The Comprehensive Machine Learning Analytics for Heart Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
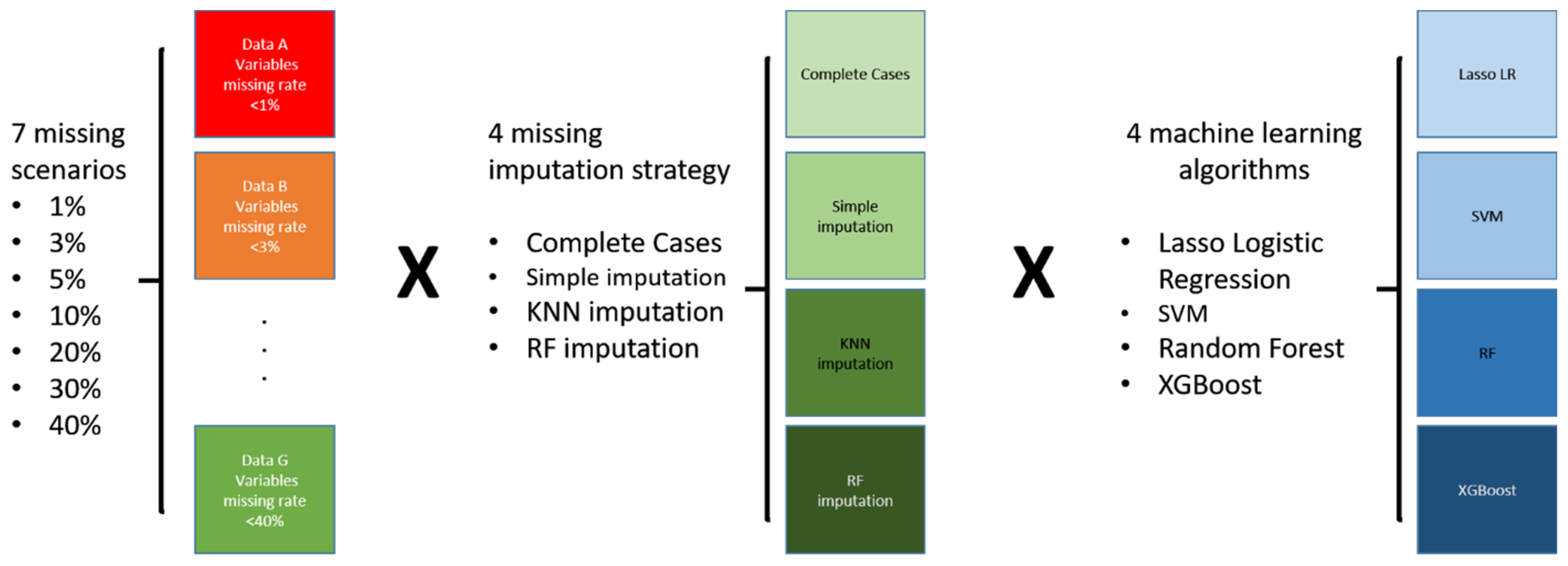
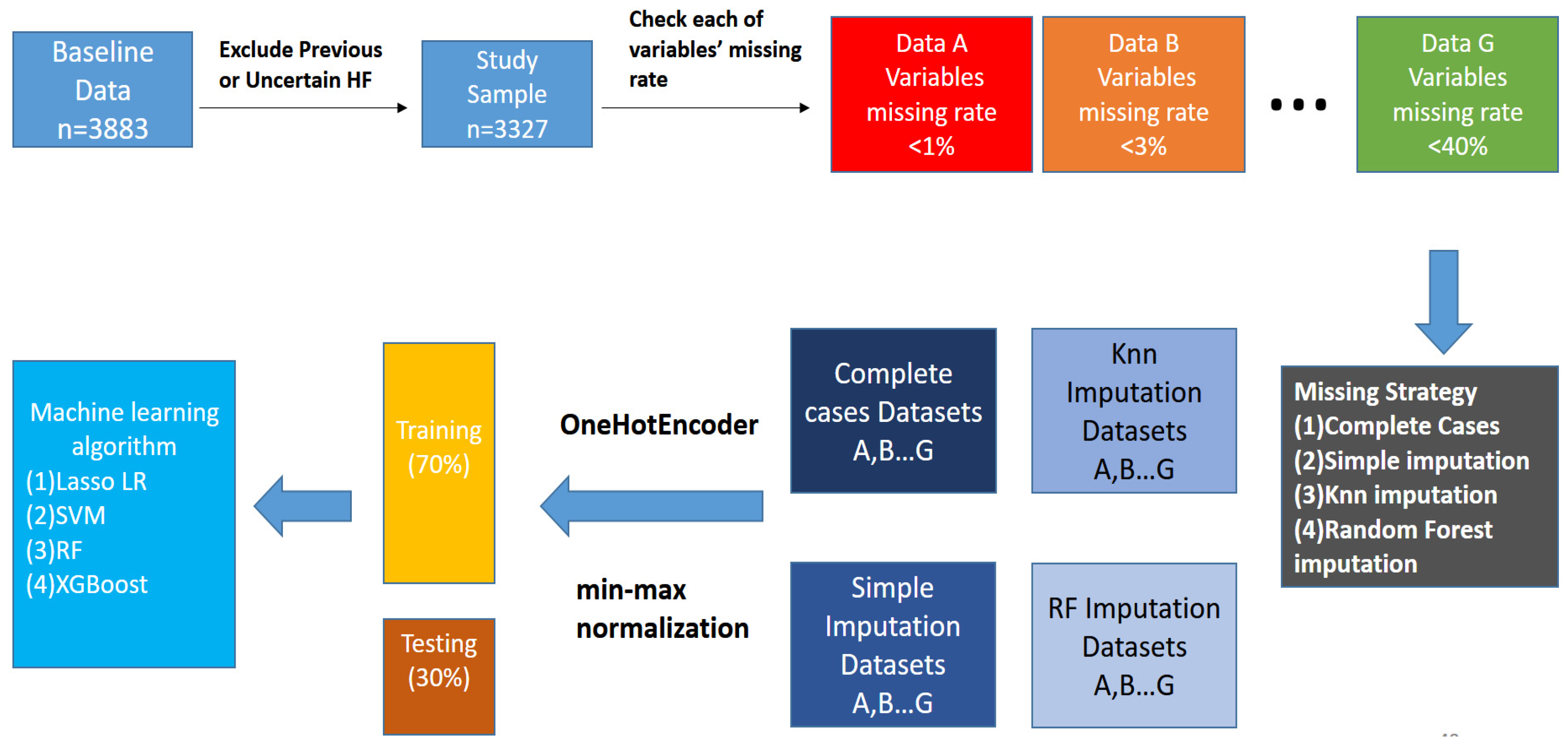
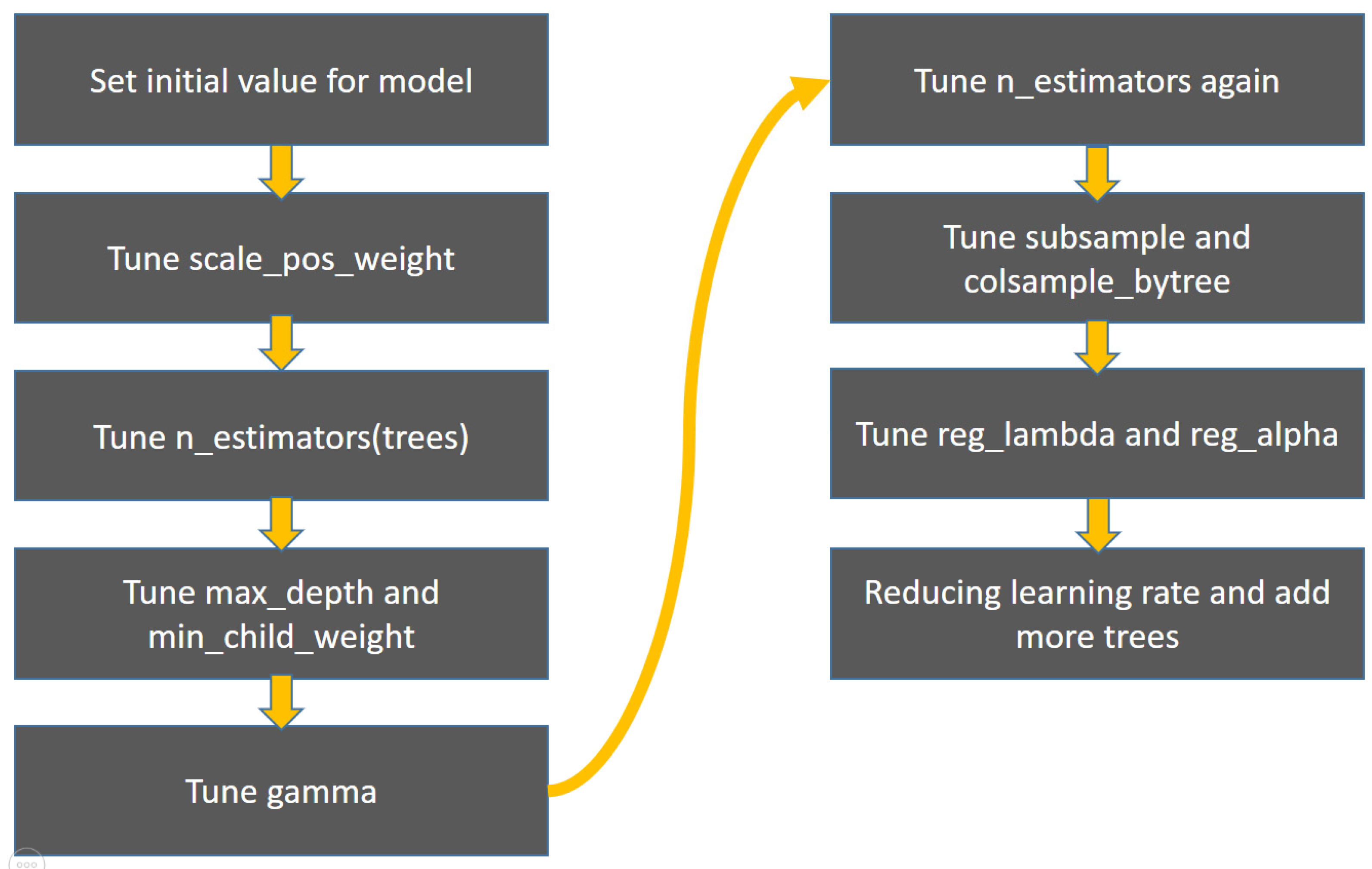
2. Materials and Methods
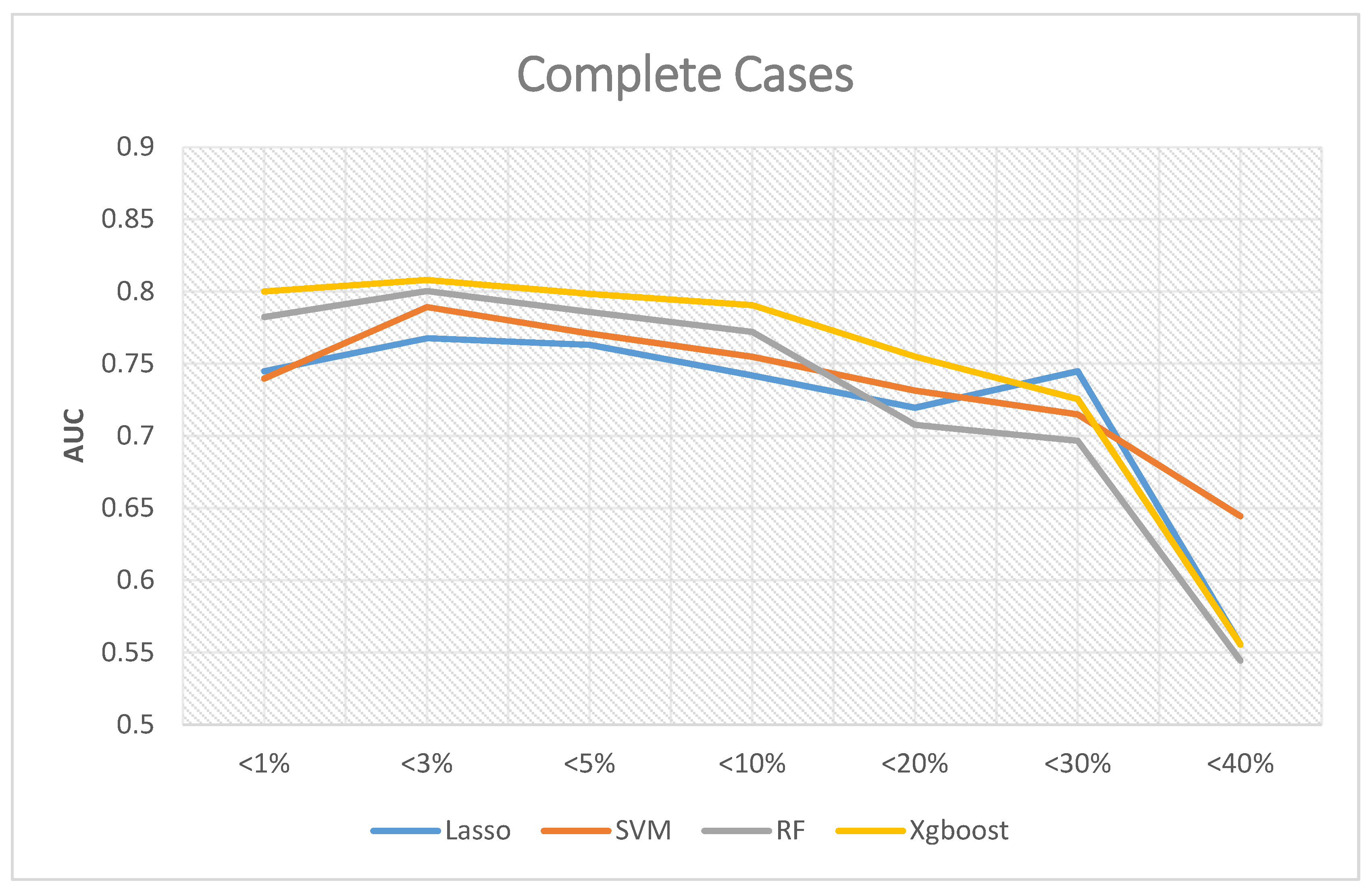
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable Name | Variable Types | Variable Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Demographics | |||
| age | Continuous | Age in Years | |
| sex | Categorical | Participant Sex | |
| alc | Categorical | Alcohol drinking in the past 12 months (Y/N) | |
| alcw | Continuous | Average number of drinks per week | |
| currentSmoker | Categorical | Self-Reported Cigarette Smoking Status | |
| everSmoker | Categorical | Self-Reported History of Cigarette Smoking | |
| 2. Anthropometrics | |||
| weight | Continuous | Weight (kg) | |
| height | Continuous | Height (cm) | |
| BMI | Continuous | Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | |
| waist | Continuous | Waist Circumference (cm) | |
| neck | Continuous | Neck Circumference (cm) | |
| bsa | Continuous | Calculated Body Surface Area (m2) | |
| obesity3cat | Categorical | Ideal Health: BMI < 25 (Normal) Intermediate Health: 25 ≤ BMI < 30 (Overweight) Poor Health: BMI ≥ 30 (Obese) | |
| 3. Medications | |||
| medAcct | Categorical | Medication Accountability | |
| BPmedsSelf | Categorical | Self-Reported Blood Pressure Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| BPmeds | Categorical | Blood Pressure Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| DMmedsIns | Categorical | Diabetic Insulin Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| DMmedType | Categorical | Diabetes Medication Type | |
| dmMedsSelf | Categorical | Defined as Yes (Treated), if the participant reported being on diabetic | |
| DMmeds | Categorical | Diabetic Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| statinMedsSelf | Categorical | Defined as Yes (Treated), if the participant reported being on statin medication. | |
| statinMeds | Categorical | Statin Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| hrtMedsSelfEver | Categorical | Self Reported HRT Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| hrtMedsSelf | Categorical | Self Reported Current HRT Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| hrtMeds | Categorical | HRT Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| betaBlkMeds | Categorical | Beta Blocker Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| calBlkMeds | Categorical | Calcium Channel Blocker Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| diureticMeds | Categorical | Diuretic Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| antiArythMedsSelf | Categorical | Defined as Yes (Treated), if the participant reported being on antiarrhythmic medication. | |
| antiArythMeds | Categorical | Antiarrhythmic Medication Status (Y/N) | |
| 4. Hypertension | |||
| sbp | Continuous | Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | |
| dbp | Continuous | Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | |
