Restraint Use for Child Occupants in Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Abstract
1. Introduction
Study Objectives
- What is the type and frequency of restraint use (i.e., CRS, booster seat and seatbelt) for child occupants aged 10 years and younger while travelling in their motor vehicles?
- What are the factors that influence the frequency of restraint use for child occupants aged 10 years and younger?
- What are the factors that influence appropriate restraint use for child occupants aged 10 years and younger?
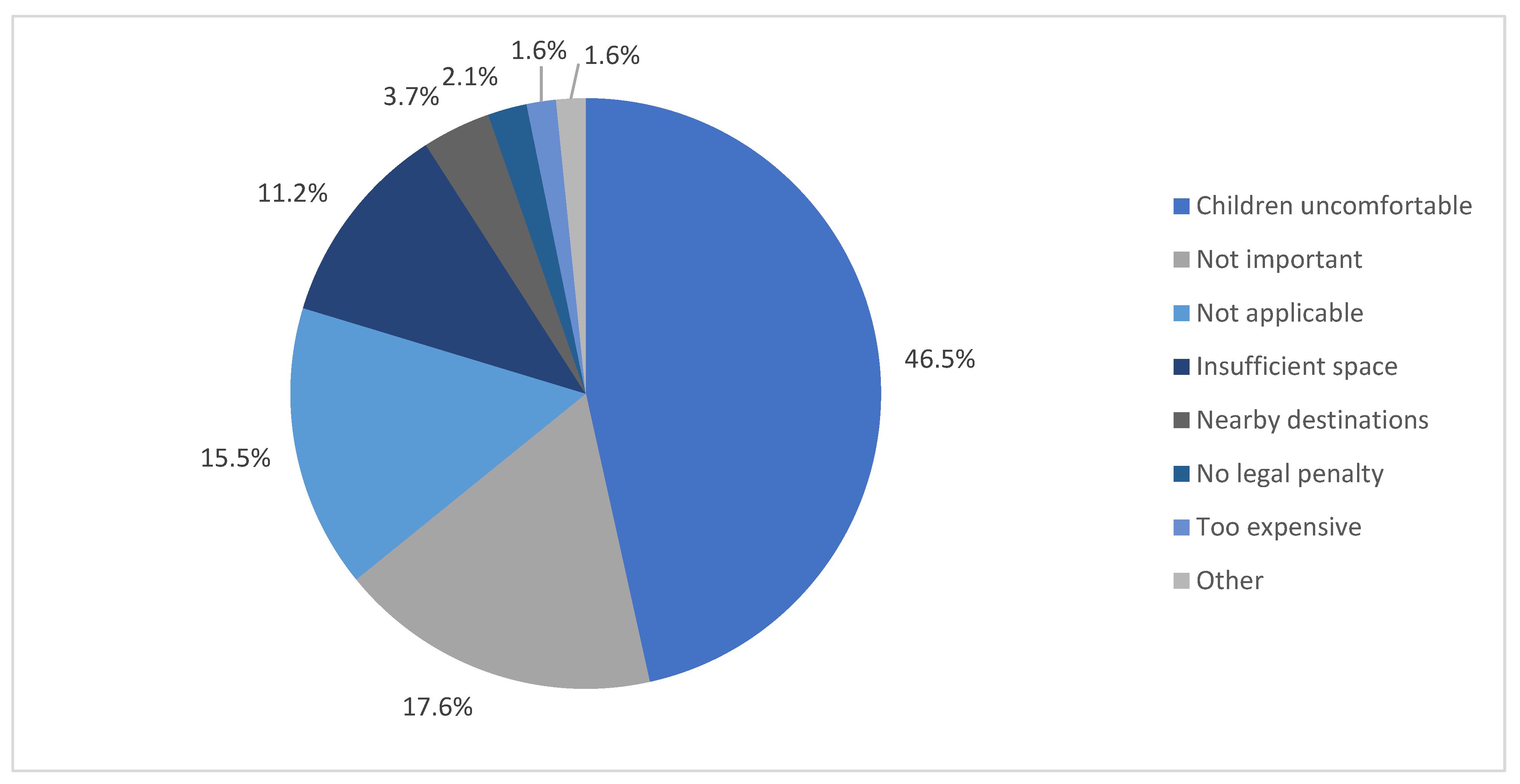
- What are the reasons for restraint non-use?
