Impact of Impulsivity, Hyperactivity, and Inattention on Discontinuation Rate among Opioid-Dependent Patients Treated with Extended-Release Naltrexone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting and Patients
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Main Outcome
2.2.2. IHI
2.2.3. Mental Health
2.3. Statistical Analysis
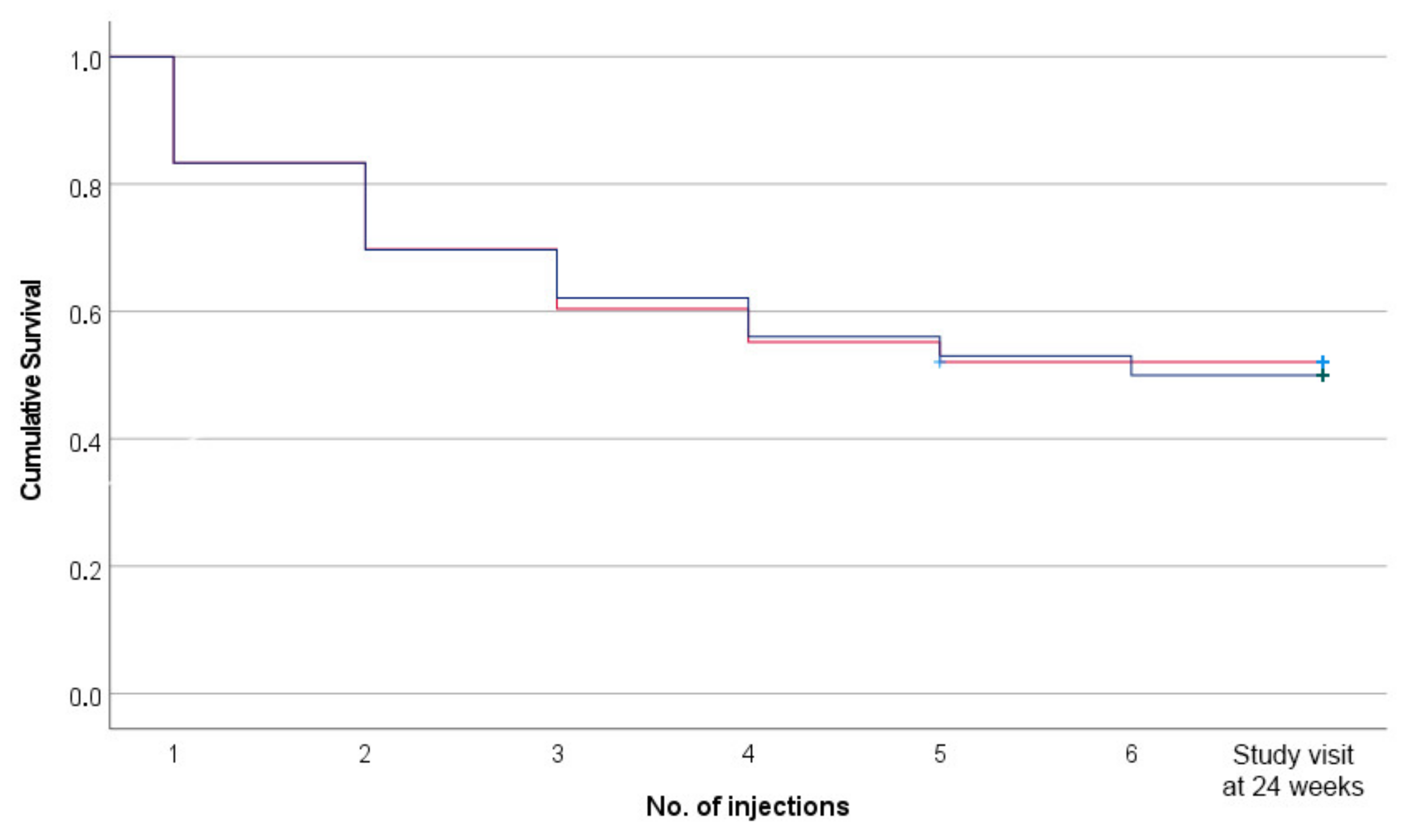
3. Results
4. Discussion
Methodological Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kosten, T.R.; George, T.P. The neurobiology of opioid dependence: Implications for treatment. Sci. Pract. Perspect 2002, 1, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, B.E.; Zheng, X.; Frank, C.A.; Petrakis, I.; Springer, S.A. A Literature Review Examining Primary Outcomes of Medication Treatment Studies for Opioid Use Disorder: What Outcome Should Be Used to Measure Opioid Treatment Success? Am. J. Addict./Am. Acad. Psychiatr. Alcohol. Addict. 2020, 29, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coe, M.A.; Lofwall, M.R.; Walsh, S.L. Buprenorphine Pharmacology Review: Update on Transmucosal and Long-acting Formulations. J. Addict. Med. 2019, 13, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanum, L.; Solli, K.K.; Latif, Z.E.; Benth, J.S.; Opheim, A.; Sharma-Haase, K.; Krajci, P.; Kunoe, N. Effectiveness of Injectable Extended-Release Naltrexone vs Daily Buprenorphine-Naloxone for Opioid Dependence: A Randomized Clinical Noninferiority Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, Y.Y.; Keating, G.M. Extended-release intramuscular naltrexone (VIVITROL(R)): A review of its use in the prevention of relapse to opioid dependence in detoxified patients. CNS Drugs 2013, 27, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, B.A.; De Jong, C.A.; Bluschke, S.M.; Krabbe, P.F.; van der Staak, C.P. Does naltrexone affect craving in abstinent opioid-dependent patients? Addict. Biol. 2007, 12, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenna, I.H.; Marciuch, A.; Birkeland, B.; Veseth, M.; Rostad, B.; Loberg, E.M.; Solli, K.K.; Tanum, L.; Weimand, B. ‘Not at all what I had expected’: Discontinuing treatment with extended-release naltrexone (XR-NTX): A qualitative study. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2022, 136, 108667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.R.; Schackman, B.R.; Weinstein, Z.M.; Walley, A.Y.; Linas, B.P. Overdose following initiation of naltrexone and buprenorphine medication treatment for opioid use disorder in a United States commercially insured cohort. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 200, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solli, K.K.; Kunoe, N.; Latif, Z.E.; Sharma-Haase, K.; Opheim, A.; Krajci, P.; Gaulen, Z.; Saltyte Benth, J.; Tanum, L. Availability of Extended-Release Naltrexone May Increase the Number of Opioid-Dependent Individuals in Treatment: Extension of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Eur. Addict. Res. 2019, 25, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brorson, H.H.; Ajo Arnevik, E.; Rand-Hendriksen, K.; Duckert, F. Drop-out from addiction treatment: A systematic review of risk factors. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2013, 33, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, A.T.; Vederhus, J.K.; Clausen, T.; Weimand, B.; Solli, K.K.; Tanum, L. Levels of Impulsivity, Hyperactivity, and Inattention and the Association with Mental Health and Substance Use Severity in Opioid-Dependent Patients Seeking Treatment with Extended-Release Naltrexone. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimand, B.M.; Solli, K.K.; Reichelt, W.H.; Tanum, L. Enablers and hindrances for longer-term abstinence in opioid dependent individuals receiving treatment with extended-release naltrexone: A Norwegian longitudinal recovery trial (NaltRec study). Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2021, 21, 100728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical, A. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric, A. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; Adler, L.; Ames, M.; Demler, O.; Faraone, S.; Hiripi, E.; Howes, M.J.; Jin, R.; Scnik, K.; Spencer, T.; et al. The World Health Organization adult ADHD self-report scale (ASRS): A short screening scale for use in the general population. Psychol. Med. 2005, 35, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, B.H.; Dalgard, O.S.; Tambs, K.; Rognerud, M. Measuring the mental health status of the Norwegian population: A comparison of the instruments SCL-25, SCL-10, SCL-5 and MHI-5 (SF-36). Nord. J. Psychiatry 2003, 57, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkevi, A.; Hartgers, C. EuropASI: European Adaptation of a Multidimensional Assessment Instrument for Drug and Alcohol Dependence. Eur. Addict. Res. 1995, 1, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, B.P.; Holtyn, A.F.; Subramaniam, S.; Tompkins, D.A.; Oga, E.A.; Bigelow, G.E.; Silverman, K. Extended-release injectable naltrexone for opioid use disorder: A systematic review. Addiction 2018, 113, 1188–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.R.; Schackman, B.R.; Leff, J.A.; Linas, B.P.; Walley, A.Y. Injectable naltrexone, oral naltrexone, and buprenorphine utilization and discontinuation among individuals treated for opioid use disorder in a United States commercially insured population. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2018, 85, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tossone, K.; Ashmead, R.; Bickert, T.; Bailey, E.; Doogan, N.J.; Mack, A.; Schmidt, S.; Bonny, A.E. Examining differences in retention on medication for opioid use disorder: An analysis of Ohio Medicaid data. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2022, 136, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmon, S.C.; Bisaga, A.; Nunes, E.V.; O’Connor, P.G.; Kosten, T.; Woody, G. Opioid detoxification and naltrexone induction strategies: Recommendations for clinical practice. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2012, 38, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, P.; Greco, P.; Meyers-Ohki, S.; Desai, A.; Rotrosen, J. Patients’ perspectives on initiating treatment with extended-release naltrexone (XR-NTX). J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2021, 122, 108183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukten, A.; Skurtveit, S.; Waal, H.; Clausen, T. Factors associated with dropout among patients in opioid maintenance treatment (OMT) and predictors of re-entry. A national registry-based study. Addict. Behav. 2014, 39, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.R.; Barbieri, V.; Mishlen, K.; Levin, F.R.; Nunes, E.V.; Mariani, J.J.; Bisaga, A. Long-term follow-up study of community-based patients receiving XR-NTX for opioid use disorders. Am. J. Addict./Am. Acad. Psychiatr. Alcohol. Addict. 