Humic Acids Affect the Detection of Metal Ions by Cyanobacteria Carbon Quantum Dots Differently
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of the CQDs
2.3. Stability and pH-Dependent FL Intensity of the CQDs
2.4. Selectivity of the CQDs to Different Metal Ions
2.5. Effects of HAs on the FL Intensity of CQDs and the Metal Ions Detection
2.6. Characterization of the CQDs
3. Results and Discussion
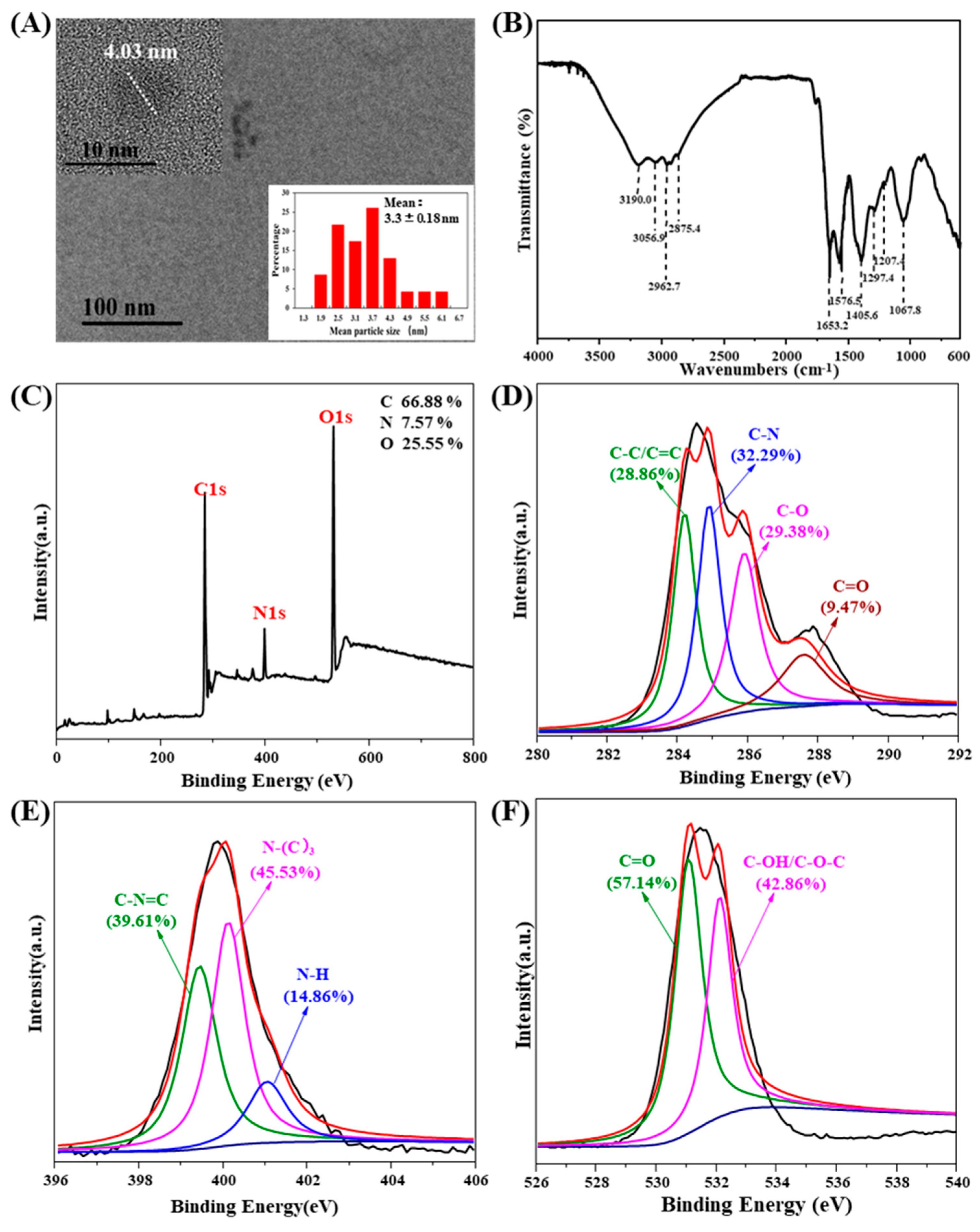
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of the Cyanobacteria CQDs
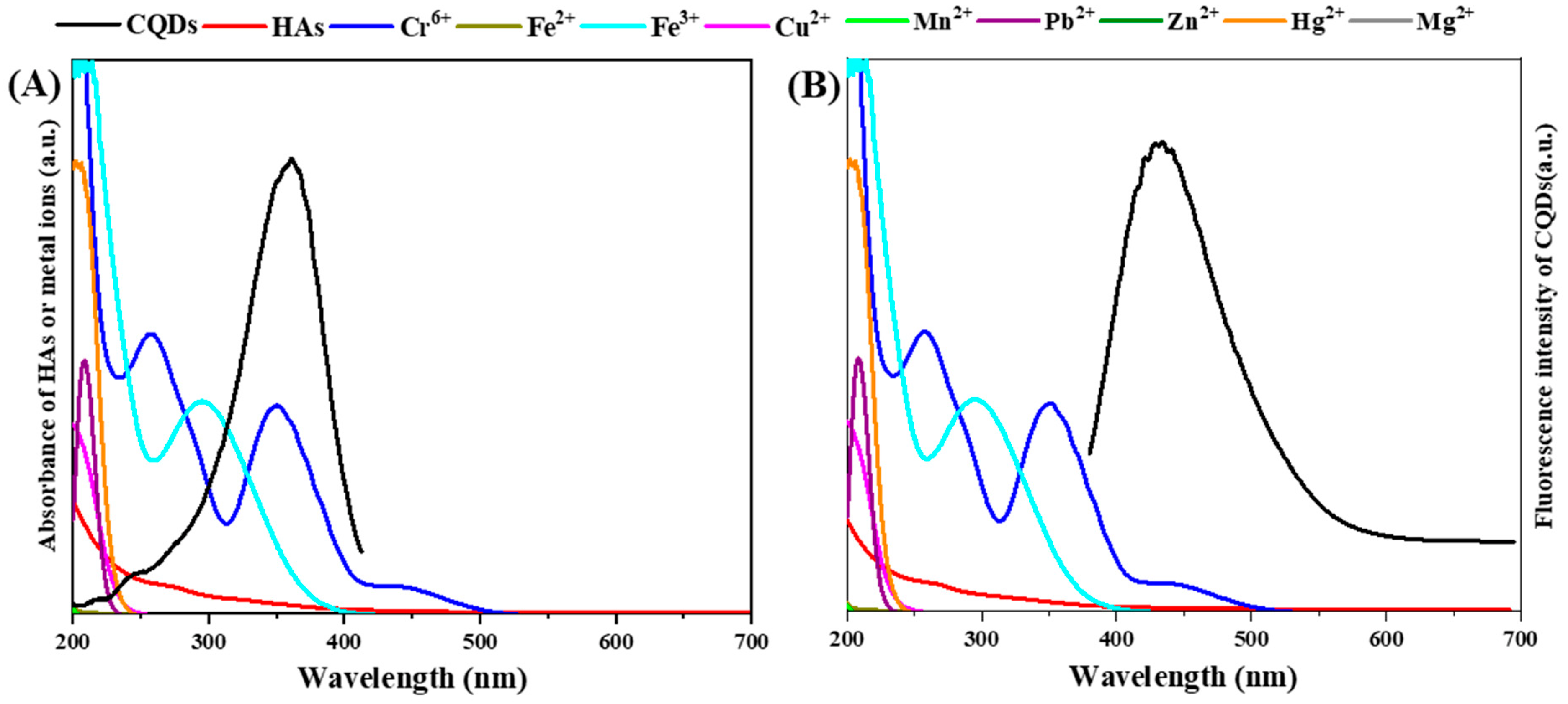
3.2. FL Quenching of the CQDs by Different Metal Ions and HAs
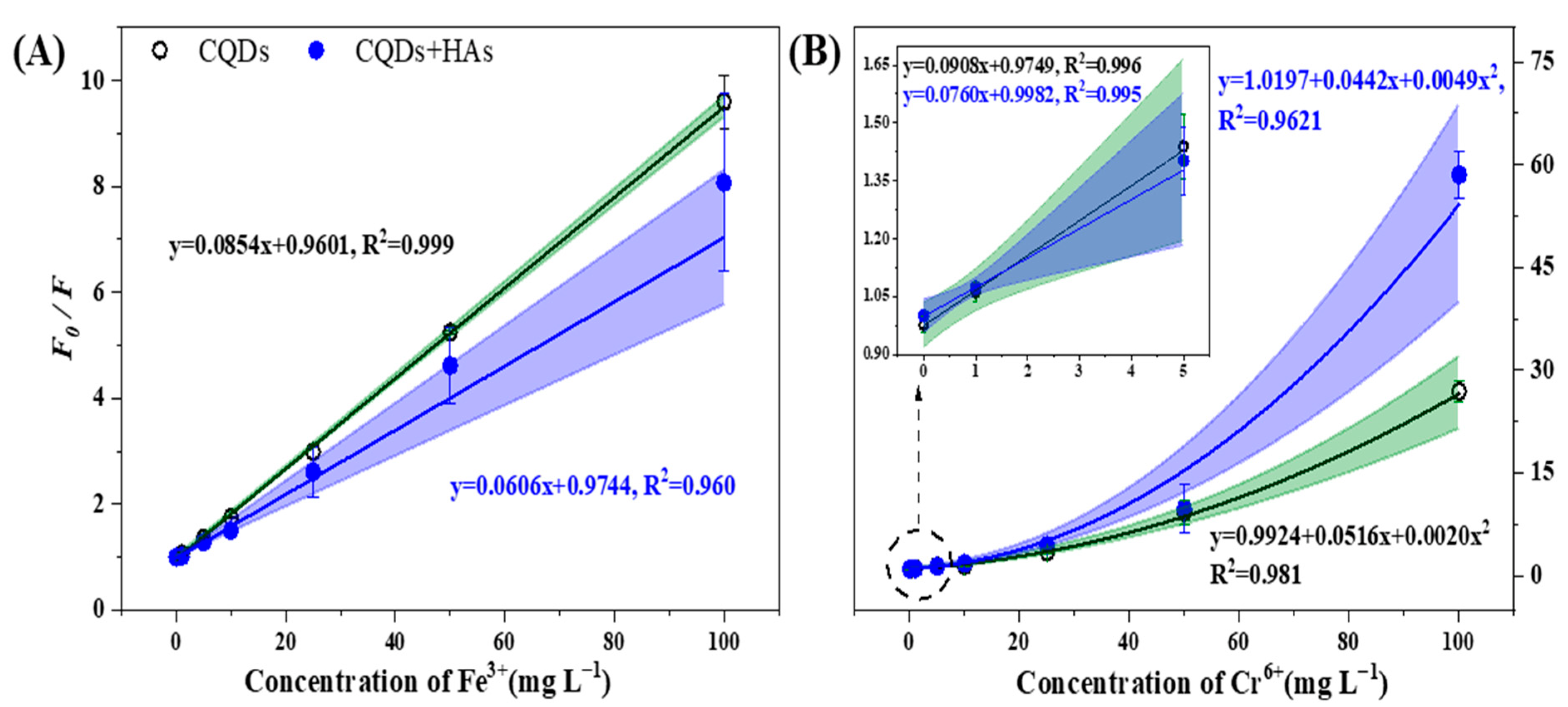
3.3. Detection of Fe3+ and Cr6+ by CQDs and the Effects of Coexisted HAs
3.4. The Mechanisms That HAs Interfered with the Detection of Fe3+ and Cr6+ Ions Using CQDs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, T.; Gooding, J.J.; Liu, J. Review of carbon and graphene quantum dots for sensing. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1732–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Su, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wong, W.-K. Near-infrared emissive lanthanide hybridized carbon quantum dots for bioimaging applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6366–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naan, A.; Nha, A.; Yl, B.; Aaab, A. Carbon quantum dots for optical sensor applications: A review. Opt Laser Technol. 2021, 139, 106928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Saini, S.; Kim, K.-H. The advanced role of carbon quantum dots in nanomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uar, A.; Lyn, A.; Cyn, B.; Em, C. A review of carbon quantum dots and their applications in wastewater treatment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 278, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Yang, C.-H. Food waste as a carbon source in carbon quantum dots technology and their applications in food safety detection. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alas, M.O.; Alkas, F.B.; Sukuroglu, A.A.; Alturk, R.G.; Battal, D. Fluorescent carbon dots are the new quantum dots: An overview of their potential in emerging technologies and nanosafety. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 15074–15105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Feng, Q.; Meng, T.; Wei, J.; Xu, C.; Han, J. Green preparation of fluorescent carbon quantum dots from cyanobacteria for biological imaging. Polymers 2019, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, Y.; Chang, H.; Won, S.; Kim, H.; Kwon, W. Biocompatible nitrogen-doped carbon dots: Synthesis, characterization, and application. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 8935–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, J.J.; McCarthy, M.J.; Gardner, W.S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Zhu, G.; Newell, S.E. Nitrification and ammonium dynamics in Taihu Lake, China: Seasonal competition for ammonium between nitrifiers and cyanobacteria. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, B.; Fan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Xu, S.; Luo, X. Nitrogen doped carbon dots: Mechanism investigation and their application for label free CA125 analysis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3053–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guan, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, W.; Shao, X.; Xue, Q.; Yue, Q. Fluorescence and photocatalytic activity of metal-free nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots with varying nitrogen contents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 531, 147344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Ma, Y.; Gunawardena, J.M.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Heavy metals transport pathways: The importance of atmospheric pollution contributing to stormwater pollution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, R.; Meng, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Ding, F.; Guo, X.; Jin, S.; Teng, Y. Pollution risk assessment based on source apportionment in a groundwater resource area, NE China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 1197–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.J.; Du Preez, H.H.; van Vuren, J. The freshwater river crab, potamonautes warreni, as a bioaccumulative indicator of iron and manganese pollution in two aquatic systems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 41, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanker, A.; Venkateswarlu, B. Chromium: Environmental pollution, health effects and mode of action. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Health; Burlington: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthanarayanan, A.; Wang, X.; Routh, P.; Sana, B.; Lim, S.; Kim, D.-H.; Lim, K.-H.; Li, J.; Chen, P. Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from 3D graphene and their application for Fe3+ sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3021–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, N.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.; Rezania, S.; Radwan, N.; Alam, J. Chromium contamination and effect on environmental health and its remediation: A sustainable approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.; Park, Y.; Cheon, B.; Park, M.-H. Carbon dots as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for metal ion detection. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kaur, S.; Lee, J.; Mehta, A.; Kumar, S.; Kim, K.