Designing for Green and Grey: Insights from Single-Use Plastic Water Bottles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What are more decisive bottle attributes of openability to increase inclusivity for the elderly in the ordinary situation of a two-handed opening, not in artificial conditions of a one-handed opening?
- What measures related to designing the bottles can help us solve a complex problem in the competition between the ecological and social sustainability perspectives?
1.1. Greying South Korea’s Enabling Environment for the Elderly
1.2. Single-Use Plastic Water Bottles: The Intersection of Ecological Perspectives and Social Values
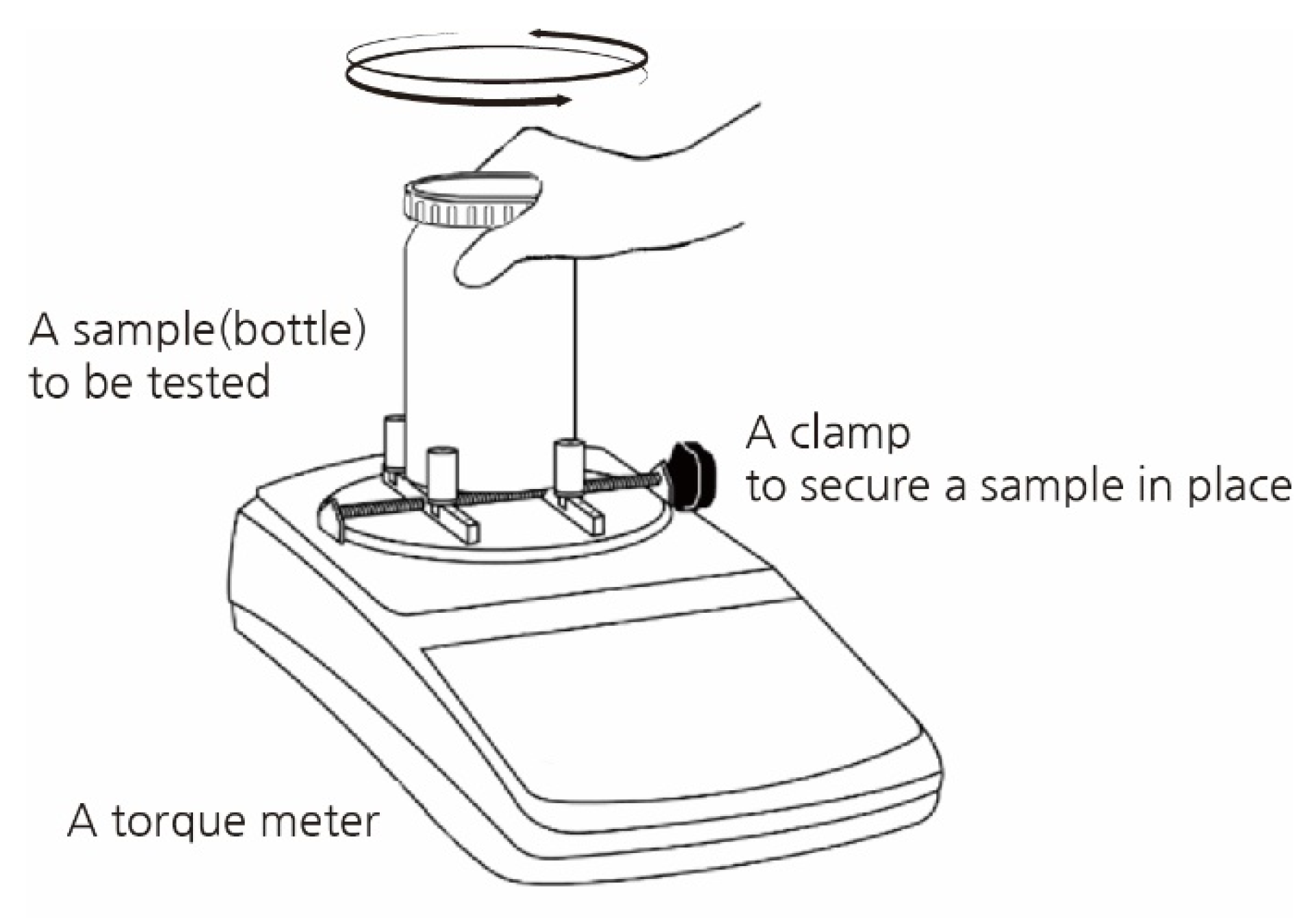
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Questionnaire Development
2.3. Test Administration
2.4. Characteristics of the Test Subjects
3. Results
3.1. Experience Difference in Opening Plastic Water Bottles by Age Groups and Bottle Types
3.2. Influential Factors of Opening Plastic Water Bottles
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Bottle Features as Inclusive Enablers for the Elderly
4.2. Business-Compatible Strategies with Ecological–Social Sustainability through the Circular Economy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beck, U. Risk Society-towards a New Modernity; Sage: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.M.; Machalaba, C.C.; Seifman, R.; Feferholtz, Y.; Karesh, W.B. Infectious disease and economics: The case for considering multi-sectoral impacts. One Health 2019, 7, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beurden, E.; Kia, A. Wicked problems and health promotion: Reflections on learning. Health Promot. J. Austr. 2011, 22, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buchanan, R. Wicked problems in design thinking. Des. Issues 1992, 8, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornman, J.C. Towards sustainable development: Implications for population ageing and the wellbeing of elderly women in developing countries. Popul. Environ. 1996, 18, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, B.S.; Sullivan, W.C.; Wiley, A.R. Green common spaces and the social integration of inner-city older adults. Environ. Behav. 1998, 30, 832–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librett, J.; Yore, M.M.; Buchner, D.M.; Schmid, T.L. Take pride in America’s health: Volunteering as a gateway to physical activity. Am. J. Health Educ. 2005, 36, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillemer, K.; Fuller-Rowell, T.E.; Reid, M.C.; Wells, N.M. Environmental volunteering and health outcomes over a 20-year period. Gerontologist 2010, 50, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y. Plastic Korea, Green Peace East Asia Seoul Office. 2019. Available online: https://www.greenpeace.org/static/planet4-korea-stateless/2019/12/f360eebd-%ED%94%8C%EB%9D%BC%EC%8A%A4%ED%8B%B1%EB%B3%B4%EA%B3%A0%EC%84%9C_final.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Ko, J.T. War on Single-Use Plastics Faces Another Setback as Virus Fears Resurge, The Korea Herald. 2020. Available online: http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20200913000204 (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Statistics Korea. 2020 Population and Housing Census of Korea (Register-Based Census), Statistics Korea. 2021. Available online: https://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/1/1/index.board?bmode=read&aSeq=391020 (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Kim, Y.W.; Shin, W.S.; Lim, S.O.; Son, J. Status Quo of Social Problems; Yangsewon: Seoul, Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Purao, S.; Tan, H.P. Value-inspired elderly care service design for aging-in-place. In Proceedings of the Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, PACIS 2016, Chiayi, Taiwan, 27 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Population Division. World Population Ageing 2017-Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/397); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Love, P. OECD Insights, Ageing: Debate the Issues; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, J.M.; Pawliczko, A.; Beales, S. Ageing in the Twenty-First Century: A Celebration and a Challenge; UNFPA: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Phillipson, C. Ageing; John Wiley & Sons: Malden, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T. Identifying stakeholders and interactions in the dementia café in Seongju through empathic service design approaches. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2018, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OECD. Paying for the Past, Providing for the Future: Intergenerational Solidarity; OECD: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Choi, J. Long-term trends in living alone among Korean adults age, gender, and educational differences. Demogr. Res. 2015, 32, 1177–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.H. Creating a physical environment for an aged society: Korea’s experience. Age Integr. Ageing Soc. Issue Focus. 2019, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Age-Friendly Seoul. 2013~2015 Age-Friendly Seoul Initiative Assessment Interim Report. 2014. Available online: https://afc.welfare.seoul.kr/afc/about/result.action (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Choi, K.J.; Gil, M. Insights from Companies’ Response to the Silver Market, The Korea Chamber of Commerce & Industry. 2015. Available online: http://www.korcham.net/nCham/Service/Economy/appl/KcciReportDetail.asp?SEQ_NO_C010=20120930050&CHAM_CD=B001 (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Kim, T.S.; Cho, J.K. Development direction of senior friendly products by lifestyles of the elderly. J. Korean Soc. Des. Cult. 2016, 22, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lalumandier, J.A.; Ayers, L.W. Fluoride and bacterial content of bottled water vs tap water. Arch. Fam. Med. 2000, 9, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anadu, E.C.; Harding, A.K. Risk perception and bottled water use. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2000, 92, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevise, F. La préoccupation des français pour la qualité de l’eau. Données Environ. 2000, 57, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gleick, P.H. The myth and reality of bottled water. In The World’s Water 2004–2005: The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources; Cain, N., Gleick, P., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 17–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, H.K.; Lee, H.C. Determinants of valuation and estimation of willingness to pay for bottled water. Food Serv. Ind. J. 2020, 14, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H. Bottled Water Consumption is on the Rise…The Market Will Reach 1 Trillion Won by 2020. Available online: https://www.yna.co.kr/view/AKR20170613157000030 (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Kim, S.; Bae, D. The Economist 1516. Available online: https://jmagazine.joins.com/economist/view/328700 (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Su, F.C.; Chiu, H.Y.; Chang, J.H.; Lin, C.F.; Hong, R.F.; Kuo, L.C. Jar-opening challenges. Part 1: An apparatus for assessing hand and finger torques and forces in a jar-opening activity. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2009, 223, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duizer, L.M.; Robertson, T.; Han, J. Requirements for packaging from an ageing consumer’s perspective. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2009, 22, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, D.J.; Riley, M.W. An evaluation of knife handle guarding. Hum. Factors 1986, 28, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.C.; Wang, M.J.J. Hand/tool interface effects on human torque capacity. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 1996, 18, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, R.; Yoxall, A. Human ability and openability: Producing design limits for consumer packaging. In International Conference on Inclusive Design; Royal College of Art: London, UK, 2005; p. 91. [Google Scholar]
