The Relationship between Attachment Styles and Compulsive Online Shopping: The Mediating Roles of Family Functioning Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants, Procedure, and Ethics
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Compulsive Online Shopping Scale (COSS)
2.2.2. Relationship Questionnaire (RQ)
2.2.3. Family Adaptability and Cohesion Evaluation Scales-IV (FACES IV)
2.3. Data Analysis
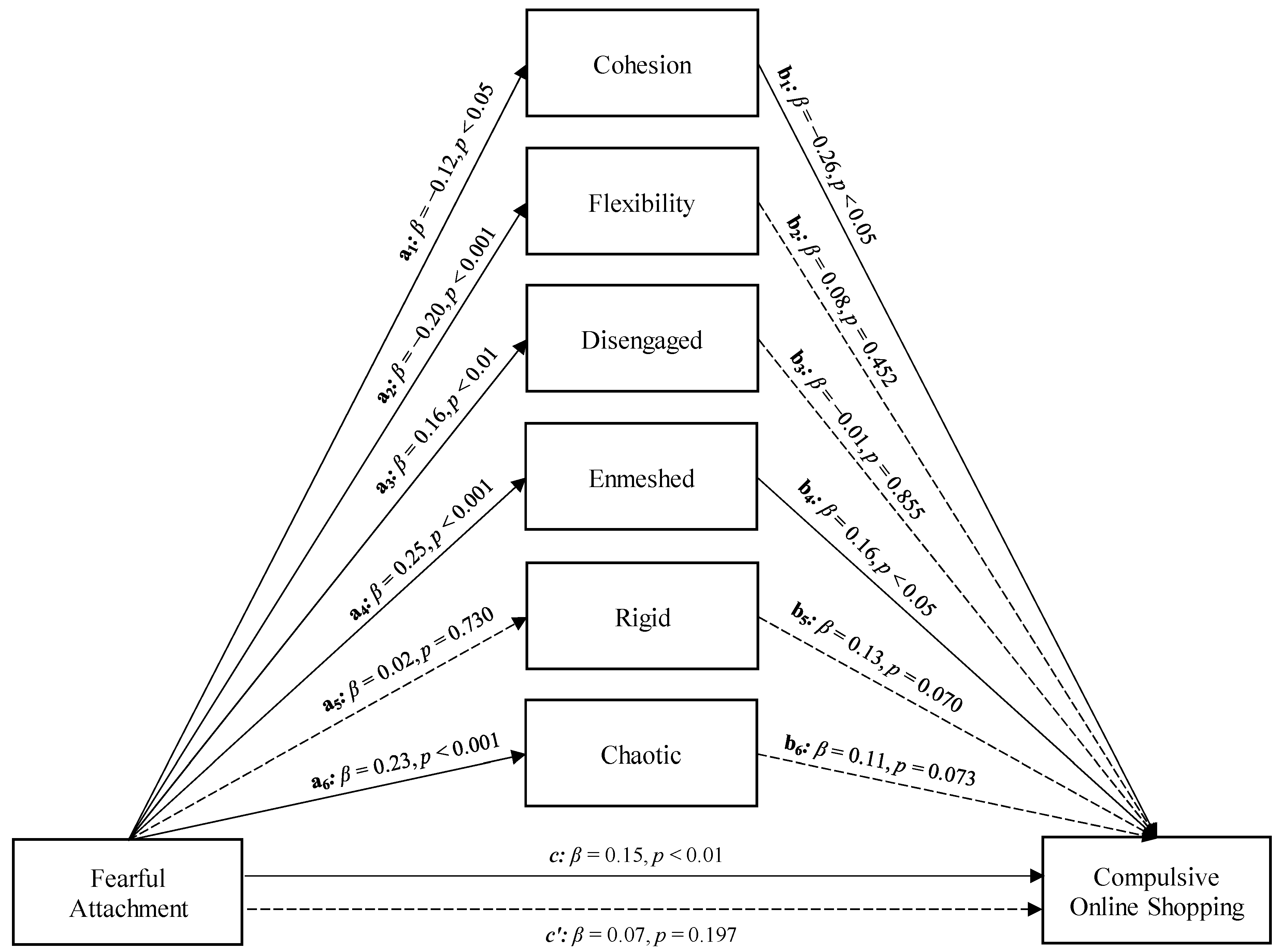
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rose, S.; Dhandayudham, A. Towards an understanding of Internet-based problem shopping behaviour: The concept of online shopping addiction and its proposed predictors. J. Behav. Addict. 2014, 3, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savci, M.; Ugur, E.; Ercengiz, M.; Griffiths, M.D. The development of the Turkish craving for online shopping scale: A validation study. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2021; online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Laskowski, N.M.; Trotzke, P.; Ali, K.; Fassnacht, D.B.; de Zwaan, M.; Brand, M.; Häder, M.; Kyrios, M. Proposed diagnostic criteria for compulsive buying-shopping disorder: A Delphi expert consensus study. J. Behav. Addict. 2021, 10, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchiraju, S.; Sadachar, A.; Ridgway, J.L. The compulsive online shopping scale (COSS): Development and validation using panel data. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2017, 15, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tian, W.; Xin, T. The development and validation of the online shopping addiction scale. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Brand, M.; Mitchell, J.E.; de Zwaan, M. Internet-Shopping Disorder. In The Oxford Handbook of Digital Technologies and Mental Health; Potenza, M.N., Faust, K., Faust, D., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 214–225. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, A.; Laskowski, N.M.; Wegmann, E.; Steins-Loeber, S.; Brand, M. Problematic Online Buying-Shopping: Is it Time to Considering the Concept of an Online Subtype of Compulsive Buying-Shopping Disorder or a Specific Internet-Use Disorder? Curr. Addict. Rep. 2021, 8, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duroy, D.; Gorse, P.; Lejoyeux, M. Characteristics of online compulsive buying in Parisian students. Addict. Behav. 2014, 39, 1827–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.O.; Khoi, N.H.; Tuu, H.H. The “Well-Being” and “Ill-Being” of Online Impulsive and Compulsive Buying on Life Satisfaction: The Role of Self-Esteem and Harmony in Life. J. Macromarketing 2021, 42, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Joshi, M.; Thomas, T.A. Excessive shopping on the internet: Recent trends in compulsive buying-shopping disorder. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2022, 44, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, D.W. Compulsive Shopping: A Review and Update. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2022, 46, 101321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Topino, E.; Casale, S. Assessment of online compulsive buying: Psychometric properties of the Italian Compulsive Online Shopping Scale (COSS). Addict. Behav. 2022, 129, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk, G. Compulsive and compensative buying among online shoppers: An empirical study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, 0252563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-L.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Sun, S.-C. Conceptualizing the Internet Compulsive-Buying Tendency: What We Know and Need to Know in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowlby, J. Attachment and Loss; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1969; volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby, J. A Secure Base: Clinical Applications of Attachment Theory; Routledge: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew, K.; Horowitz, L.M. Attachment styles among young adults: A test of a four-category model. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1991, 61, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, P.J. Addiction as An Attachment Disorder; Jason Aronson: Lanham, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schimmenti, A.; Guglielmucci, F.; Barbasio, C.; Granieri, A. Attachment disorganization and dissociation in virtual worlds: A study on problematic Internet use among players of online role playing games. Clin. Neuropsychiatry 2012, 9, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Gori, A.; Topino, E.; Craparo, G.; Bagnoli, I.; Caretti, V.; Schimmenti, A. A comprehensive model for gambling behaviors: Assessment of the factors that can contribute to the vulnerability and maintenance of gambling disorder. J. Gambl. Stud. 2022, 38, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, A.; Topino, E.; Cacioppo, M.; Craparo, G.; Schimmenti, A.; Caretti, V. An Addictive Disorders Severity model: A chained mediation analysis using structural equation modelling. J. Addict. Dis. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ünübol, B.; Ünsalver, B.Ö.; Ünübol, H.; Sayar, G.H. The prevalence and psychological relation of problem shopping: Data from a large-scale sample from Turkey. BMC Psychol. 2022, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estévez, A.N.A.; Jáuregui, P.; Sánchez-Marcos, I.; López-González, H.; Griffiths, M.D. (2017). Attachment and emotion regulation in substance addictions and behavioral addictions. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Koh, E. Avoidant attachment and smartphone addiction in college students: The 404 mediating effects of anxiety and self-esteem. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 84, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretti, V.; Gori, A.; Craparo, G.; Giannini, M.; Iraci-Sareri, G.; Schimmenti, A. A new measure for assessing substance-related and addictive disorders: The addictive behavior questionnaire (ABQ). J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monacis, L.; de Palo, V.; Griffiths, M.D.; Sinatra, M. Exploring individual differences in online addictions: The role of identity and attachment. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2017, 15, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monacis, L.; de Palo, V.; Griffiths, M.D.; Sinatra, M. Social networking addiction, attachment style, and validation of the Italian version of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. A review of theories and models applied in studies of social media addiction and implications for future research. Addict. Behav. 2021, 114, 106699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakhour, M.; Haddad, C.; Salameh, P.; Akel, M.; Fares, K.; Sacre, H.; Hallit, S.; Obeid, S. Impact of the interaction between alexithymia and the adult attachment styles in participants with alcohol use disorder. Alcohol 2020, 83, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, E.B.; del Río, E.F.; Calafat, A.; Hermida, J.R.F. Attachment and substance use in adolescence: A review of conceptual and methodological aspects. Adicciones 2014, 26, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensink, K.; Fonagy, P.; Normandin, L.; Rozenberg, A.; Marquez, C.; Godbout, N.; Borelli, J.L. Post-traumatic Stress Disorder in Sexually Abused Children: Secure Attachment as a Protective Factor. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 646680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armour, C.; Elklit, A.; Shevlin, M. Attachment typologies and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression and anxiety: A latent profile analysis approach. Eur. J. Psychotraumatol. 2011, 2, 6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, M.F.; Ribeiro, T.; Shelton, K.H. Romantic attachment and family functioning: The mediating role of marital satisfaction. J. Child. Fam. Stud. 2015, 24, 3482–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doba, K.; Nandrino, J.L.; Dodin, V.; Antoine, P. Is there a family profile of addictive behaviors? Family functioning in anorexia nervosa and drug dependence disorder. J. Clin. Psychol. 