Identifying Algicides of Enterobacter hormaechei F2 for Control of the Harmful Alga Microcystis aeruginosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth Conditions of Algicidal Bacteria and Cyanobacterial Cells
2.2. Algicidal Activity
2.3. Nucleic Acid-Related Manipulation
2.4. Extraction and Purification of the Algicidal Compound
2.5. Liquid Chromatograph–Mass Spectrometer (LC–MS) Analysis
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
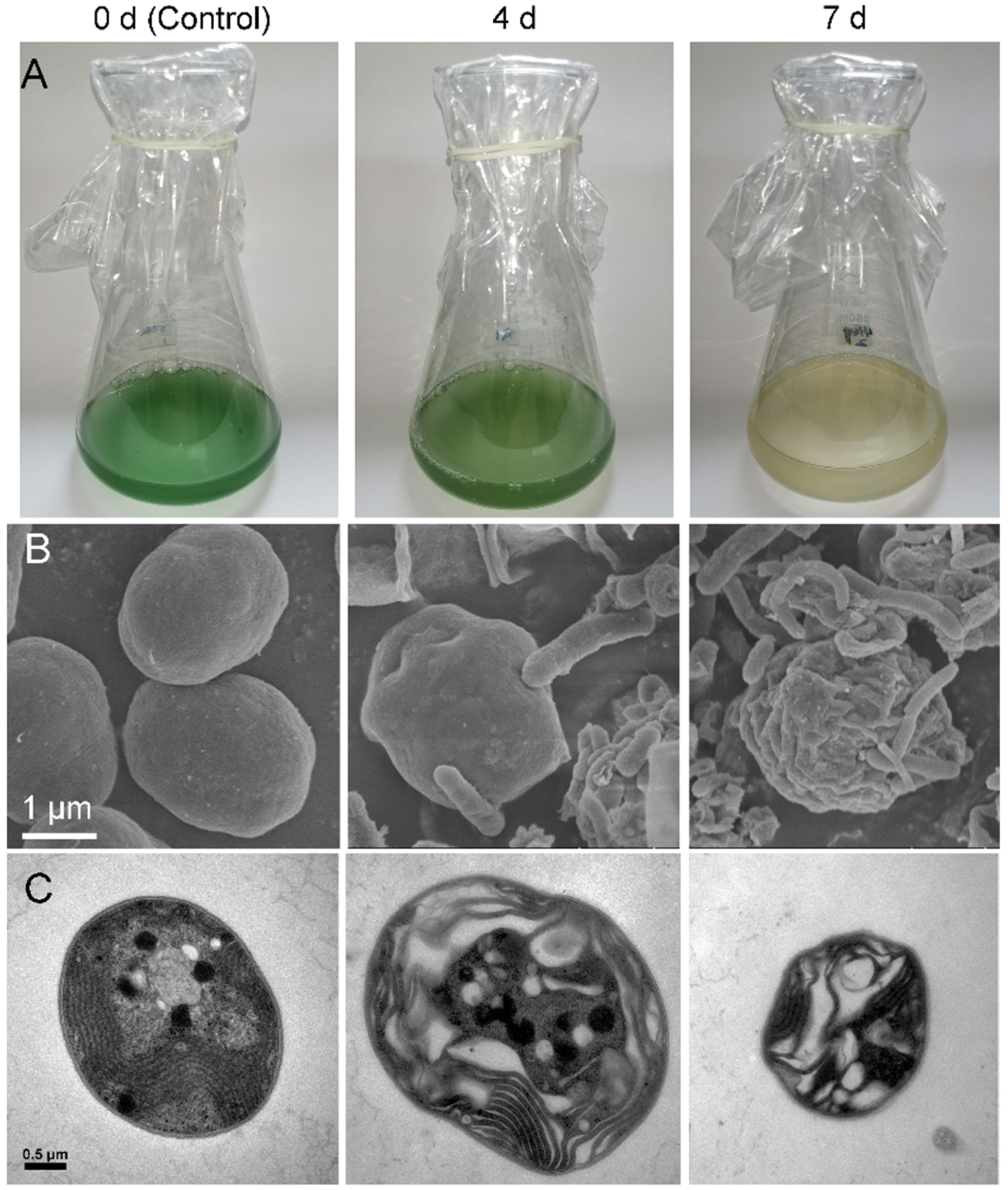
3.1. Algicidal Effects of the Strain
3.2. Detection of Algicides
3.2.1. Separation and Identification of Algicides
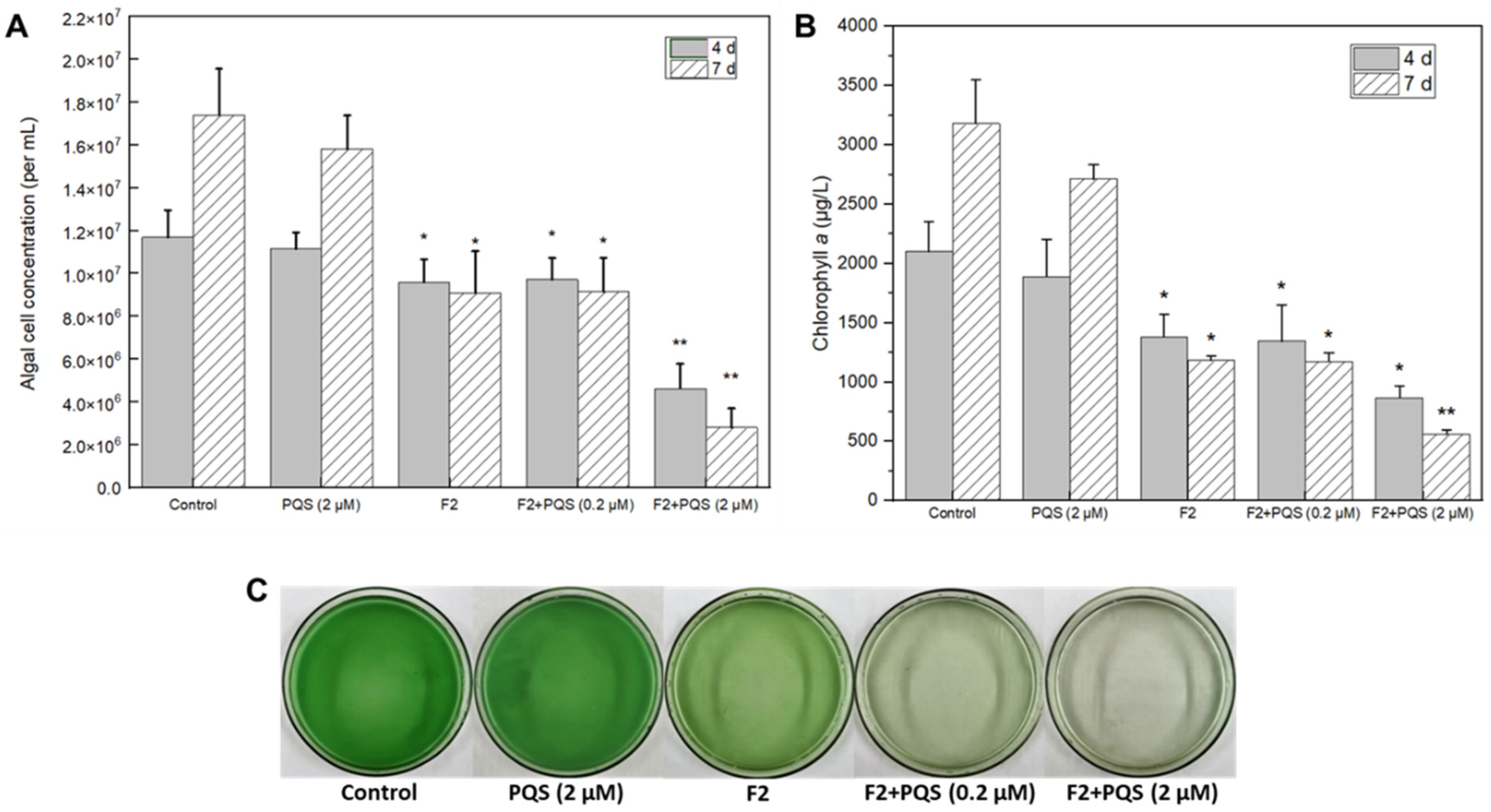
3.2.2. Algicidal Effects of Identified Substances
Prodigiosin as a Potential Algicide
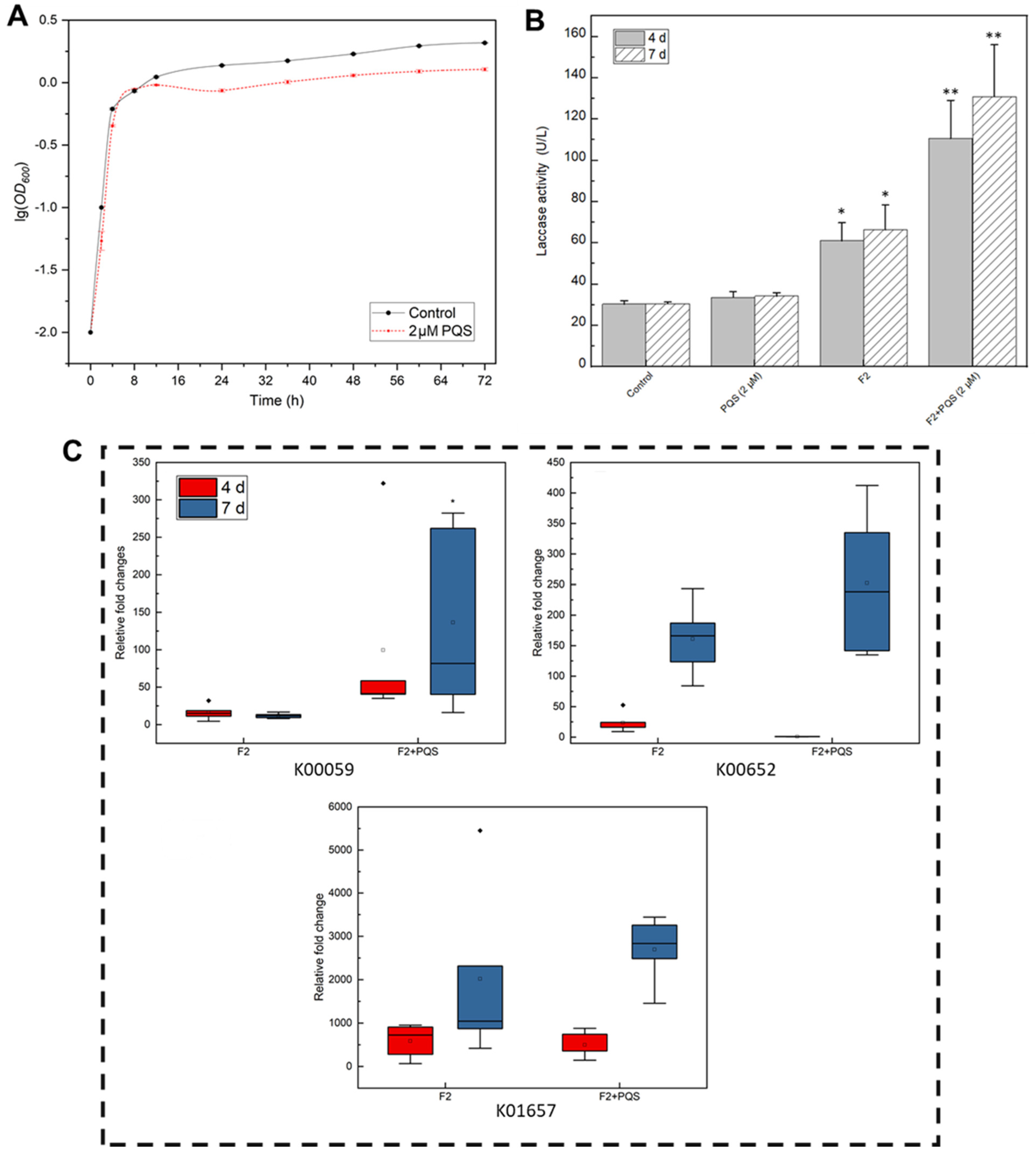
PQS Might Act as a QS Molecule That Regulates Algicidal Genes and Enzymes
3.3. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Algicidal Mechanism of the Strain
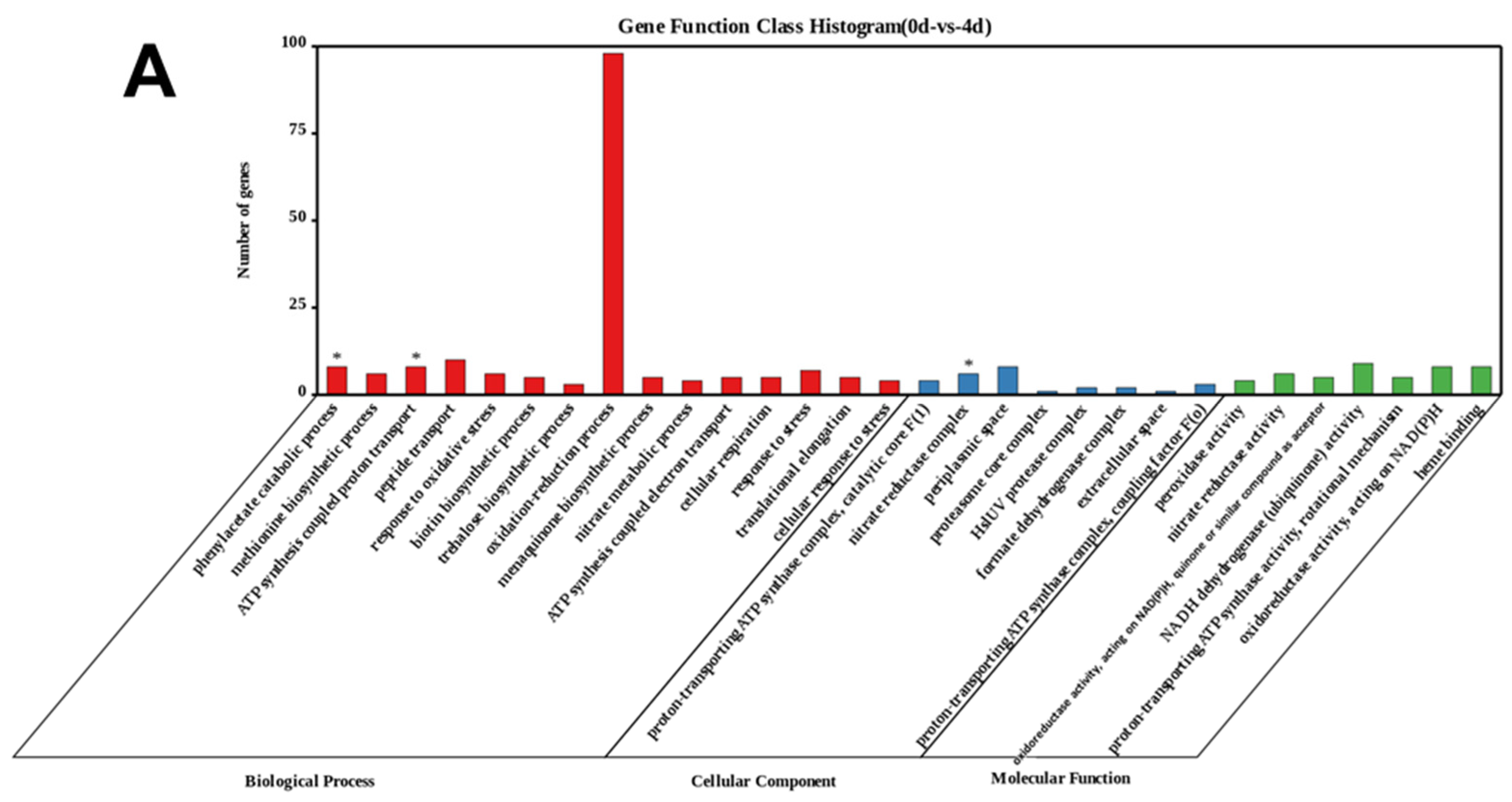
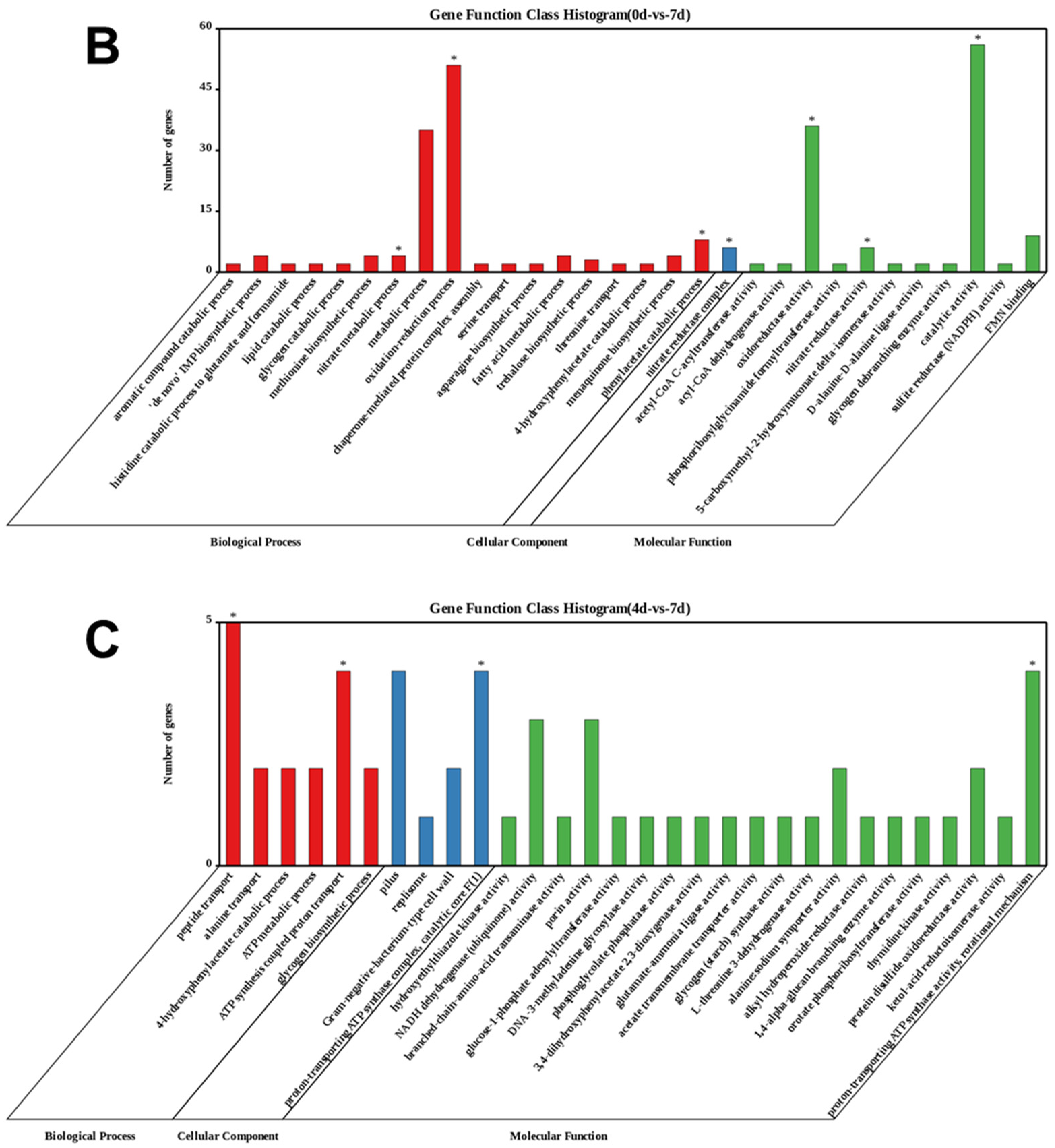
3.3.1. Enrichment of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) during the Algicidal Process
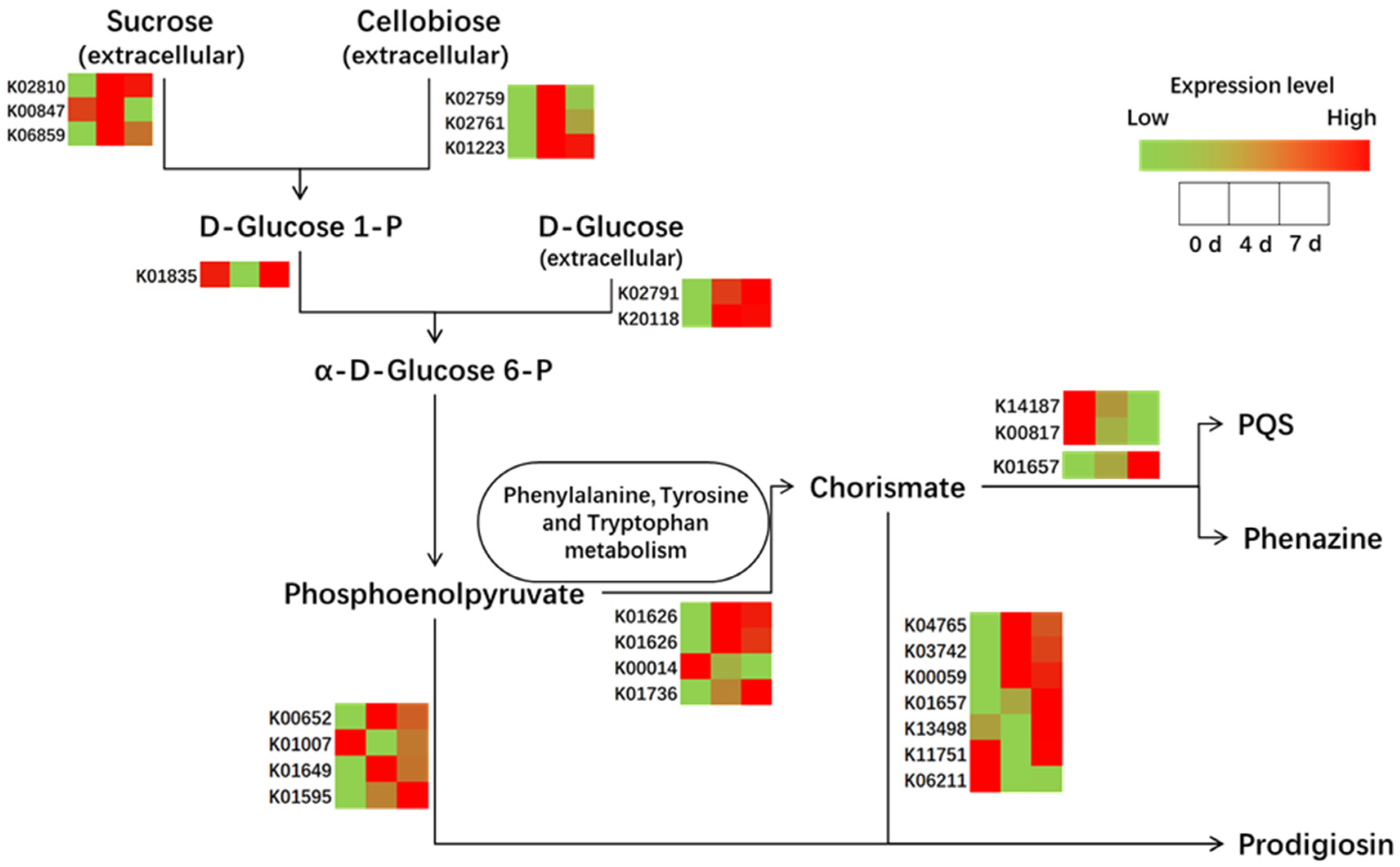
3.3.2. Comparative Genome and RNA Seq Analysis to Decipher the Associated Pathway
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janssen, E.M.