Exploring Unobserved Heterogeneity in Cyclists’ Occupying Motorized Vehicle Lane Behaviors at Different Bike Facility Configurations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
- To estimate a random parameter logit model for the behavior of cyclists in occupying motorized vehicle lanes;
- To determine the effects of individual characteristics, geometric road design, environmental characteristics, and traffic variables on the behavior decisions of cyclists using risk factor analysis and simulated probability; and
- To demonstrate the effect of the different bike facility configurations on the behavior of cyclists occupying motorized vehicle lanes that will assist traffic management authorities in developing appropriate countermeasures.
3. Data
3.1. Definition of Cyclists Occupying Motorized Vehicle Lanes
3.2. Data Collection
3.2.1. Data Investigation
3.2.2. Data Extraction and Description
4. Methodology
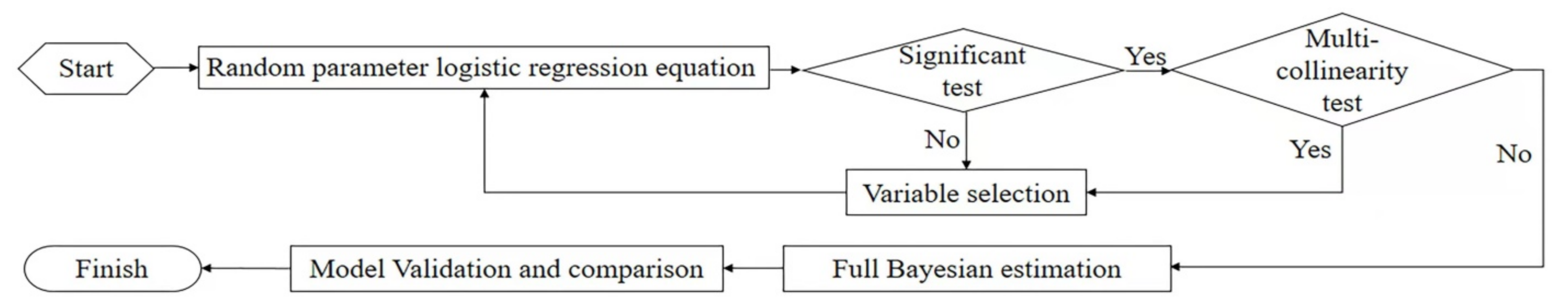
4.1. Random Parameter Logit Model
4.2. Full Bayesian Estimation
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Comparison of Estimation Results
5.2. Results of Cyclists’ Occupying Motorized Vehicle Lane Behavior at All Bike Facility Configurations
5.2.1. Interpretation of Individual Characteristic Variables
5.2.2. Road Geometric Design Variables
5.2.3. Traffic Condition Variables
5.2.4. Environmental Condition and Other Variables
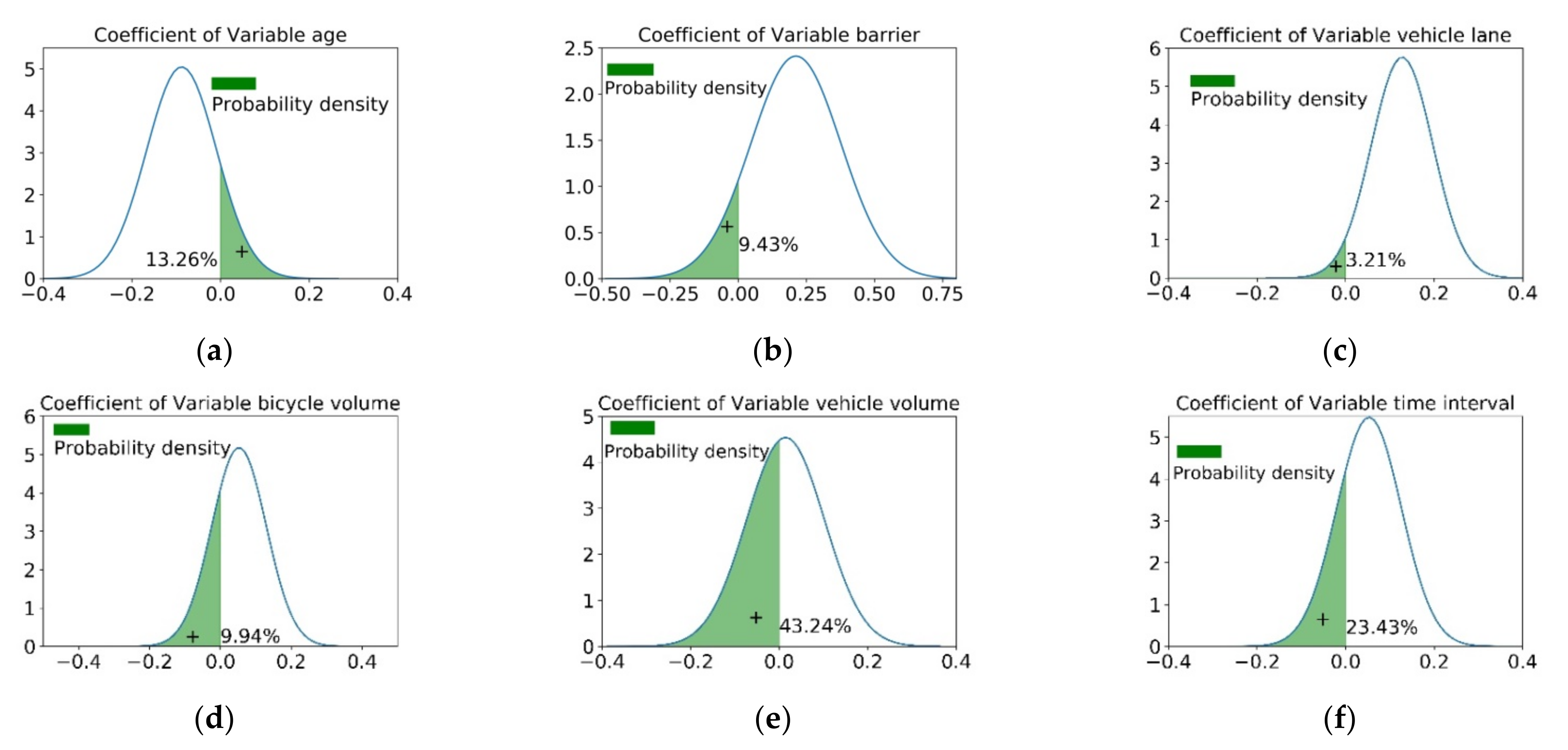
5.3. Comparision Results of COMB According to Bicycle Facility Configurations
5.3.1. Estimation of COMB at Greenbelt Dividing Strip
5.3.2. Estimation of COMB at Barriers Dividing Strip
5.3.3. Estimation of COMB at Bike Lane with Marking Dividing Strip
5.3.4. Estimation of COMB at Pedestrian–Bicycle Shared Lane
5.3.5. Estimation of COMB at Mixed Traffic
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, T.; Kim, I.; Currie, G. The two-wheeled renaissance in China—An empirical review of bicycle, E-bike, and motorbike development. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2021, 15, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Yang, H.; Mayhue, A.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ma, Y. E-scooter safety: The riding risk analysis based on mobile sensing data. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 151, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- People’s Republic of China Central People’s Government Network. China’s Bicycle Society Has Nearly 400 Million Bicycles and Ranks First in the World. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-11/22/content_5454675.htm (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Short, J.; Caulfield, B. The safety challenge of increased cycling. Transp. Policy 2014, 33, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikitas, A.; Vitel, A.; Cotet, C. Autonomous vehicles and employment: An urban futures revolution or catastrophe? Cities 2021, 114, 103203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S. Integrating e-scooters in urban transportation: Problems, policies, and the prospect of system change. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 79, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jashami, H.; Cobb, D.; Hurwitz, D.S.; McCormack, E.; Goodchild, A.; Sheth, M. The impact of commercial parking utilization on cyclist behavior in urban environments. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2020, 74, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Jiang, H. Evaluating bicycle–vehicle conflicts and delays on urban streets with bike lane and on-street parking. Transp. Lett. 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.; Miranda-Moreno, L.F.; Morency, P. Mapping Cyclist Activity and Injury Risk in a Network Combining Smartphone Gps Data and Bicycle Counts. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2015, 83, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S.; Giacomo Prato, C. A Spatial Analysis of Land Use and Network Effects on Frequency and Severity of Cyclist-Motorist Crashes in the Copenhagen Region. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2015, 16, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Bureau Statistics Network. Traffic Accident Statistics. Available online: https://data.stats.gov.cn/ (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Bella, F.; Silvestri, M. Interaction driver–bicyclist on rural roads: Effects of cross-sections and road geometric elements. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2017, 102, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yang, D.; Zhou, J.; Feng, Z.; Yuan, Q. Risk riding behaviors of urban e-bikes: A literature review. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, C.; Huang, W.; Tao, H.; Wang, K.; Feng, Z.; Hu, Z. Investigating factors affecting riders’ behaviors of occupying motorized vehicle lanes on urban streets. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 122, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleinitz, K.; Petzoldt, T.; Kröling, S.; Gehlert, T.; Mach, S. (E-) Cyclists running the red light–The influence of bicycle type and infrastructure characteristics on red light violations. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 122, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkritza, K. Modeling motorcycle helmet use in Iowa: Evidence from six roadside observational surveys. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2009, 41, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, J.; Wardman, M.; Page, M. Models of Perceived Cycling Risk and Route Acceptability. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2007, 39, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turner, S.; Wood, G.; Hughes, T.; Singh, R. Safety performance functions for bicycle crashes in New Zealand and Australia. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2011, 2236, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakogiannis, E.; Vlastos, T.; Athanasopoulos, K.; Vassi, A.; Christodoulopoulou, G.; Karolemeas, C.; Tsigdinos, S.; Kyriakidis, A.; Noutsou, M.; Siti, M.; et al. Exploring Motivators and Deterrents of Cycling Tourism Using Qualitative Social Research Methods and Participative Analytical Hierarchy Process (Ahp). Sustainability 2020, 12, 2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campisi, T.; Acampa, G.; Marino, G.; Tesoriere, G. Cycling Master Plans in Italy: The I-BIM feasibility tool for cost and safety assessments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impacts on Safety and Feeling on Safety of Cycling Infrastructure in Copenhagen. Available online: https://viastrada.nz/sites/default/files/velocity2007_Rasmussen.