- What is the level of awareness regarding the introduction of CRS and boosters seat legislation in the UAE?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Socio-Demographic Characteristics
2.2.2. Child Characteristics and Restraint Use
2.2.3. Non-Use of Restraint for Children
2.2.4. General Knowledge
2.2.5. Responses
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Socio-Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Child Characteristics and Restraint Use
3.3. Factors That Influence Frequency of Restraint Use for Child Occupants
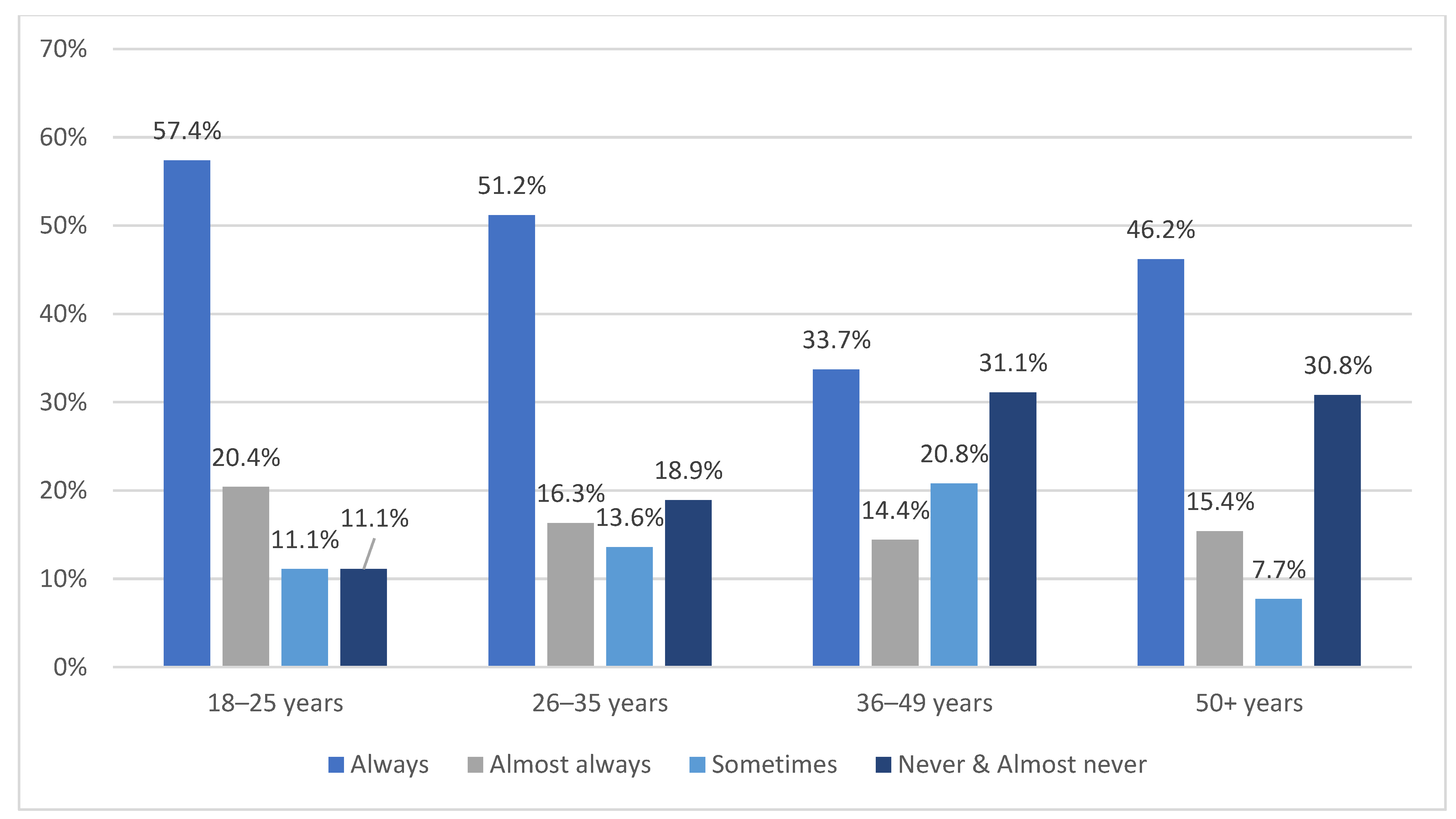
3.3.1. Participants’ Age Group by Frequency of Child’s Restraint Use
3.3.2. Participants’ Gender by Frequency of Child’s Restraint Use
3.3.3. Participants’ Education Level by Frequency of Child’s Restraint Use
