Laboratory Chamber Evaluation of Flow Air Quality Sensor PM2.5 and PM10 Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Low-Cost Sensors Evaluated
2.2. Chamber Experiments
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Inter-Flow Variation
2.5. Flow and Plantower A003 Comparison
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Environmental Protection Agency. Air Data: Air Quality Data Collected at Outdoor Monitors across the US. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/outdoor-air-quality-data (accessed on 27 June 2020).
- Environmental Protection Agency. NAAQS Table. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/criteria-air-pollutants/naaqs-table (accessed on 27 June 2020).
- Steinle, S.; Reis, S.; Sabel, C.E. Quantifying human exposure to air pollution—Moving from static monitoring to spatio-temporally resolved personal exposure assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovašević-Stojanović, M.; Bartonova, A.; Topalović, D.; Lazović, I.; Pokrić, B.; Ristovski, Z. On the use of small and cheaper sensors and devices for indicative citizen-based monitoring of respirable particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowther, S.D.; Jones, K.C.; Wang, X.; Whyatt, J.D.; Wild, O.; Booker, D. Particulate Matter Measurement Indoors: A Review of Metrics, Sensors, Needs, and Applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11644–11656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulot, F.M.J.; Russell, H.S.; Rezaei, M.; Johnson, M.S.; Ossont, S.J.J.; Morris, A.K.R.; Basford, P.J.; Easton, N.H.C.; Foster, G.L.; Loxham, M.; et al. Laboratory Comparison of Low-Cost Particulate Matter Sensors to Measure Transient Events of Pollution. Sensors 2020, 20, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leech, J.A.; Nelson, W.C.; Burnett, R.T.; Aaron, S.; Raizenne, M.E. It’s about time: A comparison of Canadian and American time-activity patterns. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2002, 12, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adgate, J.L.; Ramachandran, G.; Pratt, G.C.; Waller, L.A.; Sexton, K. Longitudinal variability in outdoor, indoor, and personal PM2.5 exposure in healthy non-smoking adults. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Martani, C.; Biskos, G.; Neophytou, M.; Di Sabatino, S.; Bell, M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. The rise of low-cost sensing for managing air pollution in cities. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stewart, J.A.; Mitchell, M.A.; Edgerton, V.S.; VanCott, R. Environmental Justice and Health Effects of Urban Air Pollution. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2015, 107, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Environmental Justice. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/environmentaljustice (accessed on 27 June 2020).
- Hall, E.; Kaushik, S.; Vanderpool, R.; Duvall, R.; Beaver, M.; Long, R.; Solomon, P. Integrating Sensor Monitoring Technology into the Current Air Pollution Regulatory Support Paradigm: Practical Considerations. Am. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 4, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flow, Plume Labs. The First Smart Air Quality Tracker. Available online: https://plumelabs.com/en/flow/ (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- South Coast. Air Quality Management District Sensors. Available online: https://www.aqmd.gov/aq-spec/sensors (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- South Coast. AQMD Air Quality Sensor Performance Evaluation Center Field Evaluation Plume Labs Flow 2. Available online: https://www.aqmd.gov/aq-spec/sensordetail/plume-labs---flow-2 (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- Plume Labs. How Can I Make Sure My Flow Is Accurate? Available online: https://plumelabs.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360010791514-How-can-I-make-sure-my-Flow-is-accurate- (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Levy Zamora, M.; Xiong, F.; Gentner, D.; Kerkez, B.; Kohrman-Glaser, J.; Koehler, K. Field and Laboratory Evaluations of the Low-Cost Plantower Particulate Matter Sensor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantower Technology. Available online: www.plantower.com/list/?5_1.html (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Plume Labs. How Does Flow Work? Available online: https://plumelabs.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360009014973-How-does-Flow-work- (accessed on 27 June 2020).