-L. Cyanobacterial peptides beyond microcystins—A review on co-occurrence, toxicity, and challenges for risk assessment. Water Res. 2019, 151, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Hou, J.; Guo, H.H.; Li, L.; Wang, L.K.; Zhang, D.D.; Li, D.P.; Tang, R. The synergistic effects of waterborne microcystin-LR and nitrite on hepatic pathological damage, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant responses of male zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhang, C.L.; Xiang, Z.; Ding, J.; Han, X.D. Learning and memory deficits and alzheimer’s disease-like changes in mice after chronic exposure to microcystin-LR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 504–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurbuz, F.; Uzunmehmetoglu, O.Y.; Diler, O.; Metcalf, J.S.; Codd, G.A. Occurrence of microcystins in water, bloom, sediment and fish from a public water supply. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.R.; Beversdorf, L.J.; Weirich, C.A.; Bartlett, S.L. Cyanobacterial Toxins of the Laurentian Great Lakes, Their Toxicological Effects, and Numerical Limits in Drinking Water. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Steinman, A.D.; Gu, Y.R.; Zhu, G.W.; Shu, X.B.; Xue, Q.J.; Zou, W.; Xie, L.Q. Occurrence and risk assessment of microcystin and its relationship with environmental factors in lakes of the eastern plain ecoregion, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45095–45107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodani, S.; Imoto, A.; Mitsutani, A.; Murakami, M. Isolation and identification of the antialgal compound, harmane (1-methyl-beta-carboline), produced by the algicidal bacterium, Pseudomonas sp. K44-1. J. Appl. Phycol. 