Knowledge Gaps and Research Priorities on the Health Effects of Heatwaves: A Systematic Review of Reviews
Abstract
:1. Introduction
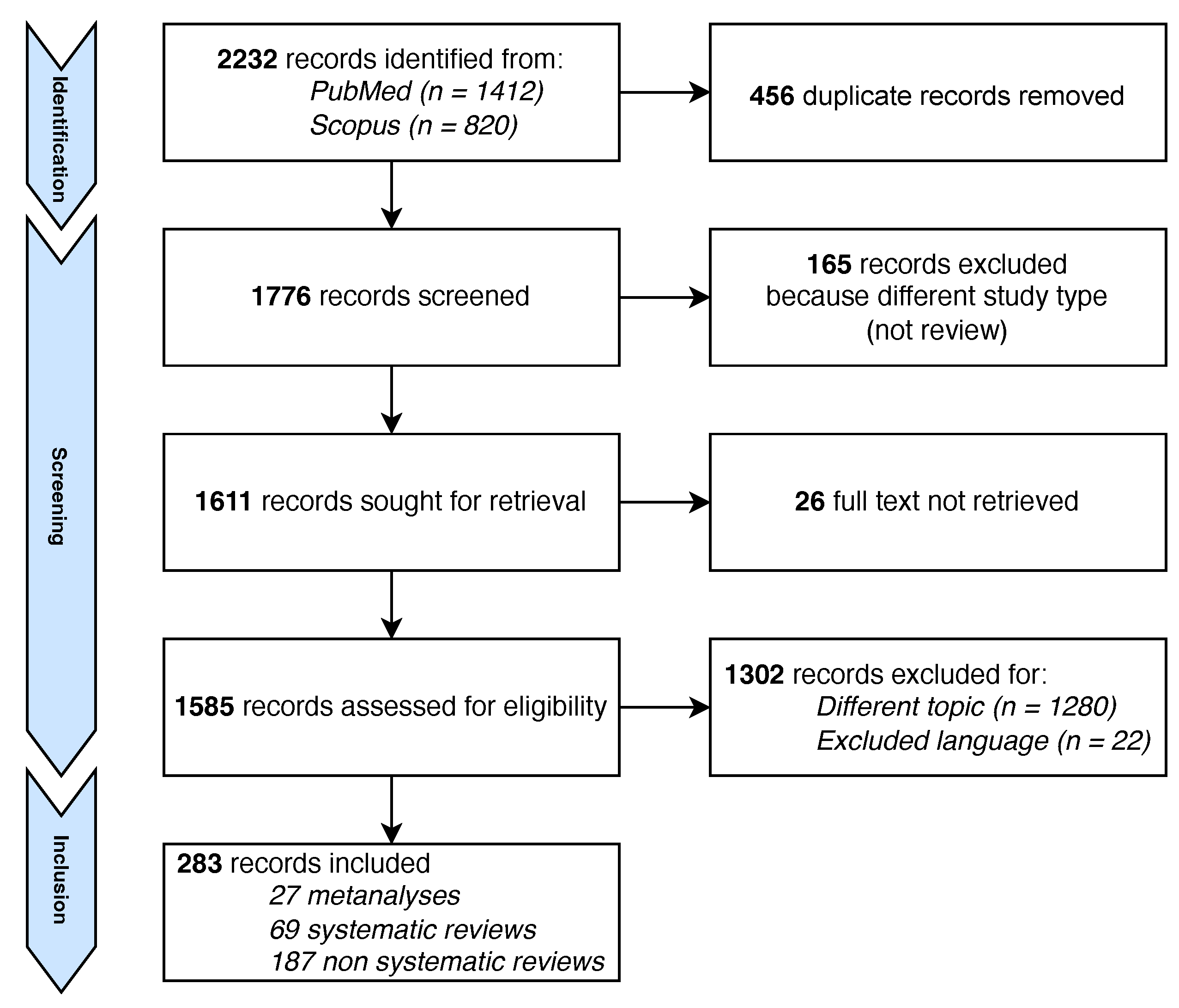
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
Data Extraction, Analysis, and Synthesis
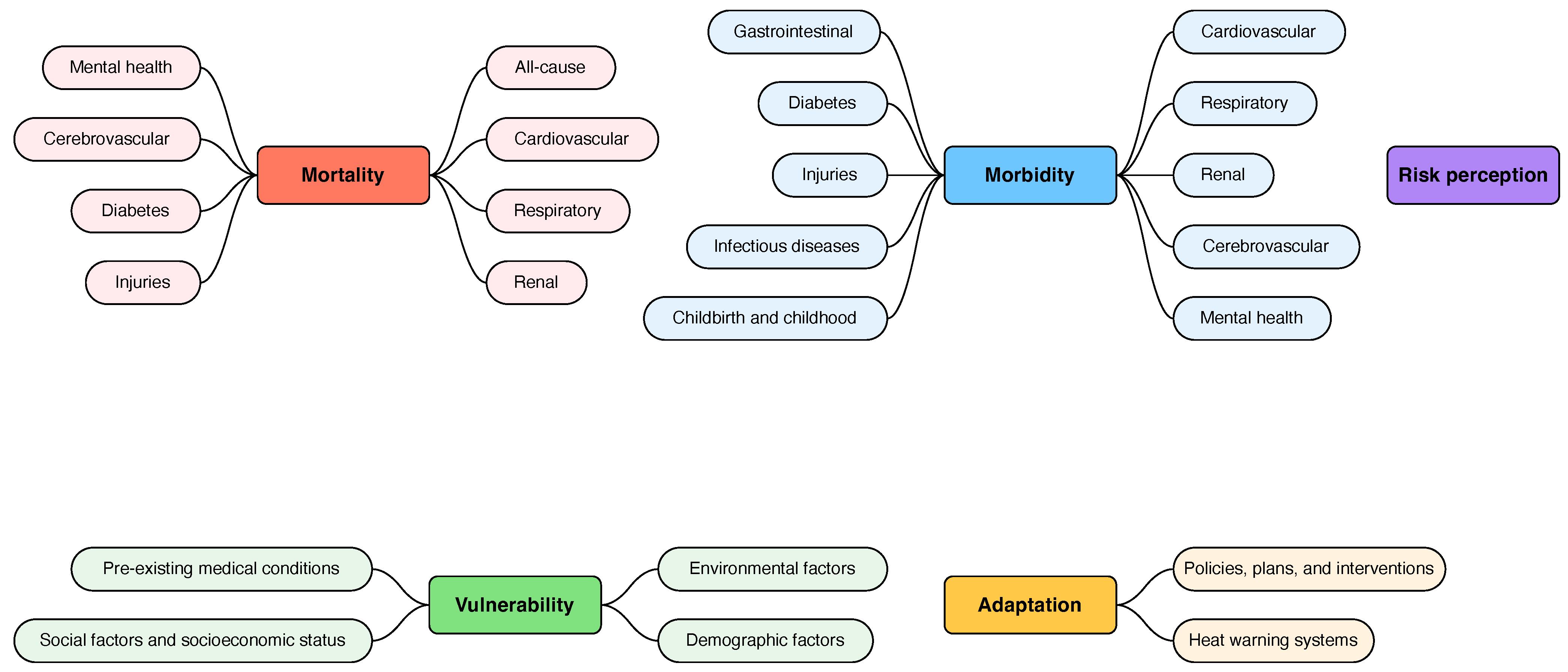
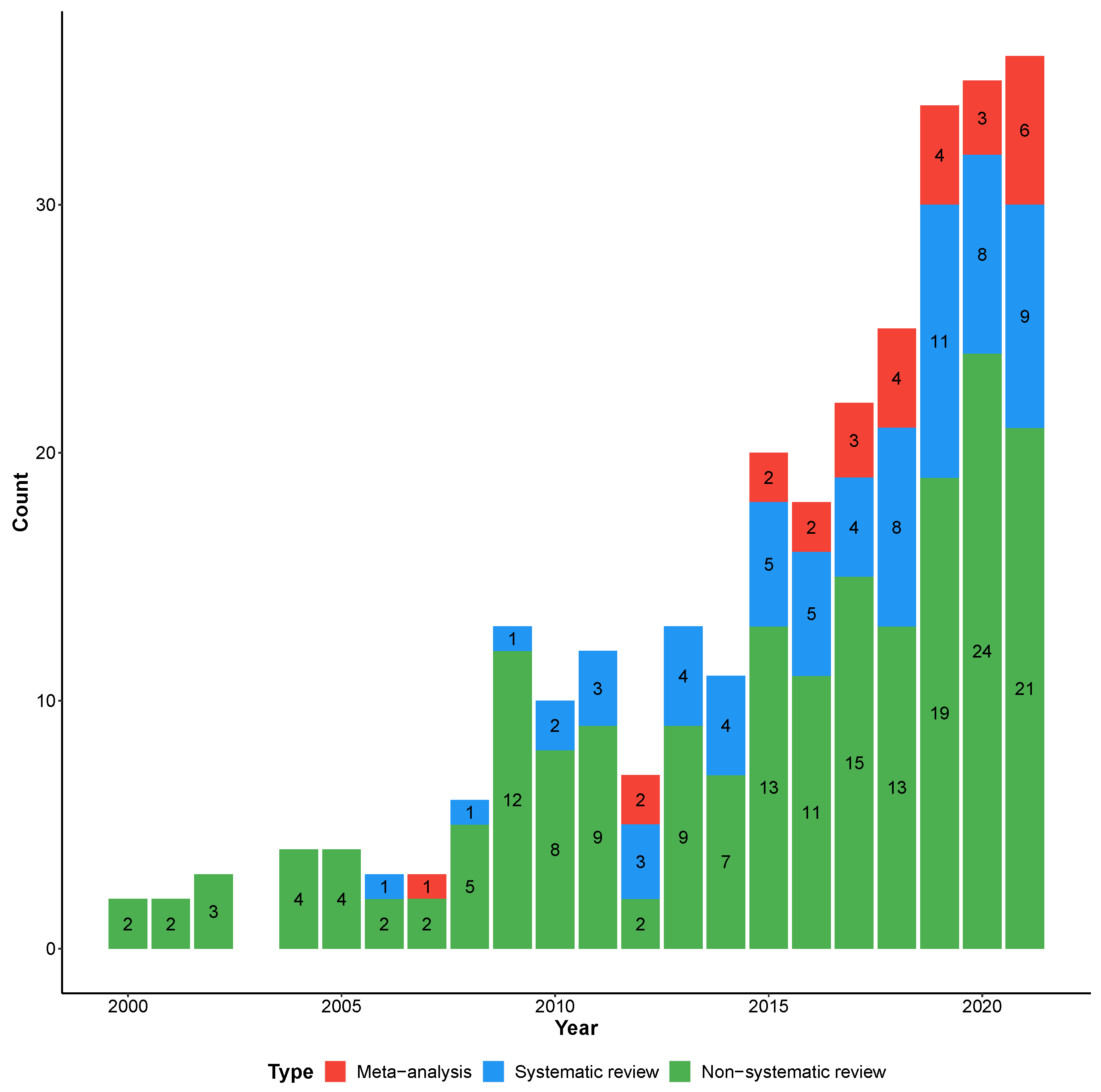
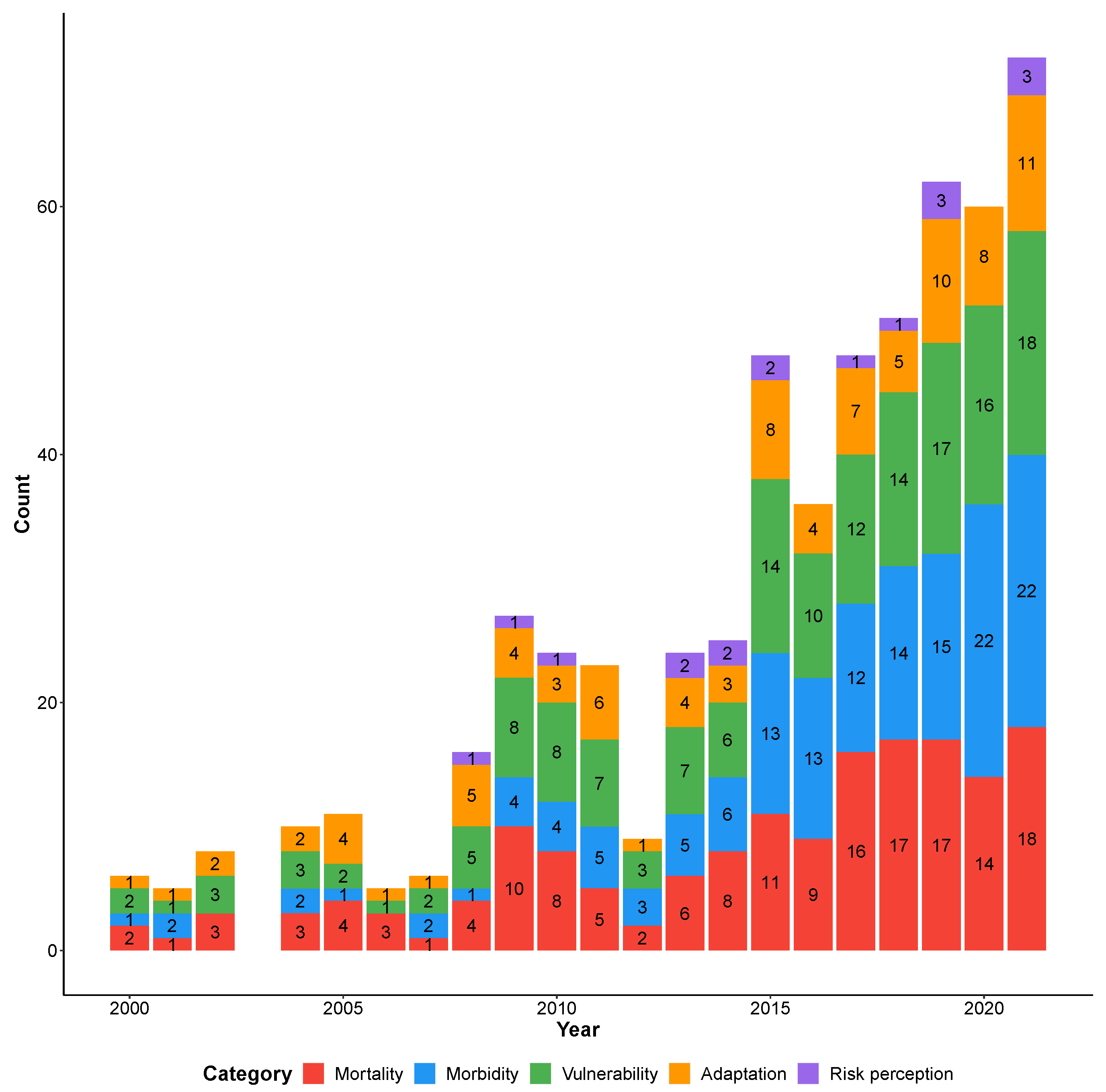
3. Results
3.1. Mortality
3.1.1. All-Cause Mortality
3.1.2. Mortality for Cardiovascular Diseases
3.1.3. Mortality for Respiratory Diseases
3.1.4. Mortality for Renal Diseases
3.1.5. Mortality for Cerebrovascular Diseases
3.1.6. Mortality for Mental Diseases
3.1.7. Mortality for Diabetes
3.1.8. Mortality for Injuries
3.2. Morbidity
3.2.1. Morbidity for Cardiovascular Diseases
3.2.2. Morbidity from Respiratory Diseases
3.2.3. Morbidity for Renal Diseases
3.2.4. Morbidity for Cerebrovascular Disease
3.2.5. Morbidity for Mental Diseases
3.2.6. Morbidity for Injuries
3.2.7. Morbidity for Childbirth Diseases
3.2.8. Morbidity for Diabetes
3.2.9. Morbidity for Infectious Diseases
3.3. Vulnerability
3.3.1. Pre-Existing Health Conditions
3.3.2. Demographic Factors
3.3.3. Environmental Factors
3.3.4. Social and Economic Factors
3.4. Adaptation
3.4.1. Policies, Plans, and Interventions
3.4.2. Heat Warning Systems
3.5. Risk Perception
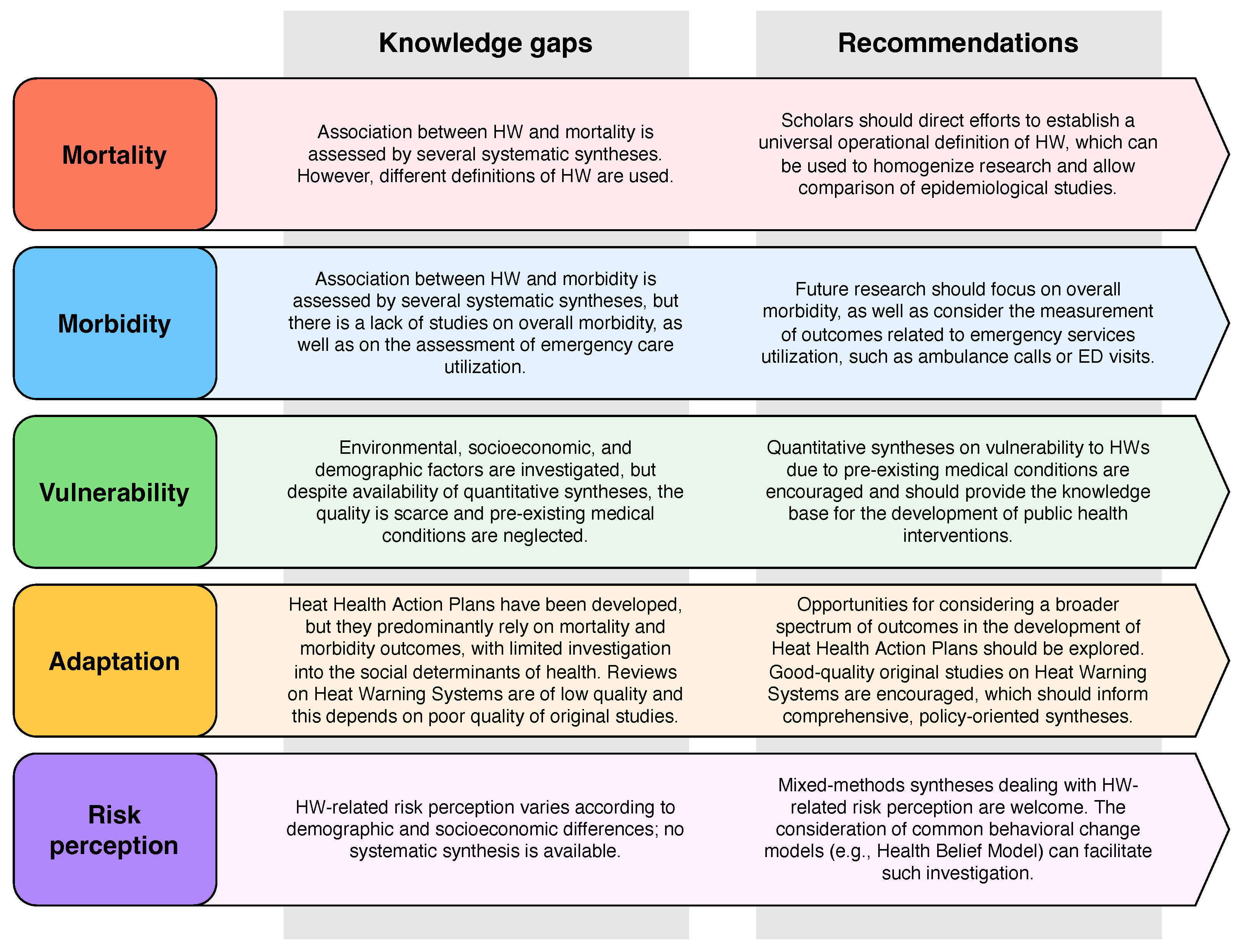
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HW | Heatwave |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| RR | Relative risk |
| iRR | Interaction relative risk |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| N | Number of considered studies |
| ED | Emergency department |
| SES | Socioeconomic status |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
References
- Luterbacher, J.; Werner, J.P.; Smerdon, J.E.; Fernández-Donado, L.; González-Rouco, F.J.; Barriopedro, D.; Ljungqvist, F.C.; Büntgen, U.; Zorita, E.; Wagner, S.; et al. European summer temperatures since Roman times. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change-Working Group I. Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis (Summary for Policymakers). 2021. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/ (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Field, C.; Barros, V.; Stocker, T.; Qin, D.; Dokken, D.; Ebi, K.; Mastrandrea, M.; Mach, K.; Pattner, G.; Allen, S.; et al. Glossary of Terms. In Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation. A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); Cambridge University Press: Cabridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 555–564. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, M.O.; Sánchez, E.; Gutiérrez, C. Future heat waves over the Mediterranean from an Euro-CORDEX regional climate model ensemble. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Yuan, X.; Jiao, Y.; Ji, P. Unprecedented Europe Heat in June–July 2019: Risk in the Historical and Future Context. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X. Heat wave trends in Southeast Asia during 1979–2018: The impact of humidity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, S.B.; Dawson, R.J.; Kilsby, C.; Lewis, E.; Ford, A. Future heat-waves, droughts and floods in 571 European cities. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 034009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.E.; Jeong, S.; Harrington, L.J.; Lee, M.I.; Zheng, C. Population ageing determines changes in heat vulnerability to future warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 114043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuholske, C.; Caylor, K.; Funk, C.; Verdin, A.; Sweeney, S.; Grace, K.; Peterson, P.; Evans, T. Global urban population exposure to extreme heat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024792118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Heat and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, T.; Anderegg, W.R. A vast increase in heat exposure in the 21st century is driven by global warming and urban population growth. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 73, 103098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Association. WMO Atlas of Mortality and Economic Losses from Weather, Climate and Water Extremes (1970–2019); Technical Report; World Meteorological Association: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, W.; Haunschild, R.; Bornmann, L. Heat waves: A hot topic in climate change research. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 146, 781–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.; Remenyi, T.A.; White, C.J.; Johnston, F.H. Heatwave and health impact research: A global review. Health Place 2018, 53, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Glasgow Climate Pact. 2021. Available online: https://unfccc.int/documents/310475 (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Pörtner, H.O.; Roberts, D.C.; Tignor, M.; Poloczanska, E.S.; Mintenbeck, K.; Alegrìa, A.; Craig, M.; Langsdorf, S.; Löschke, V.; Möller, V.; et al. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Technical report; IPCC: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-González, D.; Carrasco-Portiño, M.; Vives-Cases, C.; Agudelo-Suárez, A.A.; Castejón Bolea, R.; Ronda-Pérez, E. Is health a right for all? An umbrella review of the barriers to health care access faced by migrants. Ethn. Health 2015, 20, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halas, G.; Schultz, A.S.H.; Rothney, J.; Wener, P.; Holmqvist, M.; Cohen, B.; Kosowan, L.; Enns, J.E.; Katz, A. A Scoping Review of Foci, Trends, and Gaps in Reviews of Tobacco Control Research. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2020, 22, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; FitzGerald, G.; Guo, Y.; Jalaludin, B.; Tong, S. Impact of heatwave on mortality under different heatwave definitions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2016, 89–90, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrova, A.; Ingole, V.; Basagaña, X.; Ranzani, O.; Milà, C.; Ballester, J.; Tonne, C. Association between ambient temperature and heat waves with mortality in South Asia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odame, E.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Vaidyanathan, A.; Silver, K. Assessing Heat-Related Mortality Risks among Rural Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiological Evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Q.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.; Han, X.; Jaakkola, J.J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between daily mean temperature and mortality in China. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Bambrick, H.; Prescott, V.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Su, H.; Tong, S.; Hu, W. Cardiorespiratory effects of heatwaves: A systematic review and meta-analysis of global epidemiological evidence. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, C.; Xu, D.; Li, T. Effects of ambient temperature on myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadamnia, M.T.; Ardalan, A.