Typical Karstic River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Azim, H.; El-Moselhy, K.M. Determination and partitioning of metals in sediments along the Suez Canal by sequential extraction. J. Mar. Syst. 2005, 56, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zou, S.; Ye, S.; Xie, Z. Spatial distribution of heavy metals and their potential sources in the soil of Yellow River Delta: A traditional oil field in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 42, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control-a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, P.; Chen, B.; Gao, F.; Song, H.; Li, M. Distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Luanhe River Estuary, northwest of the Bohai Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Yan, Y.; Dai, Y.Y.; Gan, Z. Distribution and risk assessment of metals in water, sediments, and wild fish from Jinjiang River in Chengdu, China. Chemosphere 2017, 196, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEPA. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB3838-2002); State Environmental Protection Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Zhao, X.M.; Yao, L.A.; Ma, Q.L.; Zhou, G.J.; Wang, L.; Fang, Q.L.; Xu, Z.C. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of cadmium in water and sediment in Longjiang River, China: Implication on water quality management after pollution accident. Chemosphere 2017, 194, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.L.; Ning, Z.P.; Xiao, Q.X.; Huang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Xiao, T.F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Shi-Liang, W.U. Spatial Distribution, Sources and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediments of Longjiang River, Southern China. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 748–757. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Ding, M.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Jin, X.; Xu, Z. Seasonal varieties and influential factors of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 17, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen, P.; Steinnes, E. Influence of pH and OM concentration on Cu, Zn, Cd, and Al speciation in rivers. Water Res. 2003, 37, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, J.; Mcdonald, P.; Plater, A.; Oldfield, F. Relationships Between Radionuclide Content and Textural Properties in Irish Sea Intertidal Sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 99, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Determination of model and calculation parameters of oxygen production by photosynthesis of algae in river. Environ. Sci. 1988, 9, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Li, S. Study on adsorption of Cr (VI) from purple soil under the influence by different pH environment. Environ. Eng. 2015, 33, 866–869. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, W.; Guo, H.; Shen, J.; Liu, S.; Ding, S.; Hou, W.; Ma, J.; Dong, H. Stimulation of Fe(II) Oxidation, Biogenic Lepidocrocite Formation, and Arsenic Immobilization by Pseudogulbenkiania Sp. Strain 2002. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Guo, H. Hot Topics and Trends in the Study of High Arsenic Groundwater. Adv. Earth Sci. 2013, 28, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
| DO | EC | pH | Eh | TDS | Turbidity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | −0.096 | −0.148 | −0.358 | −0.280 | −0.148 | 0.648 ** |
| Pb | −0.181 | −0.053 | −0.168 | −0.089 | −0.054 | 0.181 |
| Zn | 0.400 | 0.408 * | 0.177 | −0.130 | 0.407 * | −0.136 |
| Cr | 0.254 | 0.429 * | −0.114 | 0.041 | 0.428 * | 0.134 |
| Cd | 0.480 * | 0.232 | 0.076 | 0.224 | 0.232 | −0.272 |
| As | 0.307 | 0.128 | 0.290 | 0.271 | 0.127 | −0.486 * |
| DO | EC | pH | Eh | TDS | Turbidity | MZ | OM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.163 | 0.189 | −0.084 | 0.093 | 0.192 | −0.415 * | −0.666 ** | 0.889 ** |
| Pb | 0.381 | 0.286 | 0.032 | 0.500 * | 0.286 | −0.659 ** | −0.404 | 0.454 * |
| Zn | 0.347 | 0.295 | 0.083 | 0.459 * | 0.295 | −0.612 ** | −0.424 * | 0.331 |
| Cr | 0.242 | 0.272 | −0.103 | −0.214 | 0.272 | −0.167 | −0.579 ** | 0.486 * |
| Cd | 0.109 | 0.732 ** | −0.501 * | 0.739 ** | 0.729 ** | −0.321 | −0.045 | 0.025 |
| As | 0.078 | −0.200 | 0.169 | 0.236 | −0.200 | −0.379 | 0.156 | −0.225 |
| Hg | 0.075 | −0.061 | −0.031 | −0.134 | −0.060 | −0.226 | 0.183 | −0.163 |
| WCr | WCu | WZn | WCd | WPb | WAs | WHg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fr1 | 0.096 | 0.275 | −0.012 | 0.620 ** | −0.280 | 0.232 | - |
| Fr2 | 0.026 | −0.330 | 0.312 | 0.513 * | −0.101 | 0.491 * | - |
| Fr3 | 0.163 | 0.068 | 0.448 * | 0.526 ** | −0.312 | 0.631 ** | - |
| Fr4 | −0.049 | −0.427 * | 0.400 | 0.577 ** | −0.400 | 0.397 | - |
| Fr5 | 0.007 | −0.330 | −0.004 | 0.394 | −0.477 * | 0.515 * | - |
| Total | 0.010 | −0.274 | 0.286 | 0.524 * | −0.356 | 0.522 ** | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, X.; Song, M.; Xu, G.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, H. The Accumulation and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin in Southern China and Their Threatening on Water Security. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031619
Miao X, Song M, Xu G, Hao Y, Zhang H. The Accumulation and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin in Southern China and Their Threatening on Water Security. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031619
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Xiongyi, Mian Song, Gaohai Xu, Yupei Hao, and Hucai Zhang. 2022. "The Accumulation and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin in Southern China and Their Threatening on Water Security" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031619
APA StyleMiao, X., Song, M., Xu, G., Hao, Y., & Zhang, H. (2022). The Accumulation and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin in Southern China and Their Threatening on Water Security. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031619