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Nikiforiadis, A.; Basbas, S. Can pedestrians and cyclists share the same space? The case of a city with low cycling levels and experience. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 46, 101453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforiadis, A.; Basbas, S.; Campisi, T.; Tesoriere, G.; Garyfalou, M.; Meintanis, I.; Papas, T.; Trouva, M. Quantifying the Negative Impact of Interactions between Users of Pedestrians-Cyclists Shared Use Space. In International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 809–818. [Google Scholar]
- Torrisi, V.; Ignaccolo, M.; Inturri, G.; Tesoriere, G.; Campisi, T. Exploring the factors affecting bike-sharing demand: Evidence from student perceptions, usage patterns and adoption barriers. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 52, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthie, J.; Brady, J.F.; Mills, A.F.; Machemehl, R.B. Effects of on-street bicycle facility configuration on bicyclist and motorist behavior. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2010, 2190, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.L.; Meuleners, L.B. Risk factors for unsafe events involving a motor vehicle for group riders (cyclists): A naturalistic case-crossover study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 146, 105758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, C. Exploring unobserved heterogeneity in bicyclists’ red-light running behaviors at different crossing facilities. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 115, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Ulfarsson, G.F.; Shankar, V.N.; Mannering, F.L. A note on modeling pedestrian-injury severity in motor-vehicle crashes with the mixed logit model. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2010, 42, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J. Modeling the unobserved heterogeneity in E-Bike collision severity using full Bayesian random parameters multinomial logit regression. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannering, F.L.; Shankar, V.; Bhat, C.R. Unobserved heterogeneity and the statistical analysis of highway accident data. Anal. Methods Accid. Res. 2016, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, L.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Tay, R. A random parameter logistic model of fatigue-related motorcycle crash involvement in Hanoi, Vietnam. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 144, 105627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnood, A.; Mannering, F. Determinants of bicyclist injury severities in bicycle-vehicle crashes: A random parameters approach with heterogeneity in means and variances. Anal. Methods Accid. Res. 2017, 16, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraneeprakarn, P.; Huang, S.; Shankar, V.; Mannering, F.; Venkataraman, N.; Milton, J. Occupant injury severities in hybrid-vehicle involved crashes: A random parameters approach with heterogeneity in means and variances. Anal. Methods Accid. Res. 2017, 15, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, D.; Pan, F.; Fan, Y. Personal characteristics of e-bike riders and illegal lane occupation behavior. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Basyouny, K.; Sayed, T. Accident prediction models with random corridor parameters. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2009, 41, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xiao, W.; Deng, C.; Schwebel, D.C.; Hu, G. Unsafe riding behaviors of shared-bicycle riders in urban China: A retrospective survey. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 131, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Road | Distance to Intersection (m) | Dividing Strip | Bike Lane Width (m) | Vehicle Lane Number | On-Street Parking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jianshe Road | 200 | Greenbelt | 4.5 | 4 | No |
| Guangming Road | 100 | Greenbelt | 3.5 | 2 | Yes |
| Kaiyuan Road (N) | 100 | Marking | 2.5 | 2 | Yes |
| Kaiyuan Road (S) | 150 | Barriers | 2.5 | 2 | No |
| Kuanggong Road | 150 | Marking | 2.5 | 3 | No |
| Lingyun Road | 100 | Barriers | 2.5 | 3 | No |
| Zhanbei Road | 100 | Pedestrian–bicycle shared | 2.5 | 1 | No |
| Shuguang road | 100 | Mixed | 1.5 | 1 | Yes |
| Variable | Definition | Frequency | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual characteristics | Gender | 0: Female 1: Male | 18,014 16,617 | 52.0% 48.0% |
| Age | 1: Young: <35 2: Middle-aged: 35–60 3: Old: >60 | 6362 24,363 3906 | 18.4% 70.4% 11.3% | |
| Bike type | 1: C-bike 2: E-bike 3: E-scooter 4: Electric tricycle | 1944 10,656 19,348 2683 | 5.6% 30.8% 55.9% 7.7% | |
| Road Geometric Design | Bike lane width(m) | 1: 4.5 2: 2.5 3: 3.5 4: 1.5 | 5052 22,518 5650 1411 | 14.6% 65.0% 16.3% 4.1% |
| Vehicle lane number | 1: 2 2: 3 3: 4 4: 1 | 16,925 7788 5052 4866 | 48.9% 22.5% 14.6% 14.1% | |
| Dividing strip types | 1: Green belt 2: Barriers 3: Marking 4: Pedestrian–bicycle shared 5: Mixed | 10,702 9433 9630 3455 1411 | 30.9% 27.2% 27.8% 10.0% 4.1% | |
| Traffic condition | Bike volumeveh/(5 min·m) | 1: Low: ≤33 2: Medium:34–53 3: High: ≥53 | 7826 10,689 16,116 | 22.6% 30.9% 46.5% |
| Vehicle volumeveh/(5 min·lane) | 1: Low: ≤19 2: Medium: 20–38 3: High: ≥39 | 5239 26,818 2574 | 15.1% 77.4% 7.4% | |
| On-street parking | 0: No 1: Yes | 23,158 11,473 | 66.9% 33.1% | |
| Temporary parking | 0: No 1: Yes | 31,878 2 753 | 92.1% 7.9% | |
| Environment condition | Weather | 1: Sunny 2: Cloudy 3: Rainy | 17,409 16,195 1027 | 50.3% 46.7% 3.0% |
| Time intervals | 1: Morning 2: Noon 3: Evening | 12,352 10,561 11,718 | 35.7% 30.5% 33.8% | |
| Others | Manned riding | 0: No | 28,438 | 82.1% |
| 1: Yes | 6193 | 17.9% | ||
| Workday | 0: No | 10,701 | 29.2% | |
| 1: Yes | 23,930 | 70.8% |
| Variable | Mean | S.D. | 2.5% | 97.5% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.675 | 0.748 | −6.250 | −3.594 | |
| Gender | Male vs. Female | 0.621 | 0.031 | 0.560 | 0.681 |
| Age | Middle-aged vs. Young | −0.088 | 0.038 | −0.163 | −0.013 |
| Old vs. Young | −0.334 | 0.059 | −0.451 | −0.218 | |
| Bike type | E-bike vs. C-bike | 1.189 | 0.082 | 1.031 | 1.352 |
| E-scooter vs. C-bike | 1.822 | 0.080 | 1.670 | 1.982 | |
| Tricycle vs. C-bike | 2.161 | 0.091 | 1.985 | 2.341 | |
