Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine during the COVID-19 Pandemic—A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
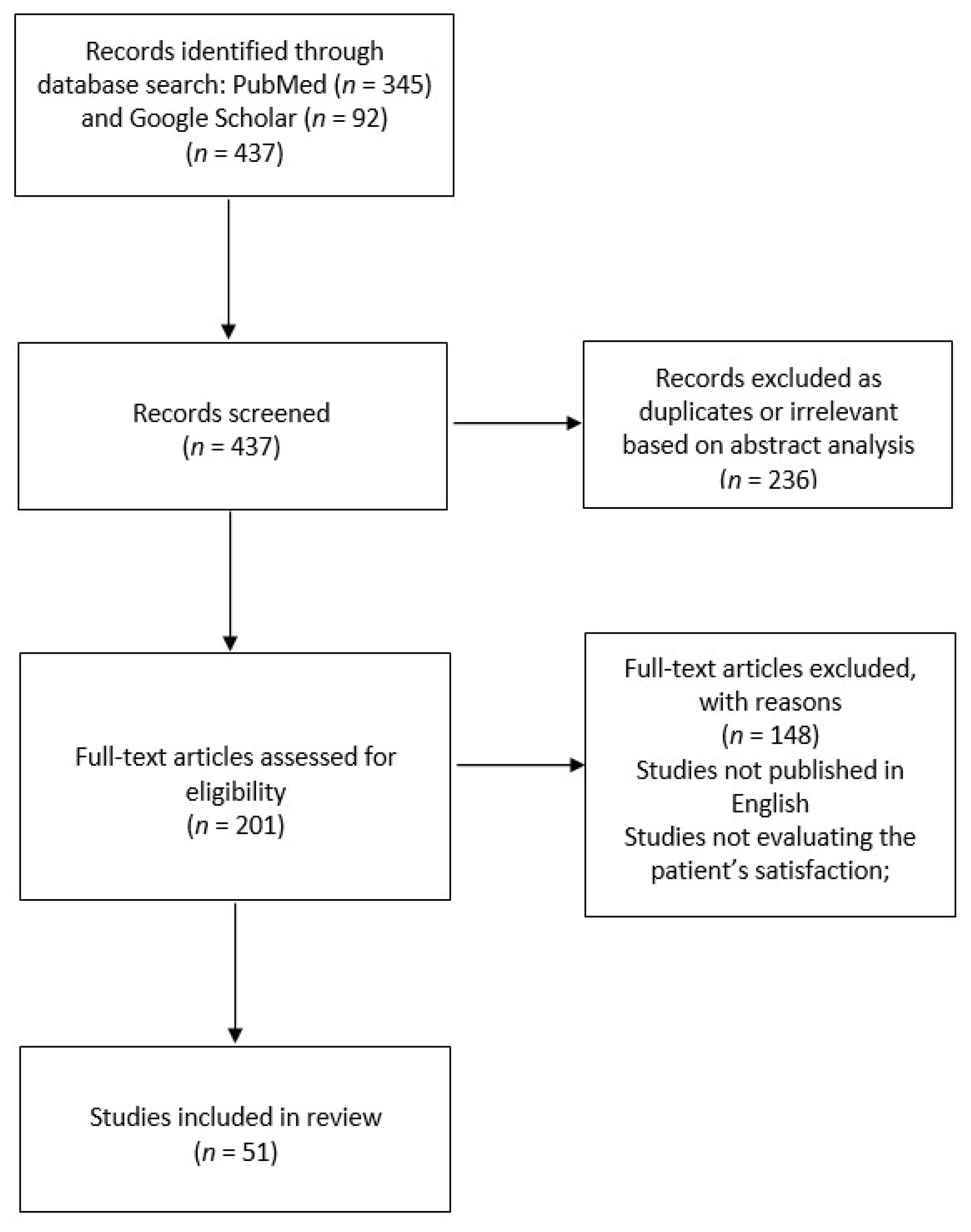
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Satisfaction Rate
3.2. Other Aspects of Virtual Consulations
3.2.1. Missed Appointment Rate
3.2.2. Clinical Needs of Patients
3.2.3. Technical Aspects
3.2.4. Time and Cost Savings
3.2.5. Willingness to Use Telehealth in the Future
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages of Telemedicine
4.2. Limitations of Telemedicine
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Downes, M.J.; Mervin, M.C.; Byrnes, J.M.; Scuffham, P.A. Telephone consultations for general practice: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brant, H.; Atherton, H.; Ziebland, S.; McKinstry, B.; Campbell, J.; Salisbury, C. Using alternatives to face-to-face consultations: A survey of prevalence and attitudes in general practice. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2016, 66, e460–e466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atherton, H.; Brant, H.; Ziebland, S.; Bikker, A.; Campbell, J.; Gibson, A.; McKinstry, B.; Porqueddu, T.; Salisbury, C. Alternatives to the face-to-face consultation in general practice: Focused ethnographic case study. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2018, 68, e293–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammersley, V.; Donaghy, E.; Parker, R.; McNeilly, H.; Atherton, H.; Bikker, A.; Campbell, J.; McKinstry, B. Comparing the content and quality of video, telephone, and face-to-face consultations: A non-randomised, quasi-experimental, exploratory study in UK primary care. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2019, 69, e595–e604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19 [Internet]. 2021 August. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---10-august-2021 (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- World Health Organization. COVID-19: Operational Guidance for Maintaining Essential Health Services during an Outbreak: Interim Guidance. [Internet]. March 2020. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331561 (accessed on 22 August 2021).
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Significantly Impacts Health Services for Noncommunicable Diseases. [Internet]. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/noncommunicable-diseases/covid-19 (accessed on 4 September 2021).
