The Acute Effect of Hyperoxia on Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation (OBLA) and Performance in Female Runners during the Maximal Treadmill Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
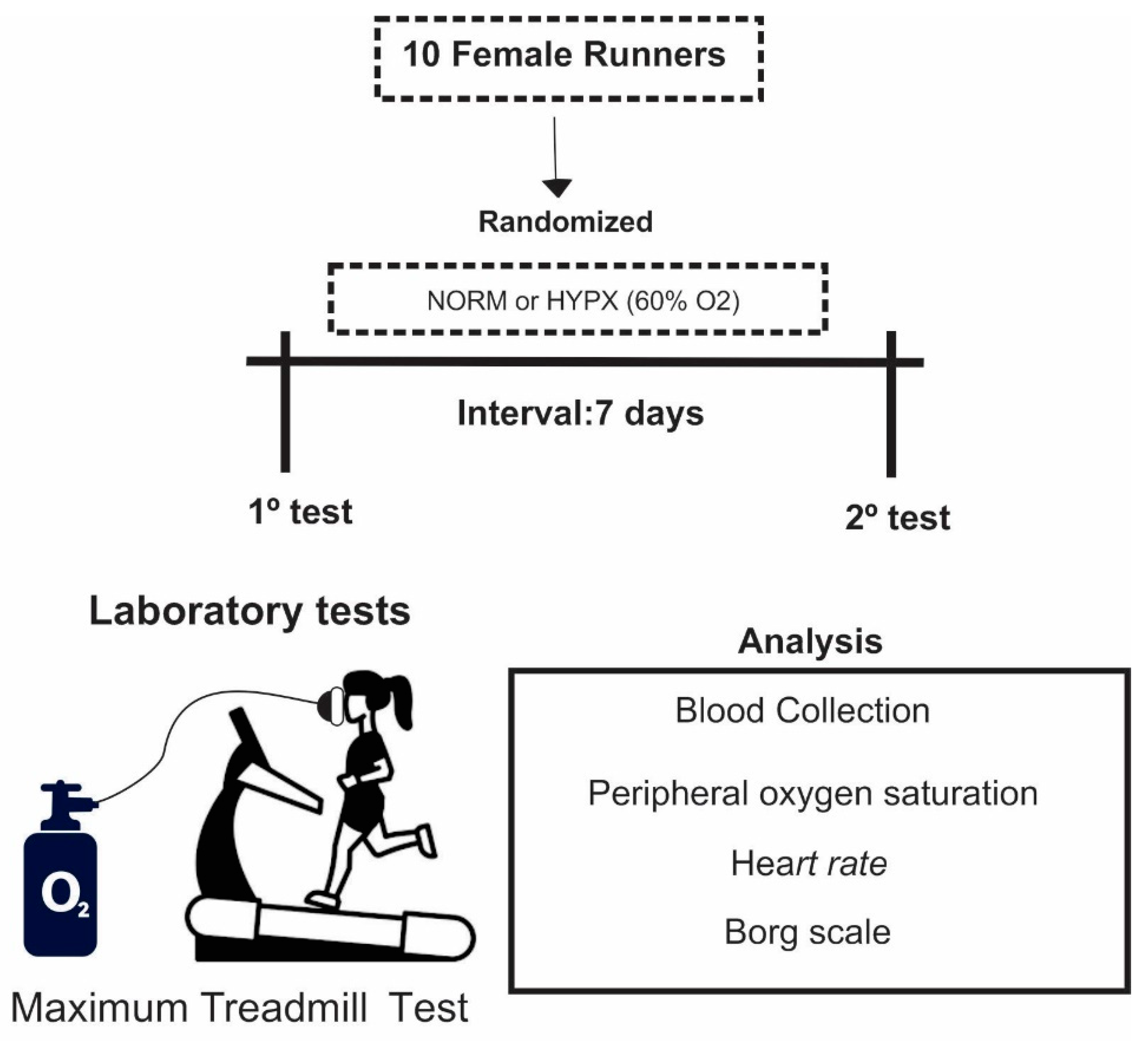
2.1. Design and Sample
2.2. Protocol
2.3. Statistical Analysis
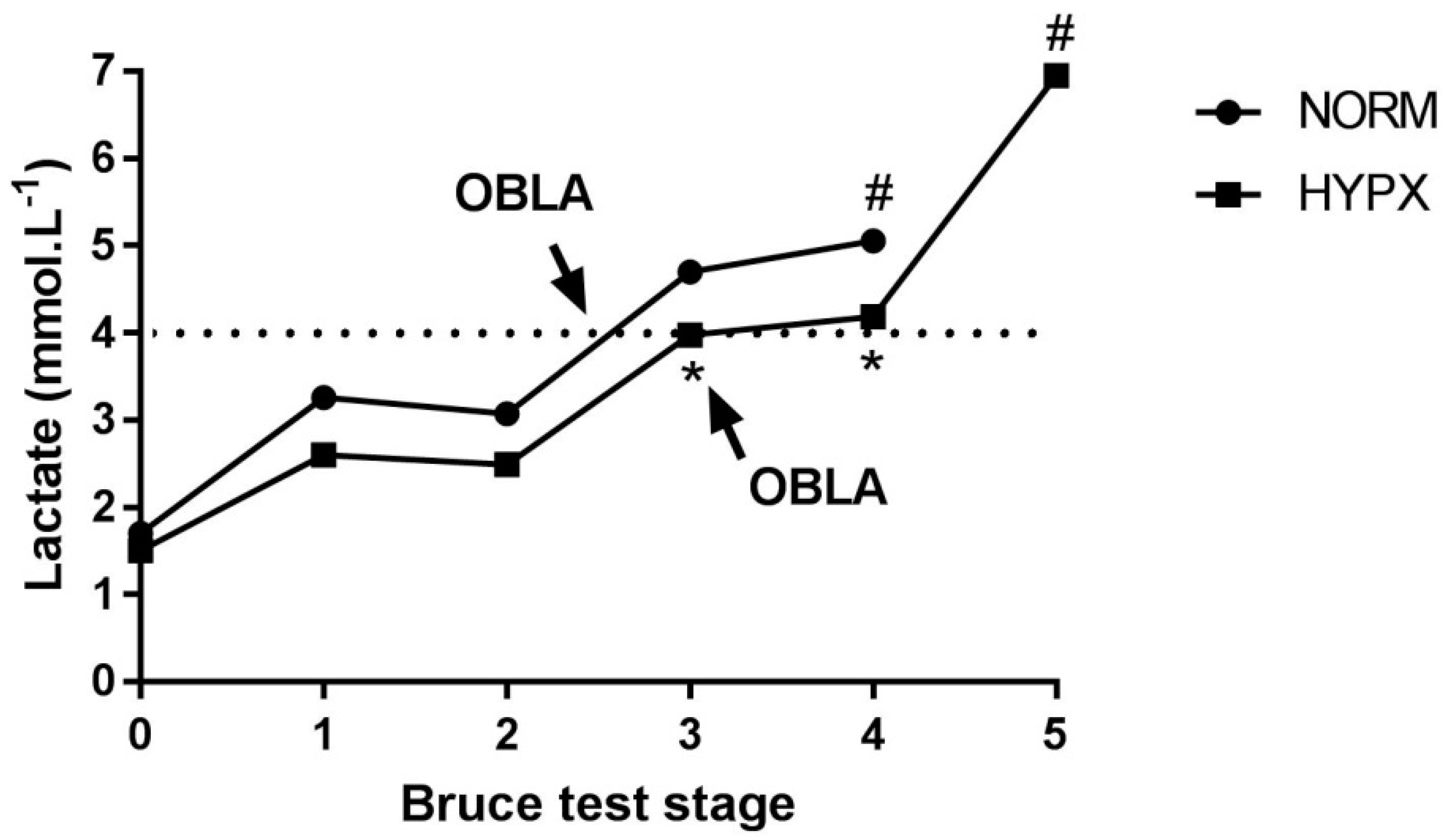
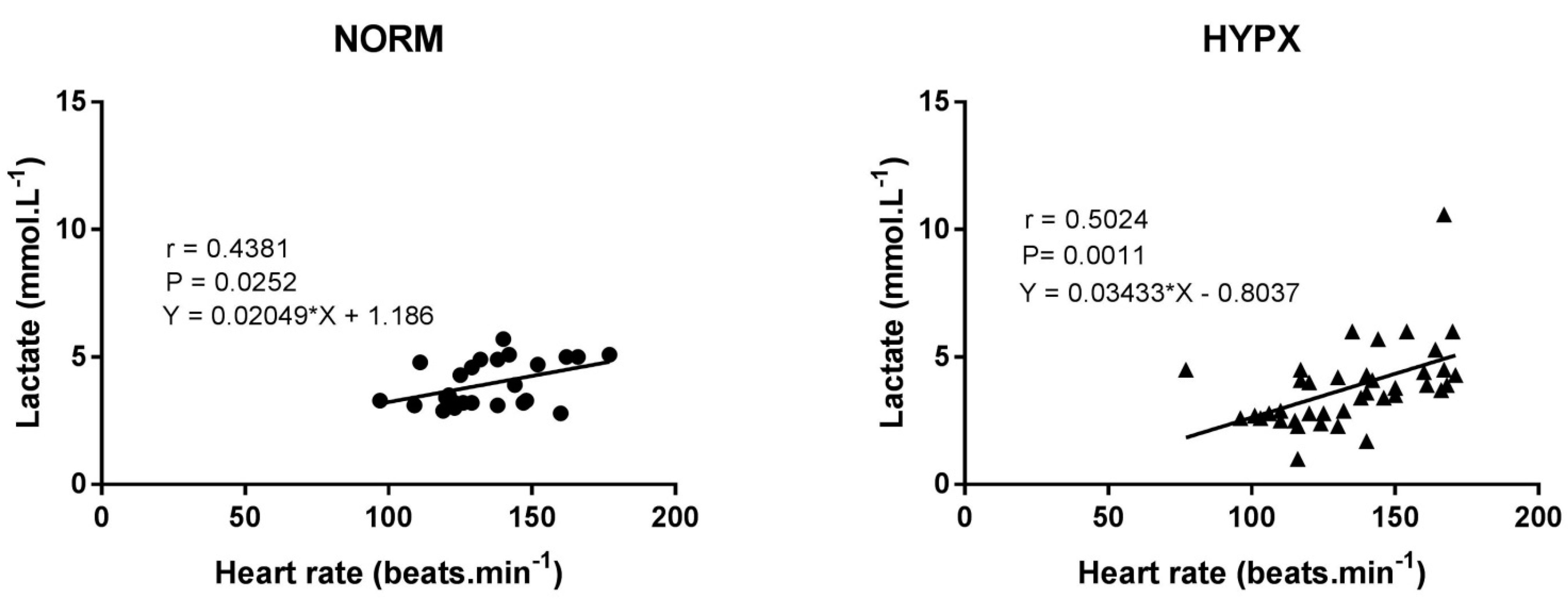
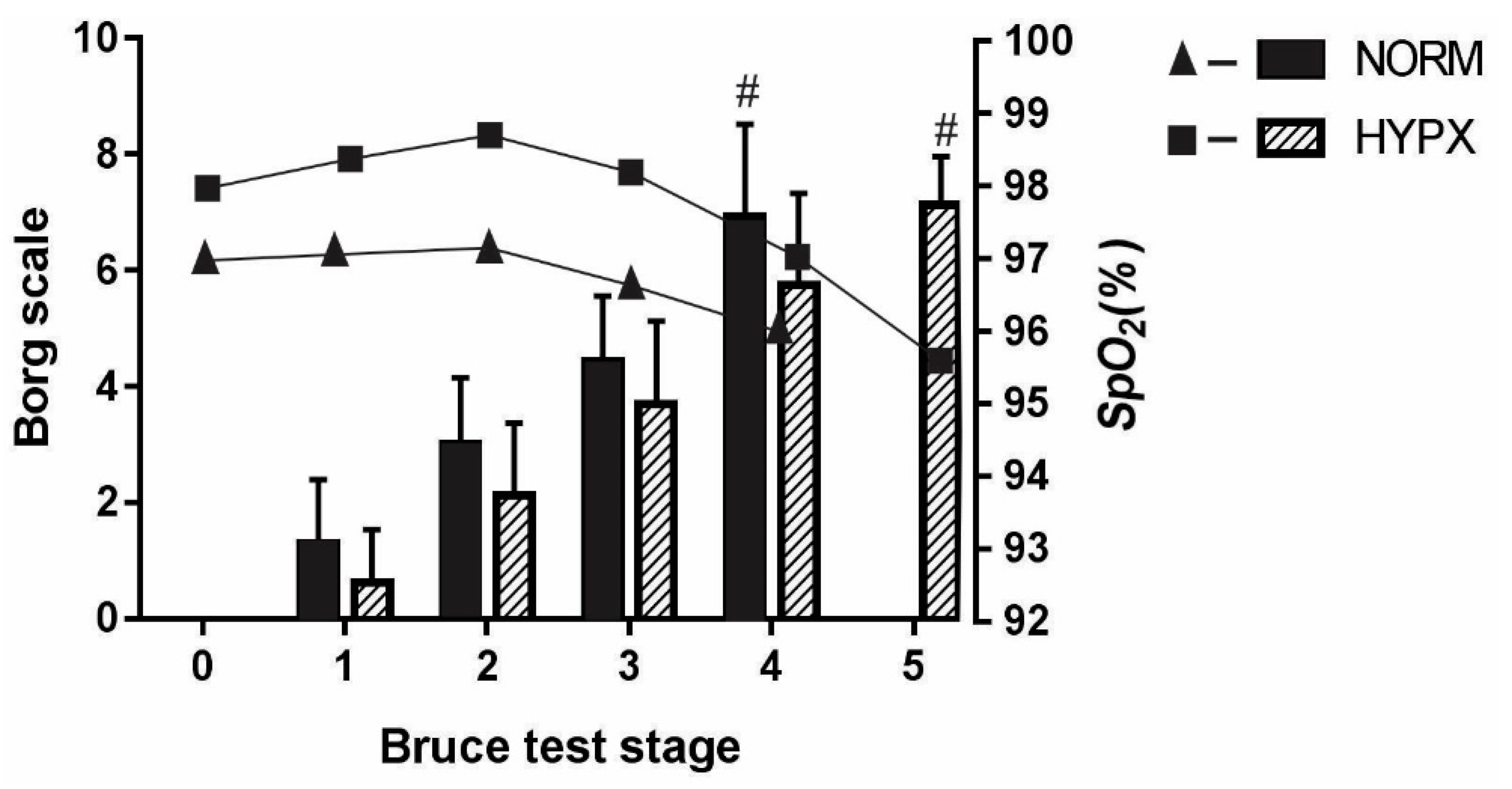
3. Results
4. Discussion
Future Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauser, A.; Zinner, C.; Born, D.-P.; Wehrlin, J.P.; Sperlich, B. Does hyperoxic recovery during cross-country skiing team sprints enhance performance? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallette, M.M.; Stewart, D.G.; Cheung, S.S. The Effects of Hyperoxia on Sea-Level Exercise Performance, Training, and Recovery: A Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 48, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, D.P.; Joyner, M.J.; Claus, P.L.; Curry, T.B. Hyperbaric hyperoxia reduces exercising forearm blood flow in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H1892–H1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.S.; Grassi, B.; Gavin, T.P.; Haseler, L.J.; Tagore, K.; Roca, J.; Wagner, P.D. Evidence of O2 supply-dependent VO2 max in the exercise-trained human quadriceps. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 86, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Howley, E.T. Fisiologia do Exercício: Teoria e Aplicação ao Condicionamento e ao Desempenho, 8th ed.; Manole: São Paulo, Brasil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sperlich, B.; Calbet, J.A.; Boushel, R.; Holmberg, H.C. Is the use of hyperoxia in sports effective, safe and ethical? Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.G.R.; Talanian, J.L.; Heigenhauser, G.J.F.; Spriet, L.L. The effects of training in hyperoxia vs. normoxia on skeletal muscle enzyme activities and exercise performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Linossier, M.; Dormois, D.; Arsac, L.; Denis, C.; Gay, J.; Geyssant, A.; Lacour, R. Effect of hyperoxia on aerobic and anaerobic performances and muscle metabolism during maximal cycling exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2000, 168, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, D.A.; Ekblom, B. Hyperoxia for performance and training. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperlich, B.; Zinner, C.; Krueger, M.; Wegrzyk, J.; Achtzehn, S.; Holmberg, H.-C. Effects of hyperoxia during recovery from 5x30-s bouts of maximal-intensity exercise. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susta, D.; Dudnik, E.; Glazachev, O.S. A programme based on repeated hypoxia-hyperoxia exposure and light exercise enhances performance in athletes with overtraining syndrome: A pilot study. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2017, 37, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czuba, M.; Waskiewicz, Z.; Zajac, A.; Poprzecki, S.; Cholewa, J.; Roczniok, R. The effects of intermittent hypoxic training on aerobic capacity and endurance performance in cyclists. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2011, 10, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sperlich, B.; Zinner, C.; Hauser, A.; Holmberg, H.C.; Wegrzyk, J. The Impact of Hyperoxia on Human Performance and Recovery. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugniaux, J.V.; Coombs, G.B.; Barak, O.F.; Dujic, Z.; Sekhon, M.S.; Ainslie, P.N. Highs and lows of hyperoxia: Physiological, performance, and clinical aspects. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 315, R1–R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stellingwerff, T.; LeBlanc, P.J.; Hollidge, M.G.; Heigenhauser, G.J.; Spriet, L.L. Hyperoxia decreases muscle glycogenolysis, lactate production, and lactate efflux during steady-state exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 290, E1180–E1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, F.D., Jr.; Snell, P.G.; Stray-Gundersen, J. Effects of 100% Oxygen on Performance of Professional Soccer Players. JAMA 1989, 262, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinner, C.; Hauser, A.; Born, D.