3.3.4. Participants’ Nationality by Frequency of Child’s Restraint Use
3.3.5. Participants’ Seatbelt Use by Frequency of Child’s Restraint Use
3.3.6. Participants’ Emirate of Residency by Frequency of Child’s Restraint Use
3.4. Child-Related Factors That Influence Restraint Use
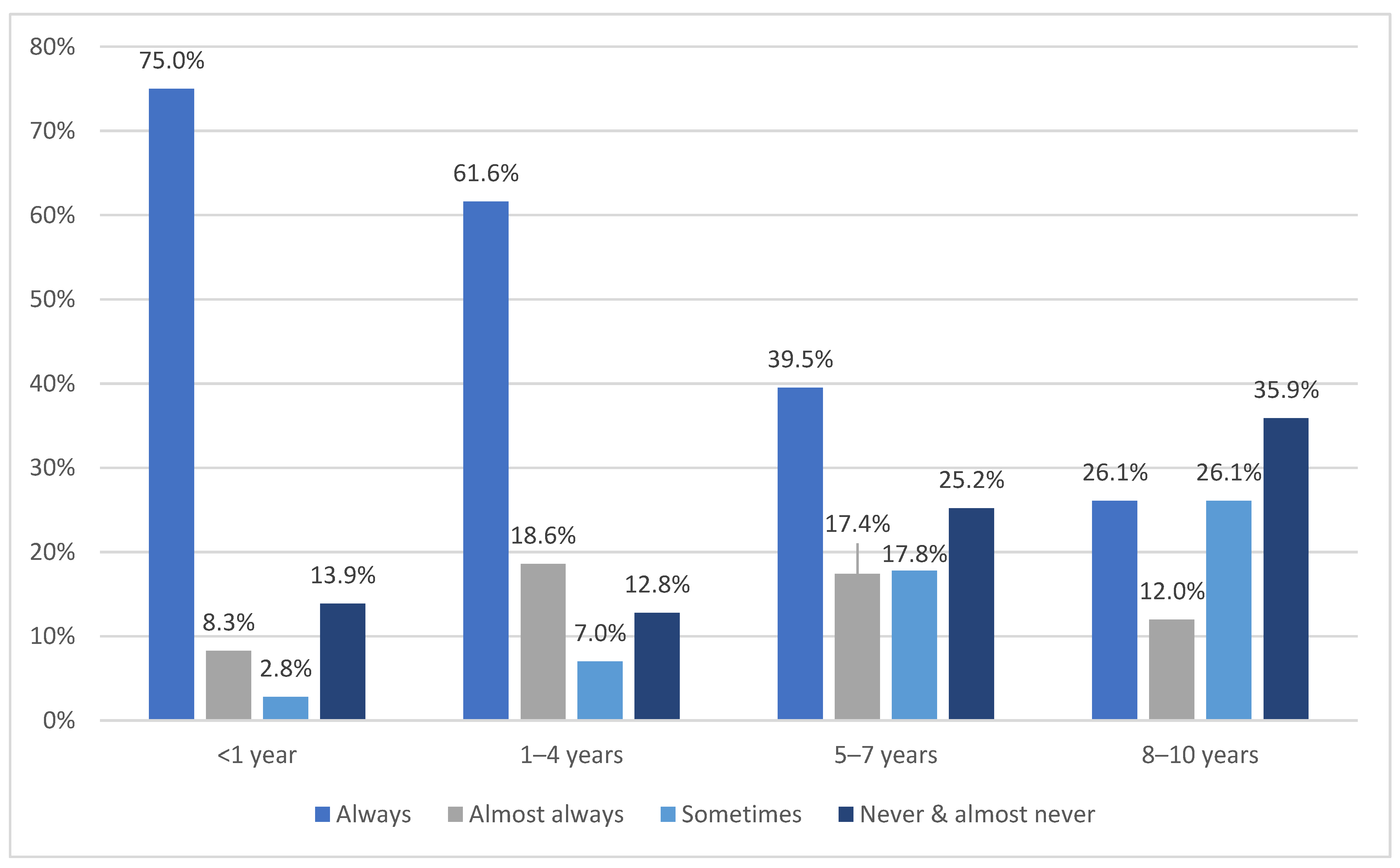
3.4.1. Child’s Age Group by Frequency of Restraint Use
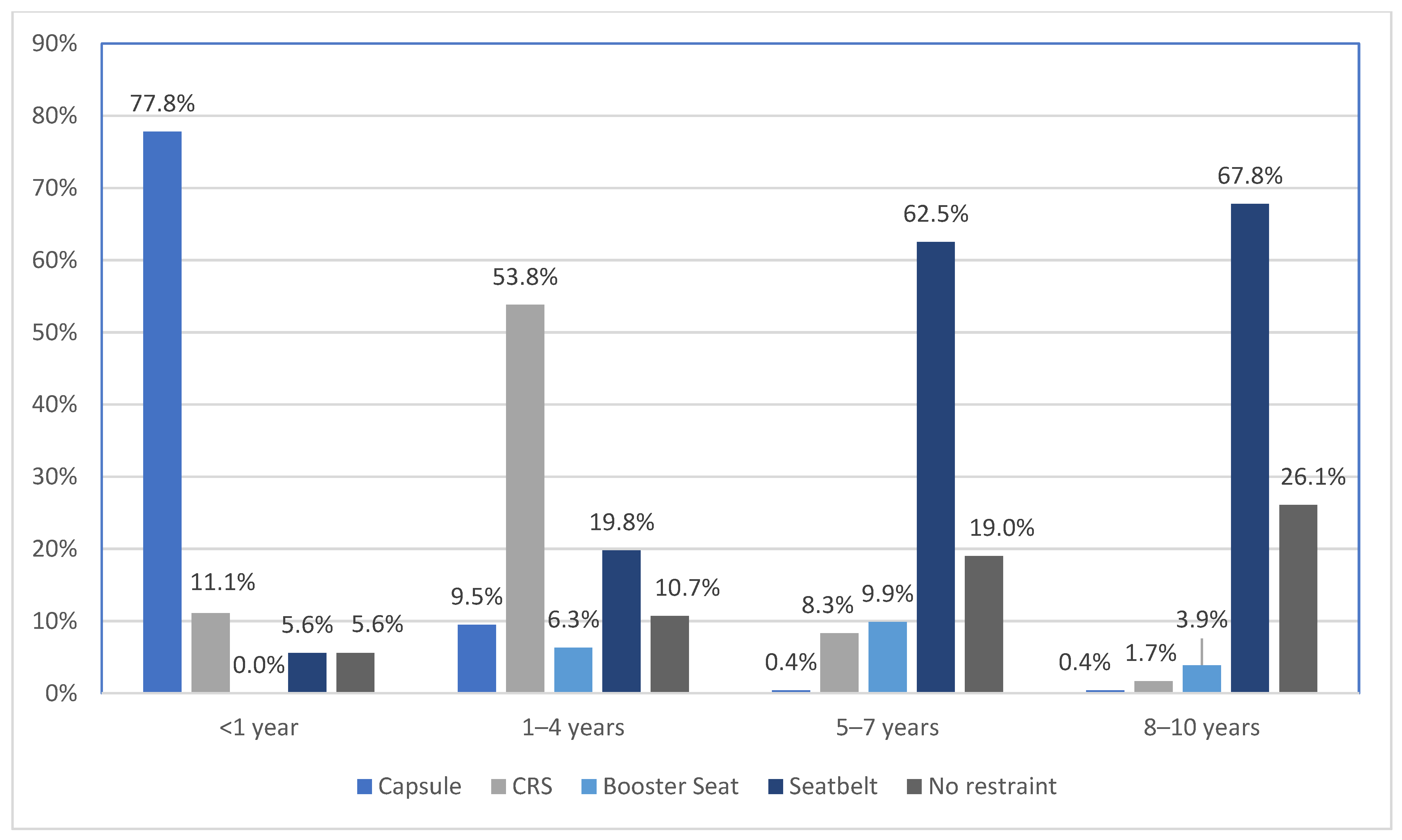
3.4.2. Child’s Age Group by Type of Restraint Use