- Mohanty, A.; Srinivasan, V.M.; Burkhardt, J.-K.; Johnson, J.; Patel, A.J.; Sheth, S.A.; Viswanathan, A.; Yoshor, D.; Kan, P. Ambulatory neurosurgery in the COVID-19 era: Patient and provider satisfaction with telemedicine. Neurosurg. Focus 2020, 49, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.J.; Tong, D.; Anton, G.M.; Jasinski, J.M.; Claus, C.F.; Soo, T.M.; Kelkar, P.S. Patient Satisfaction with Neurosurgery Telemedicine Visits During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: A Prospective Cohort Study. World Neurosurg. 2020, 145, e184–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porche, K.; Vaziri, S.; Mehkri, Y.; Christie, C.; Laurent, D.; Wang, Y.; Rahman, M. Patient satisfaction scores with telemedicine in the neurosurgical population. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 205, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheja, A.; Manjunath, G. Turning a New Chapter in Neurosurgery Outpatient Services: Telemedicine A “Savior” in this Pandemic. Neurol. India. 2021, 69, 344–351. [Google Scholar]
- Drerup, B.; Espenschied, J.; Wiedemer, J.; Hamilton, L. Reduced No-Show Rates and Sustained Patient Satisfaction of Telehealth During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Telemed. e-Health 2021, 27, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlach, F.; McKinlay, E.; Middleton, L.; Kennedy, J.; Pledger, M.; Russell, L.; Churchward, M.; Cumming, J.; McBride-Henry, K. Telehealth consultations in general practice during a pandemic lockdown: Survey and interviews on patient experiences and preferences. BMC Fam. Pract. 2020, 21, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, J.; Fox, A.; Kammire, M.S.; Hollis, A.N.; Khairat, S. Evaluating the Experiences of New and Existing Teledermatology Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Cross-sectional Survey Study. JMIR Dermatol. 2021, 4, e25999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeganathan, S.; Prasannan, L.; Blitz, M.J.; Vohra, N.; Rochelson, B.; Meirowitz, N. Adherence and acceptability of telehealth appointments for high-risk obstetrical patients during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020, 2, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, A.M.; Polachek, W.S.; Dulas, M.; Strelzow, J.A.; Hynes, K.K. The new ‘normal’: Rapid adoption of telemedicine in orthopaedics during the COVID-19 pandemic. Injury 2020, 51, 2816–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, A.; Arora, R.; Sehrawat, R. Feasibility of telemedicine in maintaining follow-up of orthopaedic patients and their satisfaction: A preliminary study. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, S704–S710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisson, L.J.; Kluczynski, M.A.; Lindborg, C.M.; Rauh, M.A.; DiPaola, M.J.; Haider, M.N.; Pavlesen, S. The Association Between Patient Satisfaction and Mode of Visit (Telemedicine Versus In-Person) in a Large Orthopaedic Practice during the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown: A Retrospective Study. JAAOS: Glob. Res. Rev. 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Lindgren, B.R.; Blaes, A.H.; Parsons, H.M.; LaRocca, C.J.; Farah, R.; Hui, J.Y.C. ASO Visual Abstract: The New Normal? Patient Satisfaction and Usability of Telemedicine in Breast Cancer Care. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5668–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardo, E.; Baù, M.G.; Anatrone, C.; Mondino, A.; Surace, A.; Gallo, F.; Danese, S.; Mitidieri, M. Oncophone20 study: Patients’ perception of telemedicine in the COVID-19 pandemic during follow-up visits for gynecological and breast cancers. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2021, 155, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojdehbakhsh, R.P.; Rose, S.; Peterson, M.; Rice, L.; Spencer, R. A quality improvement pathway to rapidly increase telemedicine services in a gynecologic oncology clinic during the COVID-19 pandemic with patient satisfaction scores and environmental impact. Gynecol. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 36, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyaraj, A.; Lopez, H.; Surapaneni, R. Patient satisfaction with telemedicine for prechemotherapy evaluation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Futur. Oncol. 2021, 17, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.J.C.; Jay, G.M.; Kalpakjian, C.; Andrews, C.; Smith, S. Patient and Provider-Reported Satisfaction of Cancer Rehabilitation Telemedicine Visits During the COVID -19 Pandemic. PM&R 2021, 13, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrke, A.; Younger, E.; Wilson, R.; Husson, O.; Farag, S.; Merry, E.; Macklin-Doherty, A.; Cojocaru, E.; Arthur, A.; Benson, C.; et al. Telemedicine During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Impact on Care for Rare Cancers. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2020, 6, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meno, M.; Abe, J.; Fukui, J.; Braun-Inglis, C.; Pagano, I.; Acoba, J. Telehealth amid the COVID-19 pandemic: Perception among Asian, Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander cancer patients. Futur. Oncol. 2021, 17, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.; Lester, S.; Hoon, E.; van der Haak, H.; Proudman, C.; Hall, C.; Whittle, S.; Proudman, S.; Hill, C.L. Patient satisfaction and acceptability with telehealth at specialist medical outpatient clinics during the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia. Intern. Med. J. 2021, 51, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortezavi, M.; Lokineni, S.; Garg, M.; Chen, Y.L.; Ramsey, A. Rheumatology Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the United States. J. Patient Exp. 2021, 8, 23743735211008825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornero-Molina, J.; Sánchez-Alonso, F.; Fernández-Prada, M.; Bris-Ochaita, M.-L.; Sifuentes-Giraldo, A.; Vidal-Fuentes, J. Tele-Rheumatology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Reumatol. Clin. 2021, 18, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Arif, R.; Rai, A. Patient Experiences with Telemedicine in a National Health Service Rheumatology Outpatient Department During Coronavirus Disease-19. J. Patient Exp. 2021, 8, 237437352110349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, E.L.; Triantafillou, V.; Prasad, A.; Deng, J.; Shanti, R.M.; Newman, J.G.; Rajasekaran, K. Telemedicine for head and neck ambulatory visits during COVID-19: Evaluating usability and patient satisfaction. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisada, M.V.; Hwang, J.; Gill, A.S.; Wilson, M.D.; Strong, E.B.; Steele, T.O. Telemedicine, Patient Satisfaction, and Chronic Rhinosinusitis Care in the Era of COVID-19. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2020, 35, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, F.; Cabrera, C.I.; D’Anza, B.; Rodriguez, K. Patient satisfaction with telemedicine in rhinology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.; Lin, M.; Abdur-Rahman, F.; Mack, W.J.; Volker, C.C. Telemedicine in Otolaryngology During COVID-19: Patient and Physician Satisfaction. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, P.E.; Fischer, J.L.; Nagy, R.E.; Watson, N.L.; McCoul, E.D.; Tolisano, A.M.; Riley, C.A. Patient and Provider Satisfaction With Telemedicine in Otolaryngology. OTO Open 2021, 5, 2473974X20981838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fieux, M.; Duret, S.; Bawazeer, N.; Denoix, L.; Zaouche, S.; Tringali, S. Telemedicine for ENT: Effect on quality of care during COVID-19 pandemic. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2020, 137, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass Clark, S.; Bradley, M. 32 Patient satisfaction with urogynecology telemedicine office visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 224, S764–S765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Mountjoy, N.; McElroy, D.; Mittal, S.; Al Hemyari, B.; Coffey, N.; Miller, K.; Gaines, K. Patient Perspectives with Telehealth Visits in Cardiology During COVID-19: Online Patient Survey Study. JMIR Cardio 2021, 5, e25074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haxhihamza, K.; Arsova, S.; Bajraktarov, S.; Kalpak, G.; Stefanovski, B.; Novotni, A.; Milutinovic, M. Patient Satisfaction with Use of Telemedicine in University Clinic of Psychiatry: Skopje, North Macedonia During COVID-19 Pandemic. Telemed. e-Health 2021, 27, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrange, S.; Patel, A.; Mack, W.J.; Cassetta, J. Patient Satisfaction and Trust in Telemedicine During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Retrospective Observational Study. JMIR Hum. Factors 2021, 8, e28589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.S.; Yang, L.; Mortezavi, M.; Vadamalai, K.; Ramsey, A. Patient satisfaction with telemedicine encounters in an allergy and immunology practice during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 125, 478–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, K.; Kuruvilla, M.; Shih, J. Patient satisfaction and utilization of telemedicine services in allergy: An institutional survey. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 9, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Galloway, G.K.; Oyibo, S.O. Patient Satisfaction with the Use of Telemedicine in the Management of Hyperthyroidism. Cureus 2020, 12, e9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Ali, A.; Usman, M. Tele-Gastroenterology Midst COVID-19 Pandemic: Patients’ Perspective. Cureus 2021, 13, e14708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satin, A.M.; Shenoy, K.; Sheha, E.D.; Basques, B.; Schroeder, G.D.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Lieberman, I.H.; Guyer, R.D.; Derman, P.B. Spine Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study. Glob. Spine J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuva, S.; Lankford, C.; Patel, N.; Haddas, R. Implementation and Patient Satisfaction of Telemedicine in Spine Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Patients during the COVID-19 Shutdown. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 99, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, K.; Lovecchio, F.; Forston, K.; Wyss, J.; Casey, E.; Press, J.; Creighton, A.; Sandhu, H.; Iyer, S. The Efficacy of Telehealth for the Treatment of Spinal Disorders: Patient-Reported Experiences During the COVID-19 Pandemic. HSS J. Musculoskelet. J. Hosp. Spéc. Surg. 2020, 16, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, T.; Alsabbagh, A.; McGoldrick, D.; Bhatia, S.; Messahel, A. Oral and maxillofacial surgery patient satisfaction with telephone consultations during the COVID-19 pandemic. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 59, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhahri, A.A.; Iqbal, M.R.; Pardoe, H. Agile Application of Video Telemedicine During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Cureus 2020, 12, e11320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de la Hermosa AViejo-Martínez, E.; Valdazo-Gómez, A.; Camacho-Aroca, A.; Marques-Medina, E.; Paseiro-Crespo, G. Teleconsultation in general surgery during COVID-19 pandemic, satisfaction survey and feasibility for future. Minerva Surg. 2021; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.; Shang, M.; Vallabhajosyula, I.; Mori, M.; Chinian, R.; Assi, R.; Bonde, P.; Geirsson, A.; Vallabhajosyula, P.; Bs, M.S.; et al. Telemedicine in the era of coronavirus 19: Implications for postoperative care in cardiac surgery. J. Card. Surg. 2021, 36, 3731–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiadji, E.; Mackenzie, L.; Reeder, P.; Gani, J.S.; Ahmadi, S.; Carroll, R.; Smith, S.; Frydenberg, M.; O’Neill, C.J. Patient perceptions of surgical telehealth consultations during the COVID 19 pandemic in Australia: Lessons for future implementation. ANZ J. Surg. 2021, 91, 1662–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Anguita, R.; Dacruz, L. Telemedicine for postoperative consultations following vitrectomy for retinal detachment repair during the COVID-19 crisis: A patient satisfaction survey. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 56, e46–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golash, V.; Athwal, S.; Khandwala, M. Teleophthalmology and COVID-19: The patient perspective. Futur. Health J. 2021, 8, e54–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.E.; Andrews, J.R.; Joshi, V.B.; Mynderse, L.A.; Tollefson, M.K.; Karnes, R.J.; Kwon, E.D. Patient Satisfaction of Telemedicine Visits in an Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinic During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2021, 5, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efthymiadis, A.; Hart, E.J.; Guy, A.M.; Harry, R.; Mahesan, T.; Chedid, W.A.; Uribe-Lewis, S.; Perry, M.J. Are telephone consultations the future of the NHS? The outcomes and experiences of an NHS urological service in moving to telemedicine. Futur. Health J. 2020, 8, e15–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-Y.; Kwon, Y.-M.; Jun, H.-R.; Jung, S.-E.; Kwon, S.-Y. Satisfaction Survey of Patients and Medical Staff for Telephone-Based Telemedicine During Hospital Closing Due to COVID-19 Transmission. Telemed. e-Health 2020, 27, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T. A Survey of Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine during the COVID-19 Pandemic at a Student-Run Free Clinic. Free Clin. Res. Collect. 2020, 6. Available online: https://www.themspress.org/journal/index.php/freeclinic/article/view/456 (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Ramaswamy, A.; Yu, M.; Drangsholt, S.; Ng, E.; Culligan, P.J.; Schlegel, P.N.; Hu, J.C. Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Med Internet Res. 2020, 22, e20786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solimini, R.; Busardò, F.P.; Gibelli, F.; Sirignano, A.; Ricci, G. Ethical and Legal Challenges of Telemedicine in the Era of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Medicina 2021, 57, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferorelli, D.; Nardelli, L.; Spagnolo, L.; Corradi, S.; Silvestre, M.; Misceo, F.; Marrone, M.; Zotti, F.; Mandarelli, G.; Solarino, B.; et al. Medical Legal Aspects of Telemedicine in Italy: Application Fields, Professional Liability and Focus on Care Services During the COVID-19 Health Emergency. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2020, 11, 2150132720985055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Notification of Enforcement Discretion for Telehealth Remote Communications During the COVID-19 Nationwide Public Health Emergency. 2021 January 20. Available online: https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/special-topics/emergency-preparedness/notification-enforcement-discretion-telehealth/index.html (accessed on 4 May 2022).
