Food Consumption Structure and Food Security—Through Mediating Effect Analysis of Agricultural R&D and Agricultural Investment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
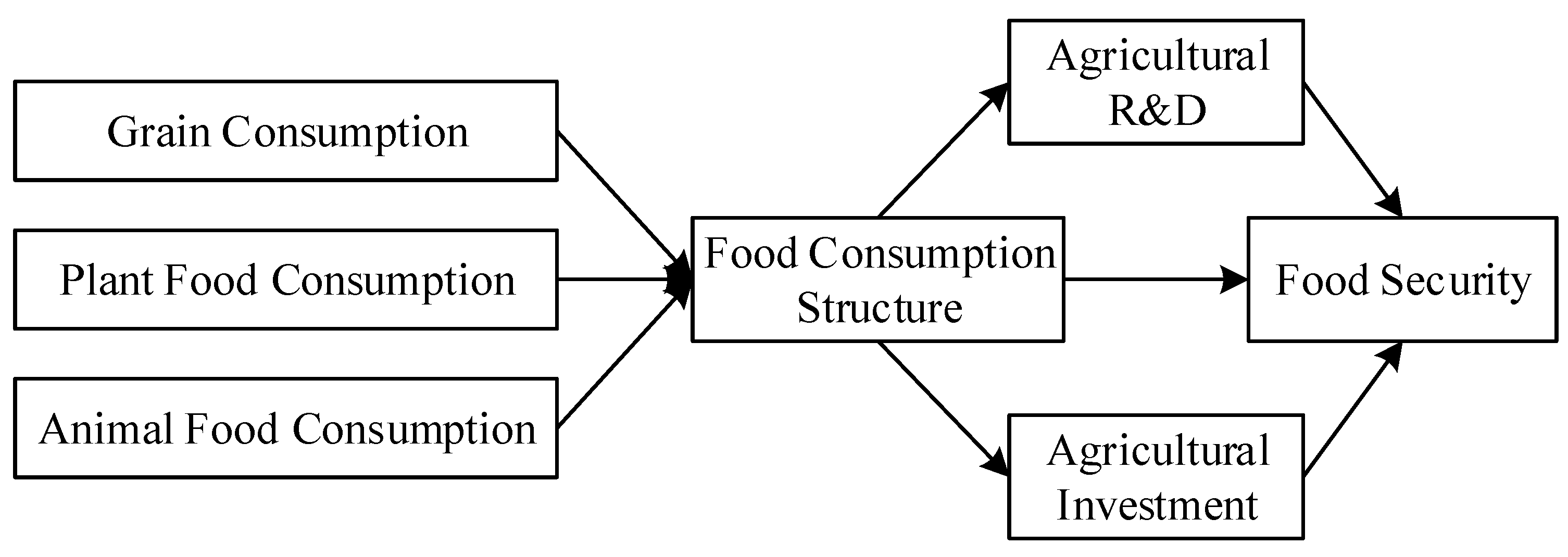
2.1. Food Consumption Structure and Food Security
2.2. Food Consumption Structure, Agricultural R&D, and Food Security
2.3. Food Consumption Structure, Agricultural Investment, and Food Security
3. Empirical Methods and Data Description
3.1. Data Sources and Variables
3.2. Empirical Models
4. Results and Analyses
4.1. Baseline Regression Results
4.2. Results of Mediating Effect Analysis
4.3. Robustness Test
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Suggestions
5.3. Theoretical Contribution
5.4. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deaton, B.J.; Deaton, B.J. Food security and Canada’s agricultural system challenged by COVID-19. Can. J. Agric. Econ. 2020, 2, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L. Dietary structure upgrade of China’s residents, international trade and food security. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 6, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Liu, H. Spatiotemporal changes in the state of food security across mainland china during 1990–2015: A multi-scale analysis. Food Energy Secur. 2022, 11, e318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, K.; Thomassin, P.J.; Zhang, J. Food security in China at 2050: A global CGE exercise. J. Econ. Struct. 2018, 7, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.; Ajates, R.; Arnall, A.; Blake, L.; Borrelli, R.; Collier, R.; de Frece, A.; Häsler, B.; Lang, T.; Pope, H.; et al. A future workforce of food-system analysts. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, S.J.; Phillips, P.W.; Kerr, W.A. Food security and the evaluation of risk. Glob. Food Secur. 2015, 4, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gu, X. An Analysis and Forecast of China’s Demand for Grain and the Structure in 2020: With the Perspective of Nutrition Criteria. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2010, 6, 4–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, C. Future grain consumption trends and implications on grain security in China. Sustainability 2019, 19, 5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovhannisyan, V.; Gould, B.W. Structural change in urban Chinese food preferences. Agric. Econ. 2014, 2, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Impact of Income Growth on Food Consumption Patterns in Urban China. China Econ. Q. 2016, 1, 263–288. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, G. Land Transfer, Appetite for Risk and Crop Pattern-Empirical Analysis Based on Micro Data of CHFS. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2021, 8, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. Spatial–temporal heterogeneity and driving factors of rural residents’ food consumption carbon emissions in China—Based on an ESDA-GWR model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, C.P. Food security, structural transformation, markets and government policy. Asia Pac. Policy Stud. 2017, 1, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, J.B.; Cissé, J.D.; Barrett, C.B. Food security as resilience: Reconciling definition and measurement. Agric. Econ. 2016, 11, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puma, M.J.; Bose, S.; Chon, S.Y.; Cook, B.I. Assessing the evolving fragility of the global food system. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 2, 24007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Focus on Food Insecurity and Vulnerability—A Review of the UN System Common Country Assessments and World Bank Poverty Reduction Strategy Papers; FIVIMS Secretariat and Wageningen University and Research Centre: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2003; Available online: www.fao.org/DOCREP/006/Y5095E/Y5095E00.htm (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Barrett, C.B. Measuring food insecurity. Science 2015, 327, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Build it back better: Deconstructing food security for improved measurement and action. Glob. Food Secur. 2013, 3, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devereux, S.; Béné, C.; Hoddinott, J. Conceptualising COVID-190s Impacts on Household. Food Secur. 2020, 4, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, D.; Martin, W.; Swinnen, J.; Vos, R. COVID-19 risks to global food security. Science 2020, 369, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allee, A.; Lynd, L.R.; Vaze, V. Cross-national analysis of food security drivers: Comparing results based on the Food Insecurity Experience Scale and Global Food Security Index. Food Secur. 2021, 5, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosratabadi, S.; Khazami, N.; Abdallah, M.B.; Lackner, Z.; Shabad, Z.B.; Mosavi, A.; Mako, C. Social Capital Contributions to Food Security: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Foods 2020, 9, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, J.; Graef, F.; König, H.J.; Mchau, D. Developing community based food security criteria in rural Tanzania. Food Secur. 2017, 9, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Nie, C. Study on Food Secunity in China Based on Evaluation Index System. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 8, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Dai, Y. The Impact of Rural Tourism Development on Food Security-Analysis of Threshold panel. J. Jishou Univ. 2020, 3, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, U.; Kumar, R. COVID-19 pandemic impact on food security and food system of India:Lessons for future. Environ. Resil. Transform. Times COVID-19 2021, 34, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhu, W. Can Agricultural Insurance Contribute to Ensuring Food Security. Insur. Stud. 2021, 10, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.D.; Ngure, F.M.; Pelto, G.; Young, S.L. What Are We Assessing When We Measure Food Security? A Compendium and Review of Current Metrics. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 5, 481–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headey, D.; Ecker, O. Rethinking the measurement of food security: From first principles to best practice. Food Secur. 2013, 5, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. Achieving food security in China: Past three decades and beyond. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2010, 2, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairagi, S.; Mohanty, S.; Baruah, S.; Thi, H.T. Changing food consumption patterns in rural and urban Vietnam: Implications for a future food supply system. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2020, 3, 750–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobiac, L.; Irz, X.; Leroy, P.; Requillart, V.; Scarborough, P.; Soler, L.G. Accounting for consumers’ preferences in the analysis of dietary recommendations. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 73, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Qiang, W.; Niu, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, S. Options of Chinese dietary pattern based on multi-objective optimization. Resour. Sci. 2021, 6, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. On influence of Consumption onproduction-Aslo on How to Expand Domestic Consumption Demand. Teach. Res. 2021, 3, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Tu, S.; Ge, D.; Li, T.; Liu, Y. The allocation and management of critical resources in rural China under restructuring: Problems and prospects. J. Rural. Stud. 2016, 47, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurayevich, M.B.; Bulturbayevich, M.B. Attracting Foreign Investment in The Agricultural Economy. Int. J. Bus. Law Educ. 2020, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headey, D.; Ecker, O. Improving the Measurement of Food Security. SSRN Electron. J. 2012, 31, 12315–12320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Xu, T.; Li, X. Path technological Change and Food Security in China -Simulation Based on GTAP Model. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2021, 2, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Wang, H.L. Analysis on enviornmental planning, agricultural technological innovation and agriculural carbon emission. J. Hubei Univ. 2020, 4, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buks, J.; Obiedzińska, A.; Prandecki, K. Environmental externalities and food security. J. Agribus. Rural. Dev. 2016, 2, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haysom, G.; Tawodzera, G. “Measurement drives diagnosis and response”: Gaps in transferring food security assessment to the urban scale. Food Policy 2018, 74, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, C.M.; Kenny, D.A. Process analysis: Estimating mediation in treatment evaluations. Eval. Rev. 1981, 5, 602–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author and Year | Food Security Evaluation Index |
|---|---|
| FAO (2003) [16] | Four main dimensions of food security can be identified according to FAO. Physical availability of food, Economic and physical Access to food, Food utilization, Stability. |
| Cui et al. (2019) [24] | Five aspects: Quantity security, Quality security, Ecological security, Economic security, and resource security, Including fluctuation coefficients of grain production, Sown area and unit area output, Per capita grain Possession, Pesticide and fertilizer application, Financial support for agriculture, Proportion of grain disasters, Engel coefficient, Grain sales price index, Unit cultivated land area, and water resources. |
| Fang et al. (2020) [25] | Four dimensions: Supply ability, Availability, Stability, and sustainability, Including food share, Production fluctuation coefficient and disaster rate, Pesticide and fertilizer application, and mulch film use. |
| Mina and Kumar (2021) [26] | It includes food security outcomes of these activities related to availability and utilization of, and access to food as well as other socioeconomic and environmental factors. |
| Schindler et al. (2017) [23] | Environmental, Social, and economic analysis, Including crop diversity, Land fertility, Food intake diversity, Social eating habits, Grain yield, Dependence on foreign agricultural trade, and utilization of agricultural resources. |