| Dividing strip | Barriers vs. green belt | 0.211 | 1.538 | 0.314 | 0.109 |
| Marking vs. green belt | 2.250 | 3.604 | −2.988 | 8.519 | |
| Pedestrian–bicycle vs. green belt | 1.724 | 6.997 | −11.41 | 10.52 | |
| mixed vs. green belt | 1.937 | 1.536 | −0.749 | 4.462 | |
| bike lane width | 2.5 vs. 4.5 | 1.115 | 0.740 | −0.008 | 2.673 |
| 3.5 vs. 4.5 | −0.416 | 1.616 | −3.677 | 2.660 | |
| 1.5 vs. 4.5 | 4.142 | 8.362 | −7.172 | 18.09 | |
| vehicle lane number | 2 vs. 1 | 0.127 | 0.080 | −0.029 | 0.286 |
| 3 vs. 1 | 1.065 | 1.582 | −2.578 | 3.948 | |
| 4 vs. 1 | −1.851 | 4.769 | −9.742 | 5.271 | |
| bike volume | Middle vs. Low | 0.052 | 0.054 | −0.053 | 0.157 |
| High vs. low | 0.322 | 0.066 | 0.196 | 0.452 | |
| Vehicle volume | Middle vs. Low | 0.014 | 0.004 | −0.021 | 0.053 |
| High vs. low | −0.213 | 0.097 | −0.405 | −0.023 | |
| On-street parking | Yes vs. No | −1.022 | 0.098 | −1.209 | −0.826 |
| Temporary parking | Yes vs. No | 1.147 | 0.055 | 1.039 | 1.253 |
| Weather | Cloudy vs. sunny | −0.231 | 0.073 | −0.374 | −0.089 |
| Rainy vs. sunny | −0.712 | 0.152 | −1.010 | −0.418 | |
| Time interval | Noon vs. morning | 0.299 | 0.038 | 0.224 | 0.372 |
| Evening vs. morning | 0.053 | 0.037 | −0.020 | 0.124 | |
| Others | Manned riding | −0.197 | 0.040 | −0.276 | −0.197 |
| Work day | 1.141 | 1.321 | −1.668 | 3.475 | |
| DIC | 33,230 | ||||
| Variable | Mean | S.D. | 2.5% | 97.5% | OR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.680 | 0.034 | 0.017 | 0.084 | ||
| Gender | Male vs. female | 0.621 | 0.026 | 0.569 | 0.674 | 1.860 |
| Age | Middle-aged vs. young | −0.088 | 0.029 | −0.145 | −0.030 | 0.916 |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.079 | 0.113 | 0.020 | 0.292 | ||
| Old vs. young | −0.333 | 0.040 | −0.414 | −0.252 | 0.716 | |
| Bike type | E-bike vs. C-bike | 1.188 | 0.035 | 1.117 | 1.261 | 3.281 |
| E-scooter vs. C-bike | 1.822 | 0.034 | 1.751 | 1.892 | 6.184 | |
| Tricycle vs. C-bike | 2.161 | 0.040 | 2.078 | 2.243 | 8.680 | |
| Dividing strip | Barriers vs. green belt | 0.212 | 0.050 | 0.315 | 0.110 | 1.236 |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.165 | 0.052 | 0.020 | 0.196 | ||
| Marking vs. green belt | 2.251 | 0.055 | 2.140 | 2.362 | 9.497 | |
| Pedestrian–bicycle vs. green belt | 1.726 | 0.063 | 1.602 | 1.858 | 5.618 | |
| Mixed vs. green belt | 1.936 | 0.048 | 1.834 | 2.032 | 6.931 | |
| bike lane width | 2.5 vs. 4.5 | 1.116 | 0.069 | 0.987 | 1.252 | 3.053 |
| 3.5 vs. 4.5 | −0.415 | 0.070 | −0.553 | −0.274 | 0.660 | |
| 1.5 vs. 4.5 | 4.140 | 0.068 | 3.999 | 4.279 | 62.803 | |
| vehicle lane number | 2 vs. 1 | 0.128 | 0.035 | 0.058 | 0.198 | 1.136 |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.069 | 0.061 | 0.020 | 0.217 | ||
| 3 vs. 1 | 1.065 | 0.057 | 0.948 | 1.181 | 2.901 | |
| 4 vs. 1 | −1.852 | 0.051 | −1.954 | −1.749 | 0.157 | |
| bike volume | Middle vs. Low | 0.053 | 0.033 | −0.013 | 0.120 | 1.055 |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.077 | 0.107 | 0.020 | 0.287 | ||
| High vs. low | 0.324 | 0.035 | 0.253 | 0.394 | 1.383 | |
| Vehicle volume | Middle vs. low | 0.015 | 0.004 | −0.027 | 0.058 | 1.015 |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.088 | 0.138 | 0.021 | 0.333 | ||
| High vs. low | −0.212 | 0.050 | −0.316 | −0.106 | 0.809 | |