- Plume Labs. How Do you Measure Air Pollution? Available online: http://air.plumelabs.com/learn/en/how-do-you-measure-air-pollution?%2F%2Fen%2Fhow-do-you-measure-air-pollution= (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Plume Labs. How Long Does the Battery Last? Available online: https://plumelabs.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/115002105594--How-long-does-the-battery-last- (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Clougherty, J.E.; Kheirbek, I.; Eisl, H.M.; Ross, Z.; Pezeshki, G.; Gorczynski, J.E.; Johnson, S.; Markowitz, S.; Kass, D.; Matte, T. Intra-urban spatial variability in wintertime street-level concentrations of multiple combustion-related air pollutants: The New York City Community Air Survey (NYCCAS). J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.E.; Whitaker, J.; Petty, A.; Widmer, C.; Dybwad, A.; Sleeth, D.; Martin, R.; Butterfield, A. Ambient and laboratory evaluation of a low-cost particulate matter sensor. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvlin, G.; Lugo, H.; Olmedo, L.; Bejarano, E.; Wilkie, A.; Meltzer, D.; Wong, M.; King, G.; Northcross, A.; Jerrett, M.; et al. Development and field validation of a community-engaged particulate matter air quality monitoring network in imperial, CA. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, A.J.; Xu, X.; Kulka, R.; You, H.; Wallace, L.; Mallach, G.; Ryswyk, K.V.; MacNeill, M.; Kearney, J.; Rasmussen, P.E.; et al. Windsor, Ontario Exposure Assessment Study: Design and Methods Validation of Personal, Indoor, and Outdoor Air Pollution Monitoring. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plume Labs. What Are the Flow Warm-Up and Burn-In Periods? Available online: https://plumelabs.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360008681194-What-are-the-Flow-Warm-up-and-Burn-in-Periods- (accessed on 5 June 2022).
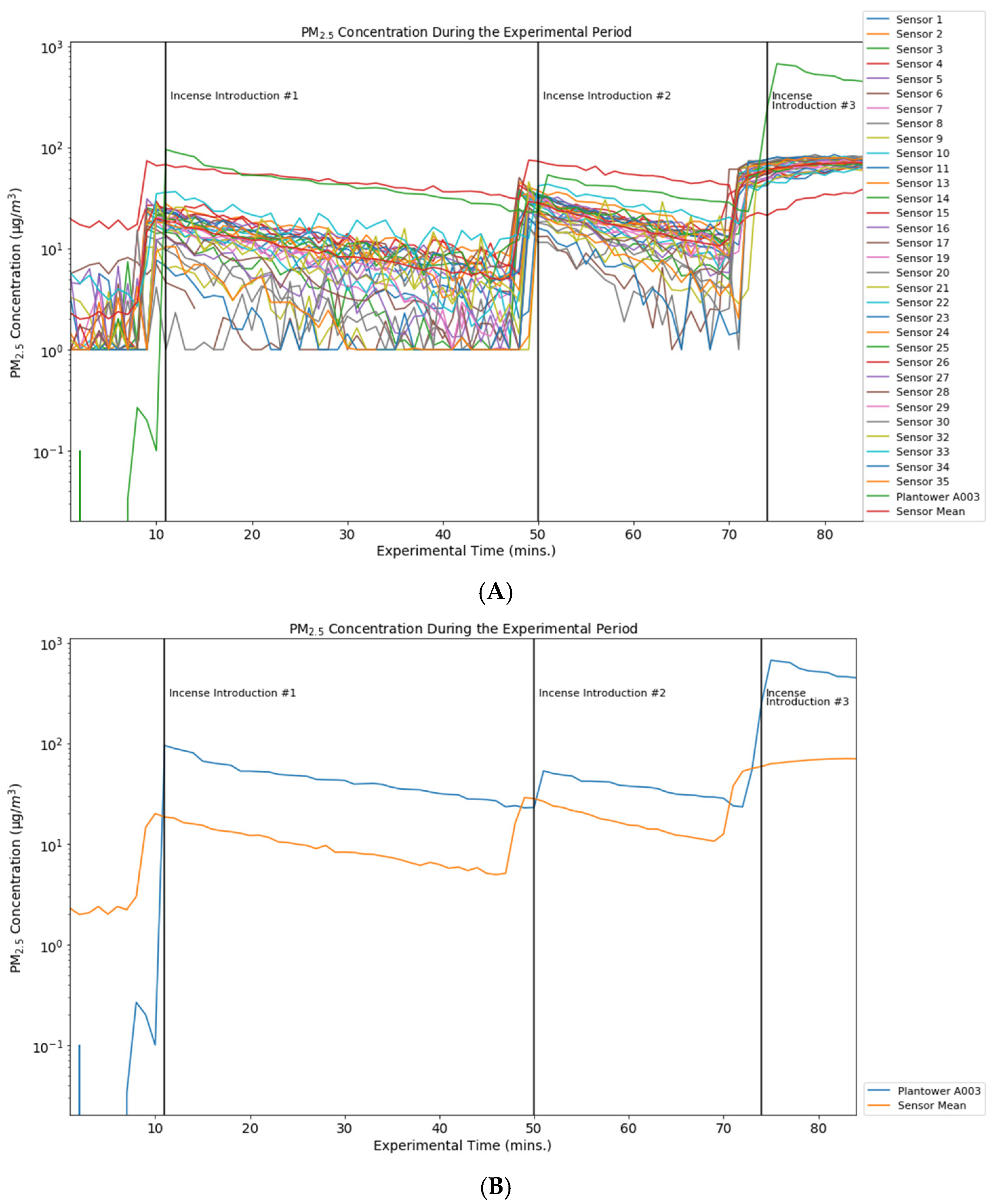

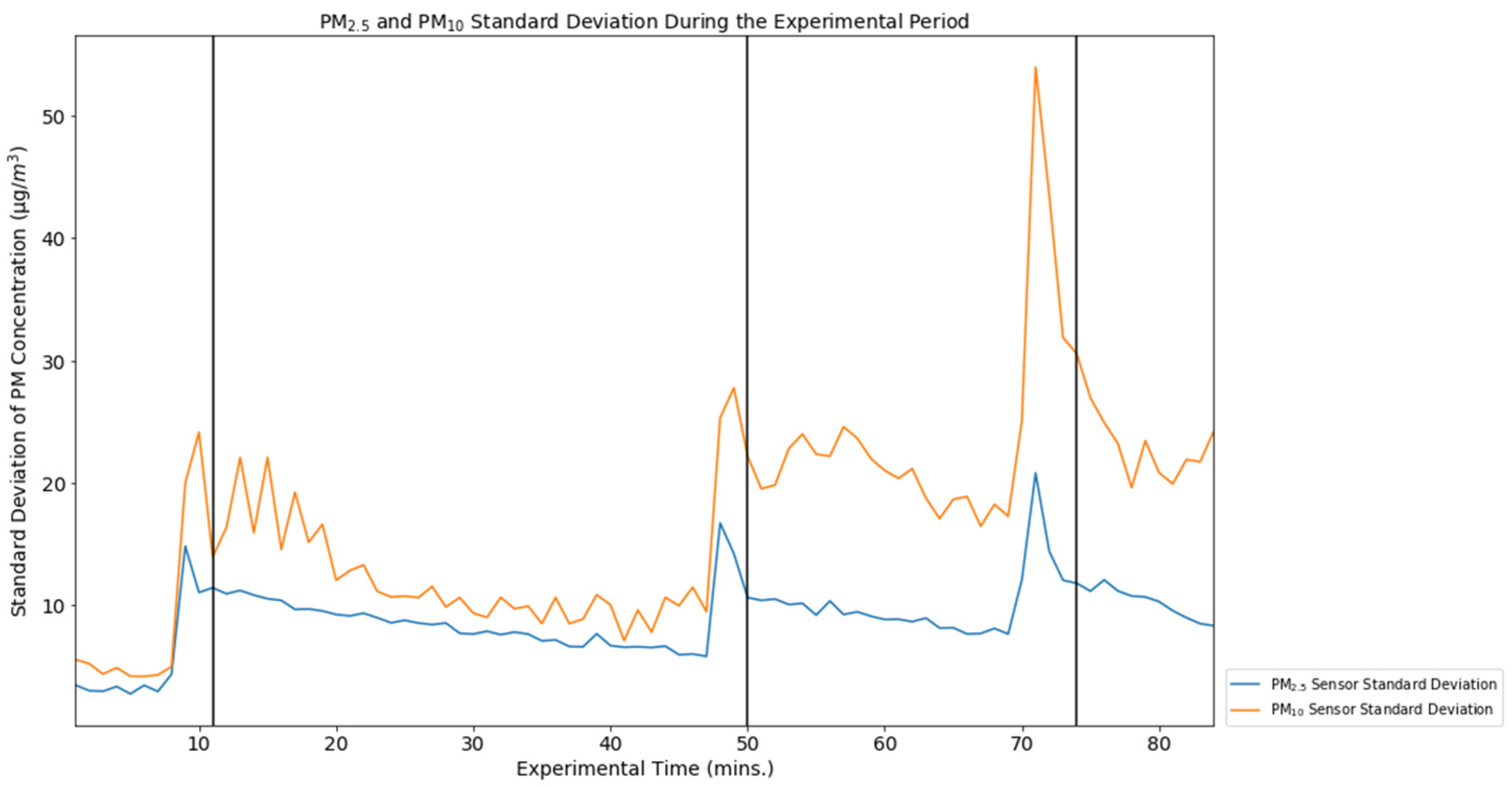
| Overall Precision Evaluation | Overall Precision PM10 | Overall Precision PM2.5 |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor 1 | 47.61 | 54.13 |
| Sensor 2 | 48.06 | 59.87 |
| Sensor 3 | 45.66 | 47.36 |
| Sensor 4 | 45.74 | 55.61 |
| Sensor 5 | 48.53 | 50.53 |
| Sensor 6 | 101.88 | 97.78 |
| Sensor 7 | 45.44 | 49.03 |
| Sensor 8 | 49.80 | 68.29 |
| Sensor 9 | 60.25 | 79.81 |
| Sensor 10 | 46.40 | 46.57 |
| Sensor 11 | 47.63 | 47.41 |
| Sensor 13 | 45.06 | 46.35 |
| Sensor 14 | 50.49 | 59.08 |
| Sensor 15 | 55.65 | 52.91 |
| Sensor 16 | 56.10 | 51.72 |
| Sensor 17 | 46.84 | 51.15 |
| Sensor 19 | 48.44 | 50.73 |
| Sensor 20 | 49.29 | 67.54 |
| Sensor 21 | 49.73 | 50.29 |
| Sensor 22 | 46.47 | 48.40 |
| Sensor 23 | 49.68 | 50.33 |
| Sensor 24 | 46.08 | 45.96 |
| Sensor 25 | 45.89 | 49.65 |
| Sensor 26 | 86.52 | 126.75 |
| Sensor 27 | 45.96 | 60.82 |
| Sensor 28 | 44.83 | 55.13 |
| Sensor 29 | 47.59 | 48.61 |
| Sensor 30 | 81.80 | 85.63 |
| Sensor 32 | 54.47 | 53.87 |
| Sensor 33 | 62.59 | 75.63 |
| Sensor 34 | 70.46 | 87.40 |
| Sensor 35 | 59.68 | 74.48 |