- Rohles, F.H.; Moldrup, K.L.; Laviana, J.E. Opening jars: An anthropometric study of the wrist-twisting strength of the elderly. Proc. Hum. Factors Soc. Annu. Meet. 1983, 27, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, S.; Brombach, C.; Artigas, G.; Järvenpää, E.; Steinemann, N.; Ziesemer, K.; Yildirim, S. Evaluation of the accessibility of selected packaging by comparison of quantitative measurements of the opening forces and qualitative surveys through focus group studies. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2016, 29, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imrhan, S.N.; Loo, C. Torque capabilities of the elderly in opening screw top containers. Proc. Hum. Factors Soc. Annu. Meet. 1986, 30, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, R. Openability of Vacuum Lug Closures. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, J.O.; Wanibe, E.; Nayak, L. The interaction between lid diameter, height and shape on wrist torque exertion in younger and older adults. Ergonomics 2002, 45, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imrhan, S.N. An analysis of different types of hand strength in the elderly and implications for ergonomic design. In Advances in Industrial Ergonomics and Safety V; Nielsen, R., Jorgensen, K., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1993; pp. 390–394. [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima, K.; Konz, S. Jar lids: Effect of diameter, gripping materials and knurling. Proc. Hum. Factors Soc. Annu. Meet. 1986, 30, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorbij, A.I.; Steenbekkers, L.P. The twisting force of aged consumers when opening a jar. Appl. Ergon. 2002, 33, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoxall, A.; Langley, J.; Janson, R.; Lewis, R.; Wearn, J.; Hayes, S.A.; Bix, L. How wide do you want the jar? The effect on diameter for ease of opening for wide-mouth closures. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2010, 23, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg, B.; Mumford, E. The design of computer systems: Mans vision of man as an integral part of the systems design process. In Human Choice and Computers; Mumford, E., Sackman, H., Eds.; North-Holland Publishing Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; pp. 31–59. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, F. Human resource management and the socio-technical approach. In New Technology: International Perspectives on Human Resources and Industrial Relations; Bamber, G., Lansbury, R.D., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 1989; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Iannuzzi, S.M.; Prestwood, K.M.; Kenny, A.M. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and predictors of skeletal muscle mass in healthy, older men and women. J. Gerontol. A Biol. 2002, 57, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.I. Development of Eco-Friendly Packaging Design Technology for Packaging Waste Reduction and Recycling. Ministry of Environment of South Korea. 2014. Available online: https://dl.nanet.go.kr/SearchDetailView.do?cn=MONO1201519329 (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Hanwha Solution. Plastics in Daily Lives; PET Lids, HDPE’ Hanwha Chemical. Available online: https://www.chemidream.com/2491 (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Yamabe, E.; Matsumura, T.; Aiba, H.; Yoshida, H.; Yashiro, S.; Spring Water National Emblem; Iwamoto, T. About a correlation of results-X-rays results and ADL disorder of the conservative treatment for the fracture of the distal radius. J. Jpn. Soc. Fract. Repair 2003, 25, 763–766. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.; Norris, B.; Peebles, L. Older Adultdata: The Handbook of Measurements and Capabilities in the Older Adult: Data for Design Safety; Department of Trade and Industry (DTI): London, UK, 2000.
