Assessment of the Hearing Status of School-Age Children from Rural and Urban Areas of Mid-Eastern Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Otoscopy
3.2. Impedance Audiometry (IA)
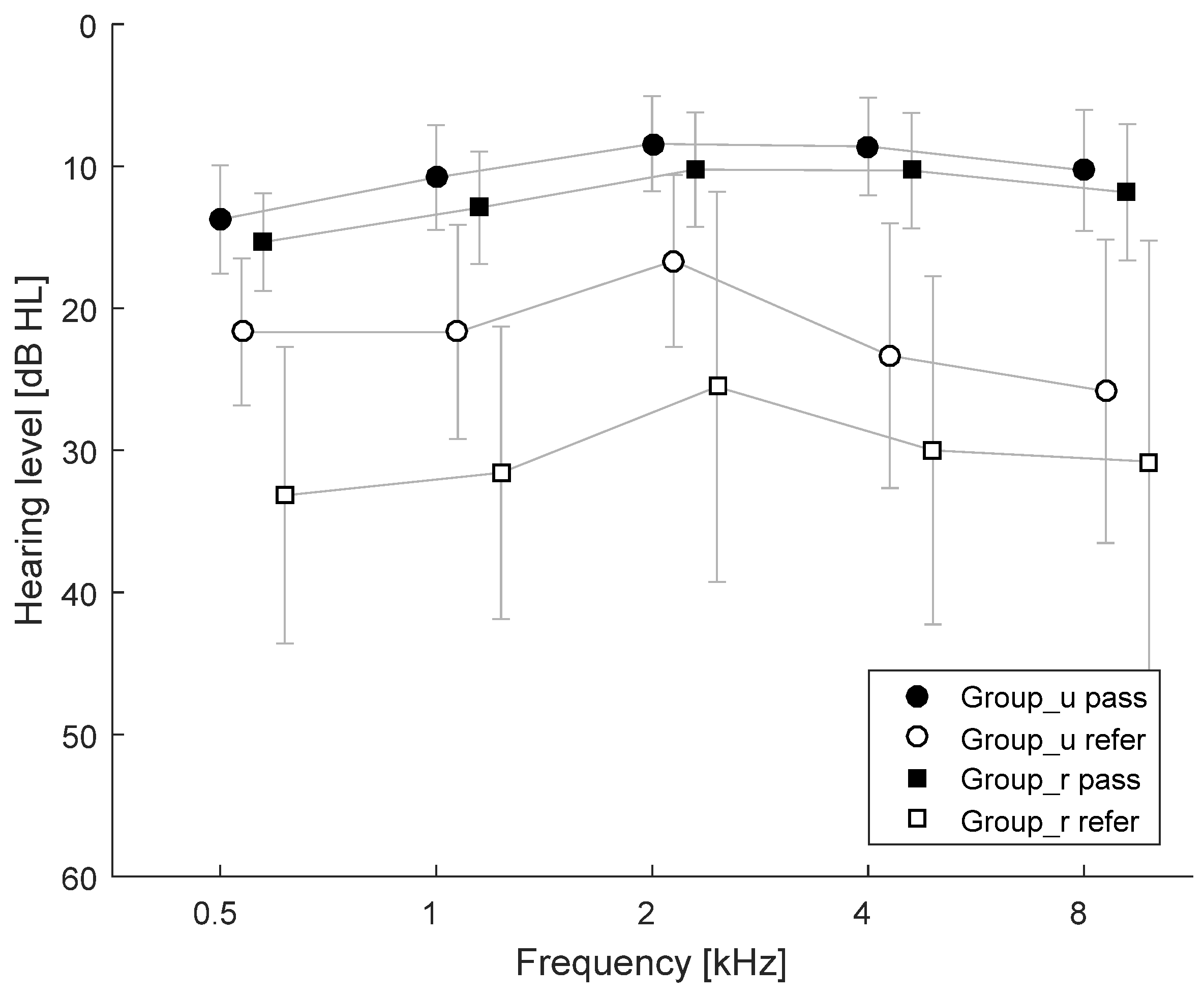
3.3. Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA)