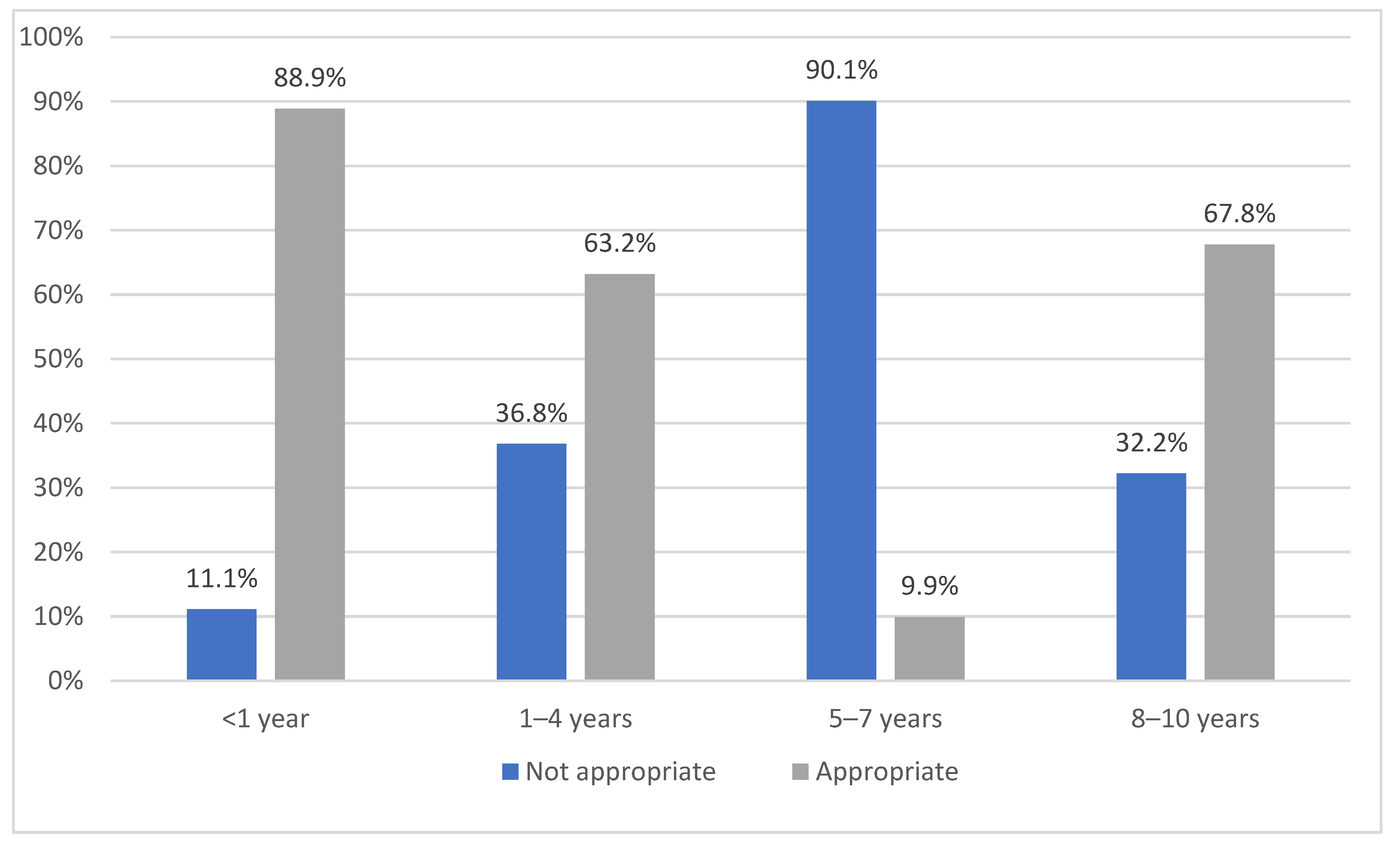
3.4.3. Childs’ Age Group by Appropriateness of Restraint Type
3.5. Non-Use of Restraint for Children
3.6. Parents’ Awareness of the Introduction of CRS and Boosters Seat Legislation
4. Discussion
- What is the type and frequency of restraint use (i.e., CRS, booster seat and seatbelt) for child occupants aged 10 years and younger while travelling in their vehicles?