| BPjnc7 | Categorical | JNC 7 BP Classification | |
| HTN | Categorical | Hypertension Status | |
| ABI | Continuous | Ankle Brachial Index | |
| 5. Diabetes | |||
| FPG | Continuous | Fasting Plasma Glucose Level (mg/dL) | |
| FPG3cat | Categorical | Fasting Plasma Glucose Categorization | |
| HbA1c | Continuous | NGSP Hemoglobin HbA1c (%) | |
| HbA1c3cat | Categorical | NGSP Hemoglobin HbA1c (%) Categorization | |
| HbA1cIFCC | Continuous | IFCC Hemoglobin HbA1c in SI units (mmol/mol) | |
| HbA1cIFCC3cat | Categorical | IFCC Hemoglobin HbA1c in SI units (mmol/mol) Categorization | |
| fastingInsulin | Continuous | Fasting Insulin (Plasma IU/mL) | |
| HOMA-B | Continuous | HOMA-B | |
| HOMA-IR | Continuous | HOMA-IR | |
| Diabetes | Categorical | Diabetes Status (ADA 2010) | |
| diab3cat | Categorical | Diabetes Categorization | |
| 6. Lipids | |||
| ldl | Continuous | Fasting LDL Cholesterol Level (mg/dL) | |
| ldl5cat | Categorical | Fasting LDL Categorization | |
| hdl | Continuous | Fasting HDL Cholesterol Level (mg/dL) | |
| hdl3cat | Categorical | Fasting HDL Categorization | |
| trigs | Continuous | Fasting Triglyceride Level (mg/dL) | |
| trigs4cat | Categorical | Fasting Triglyceride Categorization | |
| totChol | Continuous | Fasting Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | |
| 7. Biomarkers | |||
| hsCRP | Continuous | High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (Serum mg/dL) | |
| endothelin | Continuous | Endothelin-1 (Serum pg/mL) | |
| sCort | Continuous | Concentration of Cortisol Levels (Serum µg/dL) | |
| reninRIA | Continuous | Renin Activity RIA (Plasma ng/mL/hr) | |
| reninIRMA | Continuous | Renin Mass IRMA (Plasma pg/mL) | |
| aldosterone | Continuous | “Concentration of Aldosterone | |
| leptin | Continuous | (Serum ng/dL)” | |
| adiponectin | Continuous | Concentration of Leptin (Serum ng/mL) | |
| 8. Renal | |||
| SCrCC | Continuous | CC Calibrated Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) | |
| SCrIDMS | Continuous | IDMS Tracebale Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) | |
| eGFRmdrd | Continuous | eGFR MDRD | |
| eGFRckdepi | Continuous | eGFR CKD-Epi | |
| CreatinineU24hr | Continuous | 24-hour urine creatinine (g/24hr) | |
| CreatinineUSpot | Continuous | Random spot urine creatinine (mg/dL) | |
| AlbuminUSpot | Continuous | Random spot urine albumin (mg/dL) | |
| AlbuminU24hr | Continuous | 24-hour urine albumin (mg/24hr) | |
| DialysisEver | Categorical | Self-reported dialysis | |
| DialysisDuration | Continuous | Self-reported duration on dialysis (years) | |
| CKDHx | Categorical | Chronic Kidney Disease History | |
| 9. Respiratory | |||
| asthma | Categorical | Physician-Diagnosed Asthma | |
| maneuvers | Continuous | Successful Spirometry Maneuvers | |
| FVC | Continuous | Forced Vital Capacity (L) | |
| FEV1 | Continuous | Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 s (L) | |
| FEV6 | Continuous | Forced Expiratory Volume in 6 s (L) | |
| FEV1PP | Continuous | FEV1 % Predicted | |
| FVCPP | Continuous | FVC % Predicted | |
| 10. Echocardiogram | |||