2002, 14, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukenik, A.; Kaplan, A. Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms in Aquatic Ecosystems: A Comprehensive Outlook on Current and Emerging Mitigation and Control Approaches. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, S.W.; Park, Y. Selective Algicidal Action of Peptides against Harmful Algal Bloom Species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataev, A.A.; Andreeva-Kovalevskaya, Z.I.; Solonin, A.S.; Ternovsky, V.I. Bacillus cereus can attack the cell membranes of the alga Chara corallina by means of HlyII. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dai, W.; Zhang, S.L.; Lin, Y.J.; Bi, X.D.; Yan, R.J.; Xing, K.Z. Allelopathic Effects of Berberine, a Plant Alkaloid, on the Algae, Microcystis aeruginosa (FACHB-905), at Different Initial Densities. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2013, 65, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Kong, L.J.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, J.Z.; Shi, Y.; Xie, S.L.; Li, B. Effect of protopine exposure on the physiology and gene expression in the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64666–64673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenneman, E.M.; Wang, P.; Barney, B.M. Potential application of algicidal bacteria for improved lipid recovery with specific algae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 354, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-T.; Chiang, Y.-R.; Huang, W.-Y.; Jane, W.-N. Cytotoxic effects of free fatty acids on phytoplankton algae and cyanobacteria. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Xie, W.J.; Hou, F.R.; Hu, J.; Yao, Z.Y.; Zhao, Q.F.; Zhang, D.M. Response of microbial community to the lysis of Phaeocystis globosa induced by a biological algicide, prodigiosin. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, W.; Wang, H. Physiological response and morphological changes of Heterosigma akashiwo to an algicidal compound prodigiosin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, W.; Yao, Z.Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Z.; Tao, Z.; Zheng, T.L. Toxic Effects of Prodigiosin Secreted by Hahella sp. KA22 on Harmful Alga Phaeocystis globosa. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Matsuyama, Y.; Muraoka, W.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. Producing mechanism of an algicidal compound against red tide phytoplankton in a marine bacterium γ-proteobacterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Chen, Q.L.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Lei, X.Q.; Chen, Z.R.; Li, Y.; Hong, Y.L.; Ma, X.H.; Zheng, W.; et al. The algicidal mechanism of prodigiosin from Hahella sp. KA22 against Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Yang, J.; Tian, Y.N.; Zhou, X.G.; Wang, S.W.; Zhu, J.R.; Sun, D.; Liu, C. An in situ extractive fermentation strategy for enhancing prodigiosin production