-H.; Basu, S.; Rawat, M. Highly fluorescent carbon dots derived from Mangifera indica leaves for selective detection of metal ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, T.K.; Mondal, S.; Ghorai, U.K.; Saha, S.K. White light emitting lanthanide based carbon quantum dots as toxic Cr (VI) and pH sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 553, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.-F.; Huang, B.-C.; Qian, C.; Yu, H.-Q. Quantification of humic substances in natural water using nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14092–14099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Hou, Q.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Hou, J.; Ai, S.; Li, X. A simple aptamer-based fluorescent aflatoxin B1 sensor using humic acid as quencher. Talanta 2019, 205, 120131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislenko, V.; Oliynyk, L. Treatment of humic acids with ferric, aluminum, and chromium ions in water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 269, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguta, P.; D’Orazio, V.; Senesi, N.; Sokołowska, Z.; Szewczuk-Karpisz, K. Insight into the interaction mechanism of iron ions with soil humic acids. The effect of the pH and chemical properties of humic acids. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.-M.; Dong, G.-M.; Yang, R.-J.; Li, X.-C.; Chen, Q. Study on fluorescence interaction between humic acid and PAHs based on two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1217, 128428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Li, X.; Lian, F.; Wang, C.; White, J.C.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Nanoscale Iron trioxide catalyzes the synthesis of auxins analogs in artificial humic acids to enhance rice growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Xu, N.; Xu, L.; Chen, S.; Mei, C.; Xu, C. Facile synthesis of phosphorus-nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots from cyanobacteria for bioimaging. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 99, 1926–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Molaei, K.; Molaabasi, F.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Alizadeh, N.; Alipour, M.; Moassess, S. One-step synthesis and characterization of highly luminescent nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots and their application as highly selective and sensitive nanoprobes for low level detection of uranyl ion in hair and water samples and application to cellular imaging. Sens. Actuators Chem. 2018, 257, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, N.; Kim, J. Synthesis of carbon quantum dots from Broccoli and their ability to detect silver ions. Mater. Lett. 2018, 219, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-L.; Ou, C.-M.; Huang, C.-C.; Wu, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Lin, T.-E.; Ho, L.-C.; Wang, C.-W.; Shih, C.-C.; Zhou, H.-C.; et al. Carbon dots prepared from ginger exhibiting efficient inhibition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4564–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, W.