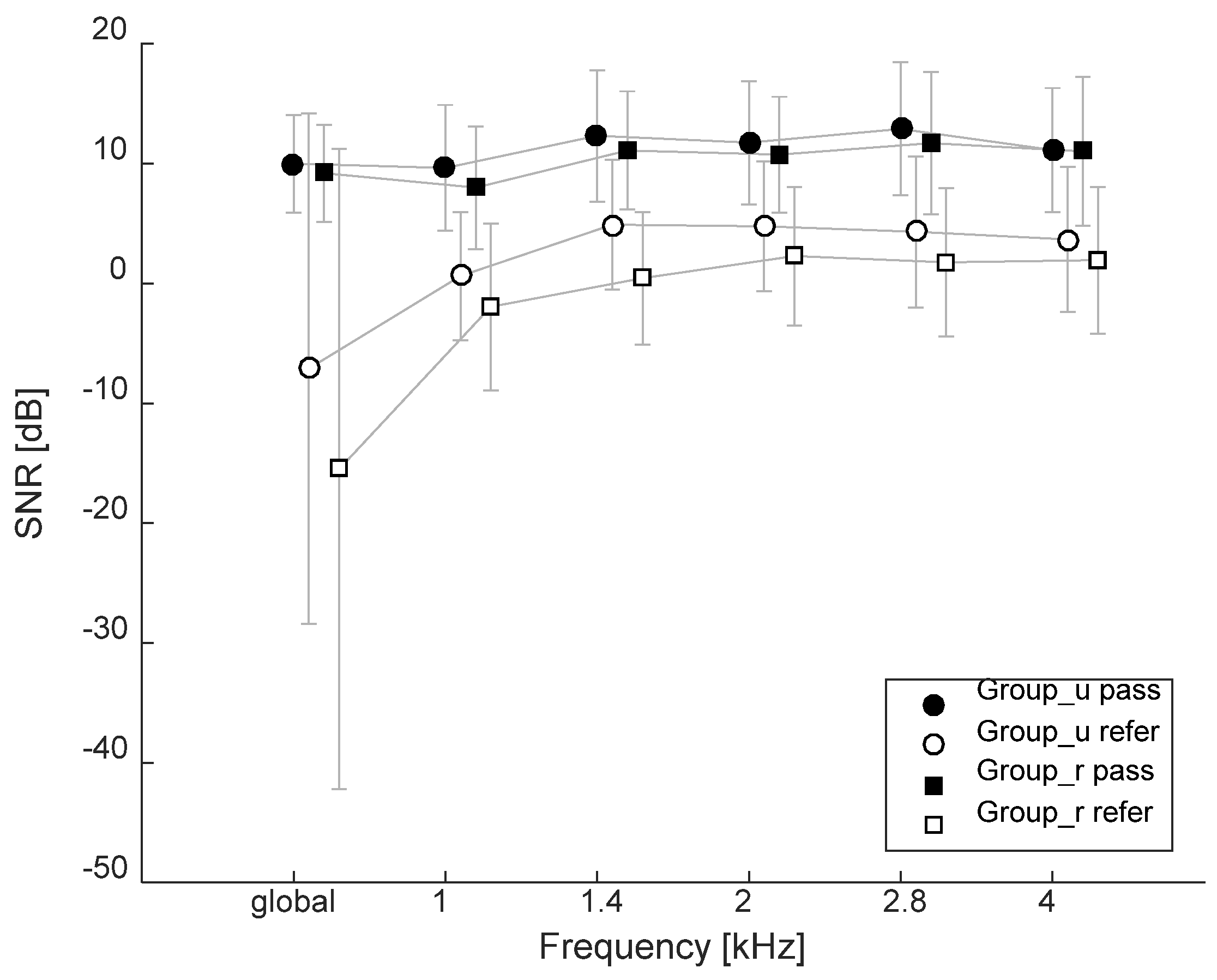
3.4. Transient-Evoked Otoacoustic Emissions (TEOAEs)
3.5. Summary of Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Deafness and Hearing Loss. Available online: http://www.who.int/newsroom/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 6 June 2019).