- Saito, K.; Shimizu, J. Thumb pressure required to open containers and packages of daily commodities. J. Tsuruma Health Sci. Soc. 2010, 34, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Verghese, K.; Crossin, E.; Chine, S.; Lockrey, S.; Williams, H.; Rio, M.; Wikstrom, F. The greenhouse gas profile of a “Hungry planet”; quantifying the impacts of the weekly food purchases including associated packaging and food waste of three families. In 19th IAPRI World Conference on Packaging; Elsevier: Melbourne, Australia, 2014; pp. 709–720. [Google Scholar]
- Yoxall, A.; Janson, R.; Bradbury, S.; Langley, J.; Wearn, J.; Hayes, S. Human ability and openability: Producing design limits for consumer packaging. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2006, 19, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, J. Cannibals with Forks: The Triple Bottom Line of 21st Century Business; Capstone: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer, L.L.; Pigosso, D.C.A.; Niero, M.; Bech, N.M.; McAloone, T.C. Product/Service-systems for a circular economy: The route to decoupling economic growth from resource consumption? J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korhonen, J.; Nuur, C.; Feldmann, A.; Birkie, S.E. Circular economy as an essentially contested concept. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.J. Less Than Half the Recycling Rate of Collected PET Bottles. Available online: https://www.donga.com/news/Society/article/all/20190220/94200392/1 (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Shin, J. PET Bottle Recycling Campaign Spreads, Spurring Trend of ESG Management. Available online: http://koreabizwire.com/pet-bottle-recycling-campaign-spreads-spurring-trend-of-esg-management/183462 (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Ko, D.H. Gov’t Says Label-Less Bottles Among Top 3 Environmental Policies This Year. Available online: http://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/nation/2021/06/371_308273.html (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Kim, M.J. Lotte Chilsung Beverage, “Korea’s First rPET Application Technology Verification”. Available online: http://www.koreaittimes.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=106890 (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Sparrow, N. Evian Debuts Pet Bottle Made with 100% Recycled Plastic. Available online: https://www.plasticstoday.com/packaging/evian-debuts-pet-bottle-made-100-recycled-plastic (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- SK Chemicals News. SK Chemicals and Jeju Sam DaSoo Aim to Establish a PET Bottle Recycling Ecosystem. Available online: https://www.skchemicals.com/en/prcenter/new_view.aspx?serno=2953 (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Glen, J.M.; Lord, M. New product development processes within the UK medical device industry. Med. Eng. Phys. 1996, 18, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Dey, A.; Singh, G. Connecting corporations and communities: Towards a theory of social inclusive open innovation. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2017, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, J.J.; Zhao, X.; Jung, K.; Yigitcanlar, T. The culture for open innovation dynamics. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Question Category | Question Topic |
|---|---|
| Demographic information | Age |
| Gender | |
| Hand strength | |
| Before-opening experience | Visual appearance |
| Visual preference | |
| After-opening experience | Bottle thickness |
| Cap height | |
| Cap ridges | |
| Perceived difficulties to open | |
| Feeling of spilling bottle content | |
| Overall preference |
| Item | Bottle A | Bottle B | Bottle C | Bottle D | Bottle E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image |  |  |  |  |  |
| Overall Bottle shape | Rounded square | Circle | Circle | Circle | Circle |
| Bottle thickness by weight | 18 g | 20 g | 12 g | 13 g | 14 g |
| Easy-to-squeeze pattern | None | None | Yes | None | Yes |
| Cap height (upper + lower part) | 17.1 mm (13 + 4.1) | 19.7 mm (12.7 + 7) | 13.2 mm (9.7 + 3.5) | 17.2 mm (11.7 + 5.5) | 16.3 mm (12.3 + 4) |
| Cap Ridges | Regular | Regular | Wide | Regular | Regular |
| Mean opening torque (min/max) | 107.04 (95.84/119.04) | 117.01 (106.40/127.68) | 146.83 (126.40/160.48) | 129.92 (122.40/135.20) | 122.29 (119.68/126.24) |