2017, 26, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.E.; Bjornestad, R.; Clausen, T. Dissatisfaction with opioid maintenance treatment partly explains reported side effects of medications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018, 187, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, A.T.; Lewis, D.C.; O’Brien, C.P.; Kleber, H.D. Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: Implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA 2000, 284, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | ASRS < 9 | ASRS ≥ 9 (n = 66) | Total (n = 162) |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 96 | n = 66 | n = 162 | |
| Female gender | 21 (22%) | 18 (27%) | 39 (24%) |
| Age, years | 38 (10) | 37 (10) | 38 (10) |
| Unstable living conditions past 6 months | 11 (11%) | 7 (11%) | 18 (11%) |
| Years of completed education | 12.2 (2.5) | 11.4 (2.5) | 11.9 (2.5) |
| Not in OMT before enrollment in study | 41 (43%) | 20 (30%) | 61 (38%) |
| Severity variables at baseline: | |||
| Alcohol use | 0.04 (0.06) | 0.08 (0.12) | 0.06 (0.09) |
| Drug use | 0.31 (0.16) | 0.35 (0.19) | 0.33 (0.17) |
| Mental distress (H-SCL-25 GSI) | 1.79 (0.49) | 2.16 (0.65) | 1.94 (0.58) |
| Variable | Β | HR | CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASRS > cut-off | −0.14 | 0.87 | 0.53–1.45 | 0.594 |
| Gender | 0.34 | 1.40 | 0.86–2.29 | 0.179 |
| Age | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.98–1.02 | 0.955 |
| Years of education | −0.06 | 0.94 | 0.85–1.05 | 0.267 |
| Living conditions past 6 months | 0.41 | 1.50 | 0.77–2.92 | 0.228 |
| In OMT prior to study inclusion | 0.33 | 1.39 | 0.82–2.36 | 0.219 |
| Baseline severity alcohol use | −1.50 | 0.22 | 0.01–4.12 | 0.314 |
| Baseline severity drug use | −0.34 | 0.71 | 0.17–3.01 | 0.646 |
| Baseline SCL-GSI | 0.30 | 1.35 | 0.88–2.06 | 0.165 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karlsson, A.T.; Vederhus, J.-K.; Clausen, T.; Weimand, B.; Solli, K.K.; Tanum, L. Impact of Impulsivity, Hyperactivity, and Inattention on Discontinuation Rate among Opioid-Dependent Patients Treated with Extended-Release Naltrexone. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811435
Karlsson AT, Vederhus J-K, Clausen T, Weimand B, Solli KK, Tanum L. Impact of Impulsivity, Hyperactivity, and Inattention on Discontinuation Rate among Opioid-Dependent Patients Treated with Extended-Release Naltrexone. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(18):11435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811435
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarlsson, Ann Tarja, John-Kåre Vederhus, Thomas Clausen, Bente Weimand, Kristin Klemmetsby Solli, and Lars Tanum. 2022. "Impact of Impulsivity, Hyperactivity, and Inattention on Discontinuation Rate among Opioid-Dependent Patients Treated with Extended-Release Naltrexone" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 18: 11435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811435
APA StyleKarlsson, A. T., Vederhus, J.-K., Clausen, T., Weimand, B., Solli, K. K., & Tanum, L. (2022). Impact of Impulsivity, Hyperactivity, and Inattention on Discontinuation Rate among Opioid-Dependent Patients Treated with Extended-Release Naltrexone. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(18), 11435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811435