| PM10 | PM2.5 | |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Average Standard Deviation | 16.67 µg/m3 | 8.87 µg/m3 |
| Flow Standard Deviation Minimum | 4.20 µg/m3 | 2.77 µg/m3 |
| Flow Standard Deviation Maximum | 53.96 µg/m3 | 20.82 µg/m3 |
| Flow Coefficient of Variation | 0.52 | 0.76 |
| Overall Accuracy (Flow Sensors vs. Plantower A003) | −380.59% | −433.72% |
| Linear Regression R2 | 0.73 | 0.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crnosija, N.; Levy Zamora, M.; Rule, A.M.; Payne-Sturges, D. Laboratory Chamber Evaluation of Flow Air Quality Sensor PM2.5 and PM10 Measurements. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127340
Crnosija N, Levy Zamora M, Rule AM, Payne-Sturges D. Laboratory Chamber Evaluation of Flow Air Quality Sensor PM2.5 and PM10 Measurements. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(12):7340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127340
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrnosija, Natalie, Misti Levy Zamora, Ana M. Rule, and Devon Payne-Sturges. 2022. "Laboratory Chamber Evaluation of Flow Air Quality Sensor PM2.5 and PM10 Measurements" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 12: 7340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127340
APA StyleCrnosija, N., Levy Zamora, M., Rule, A. M., & Payne-Sturges, D. (2022). Laboratory Chamber Evaluation of Flow Air Quality Sensor PM2.5 and PM10 Measurements. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(12), 7340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127340