- What are the factors that influence the frequency of restraint use for child occupants aged 10 years and younger?
- What are the factors that influence appropriate restraint use for child occupants aged 10 years and younger?
- What are the reasons for restraint non-use?
- What is the level of awareness regarding the introduction of CRS and booster seat legislation in the UAE?
4.1. Type and Frequency of Restraint Use
4.2. Significant Factors That Influence Frequency of Restraint Use for Child Occupants
4.3. Factors That Influence Appropriate Restraint Use for Child Occupants
4.4. Non-Restraint Use Factors
4.5. Knowledge of the Impending CRS and Boosters Seat Legislation in the UAE
5. Challenges and Opportunities
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Road Safety 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Health Authority Abu Dhabi. Secure Your Child in a Car Seat, Every Time, Every Trip. Available online: https://www.haad.ae/roadsafety/childseatbelt.html (accessed on 19 July 2017).
- World Health Organization. Seat-Belts and Child Restraints: A Road Safety Manual for Decision-Makers and Practitioners; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwall, N. National Child Restraint Use Special Study; National Highway Traffic Safety Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, M.R.; Kallan, M.J.; Durbin, D.R.; Winston, F.K. Effectiveness of child safety seats vs seat belts in reducing risk for death in children in passenger vehicle crashes. Arch. Pediatrics Adolesc. Med. 2006, 160, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The United Arab Emirates Government Portal. Road Safety. Available online: https://government.ae/en/information-and-services/justice-safety-and-the-law/road-safety (accessed on 19 July 2017).
- Anund, A.; Falkmer, T.; Forsman, Å.; Gustafsson, S.; Matstoms, Y.; Sörensen, G.; Turbell, T.; Wenäll, J. Child Safety in Cars: Literature Review; Statens Väg-och Transportforskningsinstitut: Linköping, Sweden, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, A.E.; Wybourn, C.A.; Mendoza, M.A.; Cruz, M.J.; Juillard, C.J.; Dicker, R.A. The worldwide approach to Vision Zero: Implementing road safety strategies to eliminate traffic-related fatalities. Curr. Trauma Rep. 2017, 3, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Health Abu Dhabi. DOH Guideline for Safe Transportation of Children at Hospital Discharge; Department of Health Abu Dhabi: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, K.A.; Mourad, A.H.I.; Muhammad, A.U. Child Passenger Safety in the United Arab Emirates: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2020 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 4 February–9 April 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dah, M.K. Causes and Consequences of Road Traffic Crashes in Dubai, UAE and Strategies for Injury Reduction; Loughborough University: Loughborough, England.
- Durbin, D.R.; Chen, I.; Smith, R.; Elliott, M.R.; Winston, F.K. Effects of seating position and appropriate restraint use on the risk of injury to children in motor vehicle crashes. Pediatrics 2005, 115, e305–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivna, M.; Barss, P.; El-Sadig, M. Epidemiology and Prevention of Child Injuries in the United Arab Emirates: A Report for SafeKids Worldwide; Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Roadway Transportation and Traffic Safety Research Center: Al Ain, United Arab Emirates, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Road Safety 2015; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Road Safety, Time For Action. Inj. Prev. 2015, 15, 286. [Google Scholar]
- Assiry, K.; Abdulmutali, H.; Alqahtani, A.; Alyahya, A.; Elawad, M. Traumatic head injuries in children: Experience from Asir, KSA. Online J. Med. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zahrany, M.S.; Al-Shuwair, F.N.; Al-Zahrani, M.A.; Temsah, M.-H.; Al-Sohime, F.; Al-Mosned, B.S.; Al-Soliman, M.A.; Abaalkhail, M.S. Self-reported Unintentional Injuries in Families Visiting the ‘Childhood Safety Campaign’ in Saudi Arabia. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2018, 71, 2280–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barss, P.; Al-Obthani, M.; Al-Hammadi, A.; Al-Shamsi, H.; El-Sadig, M.; Grivna, M. Prevalence and issues in non-use of safety belts and child restraints in a high-income developing country: Lessons for the future. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2008, 9, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivna, M.; Al-Shamsi, H.; Al-Hammadi, A.; Al-Obthani, M.; Al-Ali, M.; Al-Senani, A.; El-Sadig, M.; Bernsen, R.; Barss, P. Child restraints a cross-sectional study on knowledge, attitude and practice of traffic police in United Arab Emirates. Inj. Prev. 2010, 16, A241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.N.; Hawas, Y.E.; Maraqa, M.A. A holistic approach for assessing traffic safety in the United Arab Emirates. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2012, 45, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromfield, N.; Mahmoud, M. An exploratory investigation of child safety seat use among citizens of the United Arab Emirates. J. Transp. Saf. Secur. 2016, 9, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendak, S.; Alkhaledi, K. Child restraint system use in the United Arab Emirates. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2017, 51, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhalik, M.; El-Atawi, K.; Mahfouz, R. Assessment of mother’s knowledge on importance and need for Child Car Safety Seat in UAE. J. Pediatr. Neonatal. Care 2018, 8, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najah, A.; Abuzwidah, M.; Khalil, D. The Impact of The Rear Seat Belt Use on Traffic Safety in the UAE. In Proceedings of the 2020 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 4 February–9 April 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrahman, K.S.F. Child Safety in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Ph.D. Dissertation, School of Health Sciences, Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Awadalla, D.M.; de Albuquerque, F.D.B. Fatal road crashes in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi: Contributing factors and data-driven safety recommendations. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 52, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomani, H.; Fareed, A.; Ibrahim, H.; Shaltoot, A.; Elhalawany, A.; Alhajjaj, M.; Dakhel, A.; Alshammasi, M.; Almosallam, O. Pediatric trauma at a single center in the Qassim region of Saudi Arabia. Ann. Saudi Med. 2021, 41, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, A.H.; Thomas, L.; Kirley, B.; Hall, W.; O’Brien, N.P.; Hill, K. Countermeasures That Work: A Highway Safety Countermeasure Guide for State Highway Safety Offices: 2015; National Highway Traffic Safety Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Decina, L.E.; Will, K.E.; Maple, E.L.; Perkins, A.M.; Kirley, B.; Mastromatto, T.; TransAnalytics, L.L.C. Effectiveness of Child Passenger Safety Information for the Safe Transportation of Children; National Highway Traffic Safety Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zaidan, E. Usage of Child Car Safety Seat in Qatar: Behaviors, Knowledge, and Attitudes. OIDA Int. J. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 10, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bendak, S.; Alnaqbi, S.S. Rear seat belt use in the United Arab Emirates. Policy Pract. Health Saf. 2019, 17, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fildes, B.; Stevenson, M.; Hoque, S.; Hammid, A. Restraint use in the Eastern Province of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2016, 17, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, S.R.; Landry, M.D.; Ottensmeyer, C.A.; Jacob, S.; Hamdan, E.; Bouhaimed, M. Keeping our children safe in motor vehicles: Knowledge, attitudes and practice among parents in Kuwait regarding child car safety. Int. J. Inj. Contr. Saf. Promot. 2013, 20, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Li, L. Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviors on Child Passenger Safety among Expectant Mothers and Parents of Newborns: A Qualitative and Quantitative Approach. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, L. Has Child Restraint System Use Increased among Parents of Children in Shantou, China? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.K.; Bilston, L.; Brown, J. Child restraint use and parental perceptions of comfort. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2016, 17, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nelson, A.; Modeste, N.; Hopp Marshak, H.; Hopp, J.W. Saudi women’s beliefs on the use of car infant restraints: A qualitative study. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2015, 16, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Bawaba. Accidental Injuries Prime Death Cause of Children in the United Arab Emirates; Al Bawaba: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2010. [Google Scholar]