| Classification | Younger Adults | Older Adults | Total, n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ≤30 | 14 | - | 14 (19.44) |
| 31–40 | 14 | - | 14 (19.44) | |
| 41–50 | 6 | - | 6 (8.33) | |
| 51–60 | 0 | - | 0 (0) | |
| 61–70 | - | 15 | 15 (20.83) | |
| 71–80 | - | 16 | 16 (22.22) | |
| ≥81 | - | 7 | 7 (9.72) | |
| Total | 34 | 38 | 72 (100) | |
| Gender | Male | 16 | 14 | 30 (41.67) |
| Female | 18 | 24 | 42 (58.33) | |
| Total | 34 | 38 | 72 (100) | |
| Hand strength (kg) | ≤10 | 0 | 4 | 4 (5.56) |
| 11–20 | 0 | 8 | 8 (11.11) | |
| 21–30 | 17 | 13 | 30 (41.67) | |
| 31–40 | 7 | 12 | 19 (26.39) | |
| 41–60 | 9 | 1 | 10 (13.89) | |
| ≥61 | 1 | 0 | 1 (1.39) | |
| Total | 34 | 38 | 72 (100) | |
| Participant Group | Bottle Type | N | Mean | Std. Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Younger adults | A | 34 | 3.59 | 1.05 |
| B | 34 | 3.82 | 1.06 | |
| C | 34 | 2.62 | 1.02 | |
| D | 34 | 3.06 | 0.92 | |
| E | 34 | 3.00 | 0.89 | |
| Older adults | A | 38 | 3.79 | 0.78 |
| B | 38 | 4.08 | 0.82 | |
| C | 38 | 3.16 | 1.22 | |
| D | 38 | 3.61 | 0.68 | |
| E | 38 | 3.35 | 0.83 | |
| Total | A | 72 | 3.69 | 0.91 |
| B | 72 | 3.96 | 0.94 | |
| C | 72 | 2.90 | 1.15 | |
| D | 72 | 3.35 | 0.84 | |
| E | 72 | 3.19 | 0.87 |
| Predictor | SS | df | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ages | 12.93 | 1 | 12.93 | 14.8 | 0 |
| Bottle types | 50.67 | 4 | 12.67 | 14.51 | 0 |
| A > C, E | |||||
| B > C, D, E | |||||
| Ages Ⅹ Bottle types | 1.83 | 4 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.72 |
| Error | 307.4 | 352 | 0.87 | ||
| Corrected total | 4599 | 362 |
| Group | Predictor | Unstandardised Coefficient | Standardised Coefficient | t | p | Tolerance | VIF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | β | |||||||
| Younger adults | Before-opening | Visual attractiveness | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 1.71 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 1.68 |
| Expected easiness | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 1.11 | 0.27 | 0.65 | 1.54 | ||
| After-opening | Satisfaction with bottle thickness | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 1.81 | |
| Satisfaction with cap height | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 1.17 | 0.24 | 0.44 | 2.30 | ||
| Satisfaction with cap ridges | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.73 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 2.02 | ||
| Satisfaction with hand strength required | 0.54 | 0.07 | 0.58 | 8.13 | 0.00 ** | 0.56 | 1.67 | ||
| Satisfaction with feeling of spilling out | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.58 | 0.82 | 0.41 | 0.62 | 1.61 | ||
| Older adults | Before-opening | Visual attractiveness | −0.00 | 0.05 | −0.01 | −0.09 | 0.93 | 0.76 | 1.31 |
| Expected easiness | −0.05 | 0.10 | −0.04 | −0.51 | 0.61 | 0.70 | 1.43 | ||
| After-opening | Satisfaction with bottle thickness | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 2.76 | 0.01 * | 0.64 | 1.57 | |
| Satisfaction with cap height | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.92 | 0.36 | 0.27 | 3.69 | ||
| Satisfaction with cap ridges | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 1.66 | 0.10 | 0.68 | 1.47 | ||
| Satisfaction with hand strength required | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.22 | 2.81 | 0.01 * | 0.60 | 1.68 | ||
| Satisfaction with feeling of spilling out | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.32 | 0.75 | 0.76 | 1.31 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.; Lee, S.-D. Designing for Green and Grey: Insights from Single-Use Plastic Water Bottles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031423
Kim T, Lee S-D. Designing for Green and Grey: Insights from Single-Use Plastic Water Bottles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031423
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Taesun, and Sang-Don Lee. 2022. "Designing for Green and Grey: Insights from Single-Use Plastic Water Bottles" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031423
APA StyleKim, T., & Lee, S.-D. (2022). Designing for Green and Grey: Insights from Single-Use Plastic Water Bottles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031423