| Author | Sample | Clinical Description | Country | Outcome Measure | Patient Satisfaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bryan A. Johnson et al. | n = 785 patients Response rate = 38.4% | Oncology Clinic | USA | 40—questions survey with a 7-point Likert scale ranging responses | The median patient satisfaction score was 5.5 (interquartile range [IQR] 4.25–6.25). The median telemedicine usability score was 5.6 (IQR 4.4–6.2). A strong positive correlation was seen between satisfaction and usability, with a Spearman correlation coefficient (ρ) of 0.80 (p < 0.001) [19] |
| Mohamed E. Ahmed et al. | n = 52 patients | Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinic | USA | 28—item survey; patient satisfaction were measured with both closed 5—point Likert scale ranging responses, | The median degree of satisfaction was 9 on a 10-point scale, with 10 being the highest level of satisfaction [54] |
| Elisa Picardo et al. | n = 345 patients | Oncology Clinic | Italy | 22—item survey with both closed 6—point Likert scale ranging responses | The results of the present study show that patients with pelvic cancer were more satisfied with telemedicine compared to patients in the breast cancer group (p = 0.058). Moreover, the breast cancer group reported telemedicine as comparable as face-to-face consultation more than pelvic cancer group, even though they were overall less satisfied (p = 0.0001) [20] |
| Rachel P. Mojdehbakhsh et al. | n = 113 patients Response rate = 74.8% | Gynaecologic Oncology Clinic | USA | 10—question survey with patient satisfaction rate measured using 4—point scale | The overall telemedicine treatment experience was rated as excellent by 63.7% of patients (n = 72), good by an additional 24.8% (n = 28). Overall, 82.3% of patients endorsed using telemedicine again and 85.8% would recommend using telemedicine to another person [21] |
| Ajithray Sathiyaraj et al. | n = 70 patients Response rate = 21% | Cancer Center | USA | 11—questions survey | 73% of cancer patients undergoing prechemotherapy evaluation were satisfied with the video visit experience. 70% of patients believed that video visits were as good as in-person visits, but 65% of patients stated that an in-person visit was their preferred method [22] |
| Philip J. Chang et al. | n = 76 patients Response rate = 45.8% | Rehabiliation Cancer Center | USA | 7—items survey with 5—point Likert scale ranging | 94.8% of patient responses reported “quite a bit” or “very much” for the telemedicine visit being a good experience; 63.1% of patient responses reported “quite a bit” or “very much” for interest in using telemedicine visits in the future [23] |
| Michael Meno et al. | n = 212 patients Response rate = 49.8% | Cancer Clinic | USA | 5—item survey with 5 -point Likert scale ranging responses; | Most patients felt that the overall quality of the telehealth visit was the same as that experienced with an office visit (55.2%) or better (10.4%). Half of the patients (50%) found the personal connection in office visits to be better [25] |
| Adeel Abbas Dhahri et al. | n = 43 patients | Surgery Clinics | United Kingdom | 12—question survey with 5—point Likert scale measuring patient satisfaction | Overall experience with most of the patients was positive (41/43; 95.34%). All (100%) patients thought that the video telemedicine solution met their needs. 93% of respondents recommended to use it for future consultations [48] |
| T. J. Horgan et al. | n = 109 patients Response rate = 80.74% | Oral and Miaxillofacial Surgery Department | USA | 16—question survey (G-MISS) with 5—point Liker scale ranging and additional survey | The total mean (SD) G-MISS score for satisfaction was high at 82.12 (7.96) indicating a high level of satisfaction among all patients. 83.48% found telephone consultation to be as convenient [47] |
| Alicia Ruiz de la Hermosa et al. | n = 1706 patients | General Surgery Clinic | Spain | 5—question survey; patient satisfaction measured with 10—point scale ranging responses | The overall satisfaction was 8.7 out of 10. 37.2% would preferred a face-to-face visit because of difficulties with the teleconsultation [49] |
| Aminah Sallam et al. | n = 50 patients Response rate = 57.5% | Cardiac Surgery Clinic | USA | 24—item survey; patient satisfaction measured with 5—point Likert scale ranging; | Patients described the ability of their surgeons to diagnose problems and the thoroughness and skill of their surgeon in treating their conditions as good to excellent (mean score of 4.3, SD 0.9). Patients expressed satisfaction with the care they received (mean score 4.8, SD 0.5) [50] |
| Elvina Wiadji et al. | n = 1166 patients Response rate = 12.3% | Surgery Clinic | Australia | 29—item survey; patient satisfaction measured using 4—point scale ranging responses; | The majority of patients (94%), were satisfied with the quality of their surgical telehealth consultation and 75% felt it delivered the same level of care as face-to-face encounters [51] |
| Brenden Drerup et al. | n = 65 patients Response rate = 67.7% | Primary and Specialty Care Clinic | USA | 9—question survey using both closed 5—point Likert scale responses | Patients who experienced telehealth visits had similar responses to seven of nine satisfaction metrics when compared with those who attended in-office visits [12] |
| Fiona Imlach et al. | n = 1010 patients Response rate = 84.87% | Primary Care Clinic | New Zealand | Online patient survey with open-ended questions | Overall satisfaction with telehealth was high, at 91% for video and 86% for telephone consultations, but was slightly lower than in-person visits (92%) [13] |
| Ashwin Ramaswamy et al. | n = 38.609 patients | Outpatient Clinic | USA | 19—item survey with 5—point Likert scale ranging responses | Patient satisfaction with video was significantly higher than in-person visits (94.9% vs. 92.5%, p < 0.001) [58]. |
| Tanya Ngo | n = 86 patients | Student—Run Free Clinic | USA | Survey with patient satisfaction rate measuring with 8—question with 3—point Likert scale ranging | Overall, most patients reported feeling satisfied with their telehealth experience (97.6%). However, only 64 patients (74.4%) felt that their telemedicine visits were as good as in-person clinic appointments [57] |
| Hyung Youl Park et al. | n = 906 patients Response rate = 13.2% | Outpatient Clinic and Emergency Room | Republic of Korea | 5—item patient survey; | Overall satisfaction was reported by 86% of patients, whereas only 52.7% of doctors were satisfied with telemedicine (p = 0.000 for both doctors and nurses compared with patients). 87.1% of patients thought telemedicine had the same reliability as in-person visits [56] |
| Lucinda Adams et al. | n = 128 patients Response rate = 29% | Rheumatology Clinic | Australia | 18—questions survey using both closed 5-point Likert scales ranging responses and four free-text questions | 61.7% agreed or strongly agreed when asked, ‘In general, I am satisfied with the telemedicine system’ [26]. |
| Mahta Mortezavi et al. | n = 359 patients Response rate = 70.1% | Rheumatology Clinic | USA | 3—item survey with both closed 5—point Likert scale ranging responses | The majority of patients (74%) were satisfied with their virtual visit, but they were more likely to be satisfied if their visit was over video rather than phone. They preferred an in-person visit if they were meeting a doctor for the first time [27] |
| Jesus Tornero—Molina et al. | n = 469 patients | Rheumatology Clinic | Spain | Survey with 10—point scale measuring patient satisfaction | The mean levels of satisfaction with the rheumatology teleconsultation procedure were very high (8.62). Over 80% of patients attended would repeat the teleconsultation and 79.3% considered them useful. The need for a face-to-face consultation after teleconsultation was not analyzed [28] |