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, W.; Wu, M. Graphene structure boosts electron transfer of dual-metal doped carbon dots in photooxidation. Carbon 2018, 126, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoolphak, W.; Goto, M.; Sasaki, M.; Suphantharika, M.; Muangnapoh, C.; Prommuag, C.; Shotipruk, A. Hydrothermal decomposition of yeast cells for production of proteins and amino acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Bao, Q.; Wu, C.; Hu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Carbon dots derived from Poria cocos polysaccharide as an effective “on-off” fluorescence sensor for chromium (VI) detection. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zheng, M.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, B.-D.; Tian, Z.-F.; He, X.-S. Bioreduction of hexavalent chromium: Effect of compost-derived humic acids and hematite. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2693–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Tong, L.; Lin, X.; Zhu, J.; Tong, Q. High quantum yield nitrogen-doped carbon dots: Green synthesis and application as “off-on” fluorescent sensors for the determination of Fe3+ and adenosine triphosphate in biological samples. Sensors Actuators B-Chem. 2018, 276, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Zhou, J.; Feng, H.; Tang, C.; Huang, Y.; Qian, Z. Functionalized carbon quantum dots with dopamine for tyrosinase activity monitoring and inhibitor screening: In vitro and intracellular investigation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23564–23574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, P.; Wood, P.J.; Reid, I. The impairment of river systems by metal mine contamination: A review including remediation options. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 2017–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, R.; Tang, D.; Hou, X.; Wu, P. Optically-active nanocrystals for inner filter effect-based fluorescence sensing: Achieving better spectral overlap. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashimi, B.; Omer, K.M.; Rahman, H.S. Inner filter effect (IFE) as a simple and selective sensing platform for detection of tetracycline using milk-based nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots as fluorescence probe. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5151–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neema, P.; Tomy, A.M.; Cyriac, J. Chemical sensor platforms based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and 2D materials. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Han, S.; Kang, A.; Deng, H.; Chi, Y.; Zhu, D.; Lu, Y. FÖrster resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based biosensors for biological applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 138, 111314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Aseer, K.R.; Perumal, S.; Lee, Y.R. Hydrothermal conversion of Magnolia liliiflora into nitrogen-doped carbon dots as an effective turn-off fluorescence sensing, multi-colour cell imaging and fluorescent ink. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 169, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfajri, M.; Liu, K.-C.; Pu, Y.-H.; Rasool, A.; Dayalan, S.; Huang, G.G. Utilization of carbon dots derived from volvariella volvacea mushroom for a highly sensitive detection of Fe3+ and Pb2+ ions in aqueous solutions. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, S.; Roy, S.; Chanda, D.K.; Mondal, D.; Das, S.; Das, S. Flexible and reusable carbon dot decorated natural microcline membrane: A futuristic probe for multiple heavy metal induced carcinogen detection. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Kappler, A. Kinetics of microbial and chemical reduction of humic substances: Implications for electron shuttling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3563–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.K.; Weisenhorn, P.B.; Megonigal, J.P. Humic acids as electron acceptors in wetland decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wei, W.; Fu, Z.; Gao, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Deng, F.; Lu, X. Review on carbon dots in food safety applications. Talanta 2019, 194, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Chen, S.; Quan, X.; Zhao, H. Photochemical activity and characterization of the complex of humic acids with iron(III). J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Berti, L.; Medintz, I.L. Materials for fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis: Beyond traditional donor–acceptor combinations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4562–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Humic Acids Affect the Detection of Metal Ions by Cyanobacteria Carbon Quantum Dots Differently. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610225
Liu S, Shi Y, Li X, Wang Z. Humic Acids Affect the Detection of Metal Ions by Cyanobacteria Carbon Quantum Dots Differently. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(16):10225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Simin, Yishen Shi, Xiaona Li, and Zhenyu Wang. 2022. "Humic Acids Affect the Detection of Metal Ions by Cyanobacteria Carbon Quantum Dots Differently" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 16: 10225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610225
APA StyleLiu, S., Shi, Y., Li, X., & Wang, Z. (2022). Humic Acids Affect the Detection of Metal Ions by Cyanobacteria Carbon Quantum Dots Differently. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), 10225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610225





