Atmospheric Deposition of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Coastal Urban Environment of Poland: Sources and Transport Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Details of Field Measurement Strategy
2.2. PM2.5-Bound PAHs Pretreatment and Analysis
2.3. Calculation of PAHs Deposition Fluxes
2.4. FLEXTRA Model Application
3. Results
3.1. PAHs Deposition in Gdynia and Other Worldwide Sites
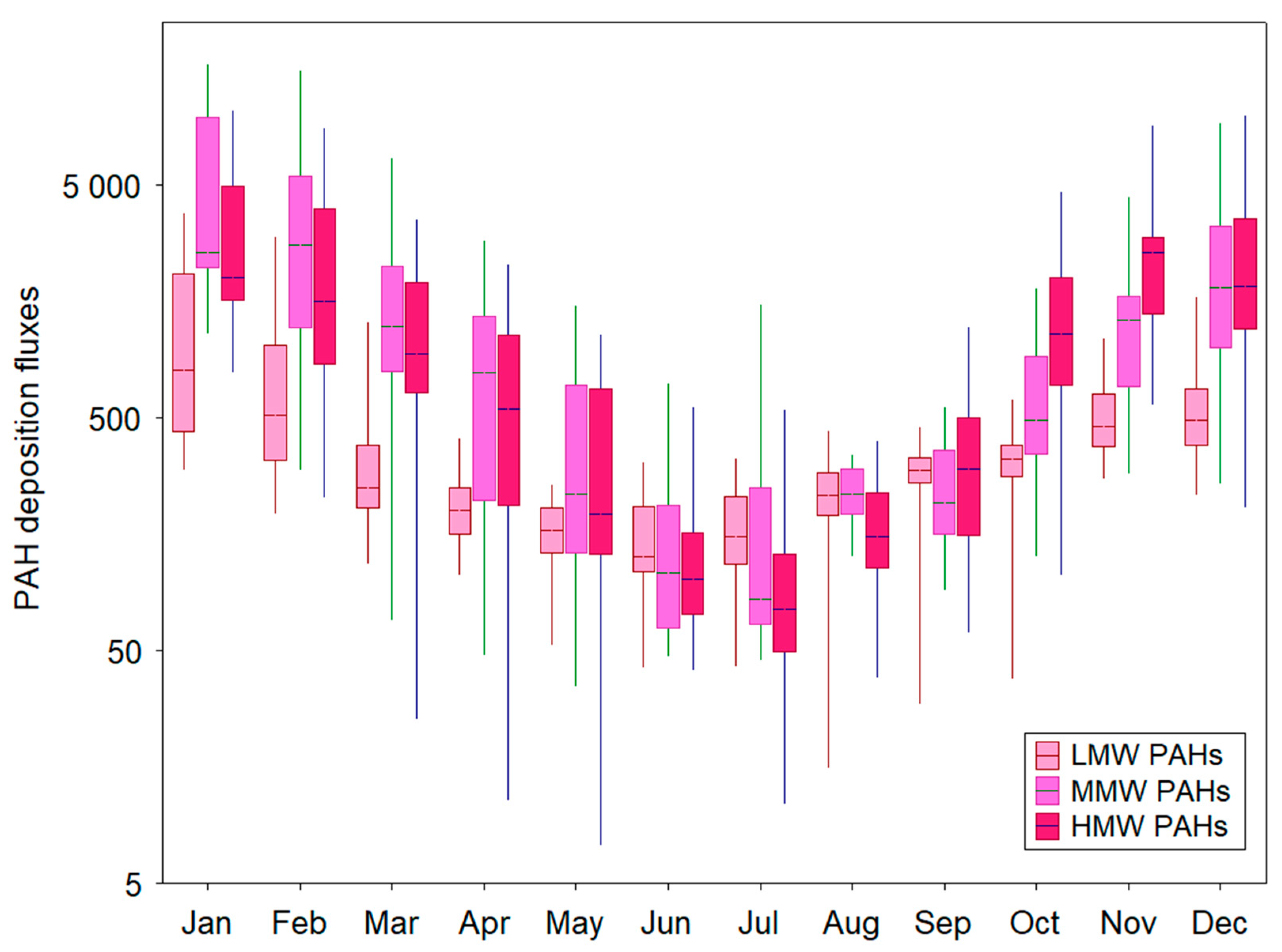
3.2. Seasonal Variability of PAHs Deposition Fluxes
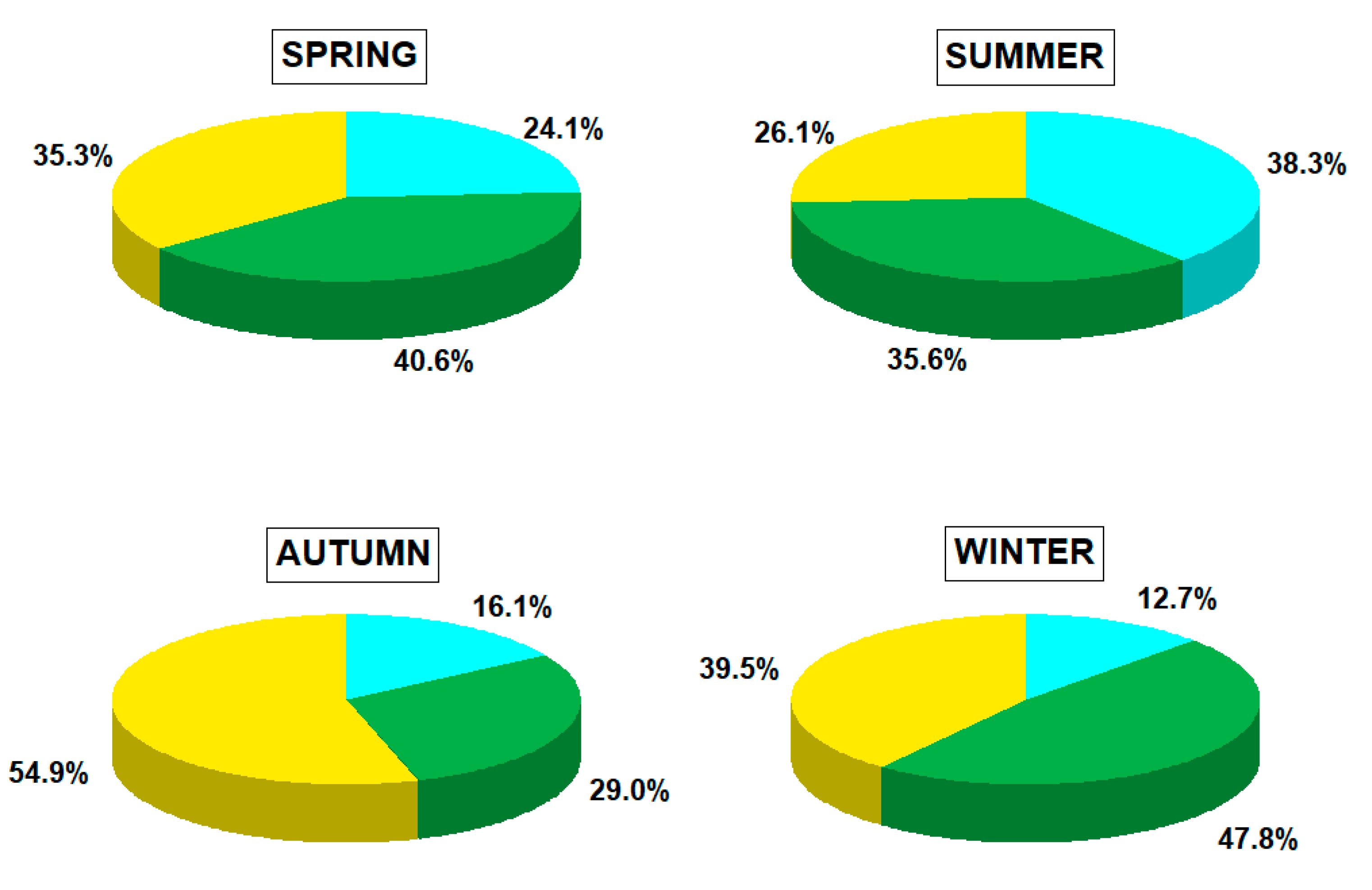
3.3. Interseasonal Contributions to Deposition Fluxes
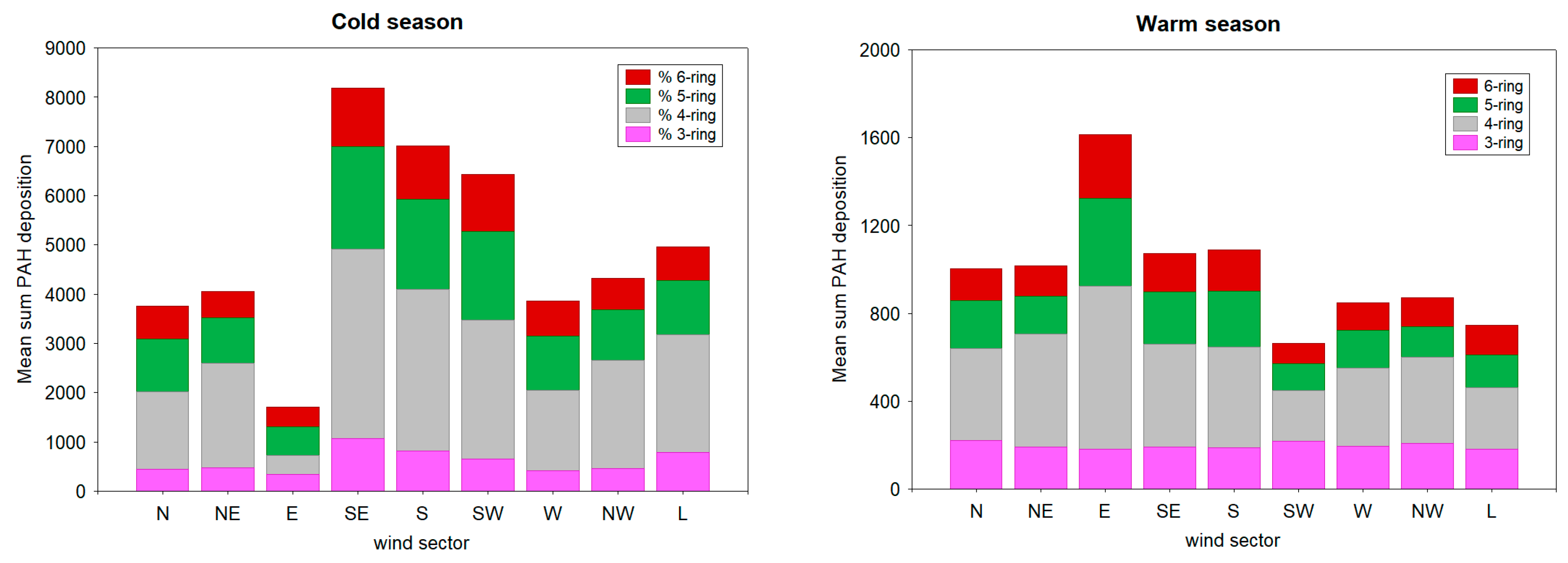
3.4. Overview of PAHs Deposition Fluxes in Different Wind Regimes
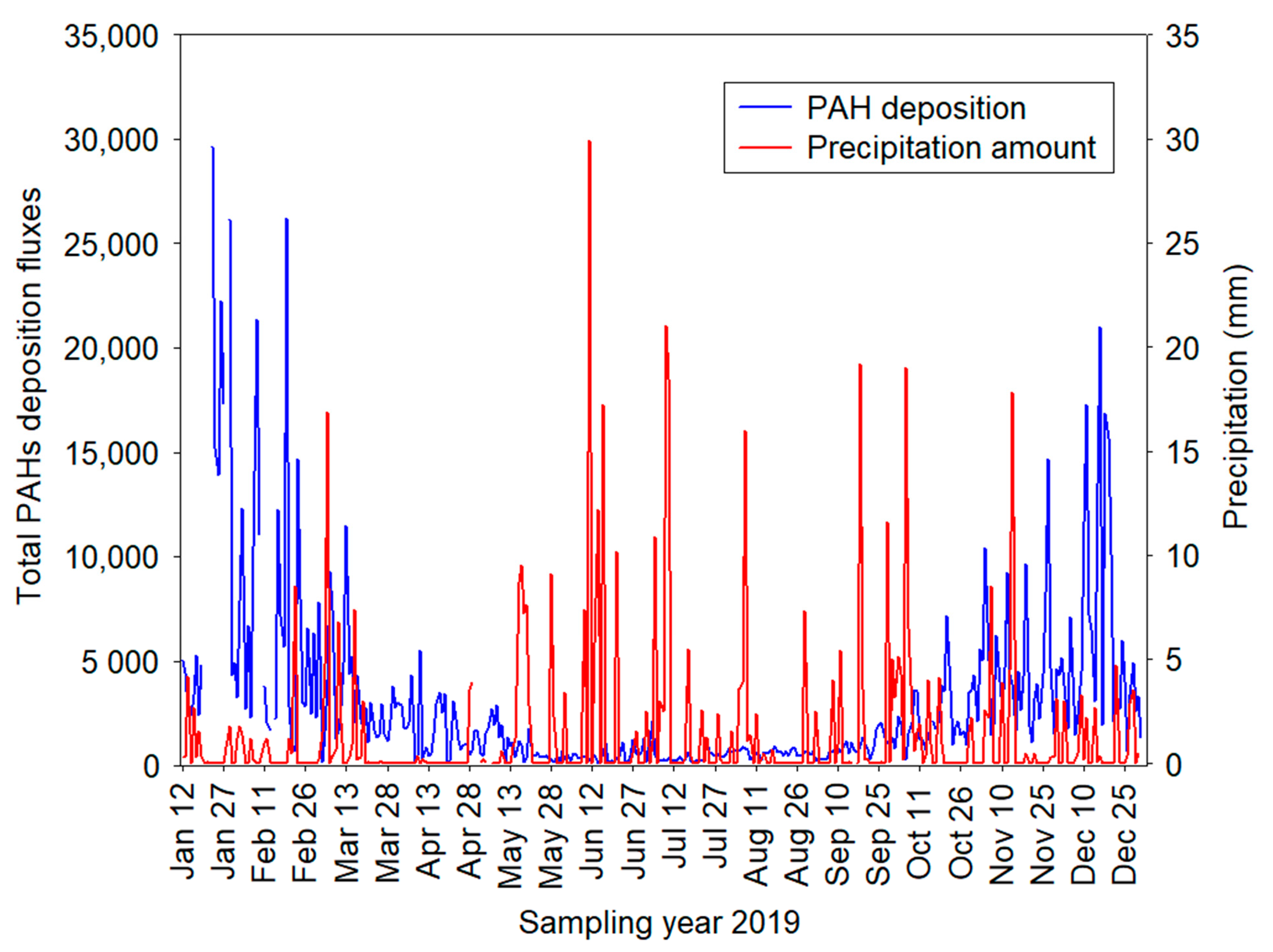
3.5. Impact of Precipitation on PM2.5-Bound PAHs: Concentrations and Deposition Fluxes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niu, X.; Ho, S.S.H.; Ho, K.F.; Huang, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, J. Atmospheric levels and cytotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and oxygenated-PAHs in PM2.5 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaz, S.; Shahpoury, P.; Jaffrezo, J.-J.; Lammel, G.; Perraudin, E.; Villenave, E.; Albinet, A. One-year study of polycyclic aromatic compounds at an urban site in Grenoble (France): Seasonal variations, gas/particle partitioning and cancer risk estimation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.A.; Vicente, A.M.; Custódio, D.; Cerqueira, M.; Nunes, T.; Pio, C.; Lucarelli, F.; Calzolai, G.; Nava, S.; Diapouli, E.; et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives (nitro-PAHs, oxygenated PAHs, and azaarenes) in PM2.5 from Southern European cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, T.; Han, Y.; Lv, D. PM2.5-bound PAHs in three indoor and one outdoor air in Beijing: Concentration, source and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, A.; Calvo, A.; Fernandes, A.P.; Nunes, T.; Monteiro, C.; Pio, C.; Alves, C. Hydrocarbons in particulate samples from wildfire events in central Portugal in summer 2010. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 53, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, L.C.