| Matthew T. Jones et al. | n = 297 patients | Rheumatology Clinic | United Kingdom | 30-item questionnaire consisted of single and Likert scale responses. | Overall, 150 (52%) and 69 (24%) responses indicated satisfaction with the telephone consultation by either agreeing or strongly agreeing, respectively. 60% would be happy to have future routine follow-up telephone consultations [29] |
| Eleanor Layfield et al. | n = 100 patients Response rate 68.49% | Head and Neck Otolaryngology Clinic | USA | 21—questions survey with both closed 7—point Likert scale ranging responses | The total average score was 6.01. The highest scores were for questions related to satisfaction with telehealth (6.29), while the lowest was related to reliability (4.86) [30] |
| Janet S. Choi et al. | n = 407 patients Response rate = 19% | Otolaryngology Clinic | USA | 14—item survey with 5—point Likert scale ranging (TQS) | Mean Press Ganey patient satisfaction scores during COVID-19 remained high at 94.5 (SD, 8.8; range, 20–100) for telemedicine visits. Patient satisfaction (TSQ score) for all telemedicine encounters was high at 4.17 (SD, 0.2; range, 1–5). Mean (SD) TSQ scores were 4.2 (0.67) and 3.67 (0.83) for videoconference and telephone encounters, respectively [33] |
| Phoebe Elizabeth Riley et al. | n = 325 patients | Otolaryngology Clinic | USA | 10—question survey with 5—point Likert scale ranging | Patients demonstrated the high satisfaction with telemedicine (average score, 4.49 of 5). High satisfaction was consistent across groups for distance to travel, age, and reason for referral [34]. |
| M. Fieux et al. | n = 100 patients | Otolaryngology Clinic | France | 12—question survey with 5—point Likert scale | 98% of patients responded that the physician had answered all of their questions, while 49% felt teleconsultation was not equivalent to face-to-face consultation [35] |
| Andrew M. Rizzi et al. | n = 299 patients Response rate = 66.4% | Orthopaedic Clinic | USA | standardized validated post-visit satisfaction survey | Not recorded [16] |
| Sandeep Kumar et al. | n = 450 patients Response rate = 88.67% | Orthopaedic Clinic | India | 6—questions survey | The overall satisfaction-rate to telemedicine was 92%, and only 7.2% of patients had difficulty in understanding or following telemedicine-based advice [17] |
| Lesslie J. Bisson et al. | n = 2049 patients | Orthopaedic Practise | USA | 9—question survey with 5—point Likert scale ranging. The Patient Satisfaction Aggregate (PSA) score was estimated by taking the average of the five questions stated above with 5-point interval scales and transformed to a 0 to 1 continuous scale | No significant differences between modes of visit were observed for explanation (p = 0.22), spending enough time (p = 0.23), overall service from physician (p = 0.28), recommend to others (p = 0.59), call center (p = 0.49), physical therapy (p = 0.75), physician staff (p = 0.16), or billing staff (p = 0.23) [18] |
| Megan V. Morisada et al. | n = 69 patients | Rhinology Clinic | USA | 18—item survey with 5—point Likert scale ranging responses | There was no difference in patient satisfaction between the virtual visits (mean total sum score = 78.1) and clinic visits (mean total sum score = 78.4) groups (p = 0.67) [31] |
| Firas Hentati et al. | n = 45 patients Response rate = 42.1% | Rhinology Clinic | USA | The survey consisted of 8 close—ended and 3 open—ended question on patient experience and satisfaction | 80% of patients stated that their needs were met during their telemedicine visit. 77.8% of respondents declared they would do another virtual visit in the future if the pandemic ends [32] |
| S.M. Shahid et al. | n = 53 patients | Ophthalmology Clinic | United Kingdom | 11—question survey with patient satisfaction rate measuring with 5—point Likert scale | The patients scored the overall satisfaction at a mean of 4.3 out of 5. 91% of respondents felt that they received the appropriate advice regarding the postoperative drop regime [52] |
| Vidushi Golash et al. | n = 120 patients | Oculoplastic Clinic | United Kingdom | 20/22—question survey with 10—point scale measuring convenience and patient satisfaction | 55 % of telephone and 82.5% of video consultation patients felt face-to-face reviews would not have changed the appointment outcome. Satisfaction scores of 10/10 were given by 71.3% of telephone and 72.5% of video consultation patients [53] |
| Alexander M. Satin et al. | n = 772 patients Response rate = 21.9% | Spine Surgeon Private Clinic | USA | 8—questions survey with patient satisfaction rate measured using 5—point Likert scale | Overall, 87.7% of patients reported that they were satisfied with their telemedicine visit with 70% reporting a score of 5 out of 5 (“very satisfied”) [44] |
| Sheena Bhuva et al. | n = 172 patients Response rate = 25% | Spine Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinic | USA | 10—questions survey with patient satisfaction rate measured using 5—point Likert scale | 97.6% were very satisfied or satisfied (83.7% of the patients were very satisfied) with their telemedicine appointment. 64.5% of the patients preferred telemedicine over in-person appointments [45] |
| Karim Shafi et al. | n = 84 patients Response rate = 76% | Spinal Disorders Facility | USA | 7—question survey with 5—point Likert scale measuring patient satisfaction | 81.0% of respondents reported that they were “extremely satisfied” (5/5) with their visit. 75.6% of patients noted that they were “extremely satisfied” with their treatment plan, with a mean score of 4.71 (SD = 0.55) [46] |
| Amol Raheja et al. | n = 231 patients | Neurosurgery Clinic | India | 16—question survey with patient satisfaction measured using 5—point Liker scale ranging responses | The majority of the respondents (58%) either agreed/strongly agreed that teleconsultation helped them tide over the medical exigency during the lockdown; however, the clinical diagnosis did not influence this response (p = 0.21). The vast majority of the respondents felt that teleconsultation is beneficial (97%), as it minimizes their exposure to COVID-19 [11]. |
| Ken Porche et al. | n = 698 patients | Neurosurgery Clinic | USA | 9—question surveys with patient satisfaction rate measured using 5—point Likert scale | Patient overall satisfaction score was slightly higher with telemedicine visits compared to in-person corrected for care provider differences (94.2 ± 12.2 vs. 93.1 ± 13.4, p = 0.085) [10]. |
| Alina Mohanty et al. | n = 122 patients Response rate = 20% | Neurosurgery Clinic | USA | 13—question survey using both closed 5—point Likert scale responses and multiple choice responses | 92 % of patients were satisfied with particular telehealth visit. 88 % of patients claimed that telehealth visit was more convenient for them than an in-person visit [8] |
| Elise J. Yoon et al. | n = 310 patients Response rate = 52.6% | Neurosurgery Division | USA | Survey using both closed 7—point Likert scale ranging responses | The mean overall satisfaction score was 6.32 ± 1.27. Subgroup analyses by new/established patient status and distance from their home to the clinic showed no significant difference in mean satisfaction scores between groups [9] |
| S. Shahzad Mustafa et al. | n = 177 patients Response rate = 61% | Allergology and Immunology Practise | USA | Survey using both closed 5—point Linkert scale ranging responses | Nearly 97% of patients were satisfied with their telemedicine encounter, and 77.4% believed it was as satisfactory as an in-person encounter [40] |
| Kasey Lanier et al. | n = 162 patients Response rate = 58% | Allergology Clinic | USA | 6—question survey with responses scaled from 0 to 10 (the highest satisfaction score). The scale was dichotomized as a response of 10 versus less than 10, in accordance with other measures of patient satisfaction. | Overall, 88% of patients rated their comfort level seeing a doctor via telemedicine as a 10. 93% of respondents stated that their doctor explained their condition in an easily understood manner. 77% of patients would strongly recommend telemedicine services to others [41] |