| Jiang and Zhu (2021) [27] | Includes nutrition, Availability, Affordability, Stability, Sustainability, and Policy support. Including pesticide application, Fertilizer application, Density of population, Proportion of food disasters, Engel’s coefficient, Grain sown area, Road density, Food price volatility, Agricultural machinery power. |
| Jones et al. (2013) [28] | Malnutrition rates, Proportion of household food expenditure, Dietary structure index, Food price volatility index, Food adequacy, Cultural acceptability and food stability. |
| Headey et al. (2012) [29] | Personal nutrition, whether there are seasonal shortages, Dietary diversity, Calorie consumption, Malnutrition rates, Household food safety perceptions. |
| Zhou (2010) [30] | Adequacy of food supply includes Nutritional adequacy, Food safety and quality, Cultural acceptability. Stability of food supply and access includes Environmental stability, Social stability. |
| Upton et al. (2016) [14] | Four aspects: Accessibility, Sustainability, Availability, and stability, Including: Food supply and access, Household poverty rate, Total food supply, Food diversity score, Dietary diversity score, Food frequency score, and food consumption score. |
| Dimension | Indicator | Definition | Type | Wight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Availability | Grain production per unit area (tons/km2) | Total yield as a proportion of total sown area | Positive | 0.07 |
| Grain sown area/% | The proportion of sown area in the provincial area | Positive | 0.07 | |
| Agricultural machinery power/10,000 kW | The total power of agricultural machinery power | Positive | 0.10 | |
| Fiscal Support for Agriculture/% | Agricultural expenditure as a proportion of total fiscal expenditure | Positive | 0.17 | |
| Food share per capita(kg/person) | The extent to which grain production meets the needs of the province | Positive | 0.10 | |
| Stability | Fluctuation coefficient of food production/% | The difference between grain production and the average grain production accounts for the proportion of the average grain production | Negative | 0.16 |
| Proportion of food disasters/% | The affected area as a proportion of the total sown area | Negative | 0.15 | |
| Sustainability | Pesticide application (tons/thousand hectares) | The proportion of pesticide application to total sown area | Negative | 0.05 |
| Fertilizer application (10,000 tons/1000 ha) | The proportion of chemical fertilizer application to total sown area | Negative | 0.04 | |
| Plastic film use (tons/1000 ha) | The proportion of plastic film used to total sown area | Negative | 0.09 |
| Indicator | Year | Grain | Edible Oil | Vegetable | Meat | Poultry | Sea Food | Egg | Plant Food | Animal Food | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food purchases per inhabitant (kg/person) | 2015 | 134.50 | 10.61 | 94.88 | 26.20 | 8.36 | 11.18 | 9.46 | 94.88 | 55.20 | 295.18 |
| 2016 | 132.82 | 10.61 | 96.95 | 26.10 | 9.13 | 11.44 | 9.66 | 96.95 | 56.32 | 296.70 | |
| 2017 | 130.12 | 10.42 | 96.11 | 26.67 | 8.89 | 11.46 | 10.01 | 96.11 | 57.03 | 293.68 | |
| 2018 | 127.23 | 9.64 | 93.01 | 29.52 | 9.00 | 11.39 | 9.70 | 93.01 | 59.61 | 289.49 | |
| 2019 | 130.11 | 9.47 | 95.21 | 26.91 | 10.80 | 13.57 | 10.66 | 95.21 | 61.93 | 296.72 | |
| Proportion of various types of food (%) | 2015 | 45.56 | 3.59 | 32.14 | 8.87 | 2.83 | 3.78 | 3.20 | 32.14 | 18.70 | 100.00 |
| 2016 | 44.76 | 3.57 | 32.67 | 8.79 | 3.07 | 3.85 | 3.26 | 32.67 | 18.94 | 100.00 | |
| 2017 | 44.30 | 3.54 | 32.72 | 9.08 | 3.02 | 3.90 | 3.41 | 32.72 | 19.41 | 100.00 | |