-P.; Wehrlin, J.P.; Holmberg, H.-C.; Sperlich, B. Influence of Hypoxic Interval Training and Hyperoxic Recovery on Muscle Activation and Oxygenation in Connection with Double-Poling Exercise. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzakis, M.; González-Alonso, J.; Graham, T.E.; Saltin, B. Hemodynamics and O2 uptake during maximal knee extensor exercise in untrained and trained human quadriceps muscle: Effects of hyperoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, D.R.; Poole, D.C.; Hogan, M.C.; Bebout, D.E.; Wagner, P.D. Effect of inspired O2 concentration on leg lactate release during incremental exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1996, 81, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, P.K.; Kiens, B.; Saltin, B. Hyperoxia does not increase peak muscle oxygen uptake in small muscle group exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1999, 166, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, M.C.; Cox, R.H.; Welch, H.G. Lactate accumulation during incremental exercise with varied inspired oxygen fractions. J. Appl. Physiol. 1983, 55, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.W.; Lantis, D.J.; Ade, C.J.; Cantrell, G.S.; Larson, R.D. Aerobic exercise supplemented with muscular endurance training improves onset of blood lactate accumulation. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, B.; Jacobs, I. Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation and Marathon Running Performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 1981, 2, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellish, R.L.; Goslin, B.R.; Olson, R.E.; McDonald, A.; Russ, G.D.; Moudgil, V.K. Longitudinal modeling of the relationship between age and maximal heart rate. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grissom, R.; Kim, J. Effect Sizes for Research: A Broad Practical Approach; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Batterham, A.M.; Hopkins, W.G. Making meaningful inferences about magnitudes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2006, 1, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, J.B.; Mulkey, D.K.; Henderson, R.A.; Potter, S.J.; Putnam, R.W. Hyperoxia, reactive oxygen species, and hyperventilation: Oxygen sensitivity of brain stem neurons. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spriet, L.L.; Howlett, R.A.; Heigenhauser, G.J. An enzymatic approach to lactate production in human skeletal muscle during exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, H.G.; Bonde-Petersen, F.; Graham, T.; Klausen, K.; Secher, N. Effects of hyperoxia on leg blood flow and metabolism during exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1977, 42, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, M.L.; Ellis, C.G.; Goldman, D.; Stephenson, A.H.; Dietrich, H.H.; Sprague, R.S. Erythrocytes: Oxygen sensors and modulators of vascular tone. Physiology 2009, 24, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprague, R.S.; Ellsworth, M.L.; Stephenson, A.H.; Lonigro, A.J. Participation of cAMP in a signal-transduction pathway relating erythrocyte deformation to ATP release. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 281, C1158–C1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gole, Y.; Gargne, O.; Coulange, M.; Steinberg, J.-G.; Bouhaddi, M.; Jammes, Y.; Regnard, J.; Boussuges, A. Hyperoxia-induced alterations in cardiovascular function and autonomic control during return to normoxic breathing. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, W.S.; Thomson, A.J.; Adwani, S.H.; Rosseel, A.J.; Potter, J.F.; Webb, D.J.; Maxwell, S.R.J. Cardiovascular effects of acute oxygen administration in healthy adults. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2003, 42, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.M. The roles of adenosine and related substances in exercise hyperaemia. J. Physiol. 2007, 583, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulding, R.P.; Roche, D.M.; Marwood, S. Effect of Hyperoxia on Critical Power and V˙ O2 Kinetics during Upright Cycling. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhatalo, A.; Fulford, J.; DiMenna, F.J.; Jones, A.M. Influence of hyperoxia on muscle metabolic responses and the power–duration relationship during severe-intensity exercise in humans: A 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Exp. Physiol. 2010, 95, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Dawson, B.; Landers, G.; Croft, K.; Peeling, P. Effect of supplemental oxygen on post-exercise inflammatory response and oxidative stress. Eur. J. Appl Physiol. 2013, 113, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapalamadugu, K.C.; Panguluri, S.K.; Bennett, E.S.; Kolliputi, N.; Tipparaju, S.M. High level of oxygen treatment causes cardiotoxicity with arrhythmias and redox modulation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 282, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummela, A.; Hamalaine, I.; Rusko, H. Effect of hyperoxia on metabolic responses and recovery in intermittent exercise. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2002, 12, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terziyski, K.; Andonov, V.; Marinov, B.; Kostianev, S. Exercise performance and ventilatory efficiency in patients with mild and moderate liver cirrhosis. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 35, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenette, J.A.; Diep, T.T.; Koehle, M.S.; Foster, G.E.; Richards, J.C.; Sheel, A.W. Acute hypoxic ventilatory response and exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia in men and women. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2004, 143, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, C.A.; McClaran, S.R.; Nickele, G.A.; Pegelow, D.F.; Nelson, W.B.; Dempsey, J.A. Exercise-induced arterial hypoxaemia in healthy young women. J. Physiol. 1998, 507, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, S.; Levine, B.D. Beyond the Bruce Protocol: Advanced Exercise Testing for the Sports Cardiologist. Cardiol. Clin. 2016, 34, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Condition | Stage 1 (Beats.min−1) | Stage 2 (Beats.min−1) | Stage 3 (Beats.min−1) | Stage 4 (Beats.min−1) | Stage 5 (Beats.min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HYPX | 108.2 ± 8.8 | 128.7 ± 11.6 | 144.7 ± 29.7 * | 139.7 ± 21.9 * | 152.2 ± 15.5 * |