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Keshtkar, A.; Naddafi, K.; Yekaninejad, M.S. Ambient temperature and cardiovascular mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Varghese, B.M.; Hansen, A.; Borg, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Driscoll, T.; Morgan, G.; Dear, K.; Gourley, M.; Capon, A.; et al. Hot weather as a risk factor for kidney disease outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Ruan, Y.; Liang, R.; Liu, X.; Fan, Z. Short-Term Effect of Ambient Temperature and the Risk of Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9068–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Varghese, B.M.; Hansen, A.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dear, K.; Gourley, M.; Driscoll, T.; Morgan, G.; Capon, A.; et al. Is there an association between hot weather and poor mental health outcomes? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Hu, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; Huang, W.; Meng, Y.; et al. Impact of short-term exposure to extreme temperatures on diabetes mellitus morbidity and mortality? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 58035–58049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J. The effect of the heatwave on the morbidity and mortality of diabetes patients; a meta-analysis for the era of the climate crisis. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; Kjellstrom, T.; Baldasseroni, A. Impact of climate change on occupational health and productivity: A systematic literature review focusing on workplace heat. Med. Del Lav. 2018, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafede, M.; Marinaccio, A.; Asta, F.; Schifano, P.; Michelozzi, P.; Vecchi, S. The association between extreme weather conditions and work-related injuries and diseases. A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Ann. Dell’Ist. Super. Sanita 2016, 52, 357–367. [Google Scholar]
- Phung, D.; Thai, P.K.; Guo, Y.; Morawska, L.; Rutherford, S.; Chu, C. Ambient temperature and risk of cardiovascular hospitalization: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 1084–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.R.; Barnett, A.G.; Connell, D.; Tong, S. Ambient Temperature and Cardiorespiratory Morbidity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.S.; Kim, W.S.; Lim, Y.H.; Hong, Y.C. High