| LVMecho | Continuous | Left Ventricular Mass (g) from Echo | |
| LVMindex | Continuous | Left Ventricular Mass Indexed by Height(m)^2.7 | |
| LVH | Categorical | Left Ventricular Hypertrophy | |
| EF | Continuous | Ejection Fraction | |
| EF3cat | Categorical | Ejection Fraction Categorization | |
| DiastLVdia | Continuous | Diastolic LV Diameter (mm) | |
| SystLVdia | Continuous | Systolic LV Diameter (mm) | |
| FS | Categorical | Fractional Shortening | |
| RWT | Continuous | Relative Wall Thickness | |
| 11. Electrocardiogram | |||
| ConductionDefect | Categorical | Conduction Defect | |
| MajorScarAnt | Categorical | Anterior QnQs Major Scar | |
| MinorScarAnt | Categorical | Anterior QnQs Minor Scar | |
| RepolarAnt | Categorical | Anterior Repolarization Abnormality | |
| MIAnt | Categorical | Anterior ECG defined MI | |
| MajorScarPost | Categorical | Posterior QnQs Major Scar | |
| MinorScarPost | Categorical | Posterior QnQs Minor Scar | |
| RepolarPost | Categorical | Posterior Repolarization Abnormality | |
| MIPost | Categorical | Posterior ECG defined MI | |
| MajorScarAntLat | Categorical | Anterolateral QnQs Major Scar | |
| MinorScarAntLat | Categorical | Anterolateral QnQs Minor Scar | |
| RepolarAntLat | Categorical | Anterolateral Repolarization Abnormality | |
| MIAntLat | Categorical | Anterolateral ECG defined MI | |
| MIecg | Categorical | ECG determined MI | |
| ecgHR | Continuous | Heart Rate (bpm) | |
| Afib | Categorical | Atrial Fibrillation | |
| Aflutter | Categorical | Atrial Flutter | |
| QRS | Continuous | QRS Interval (msec) | |
| QT | Continuous | QT Interval (msec) | |
| QTcFram | Continuous | Framingham Corrected QT Interval (msec) | |
| QTcBaz | Continuous | Bazett Corrected QT Interval (msec) | |
| QTcHod | Continuous | Hodge Corrected QT Interval (msec) | |
| QTcFrid | Continuous | Fridericia Corrected QT Interval (msec) | |
| CV | Continuous | Cornell Voltage (microvolts) | |
| LVHcv | Categorical | Cornell Voltage Criteria | |
| 12. Stroke History | |||
| speechLossEver | Categorical | History of Speech Loss | |
| visionLossEver | Categorical | History of Sudden Loss of Vision | |
| doubleVisionEver | Categorical | History of Double Vision | |
| numbnessEver | Categorical | History of Numbness | |
| paralysisEver | Categorical | History of Paralysis | |
| dizzynessEver | Categorical | History of Dizziness | |
| strokeHx | Categorical | History of Stroke | |
| 13. CVD History | |||
| MIHx | Categorical | Self-Reported History of MI | |
| CardiacProcHx | Categorical | Self-Reported history of Cardiac Procedures | |
| CHDHx | Categorical | Coronary Heart Disease Status/History | |
| CarotidAngioHx | Categorical | Self-Reported history of Carotid Angioplasty | |
| CVDHx | Categorical | Cardiovascular Disease History | |
| 14. Healthcare Access | |||
| Insured | Categorical | Visit 1 Health Insurance Status | |
| 15. Psychosocial | |||
| Income | Categorical | Income Status | |
| occupation | Categorical | Occupational Status | |
| edu3cat | Categorical | Education Attainment Categorization | |
| HSgrad | Categorical | High School Graduate | |