| NORM | 118.8 ± 16.1 | 133.8 ± 15.3 | 134.1 ± 13.6 | 155.8 ± 18.3 * | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, T.C.; Aidar, F.J.; Zanona, A.d.F.; Matos, D.G.; Pereira, D.D.; Rezende, P.E.N.; Ferreira, A.R.P.; Junior, H.A.; Santos, J.L.d.; Silva, D.d.S.; et al. The Acute Effect of Hyperoxia on Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation (OBLA) and Performance in Female Runners during the Maximal Treadmill Test. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094546
Silva TC, Aidar FJ, Zanona AdF, Matos DG, Pereira DD, Rezende PEN, Ferreira ARP, Junior HA, Santos JLd, Silva DdS, et al. The Acute Effect of Hyperoxia on Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation (OBLA) and Performance in Female Runners during the Maximal Treadmill Test. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(9):4546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094546
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Thays C., Felipe J. Aidar, Aristela de Freitas Zanona, Dihogo Gama Matos, Danielle D. Pereira, Paulo Emmanuel Nunes Rezende, Alexandre Reis Pires Ferreira, Heleno Almeida Junior, Jymmys Lopes dos Santos, Devisson dos Santos Silva, and et al. 2021. "The Acute Effect of Hyperoxia on Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation (OBLA) and Performance in Female Runners during the Maximal Treadmill Test" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 9: 4546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094546
APA StyleSilva, T. C., Aidar, F. J., Zanona, A. d. F., Matos, D. G., Pereira, D. D., Rezende, P. E. N., Ferreira, A. R. P., Junior, H. A., Santos, J. L. d., Silva, D. d. S., Barbosa, F. D. S., Thuany, M., & Souza, R. F. d. (2021). The Acute Effect of Hyperoxia on Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation (OBLA) and Performance in Female Runners during the Maximal Treadmill Test. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(9), 4546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094546