- Cho Lieu, J.E. Speech-language and educational consequences of unilateral hearing loss in children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, B.O.; Ruben, R.J.; Parving, A. Reducing the burden of communication disorders in the developing world: An opportunity for the millennium development project. JAMA 2006, 296, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Clercq, C.M.P.; Labuschagne, L.J.E.; Franken, M.C.; Baatenburg de jong, R.J.; Luijk, M.P.C.M.; Jansen, P.W.; van der Schroeff, M.P. Association of slight to mild hearing loss with behavioral problems and school performance in children. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, C.E.; Grøntved, A.M. Cochlear implantation and change in quality of life. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000, 120, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, W.; Anvizino, R.; Giannantonio, S.; Schinaia, L.; Paludetti, G. The effects of cochlear implantation on quality of life in the elderly. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, F.; Freni, F.; Gazia, F.; Galletti, B. Endomeatal approach in cochlear implant surgery in a patient with small mastoid cavity and procident lateral sinus. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e229518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czechowicz, J.A.; Messner, A.H.; Alarcon-Matutti, E.; Alarcon, J.; Quinones-Calderon, G.; Montano, S.; Zunt, J.R. Hearing impairment and poverty: The epidemiology of ear disease in Peruvian schoolchildren. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 142, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weinhold, I.; Gurtner, S. Understanding shortages of sufficient health care in rural areas. Health Policy 2014, 118, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douthit, N.; Kiv, S.; Dwolatzky, T.; Biswas, S. Exposing some important barriers to health care access in the rural USA. Public Health 2015, 129, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elpers, J.; Lester, C.; Shinn, J.B.; Bush, M.L. Rural family perspectives and experiences with early infant hearing detection and intervention: A qualitative study. J. Community Health 2016, 41, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, M.L.; Kaufman, M.R.; McNulty, B.N. Disparities in access to pediatric hearing healthcare. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 25, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Guo, H.-R.; Lai, D.-C. Prevalence of childhood hearing impairment of different severities in urban and rural areas: A nationwide population-based study in Taiwan. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, M.; Duncan, J.; Dally, K. A systematic review of services to DHH children in rural and remote regions. J. Deaf Stud. Deaf Educ. 2018, 23, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Malesińska, M.; Skarzyński, H.; Ołtarzewski, M.; Szymborski, J.; Ratyńska, J. Project of the countrywide data collecting system for neonatal hearing screening programme in Poland. Scand. Audiol. 2001, 52, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Dantas, M.B.; dos Anjos, C.A.L.; Camboim, E.D.; de Carvalho Ramos Pimentel, M. Results of a neonatal hearing screening program in Maceio. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 75, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Hind, S. The newborn hearing screening programme in England. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2003, 67, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uloziene, I.; Grandori, F. The European project AHEAD II on newborn hearing screening. Int. Congr. 2003, 1240, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabli, H.; Genc, G.A.; Kayikci, M.E.K.; Turkyilmaz, M.D.; Ozturk, B.; Karabulut, E.; Korkmaz, A.; Belgin, E. Hearing screening protocols of babies with hearing loss risk factors in Turkey. Int. Adv. Otol. 2010, 6, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization; Wilson, J.M.G.; Jungner, G. Principles and Practice of Screening for Disease. Geneva. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/37650 (accessed on 6 June 2019).