| 2018 | 43.94 | 3.33 | 32.12 | 10.19 | 3.10 | 3.93 | 3.35 | 32.12 | 20.59 | 100.00 | |
| 2019 | 43.84 | 3.19 | 32.08 | 9.06 | 3.63 | 4.57 | 3.59 | 32.08 | 20.87 | 100.00 |
| Type | Variables | Definition | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Food Security | Calculated from food security assessment indicators and logarithm taken | 6.6131 | 0.3796 | 5.7849 | 7.5180 |
| Independent variables | Grain Consumption | Cereals, potatoes, legumes, and cooking oils account for the total food consumption | 0.4906 | 0.0787 | 0.3716 | 0.8185 |
| Plant Food Consumption | Fresh vegetables account for the proportion of total food consumption | 0.3239 | 0.0500 | 0.0686 | 0.4165 | |
| Animal Food Consumption | Meat, poultry, aquatic products, and eggs account for the proportion of total food consumption | 0.1855 | 0.0491 | 0.0954 | 0.3031 | |
| Mediating variables | Agricultural R&D | The number of patents for agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery in each province accounts for the proportion of the number of patents in the country | 0.0323 | 0.0280 | 0.0004 | 0.1111 |
| Agricultural Investment | The amount of investment in agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery in the investment in agricultural fixed assets | 0.6899 | 0.6320 | 0.0010 | 3.1540 | |
| Control variables | Transport Infrastructure | The mileage of transportation (railway, highway, waterway) line per square kilometer accounts for the proportion of the provincial area | 1.0216 | 0.5952 | 0.0644 | 2.5290 |
| Degree of Opening Up | The total import and export volume of each province accounts for the proportion of regional GDP | 0.2617 | 0.2954 | 0.0884 | 1.7881 | |
| Industrial Structure | The output value of the primary industry accounts for the proportion of total output value | 0.0921 | 0.0496 | 0.0030 | 0.2340 | |
| Density of Population | The number of permanent residents in square kilometers (transformed into logarithms) | 5.3352 | 1.4933 | 0.9701 | 8.2569 | |
| Per Capita Disposable Income | Per capita disposable income (transformed into logarithms) | 10.1021 | 0.3472 | 9.4136 | 11.1482 |
| Variables | Food Security | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
| Grain Consumption | 2.1514 *** | ||
| (0.6967) | |||
| Plant Food Consumption | −1.0027 * | ||
| (0.5906) | |||
| Animal Food Consumption | −2.0972 ** | ||
| (0.9572) | |||
| Transport Infrastructure | 0.1725 ** | 0.1672 * | 0.2330 ** |
| (0.0854) | (0.0876) | (0.0903) | |
| Degree of Opening Up | −0.8241 *** | −0.8853 *** | −0.6561 ** |
| (0.2865) | (0.2686) | (0.2615) | |
| Industrial Structure | 3.1391 ** | 1.7706 | 2.9294 ** |
| (1.2559) | (1.3967) | (1.1342) | |
| Density of Population | 0.1562 *** | 0.1099 ** | 0.0822 ** |
| (0.0467) | (0.0458) | (0.0355) | |
| Per Capita Disposal Income | 0.4758 * | 0.2442 | 0.3375 |
| (0.2793) | (0.2512) | (0.2465) | |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | −0.1795 | 3.9338 | 2.9402 |
| (2.9500) | (2.4291) | (2.3750) | |
| Observations | 155 | 155 | 155 |
| F | 4.5813 | 5.0824 | 4.8855 |
| R-squared | 0.3122 | 0.2778 | 0.2949 |
| Variables | Agricultural R&D | Food Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| Grain Consumption | 0.0148 * | 2.0358 *** | ||||
| (0.0082) | (0.6310) | |||||
| Plant Food Consumption | −0.1771 | 0.0989 | ||||
| (0.1561) | (0.6137) | |||||
| Animal Food Consumption | 0.2101 *** | −3.6125 *** | ||||
| (0.0568) | (0.7812) | |||||
| Agricultural R&D | 6.1047 *** | 6.2204 *** | 7.2114 *** | |||