| On-street parking | Yes vs. no | −1.021 | 0.041 | −1.103 | −0.938 | 0.360 |
| Temporary parking | Yes vs. no | 1.147 | 0.044 | 1.058 | 1.238 | 3.149 |
| Weather | Cloudy vs. sunny | −0.230 | 0.039 | −0.309 | −0.149 | 0.795 |
| Rainy vs. sunny | −0.711 | 0.072 | −0.862 | −0.556 | 0.491 | |
| Time interval | Noon vs. morning | 0.299 | 0.028 | 0.244 | 0.356 | 1.348 |
| Evening vs. morning | 0.053 | 0.028 | −0.003 | 0.110 | 1.055 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.073 | 0.111 | 0.019 | 0.275 | ||
| Others | Manned riding vs. no | −0.197 | 0.034 | −0.265 | −0.129 | 0.821 |
| Work day vs. no | 1.143 | 0.073 | 1.004 | 1.288 | 3.136 | |
| DIC | 33,210 | |||||
| Variable | Random Parameter Logit Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | S.D. | 2.5% | 97.5% | OR | ||
| Intercept | −3.148 | 0.101 | −3.354 | −2.933 | ||
| Individual characteristic | Gender | |||||
| Male vs. famle | 0.906 | 0.056 | 0.792 | 1.021 | 2.475 | |
| Age | ||||||
| Middle-aged vs. young | −0.095 | 0.054 | −0.204 | −0.095 | 0.909 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.109 | 0.166 | 0.022 | 0.436 | ||
| Older vs. young | −0.271 | 0.070 | −0.418 | −0.122 | 0.762 | |
| Road Geometric Design | Bike type | |||||
| E-bike vs. C-bike | 0.450 | 0.064 | 0.316 | 0.581 | 1.568 | |
| E-scooter vs. C-bike | 1.067 | 0.059 | 0.944 | 1.188 | 2.907 | |
| Tricycle vs. C-bike | 1.200 | 0.073 | 1.041 | 1.352 | 3.320 | |
| Traffic condition | bike volume | |||||
| Middle vs. low | 0.057 | 0.055 | −0.057 | 0.170 | 1.059 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.113 | 0.461 | 0.022 | 0.428 | ||
| High vs. low | 0.414 | 0.068 | 0.269 | 0.554 | 1.513 | |
| Vehicle volume | ||||||
| Middle vs. low | −0.239 | 0.085 | −0.416 | −0.066 | 0.787 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.143 | 0.277 | 0.024 | 0.613 | ||
| High vs. low | −0.340 | 0.100 | −0.553 | −0.126 | 0.712 | |
| On-street parking | −0.477 | 0.061 | −0.602 | −0.350 | 0.620 | |
| Environment condition and others | Weather | |||||
| Cloudy vs. sunny | −0.304 | 0.054 | −0.416 | −0.194 | 0.738 | |
| Rainy vs. sunny | −1.813 | 0.114 | −2.065 | −1.565 | 0.163 | |
| Time interval | ||||||
| Noon vs. morning | 0.331 | 0.053 | 0.221 | 0.441 | 1.392 | |
| Evening vs. morning | 0.336 | 0.060 | 0.211 | 0.460 | 1.399 | |
| Manned riding | −0.539 | 0.068 | −0.681 | −0.399 | 0.583 | |
| Variable | Random Parameter Logit Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | S.D. | 2.5% | 97.5% | OR | ||
| Intercept | −4.536 | 0.082 | −4.698 | −4.359 | ||
| Individual characteristic | Gender | |||||
| Male vs. famle | 1.029 | 0.049 | 0.931 | 1.129 | 2.798 | |
| Age | ||||||
| Middle-aged vs. young | 0.067 | 0.049 | −0.035 | 0.166 | 1.069 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.107 | 0.163 | 0.022 | 0.419 | ||
| Older vs. young | −0.140 | 0.070 | −0.290 | 0.005 | 0.870 | |
| Bike type | ||||||
| E-bike vs. C-bike | 1.043 | 0.057 | 0.920 | 1.158 | 2.838 | |
| E-scooter vs. C-bike | 1.717 | 0.053 | 1.603 | 1.821 | 5.568 | |
| Tricycle vs. C-bike | 2.147 | 0.063 | 2.014 | 2.274 | 8.559 | |
| Road Geometric Design | vehicle lane | |||||
| 3 vs. 2 | 0.065 | 0.065 | −0.070 | 0.198 | 1.067 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.627 | 0.119 | 0.024 | 2.129 | ||