| dailyDiscr | Continuous | Everyday Discrimination Experiences | |
| lifetimeDiscrm | Continuous | Major Life Events Discrimination | |
| discrmBurden | Continuous | Discrimination Burden | |
| depression | Continuous | Total Depressive Symptoms Score | |
| weeklyStress | Continuous | Total Weekly Stress Score | |
| perceivedStress | Continuous | Total Global Stress Score | |
| 16. Life’s Simple 7 | |||
| SMK3cat | Categorical | AHA Smoking Categorization | |
| idealHealthSMK | Categorical | Indicator for Ideal Health via Smoking Status | |
| BMI3cat | Categorical | AHA BMI Categorization | |
| idealHealthBMI | Categorical | Indicator for Ideal Health via BMI | |
| PA3cat | Categorical | AHA Physical Activity Categorization | |
| idealHealthPA | Categorical | Indicator for Ideal Health via Physical Activity | |
| nutrition3cat | Categorical | AHA Nutrition Categorization | |
| idealHealthNutrition | Categorical | Indicator for Ideal Health via Nutrition | |
| totChol3cat | Categorical | AHA Total Cholesterol Categorization | |
| idealHealthChol | Categorical | Indicator for Ideal Health via Total Cholesterol | |
| BP3cat | Categorical | AHA BP Categorization | |
| idealHealthBP | Categorical | Indicator for Ideal Health via BP | |
| glucose3cat | Categorical | AHA Glucose Categorization | |
| idealHealthDM | Categorical | Indicator for Ideal Health via Glucose | |
| 17. Nutrition | |||
| vitaminD2 | Continuous | 25(OH) Vitamin D2 (ng/mL) | |
| vitaminD3 | Continuous | 25(OH) Vitamin D3 (ng/mL) | |
| vitaminD3epimer | Continuous | ep-25(OH) Vitamin D3 (ng/mL) | |
| darkgrnVeg | Continuous | Dark-green Vegetables | |
| eggs | Continuous | Eggs | |
| fish | Continuous | Fish | |
| 18. Physical Activity | |||
| sportIndex | Continuous | Sport Index | |
| hyIndex | Continuous | Home/Yard Index | |
| activeIndex | Continuous | Active Living Index | |
| 19. Risk Scores | |||
| frs_chdtenyrrisk | Continuous | Framingham Risk Score-Coronary Heart Disease | |
| frs_cvdtenyrrisk | Continuous | Framingham Risk Score-Cardiovascular Disease | |
| frs_atpiii_tenyrrisk | Continuous | Framingham Risk Score-Adult Treatment Panel (III)—Coronary Heart Disease | |
| rrs_tenryrisk | Continuous | Reynolds Risk Score | |
| ascvd_tenyrrisk | Continuous | American College of Cardiology—American Heart Association—Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease |
References
- Conrad, N.; Judge, A.; Tran, J.; Mohseni, H.; Hedgecott, D.; Crespillo, A.P.; Allison, M.; Hemingway, H.; Cleland, J.G.; McMurray, J.J.V.; et al. Temporal trends and patterns in heart failure incidence: A population-based study of 4 million individuals. Lancet 2018, 391, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, V.L. Epidemiology of heart failure. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, H.; Kronmal, R.; Bluemke, D.A.; Olson, J.; Shea, S.; Liu, K.; Burke, G.L.; Lima, J.A. Differences in the incidence of congestive heart failure by ethnicity: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Pletcher, M.J.; Lin, F.; Vittinghoff, E.; Gardin, J.M.; Arynchyn, A.; Lewis, C.E.; Williams, O.D.; Hulley, S.B. Racial differences in incident heart failure among young adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, P. Elements of Machine Learning; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Leinweber, D.J. Stupid data miner tricks: Overfitting the S&P 500. J. Invest. 