- Berg, A.L.; Papri, H.; Ferdous, S.; Khan, N.Z.; Durkin, M.S. Screening methods for childhood hearing impairment in rural Bangladesh. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 70, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minja, B.M.; Machemba, A. Prevalence of otitis media, hearing impairment and cerumen impaction among school children in rural and urban Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1996, 37, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraeni, R.; Hartanto, W.W.; Djelantik, B.; Ghanie, A.; Utama, D.S.; Setiawan, E.P.; Lukman, E.; Hardiningsih, C.; Asmuni, S.; Budiarti, R.; et al. Otitis media in Indonesian urban and rural school children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Rupa, V.; Job, A.; Joseph, A. Hearing impairment and otitis media in a rural primary school in South India. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1997, 39, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarżyński, P.H.; Świerniak, W.; Gocel, M.; Tarczyński, K.; Soćko, S.; Król, B.; Kochanek, K.; Doliński, P.; Skarżyński, H. Program badań przesiewowych słuchu dla uczniów klas pierwszych szkół podstawowych z województwa mazowieckiego. Now Audiofonol. 2020, 9, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarzyński, H.; Gos, E.; Świerniak, W.; Skarżyński, P.H. Prevalence of hearing loss among polish school-age children from rural areas—Results of hearing screening program in the sample of 67,416 children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 128, 109676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarzyński, P.H.; Kochanek, K.; Ludwikowski, M.; Zapert, A.; Ganc, M.; Senderski, A.; Skarżyński, H.; Piłka, A.; Piotrowska, A.; Król, B. Hearing screening in 6th grade children in primary schools in Warsaw. J. Hear. Sci. 2011, 1, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Danielewicz, A.; Zapert, A.; Ludwikowski, M.; Kochanek, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Skarżyński, H.; Skarżyński, P.H. Analiza wyników badań przesiewowych słuchu u dzieci w wieku szkolnym z tere-nów wiejskich w roku 2011 [Abstrakt]. VII Konferencja Sekcji Audiologicznej i Foniatrycznej Polskiego Towarzystwa Otorynolaryngologów—Chirurgów Głowy i Szyi,1–2.06.2012, Wrocław. Now Audiofonol. 2012, 1, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Skarżyński, P.H.; Piłka, A.; Ludwikowski, M.; Skarżyński, M.B. Comparison of the frequency of positive hearing screening outcomes in schoolchildren from Polnad and other Countries of Europe, central Asia, and Africa. J. Hear. Sci. 2014, 4, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Skarżyński, P.H.; Cyran, O.; Świerniak, W.; Wołujewicz, K.; Barylyak, R.; Skarżyński, H. Pilot hearing screening in schoolchildren from Armenia, Russia, Kyrgyzstan, and Azerbaijan. J. Hear. Sci. 2020, 10, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Feder, K.P.; Michaud, D.; McNamee, J.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Ramage-Morin, P.; Beauregard, Y. Prevalence of hearing loss among a representative sample of Canadian children and adolescents, 3 to 19 years of age. Ear Hear. 2016, 38, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnaraajan, S.; Maharajan, R.; Nandhan, R.; Kameswaran, M. Prevalence of ear disease among school children in pondicherry, South India: Cross-sectional survey. Otolaryngol (Sunnyvale) 2019, 9, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Niskar, A.S.; Kieszak, S.M.; Holmes, A.; Esteban, E.; Rubin, C.; Brody, D.J. Prevalence of hearing loss among children 6 to 19 years of age: The third national health and nutrition examination survey. JAMA 1998, 279, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Pillion, J.P.; LeClerq, S.C.; Khatry, S.K.; Wu, L.S.-F.; Prasad, R.; Karna, S.L.; Shrestha, S.R.; West, K.P., Jr. Prevalence of hearing loss and ear morbidity among adolescents and young adults in rural southern Nepal. Int. J. Audiol. 2010, 49, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Clercq, C.M.P.; van Ingen, G.; Ruytjens, L.; Goedegebure, A.; Moll, H.A.; Raat, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Baatenburg de Jong, R.J.; van der Schroeff, M.P. Prevalence of hearing loss among children 9 to 11 Years old: The generation R study. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewboonchoo, O.; Morioka, I.; Miyashita, K.; Takeda, S.; Wang, Y.X.; Li, S.C. Hearing impairment among young Chinese in an urban area. Public Health 1998, 112, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, D.L.; Rhoades, J.A.; Longenecker, A.L.; Beiler, J.S.; King, T.S.; Widome, M.D.; Paul, I.M. Improving detection of adolescent hearing loss. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2011, 165, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jun, H.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.E.; Song, J.J.; Chae, S. The prevalence of hearing loss in South Korea: Data from a population-based study. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, D.C.; Schmitt, L.; Murphy, W.J. Comparison of headphones for audiometric screening and hearing protector fit-testing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, R.W. Pure tone evaluation. In Handbook of Clinical Audiology, 5th ed.; Katz, J., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- International Bureau for Audiophonologie. Available online: https://www.biap.org (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Jerger, J. Clinical experience with impedance audiometry. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1970, 92, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liden, G.; Harford, E.; Hallen, O. Automatic tympanometry in clinical practice. Audiology 1974, 13, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgar, Z.; Kollar, A. Prakticka Audiometria; Vydovatelstro Osveta: Martin, Slovakia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Maxon, A.B.; White, K.R.; Vohr, B.R.; Behrens, T.R. Using transient evoked otoacoustic emissions for neonatal hearing screening. Br. J. Audiol. 1993, 27, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, D.T. Otoacoustic emissions, travelling waves and cochlear mechanisms. Hear. Res. 1986, 22, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dort, J.C.; Tobolski, C.; Brown, D. Screening strategies for neonatal hearing loss: Which test is best? J. Otolaryngol. 2000, 29, 206–210. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, B.; Li, S.F.; Shi, B.X.; Tang, J.L.; Wong, B.Y. Neonatal hearing screening: Evaluation of tone-burst and click-evoked otoacoustic emission test criteria. Ear Hear. 2006, 27, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzaskowski, B.; Pilka, E.; Jedrzejczak, W.W.; Skarzynski, H. Criteria for detection of transiently evoked otoacoustic emissions in schoolchildren. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.S.; Subramanyam, M.A.; Nair, N.S.; Rajashekhar, B. Hearing impairment and ear diseases among children of school entry age in rural South India. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2002, 64, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bess, F.H.; Dodd-Murphy, J.; Parker, R.A. Children with minimal sensorineural hearing loss: Prevalence, educational performance, and functional status. Ear Hear. 1998, 19, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairi Md Daud, M.; Noor, R.M.; Rahman, N.A.; Sidek, D.S.; Mohamad, A. The effect of mild hearing loss on academic performance in primary school children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 4, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarżyński, P.H.; Kochanek, K.; Skarżyński, H.; Senderski, A.; Wysocki, J.; Szkiełkowska, A.; Bartnik, G.; Lorens, A.; Piotrowska, A.; Śliwa, L.; et al. Hearing screening program in school-age children in Western Poland. Int. Adv. Otol. 2011, 7, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Skarzyński, P.H.; Świerniak, W.; Piłka, A.; Skarżynska, M.; Włodarczyk, A.W.; Kholmatov, D.; Makhamadiev, A.; Hatzopoulos, S. A hearing screening program for children in primary schools in Tajikistan: A telemedicine model. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016, 22, 2424–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.M.; Chan, D.K. Prevalence of hearing loss in US children and adolescents: Findings from NHANES 1988–2010. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiengprugsawan, V.; Hogan, A. Ear infection and its associated risk factors, comorbidity, and health service use in Australian children. Int. J. Pediatr. 2013, 2013, 963132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, G.; Piacentini, E.; Incorvaia, C.; Consonni, D. Sinusitis and Eustachian tube dysfunction in children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 18, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeve, S.L.; Margolis, R.H.; Levine, S.C.; Fournier, E.M. Effect of ear-canal air pressure on evoked otoacoustic emissions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91 Pt 2, 20091–22095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrzejczak, W.W.; Pilka, E.; Skarzynski, P.H.; Olszewski, L.; Skarzynski, H. Tone burst evoked otoacoustic emissions in different age-groups of schoolchildren. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopka, W.; Pietkiewicz, P.; Zalewski, P. Otoacoustic emission examinations in soldiers before and after shooting. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2000, 54, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hendler, B.; Fiszer, M.; Śliwińska-Kowalska, M. Zastosowanie emisji otoakustycznej wywołanej trzaskiem w monitorowaniu uszkodzeń słuchu spowodowanych hałasem. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2002, 1, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Murnane, O.D.; Kelly, J.K. The effects of high-frequency hearing loss on low-frequency components of the click-evoked otoacoustic emission. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2003, 14, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piłka, E.; Trzaskowki, B.; Jędrzejczak, W.W.; Kochanek, K.; Sarzyński, H. Ocena możliwości wykorzystania emisji otoakustycznych w badaniach przesiewowych słuchu u dzieci szkolnych w wieku 6–13 lat. Otorynolaryngologia 2012, 11, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.; Hixon, B.; Adkins, M.; Shinn, J.B.; Bush, M.L. Rurality and determinants of hearing healthcare in adult hearing aid recipients. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariel-Donges, A.H.; Gordon, E.L.; Dixon, B.N.; Eastman, A.J.; Bauman, V.; Ross, K.M.; Perri, M.G. Rural/urban disparities in access to the National Diabetes Prevention Program. Transl. Behav. Med. 2020, 10, 1554–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, N.M.; Nagourney, E.M.; Pollard, S.L.; Siddharthan, T.; Kalyesubula, R.; Surkan, P.J.; Hurst, J.R.; Checkley, W.; Kirenga, B.J. Urban-rural disparities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease management and access in Uganda. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2019, 6, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, J.M.; Abshire, D.A.; Undeberg, M.; Forman, L.; Amiri, S. Rural-urban disparities in access to medicaid-contracted pharmacies in Washington State 2017. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2020, 17, E92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandak, A.; Nayar, P.; Lin, G. Rural-urban disparities in access to breast cancer screening: A spatial clustering analysis. J. Rural Health 2019, 35, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarżyński, H.; Piotrowska, A. Prevention of communication disorders—Screening pre-school and school-age children for problems with hearing, vision and speech: European Consensus Statement. Med. Sci. Monit. 2012, 18, SR17–SR21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, B.; Gazia, F.; Freni, F.; Nicita, R.A.; Bruno, R.; Galletti, F. Chronic otitis media associated with cholesteatoma in a case of the Say-Barber-Biesecker-Young-Simpson variant of Ohdo syndrome. Am. J. Case Rep. 2019, 20, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tympanogram Type (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | |
| Group_u | 89.8 | 4.1 | 6.1 |
| Group_r | 76.9 | 8.2 | 14.9 |
| Age (Years) | Group_u Tympanogram Type (%) | Group_r Tympanogram Type (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| 8 | 83 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 94.1 | 5.9 | 0 |
| 9 | 86.8 | 10.5 | 2.6 | 54.2 | 16. 7 | 29.2 |
| 10 | 90.3 | 0 | 9.7 | 76.7 | 0 | 23.3 |
| 11 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 86.2 | 6.9 | 6.9 |
| 12 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 79.5 | 6.8 | 13.6 |
| 13 | 91.5 | 0 | 8.5 | 92.6 | 7.4 | 0 |
| Age (Years) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | |
| Group_u pass | 88.9 | 94.7 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 95.7 |
| Group_u refer | 11.1 | 5.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.3 |
| Group_r pass | 94.1 | 77.1 | 93.7 | 100 | 90.9 | 96.3 |
| Group_r refer | 5.9 | 22.9 | 6.3 | 0 | 9.1 | 3.7 |
| Age (Years) | TEOAE “Pass” (%) | TEOAE “Refer” (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 78.1 | 21.9 |
| 9 | 84.3 | 18.7 |
| 10 | 82.0 | 18.0 |
| 11 | 81.4 | 18.6 |
| 12 | 72.9 | 27.1 |
| 13 | 79.7 | 20.3 |
| Test | N of “Refer” Results in Group_u | N of “Refer” Results in Group_r |
|---|---|---|
| PTA | 6 (3.0%) | 19 (9.7%) |
| IA | 20 (10.1%) | 45 (23.1%) |
| TEOAE | 34 (17.3%) | 62 (31.8%) |
| PTA or IA | 20 (10.1%) | 45 (23.1%) |
| PTA or TEOAE | 34 (17.3%) | 62 (31.8%) |
| IA or TEOAE | 38 (19.3%) | 66 (33.8%) |
| PTA or IA or TEOAE | 38 (19.3%) | 66 (33.8%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pilka, E.; Jedrzejczak, W.W.; Kochanek, K.; Pastucha, M.; Skarzynski, H. Assessment of the Hearing Status of School-Age Children from Rural and Urban Areas of Mid-Eastern Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084299
Pilka E, Jedrzejczak WW, Kochanek K, Pastucha M, Skarzynski H. Assessment of the Hearing Status of School-Age Children from Rural and Urban Areas of Mid-Eastern Poland. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(8):4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084299
Chicago/Turabian StylePilka, Edyta, W. Wiktor Jedrzejczak, Krzysztof Kochanek, Malgorzata Pastucha, and Henryk Skarzynski. 2021. "Assessment of the Hearing Status of School-Age Children from Rural and Urban Areas of Mid-Eastern Poland" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 8: 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084299
APA StylePilka, E., Jedrzejczak, W. W., Kochanek, K., Pastucha, M., & Skarzynski, H. (2021). Assessment of the Hearing Status of School-Age Children from Rural and Urban Areas of Mid-Eastern Poland. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(8), 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084299