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Harley, R.A.; Miguel, A.H.; Hering, S.V.; Hammond, S.K. Characterization of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Motor Vehicle Fuels and Exhaust Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringuet, J.; Albinet, A.; Leoz-Garziandia, E.; Budzinski, H.; Villenave, E. Diurnal/nocturnal concentrations and sources of particulate-bound PAHs, OPAHs and NPAHs at traffic and suburban sites in the region of Paris (France). Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 437, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.P.; Kumar, K.; Jain, V.K. Distribution of ring PAHs in particulate/gaseous phase in the urban city of Delhi, India: Seasonal variation and cancer risk assessment. Urban Clim. 2021, 40, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyte, I.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Lammel, G.M. Chemical reactivity and long-range transport potential of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons—A review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9333–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nežiková, B.; Degrendele, C.; Čupr, P.; Hohenblum, P.; Moche, W.; Prokeš, R.; Vaňková, L.; Kukučka, P.; Martinik, J.; Audy, O.; et al. Bulk atmospheric deposition of persistent organic pollutants and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Central Europe. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23429–23441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.P.; Tao, S.; Xu, F.L.; Dawson, R.; Lan, T.; Li, B.G.; Cao, J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in dust fall in Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 345, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Yang, F.M.; Chen, S.J.; Wang, H.B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Xiang, L.; Qiao, B.Q. Atmospheric deposition of polycyclic aromatic compounds and associated sources in an urban and a rural area of Chongqing, China. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasdemir, T.; Esen, F. Dry deposition fluxes and deposition velocities of PAHs at an urban site in Turkey. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.K.; Pandit, G.G.; Puranik, V.D. Dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with atmospheric particulate matter in an urban site, Mumbai, India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2008, 4, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, M.; de Gennaro, G.; Di Gilio, A.; Tutino, M. Monitoring of the deposition of PAHs and metals produced by a steel plant in Taranto (Italy). Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014, 598301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, I.; Wu, Z.; Herner, T.; Schuster, J.; Charland, J.P.; Muir, D.; Parnis, M. Dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic compounds to various land covers in the Athabasca oil sands region. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Bi, C.; Wang, D.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Z. Atmospheric deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Shanghai: The spatio-temporal variation and source identification. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siudek, P.; Ruczyńska, W. Simultaneous Measurements of PM2.5- and PM10-bound Benzo(a)pyrene in a Coastal Urban Atmosphere in Poland: Seasonality of Dry Deposition Fluxes and influence of Atmospheric Transport. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 210044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodhe, H.; Soderlund, R.; Ekstedt, J. Deposition of airborne pollutants on the Baltic. Ambio 1980, 9, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Poor, N.; Tremblay, R.; Kay, H.; Bhethanabotla, V.; Swartz, E.; Luther, M.; Campbell, S. Atmospheric concentrations and dry deposition rates of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) for Tampa Bay, Florida, USA. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6005–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Seibert, P. Accuracy of trajectories as determined from the conservation of meteorological tracers. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 124, 1465–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Liang, B.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Tian, M. Atmospheric wet and dry depositions of polycyclic aromatic compounds in a megacity of Southwest China. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotel, J.; Gong, P.; Wang, X.; Pokhrel, B.; Wang, C.; Nawab, J. Determination of dry deposition velocity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons under the sub-tropical climate and its implication for regional cycling. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Abakumov, E.; Xie, X. Atmosphere-ocean exchange of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Russian Arctic Ocean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13789–13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, F.; Cindoruk, S.S.; Tasdemir, Y. Bulk deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in an industrial site of Turkey. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.S.; Zhang, C.; Wan, D.; Yue, D.; Ye, Y.; Wang, X. Source diagnostics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban road runoff, dust, rain and canopy through fall. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 153, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasdemir, T.; Holsen, T.M. Measurement of particle phase dry deposition fluxes of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) with water surface sampler. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ye, Y.; Shen, Q.; Hu, J.; Wang, X. Application of spatial analysis and multivariate analysis techniques in distribution and source study of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the topsoil of Beijing, China. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Limu, Y.L.M.A.B.; Lifu, D.L.N.T.; Miti, A.B.L.Y.; Wang, X.; Ding, X. Autumn and Wintertime Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 from Urumqi, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.A. Exhaust emissions from ships at berth. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3817–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Smith, D.J.T.; Luhana, L. Source apportionment of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons collected from an urban location in Birmingham, U.K. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Cui, M.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Tian, C.; Matthias, V.; et al. Emission factors and environmental implication of organic pollutants in PM emitted from various vessels in China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, L.; Yang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Mao, H. Characterization of PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives (nitro-and oxy-PAHs) emissions from two ship engines under different operating conditions. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, B.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Sahu, L.K. Temporal variability of atmospheric particulate-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) over central east India: Sources and carcinogenic risk assessment. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Park, R.; Alexandrou, N.; Dryfhout-Clark, H.; Brice, K.; Hung, H. Multi-year Analyses Reveal Different Trends, Sources, and Implications for Source-Related Human Health Risks of Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Canadian Great Lakes Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2254–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noro, K.; Yabuki, Y. Photolysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed on polyethylene microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiodra, I.; Grivas, G.; Tavernaraki, K.; Biugiatioti, A.; Apostolaki, M.; Parasekevopoulou, D.; Gogou, A.; Parinos, C.; Oikonomou, K.; Tsagkaraki, M.; et al. Annual exposure to PAHs in urban environments linked to wintertime wood-burning episodes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 17865–17883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Nakajima, D.; Lu, S.; Xiao, K.; Chowdhury, T.; Suzuki, M.; Liu, F. Industrial Source Contributions and Health Risk Assessment of Fine Particle-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) during Spring and Late Summer in the Baoshan Area, Shanghai. Processes 2021, 9, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Kang, S.; Li, C.; Rupakheti, M.; Yan, F.; Li, Q.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, W.; Sillanpää, M. Characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric aerosols in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisen, F.; Arey, J. Atmospheric Reactions Influence Seasonal PAH and Nitro-PAH Concentrations in the Los Angeles Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.S.C.; Loyola, J.; Quiterio, S.L.; da Rocha, G.O.; de Andrade, J.B.; Arbilla, G. Particle-associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their dry deposition fluxes from a bus-station in the Rio de Janeiro Metropolitan Area, Brazil. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 1565–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tai, A.P.K.; Mickley, L.J.; Jacob, D.J. Correlations between fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and meteorological variables in the United States: Implications for the sensitivity of PM2.5 to climate change. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3976–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ge, X.L.; Huang, Y.; Suo, C.; Zhang, D. Effects of emission control and meteorological parameters on urban air quality showed by the 2014 youth Olympic games in China. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 4798–4807. [Google Scholar]