2007, 16, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.D.; Perez, A.; Lozano, J.A. Sensitivity analysis of k-fold cross validation in prediction error estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 32, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.K. Random decision forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.J. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikar, R. Ensemble based systems in decision making. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2006, 6, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Stone, C.J.; Olshen, R.A. Classification and Regression Trees; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Casanova, R.; Saldana, S.; Simpson, S.L.; Lacy, M.E.; Subauste, A.R.; Blackshear, C.; Wagenknecht, L.; Bertoni, A.G. Prediction of incident diabetes in the Jackson Heart Study using high-dimensional machine learning. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; Wohlin, C. An evaluation of k-nearest neighbour imputation using likert data. In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Software Metrics, Chicago, IL, USA, 22 November 2004; pp. 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Bühlmann, P. MissForest—non-parametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boser, B.E.; Guyon, I.M.; Vapnik, V.N. A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Workshop on Computational Learning Theory (COLT’92), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–29 July 1992; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Bauters, C.; Lamblin, N.; Mc Fadden, E.P.; Van Belle, E.; Millaire, A.; De Groote, P. Influence of diabetes mellitus on heart failure risk and outcome. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2003, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damman, K.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Navis, G.; Vaidya, V.S.; Smilde, T.D.; Westenbrink, B.D.; Bonventre, J.V.; Voors, A.A.; Hillege, H.L. Tubular damage in chronic systolic heart failure is associated with reduced survival independent of glomerular filtration rate. Heart 2010, 96, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metra, M.; Cotter, G.; Gheorghiade, M.; Dei Cas, L.; Voors, A.A. The role of the kidney in heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Greene, S.J.; Papadimitriou, L.; Zannad, F.; Yancy, C.W.; Gheorghiade, M.; Butler, J. Population risk prediction models for incident heart failure: A systematic review. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinar, J.; Jarkovsky, J.; Spinarova, L.; Mebazaa, A.; Gayat, E.; Vitovec, J.; Linhart, A.; Widimsky, P.; Miklik, R.; Zeman, K.; et al. AHEAD score--Long-term risk classification in acute heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 202, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Sung, S.