Temperatures and Kidney Disease Morbidity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2019, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flouris, A.D.; Dinas, P.C.; Ioannou, L.G.; Nybo, L.; Havenith, G.; Kenny, G.P.; Kjellstrom, T. Workers’ health and productivity under occupational heat strain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e521–e531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, G.; Ding, B.; Sun, G.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, M.; Ye, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, H. The impact of ambient temperature on the incidence of urolithiasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2020, 46, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binazzi, A.; Levi, M.; Bonafede, M.; Bugani, M.; Messeri, A.; Morabito, M.; Marinaccio, A.; Baldasseroni, A. Evaluation of the impact of heat stress on the occurrence of occupational injuries: Meta-analysis of observational studies. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2019, 62, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, S.H.; Rothmore, P.; Giles, L.C.; Varghese, B.M.; Bi, P. Extreme heat and occupational injuries in different climate zones: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological evidence. Environ. Int. 2021, 148, 106384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chersich, M.F.; Pham, M.D.; Areal, A.; Haghighi, M.M.; Manyuchi, A.; Swift, C.P.; Wernecke, B.; Robinson, M.; Hetem, R.; Boeckmann, M.; et al. Associations between high temperatures in pregnancy and risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirths: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 371, m3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Meng, Y.; Xiang, H.; Lu, Y.; Liu, S. Association of Short-Term Exposure to Meteorological Factors and Risk of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchama, A. Prognostic Factors in Heat Wave–Related DeathsA Meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benmarhnia, T.; Deguen, S.; Kaufman, J.S.; Smargiassi, A. Review Article: Vulnerability to Heat-related Mortality. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinasi, L.H.; Benmarhnia, T.; De Roos, A.J. Modification of the association between high ambient temperature and health by urban microclimate indicators: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, M.; Hooper, L.; Hunter, P.R. The Effectiveness of Public Health Interventions to Reduce the Health Impact of Climate Change: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, L.; Graham, H.; White, P. Economic Evaluations of the Health Impacts of Weather-Related Extreme Events: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chersich, M.F.; Wright, C.Y. Climate change adaptation in South Africa: A case study on the role of the health sector. Glob. Health 2019, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boeckmann, M.; Rohn, I. Is planned adaptation to heat reducing heat-related mortality and illness? A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markanday, A.; Galarraga, I.; Markandya, A. A Critical Review of Cost-Benefit Analysis for Climate Change Adaptation in Cities. Clim. Chang. Econ. 2019, 10, 1950014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayrhuber, E.A.S.; Dückers, M.L.; Wallner, P.; Arnberger, A.; Allex, B.; Wiesböck, L.; Wanka, A.; Kolland, F.; Eder, R.; Hutter, H.P.; et al. Vulnerability to heatwaves and implications for public health interventions—A scoping review. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chicas, R.; Xiuhtecutli, N.; Dickman, N.E.; Scammell, M.L.; Steenland, K.; Hertzberg, V.S.; McCauley, L. Cooling intervention studies among outdoor occupational groups: A review of the literature. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2020, 63, 988–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palinkas, L.A.; O’Donnell, M.L.; Lau, W.; Wong, M. Strategies for Delivering Mental Health Services in Response to Global Climate Change: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimicombe, C.; Porter, J.J.; Di Napoli, C.; Pappenberger, F.; Cornforth, R.; Petty, C.; Cloke, H.L. Heatwaves: An invisible risk in UK policy and research. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 116, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiello, M.A.; Baldasseroni, A.; Buiatti, E.; Giacchi, M.V. Health effects of heat waves. Ig. Sanita Pubblica 2008, 64, 735–772. [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren Kownacki, K.; Gao, C.; Kuklane, K.; Wierzbicka, A. Heat Stress in Indoor Environments of Scandinavian Urban Areas: A Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vu, V.; Rutherford, S.; Phung, D. Heat