| Traffic condition | Bike volume | |||||
| Middle vs. yow | 0.422 | 0.061 | 0.295 | 0.550 | 1.525 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.145 | 0.234 | 0.022 | 0.429 | ||
| High vs. low | 0.345 | 0.061 | 0.219 | 0.472 | 1.412 | |
| Environment conditionand others | time interval | |||||
| Noon vs. morning | 0.438 | 0.046 | 0.345 | 0.531 | 1.549 | |
| Evening vs. morning | −0.629 | 0.049 | −0.730 | −0.530 | 0.533 | |
| Manned riding | −0.368 | 0.066 | −0.503 | −0.234 | 0.692 | |
| Variable | Random Parameter Logit Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | S.D. | 2.5% | 97.5% | OR | ||
| Intercept | −0.887 | 0.073 | −1.035 | −0.736 | ||
| individual characteristic | Gender | |||||
| Male vs. female | 0.435 | 0.039 | 0.356 | 0.514 | 1.546 | |
| Age | ||||||
| Middle-aged vs. young | −0.100 | 0.041 | −0.183 | −0.016 | 0.905 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.095 | 0.166 | 0.021 | 0.378 | ||
| Older vs. Young | −0.532 | 0.054 | −0.644 | −0.420 | 0.588 | |
| Bike type | ||||||
| E-bike vs. C-bike | 1.262 | 0.045 | 1.170 | 1.354 | 3.532 | |
| E-scooter vs. C-bike | 1.970 | 0.043 | 1.881 | 2.057 | 7.171 | |
| Tricycle vs. C-bike | 2.005 | 0.053 | 1.894 | 2.115 | 7.426 | |
| Traffic condition | bike volume | |||||
| Middle vs. low | 0.095 | 0.060 | −0.031 | 0.224 | 1.100 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.105 | 0.253 | 0.022 | 0.415 | ||
| High vs. low | 0.137 | 0.061 | 0.264 | 0.005 | 1.146 | |
| Vehicle volume | ||||||
| Middle vs. low | −0.271 | 0.048 | −0.368 | −0.174 | 0.763 | |
| On-street parking | −1.092 | 0.040 | −1.174 | −1.011 | 0.336 | |
| Temporary parking | 1.111 | 0.045 | 1.018 | 1.203 | 3.037 | |
| Environment condition and others | Time interval | |||||
| Noon vs. morning | 0.182 | 0.042 | 0.266 | 0.097 | 1.199 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.090 | 0.197 | 0.021 | 0.335 | ||
| Evening vs. morning | 0.198 | 0.042 | 0.113 | 0.284 | 1.219 | |
| Manned riding | −0.114 | 0.051 | −0.217 | −0.010 | 0.892 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.574 | 0.142 | 0.024 | 2.132 | ||
| Variable | Random Parameter Logit Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | S.D. | 2.5% | 97.5% | OR | ||
| Intercept | −3.885 | 0.086 | −4.06 | −3.706 | ||
| Individual characteristic | Gender | |||||
| Male vs. female | 0.205 | 0.064 | 0.071 | 0.335 | 1.228 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.716 | 0.261 | 0.024 | 2.267 | ||
| Age | ||||||
| Middle-aged vs. young | −0.321 | 0.061 | −0.451 | −0.195 | 0.726 | |
| Older vs. Young | −0.340 | 0.075 | −0.499 | −0.179 | 0.711 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.116 | 0.193 | 0.023 | 0.475 | ||
| Bike type | ||||||
| E-bike vs. C-bike | 1.654 | 0.072 | 1.504 | 1.8 | 5.228 | |
| E-scooter vs. C-bike | 2.241 | 0.068 | 2.100 | 2.378 | 9.403 | |
| Tricycle vs. C-bike | 3.658 | 0.078 | 3.492 | 3.913 | 38.784 | |
| Traffic condition | Bike volume | |||||
| Middle vs. low | 0.165 | 0.065 | 0.030 | 0.301 | 1.180 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.120 | 0.215 | 0.023 | 0.470 | ||
| High vs. low | 0.186 | 0.076 | 0.027 | 0.186 | 1.204 | |
| Vehicle volume | ||||||