-H.; Cheng, H.-M.; Huang, W.-M.; Wu, C.-L.; Huang, C.-J.; Hsu, P.-F.; Yeh, J.-S.; Guo, C.-Y.; Yu, W.-C.; et al. Performance of AHEAD Score in an Asian Cohort of Acute Heart Failure With Either Preserved or Reduced Left Ventricular Systolic Function. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.Y.; Chan, C.H.; Chou, Y.C.; Sung, S.H.; Cheng, H.M. A Statistical Predictive Model Consistent Within a 5-Year Follow-up Period for Patients with Acute Heart Failure. J. Chin. Med Assoc. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, F.S. Implementation of Machine Learning Model to Predict Heart Failure Disease. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedberg, K. Heart failure subtypes: Pathophysiology and definitions. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 13, 108815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvozdanović, Z.; Farčić, N.; Šimić, H.; Buljanović, V.; Gvozdanović, L.; Katalinić, S.; Pačarić, S.; Gvozdanović, D.; Dujmić, Ž.; Miškić, B.; et al. The Impact of Education, COVID-19 and Risk Factors on the Quality of Life in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 27, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Segar, M.W.; Vaduganathan, M.; Patel, K.V.; McGuire, D.K.; Butler, J.; Fonarow, G.C.; Basit, M.; Kannan, V.; Grodin, J.L.; Everett, B. Machine Learning to Predict the Risk of Incident Heart Failure Hospitalization Among Patients With Diabetes: The WATCH-DM Risk Score. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Roy, J.; Stewart, W.F. Prediction modeling using EHR data: Challenges, strategies, and a comparison of machine learning approaches. Med Care 2010, 48 (Suppl. 6), S106–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, B. Fundamentals of Biostatistics; Nelson Education: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Baseline Characteristic | Total Population n = 3327 | Non-HF n = 3081 (92.6%) | HF n = 246 (7.4%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 54.96 (12.59) | 54.24 (12.37) | 63.91 (11.98) |
| BMI | 31.82 (7.2) | 31.72 (7.18) | 33.02 (7.31) |
| Waist | 100.83 (16.03) | 100.4 (15.93) | 106.9 (16.14) |
| High School Graduate | 2761 (83.26%) | 2607 (84.92%) | 154 (62.60%) |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 1228 (36.91%) | 1132 (36.74%) | 96 (39.02%) |
| Female | 2099 (63.09%) | 1949 (63.26%) | 150 (60.98%) |
| Current Smoker | 406 (12.31%) | 374 (12.25%) | 32 (13.11%) |
| Hypertension (HTN) | 1845 (55.47%) | 1644 (53.38%) | 201 (81.71%) |
| Diabetes Mellitus (DM) | 710 (21.5%) | 593 (19.39%) | 117 (47.95%) |
| <1% | <3% | <5% | <10% | <20% | <30% | <40% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age (0.0923) | age (0.0213) | DMmeds (0.0492) | DMmeds (0.0222) | dmMeds (0.0178) | CVDHx (0.0267) | frs_chdtenyrrisk (0.0507) |
| DMmeds (0.0647) | RepolarAntLat (0.0189) | age (0.0290) | Diabetes (0.0192) | MIHx (0.0174) | ascvd_tenyrrisk (0.0260) | ALDOSTERONE (0.0367) |
| Diabetes (0.0431) | DMmeds (0.0187) | BP3cat (0.0270) | CVDHx (0.0189) | EF (0.0170) | rrs_tenyrrisk (0.0220) | eGFRmdrd (0.0352) |