from Serratia marcescens BWL1001 and its application to inhibiting the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 166, 107836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Xie, X.; Huang, F.Y.; Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Han, T.R.; Massey, I.Y.; Liang, G.Y.; Pu, Y.P.; Yang, F. Simultaneous Microcystis algicidal and microcystin synthesis inhibition by a red pigment prodigiosin. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.J.; Pu, G.Z.; Shao, C.; Cheng, S.J.; Cai, J.; Zhou, L.; Jia, Y.; Tian, X.J. Potential of extracellular enzymes from Trametes versicolor F21 a in Microcystis spp. degradation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.S.; Guo, X.L.; Liu, X.L.; Yang, H. NprR-NprX Quorum-Sensing System Regulates the Algicidal Activity of Bacillus sp. Strain S51107 against Bloom-Forming Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.J.; Yang, X.J.; Lai, Q.L.; Yu, X.Q.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.R.; Lei, X.Q.; Zheng, W.; Xu, H.; et al. Lysing bloom-causing alga Phaeocystis globosa with microbial algicide: An efficient process that decreases the toxicity of algal exudates. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Durrant, J.R.; Hastings, G.; Joseph, D.M.; Barber, J.; Porter, G.; Klug, D.R. Subpicosecond equilibration of excitation energy in isolated photosystem II reaction centers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 11632–11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Pan, J.; Yang, H. Synergistic