| X | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X vs. Precipitation | X vs. Precipitation | X vs. Precipitation | X vs. Precipitation | |
| Flu | −0.108 | 0.046 | 0.171 | −0.315 |
| Phe | −0.396 | 0.020 | 0.069 | −0.341 |
| Ant | −0.106 | 0.090 | −0.053 | −0.252 |
| Flt | −0.398 | 0.011 | 0.063 | −0.305 |
| Pyr | −0.368 | −0.089 | −0.128 | −0.346 |
| BaA | −0.040 | 0.121 | −0.098 | −0.266 |
| Chry | −0.353 | 0.033 | −0.028 | −0.327 |
| BbF | −0.360 | 0.076 | −0.107 | −0.358 |
| BkF | −0.340 | 0.083 | −0.089 | −0.362 |
| BaP | −0.324 | −0.029 | −0.111 | −0.325 |
| DahA | −0.150 | 0.090 | −0.094 | −0.318 |
| BghiP | −0.332 | 0.058 | −0.112 | −0.355 |
| IcdP | −0.375 | 0.065 | −0.075 | −0.303 |
| LMW PAHs | −0.328 | 0.045 | 0.063 | −0.342 |
| MMW PAHs | −0.239 | 0.087 | −0.049 | −0.342 |
| HMW PAHs | −0.323 | 0.100 | −0.108 | −0.347 |
| PM2.5 | 0.142 | −0.042 | 0.071 | −0.470 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siudek, P. Atmospheric Deposition of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Coastal Urban Environment of Poland: Sources and Transport Patterns. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114183
Siudek P. Atmospheric Deposition of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Coastal Urban Environment of Poland: Sources and Transport Patterns. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(21):14183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114183
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiudek, Patrycja. 2022. "Atmospheric Deposition of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Coastal Urban Environment of Poland: Sources and Transport Patterns" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 21: 14183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114183
APA StyleSiudek, P. (2022). Atmospheric Deposition of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Coastal Urban Environment of Poland: Sources and Transport Patterns. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(21), 14183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114183