Health Prevention Measures and Adaptation in Older Populations—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacIntyre, E.; Khanna, S.; Darychuk, A.; Copes, R.; Schwartz, B. Evidence synthesis—Evaluating risk communication during extreme weather and climate change: A scoping review. Health Promot. Chronic Dis. Prev. Can. 2019, 39, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hass, A.L.; Runkle, J.D.; Sugg, M.M. The driving influences of human perception to extreme heat: A scoping review. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, M.; Trentin, M.; Farah Dell’Aringa, M.; Bahattab, A.; Lamine, H.; Linty, M.; Ragazzoni, L.; Della Corte, F.; Barone-Adesi, F. Dealing with a changing climate: The need for a whole-of-society integrated approach to climate-related disasters. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 102718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocque, R.J.; Beaudoin, C.; Ndjaboue, R.; Cameron, L.; Poirier-Bergeron, L.; Poulin-Rheault, R.A.; Fallon, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Witteman, H.O. Health effects of climate change: An overview of systematic reviews. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e046333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thackeray, S.J.; Robinson, S.A.; Smith, P.; Bruno, R.; Kirschbaum, M.U.F.; Bernacchi, C.; Byrne, M.; Cheung, W.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Gienapp, P.; et al. Civil disobedience movements such as School Strike for the Climate are raising public awareness of the climate change emergency. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 1042–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heo, S.; Bell, M.L.; Lee, J.T. Comparison of health risks by heat wave definition: Applicability of wet-bulb globe temperature for heat wave criteria. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Park, C.; Lee, W.; Pehlivan, N.; Choi, M.; Jang, J.; Kim, H. Heatwave-Related Mortality Risk and the Risk-Based Definition of Heat Wave in South Korea: A Nationwide Time-Series Study for 2011–2017. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, S.T.; McClure, L.A.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Smith, T.T.; Gohlke, J.M. Heat Waves and Health Outcomes in Alabama (USA): The Importance of Heat Wave Definition. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Office. Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030; United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan, A.M.H.; Ataallah, A.G. Are climate change and mental health correlated? Gen. Psychiatry 2021, 34, e100648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gasparrini, A.; Li, S.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; de Sousa Zanotti Stagliorio Coelho, M.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Lavigne, E.; Tawatsupa, B.; Punnasiri, K.; et al. Quantifying excess deaths related to heatwaves under climate change scenarios: A multicountry time series modelling study. PLOS Med. 2018, 15, e1002629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitty, C.J.M. What makes an academic paper useful for health policy? BMC Med. 2015, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliver, K.; Lorenc, T.; Innvær, S. New directions in evidence-based policy research: A critical analysis of the literature. Health Res. Policy Syst. 2014, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingole, V.; Sheridan, S.C.; Juvekar, S.; Achebak, H.; Moraga, P. Mortality risk attributable to high and low ambient temperature in Pune city, India: A time series analysis from 2004 to 2012. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conti, A.; Valente, M.; Paganini, M.; Farsoni, M.; Ragazzoni, L.; Barone-Adesi, F. Knowledge Gaps and Research Priorities on the Health Effects of Heatwaves: A Systematic Review of Reviews. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19105887
Conti A, Valente M, Paganini M, Farsoni M, Ragazzoni L, Barone-Adesi F. Knowledge Gaps and Research Priorities on the Health Effects of Heatwaves: A Systematic Review of Reviews. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19105887
Chicago/Turabian StyleConti, Andrea, Martina Valente, Matteo Paganini, Marco Farsoni, Luca Ragazzoni, and Francesco Barone-Adesi. 2022. "Knowledge Gaps and Research Priorities on the Health Effects of Heatwaves: A Systematic Review of Reviews" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19105887
APA StyleConti, A., Valente, M., Paganini, M., Farsoni, M., Ragazzoni, L., & Barone-Adesi, F. (2022). Knowledge Gaps and Research Priorities on the Health Effects of Heatwaves: A Systematic Review of Reviews. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19105887