| Judy Hamad et al. | n = 184 patients Response rate = 63.88% | Dermatology Clinic | USA | 25—questions survey using both closed 12 point Likert scale responses | 86.4% (159/184) of participants reporting positive overall satisfaction and experiences with teledermatology. New patients had significantly higher Likert scores for overall satisfaction with teledermatology than those of follow-up patients (new patients: mean 4.70; existing patients: mean 4.43; p = 0.03) [14] |
| Sumithra Jeganathan et al. | n = 91 patients Response rate = 10.6% | Obstetric Clinic | USA | 11—questions survey using both closed 6 point Likert scale responses | Overall, 86.9% of patients were satisfied with the care they received and 78.3% would recommend telehealth visits to others [15] |
| S. Glass Clark et al. | n = 94 patients | Urogynecology Office | USA | 6—questions survey using both closed 5—point Likert scales ranging responses and additional comments or concerns | The majority of patients answered either “agree” or “strongly agree” with the statement “All of my questions and concerns were addressed to my satisfaction during my video visit” (n = 89, 94.7%) [36]. |
| Kadri Haxhihamza et al. | n = 28 patients | Psychiatry Clinic | North Macedonia | anonymous 18—questions survey using both closed 5—Likert scale responses | Overall satisfaction with psychiatric care was high (80.22%) [38] |
| Devinder Kaur et al. | n = 106 patient Response rate = 61.3% | Diabetes and Endocrinology Clinic | United Kingdom | Survey using the 5 -point Likert scale ranging responses | Overall, 97% of respondents indicated that they were satisfied with the quality of service being provided via telemedicine [42] |
| Zia Rahman et al. | n = 98 patients Response rate = 49.7% | Gastroenterology Clinic | United Kingdom | 15—item survey; patient satisfaction were measured with 5—point Likert scale | High satisfaction scores were reported more in patients who had a prior consultation in a face-to-face clinic, i.e., follow-up group (51/66; 77.3%), than patients who had audio-consultation in their first clinic visit, i.e., new patient (15/32; 46.9%) [43] |
| Sharon Orrange et al. | n = 368 patients Response rate = 22.7% | Internal Medicine Clinic | USA | 11—question surveys with patient satisfaction rate measured using 5—point Likert scale | Across the study, respondents were very satisfied (173/365, 47.4%) or satisfied (n = 129, 35.3%) with their telemedicine visit. Higher physician trust was associated with higher patient satisfaction (Spearman correlation r = 0.51, p < 0.001) [39] |
| Allanah Smrke et al. | n = 108 patients | Sarcoma Unit | United Kingdom | Patient experience survey (online or paper) | Mean satisfaction with telephone consultation was higher than face-to-face consultation (rating 8.99/10 v 8.35/10, respectively). The majority of patients (n = 86; 80%) indicated that they would like at least some future appointments to be performed using telemedicine [24] |
| Aniruddha Singh et al. | n = 120 patients Response rate = 11% | Cardiology Clinic | USA | 24—item survey; patient satisfaction measured with 5—point Likert scale ranging responses | The no-show rate for telehealth visits (345/2019, 17%) was nearly identical to the typical no-show rate for in-person appointments. (17%). Both in-person and telehealth were viewed favorably, but in-person was rated higher across all domains of patient satisfaction [37] |
| Agathoklis Efthymiadis et al. | n = 119 patients | Urology Clinic | United Kingdom | 7—question survey with 4—point Likert scale ranging responses; | The majority of responses to the adapted survey (Q1–7) were graded as ‘Excellent’, ranging from 79 (66%) to 112 (94%). ‘Agree’ responses ranged from 92 (77%) to 117 (98%) for questions (Q8–12), indicating high satisfaction [55] |
| Author | Patient Clinical Needs | Willingness to Use Telemedicine in the Future | Technical Aspects | Time Save | Missed Appointment Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bryan A. Johnson et al. [19] | Not recorded | Not recorded | During the telemedicine visit, most of the patients did not report any connection trouble (61.3%) | Patient characteristics, including location of residence (p = 0.421) was not significantly related to satisfaction score. | Note recorded |
| Mohamed E. Ahmed et al. [54] | All patients verified that their physician had adequately explained their diagnosis and treatment options. | 94% of the patients shared that they would participate in a future teleconsultation if it was offered | The most patients (94%) agreed that they were able to hear (and see) their physician clearly. | Patients reported that saving on travel represented the most important advantage of having virtual consultations, | Not recorded |
| Elisa Picardo et al. [20] | The breast cancer group reported telemedicine as comparable to a face-to-face appointment more than the pelvic cancer group, even though they were overall less satisfied (statistically significant, p = 0.001) | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Rachel P. Mojdehbakhsh et al. [21] | A total of 68.1% (n = 77) of patients felt that the explanation of treatment by the telemedicine staff was excellent and an additional 25.7% (n = 29) said the explanation was good. | Overall, 82.3% of patients endorsed using telemedicine again. | There was overwhelming satisfaction with voice quality of the encounter as 75.2% (n = 85) responded excellent and 21.2% (n = 24) responded good. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Ajithray Sathiyaraj et al. [22] | While most patients (70%) reported that video visits were just as good as in-person visits, none said that they were better. | 80% of patients also reported that they probably or definitely would use video visits if it were an option in the future. | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Philip J. Chang et al. [23] | Satisfaction tended to be marginally higher when encounters were for stable or were conducted through video versus phone. | 43.3% of patients are interested in using phone/video visits in the future | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Michael Meno et al. [25] | Most patients felt that the overall quality of the telehealth visit was the same as that experienced with an office visit (55.2%) or better (10.4%) | Preference for wanting some future visits to be telehealth was seen in only 57.1% of patients. | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Adeel Abbas Dhahri et al. [48] | All (100%) patients thought the video telemedicine solution met their needs. | Majority (n = 40; 93.02%) of the patients of the patients opted to choose video consultation for future again | Majority of the patients were pleased with the sound quality (33; 76.74%) and the video quality (34; 79.06%). | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| T. J. Horgan et al. [47] | Over ninety percent of patients felt as able to ask questions and 94.49% understood the information given just as easily. | Overall, 83.48% of patients said they would be willing to have a telephone consultation in future. | Not recorded | 83.48% of patients found telephone consultation to be as convenient. | Not recorded |
| Alicia Ruiz de la Hermosa et al. [49] | The 73.6% considered that teleconsultation was able to fully or partially resolve the reason for their medical appointment | Not recorded | 37.2% would preferred a face-to-face visit because of difficulties with the teleconsultation. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Aminah Sallam et al. [50] | 74 % of Patients who received telemedicine consultation and 57% of patients who received video consultation, rated their surgeon’s ability to diagnose problems as excellent. | 12% telemedicine and 39% video consultation patients said they would prefer their next postoperative appointment to be via telemedicine even if there was not a stay-at-home order in place. | The majority of respondents could hear their surgeon clearly. | Of the patients who said they preferred telemedicine visits, 79% reported an average travel distance of 23 miles, 96% reported an average travel time of 32.5min, and 87% reported an average cost of $6.70. | Not recorded |