2014, 70, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafa, M.; Baiocco, R. Addictive behavior and family functioning during adolescence. Am. J. Fam. Ther. 2009, 37, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.H.; Russell, C.S.; Sprenkle, D.H. Circumplex model of marital and family systems: Vl. Theoretical update. Fam. Process. 1983, 22, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahremand, M.; Rai, A.; Alikhani, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Shahebrahimi, K.; Janjani, P. Relationship between family functioning and mental health considering the mediating role of resiliency in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2015, 7, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rodriguez, E.M.; Donenberg, G.R.; Emerson, E.; Wilson, H.W.; Brown, L.K.; Houck, C. Family environment, coping, and mental health in adolescents attending therapeutic day schools. J. Adolesc. 2014, 37, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Huidobro, D.; Puschel, K.; Soto, G. Family functioning style and health: Opportunities for health prevention in primary care. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2012, 62, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fiese, B.; Winter, M.; Anbar, R.A.N.; Howell, K.; Poltrock, S. Family climate of routine asthma care: Associating perceived burden and mother-child interaction patterns to child well-being. Fam. Process. 2008, 47, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armour, T.A.; Norris, S.L.; Jack, L., Jr.; Zhang, X.; Fisher, L. The effectiveness of family interventions in people with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, C.; Clare, L.; Woods, B. The impact of the quality of relationship on the experiences and wellbeing of caregivers of people with dementia: A systematic review. Aging Ment. Health 2009, 13, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, N.K.; Salafia, C.; Ohannessian, C.M. Family Functioning and Anxiety Symptoms in Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Mindfulness. J. Child. Fam. Stud. 2022, 31, 1474–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; He, P.; Ling, B.; Tan, L.; Xu, L.; Hou, Y.; Kong, L.; Yang, Y. Prevalence of depression and anxiety and correlations between depression, anxiety, family functioning, social support and coping styles among Chinese medical students. BMC Psychol. 2020, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinbor, M.; Bakhshani, N.M.; Shakiba, M. Family functioning of addicted and non-addicted individuals: A comparative study. Int. J. High Risk Behav. Addict. 2012, 1, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, K.E.; Eiden, R.D. Marital and family processes in the context of alcohol use and alcohol disorders. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2007, 3, 285–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleczka, P.; Braun, B.; Grüne, B.; Bühringer, G.; Kraus, L. Family functioning and gambling problems in young adulthood: The role of the concordance of values. Addict. Res. Theory 2018, 26, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimeno, M.V.; Ricarte, J.J.; Toledano, A.; Mangialavori, S.; Cacioppo, M.; Ros, L. Role of Attachment and Family Functioning in Problematic Smartphone Use in Young Adults. J. Fam. Issues 2022, 43, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, M.; Barni, D.; Correale, C.; Mangialavori, S.; Danioni, F.; Gori, A. Do attachment styles and family functioning predict adolescents’ problematic internet use? A relative weight analysis. J. Child. Fam. Stud. 2019, 28, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Nayak, J.K. Effect of family environment on adolescent compulsive buying: Mediating role of self-esteem. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2016, 28, 396–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zeng, X. Effects of family functioning on relapse among individuals with drug addiction in compulsory isolation: A chained mediation model. Curr. Psychol. 