| (0.8068) | (0.8469) | (0.8145) | ||||
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | 0.0377 | 0.0021 | 0.2201 | −0.4097 | 3.9207 * | 1.3531 |
| (0.2161) | (0.1397) | (0.1347) | (2.8497) | (2.2184) | (2.2633) | |
| Observations | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 |
| F | 9.1516 | 7.4222 | 7.9603 | 15.8394 | 15.9315 | 15.8829 |
| R-squared | 0.2340 | 0.2773 | 0.2790 | 0.4683 | 0.4307 | 0.5000 |
| Variables | Agricultural Investment | Food Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| Grain Consumption | 1.7191 * | 1.4871 *** | ||||
| (0.9678) | (0.4950) | |||||
| Plant Food Consumption | −0.4770 * | −0.8141 ** | ||||
| (0..2672) | (0.3913) | |||||
| Animal Food Consumption | −2.2397 * | −1.2817 * | ||||
| (1.2823) | (0.6719) | |||||
| Agricultural Investment | 0.3864 *** | 0.3994 *** | 0.3934 *** | |||
| (0.0421) | (0.0439) | (0.0408) | ||||
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | −7.3181 * | −3.2932 | −5.1165 * | 2.6248 | 5.5690 *** | 4.9610 *** |
| (3.8137) | (3.0438) | (2.9745) | (1.8679) | (1.4250) | (1.4244) | |
| Observations | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 |
| F | 5.1617 | 5.9858 | 6.8459 | 20.2931 | 20.1656 | 19.9212 |
| R-squared | 0.1786 | 0.1696 | 0.1779 | 0.6548 | 0.6445 | 0.6488 |
| Variables | New Food Security | Food Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| Grain Consumption | 0.5345 *** | 2.5530 *** | ||||
| (0.1842) | (0.5597) | |||||
| Plant Food Consumption | −0.2594 * | −0.5610 * | ||||
| (0.1542) | (0.308) | |||||
| Animal Food Consumption | −1.2112 *** | −2.7694 *** | ||||
| (0.1786) | (0.5821) | |||||
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | −0.7143 | 0.5247 | −0.4069 | −1.3921 | 1.7584 | −1.4251 |
| (0.6076) | (0.4320) | (0.4398) | (1.7137) | (1.6762) | (1.5993) | |
| Observations | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 |
| F | 26.2815 | 23.9944 | 42.2838 | 29.1315 | 24.3017 | 31.2624 |
| R-squared | 0.6592 | 0.6360 | 0.7223 | 0.7149 | 0.6696 | 0.7114 |
| Variables | Food Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | |||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| Grain Consumption | 2.9744 *** | 1.4830 ** | ||||
| (0.8226) | (0.6769) | |||||
| Plant Food Consumption | −1.7149 *** | −0.4062 | ||||
| (0.6554) | (0.6102) | |||||
| Animal Food Consumption | −1.4015 * | −2.1653 ** | ||||
| (0.7540) | (0.9616) | |||||
| Transport Infrastructure | 0.2030 ** | 0.1498 * | 0.2358 ** | 0.1935 ** | 0.1870 ** | 0.2360 ** |
| (0.0836) | (0.0871) | (0.0904) | (0.0875) | (0.0894) | (0.0915) | |
| Degree of Opening Up | −0.6917 ** | −0.8728 *** | −0.6964 *** | −0.8312 *** | −0.8453 *** | −0.6334 ** |
| (0.2650) | (0.2444) | (0.2540) | (0.2751) | (0.2737) | (0.2597) | |
| Industrial Structure | 3.2872 *** | 1.6216 | 2.5035 ** | 2.7972 ** | 1.7447 | 3.0043 *** |
| (1.1691) | (1.3796) | (1.1909) | (1.3321) | (1.4004) | (1.1162) | |
| Density of Population | 0.1399 *** | 0.1164 *** | 0.0732 ** | 0.1309 *** | 0.0903 ** | 0.0795 ** |
| (0.0400) | (0.0429) | (0.0354) | (0.0480) | (0.0456) | (0.0354) | |
| Per Capita Disposal Income | 0.3195 | 0.1785 | 0.2500 | 0.3787 | 0.2101 | 0.3230 |
| (0.2429) | (0.2339) | (0.2385) | (0.2720) | (0.2550) | (0.2357) | |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | 1.1043 | 4.7476 ** | 3.7221 | 0.9960 | 4.0260 | 2.8797 |
| (2.4355) | (2.3080) | (2.3314) | (2.9474) | (2.4841) | (2.2897) | |
| Observations | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 | 155 |