| Socio-Demographics Characteristics | % (n) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 18–25 | 6.9% (54) |
| 26–35 | 48.5% (381) | |
| 36–49 | 39.7% (312) | |
| 50+ | 5.0% (39) | |
| Gender | Male | 41.7% (328) |
| Female | 58.3% (458) | |
| Highest level of completed education | Middle/High School | 22.9% (180) |
| Undergraduate degree | 67.9% (534) | |
| Postgraduate degree | 9.2% (72) | |
| Nationality | UAE | 38.9% (306) |
| Other nationality | 61.1% (480) | |
| Adult seatbelt use | Always | 72.1% (567) |
| Almost always | 14.0% (110) | |
| Sometimes | 9.9% (78) | |
| Never/Almost never | 3.8% (30) | |
| Emirate of residency | Dubai | 79.0% (621) |
| Other Emirate | 21.0% (165) | |
| Child Characteristics | % (n) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age group | <1 year | 4.6% (36) |
| 1–4 years | 32.8% (258) | |
| 5–7 years | 32.8% (258) | |
| 8–10 years | 29.8% (234) | |
| Gender | Male | 55.7% (438) |
| Female | 44.3% (348) | |
| Restraint type | Capsule | 6.9% (54) |
| CRS | 21.0% (165) | |
| Booster seat | 6.4% (50) | |
| Seatbelt | 48.0% (377) | |
| No restraint | 17.8% (140) | |
| Restraint frequency use | Always | 44.4% (349) |
| Almost always | 15.8% (124) | |
| Sometimes | 16.0% (126) | |
| Never/Almost never | 23.8% (187) | |
| Frequency of Restraint Use | Gender | |
|---|---|---|
| Female % (n) | Male % (n) | |
| Always | 48.7% (223) | 38.4% (126) |
| Almost always | 14.6% (67) | 17.4% (57) |
| Sometimes | 16.8% (77) | 14.9% (49) |
| Never/Almost never | 19.9% (91) | 29.3% (96) |
| Frequency of Restraint Use | Education Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle/High School % (n) | Undergraduate Degree % (n) | Postgraduate Degree % (n) | |
| Always | 34.4% (62) | 47.0% (251) | 50.0% (36) |
| Almost always | 10.0% (18) | 18.0% (96) | 13.9% (10) |
| Sometimes | 13.3% (24) | 17.2% (92) | 13.9% (10) |
| Never/Almost never | 42.2% (76) | 17.8% (95) | 22.2% (16) |
| Frequency of Restraint Use | Nationality | |
|---|---|---|
| UAE % (n) | Other Nationality % (n) | |
| Always | 28.9% (101) | 71.1% (248) |
| Almost always | 44.4% (55) | 55.6% (69) |
| Sometimes | 49.2% (62) | 50.8% (64) |
| Never/Almost never | 47.1% (88) | 52.9% (99) |
| Frequency of Restraint Use | Participants’ Seatbelt Use | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Never & Almost Never % (n) | Sometimes % (n) | Almost Always % (n) | Always % (n) | |
| Always | 25.8% (8) | 20.5% (16) | 31.8% (35) | 51.1% (290) |
| Almost always | 6.5% (2) | 11.5% (9) | 24.5% (27) | 15.2% (86) |
| Sometimes | 16.1% (5) | 19.2% (15) | 16.4% (18) | 15.5% (88) |
| Never & almost never | 51.6% (16) | 48.7% (38) | 27.3% (30) | 18.2% (103) |
| Frequency of Restraint Use | Emirate of Residency | |
|---|---|---|
| Dubai % (n) | Other Emirates % (n) | |
| Always | 43.8% (14) | 44.4% (335) |
| Almost always | 6.3% (2) | 16.2% (122) |
| Sometimes | 25.0% (8) | 15.6% (118) |
| Never/Almost never | 25.0% (8) | 23.7% (179) |
| Frequency of Restraint Use | Awareness of Introduction CRS and Booster Seat Legislation | |
|---|---|---|
| Aware (Yes) % (n) | Not Aware (No) % (n) | |
| Always | 47.4% (289) | 34.1% (60) |
| Almost always | 17.2% (105) | 10.8% (19) |
| Sometimes | 16.4% (100) | 14.8% (26) |
| Never/Almost never | 19.0% (116) | 40.3% (71) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, I.; Fildes, B.N.; Logan, D.B.; Koppel, S. Restraint Use for Child Occupants in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19105966
Ahmad I, Fildes BN, Logan DB, Koppel S. Restraint Use for Child Occupants in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):5966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19105966
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Inam, Brian N. Fildes, David B. Logan, and Sjaan Koppel. 2022. "Restraint Use for Child Occupants in Dubai, United Arab Emirates" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 5966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19105966
APA StyleAhmad, I., Fildes, B. N., Logan, D. B., & Koppel, S. (2022). Restraint Use for Child Occupants in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 5966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19105966