2021; online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Tan, C. The Relationship between the Family Functioning of Individuals with Drug Addiction and Relapse Tendency: A Moderated Mediation Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, L. Attaccamento e Rapporto di Coppia; Carli, L., Ed.; Raffaello Cortina: Milano, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ligiéro, D.P.; Gelso, C.J. Countertransference, attachment, and the working alliance: The therapist’s contribution. Psychol. Psychother. Theory Res. Pract. 2002, 39, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.P.; Alcalay, L.; Allensworth, M.; Allik, J.; Ault, L.; Austers, I.; Bennett, K.; Bianchi, G.; Boholst, F.; Cunen, M.A.B. Patterns and universals of adult romantic attachment across 62 cultural regions: Are models of self and of other pancultural constructs? J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 2004, 35, 367–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongpakaran, N.; DeMaranville, J.; Wongpakaran, T. Validation of the Relationships Questionnaire (RQ) against the Experience of Close Relationship-Revised Questionnaire in a Clinical Psychiatric Sample. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmenti, A.; Sideli, L.; La Marca, L.; Gori, A.; Terrone, G. Reliability, validity, and factor structure of the maladaptive daydreaming scale (MDS–16) in an Italian sample. J. Pers. Assess. 2022, 102, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D. FACES IV and the circumplex model: Validation study. J. Marital. Fam. Ther. 2011, 37, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiocco, R.; Cacioppo, M.; Laghi, F.; Tafà, M. Factorial and construct validity of FACES IV among Italian adolescents. J. Child. Fam. Stud. 2013, 22, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis Second Edition: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Niedermoser, D.W.; Petitjean, S.; Schweinfurth, N.; Wirz, L.; Ankli, V.; Schilling, H.; Zueger, C.; Meyer, M.; Poespodihardjo, R.; Wiesbeck, G.; et al. Shopping addiction: A brief review. Pract. Innov. 2021, 6, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling Rasmussen, P.; Storebø, O.J.; Løkkeholt, T.; Voss, L.G.; Shmueli-Goetz, Y.; Bojesen, A.B.; Simonsen, E.; Bilenberg, N. Attachment as a core feature of resilience: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Rep. 2019, 122, 1259–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karreman, A.; Vingerhoets, A.J. Attachment and well-being: The mediating role of emotion regulation and resilience. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2012, 53, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, M.; Gori, A.; De Sanctis, E.; Schuldberg, D. Attachment in psychotherapy: Psychometric properties of the Psychological Treatment Inventory Attachment Styles Scale (PTI-ASS). J. Psychother. Integr. 2011, 21, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.J.; LaVoie, J.C.; Mahoney, M. Interparental conflict and family cohesion: Predictors of loneliness, social anxiety and social avoidance in late adolescence. J. Adolesc. Res. 2001, 16, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.L.; Stavropoulos, V.; Burleigh, T.L.; Liew, L.W.; Beard, C.L.; Griffiths, M.D. Internet gaming disorder behaviors in emergent adulthood: A pilot study examining the interplay between anxiety and family cohesion. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2019, 17, 828–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solloski, K.L.; Monk, J.K.; Durtschi, J.A. Trajectories of early binge drinking: A function of family cohesion and peer use. J. Fam. Ther. 2015, 42, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topino, E.; Gori, A.; Cacioppo, M. Alexithymia, dissociation, and family functioning in a sample of online gamblers: A moderated mediation study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.; Russell, C.S.; Sprenkle, D.H. Circumplex Model: Systemic Assessment and Treatment of Families; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Berryhill, M.B.; Hayes, A.; Lloyd, K. Chaotic-enmeshment and anxiety: The mediating role of psychological flexibility and self-compassion. Contemp. Fam. Ther. 2018, 40, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Jonason, P.; Denes, A.; Emirtekin, E.; Tosuntaş, Ş.B.; Kircaburun, K.; Griffiths, M.D. Dark personality traits and problematic smartphone use: The mediating role of fearful attachment. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2019, 149, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyderman, I.; Young, M.A. Rumination and overgeneral autobiographical memory as mediators of the relationship between attachment and depression. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2016, 98, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifulco, A.; Kwon, J.; Jacobs, C.; Moran, P.M.; Bunn, A.; Beer, N. Adult attachment style as mediator between childhood neglect/abuse and adult depression and anxiety. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2006, 41, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khantzian, E.J. The self-medication hypothesis of addictive disorders: Focus on heroin and cocaine dependence. In The Cocaine Crisis; Allen, D.F., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Khantzian, E.J. The self-medication hypothesis of substance use disorders: A reconsideration and recent applications. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 1997, 4, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khantzian, E.J. Addiction as a self-regulation disorder and the role of self-medication. Addiction 2013, 108, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, R.; Niu, G.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z. Upward social comparison and state anxiety as mediators between passive social network site usage and online compulsive buying among women. Addict. Behav. 2020, 111, 106569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, C.; Grossman, H. Predictors of online compulsive buying: The role of personality and mindfulness. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2022, 185, 111237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Chu, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, Z. Perceived stress and online compulsive buying among women: A moderated mediation model. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 103, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, C.; Randler, C.; Horzum, M.B.; Ayas, T. Computer game addiction in adolescents and its relationship to chronotype and personality. Sage Open 2014, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markellos, K.; Markellou, P.; Rigou, M.; Sirmakessis, S.; Tsakalidis, A. Who is today’s e-customer? A description of his behavioral model. In Proceedings of the eBusiness and eWork 2002 Conference and Exhibition, Prague, Czech Republic, 16–18 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.K.; Singh, S.; Gupta, R. Biomedical Statistics; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bodor, D.; Ricijaš, N.; Filipcic, I. Treatment of gambling disorder: Review of evidence-based aspects for best practice. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry. 2021, 34, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berczik, K.; Szabó, A.; Griffiths, M.D.; Kurimay, T.; Kun, B.; Urbán, R.; Demetrovics, Z. Exercise addiction: Symptoms, diagnosis, epidemiology, and etiology. Subst. Use Misuse 2012, 47, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, A.; Topino, E.; Griffiths, M.D. Protective and risk factors in exercise addiction: A series of moderated mediation analyses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Topino, E.; Pucci, C.; Griffiths, M.D. The relationship between alexithymia, dysmorphic concern, and exercise addiction: The moderating effect of self-esteem. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musetti, A.; Gori, A.; Alessandra, A.; Topino, E.; Terrone, G.; Plazzi, G.; Cacioppo, M.; Franceschini, C. The Interplay Between Problematic Online Pornography Use, Psychological Stress, Emotion Dysregulation and Insomnia Symptoms During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mediation Analysis. Nat. Sci Sleep 2022, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, K.; Nutton, J.; Brend, D. Attachment, a matter of substance: The potential of attachment theory in the treatment of addictions. Clin. Soc. Work. J. 2015, 43, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharudin, D.F.; Mohd Hussin, A.H.; Sumari, M.; Mohamed, S.; Zakaria, M.Z.; Sawai, R.P. Family intervention for the treatment and rehabilitation of drug addiction: An exploratory study. J. Subst. Use 2014, 19, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | M ± SD | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 31.86 ± 11.925 | |||