| F | 5.3232 | 4.6994 | 4.7885 | 4.5773 | 5.3352 | 5.0978 |
| R-squared | 0.3203 | 0.2866 | 0.2846 | 0.2927 | 0.2715 | 0.2951 |
| Variables | Food Security | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Eastern Region | The Central Region | The Western Region | |||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| Grain Consumption | 5.2532 *** | 1.7895 | 1.4885 ** | ||||||
| (0.8311) | (2.2379) | (0.7308) | |||||||
| Plant Food Consumption | 0.8030 | −3.2160 ** | −3.4372 *** | ||||||
| (1.0026) | (1.4403) | (1.0645) | |||||||
| Animal Food Consumption | −5.6761 *** | −9.9319 *** | −0.0311 | ||||||
| (0.8744) | (3.0811) | (1.2915) | |||||||
| Transport Infrastructure | 0.8630 *** | 1.0309 *** | 1.1388 *** | 0.5719 ** | 0.6145 ** | 0.8200 *** | −0.2610 *** | −0.4038*** | −0.2766 ** |
| (0.1166) | (0.1616) | (0.1087) | (0.2696) | (0.2769) | (0.2881) | (0.0787) | (0.0793) | (0.1114) | |
| Degree of Opening Up | 0.0892 | −0.1998 | 0.3911 ** | −1.5214 | −1.8134 ** | −2.9642 *** | 2.0351 ** | 1.7273 * | 2.5015 ** |
| (0.1514) | (0.1647) | (0.1885) | (0.9668) | (0.8825) | (0.8259) | (0.9928) | (0.9753) | (1.0949) | |
| Industrial Structure | −2.4575 *** | −5.8037 *** | −2.5312 *** | 6.5548 *** | 6.1533 *** | 2.8425 ** | 5.6254 *** | 6.2891 *** | 4.0821 *** |
| (0.7927) | (0.8429) | (0.8439) | (1.5080) | (1.1773) | (1.2657) | (1.1146) | (1.1472) | (0.9467) | |
| Density of Population | −0.4122 *** | −0.6353 *** | −0.7241 *** | −0.0863 | −0.1265 | −0.5027** | 0.1603 *** | 0.2419 *** | 0.1126 *** |
| (0.1087) | (0.1719) | (0.1118) | (0.1565) | (0.1429) | (0.1915) | (0.0386) | (0.0543) | (0.0329) | |
| Per Capita Disposal Income | −0.6473 *** | −1.0299 *** | −0.8148 *** | 0.2149 | −0.3887 | −4.6538 *** | 0.5696 | 1.2364 * | −0.2075 |
| (0.1815) | (0.1994) | (0.1445) | (1.2371) | (0.8395) | (1.4457) | (0.5773) | (0.7007) | (0.4600) | |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | 12.4995 *** | 20.1570 *** | 19.2140 *** | 3.3087 | 11.4800 | 53.1697 *** | −1.4250 | −6.2823 | 7.2217 |
| (1.9602) | (1.6348) | (1.2345) | (13.7270) | (8.8331) | (14.6461) | (5.9356) | (6.5903) | (4.3367) | |
| Observations | 60 | 60 | 60 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| F | 26.0232 | 27.7174 | 70.8286 | 4.2023 | 4.8764 | 6.5521 | 11.2196 | 10.1654 | 9.4065 |
| R-squared | 0.8460 | 0.7433 | 0.8707 | 0.5214 | 0.5629 | 0.6064 | 0.6786 | 0.7190 | 0.6483 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, W.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Food Consumption Structure and Food Security—Through Mediating Effect Analysis of Agricultural R&D and Agricultural Investment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912524
Bi W, Song Y, Liu Y, Li Z, Zhang Y. Food Consumption Structure and Food Security—Through Mediating Effect Analysis of Agricultural R&D and Agricultural Investment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912524
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Wentai, Yu Song, Yang Liu, Zongze Li, and Ying Zhang. 2022. "Food Consumption Structure and Food Security—Through Mediating Effect Analysis of Agricultural R&D and Agricultural Investment" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912524
APA StyleBi, W., Song, Y., Liu, Y., Li, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Food Consumption Structure and Food Security—Through Mediating Effect Analysis of Agricultural R&D and Agricultural Investment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912524