| Elvina Wiadji et al. [51] | Most patients were satisfied with the quality of their telehealth consultation (94%) | Telephone consultations would be considered by 34% and video-link consultations by 49% | Only 63 (5.5%) patients reported a technical issue when connecting to telehealth. | Telehealth consultations were associated with out-of-pocket cost savings for 60% of respondents and included savings due to less time off work for themselves (19%) or their carer (1%), transport (49%), accommodation (7%), childcare (1%) and other (2%) costs. | Not recorded |
| Brenden Drerup et al. [12] | 86 % of patients claimed that providers listened to concerns. | 90.8 % of patients recommend this practice to others. | The most frequently suggested improvement from patients was related to improving technology, often quoted as the need for better internet connection and video quality (20% of patients) | Not recorded | the no-show (missed appointment) rate was 36.1% (56/155) compared with the telehealth visit no-show rate of 7.5% (14/186) |
| Fiona Imlach et al. [13] | 98 % of surveyed patients claimed the physicians explain their concerns in easily way. | 80% of patients would like to have telephone consultation and 69% would use video consultation in the future, | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Ashwin Ramaswamy et al. [58] | patient satisfaction with video was significantly higher than in-person visits (94.9% vs. 92.5%, p < 0.001) | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Tanya Ngo [57] | 83 participants (96.5%) reported satisfaction with their care in terms of the amount of time the attending provider spent with them | 75 patients (87.2%) stated that they would like to continue with telemedicine visits in the future. | Not recorded | 76% of patients reporting that remote clinic visits made it possible for them to attend an appointment they would not otherwise have been able to. | Not recorded |
| Hyung Youl Park et al. [56] | 87.1% of patients thought telemedicine had the same reliability as in-person visits. | 85.1% of patients were willing to use telemedicine service again. | Not recorded | Almost 80% of patients reported the convenience of telemedicine | Not recorded |
| Lucinda Adams et al. [26] | The most of patients (75%) reported that their physician easily resolved their problems. | 48.3% of respondents would continue to use telemedicine after COVID-19 | 50 % of patients rated telemedicine as “easy to use”. | 75% of patients confirmed the convenience and time-saving due to telemedicine. | Not recorded |
| Mahta Mortezavi et al. [27] | 74% of patients were satisfied with their telemedicine encounter. | Not recorded | 3.6% of patients would have preferred an in-person visit instead because of technical issue. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Jesus Tornero – Molina et al. [28] | Patients were more satisfied with the telemedicine when their level of education were higher (OR = 4.12) | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Matthew T. Jones et al. [29] | (84%) agreed their rheumatological health issues were satisfactorily addressed | 169 of the questionnaire responders (60%) indicated they would be happy to have telephone consultations routinely in their future care. | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Eleanor Layfield et al. [30] | Many of the patients who were willing to have another telemedicine visit agreed they felt telehealth met their needs. | Many participants (n = 25, 44.6%) also offered thoughts on the future use of telemedicine | Most patients found the connection process easy, whereas others reported technical challenges, including issues with connectivity and audio. | A common theme expressed by patients was that these visits were much more time efficient. | Not recorded |
| Janet S. Choi et al. [33] | Mean Press Ganey patient satisfaction scores during COVID-19 remained high at 94.5 (SD, 8.8; range, 20–100) for telemedicine visits | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Phoebe Elizabeth Riley et al. [34] | The majority (78.8%) of patients felt that their provider had all the information needed to make a diagnosis and treatment. | Not recorded | Not recorded | Patients reporting a distance from their provider of 21 to 50 miles demonstrated an association with decreased overall satisfaction (odds ratio, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.24–0.82; p = 0.01) when compared with patients 0 to 20 miles and ≥50 miles from their provider. | Not recorded |
| M. Fieux et al. [35] | 98% patients claimed that the physician had answered all of their questions. | The majority of patients (68%) were willing to use teleconsultation in the future. | Sound quality was judged poorly or not satisfactory by 24% of patients and video quality by 39%. | 72% appreciated the time and cost savings. | Not recorded |
| Andrew M. Rizzi et al. [16] | Patients reported that surgeons demonstrated appropriate response to their concerns rating ‘good’ or ‘very good’ 95% of the time. | 93% of patients reported they would participate in a telemedicine encounter again | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Sandeep Kumar et al. [17] | 92% of patients are satisfied with medical care they received during telemedicine | 92% of respondents would recommend telemedicine to others | 7.3% of patients found difficulty in understanding the process of teleconsultation | 22.3 % found telemedicine as convenient | Not recorded |
| Lesslie J. Bisson et al. [18] | There were no difference in patient satisfaction between telemedicine and in-person orthopedic encounters during the COVID-19 pandemic. | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Megan V. Morisada et al. [31] | There were no statistically significant differences in mean scores between the virtual visits and in-person visits with the interpersonal manner of the physician (p = 0.41), satisfaction with communication (p = 0.31), satisfaction with the time spent with doctor (p = 0.88). | Not recorded | There were no statistically significant differences in mean satisfaction scores between virtual visits and in-person visits with technical quality of care (p = 0.89) | There were no statistically significant differences in mean satisfaction scores between virtual visits and in-person visits with financial aspects of care (p = 0.89) | Not recorded |
| Firas Hentati et al. [32] | 90% of patients claimed that thier needs were met during the telemedicine visit. | 61.8% of patients were more likely to prefer the telehealth experience to being seen in-person. | The most commonly cited disadvantage to virtual visits was technological difficulties (17.8%). | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| S.M. Shahid et al. [52] | Forty-eight patients (91%) felt that they received the appropriate advice. | 19 patients (36%) felt that telemedicine is not an appropriate platform to replace face-to-face consultations, after the COVID-19 pandemic | The satisfaction score for the clarity of the phone call was 4.9 out of 5. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Vidushi Golash et al. [53] | 100% of respondents felt they were listened to by their doctor and had enough time to discuss their individual situation. | 82.5% of patients who had a video consulation felt a face-to-face review would not have changed the outcome of their consultation. | 57.5% of participants experienced no technical problems. The most common difficulty (20%) was problems with audio. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Alexander M. Satin et al. [44] | Overall, 87.7% of patients reported that they were satisfied with their telemedicine visit with 70% reporting a score of 5 out of 5 (“very satisfied”) | Not recorded | One-third of patients reported the issue with their telemedicine encounter-problems with video and audio (11.5%, and 9.7%, respectively). | Withmregard to mileage saved by a telemedicine visit, the majority of patients (56.9%) were within 25 miles round trip of their doctor’s office with a smaller subset of patients traveling over 100 miles (16.6%) | Not recorded |