| Gender | ||||
| Females | 234 | 76 | ||
| Males | 72 | 24 | ||
| Marital Status | ||||
| Single | 202 | 66 | ||
| Married | 55 | 18 | ||
| Cohabiting | 36 | 12 | ||
| Separated | 2 | 1 | ||
| Divorced | 10 | 3 | ||
| Widowed | 1 | 0 | ||
| Education | ||||
| Middle School diploma | 9 | 3 | ||
| High School diploma | 92 | 30 | ||
| University degree | 139 | 45 | ||
| Master’s degree | 50 | 16 | ||
| Post-lauream specialization | 16 | 5 | ||
| Occupation | ||||
| Student | 120 | 39 | ||
| Working student | 37 | 12 | ||
| Employee | 88 | 29 | ||
| Freelance | 21 | 7 | ||
| Manager | 2 | 1 | ||
| Entrepreneur | 5 | 2 | ||
| Trader | 6 | 2 | ||
| Artisan | 3 | 1 | ||
| Unemployed | 17 | 6 | ||
| Retired | 7 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. COSS | 1 | ||||||||||
| 2. RQ (1) | −0.172 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| 3. RQ (2) | 0.094 | −0.292 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| 4. RQ (3) | 0.155 ** | −0.169 ** | 0.258 ** | 1 | |||||||
| 5. RQ (4) | 0.052 | −0.236 ** | 0.088 | 0.01 | 1 | ||||||
| 6. FACES-IV (1) | −0.199 ** | 0.258 ** | −0.034 | −0.118 * | 0.042 | 1 | |||||
| 7. FACES-IV (2) | −0.134 * | 0.193 ** | −0.104 | −0.197 ** | 0.115 * | 0.817 ** | 1 | ||||
| 8. FACES-IV (3) | 0.216 ** | −0.157 ** | 0.196 ** | 0.161 ** | 0.178 ** | −0.390 ** | −0.224 ** | 1 | |||
| 9. FACES-IV (4) | 0.295 ** | −0.173 ** | 0.139 * | 0.250 ** | 0.006 | −0.062 | −0.106 | 0.289 ** | 1 | ||
| 10. FACES-IV (5) | 0.235 ** | −0.035 | 0.110 | 0.020 | 0.025 | 0.021 | 0.207 ** | 0.342 ** | 0.485 ** | 1 | |
| 11. FACES-IV (6) | 0.215 ** | −0.132 * | 0.276 ** | 0.227 ** | 0.076 | 0.033 | −0.010 | 0.384 ** | 0.448 ** | 0.188 ** | 1 |
| Independent Variable | Parallel Mediators | Dependent Variable | Total Effect | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect [Bootstrapping 95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secure Attachment | Family Functionings | Compulsive Online Shopping | −0.071 | −0.032 | −0.039 [−0.0649; −0.0172] |
| Preoccupied Attachment | Family Functionings | Compulsive Online Shopping | 0.042 | 0.010 | −0.031 [−0.0325; 0.0538] |
| Fearful Attachment | Family Functionings | Compulsive Online Shopping | 0.078 | 0.037 | 0.041 [0.0138; 0.0742] |
| Dismissing Attachment | Family Functionings | Compulsive Online Shopping | 0.024 | 0.061 | 0.002 [−0.0203; 0.0277] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Topino, E.; Cacioppo, M.; Gori, A. The Relationship between Attachment Styles and Compulsive Online Shopping: The Mediating Roles of Family Functioning Patterns. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19138162
Topino E, Cacioppo M, Gori A. The Relationship between Attachment Styles and Compulsive Online Shopping: The Mediating Roles of Family Functioning Patterns. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(13):8162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19138162
Chicago/Turabian StyleTopino, Eleonora, Marco Cacioppo, and Alessio Gori. 2022. "The Relationship between Attachment Styles and Compulsive Online Shopping: The Mediating Roles of Family Functioning Patterns" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 13: 8162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19138162
APA StyleTopino, E., Cacioppo, M., & Gori, A. (2022). The Relationship between Attachment Styles and Compulsive Online Shopping: The Mediating Roles of Family Functioning Patterns. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(13), 8162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19138162