| eGFRckdepi (0.0315) | Diabetes (0.0180) | HTN (0.0267) | bpjnc7_3 (0.0187) | HbA1cIFCC (0.0150) | numbnessEver (0.0203) | occupation (0.0331) |
| MIecg (0.0305) | CVDHx (0.0174) | sbp (0.0237) | CHDHx (0.0176) | HbA1c (0.0148) | nutrition3cat (0.0194) | abi (0.0317) |
| RepolarAntLat (0.0297) | eGFRmdrd (0.0173) | eGFRckdepi (0.0233) | eGFRckdepi (0.0174) | strokeHx (0.0141) | FEV1PP (0.0193) | sbp (0.0297) |
| antiArythMeds (0.028) | eGFRckdepi (0.0173) | CVDHx (0.0188) | FPG (0.0170) | Diabetes (0.0141) | totchol (0.0186) | calBlkMeds (0.0292) |
| RepolarAnt (0.0272) | statinMeds (0.0168) | QTcFrid (0.0187) | age (0.0170) | visionLossEver (0.0140) | asthma (0.0180) | FVC (0.0289) |
| statinMeds (0.0268) | edu3cat (0.0163) | BPmeds (0.0184) | sbp (0.0164) | statinMeds (0.0129) | BPmeds (0.0177) | eGFRckdepi (0.0253) |
| CVDHx (0.0262) | CardiacProcHx (0.0162) | waist (0.01831) | waist (0.0160) | frs_chdtenyrrisk (0.0129) | HTN (0.0177) | SCrCC (0.0242) |
| <1% | <3% | <5% | <10% | <20% | <30% | <40% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes (0.0455) | DMmeds (0.0346) | DMmeds (0.0588) | DMmeds (0.0233) | DMmeds (0.0630) | DMmeds (0.0210) | DMmeds (0.0337) |
| DMmeds (0.0439) | age (0.0273) | Diabetes (0.0327) | age (0.0221) | age (0.0383) | age (0.0196) | DialysisEver (0.0252) |
| age (0.0408) | CVDHx (0.0265) | DialysisEver (0.0243) | eGFRckdepi (0.0185) | Diabetes (0.0297) | Diabetes (0.0158) | CVDHx (0.0207) |
| HTN (0.0336) | eGFRckdepi (0.0263) | MIAntLat (0.0191) | Diabetes (0.0183) | DialysisEver (0.0190) | BPmeds (0.0150) | age (0.0151) |
| CVDHx (0.0277) | HTN (0.0260) | age (0.0189) | FEV1 (0.0163) | ConductionDefect (0.0183) | CVDHx (0.0147) | Afib (0.0142) |
| HSgrad (0.0273) | HSgrad (0.0246) | HSgrad (0.0157) | CVDHx (0.0158) | sex (0.0180) | age (0.0145) | MIHx (0.0136) |
| BPmeds (0.0272) | Diabetes (0.0237) | Afib (0.0148) | FVC (0.0156) | occupation (0.0159) | ConductionDefect (0.0141) | eGFRckdepi (0.0129) |
| eGFRckdepi (0.0238) | eGFRmdrd (0.0225) | edu3cat (0.0138) | CHDHx (0.0152) | MIant (0.0143) | FEV1 (0.0141) | SystLVdia (0.0128) |
| RepolarAntLat (0.0229) | MIHx (0.0212) | CVDHx (0.0135) | eGFRmdrd (0.0151) | CVDHx (0.0129) | eGFRckdepi (0.0139) | EF (0.0117) |
| ecgHR (0.0206) | sbp (0.0191) | EF (0.0130) | HbA1cIFCC (0.0148) | idealHealthSMK (0.0125) | CHDHx (0.0126) | ConductionDefect (0.0115) |
| <1% | <3% | <5% | <10% | <20% | <30% | <40% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes (0.0435) | age (0.0320) | DMmeds (0.0848) | DMmeds (0.0261) | DMmeds (0.0443) | DMmeds (0.0145) | DMmeds (0.0318) |
| DMmeds (0.0409) | DMmeds (0.0266) | age (0.0302) | age (0.0177) | age (0.0420) | age (0.0142) | DialysisEver (0.0294) |
| age (0.0386) | MIHx (0.0234) | MIant (0.0245) | CVDHx (0.0175) | CVDHx (0.0321) | eGFRmdrd (0.0138) | age (0.0234) |
| HTN (0.0299) | Diabetes (0.0213) | CVDHx (0.0241) | eGFRckdepi (0.0173) | EF (0.0188) | Diabetes (0.0130) | Diabetes (0.0145) |
| CVDHx (0.0277) | CVDHx (0.0209) | Diabetes (0.0236) | Diabetes (0.0167) | eGFRckdepi (0.0182) | SCrCC (0.0122) | Afib (0.0143) |