| High vs. middle | −0.105 | 0.067 | −0.244 | 0.035 | 0.900 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.824 | 0.343 | 0.024 | 2.257 | ||
| Environment condition and others | time interval | |||||
| noon vs. morning | 1.168 | 0.062 | 1.039 | 1.297 | 3.216 | |
| evening vs. morning | 0.557 | 0.064 | 0.424 | 0.691 | 1.745 | |
| Manned riding | 0.077 | 0.085 | −0.105 | 0.254 | 1.080 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.531 | 0.426 | 0.026 | 2.596 | ||
| Variable | Random Parameters Logit Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | S.D. | 2.5% | 97.5% | OR | ||
| Intercept | −1.458 | 0.010 | −1.662 | −1.243 | ||
| individual characteristic | Gender | |||||
| Male vs. female | 0.263 | 0.086 | 0.084 | 0.443 | 1.301 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 1.051 | 0.384 | 0.025 | 2.557 | ||
| Age | ||||||
| Middle-aged vs. young | −0.075 | 0.086 | −0.259 | 0.101 | 0.928 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.145 | 0.257 | 0.024 | 0.615 | ||
| Older vs. young | −0.442 | 0.104 | −0.666 | −0.226 | 0.643 | |
| Bike type | ||||||
| E-bike vs. C-bike | 1.428 | 0.077 | 1.261 | 1.587 | 4.170 | |
| E-scooter vs. C-bike | 1.856 | 0.077 | 1.689 | 2.017 | 6.398 | |
| Tricycle vs. C-bike | 1.674 | 0.091 | 1.478 | 1.864 | 5.333 | |
| Traffic condition | bike volume | |||||
| Middle vs. low | 0.002 | 0.096 | −0.210 | 0.205 | 1.002 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.682 | 0.895 | 0.025 | 2.674 | ||
| temporary parking | 3.493 | 0.423 | 2.585 | 4.465 | 32.884 | |
| Environment condition and others | weather | |||||
| rainy vs. sunny | 0.564 | 0.138 | 0.269 | 0.859 | 1.758 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.923 | 0.134 | 0.027 | 3.583 | ||
| time interval | ||||||
| noon vs. morning | 0.876 | 0.084 | 0.697 | 1.054 | 2.401 | |
| evening vs. morning | 0.865 | 0.087 | 0.680 | 1.048 | 2.374 | |
| Manned riding | 0.253 | 0.108 | 0.025 | 0.484 | 1.288 | |
| S.D. of parameter distribution | 0.920 | 0.231 | 0.026 | 3.123 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Jiao, S. Exploring Unobserved Heterogeneity in Cyclists’ Occupying Motorized Vehicle Lane Behaviors at Different Bike Facility Configurations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020792
Zhang L, Zhang S, Zhou B, Huang Y, Zhao D, Jiao S. Exploring Unobserved Heterogeneity in Cyclists’ Occupying Motorized Vehicle Lane Behaviors at Different Bike Facility Configurations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(2):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020792
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lei, Shengrui Zhang, Bei Zhou, Yan Huang, Dan Zhao, and Shuaiyang Jiao. 2022. "Exploring Unobserved Heterogeneity in Cyclists’ Occupying Motorized Vehicle Lane Behaviors at Different Bike Facility Configurations" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 2: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020792
APA StyleZhang, L., Zhang, S., Zhou, B., Huang, Y., Zhao, D., & Jiao, S. (2022). Exploring Unobserved Heterogeneity in Cyclists’ Occupying Motorized Vehicle Lane Behaviors at Different Bike Facility Configurations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(2), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020792