| Sheena Bhuva et al. [45] | Overall, 83.7% of the patients were very satisfied with their telemedicine appointment and 13.9% were satisfied with the telemedicine appointment. | 64.5% of the patients would rather have telemedicine over in-person appointments | Only 8% and 3% had issues with the video and audio, respectively | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Karim Shafi et al. [46] | The majority of all patients noted that they were “extremely satisfied” with their treatment plan, with a mean score of 4.71 (SD = 0.55). | Not recorded | Ease of navigation was also scored highly, with a mean score of 4.32 (SD = 0.88). Of the 84 patients, only 2.4% noted that it was “very difficult” (1/5) to navigate the telehealth visit | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Amol Raheja et al. [11] | Not recorded | 33.3% of patients will prefer teleconsultation services over physical outpatient services even after its resumption. | Overall 15% (n = 35) patients faced difficulties during teleconsults. | Reduction of travel expenditure (n = 155, 67%), efficient utilization of time and resources for patients and their caregivers (n = 113, 49%) are the crucial advantages of telemedicine. | Not recorded |
| Ken Porche et al. [10] | Patients that underwent a telemedicine visit were more satisfied with the care provider’s explanations about their medical conditions, and were more satisfied with the concern the care provider showed for their questions compared to an in-person visit. | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Alina Mohanty et al. [8] | 91% of patients agreed that their provider satisfactorily addressed their clinical needs. | 36% of patients stated they would like their future visits to be telehealth visits, with 48% patients stating they felt neutrally about this statement. | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Elise J. Yoon et al. [9] | Patients rated the physician’s involvement in providing medical care as 6.70 ± 0.85. | The mean score for willingness to use telemedicine again was 5.56 ± 1.93 (mean ± SD) | The mean score for telemedicine visit equipment was 6.12 ± 1.55. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| S. Shahzad Mustafa et al. [40] | 77.4% patient believed telemedicine was as satisfactory as an in-person encounter. | Not recorded | 4.2 % of patients experienced technical problems. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Kasey Lanier et al. [41] | 93% of patients agree/strongly agree that the doctor explained their medical condition in a way they could understand. | 46% preferred the teleconsultation over in-person visit in the future. | 79% of patients claimed that connecting and starting telemedicine appointment was easy. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Judy Hamad et al. [14] | Almost 90% of patients rated the skillfulness of their providers as “very good” or “excellent”. | Logistic regression showed that prior telehealth experience was associated with higher odds of being willing to use teledermatology in the future (odds ratio [OR] 2.39, 95% CI 1.31–4.35; p = 0.004). | Patients’ satisfaction with visual quality was slightly higher than their satisfaction with voice quality and similar between follow-up patients and new patients. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Sumithra Jeganathan et al. [15] | Almost 60% of patients “strongly agree” and 30% of patient “agree” that the most of their questions and concerns were addressed. | 78.3% would recommend telehealth visits to others | 84.7% of patients found the process of connecting to their appointment easy | Not recorded | Telehealth visits also had a lower no-show rate; however, this difference was not statistically significant. |
| S. Glass Clark et al. [36] | The majority of patients answered either “agree” or “strongly agree” with the statement “All of my questions and concerns were addressed to my satisfaction during my video visit” (n = 89, 94.7%) | majority preferred to see the specialist in person, despite travel inconveniences, at their next visit (n = 66, 70.2%} | Not recorded | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Kadri Haxhihamza et al. [38] | 71 % of respondents rated their receiving medical care just about perfect. | Not recorded | Technical quality were rated the lowest of all aspect of telemedicine. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Devinder Kaur et al. [42] | 98% of patients received adequate attention during the telephone follow-up session. | 92% of patients would use telemedicine in the future, If the situation arose | 98% of patients heard their physician clearly over the telephone. | All patients agreed telephone follow-up provides a timely and convenient service. | Not recorded |
| Zia Rahman et al. [43] | 77.5% of patients remarked that their expectations were met | Not recorded | Not recorded | (69.4%) of the survey patients commented that the telephone consultation saved them time and money. | Not recorded |
| Sharon Orrange et al. [39] | 90.1% (327/363) strongly agreed or agreed that the amount of time spent with the provider was adequate. | 77.3% (279/361) reported that they “look forward to using telehealth in the future.” | Almost one-third of patients (114/365, 31.3%) had technical issues during the visit. | Not recorded | Not recorded |
| Allanah Smrke et al. [24] | Almost half (n = 42; 48%) would not want to hear bad news over the phone, with no difference based on age, sex, or education level. | The majority of patients (n = 86; 80%) indicated that they would like at least some future appointments to be performed using telemedicine | Not recorded | Common reasons for telemedicine preference were reduced travel time (n = 45; 42%), reduced travel expenses (n = 21; 20%) and convenience (n = 32; 30%). | Not recorded |
| Aniruddha Singh et al. [37] | Not recorded | 120 respondents, 100 (83.0%) indicated they would at least consider using telehealth in the future, including 59 (49.2%) who said they were likely to or would prefer to use telehealth going forward. | Poor internet connectivity was of most concern, rated as at least somewhat of a factor by 35 (33.0%) respondents. | Reduced travel time was seen as a big advantage over traditional in-person appointments by 61 (57.5%) of the 106 respondents who participated in telehealth, | the no-show rate for telehealth visits (345/2019, 17%) was nearly identical to the typical no-show rate for in-person appointments |
| Agathoklis Efthymiadis et al. [55] | 96% of patients were satisfied with their telemedicine appointment. | 92 (77%) patients reported that they would like to use telephone consultation after the COVID-19 outbreak. | 99% of patient rated the voice quality of appointment as “excellent” or “good” | 98% of patients reported that the telephone consultation saved them time from travelling to the hospital. | Not recorded |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pogorzelska, K.; Chlabicz, S. Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine during the COVID-19 Pandemic—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106113
Pogorzelska K, Chlabicz S. Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine during the COVID-19 Pandemic—A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):6113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106113
Chicago/Turabian StylePogorzelska, Karolina, and Slawomir Chlabicz. 2022. "Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine during the COVID-19 Pandemic—A Systematic Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 6113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106113
APA StylePogorzelska, K., & Chlabicz, S. (2022). Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine during the COVID-19 Pandemic—A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 6113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106113