| BPmeds (0.0274) | eGFRckdepi (0.0205) | HSgrad (0.0206) | eGFRmdrd (0.0153) | FEV1 (0.0179) | eGFRckdepi (0.0118) | CVDHx (0.0128) |
| HSgrad (0.0264) | HSgrad (0.0176) | ConductionDefect (0.0201) | FEV1 (0.0153) | ConductionDefect (0.0174) | statinMeds (0.0115) | eGFRckdepi (0.0126) |
| eGFRckdepi (0.0222) | HTN (0.0172) | antiArythMedsSelf (0.0152) | CHDHx (0.0152) | MIHx (0.0172) | CVDHx (0.0112) | MIHx (0.0120) |
| RepolarAntLat (0.0209) | antiArythMeds (0.0171) | CHDHx (0.1431) | edu3cat (0.0142) | MajorScarAnt (0.0172) | everSmoker (0.0111) | calBlkMeds (0.0116) |
| ecgHR (0.0196) | eGFRmdrd (0.0164) | AntiArythMeds (0.1374) | DialysisEver (0.0139) | eGFRmdrd (0.0170) | rrs_tenyrrisk (0.0108) | FEV1 (0.0113) |
| <1% | <3% | <5% | <10% | <20% | <30% | <40% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes (0.0455) | antiArythMeds (0.0339) | dmMeds (0.0340) | DMmeds (0.0263) | DMmeds (0.0443) | DMmeds (0.0163) | DMmeds (0.0290) |
| DMmeds (0.0363) | DMmeds (0.0332) | age (0.0279) | age (0.0251) | DialysisEver (0.0323) | Diabetes (0.0161) | ascvd_tenyrrisk (0.0255) |
| age (0.0344) | age (0.0301) | Diabetes (0.0271) | Diabetes (0.0234) | MIAntLat (0.0241) | rrs_tenyrrisk (0.0148) | age (0.0218) |
| HTN (0.0336) | eGFRckdepi (0.0241) | eGFRckdepi (0.0269) | CVDHx (0.0218) | Diabetes (0.0208) | age (0.0132) | eGFRckdepi (0.0210) |
| CVDHx (0.0318) | HTN (0.0232) | CVDHx (0.0235) | CHDHx (0.0194) | age (0.0194) | ascvd_tenyrrisk (0.0130) | rrs_tenyrrisk (0.0191) |
| HSgrad (0.0274) | SCrIDMS (0.0220) | eGFRmdrd (0.0212) | eGFRmdrd (0.0192) | Afib (0.0184) | MIant (0.0127) | frs_cvdtenyrrisk (0.0179) |
| eGFRckdepi (0.0243) | MIHx (0.0207) | HSgrad (0.0198) | eGFRckdepi (0.0162) | calBlkMeds (0.0154) | eGFRckdepi (0.0125) | MIHx (0.0162) |
| CHDHx (0.0241) | CVDHx (0.0198) | SCrIDMS (0.0187) | HSgrad (0.0162) | CVDHx (0.0152) | CVDHx (0.0118) | LEPTIN (0.0147) |
| RepolarAntLat (0.0238) | eGFRmdrd (0.0197) | BPMeds (0.0170) | FEV1 (0.0149) | eGFRckdepi (0.0149) | FEV1 (0.0106) | calBlkMeds (0.0135) |
| QTcBaz (0.0221) | Diabetes (0.0195) | HbA1c (0.0158) | SCrIDMS (0.0148) | EF (0.0140) | CHDHx (0.0104) | CardiacProcHx (0.0127) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.-Y.; Wu, M.-Y.; Cheng, H.-M. The Comprehensive Machine Learning Analytics for Heart Failure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094943
Guo C-Y, Wu M-Y, Cheng H-M. The Comprehensive Machine Learning Analytics for Heart Failure. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(9):4943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094943
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Chao-Yu, Min-Yang Wu, and Hao-Min Cheng. 2021. "The Comprehensive Machine Learning Analytics for Heart Failure" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 9: 4943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094943
APA StyleGuo, C.-Y., Wu, M.-Y., & Cheng, H.-M. (2021). The Comprehensive Machine Learning Analytics for Heart Failure. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(9), 4943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094943