algicidal effect and mechanism of two diketopiperazines produced by Chryseobacterium sp. strain GLY-1106 on the harmful bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.K.; Park, Y.K.; Kim, J.F. Genome-Wide Screening and Identification of Factors Affecting the Biosynthesis of Prodigiosin by Hahella chejuensis, Using Escherichia coli as a Surrogate Host. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, N.; Li, F.; Luo, X.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Huang, X. Transcriptional Analysis of Microcystis aeruginosa Co-Cultured with Algicidal Bacteria Brevibacillus laterosporus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welschmeyer, N.A. Fluorometric analysis of chlorophyll a in the presence of chlorophyll b and pheopigments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Zhou, X.-N.; Zhang, H.-H.; Wan, L.; Sun, Z.-L. An integrated method for degradation products detection and characterization using hybrid ion trap/time-of-flight mass spectrometry and data processing techniques: Application to study of the degradation products of danofloxacin under stressed conditions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 2475–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.I.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Ko, I.J.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.W. Isolation and characterization of algicidal bacteria from Cochlodinium polykrikoides culture. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2011, 16, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Song, C.L. The shift of mutualistic relationships among algae, free-living and attached bacteria through different nutrient addition mode: A mesocosm study. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2020, 35, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.A.; Qureshi, A.; Faulkner, D.J.; Azam, F. 2-n-pentyl-4-quinolinol produced by a marine Alteromonas sp and its potential ecological and biogeochemical roles. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollara, S.B.; Becker, J.W.; Nunn, B.L.; Boiteau, R.; Repeta, D.; Mudge, M.C.; Downing, G.; Chase, D.; Harvey, E.L.; Whalen, K.E. Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Signal Arrests Phytoplankton Cell Division and Impacts Virus-Induced Mortality. mSphere 2021, 6, e00009-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zender, M.; Klein, T.; Henn, C.; Kirsch, B.; Maurer, C.K.; Kail, D.; Ritter, C.; Dolezal, O.; Steinbach, A.; Hartmann, R.W. Discovery and Biophysical Characterization of 2-Amino-oxadiazoles as Novel Antagonists of PqsR, an Important Regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 6761–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Li, Y.B.; Zhang, C.S.; Li, A.S.K.; Zhu, C.J. Isolation and Purification of Phenazine Pigments Produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its Effects on the Growth of Red Tide Organisms. Fudan Xuebao Zirankexueban 2004, 43, 494–499, 506. [Google Scholar]
- Hoover, S.E.; Perez, A.J.; Tsui, H.-C.T.; Sinha, D.; Smiley, D.L.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Winkler, M.E.; Lazazzera, B.A. A new quorum-sensing system (TprA/PhrA) for Streptococcus pneumoniae D39 that regulates a lantibiotic biosynthesis gene cluster. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 97, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Xie, W.; He, W.; Xie, J.; Liu, W. Identifying Algicides of Enterobacter hormaechei F2 for Control of the Harmful Alga Microcystis aeruginosa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137556
Zhang B, Yang Y, Xie W, He W, Xie J, Liu W. Identifying Algicides of Enterobacter hormaechei F2 for Control of the Harmful Alga Microcystis aeruginosa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(13):7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137556
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bin, Ying Yang, Wenjia Xie, Wei He, Jia Xie, and Wei Liu. 2022. "Identifying Algicides of Enterobacter hormaechei F2 for Control of the Harmful Alga Microcystis aeruginosa" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 13: 7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137556
APA StyleZhang, B., Yang, Y., Xie, W., He, W., Xie, J., & Liu, W. (2022). Identifying Algicides of Enterobacter hormaechei F2 for Control of the Harmful Alga Microcystis aeruginosa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(13), 7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137556




